onc lec 4: Diagnostic Imaging
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
1) is there a tumor?
2) is it malignant?
3) what is the extent or grade of cancer?
4) is the treatment effective (therapy monitoring)
what are the four goals of diagnosis?
tumor size, shape, and density
what does anatomic imaging measure?
anatomic imaging
mammography and CT are examples of
perfusion, metabolism, molecular features (in vivo tumor biology)
changes in functional/molecular processes
what does functional imaging measure?
how well a positive test detects disease
what does sensitivity tell us?
(# who test positive) / (all with disease)
as what fraction is sensitivity defined?
the false negative rate: (# who test negative) / (all with disease)
sensitivity and false negative fractions add up to 1
what is the complement to the sensitivity fraction?
how well a negative test detects non-disease
What does specificity tell us?
okay
ADD cards for specifcity fraction and false positive rate
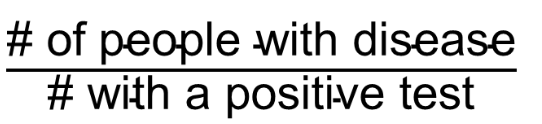
the proportion of all people with positive tests who have the disease
What is the positive predictive value?
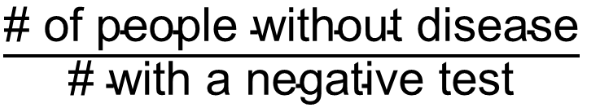
the proportion of all people with negative tests who do not have the disease
What is the negative predictive value?
sonography or ultrasonography
what are other terms for ultrasound?
a reflection of high-frequency sound waves is be constructed into an image
how does ultrasound work?
acoustic impedance
in an ultrasound, what describes tissue stiffness and brightness in the image?
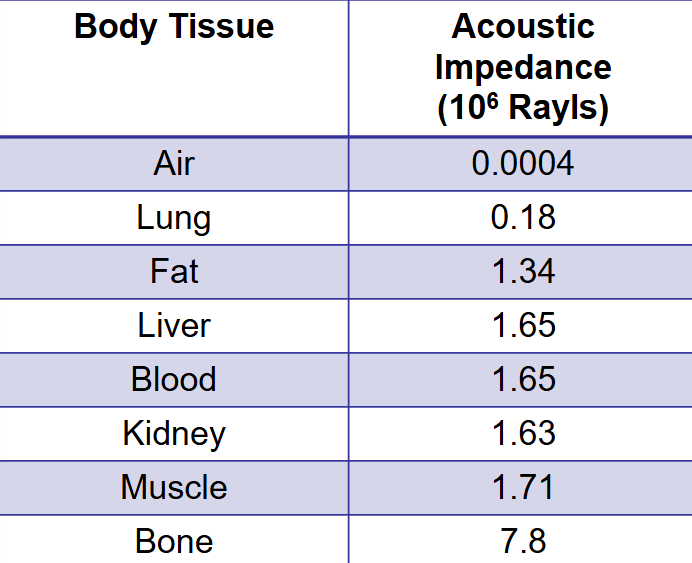
increase
does acoustic impedance increase or decrease with density?
no
is ultrasound ionizing radiation?
stiffened tissue of tumors/lumps/bumps show up differently in the ultrasound image
how are tumors/lumps/bumps seen in an ultrasound?
full bladder (liquid is a conduit for sound waves)
are ultrasounds for bladder cancer performed on a full or empty bladder?
> 1 cm
ultrasounds can only detect tumors ____
cystoscopy
a bladder ultrasound would be performed before ____ because it is less invasive
ultrasound-guided biopsy
allows real-time dynamic feedback to ensure accurate positioning
What is the most common form of image guided biopsy for the breast, kidney, liver, and other peripheral soft tissues?
the skills of the technician
the image quality of an ultrasound is heavily dependent on . . .
no
can sound waves (ultrasound) penetrate bone or pockets of air?
0.3-1 mm (axial), 1-3 mm (lateral)
what is the resolution of an ultrasound?
High frequency light goes through the body
how do x-rays and CT scans work?
electron density
X-ray absorption is proportional to . . .
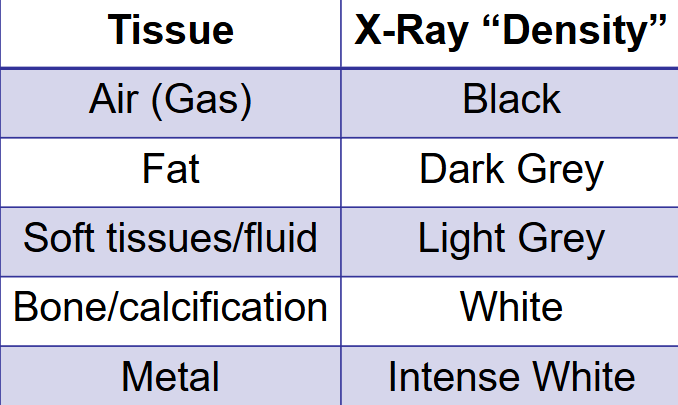
white
the denser a material is, the more ___ is looks on the x-ray
a 3D reconstruction of multiple x-ray images/projections
what is a CT (Computed Tomography) image?
an X-ray source is rotated around patient
more projections = better images
how is a CT image taken?
water and air (Hounsfield unit, HU)
what is CT intensity normalized to? (not x-ray)
less
x-rays use ___ radiation than CTs
they have no superimposition of structures
what feature of CT scans is important for areas with multiple organs?
x-ray: 0.05 to 0.1 mm
CT: 0.5 to 1 mm
what is the smallest size structure that can be resolved in an x-ray and CT?
yearly after 40 and every two years after 55.
how often are mammograms recommended?
reduces superimposition and reduces thickness (and therefore radiation dose)
why is a mammogram taken between two plates?
tumors arising from bone-producing cells
What are osteosarcomas?
between 10 - 20 years old
when are osteosarcomas most prevalent?
knee
60% of osteosarcomas are in the ___ and near other joints
ectopic bone
what can an osteosarcoma tumor produce?
soft tissue
what do x-rays and CTs not work well for?
when cancer is near either air (lung), fat (breast) or heavier atoms (bone calcium)
in what three circumstances are X-rays / CTs best?
yes - therefore a carcinogen
are x-rays ionizing radiation?
no - magnets
are MRIs ionizing radiation?
magnetic properties of certain elemental isotopes
– Most commonly 1H
how do MRIs get signals?
water and fat
what do the basic MRI contrast mechanisms focus on?
T1W: Fat bright, water dark
T2W: Water bright, fat dark
how do T1W and T2W appear in an MRI?
slower: an hour for MRI vs seconds for CT
are MRIs faster or slower than CTs?
in lungs and bones
where do MRIs get a poor signal?
no
can an MRI distinguish cancer from edema?
1-5mm in each direction
what is the resolution of an MRI?
99mTc-MDP (methylene diphosphonate)
which radiotracer is used for bone scans?
prostate, lung, breast, neuroblastoma
which four tumors commonly metastasize to bone?
multiple randomly distributed foci of increased uptake in the axial skeleton (following distribution of bone marrow)
what is the typical pattern of bone metastasis?
PET
uptake of FDG is measured by
I: 60-80%
II: 5-50%
IIIa: 10-40%
IIIb, IV: < 5%
what are the 5-year survival rates of lung cancer?
11C and 18F
what radionucleotides are detected by PET?
99mTc and 123I
what radionucleotides are detected by SPECT?
yes, but less than a diagnostic CT
do PET and SPECT give off radiation?
high cost
are PET and PET/CT generally a high or low cost?
A cluster of white blood cells and other tissue in areas of inflammation (non-cancerous) ~ may show up on a PET
what is a granuloma?