🍃 LEAVES – FLASHCARDS (OHT 101)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is the main function of leaves?
Food manufacturing through photosynthesis.
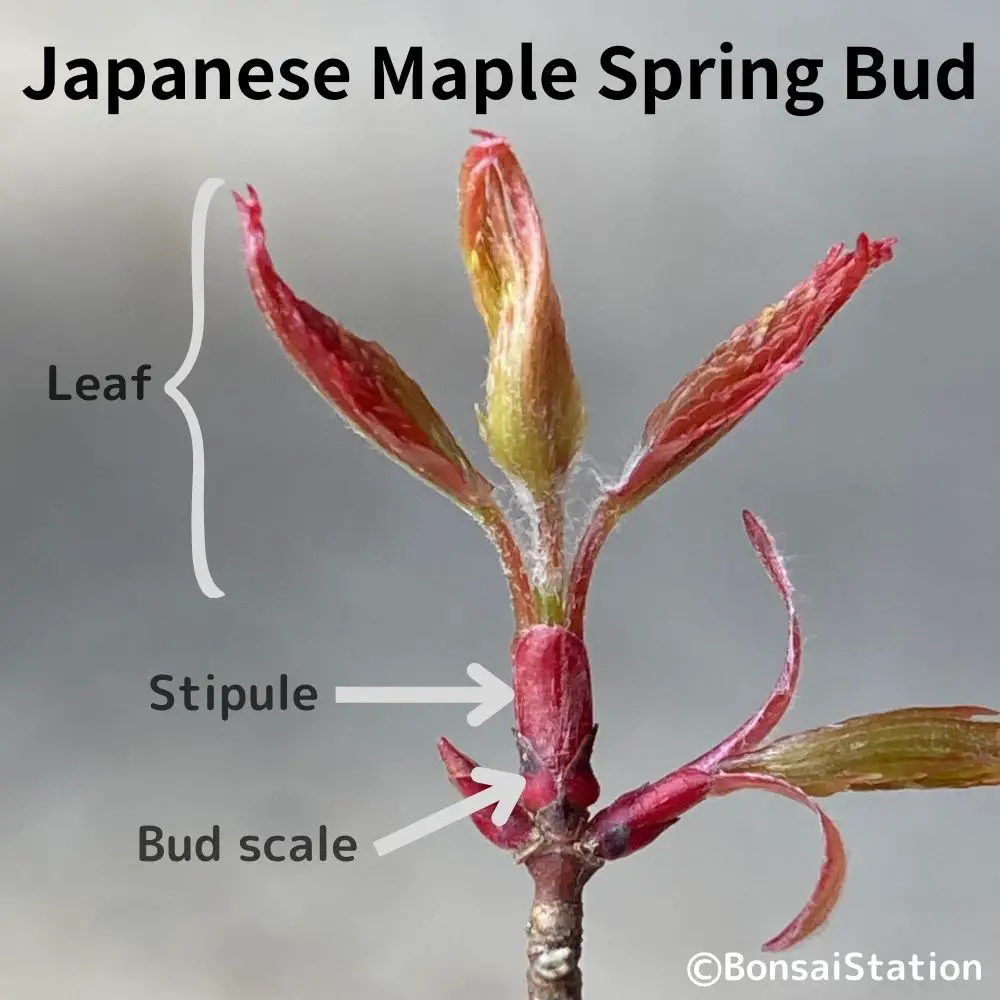
What protects buds on a plant?
Bud scales and stipules.
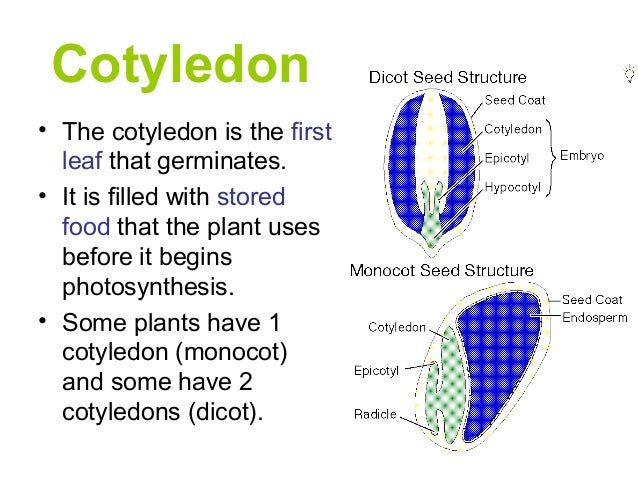
What leaf structure stores food in some plants?
Cotyledons.
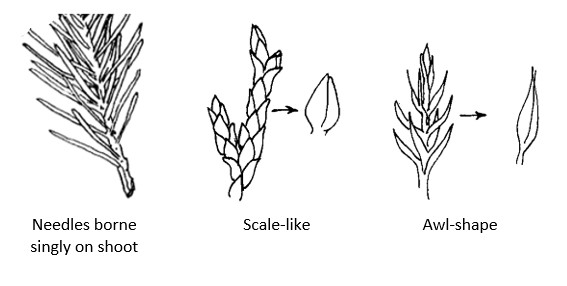
What are the three types of gymnosperm leaves?
Needles, scales, and awls.
What is a simple leaf?
A leaf with a single blade.
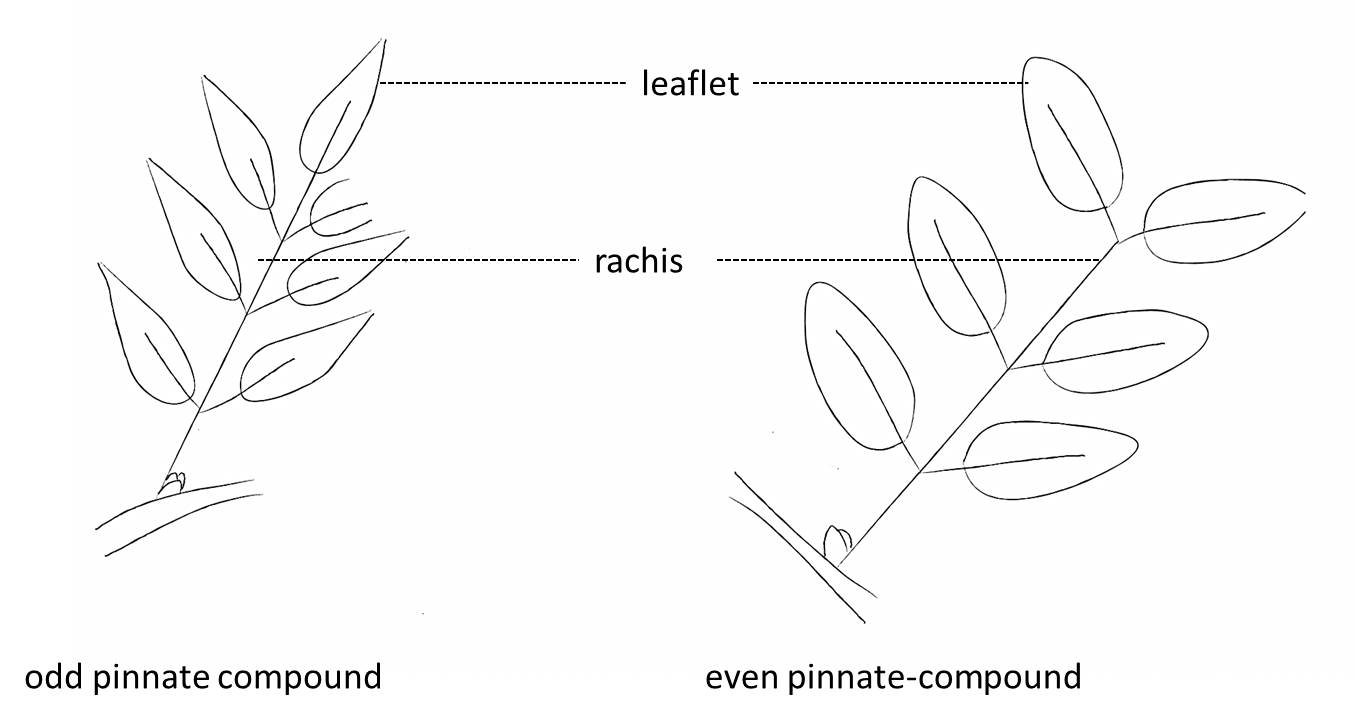
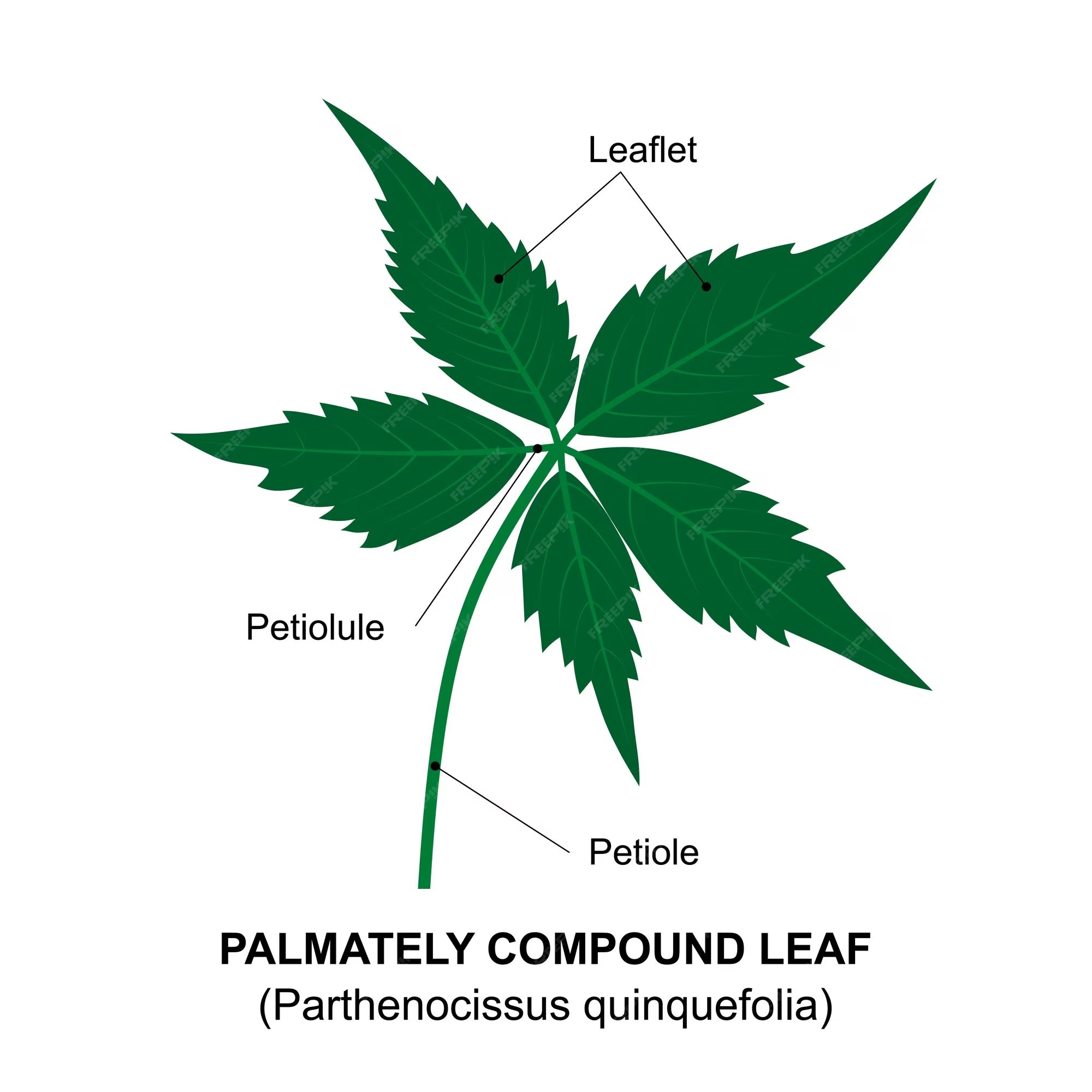
What are the three types of compound leaves?
Palmately compound, pinnately compound (odd or even), and bi-pinnate.

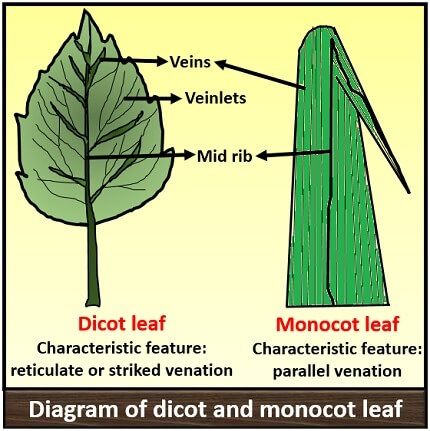
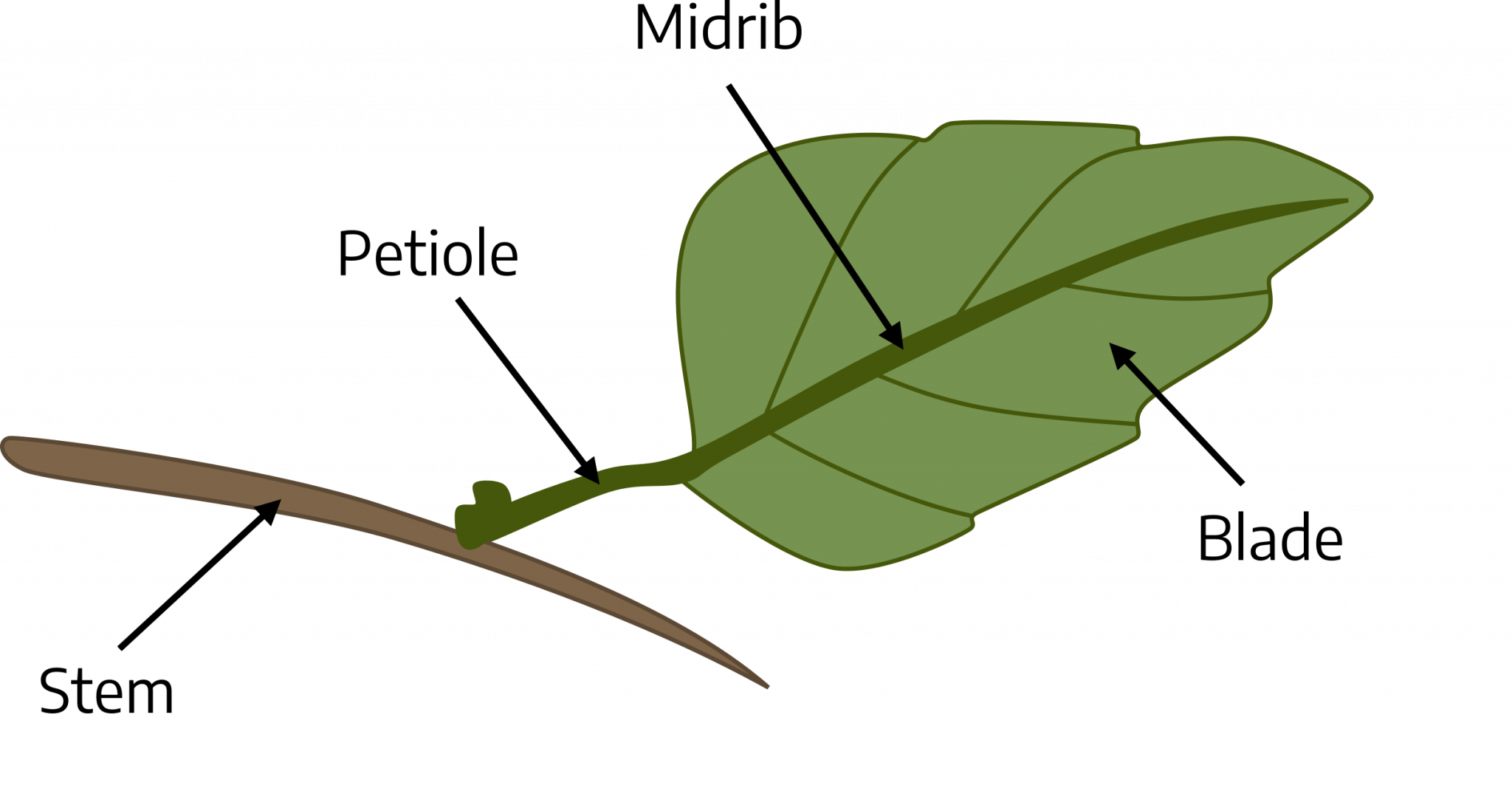
What features define simple dicot leaves?
Leaf blade (lamina), petiole, pulvinus, main midrib with secondary veins.
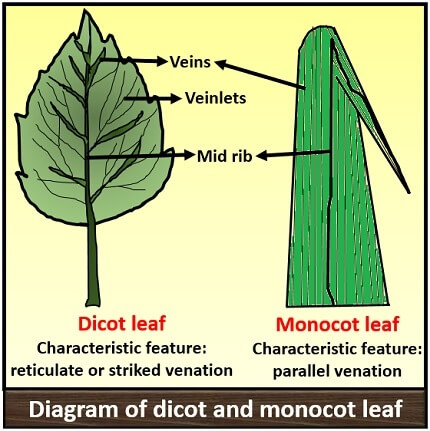
What features define simple monocot leaves?
A sheath instead of a petiole, sessile (no petiole), may have ligules and auricles.
What attaches a leaflet to the rachis?
The petiolule.
What is a rachis?
The main axis of a compound leaf.
What defines palmately compound leaves?
Leaflets attach at a single common point.
What is the pulvinus?
The swollen base of a petiole, filled with water-holding parenchyma cells.
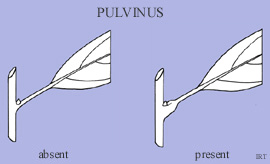
What happens to the pulvinus under water stress?
It collapses as it loses water and droops.
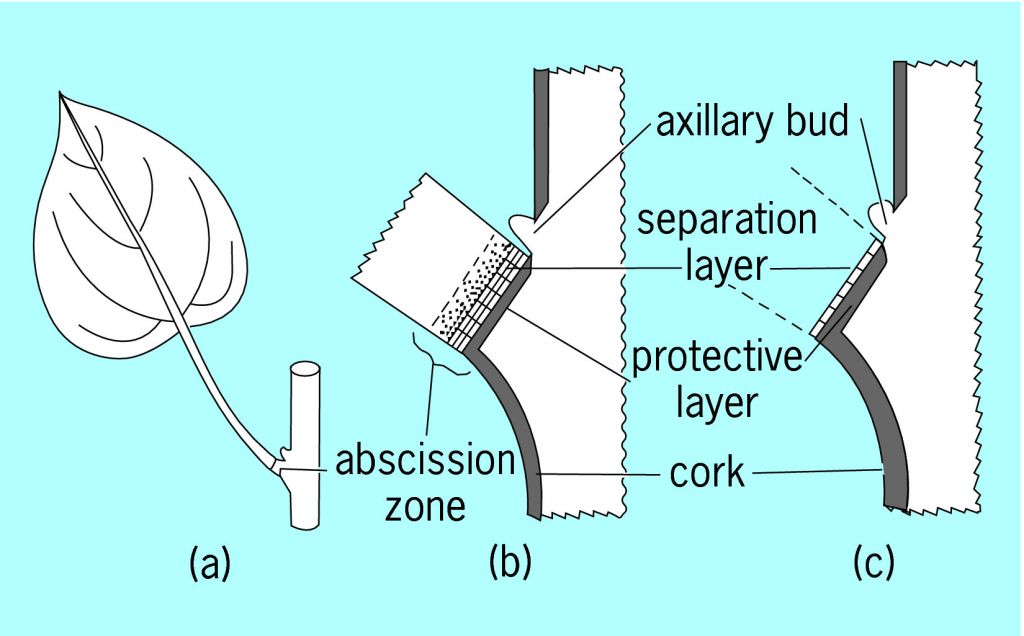
What is the abscission zone?
The base of the petiole where dicot leaves detach from the plant.
What determines leaf arrangement on a stem?
The pattern in which simple leaves are attached.
What is venation?
The arrangement of veins within a leaf.
What are stomata?
Natural openings for gas exchange and transpiration.
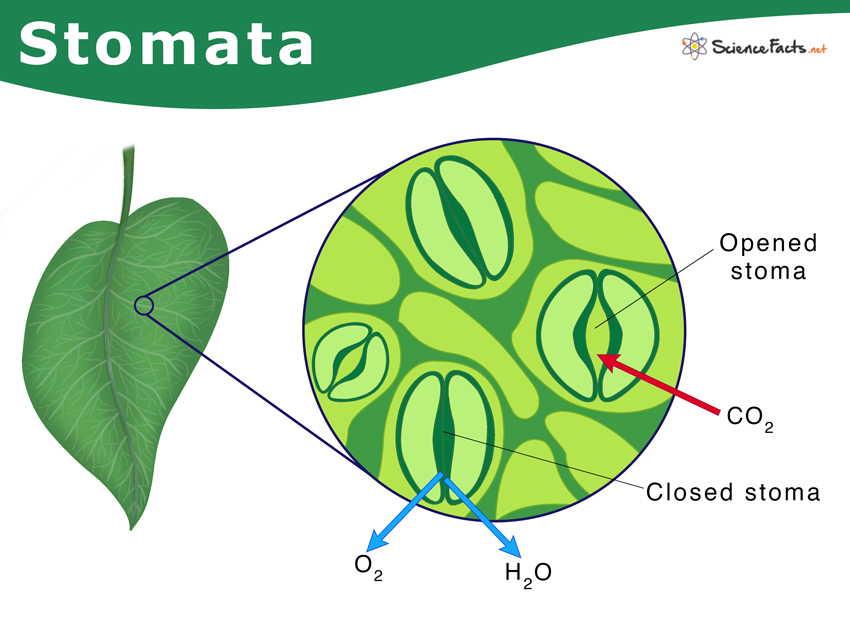
What controls stomatal opening and closing?
Guard cells.
What is mesophyll?
Leaf tissue equivalent to the cortex; used for storage.
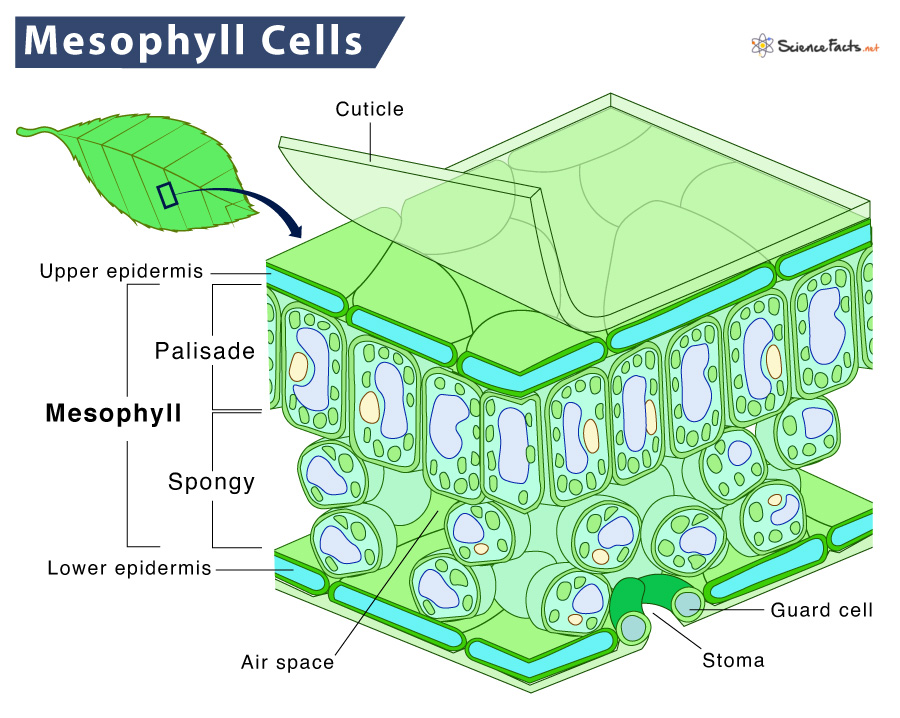
What is spongy mesophyll?
Large, airy cells near the lower epidermis; provide flexibility and buoyancy.
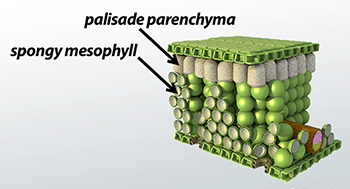
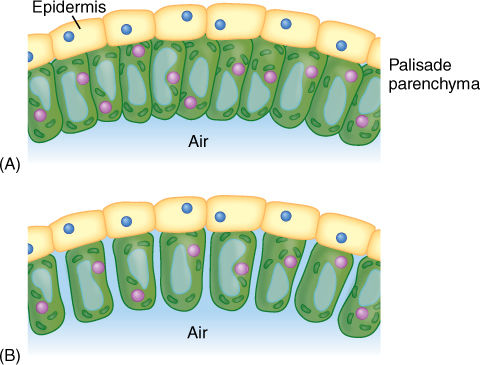
What are palisade parenchyma cells?
Cells beneath the upper epidermis that contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
What are xerophyte leaves adapted for?
Arid/desert conditions.

Name two xerophyte adaptations.
Thick cuticle; water storage cells; small leaves; dropping leaves during drought.

What is a hydrophyte leaf?
A leaf on an aquatic plant.

What adaptations do hydrophyte leaves show?
Thin cuticles and spongy mesophyll for buoyancy.

What are floral bracts?
Modified leaves protecting flowers during development; usually green and photosynthetic.
Give examples of other modified leaves.
Bud scales, tendril leaves, spines, thorns.
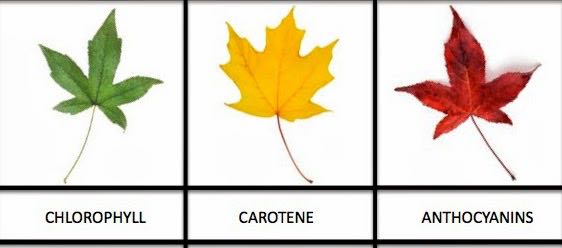
What triggers fall color changes?
Shorter photoperiod and temperature changes
Why do yellow and orange pigments become visible in fall?
Chlorophyll breaks down, revealing carotenoids that were always present.
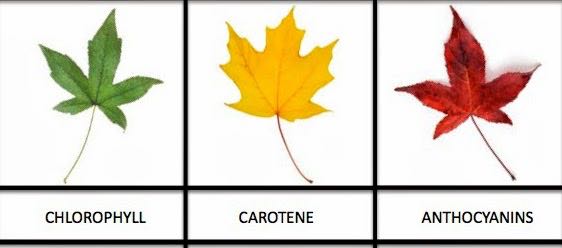
What must happen for red pigments (anthocyanins) to form?
Accumulation of sugars in leaves, sunny days, and cool nights.
What distinguishes needles from scales?
Needles are long/slender; scales are tiny and flat.
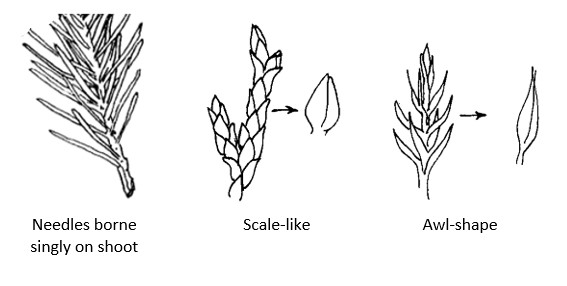
What are awl leaves?
Sharp, narrow, triangular leaves found on some conifers.