Reactivity 1.1: Types of energy change
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Define exothermic reaction
heat is released by/ transfer of thermal energy from the system to the surroundings
(exo cause exo 멤버들 계속 탈퇴)
Examples of exothermic reactions
combustion
condensation
deposition
State the characteristic of exothermic reactions’ enthalpy change
negative
Define enthalpy
measurement of energy in a thermodynamic system
(energy content of a system)
Define system
all components that participate in a chemical reaction (ex. reactants, products, catalysts, etc.)
Contents of a flask
Explain the change in enthalpy ΔH
negative → heat removed from the system
positive → heat added to the system
look at this from the point of view of a system
(If you have a negative of something, you don’t have it or you lose it. If you have a positive of something, you have it or you gain it.)
State the characteristic of a positive ΔH in terms of stability
products’ bonds are relatively more unstable
State the characteristic of a negative ΔH in terms of stability.
products’ bonds are relatively more stable
Exothermic reaction enthalpy change diagram
energy graph (y axis: enthalpy, x axis: reaction)
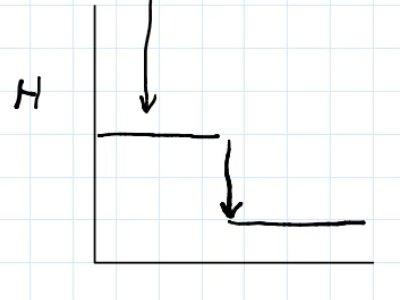
Define endothermic reactions
heat is absorbed by the system from the surroundings
State examples of endothermic reactions
photosynthesis
dehydration of hydrates
melting
vaporization
sublimation
State the enthalpy change ΔH for endothermic reactions
positive
Describe open system
Transfer of energy and matter is possible across its boundary
matter can be added or removed
energy can be transferred outside of its container
Describe closed system
No matter is transferred; energy is transferred across its boundary
matter cannot be removed or added
energy can be transferred in our out the container
Describe isolated system
No matter or energy can enter nor exit the system
State the equation for ΔT
Tfinal - Tinitial
Define heat (q)
energy that is transferred from a warmer body to a cooler body, as a result of the temperature gradient
Define temperature gradient
Explain the difference between temperature and heat