AP Bio - 1.4 Biomolecules
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
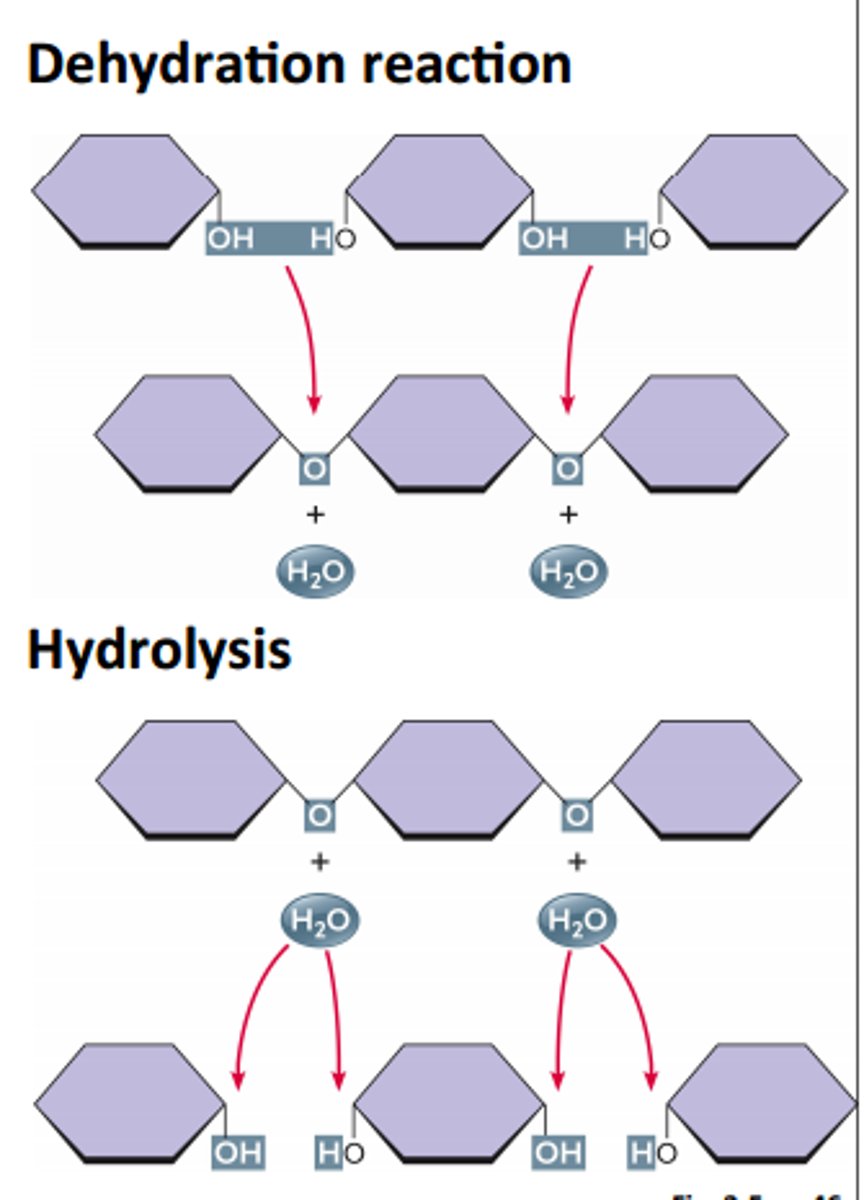
explain dehydration reaction vs hydrolysis
dehydration rxn: a chem. rxn where two molecules are covalently bonded with the loss of a water molecule forming polymers from monomers
hydrolysis: the reverse of dehydration synthesis, where water is added to break the bonds between monomers, breaking down polymers into monomers
what are Carbohydrates commonly referred to as?
sugars
What are the monomers of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides.
what are the Polymers of carbohydrates?
Polysaccharides.
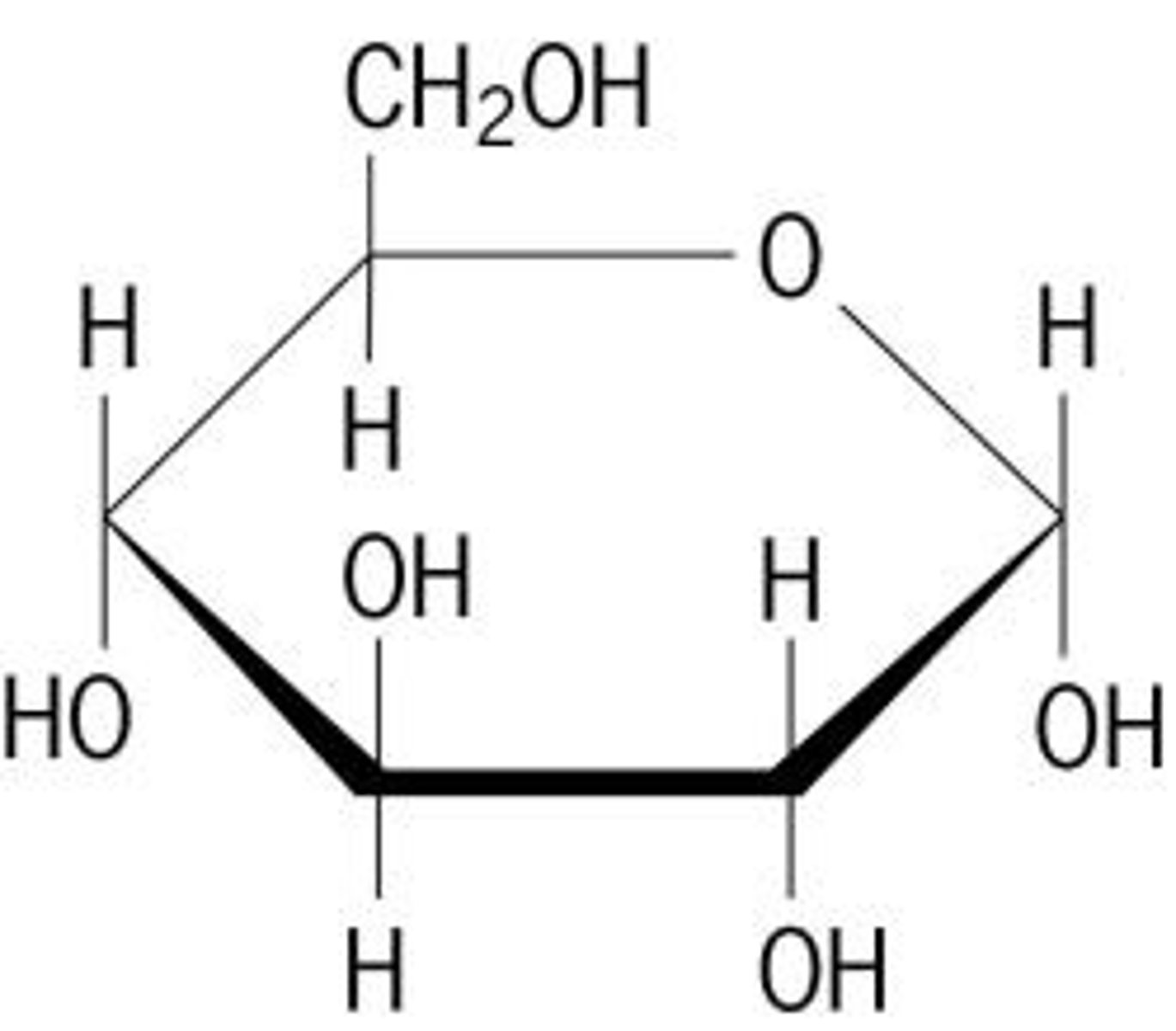
what kinds of carbohydrates are monosaccharides?
simplest form of carbohydrates: containing single sugar molecules, eg. glucose, fructose, galactose
What are disaccharides?
formed by joining of two monosaccharides through dehydration reaction
- sucrose (glucose + fructose)
- lactose (glucose + galactose)
- maltose (glucose + glucose)
what kind of carbohydrates are polysaccharides?
complex carbohydrates, long chains of monosaccharide units bonded together eg. starches and cellulose.
what is the structure of carbohydrates?
hexamer rings
Main Functions of Carbohydrates
Short term energy source, energy storage, and structure.
A structural carbohydrate found in plants.
cellulose
A structural carbohydrate found in insects and crabs.
Chitin
what is the elemental Composition of Carbohydrates
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen in a 1-Carbon: 2-Hydrogen: 1-Oxygen ratio.
what is Glucose
A monosaccharide that is broken down during aerobic cellular respiration to help make ATP energy.
what is the relationship with carbohydrates to the cell membrane?
Carbohydrates are also found in small amounts on the cell membrane and help cell types recognize each other.
what type of structure do energy Storing Carbohydrates have and how does that structure help its function?
Have a branched structure
How does it help? - More branches means more monomers can be broken off at once, allowing for cellular respiration to happen faster to make more ATP energy.
where do we see storage carbohydrates? (polysaccharides)
1. starch: storage form of glucose in plants
2. glycogen: storage form of glucose in animals
what type of structure do structural carbohydrates have and how does that structure help its function?
Have a linear structure and are able to stack.
how? - Stacking gives the carbohydrates stability, allowing for the formation of tough structures that allow for structural support.
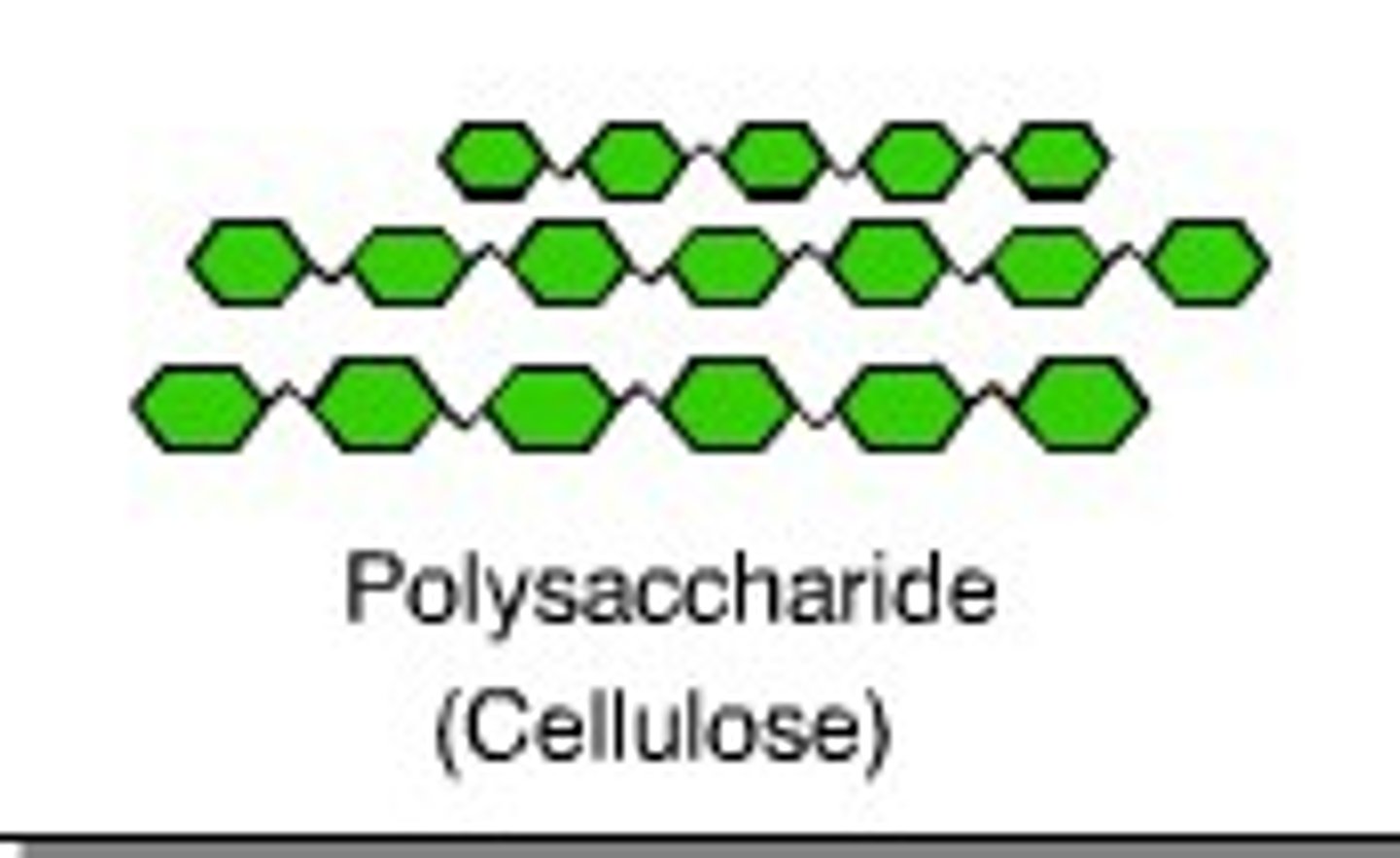
where do we see structural carbohydrates?
cellulose in plant cell walls and chitin shells in crabs.
what are lipids commonly referred to as?
fats or oils.
what are the monomers of Lipids
Fatty acids.
Polymers of Lipids
Lipids.
what are the main Functions of Lipids
Long term energy storage, insulation, and protection of organs.
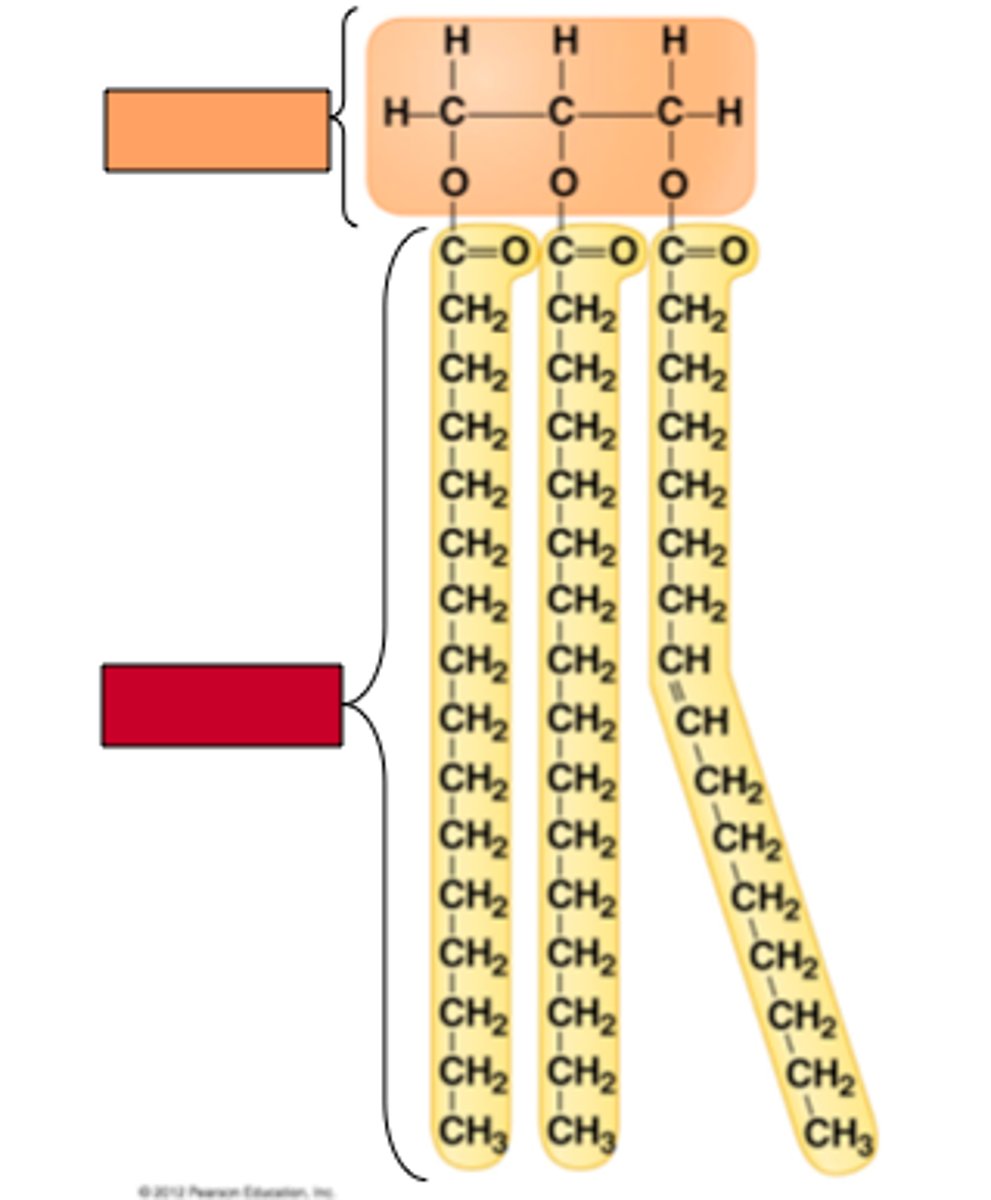
what is the structure of Lipids
Long hydrocarbon chains.
Elemental Composition of Lipids
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen with a 1-Carbon: 2-Hdrogen: very little oxygen ratio.
what are Phospholipids
A special type of lipid that makes up the main part of the cell membrane.
are lipids Hydrophobic or hydrophillic
Lipids are hydrophobic (they avoid water)
what is the structure Saturated Fats, what can they lead to and why?
- saturated fats do not have double bonds in their molecular structure.
- They are linear which means they can stack and form solids at room temp.
- They can lead to lipid build-up in blood vessels.
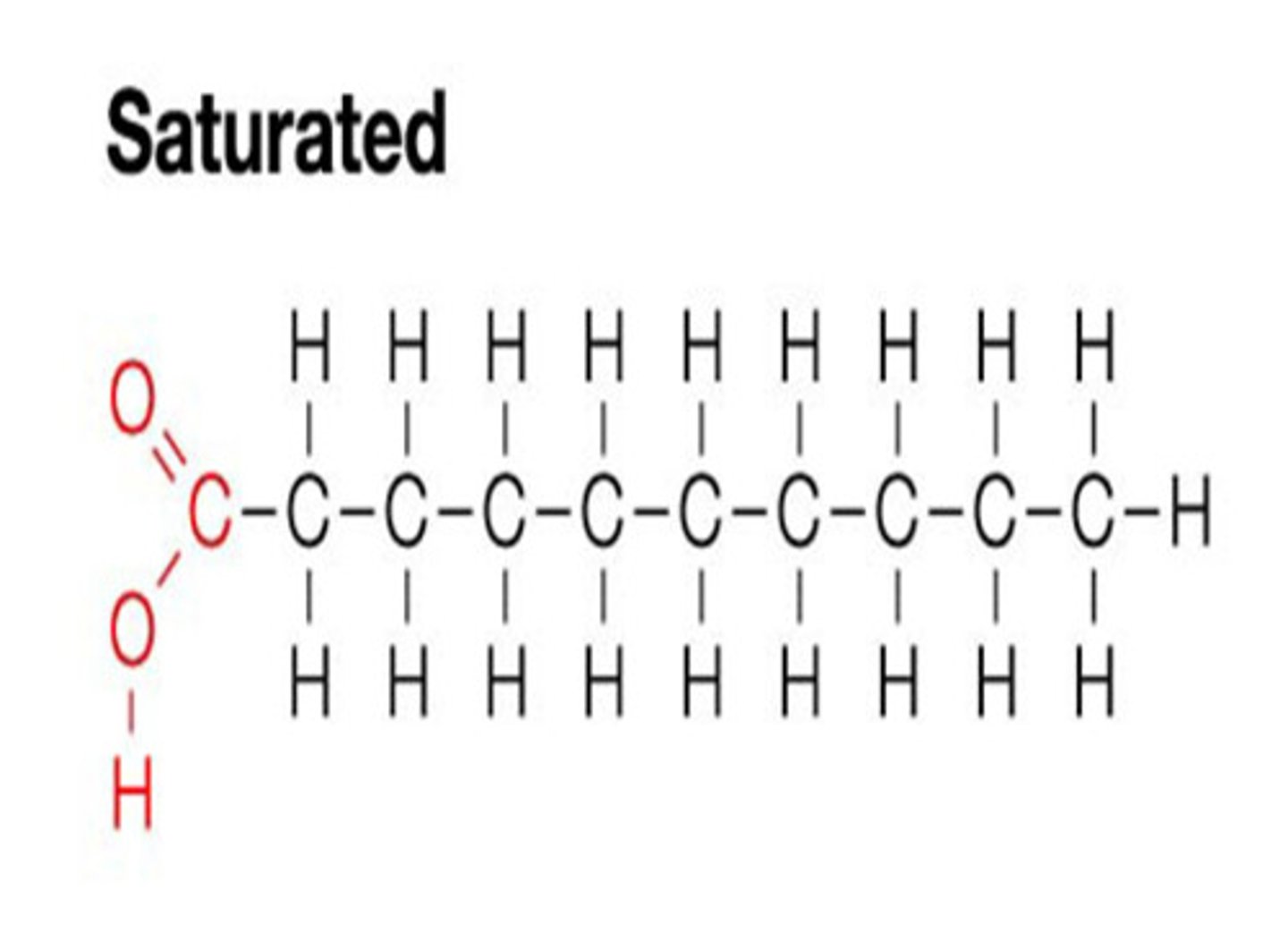
what is the structure of unsaturated Fats, what can they lead to and why?
- Have double bonds in their molecular structure,
- this prevents stacking, so they are liquid at room temperature.
- so they are less likely to clog arteries and veins
where are proteins commonly found?
meats and muscles.
monomers of proteins
amino acids
polymer of proteins
polupeptides
what is the Structure of Proteins
Very complex with four levels
what is the Elemental Composition of Proteins
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen and Sulfur (CHONS)
what are the main Functions of Proteins
1. Wounds and tissue repair
2. enzyme: catalyzing chemical reactions
3. Cell Signaling: hormones
4. antibody: defend against pathogens
5. structure: provide support/shape eg. collagen
6. transport: carry substances eg. hemoglobin
what are Enzymes
Specialized proteins that speed up (catalyze) chemical reactions in cells to help maintain homeostasis
what are Cell Membrane Proteins
proteins embedded in the cell membrane that help with transporting materials into and out of the cell.
what are Nucleic Acids commonly referred to
genetic material.
Monomers of Nucleic Acids
Nucleotides
3 Parts of a Nucleotide
Sugar, Phosphate, Nitrogenous Base
what are pyrimidines
cytosine, thymine, uracil
what are purines
Adenine and Guanine
Elemental Composition of Nucleic Acids
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen and Phosphorous (CHONP)
what are the Main Functions of Nucleic Acids
Storage of genetic material
2 Types of Nucleic Acids
DNA and RNA
what does it mean that Nucleic Acids have directionality?
they have a 5' end and 3' end
what is the structure of DNA in euk. and prokaryotes?
in eukaryotes: linear, double Stranded double helix
In prokaryotes: circular, double stranded helix
what is the purpose of DNA
stores the genetic code
what is the structure of RNA
single stranded
what are the 3 Types of RNA
Messenger RNA (mRNA), Transfer RNA (tRNA), Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
what is the purpose of rna
used for protein synthesis
what are the Nucleotides in DNA
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine
what are the Nucleotides in RNA
Adenine, Uracil, Cytosine, Guanine
difference between Sugar in dna vs rna
DNA has deoxyribose sugar, RNA has ribose sugar
what is the Stability of DNA vs RNA
DNA is more stable than RNA
Location of DNA
Eukaryotes: Nucleus,
Prokaryotes: Floating in the cytoplasm of the cell
Location of RNA
Made in the nucleus and transported to the cytoplasm
2 types of Bonding in Nucleotides
1. bonds that link two nitrogenous bases together: hydrogen bonds;
2. bonds that link nucleotides together: covalent 'phosphodiester bonds' between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and sugar group of another
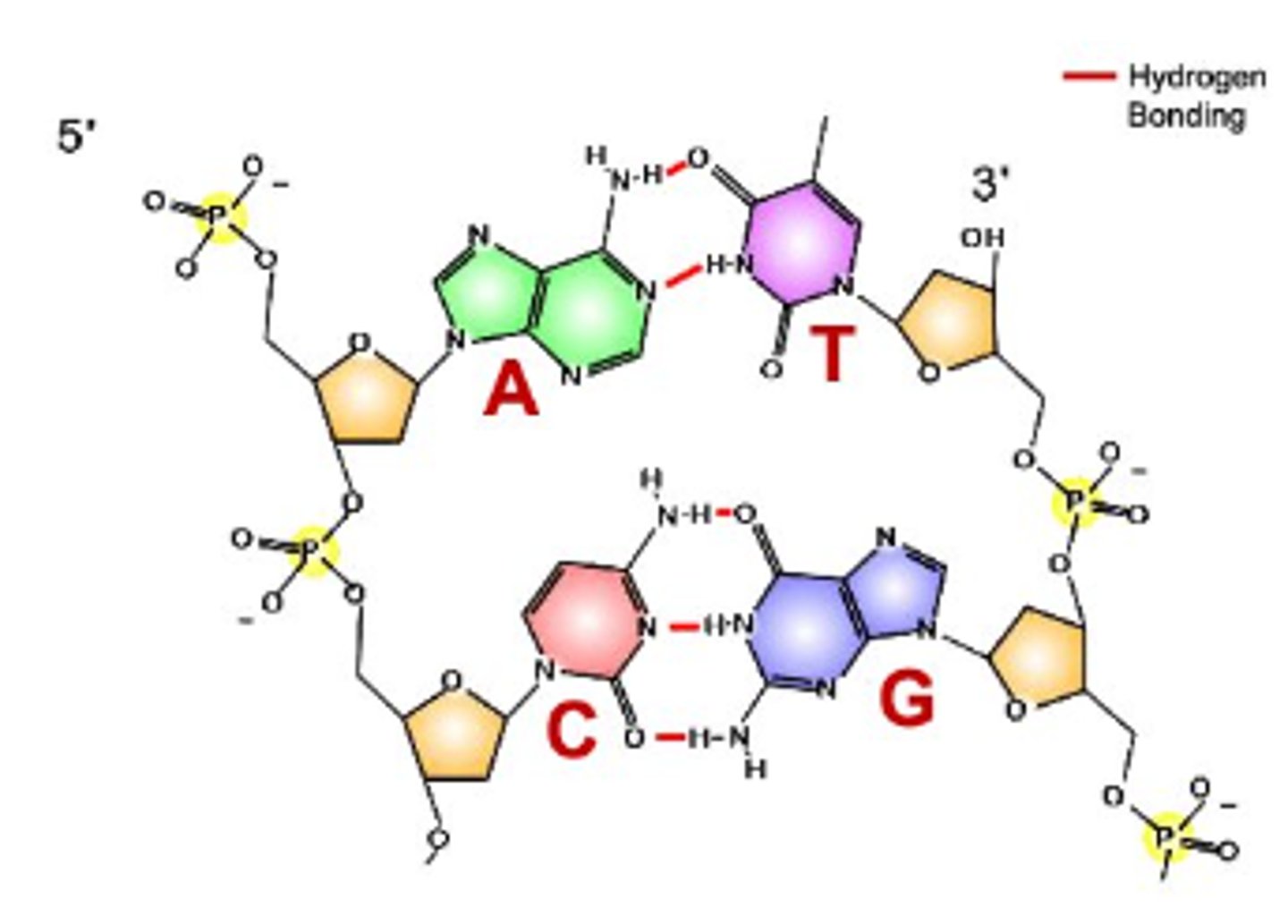
what determines the genetic information in nucleic acids
the order of nucleotides
what is the energy we get from breaking down Biomolecules?
The energy we get from breaking down biomolecules is called 'Calories'
what are broken down by the body for energy?
lipids, carbs, proteins
which biomolecule has the most energy and how much?
lipids: 9 calories in 1 gram of fat
how much Energy do Carbohydrates and Proteins have?
they have equal amounts:
4 calories in 1 gram of sugar/protein
what are not broken down for energy?
Nucleic acids are NOT broken down for energy
is a function of proteins energy storage?
no