202 - Autonomic Nervous System (pt 1&2)
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
ANS
Regulates processes normally beyond voluntary control or beneath consciousness, Controls visceral functions
PNS
sensory and motor actions are divisions of which main nervous system?
CNS
information processing occurs in which nervous system?
SNS
this division of the PNS gives motor informations to skeletal muscles:
ANS
this division of the PNS gives motor information to glands and smooth and cardiac muscles:
somatic sensory
receives touch, pain, temperature, proprioception from body
somatic motor
sends voluntary and reflexive motor to skeletal muscle
visceral sensory
receives visceral stimuli
visceral motor
sends involuntary and reflexive motor to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands
CNS
the brain is part of the:
CNS
the spinal cord is part of the:
PNS
the cranial nerves are part of the:
PNS
the spinal nerves are part of the:
General Somatic Afferent
this type of nerve fiber sends sensations from body to CNS
dorsal root ganglion
in a General Somatic Afferent nerve fiber, the cell body is located in the:
General Somatic Efferent
this type of nerve fiber sends info from the CNS to skeletal muscle
ventral horn
in a General Somatic Efferent nerve fiber, the cell body is located in the:
General Visceral Afferent
this type of nerve fiber sends visceral stimuli from body to CNS
dorsal root ganglion
in a General Visceral Afferent nerve fiber, the cell body is located in the:
General Visceral Efferent
this type of nerve fiber sends info from the CNS to smooth and cardiac muscle, glands
intermediolateral cell column
in a General Visceral Efferent nerve fiber, the pre-ganglionic cell body is located in the:
ANS
which division of the PNS has their afferent and efferent neurons travel through autonomic ganglia before reaching their destination?
autonomic ganglia
in a General Visceral Efferent nerve fiber, the post-ganglionic cell body is located in the:
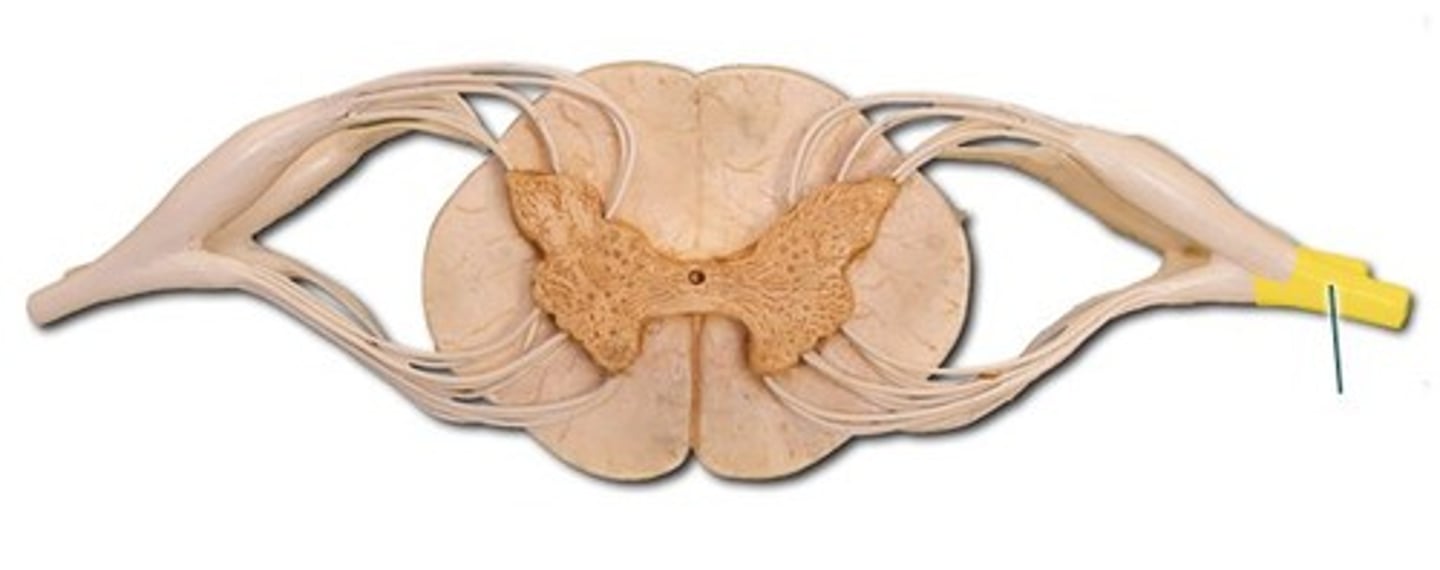
dorsal horn
identify the structure
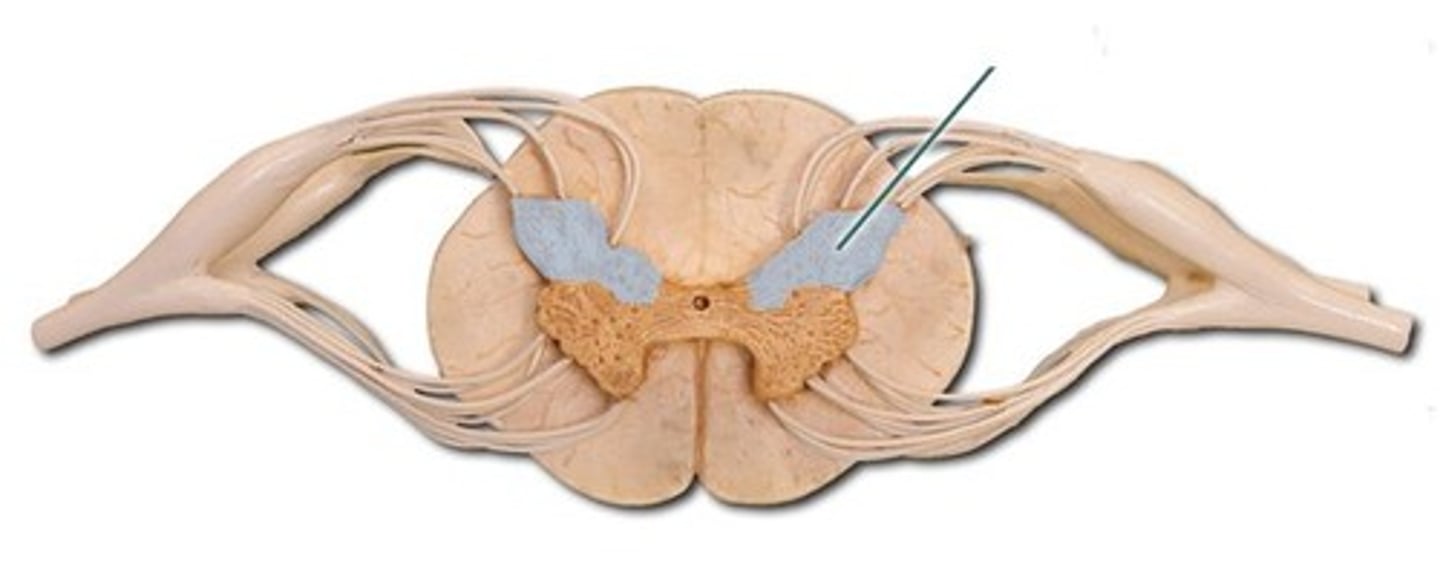
ventral horn
identify the structure
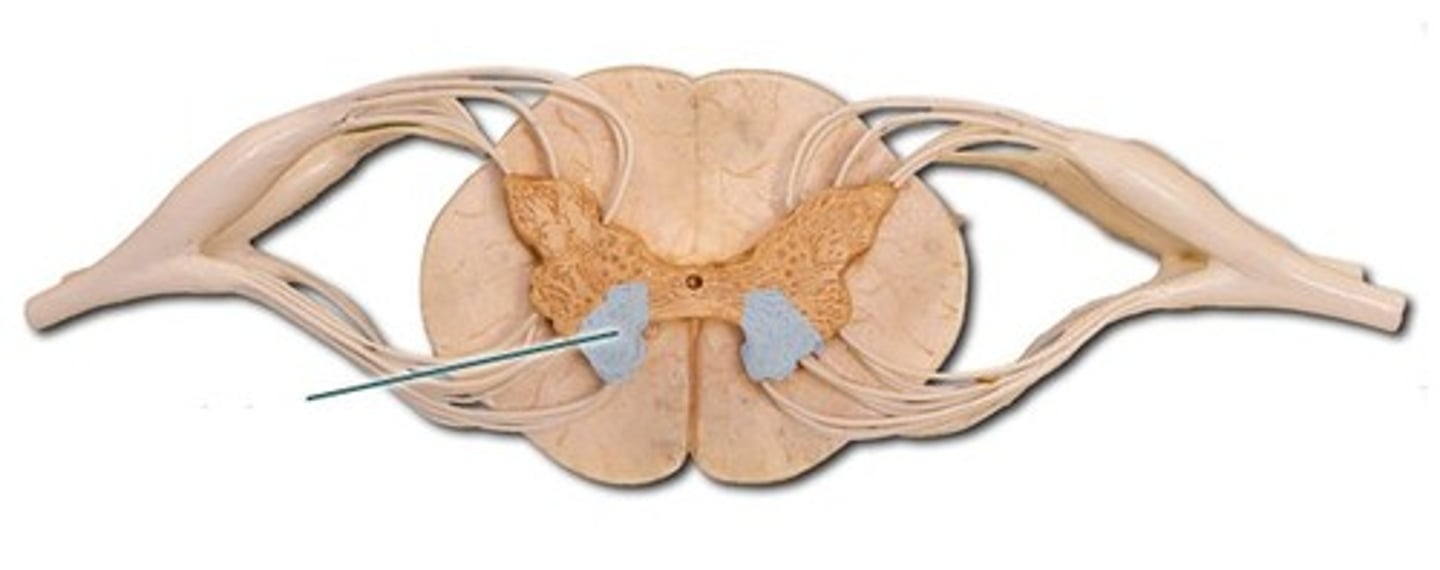
ventral roots
identify the structure
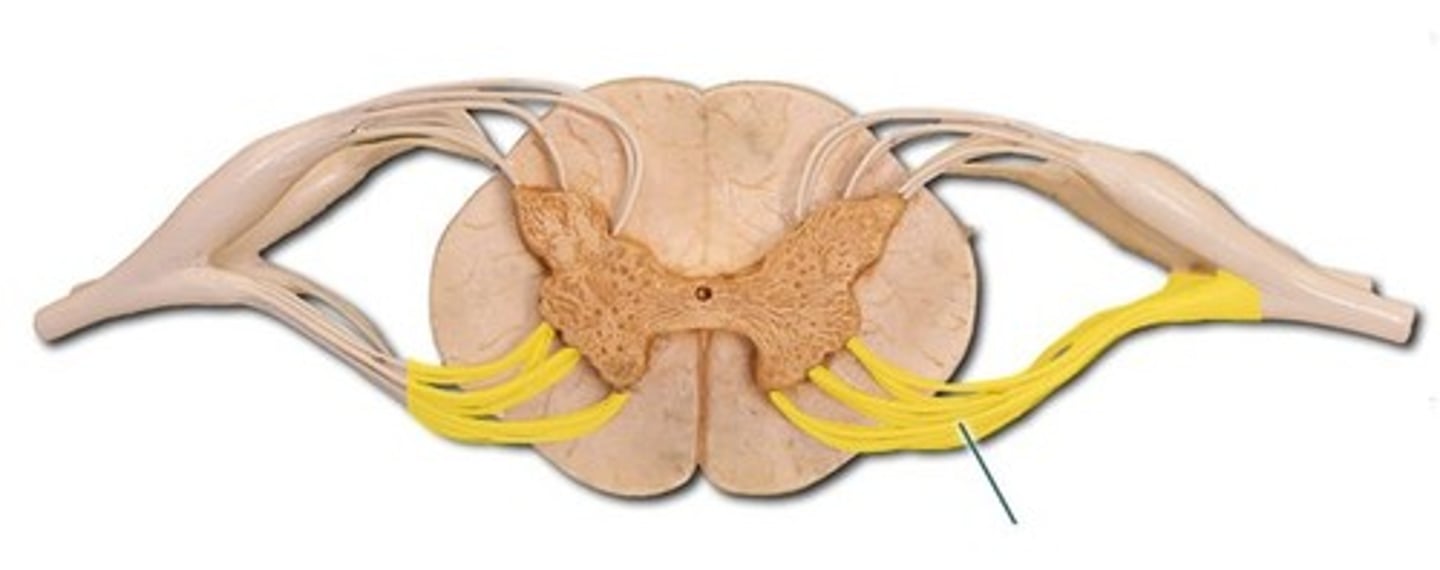
dorsal roots
identify the structure
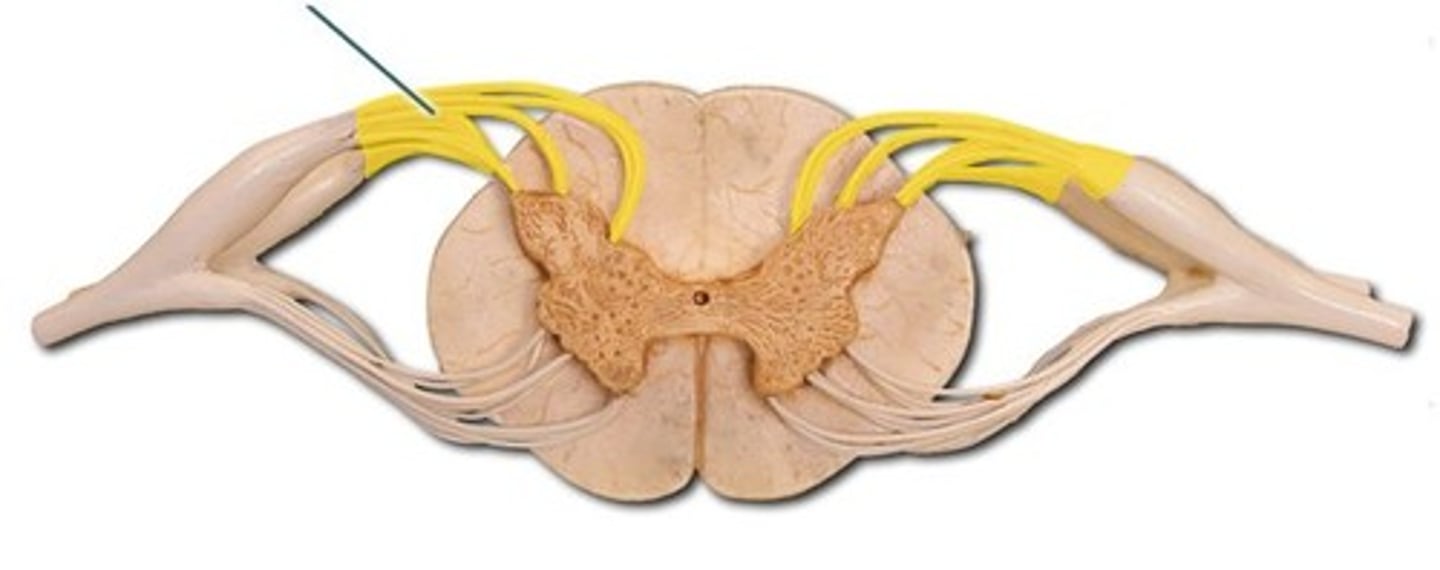
dorsal root ganglion
identify the structure
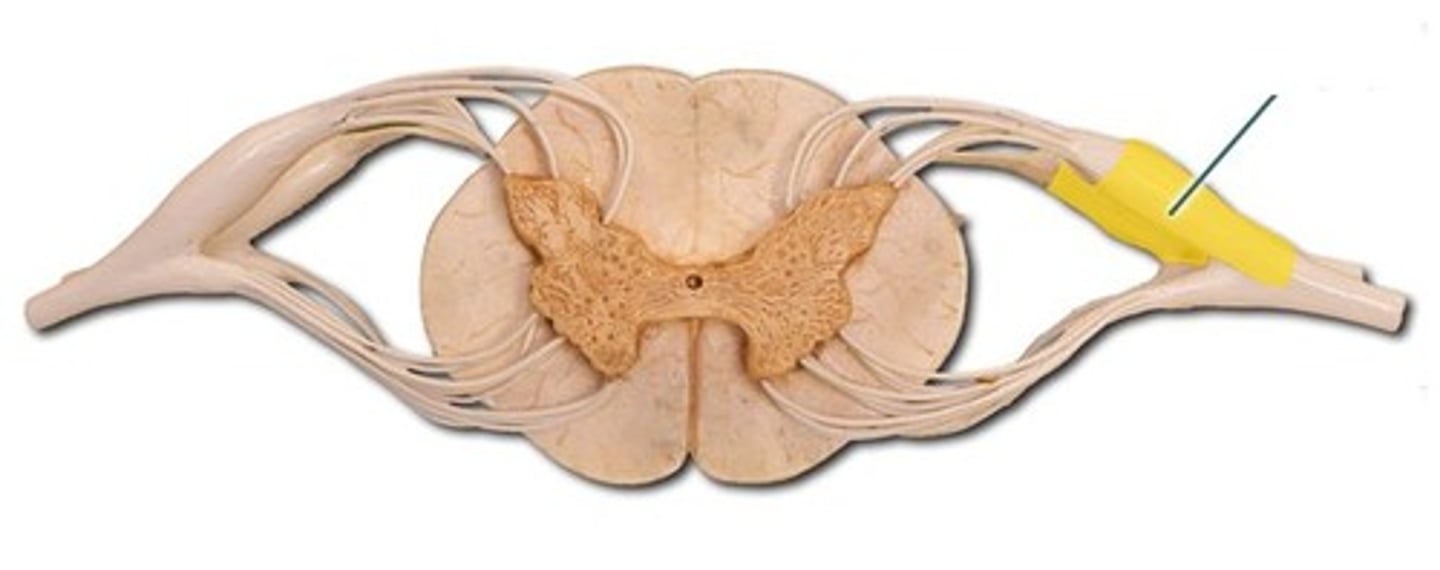
spinal nerve
identify the structure
dorsal primary ramus
identify the structure
ventral primary ramus
identify the structure
sympathetic chain
identify the structure
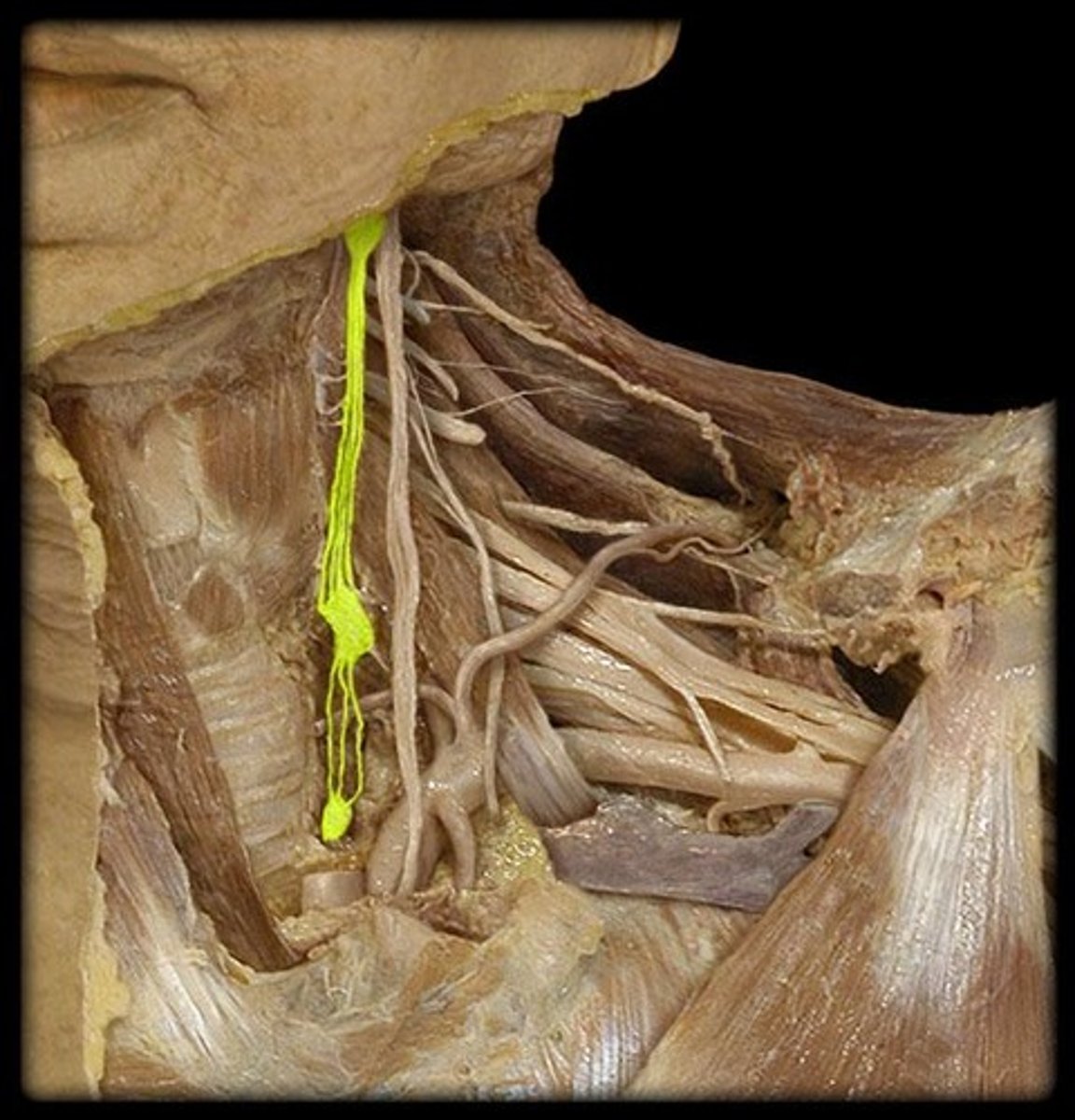
sympathetic ganglion
identify the structure
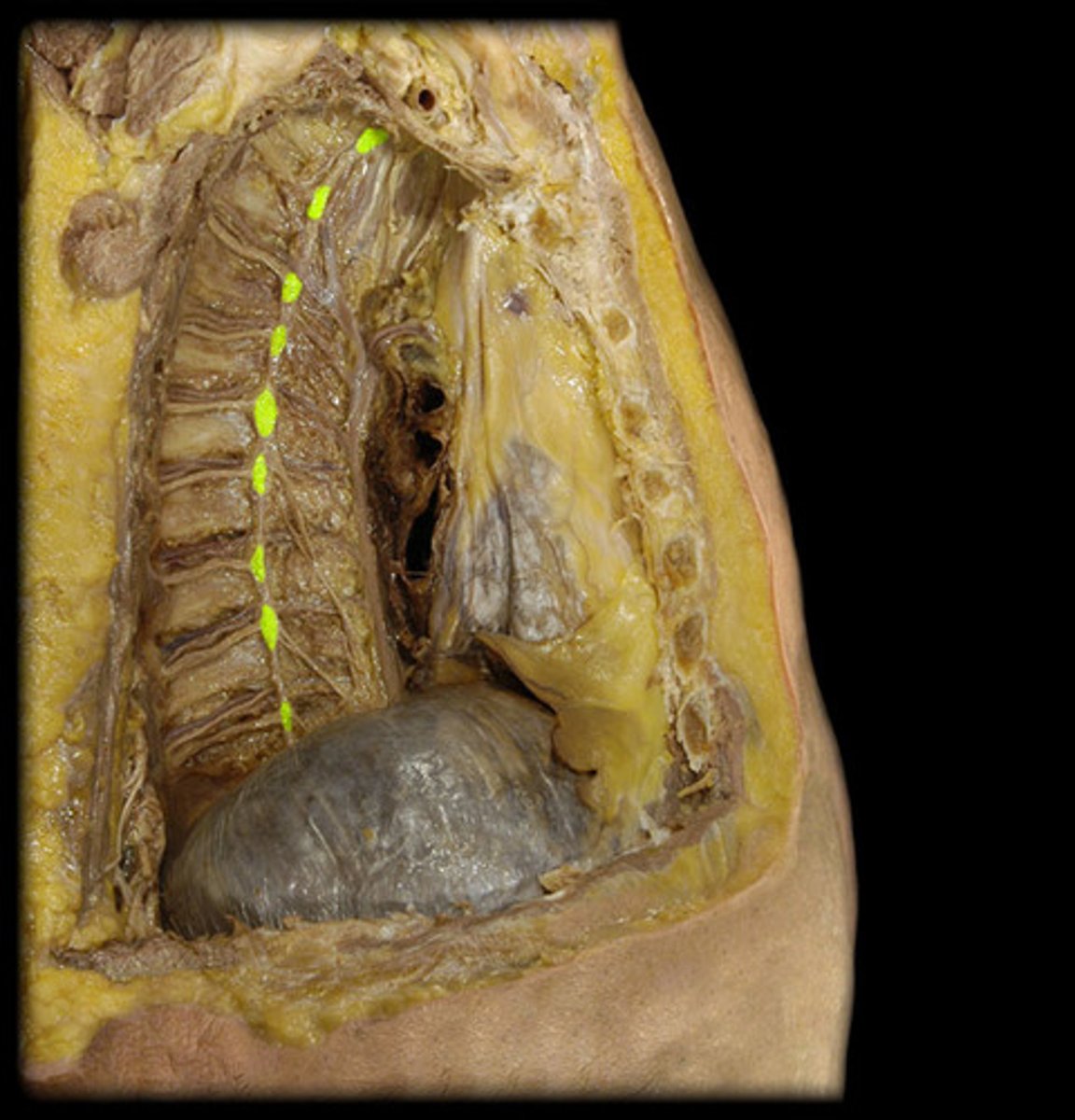
SNS
•1 motor neuron from CNS to skeletal muscle
•Cell bodies located in ventral horn of spinal cord or in brainstem nuclei
ANS
•2 motor neuron chain
•Preganglionic cell bodies located in intermediolateral cell column of spinal cord or in brainstem nucei
sympathetic division
Coordinates and directs the body's response to stressful or frightening situations
Three "E's" Emergency! Excitement Exercise
"Fight or Flight"
parasympathetic division
Conserves energy
Restores nutrients
"Rest and Digest"
sympathetic division
Dilates pupils
sympathetic division
Increases heart rate
sympathetic division
Bronchodilates
sympathetic division
Vasoconstricts to skin and GI
sympathetic division
Vasodilates coronary arteries and skeletal muscle arteries
sympathetic division
Activates arrector pili and sweat glands
sympathetic division
Secretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine
sympathetic division
Stimulates breakdown of molecules for fuel
parasympathetic division
Constricts pupils, accommodation
parasympathetic division
Decreases heart rate
parasympathetic division
Bronchoconstricts
parasympathetic division
Stimulates secretion of tears and saliva
parasympathetic division
Increases GI motility
parasympathetic division
Vasodilates to GI
parasympathetic division
know as the cranio-sacral division:
sympathetic division
know as the thoraco-lumbar division:
parasympathetic division
which sympathetic system nerves have long pre-ganglionic and short post-ganglionic axons?
sympathetic division
which sympathetic system nerves have long post-ganglionic and short pre-ganglionic axons?
grey rami communicantes
sympathetic efferent fibers that target the effectors at the same level enter the sympathetic chain via white communicates, synapse, and exit via:
ascending sympathetic chain
sympathetic efferent fibers that target the effectors above the thoraco-lumbar roots will enter the sympathetic chain via white communicates, synapse, and exit via:
descending sympathetic chain
sympathetic efferent fibers that target the effectors below the thoraco-lumbar roots will enter the sympathetic chain via white communicates, synapse, and exit via:
ascend within sympathetic chain AND Synapse at same level
sympathetic efferent fibers that target the effectors in the thorax (ie. heart and lungs) will enter the sympathetic chain via white communicates, synapse, and:
grey rami communicantes
sympathetic efferent fibers exit the sympathetic chain via the:
T1-L2
what spinal segments does the sympathetic nervous system run through?
cranial nerves
S2-S4
what spinal segments does the parasympathetic nervous system run through?
sympathetic chain
How do sympathetic fibers get to the effectors in the
head, trunk wall, and extremities?
T1-T4/5
what spinal segments do the cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves root from?
cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves
these carry postganglionic sympathetic fibers to
the heart, lungs, and esophagus
effectors in the abdomen and pelvis
sympathetic nerves traveling to this region pass through the sympathetic chain without synapse:
T5-T9
the greater splanchnic nerves originate from spinal nerve levels:
abdominopelvic splanchnic nerves
what are the preganglionic fibers of T5-L1/2 called?
T10-T11
the lesser splanchnic nerves originate from spinal nerve levels:
T12
the least splanchnic nerve originate from spinal nerve level:
L1-L2
the lumbar and sacral splanchnic nerves originate from spinal nerve level:
prevertebral ganglia
Abdominopelvic splanchnic nerves carry preganglionic sympathetic fibers to ____________ in the abdomen or pelvis
postganglionic fibers
cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves carry what type of sympathetic fibers?
preganglionic fibers
abdominopelvic splanchnic nerves carry what type of sympathetic fibers?
prevertebral ganglia
these structures hold postganglionic sympathetic cell bodies
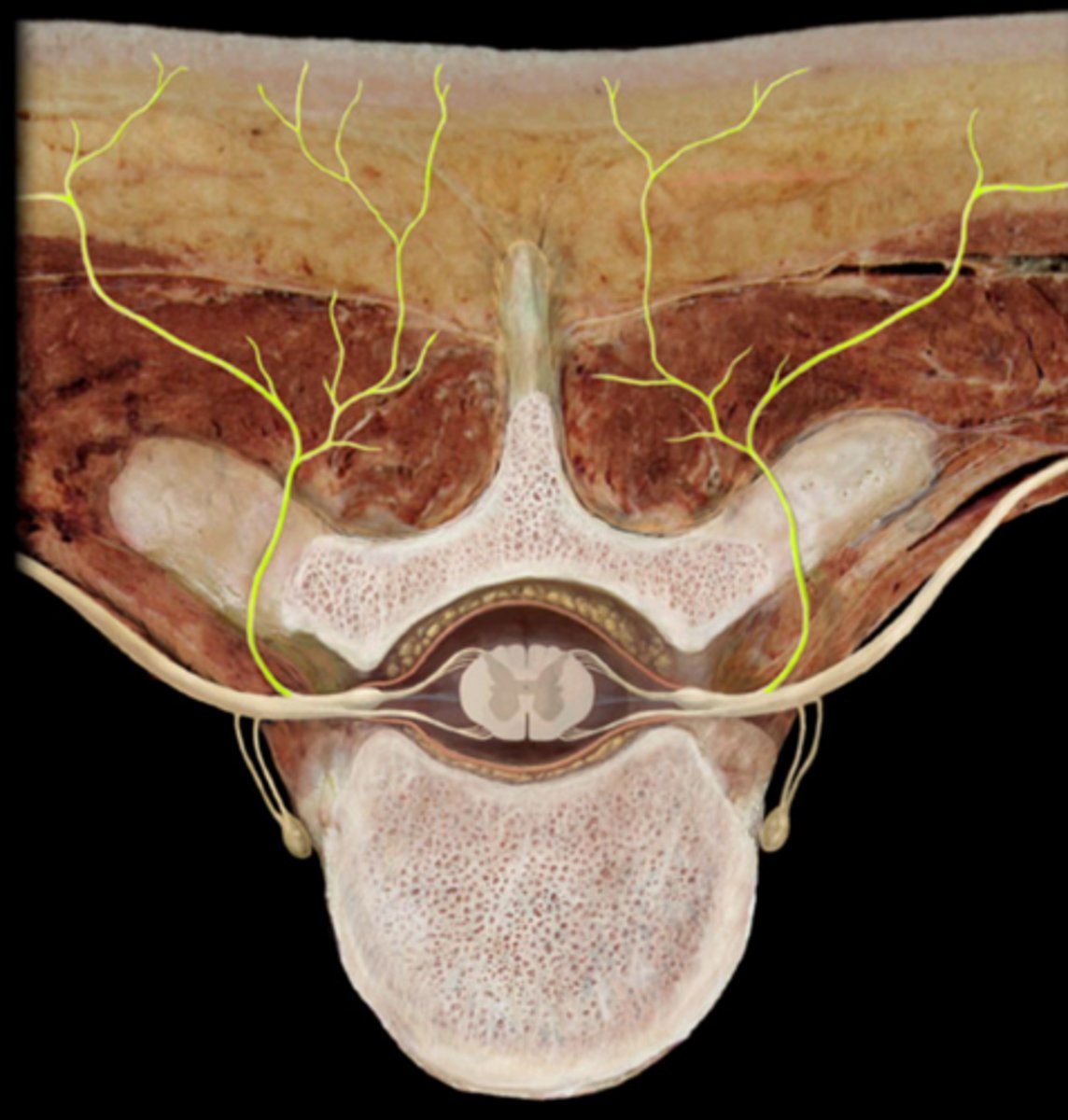
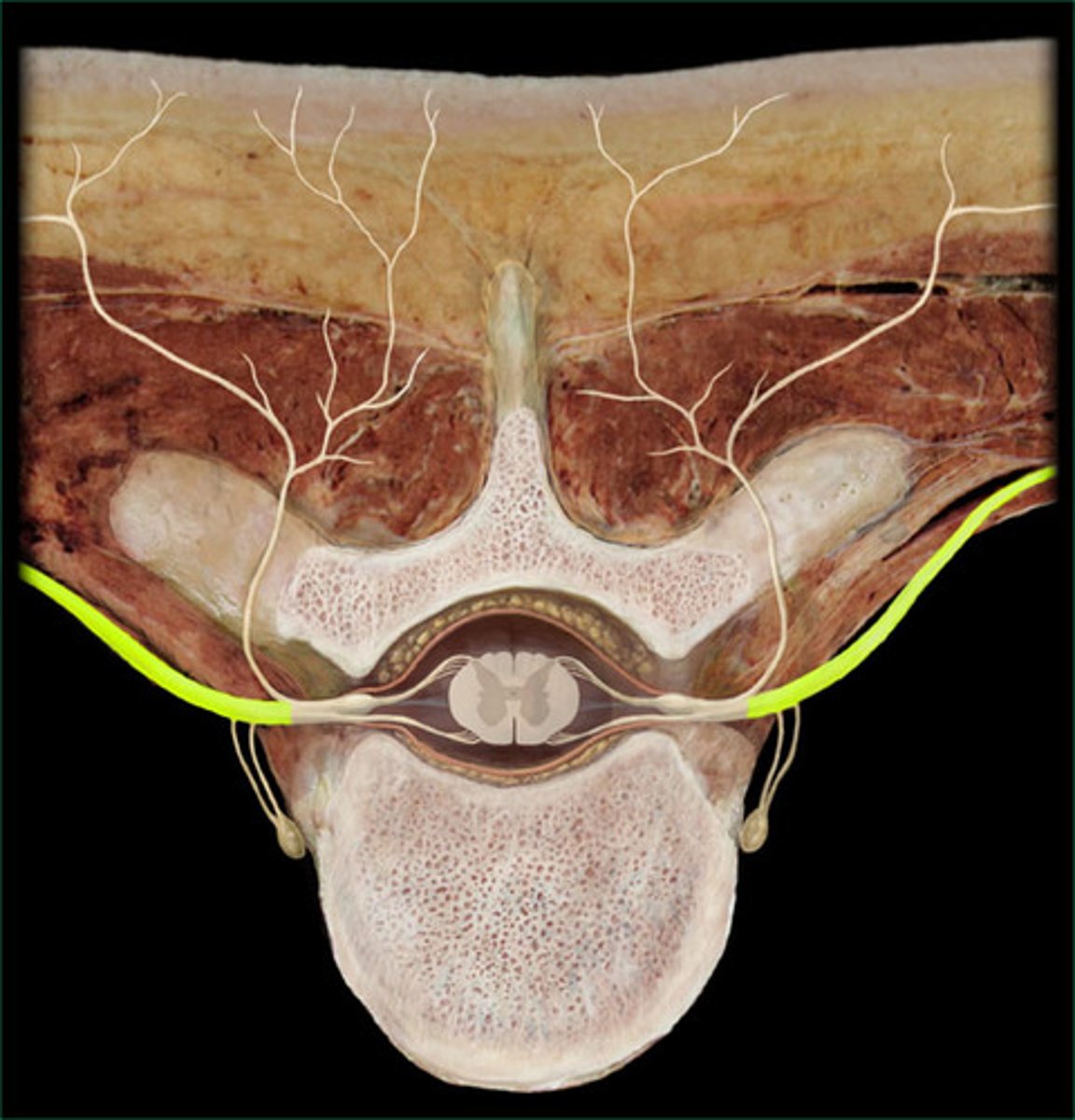
celiac ganglion
identify the structure #2
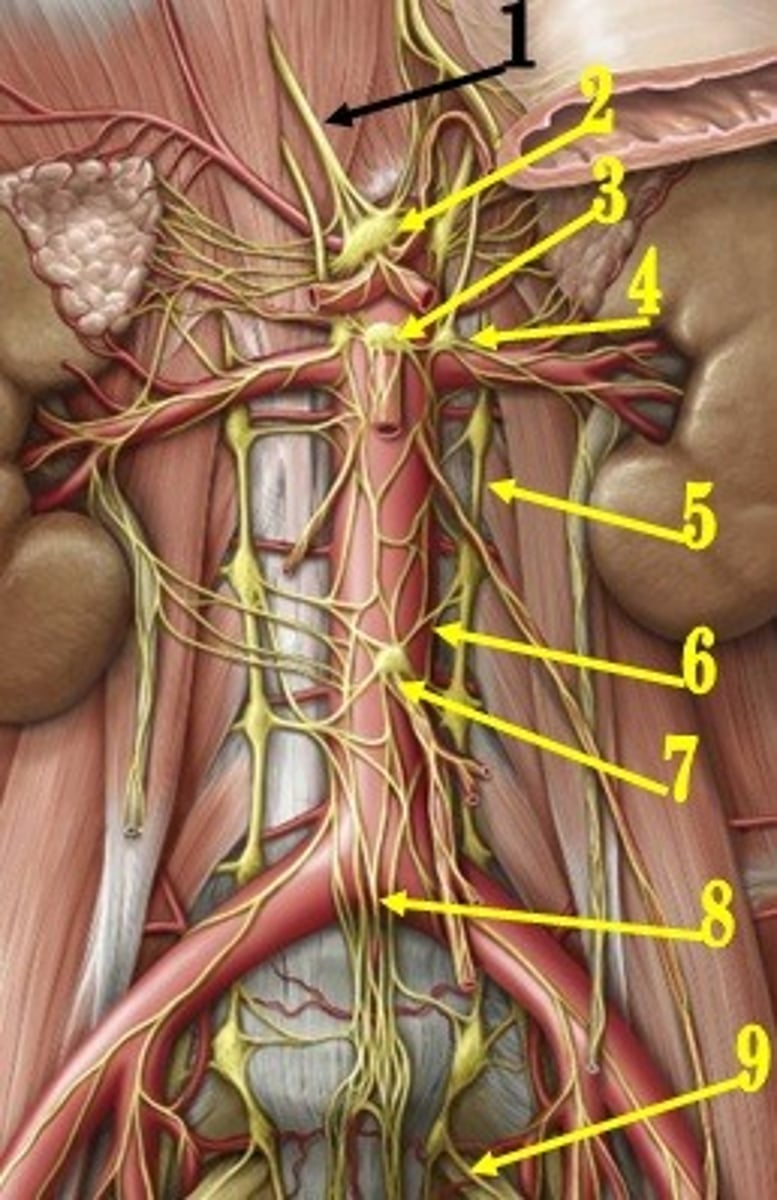
aorticorenal ganglion
identify the structure #4
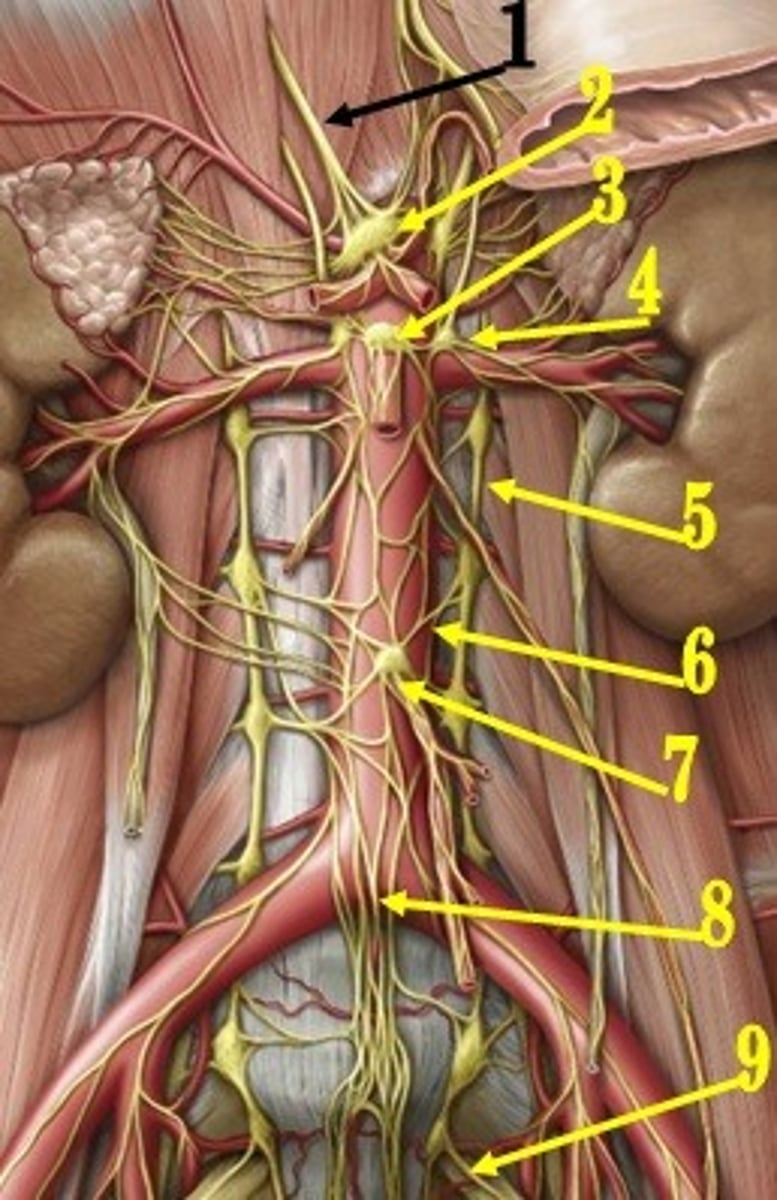
superior mesenteric ganglion
identify the structure #3
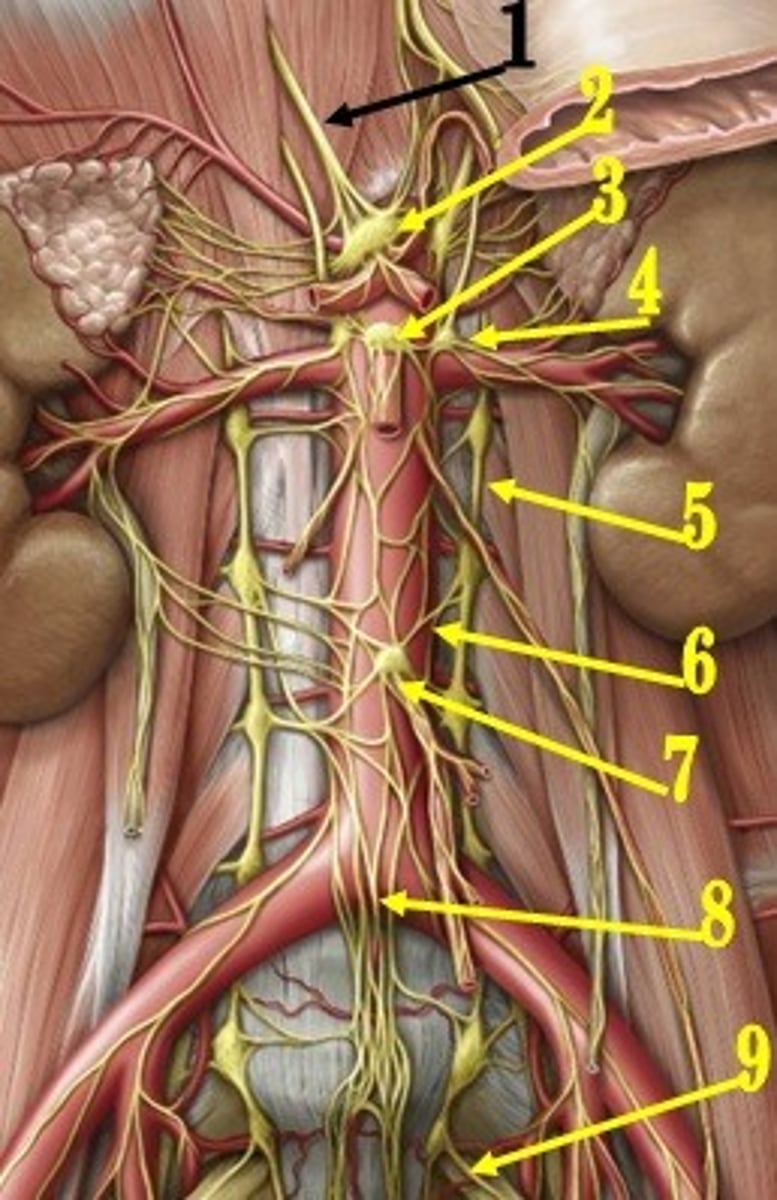
inferior mesenteric ganglion
identify the structure #7
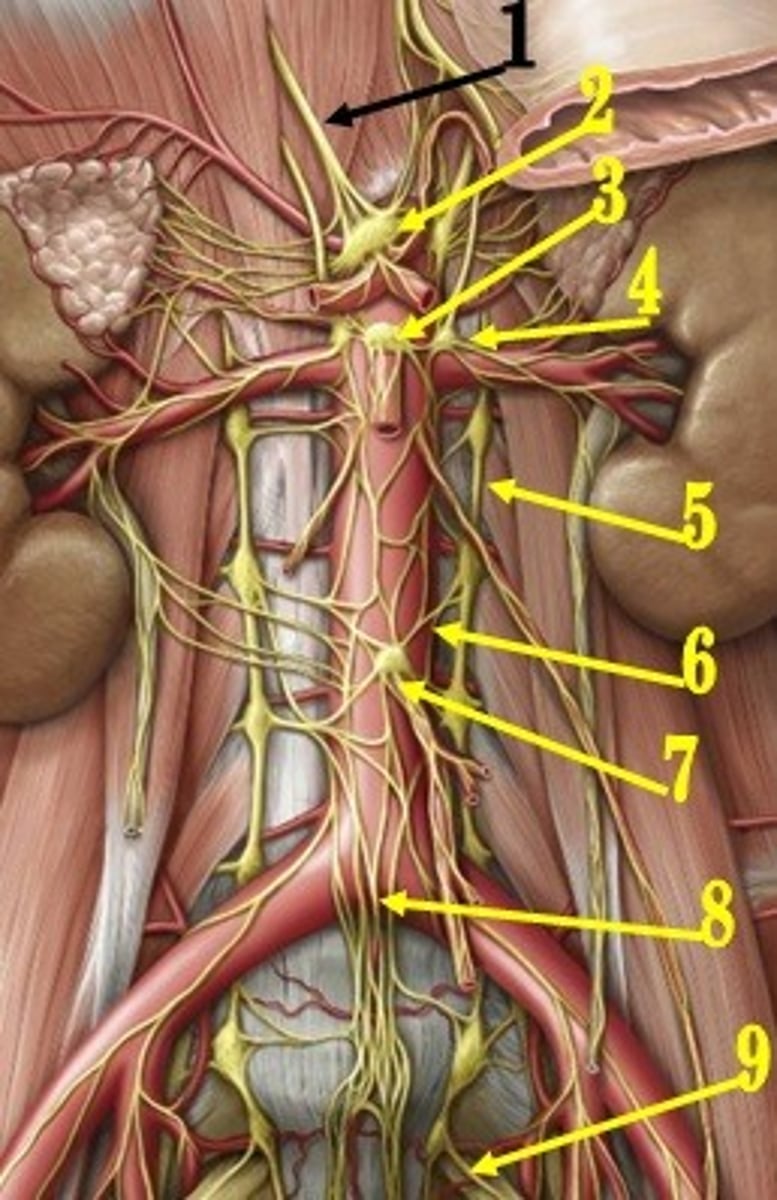
adrenal gland
which organ is the only one that has sympathetic efferent fibers that do NOT synapse at the prevertebral ganglia, but go straight through them to the effector organ?
prevertebral ganglia
where are post-ganglionic cell bodies of abdominopelvic splanchnic nerves located?
ventral horn of spinal cord
where are pre-ganglionic cell bodies of abdominopelvic splanchnic nerves located?
periarterial plexuses
Postganglionic fibers follow ________ to target organ
Oculomotor (CN III)
Facial (CN VII)
Glossopharyngeal (CN IX)
Vagus (CN X)
Preganglionic parasympathetic fibers exit brainstem via what 4 cranial nerves:
sympathetic division
most general viscaral afferent pain sensations will use which division to get back to the CNS?
parasympathetic division
Pain from viscera below "pelvic pain line" will use which division to get back to the CNS?
General Visceral Afferent
•Carry sensory information from viscera to CNS
•Usually does not reach conscious level
•Sensation that reaches conscious level = poorly localized pain, cramps
sympathetic division
Pain from most of the viscera, Ie: Ischemia or noxious stimuli in the heart, will take which autonomic division back to the CNS?
parasympathetic division
Pain from viscera below "pelvic pain line". Ie: Birth canal, will take which autonomic division back to the CNS?
T1-T4/5
pain in the heart is most often referred to what dermatome?
greater splanchnic nn.
the organs of the foregut at innervated by what splanchnic division?
lesser splanchnic nn.
the organs of the midgut at innervated by what splanchnic division?
lumbar splanchnic nn.
the organs of the hindgut at innervated by what splanchnic division?
least splanchnic nn.
the kidneys and adrenal glands are innervated by what splanchnic division?
vagus n.
parasympathetic innervation for the foregut is done by the:
vagus n.
parasympathetic innervation for the midgut is done by the:
pelvic splanchnic nerves
parasympathetic innervation for the hindgut is done by the:
pelvic splanchnic nerves
parasympathetic innervation for the pelvic structures is done by the: