6.1 - Habitat, Niche, and Species Interactions
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Habitat
Where an organism lives
Microbiome
Microorganisms in the “biome” of your body (=habitat)
Tree Microbiome has bacteria and fungi associated with tree roots which allows for…
trees to communicate with each other.
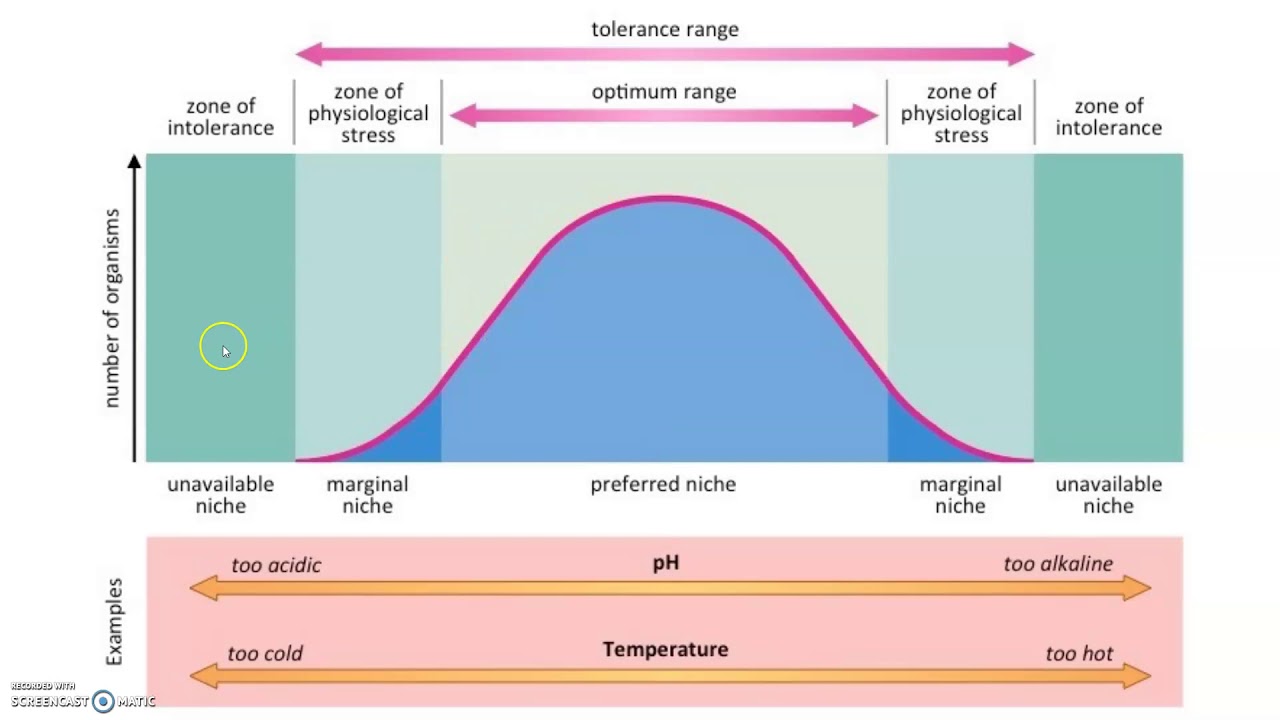
What is a “range of tolerance?”
Range of different factors where that organism can live comfortably and survive (similar to enzymes that need a specific temp/conditions)
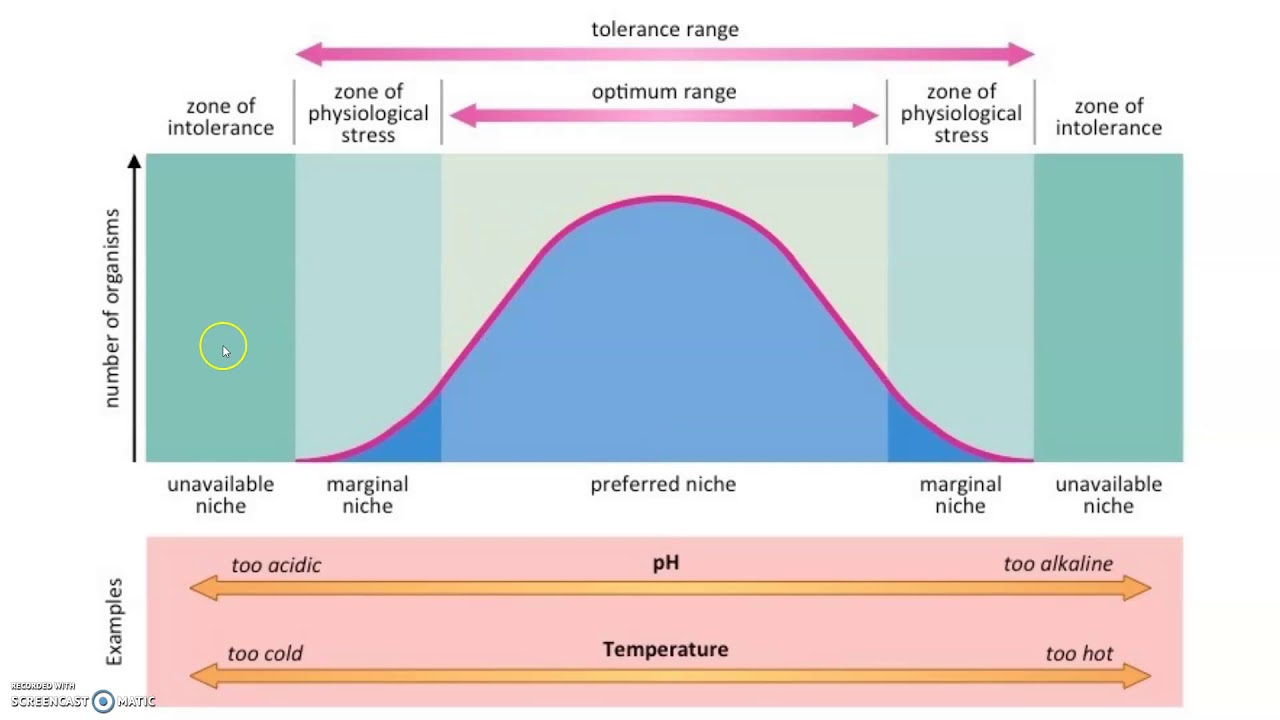
Habitat
Physical place or part of an ecosystem where an organism lives (reflects the living place of an organism)
Niche
Function or activity that is the role of an organism within an ecosystem (reflects its biotic and abiotic association with the environment in terms of its diet, reproduction and other activities.)
Community Interactions
Intraspecific competition
Interspecific
Predation/ Herbivory
Symbiotic Paratism
SymbioticMutualism
SymbioticCommensalism
What is competition?
When organisms compete for limited resource
Occurs when organisms have the same niche
May compete for space, territory, food, mates, water
Intra-specific Competition
Competition within the same species
Inter-specific Competition
Competition between different species
Competition leads to…
Competitive Exclusion - No two species can occupy the same niche at the same time in the same habitat
Predation
One species eats another species
Predator eats prey
Herbivory - animal eats plants
What are the 3 types of symbiosis?
Parasitism
Mutualism
Commensalism
What is symbiosis?
A close ecological relationship between two species
Two species live closely together
Parasitism
Parasite species benefits, Host species is harmed (+,-)
Host stays alive, usually
Mutualism
Both species benefit (+,+)
Commensalism
One species benefits, the other is neutral (+, 0)
What 2 examples of Keystone Species?
Sea otters in kelp forest (Sea otters - urchins - kelp)
Wolves in Yellowstone National Park (wolves - elk )