thermodynamics
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
what is heat?
how does it affect particles?
energy transferred as a result of temperature differences
makes particles move randomly
what is work?
how does it affect particles?
as a result of motion against an opposing force
makes particles move in an ordered way
what is an open system?
matter can be transferred
heat can be conducted through flask walls
what is a closed system?
no matter can be transferred
heat can be conducted through flask walls
what is an isolated system?
heat transfer is prevented by vacuum flask
matter cannot be transferred
when does the system lose energy? what sign?
does work
transfers heat to the surroundings
sign is negative
when does the system gain energy? what sign?
does work
heat is transferred to surroundings
sign is positive
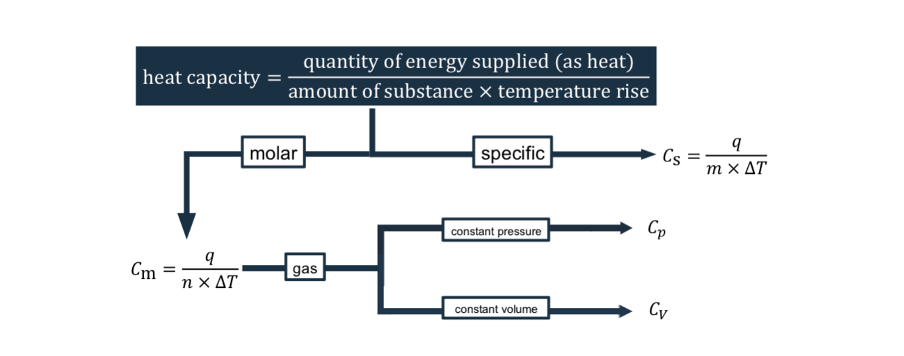
heat capacity equation?
molar and specific
what is internal energy?
quantity of energy necessary to bring the system from its standard internal state to its present internal state
what is enthalpy?
heat transferred between a system and its surroundings at constant pressure
heat transferred when container is sealed
heat transferred is internal energy change (constant volume)
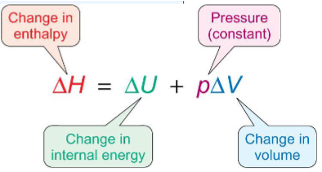
enthalpy and internal energy equation
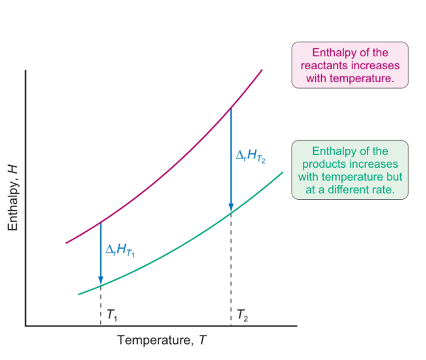
what is the Kirchhoff equation?

enthalpy vs temperature change graph
reactants vs products?
how to calculate ΔCp?
include coefficients

what does a calorimeter do?
measures heat change during a chemical reaction
what is a bomb calorimeter?
what does it measure? what is kept constant?
tightly sealed reaction chamber, constructed from thick stainless steel
volume of the system is kept constant
- Measures ΔU
why must a calorimeter be calibrated?
how can this be done?
must be calibrated so you know how much energy it takes to change the temperature of the water by 1K
you can do this by using a reaction where ΔU is already known
what is the calibration factor?
temperature rise produced by burning known mass of compound is used to calculate relationship between E released and temperature rise of water
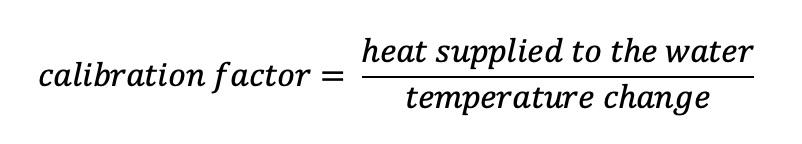
what do enthalpy changes arise from?
breaking and forming chemical bonds
what is the conditions for standard enthalpy change?
1 bar
1 mol dm-3
298 K
what is bond dissociation enthalpy?
positive or negative?
enthalpy change per mole when chemical bond is broken under standard conditions in gas phase
positive - endothermic as bonds are breaking
what is mean bond enthalpy?
what does it indicate?
mean value of bond dissociation enthalpy for a specific bond averaged across range of related compounds
indicates stability and reactivity of chemical bonds
what is the equation for enthalpy using Boltzmann constant?
what do the terms mean?
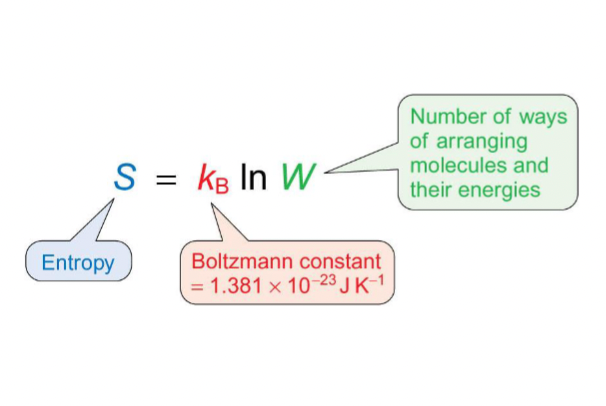
what does entropy measure?
the number of ways energy and molecules can be arranged in a system
what is the second law of thermodynamics?
spontaneous processes increase total entropy of universe
general equation for entropy change
ΔS = qrev / T
when does ΔH = qrev?
in phase changes
equation for entropy change of vaporisation?
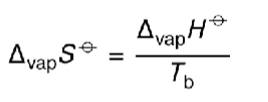
equation for entropy change of fusion?
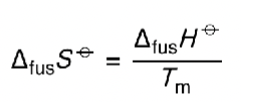
equation for entropy change when there is change in temp?
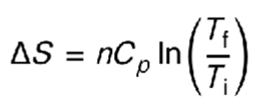
what is the third law of thermodynamics?
establishes a reference point
absolute entropy = entropy of 1 mole of substance at 1 bar pressure, usually at 298 K
relative to the reference state where S = 0 at 0K
what is the entropy of a perfect crystal at 0K?
how does this differ from real crystals?

what are other names for absolute entropy?
what is the symbol?
standard molar entropy
third law entropy
S⦵
formula for q
q = n Cp ΔT
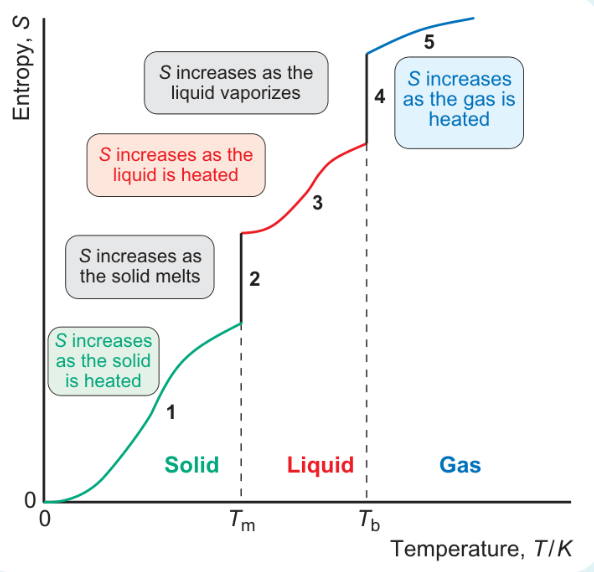
formula for area under graph when heated from 0 to Tm?
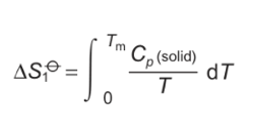
formula for area under graph when melting at Tm?
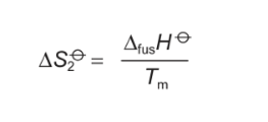
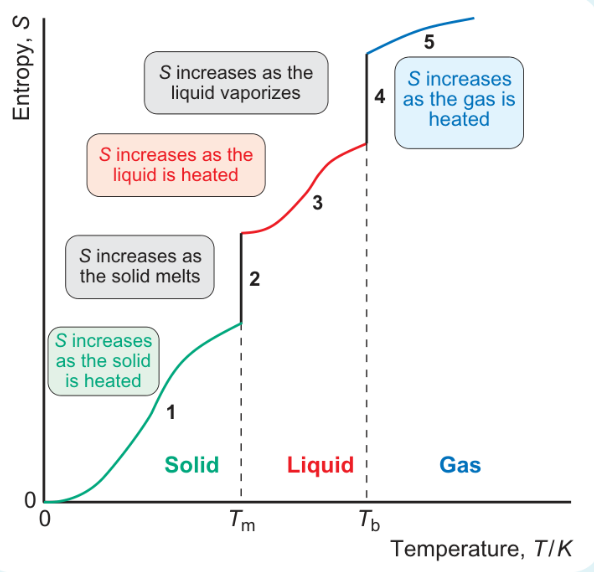
formula for area under graph heating from Tm to Tb?
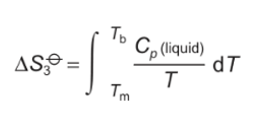
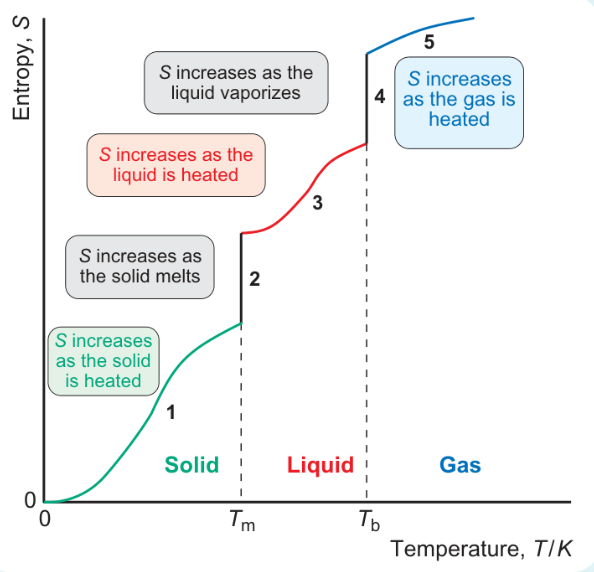
formula for area under graph vaporisation at Tb?
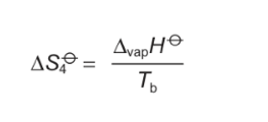
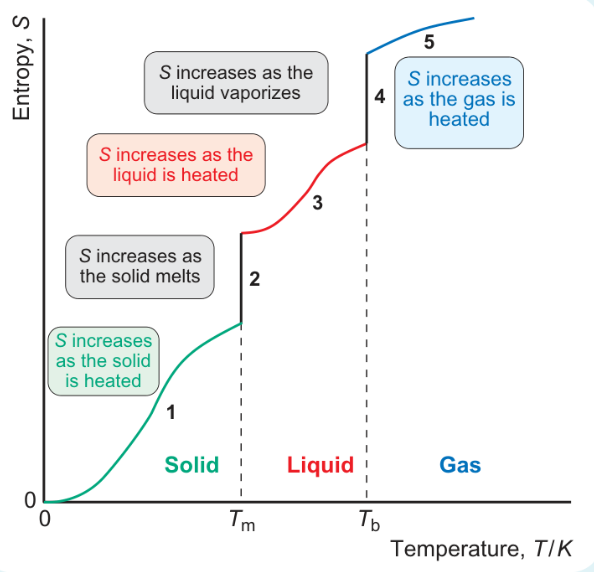
formula for area under graph heating from Tb to 298?
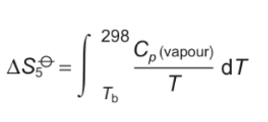
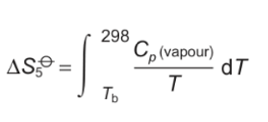
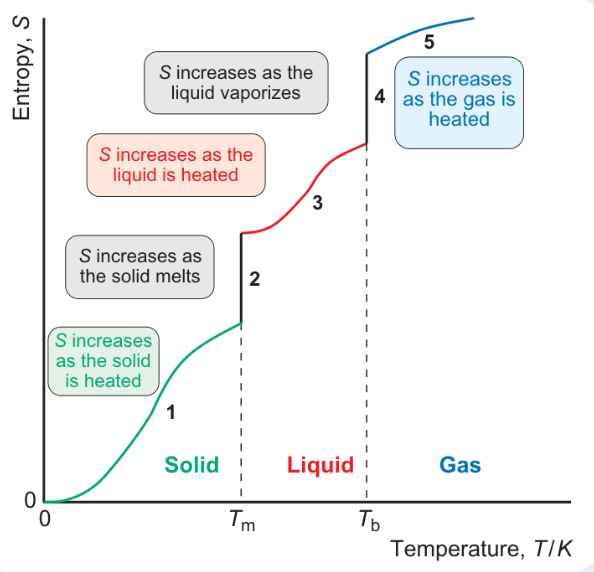
why is jump in entropy bigger at stages 2 and 4 than when heated?
increase in entropy bigger at phase changes
increase in number of ways molecules can distribute energy is much greater when there is a phase change than when heating
what are the patterns in standard entropies?
which state is lowest/highest?
how does complexity affect?
lowest is solids, highest is gases
more complex is higher standard entropy
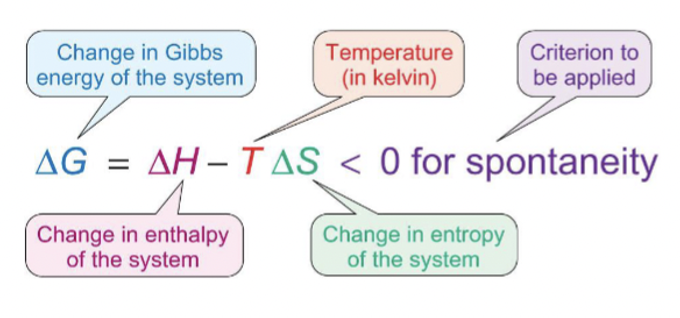
equation for Gibbs energy using enthalpy
equation for Gibbs energy using K?
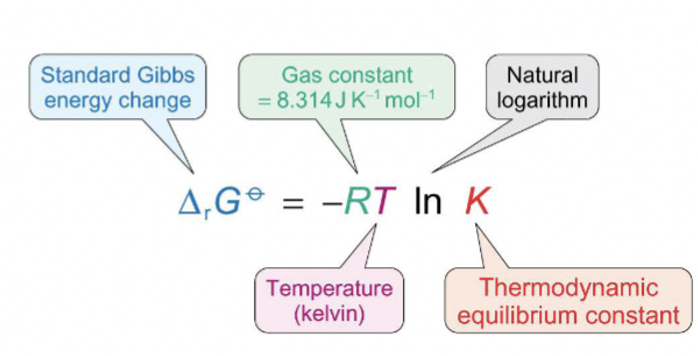
what are the conditions for ΔG?
constant temperature and pressure
how to calculate activity of a gas?
partial pressure / p⦵
p⦵ is 1 bar
how to calculate activity of a solution?
[A] / [A]⦵
[A]⦵ = 1 mol dm-3
what is activity of pure liquid or solid?
1
what is the equation for G (using standard G)?
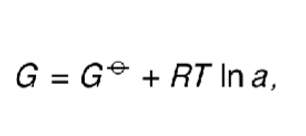
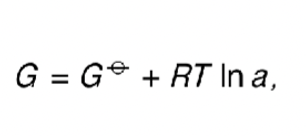
how does this equation become -RTlnK at equilibrium?
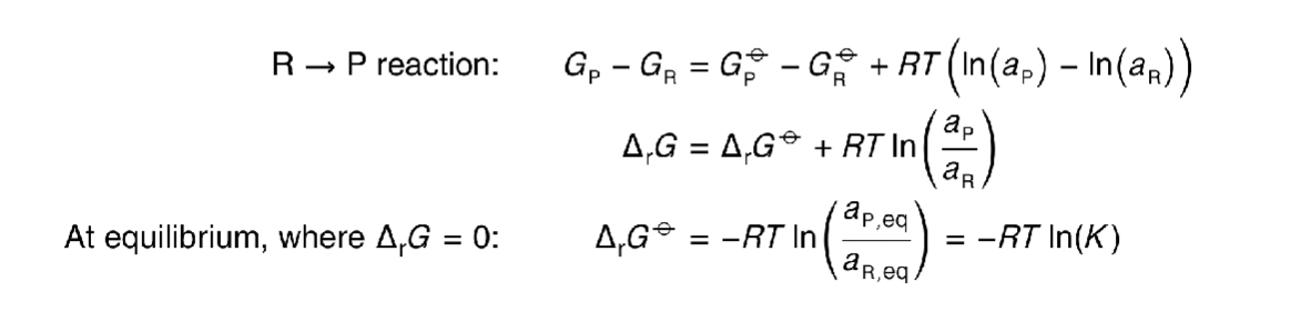
what is the graph of Gibbs energy vs reaction progress? (showing Q relative to K and spontaneity?)
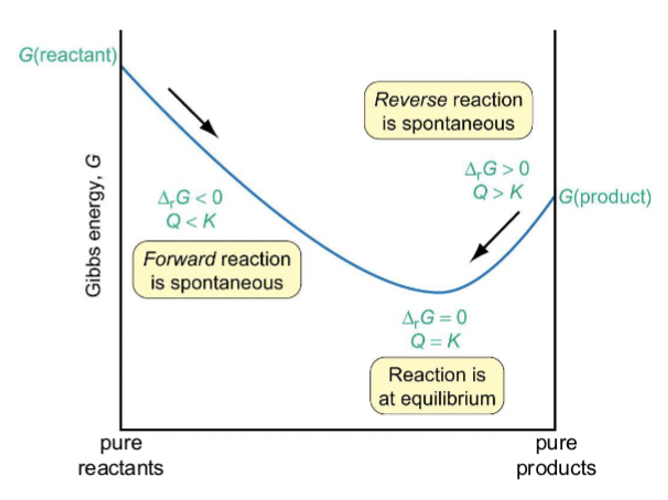
for what values of ΔG and Q is reverse reaction spontaneous?
ΔG > 0
Q > K
for what values of ΔG and Q is reaction at equilibrium?
ΔG = 0
Q = K
for what values of ΔG and Q is forwards reaction spontaneous?
ΔG < 0
Q < K
how does Gibbs equation become van t’ Hoff equation?
divide by -RT
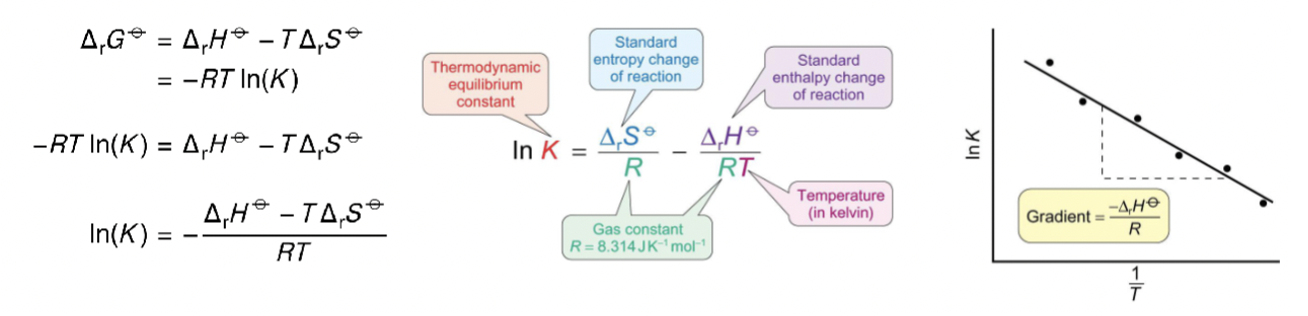
what is plotted for van t’ Hoff equation?
what is gradient and intercept?
ln K vs 1/T
gradient = -ΔH / R
intercept = ΔS / R