Chapter 10 Quiz: DNA and Chromosome Replication
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
In eukaryotes, DNA replication occurs only during the _______ phase of the cell cycle
A. G2
B. DNA replication occurs nonstop throughout the cell cycle
C. M
D. S
S
In DNA replication, the term semiconservative means:
A. Each new strand pairs with each old strand
B. Only one new strand of DNA is produced
C. each new strand produced pairs with itself, the old strands with themselves
Each new strand pairs with each old strand
Primer:
A. Must be A:T rich
B. Provided a terminus with a free 3’-OH to which nucleotides are added during DNA synthesis
C. Provides a sequence that specifies the complementary sequence of nascent DNA chain
Primer provides a terminus with a free 3’-OH to which nucleotides are added during DNA synthesis
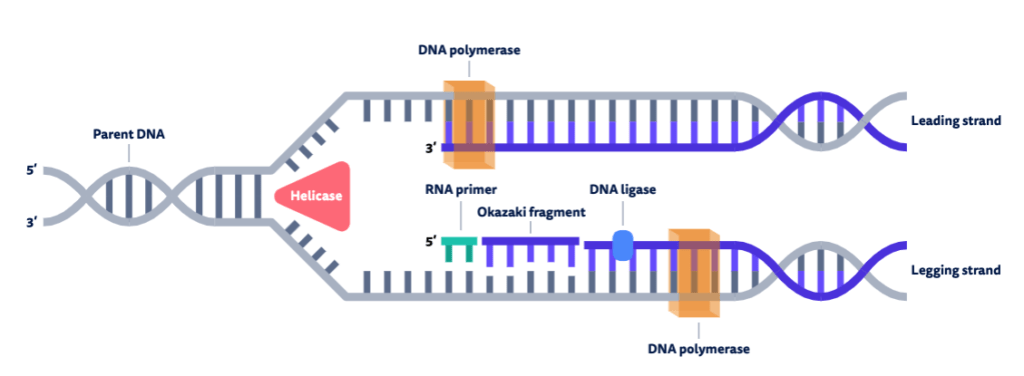
In DNA polymerase 1:
A. There is no 3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity
B. The 3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity is part of a different subunit in the multimeric structure
C. The 3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity is part of the monomeric unit
In DNA polymerase 1, the 3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity is part of the monomeric unit. It is crucial for proofreading function of DNA polymerase 1
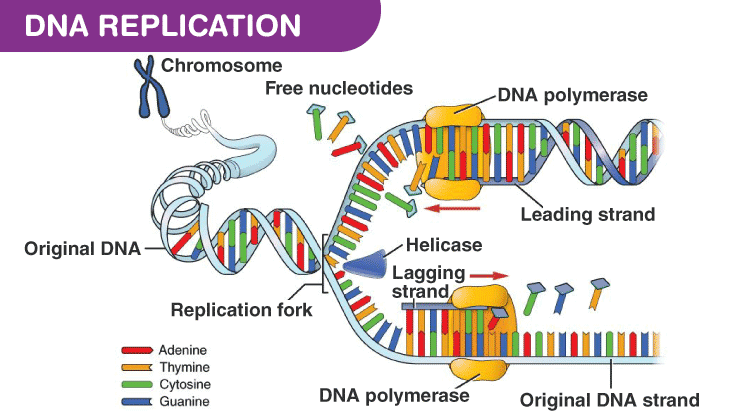
The enzyme responsible for sealing the nicks between Okazaki fragments is:
A. DNA helicase
B. DNA ligase
C. DNA polymerase 2
DNA ligase
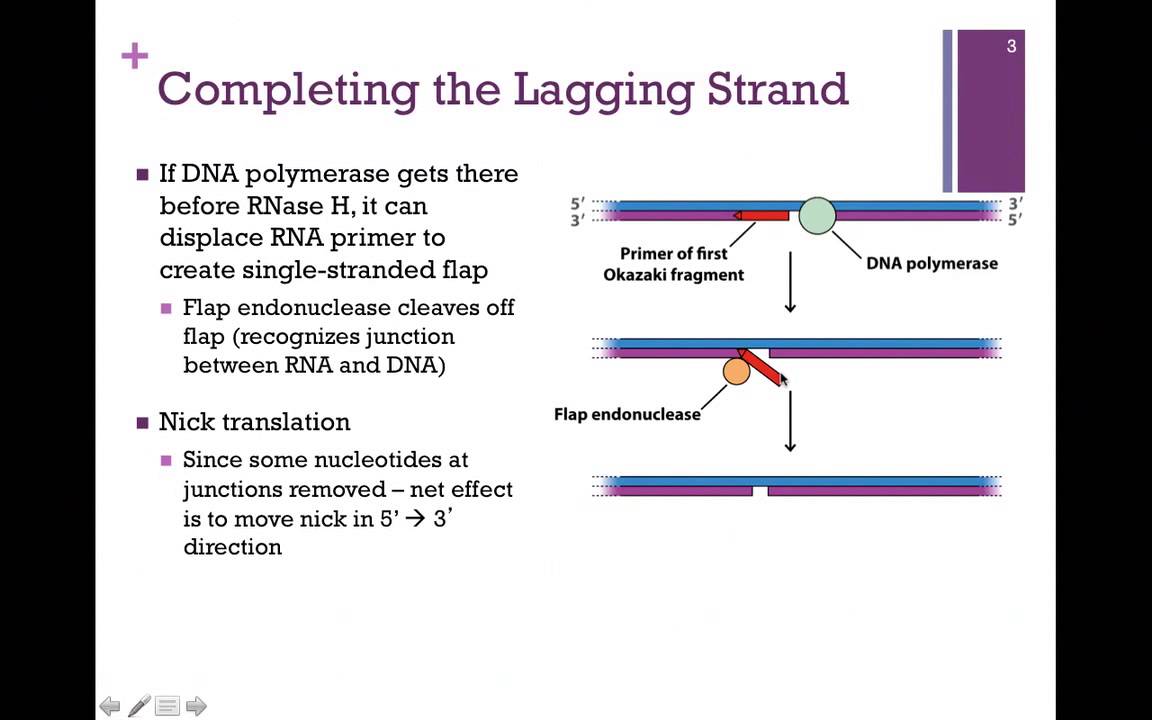
What is RNA polymerase 2 role?
RNA polymerase is a large enzyme that transcribes DNA into messenger RNA (mRNA) and small non-coding RNAs. It’s a key enzyme in eukaryotes that’s responsible for transcribing much of the genome
What is the role of DNA polymerase 2?
DNA polymerase 2 is an enzyme primarily involved in DNA repair, acting as a backup to the main responsible enzyme (DNA polymerase 3), and is responsible for synthesizing new DNA strands when necessary, particularly in situations where DNA damage occurs
DNA is unwound be the enzyme:
A. DNA topoisomereases
B. DNA helicase
C. DNA Primase
D. DNA ligase
DNA helicase
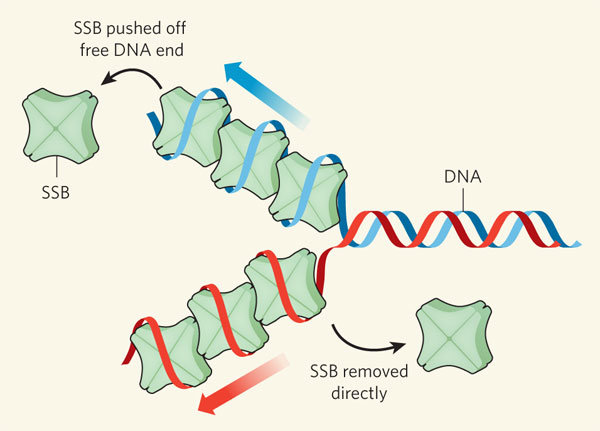
Single-strand DNA-binding proteins function to:
A. Creates nicks in the DNA to allow unwinding of supercoils
B. Maintains the unwound state in a single-stranded fashion
C. Unwind The DNA double helix
D. Seal nicks between Okazaki fragments
Maintain the unwound state in a single-stranded fashion
stabilize and protect single-stranded DNA during DNA replication, recombination, and repair processes by binding to the exposed single strands, preventing them from reannealing or becoming damaged; essentially acting as a placeholder for other proteins involved in these DNA processes to access the single strands.
DNA supercoils can be removed by:
A. Proteases
B. Helicases
C. Primases
D. Topoisomerases
Topoisomerases
Enzymes that change the topology of DNA by breaking and rejoining its strands
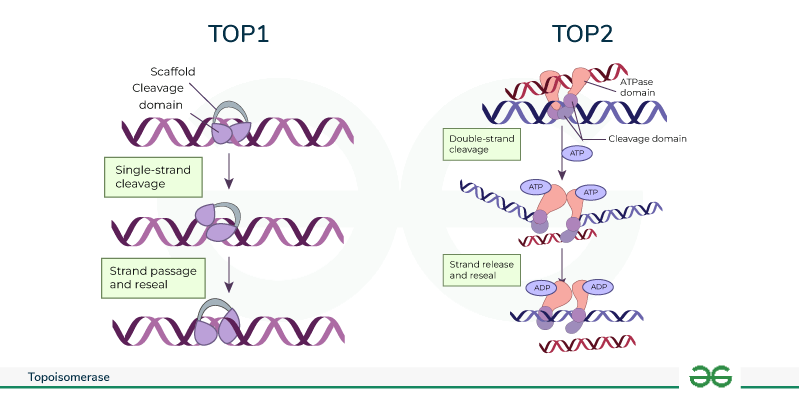
In E. Coli, the replication bubble forms at:
The origin of replication
OriC
A specific 245 bp long sequence
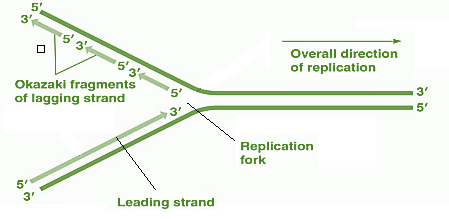
DNA synthesis occurs in what direction?
5’ to 3’
Which of the DNA polymerases is responsible for semiconservative replication in E. Coli?
A. DNA polymerase 2
B. DNA polymerase 4
C. DNA polymerase 3
DNA polymerase 3
Where are Okazaki fragments located?
The lagging strand of the replication fork
DNA polymerase 1 requires two different components of DNA, primer and template. What functions does the template component form?
It provides the nucleotide sequence that is used to make a complementary, antiparallel strand during replication
High fidelity due to proofreading in DNA replication means:
Error rates are low because of the 5’ to 3’ exonuclease activity of DNA polymerase
Which enzyme covalently bonds a 3’-OH to a 5’ phosphorus in DNA, such as when DNA is nicked or to link Okazaki fragments together?
DNA ligase
What is true about DNA replication in eukaryotes?
Nucleosomes are dissembled right before replicating a section of DNA
The cell must duplicate the nucleosome structure on the chromosome after replication
Histones are synthesized during S phase for chromatin packing
Telomerase:
A. Is required in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic DNA replication
B. Contains an RNA template for telomere synthesis
C. Contains a DNA template for telomere synthesis
D. Is not required to maintain telomere structure
Contains an RNA template for telomere synthesis
bacteria synthesize DNA ____________ and eukaryotes synthesize DNA _________
Throughout the cell cycle, in the S phase