fuel cells
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
what is a fuel cell
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell in which a fuel donates electrons at one electrode and oxygen gainselectrons at the other electrode
where are fuel cells gaining popularity?
These cells are becoming more common in the automotive industry to replace petrol or diesel engines
how is p.d set up in a cell
As the fuel enters the cell it becomes oxidised which sets up a potential difference or voltage within the cell
how can different types of fuel cells be set up?
Different electrolytes and fuels can be used to set up different types of fuel cells
what is an important cell and what does it do?
An important cell is the hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell which combines both elements to release energy and water
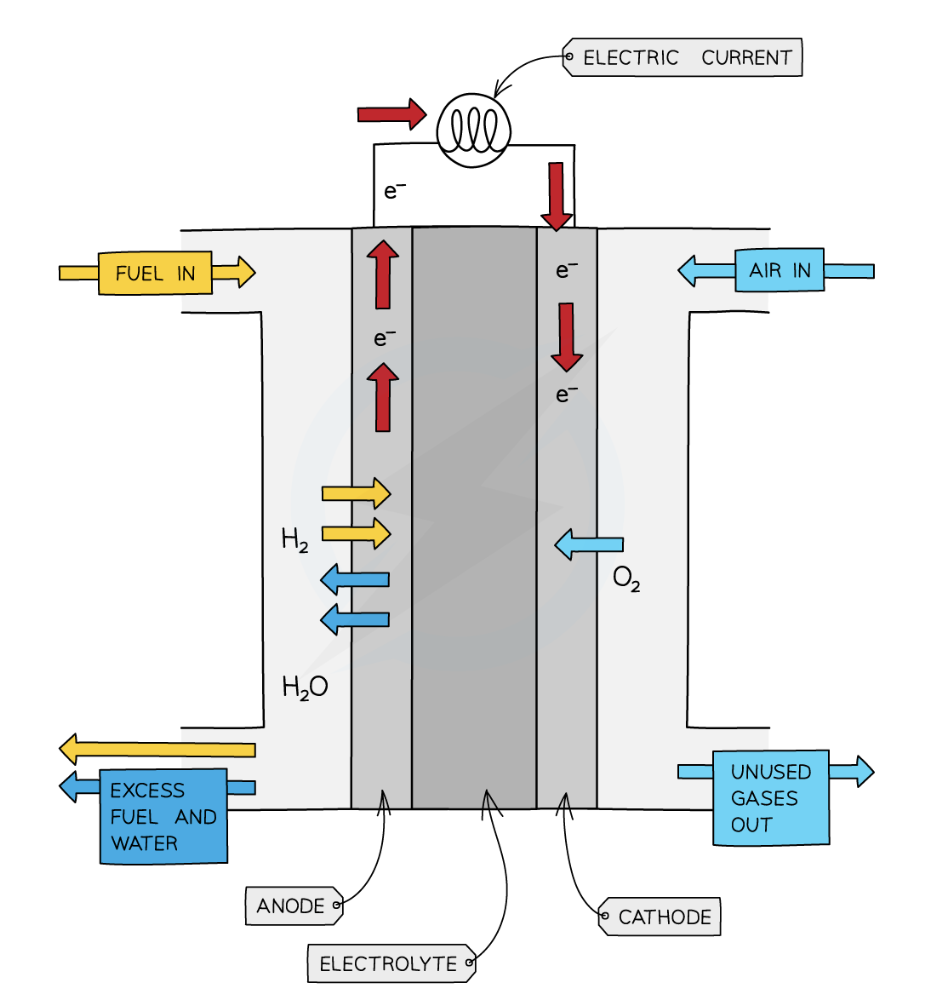
describe what is happening in this diagram (6)
At the anode , hydrogen gas is fed into the fuel cell and is oxidised to form H+H+ ions
The electrons that are donated by this process are then channeled into the external circuit , creating a current.
This current can be measured using a voltmeter .
The H+H+ ions then diffuse through the anode (usually a permeable carbon structure) and into the electrolyte .
At the cathode (5), oxygen gas is fed in and reduced by the electrons flowing in from the external circuit to form O2−O2− ions
These O2−O2− ions will the react with the H+H+ ions diffusing through the electrolyte from the anode to form H2OH2O.
how many advantages of hydrogen fuel cells are there?
5
list the advantages of hydrogen fuel cells
They do not produce any pollution
They produce more energy per kilogram than either petrol or diesel
No power is lost in transmission as there are no moving parts, unlike an internal combustion engine
No batteries to dispose of which is better for the environment
Continuous process and will keep producing energy as long as fuel is supplied
how many disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cells are there?
4
list the disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cells
Materials used in producing fuel cells are expensive
High pressure tanks are needed to store the oxygen and hydrogen in sufficient amounts which are dangerous and difficult to handle
Fuel cells are affected by low temperatures, becoming less efficient
Hydrogen is expensive to produce and store
what do hydrogen oxygen cells consist of?
The cell consists of an electrolyte which is usually phosphoric acid and porous carbon electrodes coated with a catalyst
what happens at the anode and cathode?
Hydrogen enters at the anode where it is oxidised and oxygen enters at the cathode where it is reduced
what reaction happens at the anode?
2H2 → 4H+ + 4e–
what reaction happens at the cathode?
4H+ + O2 + 4e– → 2H2O
what is the overall reaction?
2H2 + O2→ 2H2O
what is the movement of electrons?
The electrons move around the external circuit from the anode to the cathode
what is the movement of electrons used for?
This movement of electrons is used to drive an electric motor