Membrane Proteins and their functions
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Where are membrane proteins found
They are embedded in or attached to the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane
How can membrane proteins be attached
They may be permanently or temporarily attached to the membrane
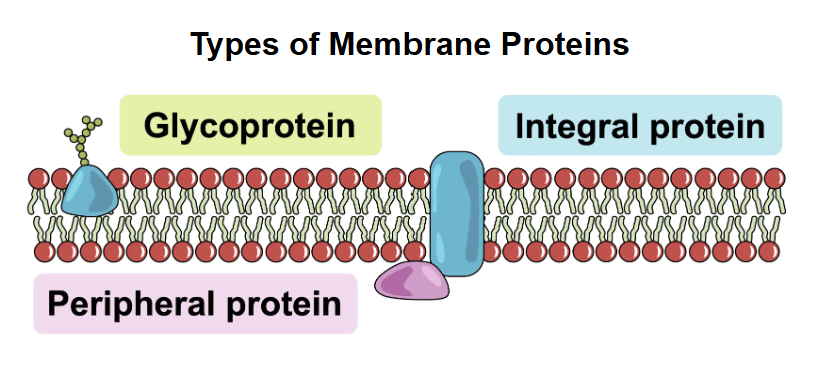
What are integral proteins
Proteins that penetrate the bilayer and are permanently attached to the membrane
Can integral proteins be easily removed from the membrane
No — removing them would disrupt the bilayer
What are examples of integral proteins
Glycoproteins, ion channels, carrier proteins, and protein pumps
What are peripheral proteins
Proteins that attach temporarily to one side of the membrane
How are peripheral proteins held in place
By attaching to integral proteins, phospholipid heads, or the cytoskeleton/extracellular matrix
How can peripheral proteins be removed
They can be removed by polar solvents without damaging the membrane
What is an example of a peripheral protein
Receptor complexes involved in cell signalling, like G proteins
What determines the composition of a membrane protein
Its function within the cell — structure matches purpose
How do non-polar (hydrophobic) amino acids behave in the membrane
They face the lipid bilayer, helping the protein stay anchored
How do polar (hydrophilic) amino acids behave in the membrane
They face the watery surroundings inside and outside the cell
What lines the inside of protein channels
Polar amino acids, allowing charged or polar molecules to pass through safely
What are the six main functions of membrane proteins
Junctions, Enzymes, Transport, Recognition, Anchorage, and Transduction
What is the role of junction proteins
They connect and join two cells together, helping form tissues
What do enzyme proteins do in membranes
They speed up chemical reactions and localise metabolic pathways
What is the function of transport proteins
They help move materials across the membrane by facilitated diffusion or active transport
What is the function of recognition proteins
They act as markers to help cells identify each other
What do anchorage proteins do
hey provide attachment points for the cytoskeleton inside the cell and the extracellular matrix outside
What is the role of transduction proteins
They act as receptors that receive signals — for example, binding peptide hormones to trigger a response inside the cell
What are the 3 types of memebrane protiens