degrees of freedom
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What does "Degrees of Freedom" (DoF) mean in motor control?
The number of parameters that are free to vary to generate an action.
Why are there infinite ways to perform a movement?
Because multiple joints have multiple DoF, leading to countless possible trajectories for the same goal.
Who introduced the concept of variability in motor actions and what was the example?
Nikolai Bernstein; he tracked hammering movements and found each trajectory was slightly different.
How do humans learn motor skills according to Bernstein?
By initially freezing DoF and gradually releasing them as skill improves.
What is motor equivalence?
The ability to achieve the same end result using different movements or effectors.
What role does the brain play in motor equivalence?
A common pattern generator in the brain guides actions, even if the end effector varies.
What is coupling in motor control?
Interactions between effectors that reduce the control required, limiting DoF.
How does coupling simplify control?
By pairing control parameters (e.g., fixing A and B together), reducing independent DoF.
Give a real-world example of coupling in animals.
Fish fins: movement of pectoral fins affects dorsal fin amplitude, showing interdependence.
Give a real-world example of coupling in humans.
When one arm changes speed, the other arm’s movement is disrupted—indicating shared control.
How does context affect motor cortex stimulation?
Stimulating the same area in a cat causes flexion when standing but extension when walking.
context dependence
What is physical coupling?
When two pendulums swing together, they eventually synchronize speed and pattern.
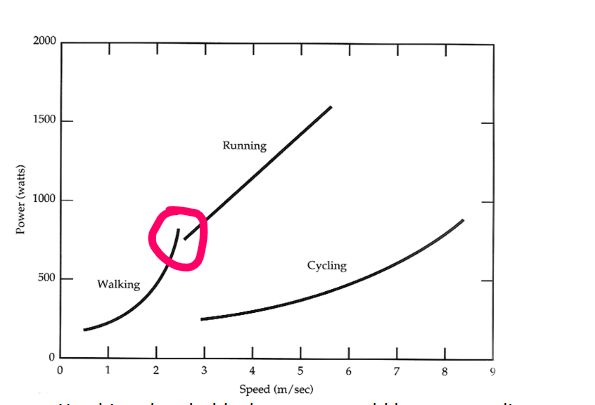
At what speed does walking transition to running?
Around 3 m/s, when walking becomes energetically inefficient compared to running.
humans switch to running to maintain efficiency
R McNiel Alexander
What is a preflex?
An immediate response with 0 ms latency, faster than a reflex (30–60 ms).
e.g. ball bouncing on the ground
What is equifinality in motor control?
Regardless of starting position, stimulating a certain point leads to the same final position.
sum up vectors in neuronal activity and always reach the same place
Which study demonstrated equifinality?
Frog limb stimulation—neuronal activity sums vectors to reach the same endpoint
Emilio Bizzi
What happens with long stimulation of motor cortex?
The final posture depends on stimulation site, not initial limb position.
posture neurons
What is the grasp height effect?
Adjusting hand position based on target shelf height for efficient action.
first order planning
What is second-order grasp planning?
Choosing an awkward initial grip to achieve a comfortable final position (end-state comfort).
What is precrastination?
Performing suboptimal actions (e.g., picking closer object first) to reduce cognitive load.
How does precrastination relate to DoF?
It simplifies physical tasks to reduce mental effort, trading efficiency for cognitive ease.