HSC302 Exam 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
1
New cards
IDEA part C
Policy establishing early intervention services
2
New cards
Physical, cognitive, communication, social, adaptive
developmental areas early intervention
3
New cards
Who is eligible for early intervention services?
children ages 0-3
diagnosed physical/mental condition
existing delay
diagnosed physical/mental condition
existing delay
4
New cards
In florida.. delay is
2 standard deviations in one of the five areas below the mean
1.5 standard deviations below the mean in 2 of the 5 areas
1.5 standard deviations below the mean in 2 of the 5 areas
5
New cards
natural environments include
same aged peers that are not experiencing delays
6
New cards
least restrictive environment
children who get special education should be in the same classrooms as other kids
7
New cards
individualized education plan (IEP)
each child has their own educational plan that will allow them to meet their educational goals
8
New cards
toxic stress
-interprets and responds to environment signals
-causes wear and tear on the body when it is under constant level of toxic stress
-causes wear and tear on the body when it is under constant level of toxic stress
9
New cards
serve/return
new neural connections from the brain as young children instinctively serve through babbling, facial expressions and gestures, and adults return by responding in a very directed, meaningful way
10
New cards
neurodevelopmental condition
identified in childhood, lifelong, group of conditions with onset in the developmental period, manifest easily
11
New cards
discrete trial training (DTT)
involves breaking down complex behaviors into a number of elements, which are separately and sequentially reinforced to build up into the desired behavior
12
New cards
evidence based trainings
-social skills groups
-PEERS (young adults)
-peer mediated interventions
-PEERS (young adults)
-peer mediated interventions
13
New cards
Intellectual disability 85%
can live independently
14
New cards
Moderate ID 10%
independent living may be achieved with moderate levels of support
15
New cards
severe ID 3.5%
required daily assistance with self care activities and safety supervision
extensive support needed for daily activities
extensive support needed for daily activities
16
New cards
profound ID 1.5%
required 24 hour care
pervasive support needed for daily routines
pervasive support needed for daily routines
17
New cards
customized employment
job carving: analyzing work duties and identifying specific tasks
job sharing: two workers share the duties of a full time job
job sharing: two workers share the duties of a full time job
18
New cards
Supported employment
job coach for training, job sharing
19
New cards
autism spectrum disorder
cause unknown, genetic, older parents, (down syn, fragile x, retts), very low birth rate
4.5x as many boys
onset usually between 12-24 months
4.5x as many boys
onset usually between 12-24 months
20
New cards
diagnosis for ASD
difficulty communicating, restricted interests, symptoms that hurt person's ability to function, early childhood symptoms, repetitive behaviors
21
New cards
echolalia
repeating certain words or behaviors
22
New cards
sensory processing disorder
sensory info goes into the brain but does not get organized into appropriate responses, info gets mixed up and responses become inappropriate
23
New cards
Severity levels ASD
1: require support
2: require substantial support
3: require very substantial support
2: require substantial support
3: require very substantial support
24
New cards
Reasons for developing CP
prenatal, perinatal, postnatal
25
New cards
PRENATAL causes of CP
heredity, infections, lack of oxygen, Rh incompatibility, prematurity, metabolic disorders
26
New cards
PERINATAL causes of CP
lack of oxygen, trauma birth injury
27
New cards
POSTNATAL causes of CP
traumatic head injuries, shaken baby, infections, brain hemorrhages, anoxia, tumor, TAKE PLACE IN 1st YEAR
28
New cards
movement with CP
-ataxia (poor muscle control causes clumsiness)
-atonia (lack of muscle tone)
-spasticity (exaggerated muscle tone resulting in muscle stiffness and contractions.. most common manifestation)
-dystonia (muscle contractions causing twisting or repetitive movements)
-hyperkinetic (any unwanted excess movement)
-atonia (lack of muscle tone)
-spasticity (exaggerated muscle tone resulting in muscle stiffness and contractions.. most common manifestation)
-dystonia (muscle contractions causing twisting or repetitive movements)
-hyperkinetic (any unwanted excess movement)
29
New cards
Types of CP
most common: pyramidal or spastic (65-75% of all cases)
extrapyramidal or nonspastic types of CP are responsible for 20% of cases
extrapyramidal or nonspastic types of CP are responsible for 20% of cases
30
New cards
CP diagnosis
difficult to diagnose, no definitive test, 40% incorrectly diagnosed
31
New cards
Used for diagnosing CP
CT, MRI, ultrasound, lumbar puncture, serum uric acid and blood urine assays, viral and parasitic titers (TORCH)..intrauterine infections, chromosomal studies
32
New cards
impact of body structures/function on activity and participation
-static (not progressive) does not get worse over time
-keeps brain from telling rest of body what to do
-difficulty talking, seeing, hearing, sitting, swallowing
-normal intelligence
-lack of control of muscle function
-gait disturbance, mobility limitations
-keeps brain from telling rest of body what to do
-difficulty talking, seeing, hearing, sitting, swallowing
-normal intelligence
-lack of control of muscle function
-gait disturbance, mobility limitations
33
New cards
interventions for CP
direct treatment is unavailable
-secondary treatments include: therapy, tone-altering meds, braces wheelchairs, crutches, orthopedic and neurosurgical procedures to correct deformities/tone
-secondary treatments include: therapy, tone-altering meds, braces wheelchairs, crutches, orthopedic and neurosurgical procedures to correct deformities/tone
34
New cards
muscular dystrophy
-chronic, incurable
-progressive
-caused by genetic tissue in producing dystrophin
-muscle cells deteriorate
-muscle fibers become fat
-progressive
-caused by genetic tissue in producing dystrophin
-muscle cells deteriorate
-muscle fibers become fat
35
New cards
function of dystrophin
strengthen muscle fibers and protect them from injury as muscle contracts and relaxes
36
New cards
Limb-girdle MD
-males and females equally
-rare
-presents in early childhood to late adulthood
-affects shoulders and hips first
(may present with lordosis or scoliosis)
-intellect and senses unaffected
-rare
-presents in early childhood to late adulthood
-affects shoulders and hips first
(may present with lordosis or scoliosis)
-intellect and senses unaffected
37
New cards
facioscapulohumeral (FSH) MD
progressive weakness to face, upper arms, shoulders
-1 in 20,000 people males and females
-possible hearing loss and retinal vasculopathy
-appears during childhood or into adulthood
-1 in 20,000 people males and females
-possible hearing loss and retinal vasculopathy
-appears during childhood or into adulthood
38
New cards
myotonic dystrophy: type 1 and 2
most common beginning in adulthood
-40,000 people in US
-rare
-inability to relax muscles following contraction
-facial and neck muscles affected first
-cataracts, cardiac conduction, infertility, droopy eyelids, mask like face
-type 1 is more common
-40,000 people in US
-rare
-inability to relax muscles following contraction
-facial and neck muscles affected first
-cataracts, cardiac conduction, infertility, droopy eyelids, mask like face
-type 1 is more common
39
New cards
Duchenne (most common MD)
- x chromosome (boys)
-inherited
-seen early
-frequent falls
-waddling gait, walking on toes, large calf muscles
-commonly using wheelchair by 12
-DMD gene encodes dystrophin
-inherited
-seen early
-frequent falls
-waddling gait, walking on toes, large calf muscles
-commonly using wheelchair by 12
-DMD gene encodes dystrophin
40
New cards
Becker MD
-slow progression
-less severe than DMD
-similar problems but milder, presents later
-symptoms begin in teens, mid 20s
-weakness affects hips, pelvis, thighs, shoulders first
-less severe than DMD
-similar problems but milder, presents later
-symptoms begin in teens, mid 20s
-weakness affects hips, pelvis, thighs, shoulders first
41
New cards
MD changes in body structure/functions
-progressive
-muscular weakness
-complications like cardiomyopathy, contractures, scoliosis and lordosis, breathing issues, swallowing problems, cognitive issues
-muscular weakness
-complications like cardiomyopathy, contractures, scoliosis and lordosis, breathing issues, swallowing problems, cognitive issues
42
New cards
interventions supporting MD
bathroom aids, standing frame, mechanical lifts, mobility aids(walkers, wheelchairs), sip and puff wheelchair, tongue drive system
-medications: steroids slow muscle damage, side effects can cause weight gain and susceptibility to infection
-respiratory treatment: spirometry, cough assist, flu shot, ventilator
-medications: steroids slow muscle damage, side effects can cause weight gain and susceptibility to infection
-respiratory treatment: spirometry, cough assist, flu shot, ventilator
43
New cards
lordosis
sway back, sticking out butt like gymnast
44
New cards
kyphosis
hump back
45
New cards
muscular fibrosis
impairs muscle function, negatively affects muscle regeneration after injury
46
New cards
causes of Cystic Fibrosis
-genetic
-chronic, incurable
-progressive
-chronic, incurable
-progressive
47
New cards
how CP affects lungs
-thick, viscous mucus obstructs airways
-chronic productive cough
-frequent infections/hospitalizations
-atelectasis
-gradual loss of pulmonary function
TREATMENT:
-chest PT
-inflatable chest, portable breathing devices
-avoiding exposure to dust, air pollutants
-breathing techniques
-dislodging mucus
-respiratory devices (vest to get rid of mucus)
-double lung transplant (extreme measure)
-chronic productive cough
-frequent infections/hospitalizations
-atelectasis
-gradual loss of pulmonary function
TREATMENT:
-chest PT
-inflatable chest, portable breathing devices
-avoiding exposure to dust, air pollutants
-breathing techniques
-dislodging mucus
-respiratory devices (vest to get rid of mucus)
-double lung transplant (extreme measure)
48
New cards
how CP affects pancreas
-mucus blocks ducts
-digestive enzymes cannot do their job
-lack of absorption of nutrients
-can lead to diabetes over time
treatment:
-oral pancreatic enzymes
-supplements A,D, E, K
-high calorie diet
-digestive enzymes cannot do their job
-lack of absorption of nutrients
-can lead to diabetes over time
treatment:
-oral pancreatic enzymes
-supplements A,D, E, K
-high calorie diet
49
New cards
how CP affects liver/intestines
- Bile obstructed
- Inflammatory process
- Scarred tissue– cirrhosis (late stage)
preventing liver damage: clinical eval, liver enzyme eval, ultrasound
Intestines:
breakdown of food incomplete, secretions thicken feces, can lead to rectal prolapse
- Inflammatory process
- Scarred tissue– cirrhosis (late stage)
preventing liver damage: clinical eval, liver enzyme eval, ultrasound
Intestines:
breakdown of food incomplete, secretions thicken feces, can lead to rectal prolapse
50
New cards
how CP affects sweat glands
-imbalance of chloride concentration in sweat
(salty sweat)
-dehydration
increased HR, fatigue, weakness, decreased BP
(salty sweat)
-dehydration
increased HR, fatigue, weakness, decreased BP
51
New cards
how CP affects reproductive system
males mostly infertile (97-98%)
-born with malformed or blocked vas deferens
-no external problems
females may be fertile
-more difficult to conceive
-born with malformed or blocked vas deferens
-no external problems
females may be fertile
-more difficult to conceive
52
New cards
causes of Sickle cell disease
-inherited disease caused by deficit in a gene
-blood disorder
-life span of 40-50 years
-blood disorder
-life span of 40-50 years
53
New cards
complications from sickle cell disease
- Acute chest syndrome (pain, cough fever, hypoxia, lung infiltrates)
- Stroke– frequently in children (may be silent)
- Retinopathy
- Cardiomegaly
- Renal problems (hematuria, proteinuria)
- Osteonecrosis (especially hip, shoulder)
- Leg ulcers (non-healing)
- Priapism
- Splenic sequestration crisis
- anemia (acquired = extrinsic ) ( inherited = intrinsic )
- Stroke– frequently in children (may be silent)
- Retinopathy
- Cardiomegaly
- Renal problems (hematuria, proteinuria)
- Osteonecrosis (especially hip, shoulder)
- Leg ulcers (non-healing)
- Priapism
- Splenic sequestration crisis
- anemia (acquired = extrinsic ) ( inherited = intrinsic )
54
New cards
treatment for sickle cell disease
blood transfusions, corticosteroids, IV immune globulin, splenectomy
55
New cards
Bone marrow transplantation
-stay in unit to avoid infection
-find suitable donor
-potent antibiotics
-can take a year for recovery
-84% cured (children)
-stem cells taken from donor
-recipient takes meds to destroy own bone marrow stem cells
-donor cells are injected
PROBLEMS:
-high risk even with correct match
-graft vs host disease
-find suitable donor
-potent antibiotics
-can take a year for recovery
-84% cured (children)
-stem cells taken from donor
-recipient takes meds to destroy own bone marrow stem cells
-donor cells are injected
PROBLEMS:
-high risk even with correct match
-graft vs host disease
56
New cards
vaso-occlusive episodes
-rigid sickle cells with increased adhesiveness
-obstruction of blood flow
-bone marrow produces RBCs (can't keep up)
-obstruction of blood flow
-bone marrow produces RBCs (can't keep up)
57
New cards
human leukocyte antigen
-type of molecule found on the surface of most cells in the body
-plays an important role in body's immune response to foreign substances
-plays an important role in body's immune response to foreign substances
58
New cards
causes of Hemophilia
-inherited chronic bleeding condition
-sporadic, acquired, rare
-lack of protein in blood
-defect in clotting factors
-sporadic, acquired, rare
-lack of protein in blood
-defect in clotting factors
59
New cards
Hemophilia A
more common, defect in clotting factor 8
60
New cards
Hemophilia B
defect in clotting factor 9
61
New cards
mild clotting
possible prolonged bleeding after injury or surgery /25% of people
62
New cards
moderate clotting
spontaneous bleeding into joints and muscles; excessive bleeding after injury or minor surgery
63
New cards
severe clotting
spontaneous bleeding into joints and muscles, brain, nose, severe bruising /60% of people
64
New cards
treatment of Hemophilia
no cure
-immediate intervention when bleeding
-HTCs, comprehensive hemophilia centers
-synthetic hormone for mild cases
-liver transplant
-replacement therapy (IV infusion... plasma)
-immediate intervention when bleeding
-HTCs, comprehensive hemophilia centers
-synthetic hormone for mild cases
-liver transplant
-replacement therapy (IV infusion... plasma)
65
New cards
Hemarthrosis
bleeding into joint
66
New cards
epistaxis
nose bleeds with no obvious reasons
67
New cards
hemostasis
-clot formation
-fibrin forms clot
-fibrin forms clot
68
New cards
inhibitor
antibody against infusion
-can be caused by infection caused by infusion
-can be caused by infection caused by infusion
69
New cards
antibody
blood protein produced in response to and counteracting a specific antigen
70
New cards
anatomy of the eyeball
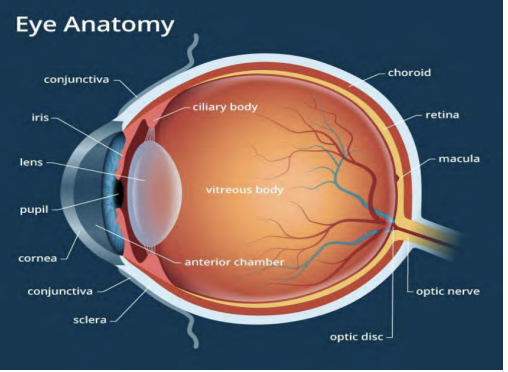
71
New cards
light passing through eye
enters through pupil --> passes through lens --> sensory info registers on retina --> conversion to electrical impulses to optic nerve --> message taken to occipital lobe
72
New cards
legal blindness
20/200
73
New cards
blind spot (scotoma)
decreased area of vision
(normal where the optic nerve and blood vessels leave eyeball)
(normal where the optic nerve and blood vessels leave eyeball)
74
New cards
nystagmus
eyes moving rapidly and involuntarily
75
New cards
strabismus
misalignment of both eyes, may be crossed, may only have one normal eye, or lazy eye
76
New cards
Shellen Eye Chart and Tumbling Es
- Positioned 20 feet away from chart
- Measures visual acuity
- Sharpness of vision
- Discernment of forms and shapes
- Does not detect glaucoma or diabetic retinopathy
- Measures visual acuity
- Sharpness of vision
- Discernment of forms and shapes
- Does not detect glaucoma or diabetic retinopathy
77
New cards
Retinal health
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
- Non- invasive imaging test
- Light waves record 3D images
- Cross sectional images of the retina
- Shows thickness of the retina
- Shows any evidence of fluid leaks
- Monitors treatment
- Determine if there is a problem with retina
- Non- invasive imaging test
- Light waves record 3D images
- Cross sectional images of the retina
- Shows thickness of the retina
- Shows any evidence of fluid leaks
- Monitors treatment
- Determine if there is a problem with retina
78
New cards
Visualization of eyeball/related structures
- P; pupils
- E; equal
- R; round
- R; reactive to
- L; light and
- A; accommodation
- Abnormal eye exam (Not of equal size
Not round
Not reactive to light
Not accommodating to focus on objects near or far)
- E; equal
- R; round
- R; reactive to
- L; light and
- A; accommodation
- Abnormal eye exam (Not of equal size
Not round
Not reactive to light
Not accommodating to focus on objects near or far)
79
New cards
intraocular pressure
tonometry
normal pressure is 12-22 mm Hg
-air puff tonometry is commonly used on children
-goldmann tonometry is very accurate (cornea is flattened, numbing drops used)
normal pressure is 12-22 mm Hg
-air puff tonometry is commonly used on children
-goldmann tonometry is very accurate (cornea is flattened, numbing drops used)
80
New cards
ophthalmologist
deals with disorders/disease of the eye, performs surgery
81
New cards
optometrist
assesses vision abnormalities, prescribes glasses/contacts
82
New cards
optician
supplies/sells optical instruments, lenses
83
New cards
cataracts
Lens becomes cloudy
- Blurry vision
- Poor night vision
- Halo around lights
- Diplopia
- Occurs in most people by the age of 80
- At risk; smokers, sunbathers, steroid users, diabetics
- Affect 1 or both eyes
- Treatment; surgery
- Blurry vision
- Poor night vision
- Halo around lights
- Diplopia
- Occurs in most people by the age of 80
- At risk; smokers, sunbathers, steroid users, diabetics
- Affect 1 or both eyes
- Treatment; surgery
84
New cards
macular degeneration
Loss of central vision
- Leading cause of vision loss for those over 50
- At risk; smokers, family history
- Slow or fast progression
- Occurs in 1 or both eyes
- Dry (most common) vs wet form
- Dry; stuff
- Wet; hemorrhaging
- Diagnosis; dilation
- Leading cause of vision loss for those over 50
- At risk; smokers, family history
- Slow or fast progression
- Occurs in 1 or both eyes
- Dry (most common) vs wet form
- Dry; stuff
- Wet; hemorrhaging
- Diagnosis; dilation
85
New cards
diabetic retinopathy
Affects blood vessels of the retina in those with diabetes
- Blurry vision
- Floating spots or streaks
- Blindness
- May cause other problems like diabetic macular edema, neurovascular glaucoma and
retinal detachment
- Serious disease
- Assessments
- Dilation
- Fluorescein angiogram
- Treatment
- Injections
- Laser TX
- Surgery
- Blurry vision
- Floating spots or streaks
- Blindness
- May cause other problems like diabetic macular edema, neurovascular glaucoma and
retinal detachment
- Serious disease
- Assessments
- Dilation
- Fluorescein angiogram
- Treatment
- Injections
- Laser TX
- Surgery
86
New cards
glaucoma
Loss of peripheral vision due to damage of the optic nerve
- At risk: over 60, black or latino over 40, family history
- Occurs in 1 or both eyes
- Slow process in developing symptoms
- Without treatment– blindness
- Common to have high intraocular pressure
- Eye pressure varies
- Dilation
- Treatment
- Eye drops
- Laser
- Surgery
- At risk: over 60, black or latino over 40, family history
- Occurs in 1 or both eyes
- Slow process in developing symptoms
- Without treatment– blindness
- Common to have high intraocular pressure
- Eye pressure varies
- Dilation
- Treatment
- Eye drops
- Laser
- Surgery
87
New cards
retinitis pigmentosa
Hereditary, degenerative disease
- Progressive peripheral vision loss
- Night vision impaired– may be first symptom
- Central vision may be adequate or may be impaired
- Tunnel vision
- No cure
- Low vision aids
- Vitamin A might help
- Progressive peripheral vision loss
- Night vision impaired– may be first symptom
- Central vision may be adequate or may be impaired
- Tunnel vision
- No cure
- Low vision aids
- Vitamin A might help
88
New cards
myopia
nearsighted, can see things up close
89
New cards
hyperopia
farsighted, can see things far away
90
New cards
vitrectomy
removes vitreous fluid from eye
91
New cards
outer ear
collects sound waves and directs to eardrum
92
New cards
middle ear
transfers acoustic energy from compression waves in air to fluid membrane waves within cochlea
93
New cards
inner ear
vibration of 3 bones stimulates hair cells, stimulating nerve endings, damage would be more permanent
94
New cards
conductive hearing loss
Most common in children
- Temporary or permanent
- One or both ears
- Infection of ear canal or middle ear
- Congenital malformation
- Perforation or scarring of eardrum
- Cerumen build up
- dislocation of the 3 middle ear bones
- Foreign objects in canal
- Otosclerosis (middle ear)
- Unusual growths in outer/ middle ear
- Temporary or permanent
- One or both ears
- Infection of ear canal or middle ear
- Congenital malformation
- Perforation or scarring of eardrum
- Cerumen build up
- dislocation of the 3 middle ear bones
- Foreign objects in canal
- Otosclerosis (middle ear)
- Unusual growths in outer/ middle ear
95
New cards
sensorineural hearing loss
Permanent
- Usually both ears
- Damage to inner ear or nerve
- Most common type of ADULT hearing loss
- May be present at birth
- Typically not treated medically/ surgically
- No good option
- May be caused by
- injury/ viral infections/ high fever
- Ototoxic drugs
- Genetic conditions
- Tumors
- Diabetes, stroke, menieres, meningitis
- Prolonged loud noise exposure
- Usually both ears
- Damage to inner ear or nerve
- Most common type of ADULT hearing loss
- May be present at birth
- Typically not treated medically/ surgically
- No good option
- May be caused by
- injury/ viral infections/ high fever
- Ototoxic drugs
- Genetic conditions
- Tumors
- Diabetes, stroke, menieres, meningitis
- Prolonged loud noise exposure
96
New cards
Prelingual/postlingual deafness/prevocational deafness
Prelingual (before 3 years):
- Can cause lag in speech production/ understanding
Postlingual:
- After they have learned how to speak
Prevocational:
- Before 19
- Can cause lag in speech production/ understanding
Postlingual:
- After they have learned how to speak
Prevocational:
- Before 19
97
New cards
cochlear implants
expensive, invasive surgery, requires auditory rehab
98
New cards
physiologic vertigo
perception of motion rotating and spinning, dizziness, tinnitus
99
New cards
benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
common, debris in semicircular canals, helps with orientation
100
New cards
presbycusis
Degenerative changes
- Age related structural changes in middle ear bones
- Slow onset– rage of mild to severe
- Higher tones affected first
- May involve word discrimination issues
- Tx; hearing aids
- Age related structural changes in middle ear bones
- Slow onset– rage of mild to severe
- Higher tones affected first
- May involve word discrimination issues
- Tx; hearing aids