A+ 220-1201 Core 1: Hardware
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Domain 3. Focused on identifying, using, and connecting hardware components like motherobards, processors, memory, storage, and exapnsion cards. Compare and contrast display components and attributes. Summarize basic cable types and their connectors, features, and purposes. Compare and contrast RAM Characteristics. Compare and contrast storage devices.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What makes a computer a computer?
Or what are the basic functions of a computer?
A device performing input, processing, storage and output
Where is data typically stored within a computer?
RAM or harddrive
Computer functions are typically performed by what part of the computer?
The central processing unit
There are several categories of computers.
Workstations, servers, laptops, tablets, smartphones, smart devices, and IoT Devices.
Please describe the differences between them
Workstations - desktop PCs with tower cases or all in once designs
Servers: rack mounted systems hosting services
Tablets, touchscreen devices running an OS without need for peripherals
IoT Devices, network-conencted devices like smart regerators or light bulbsD
The essential component types of computers include hardware, software, and firmware.
Describe what software and firmware may consist of
Software would consist of the OS, application softwares, and drivers for hardware communication
Whereas firmware is software embedded in hardware. Firmware controls hardware functions and is updated via flashing. “Software on a chip”
Describe the safety types:
Personal safety
Component Safety
Electrical Safety
Chemical safety
Personal safety
prevents injuries to technicians
Component Safety
protects computer components from damage
Electrical safety
prevents electrocution and protects equipment from power issues
Chemical safety
Ensures safe handling and disposal of hazardous materials
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) falls under component safety. Please describe it
Damage caused by the transfer of electrons from a statically charged body to an uncharged component
Use antistatic bags for component storage and use ESD wrist straps and mats to safely discharge static electricity
The point of troubleshooting is to follow a systematic and repeatable process to allow other technicians to understand the steps taken and continue troubleshooting.
List the six steps of the Comptia Troubleshooting Methdology
Identify the problem
Gather information from the user
Perform backups before making changes
Determine environmental/infrastructure changes
Identify user changes
Establish a theory of probably cause
research symptoms
question the obvious
Test the Theory to Determine the Cause
Confirm or disprove the theory by testing
Restablish a theory or escalate the issue if the theory is not confirmed
Establish a plan of action to resolve teh problem and implement the solution
Create a plan to address the identified issue
Follow manufacturer or vendor instructions when applicable
Verify Full System Functionality and Implement Preventative MEasures
Test the system to ensure the issue is resolved
Apply preventative measures to avoid future occurrences
Document Findings, Actions, and outcomes
What’s a motherboard?
The central circuit board connecting all components within a PC
What’s a Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The primary processing unit for executing instructions
What’s memory?
RAM
- temporary storage for active processes and tasks
Where is data stored for long term?
Within SSDs or HDDs
What is a power supply unit?
It supplies power to all components
What does USB stand for?
What does USB enable?
USB stands for universal serial bus
USB allows for data transfer and power delivery capabilities while supporting multiple devices via daisy-chaining
What is the predecessor to USB?
What was it used for?
Can you describe it?
The predecessor to USB was serial connection
These cables transmitted data at a speed of up to 115 Kbps, sending one bit at a time. These connections were limited to one device per port. They are now typically used within legacy applications.
When it comes to USB versions, the speed of data transfer increases. USB 1 had a cable limit of 3 meters while USB 1.1 and 2.0 increased the max length to 5 meters. USB 3.0 and later versions reduces the limit back to 3 meters.
Why? How does cable length impact performance?
The llimit was reduced in order to maintain high data transfer speed. Longer cables can result in signal deterioriation and reduced speeds.
What is faster in terms of powering a device?
The USB port on a computer or a dedicated wall charger? Explain why.
Charging a device via a dedicated wall charger would be faster because USB ports have limits on the maximum power output.
For example, USB 1.0 and 2.0 provide a maximum power output of 500 mA while USB 3.0 offers a mximum of 900 mA. Dedicated powered USB ports (power delivery) can offer up to 1.5A.
What are some USB Connectivity Considerations?
Bandwidth is shared across all devices connected to a single USB port; more connected devices can reduce the available speed for each one but using a powered USB hub can help maintain performacne by supplying additional power to connecetd devices
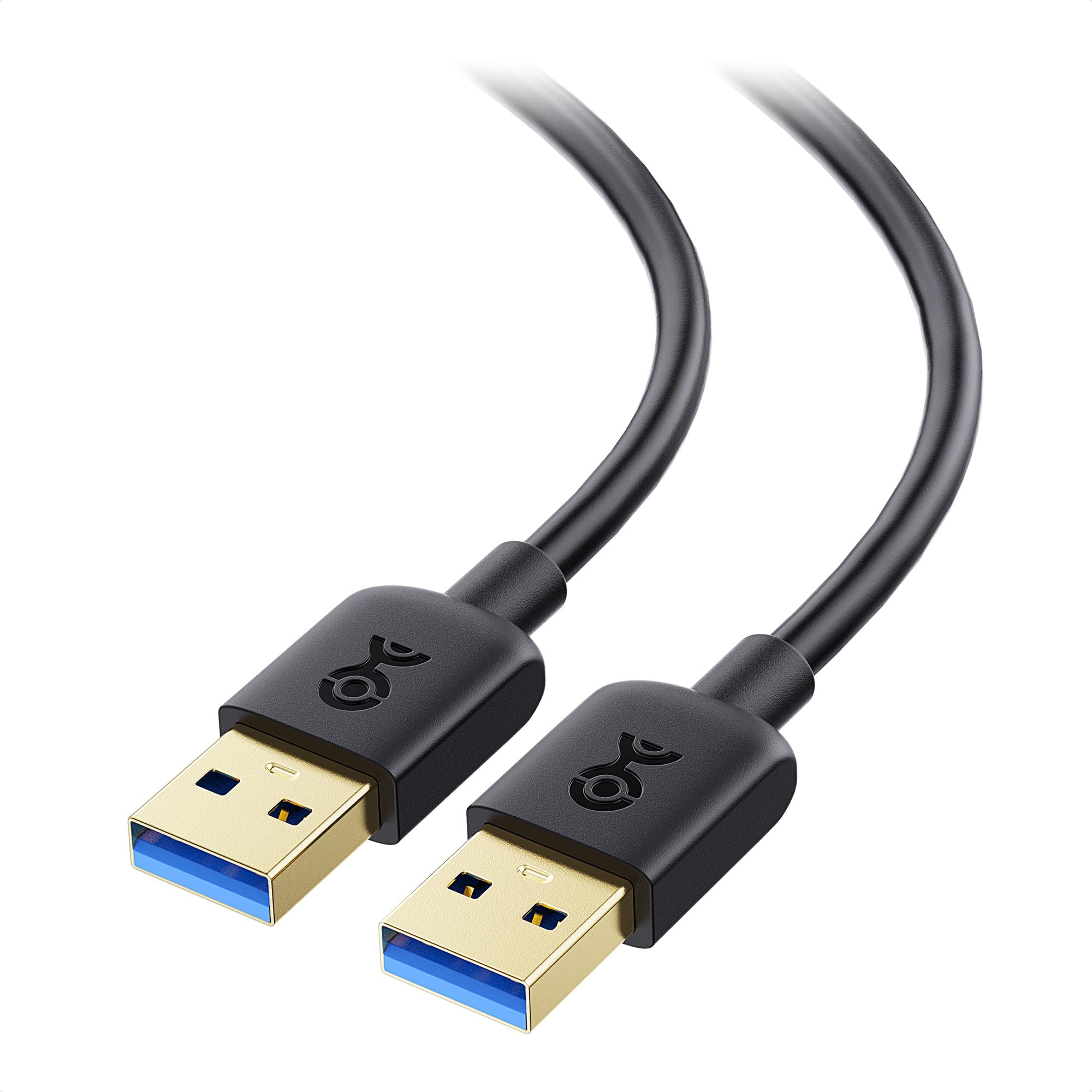

What cable is this? What versions use it? How does it work and what devices is it normally found on?
This is USB A cable.
Used in USB 1, 1.1, 2, 3 and above.
It only connects in one direction due to a blocking piece inside the port
Commonly found on desktops and laptops
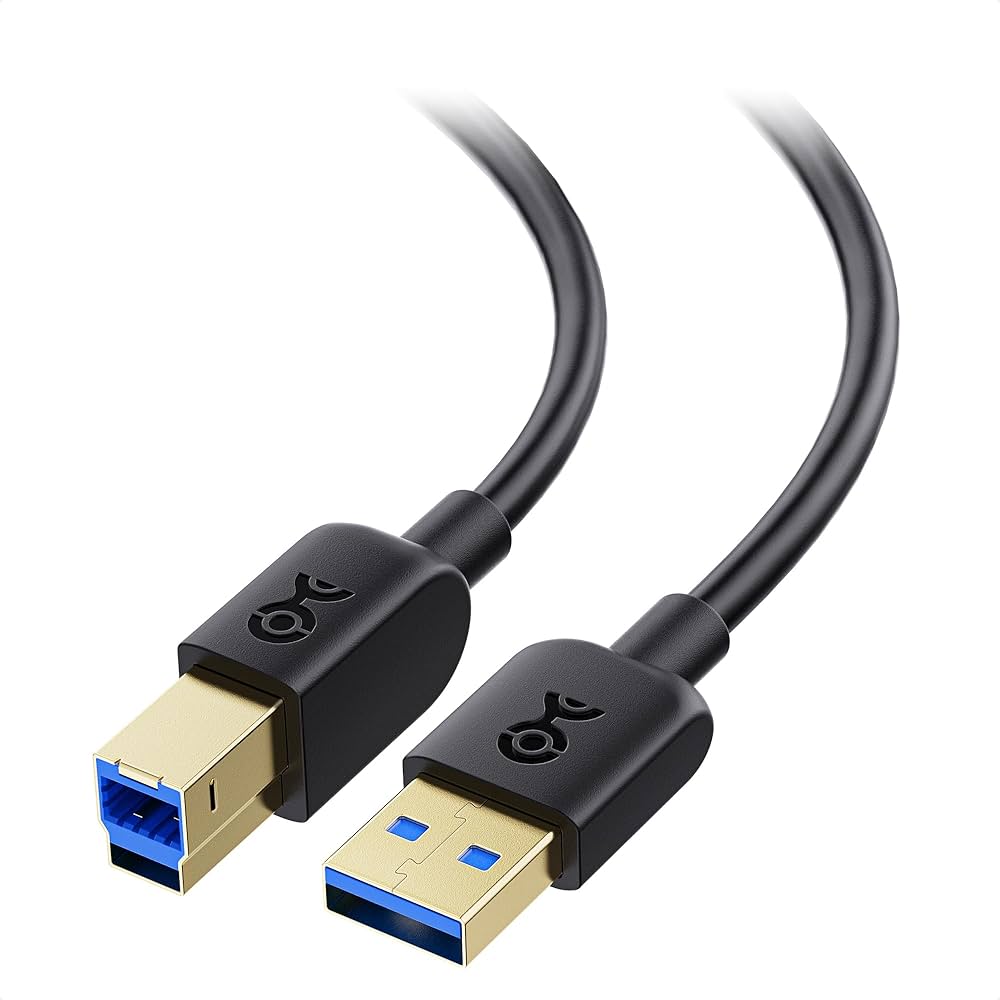

What cable is this? What versions use it? How does it work and what devices is it normally found on?
USB B
Used for larger devices like printers
USB type B has multiple variations: connector, mini connector, and micro connector
Mini connector is found on early tablets and smartphones
Micro is used for wearables, smart glasses, and small music players
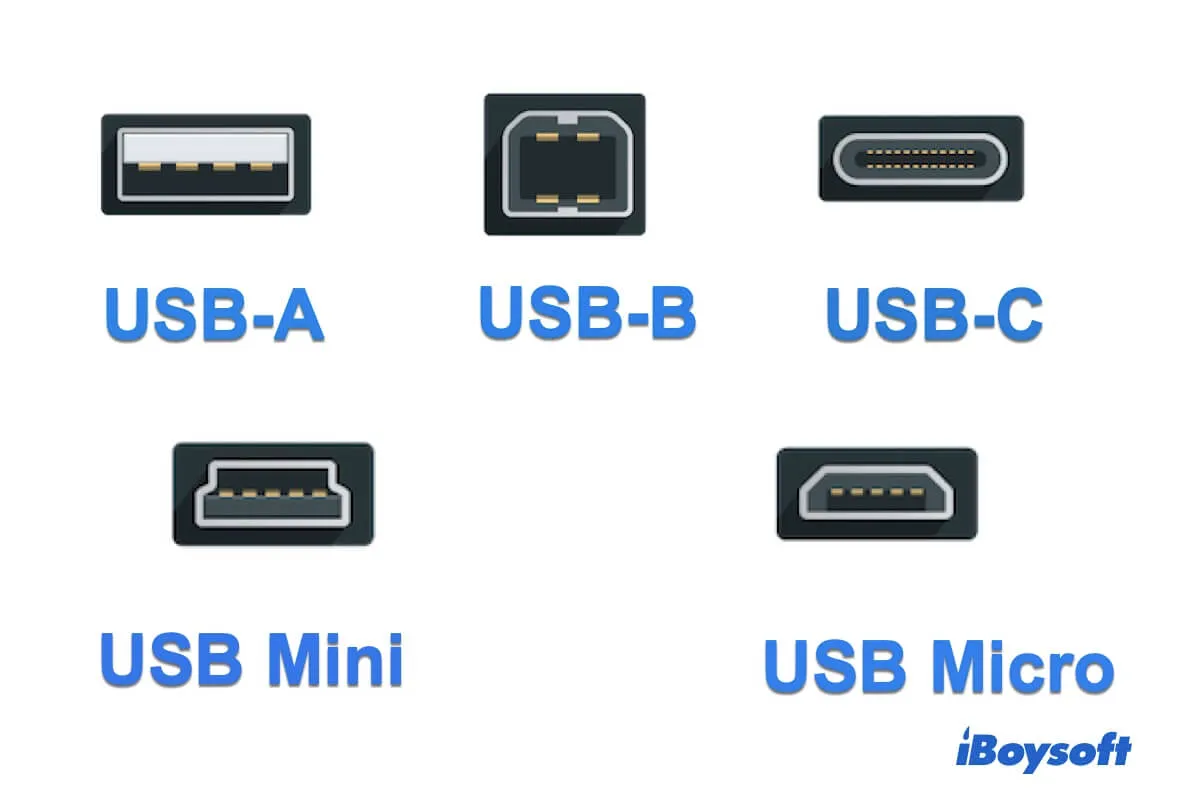
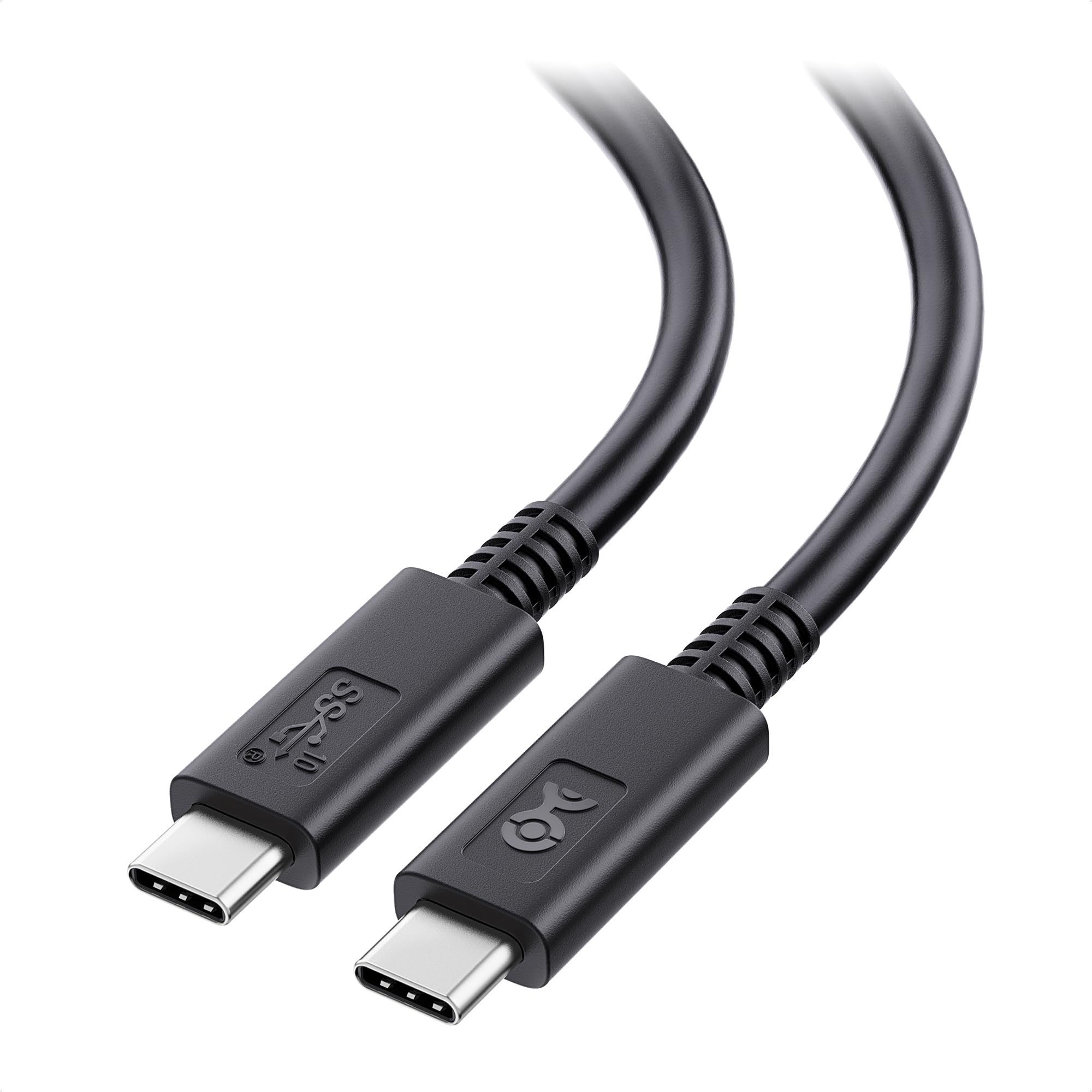


What cable is this? What versions use it? How does it work and what devices is it normally found on?
USB C
Compatible with USB 3 and 4
Reversible design allows insertion in either direction
Commonly used in modern laptops, tablets, and smartphones
True or false
USB 2 and USB 3 Connectors of the same type are not interchangeable
True
What are video cables used for?
What are the more common types of video cables?
Cables used to connect devices such as computers, gaming consoles, and media players to display including TVs and monitors
HDMI
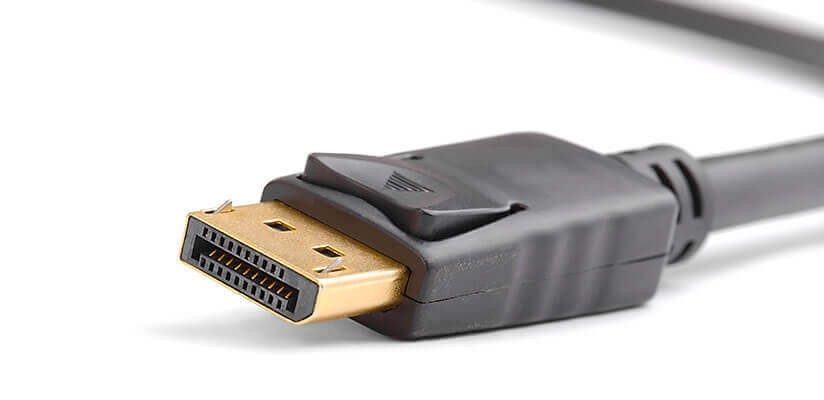
Display Port
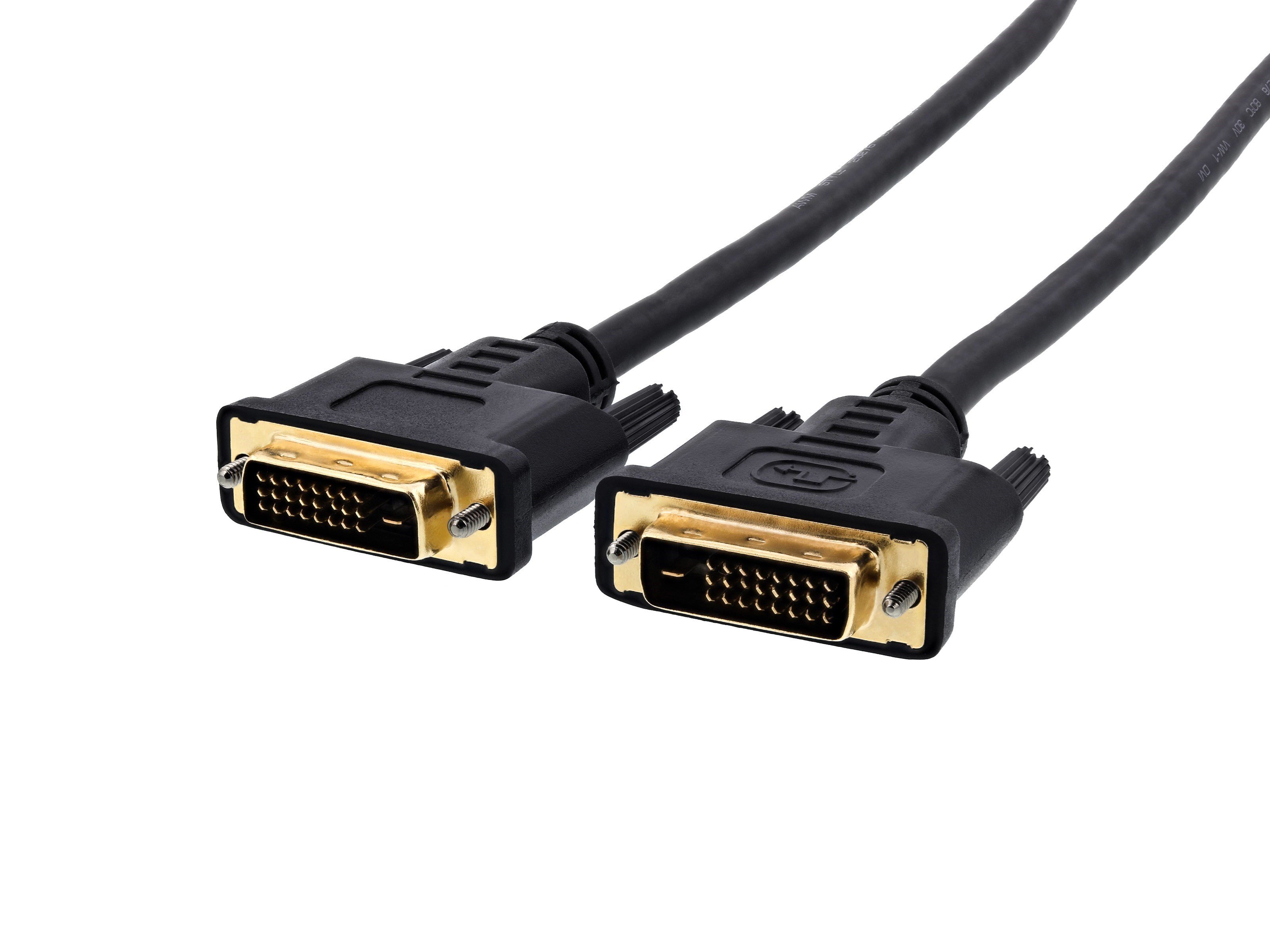
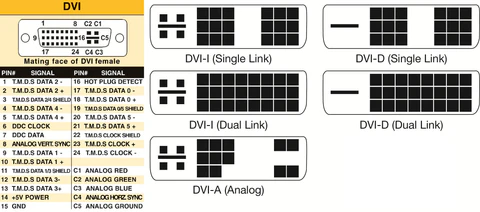
DVI
VGA
Thunderbolt
USB Type C