Scapula Anatomy
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
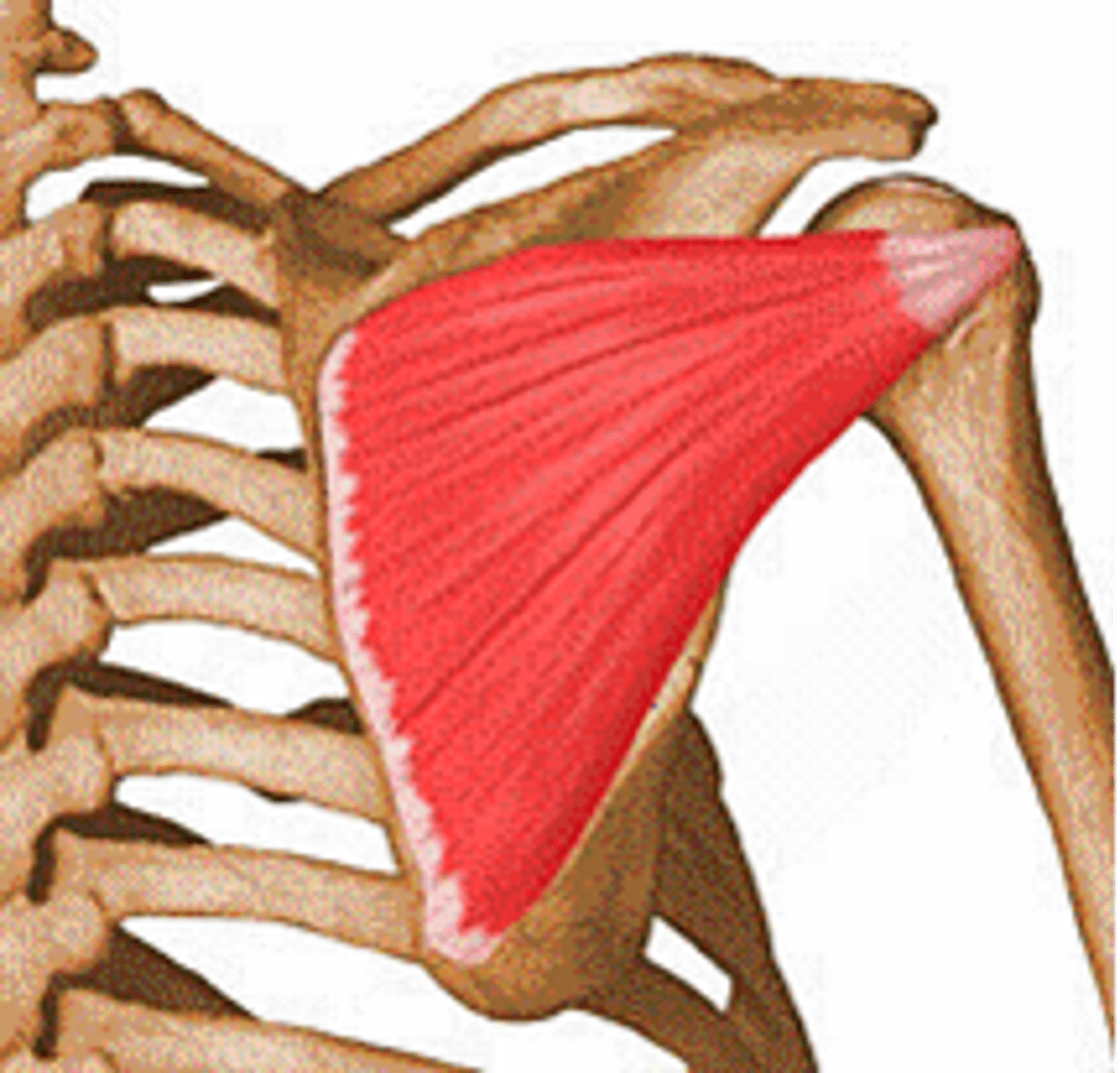
Scapula
Shoulder blade, The primary function of the scapula is to attach the upper arm to the thorax, or trunk of the body. This connection stabilizes the arm and provides for arm movement at the shoulder.
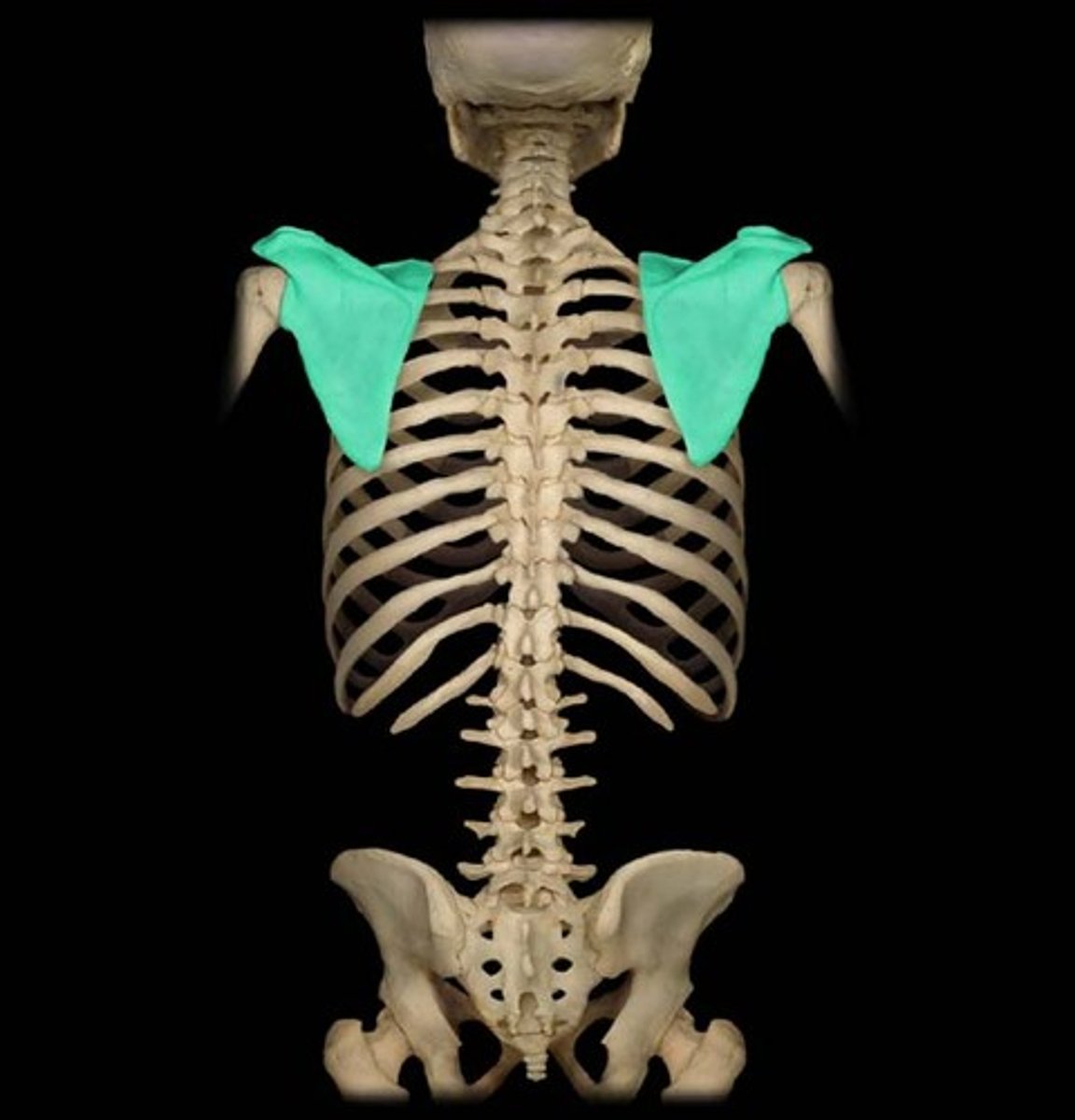
Acromion
Outward extension of the shoulder blade forming the point of the shoulder.Together with the coracoid process it extends laterally over the shoulder joint. The acromion is a continuation of the scapular spine, and hooks over anteriorly.
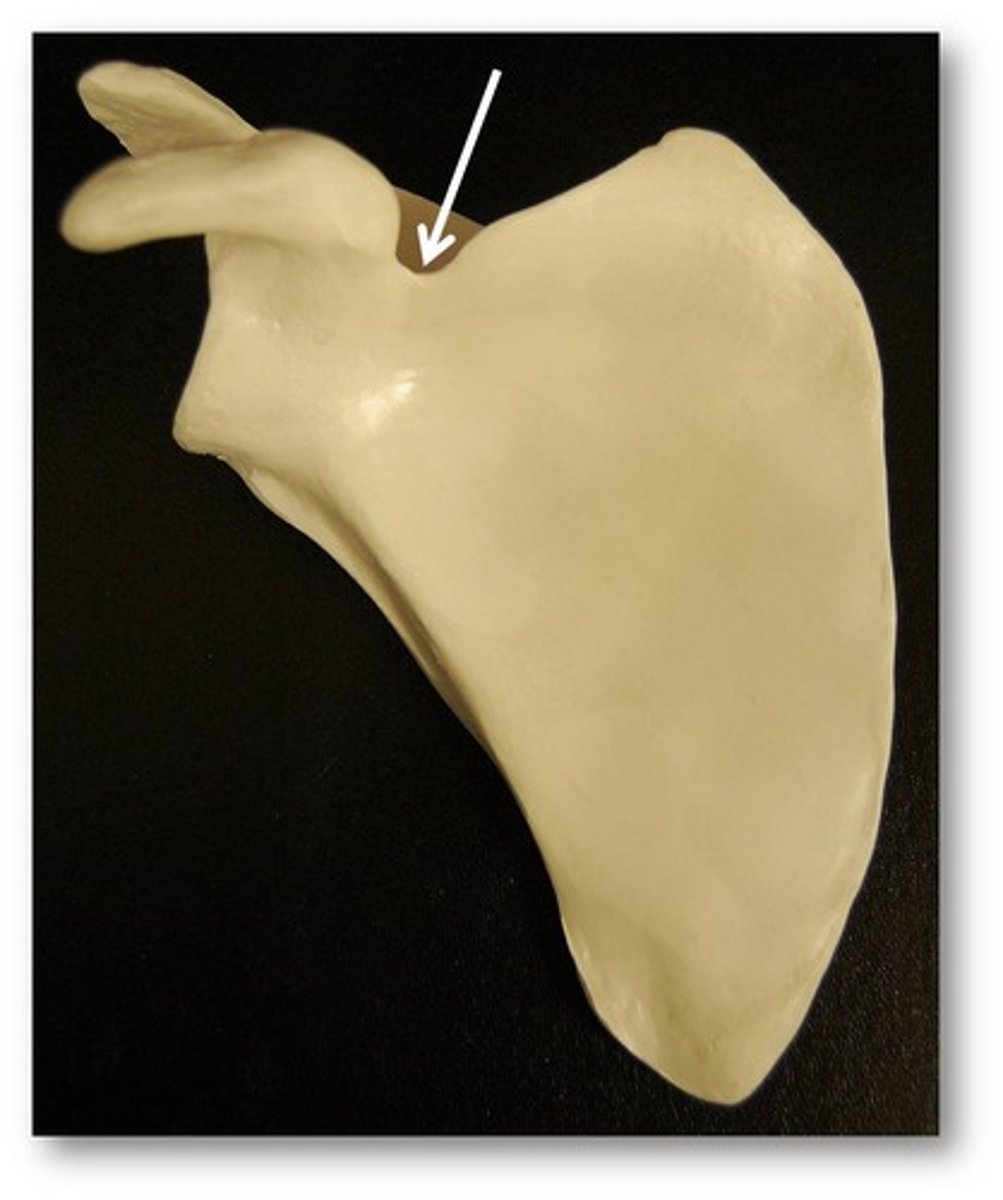
Suprascapular notch
notch that is a passageway for the suprascapular nerve
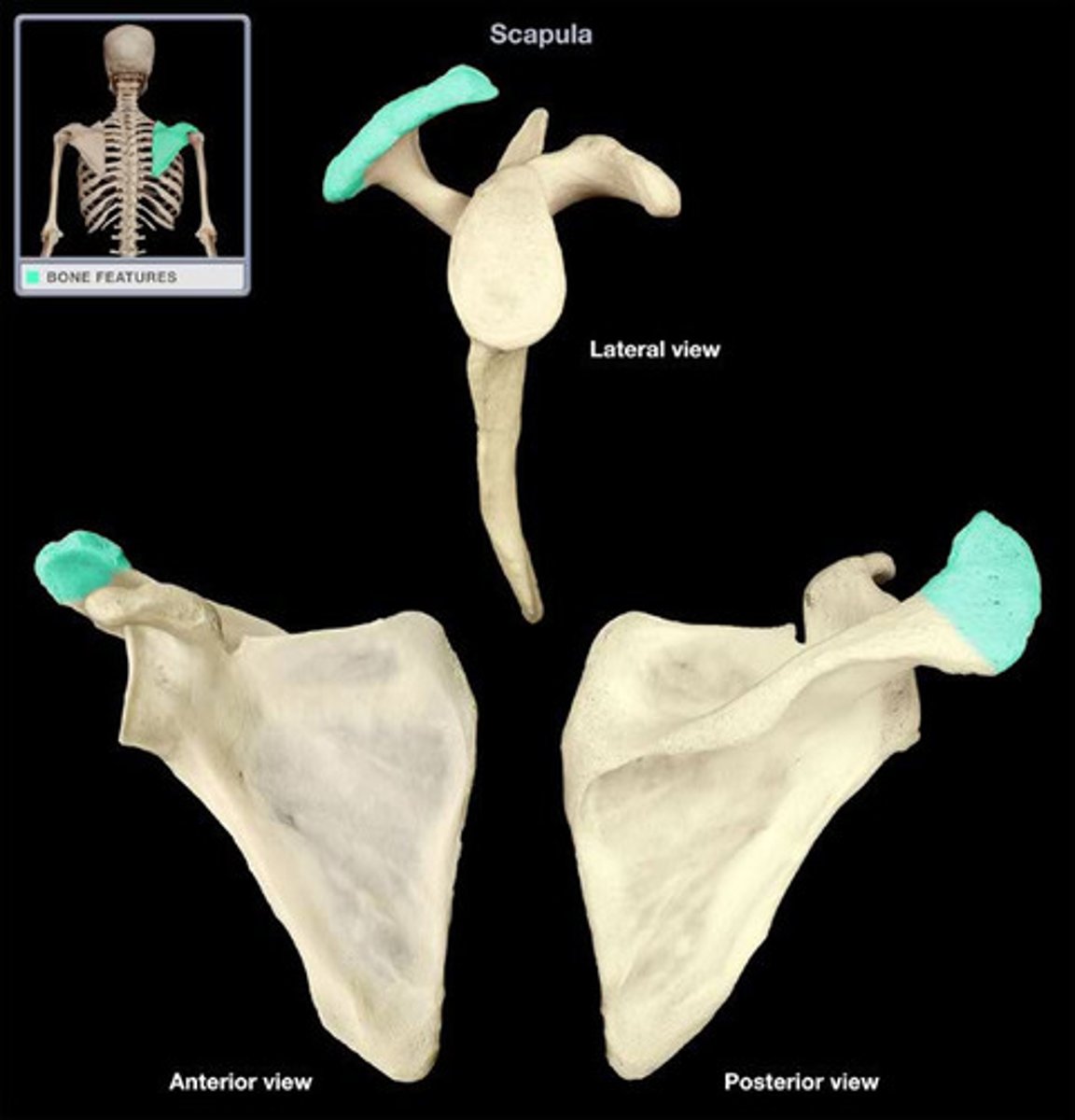
Coracoid process
flat, long protrusion of bone behind the scapular notch, serves to stabilize the shoulder joint.
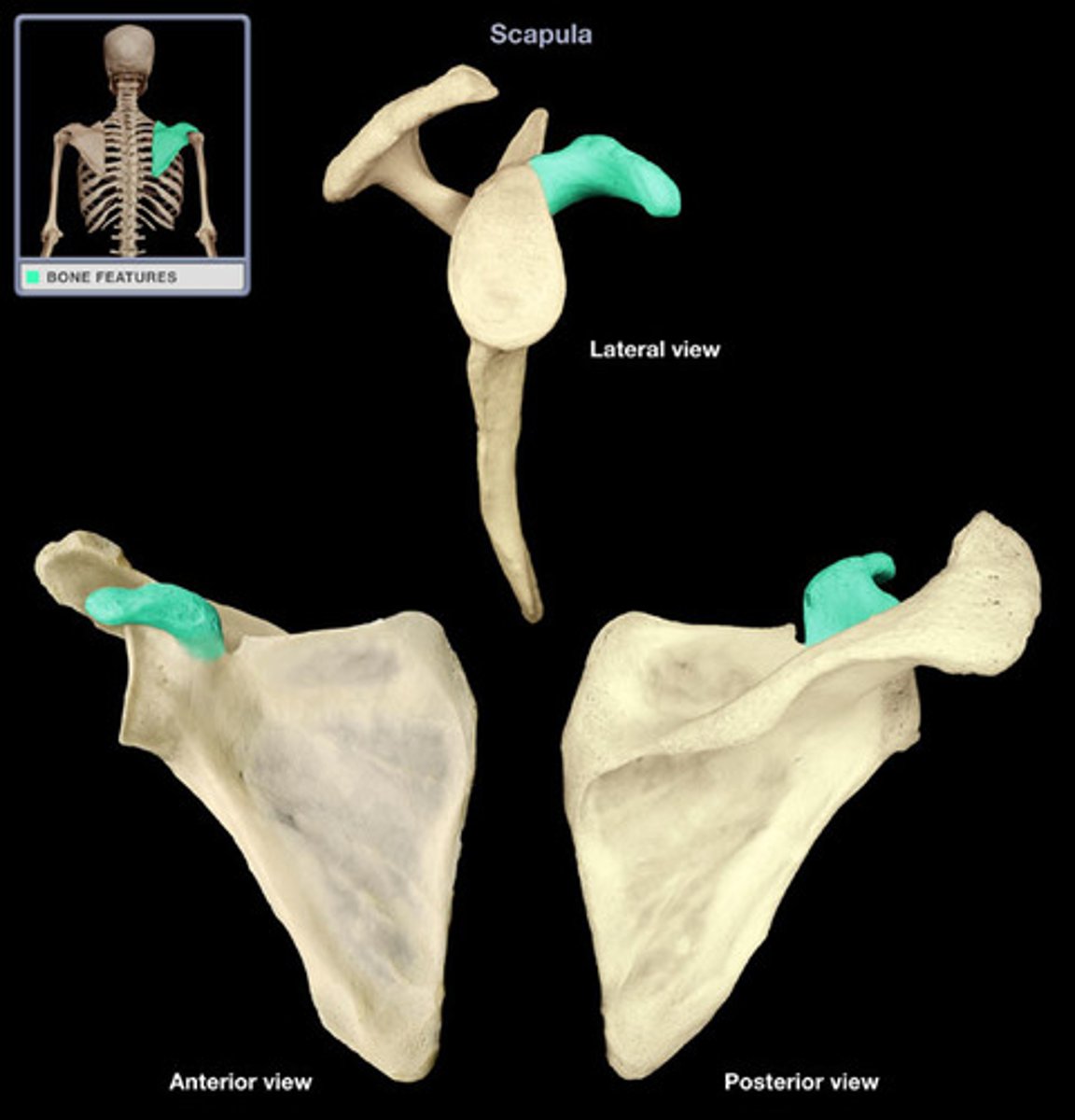
Glenoid cavity
The glenoid cavity or glenoid fossa of scapula is a part of the shoulder. It is a shallow, pyriform articular surface, which is located on the lateral angle of the scapula.
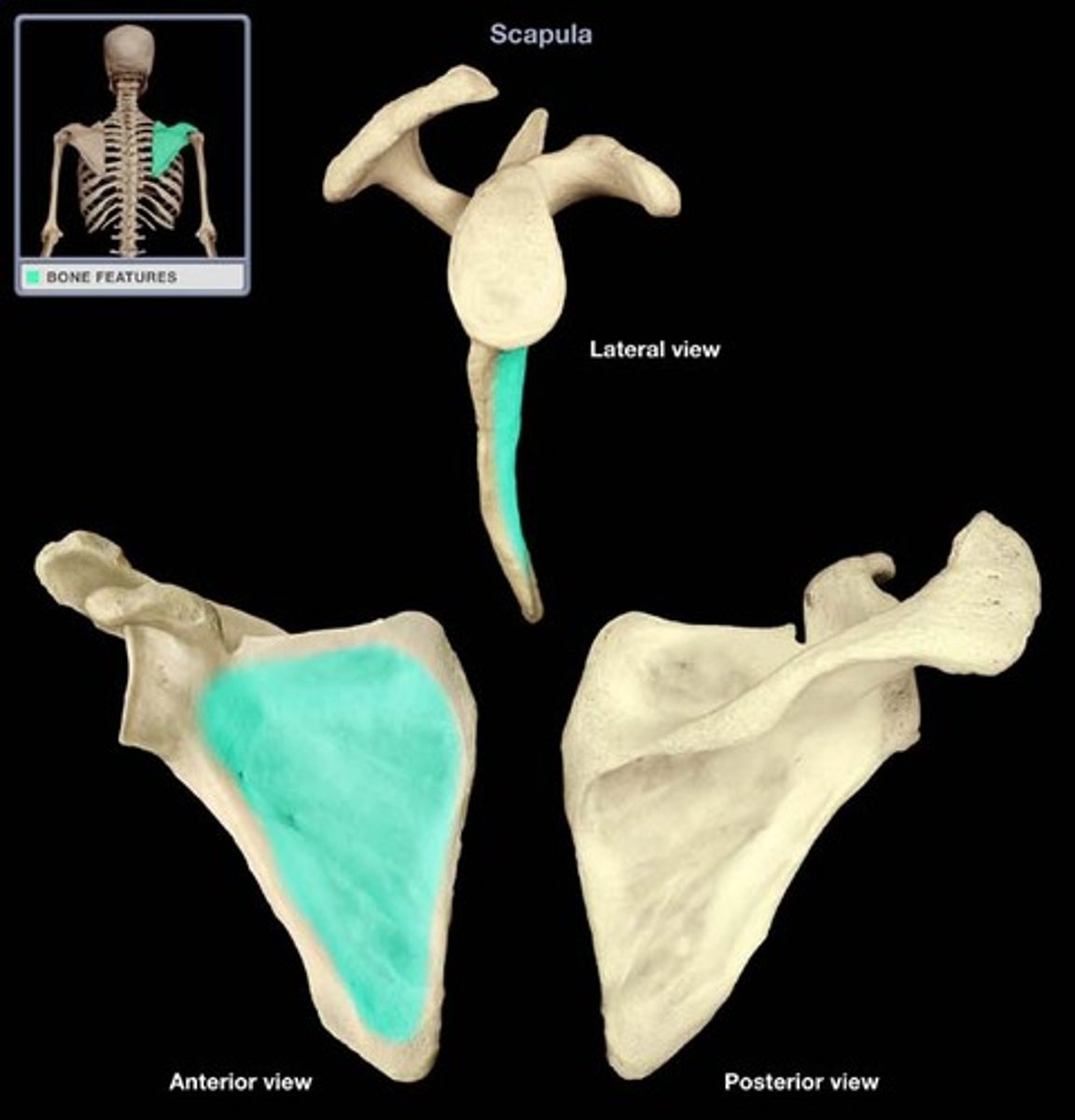
Later border
which is mainly responsible for stabilization and rotation of the scapula, consists of the trapezius, serratus anterior, levator scapulae, and rhomboid muscles and attach to the medial, superior, and inferior borders of the scapula.
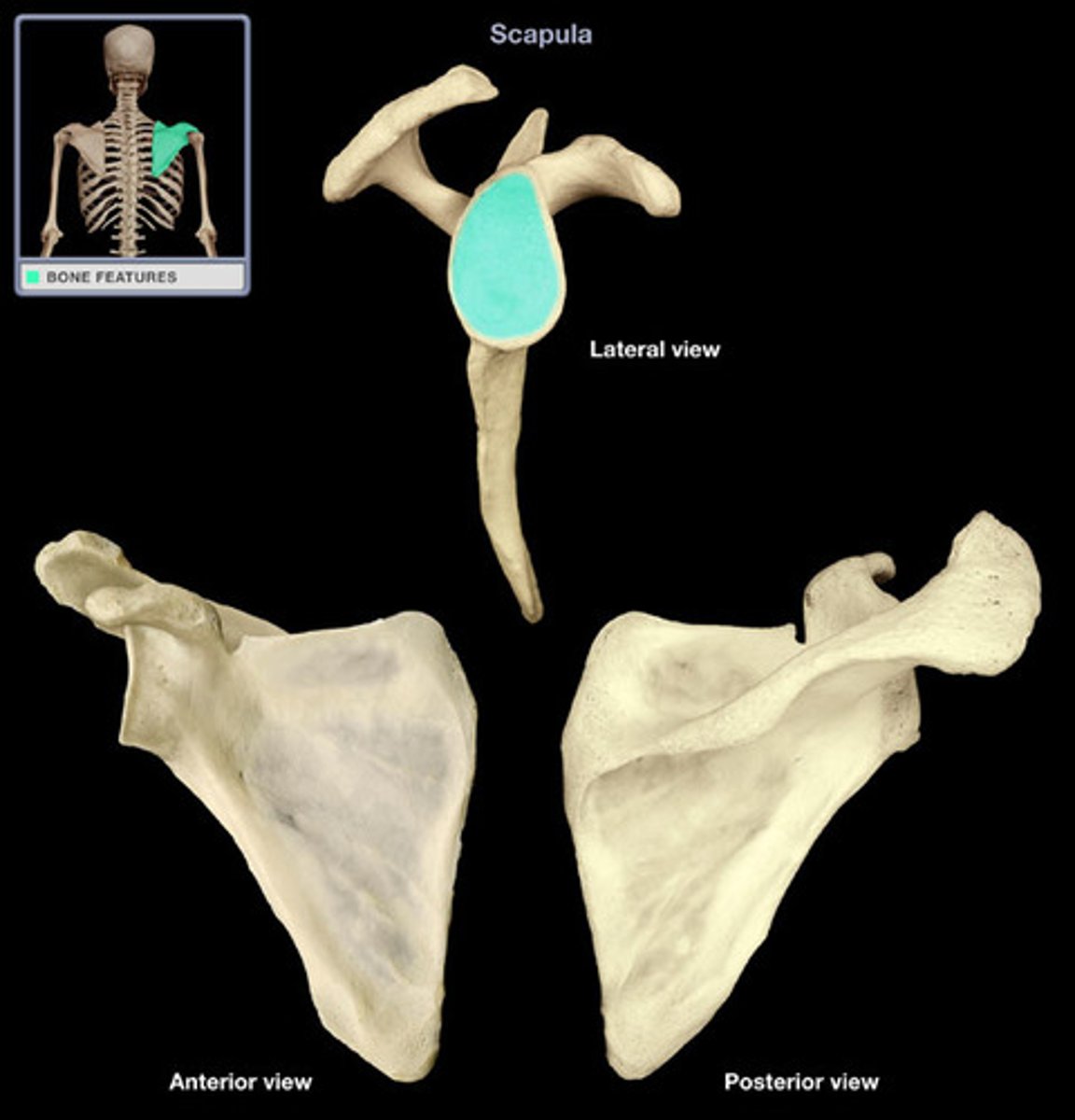
Subscapular Fossa
The subscapular fossa of the scapula is of functional importance because it is the origin for: 1. the subscapularis muscle (one of the four rotator cuff muscles).
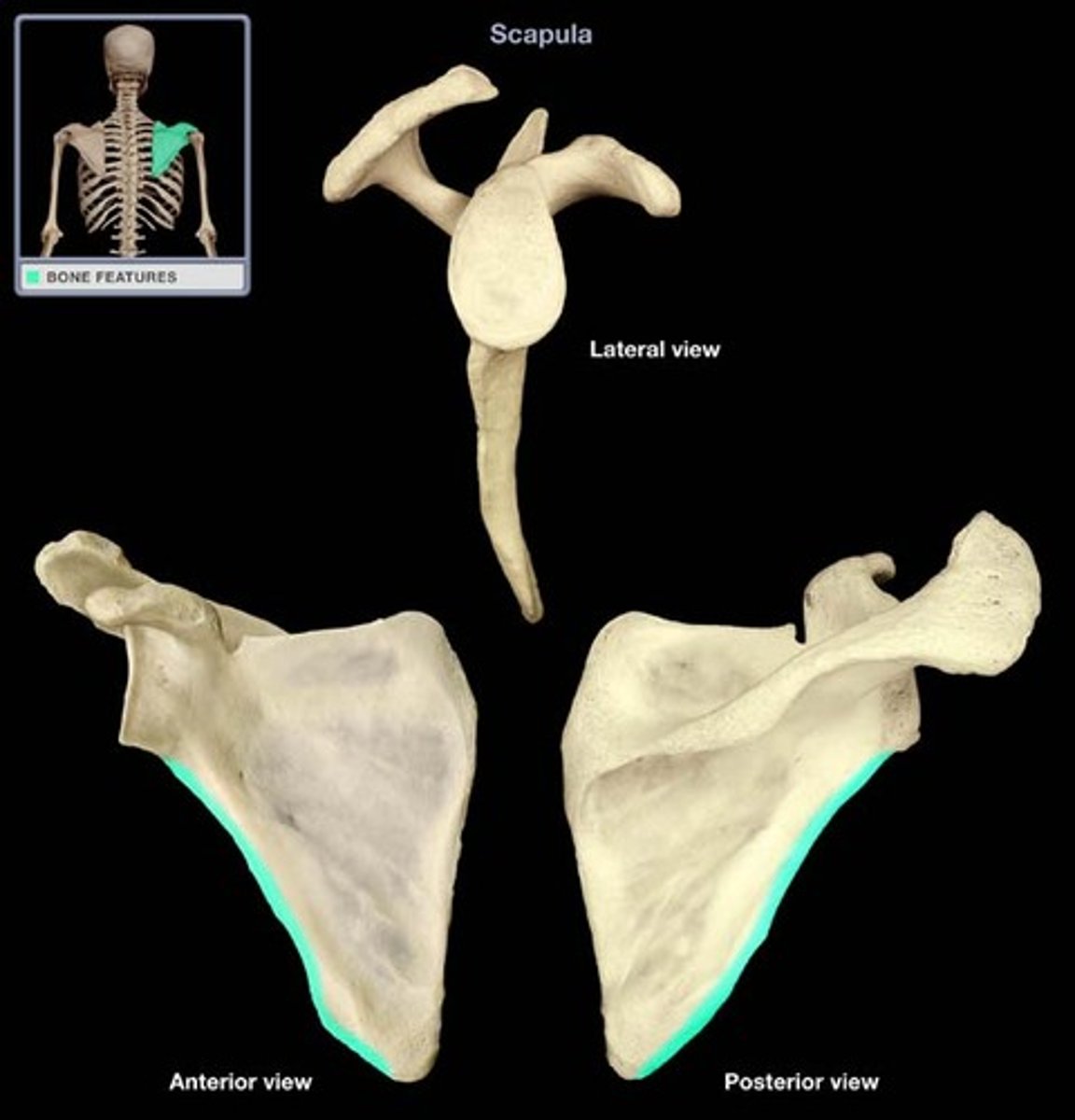
Medial border
which is mainly responsible for stabilization and rotation of the scapula, consists of the trapezius, serratus anterior, levator scapulae, and rhomboid muscles and attach to the medial, superior, and inferior borders of the scapula.
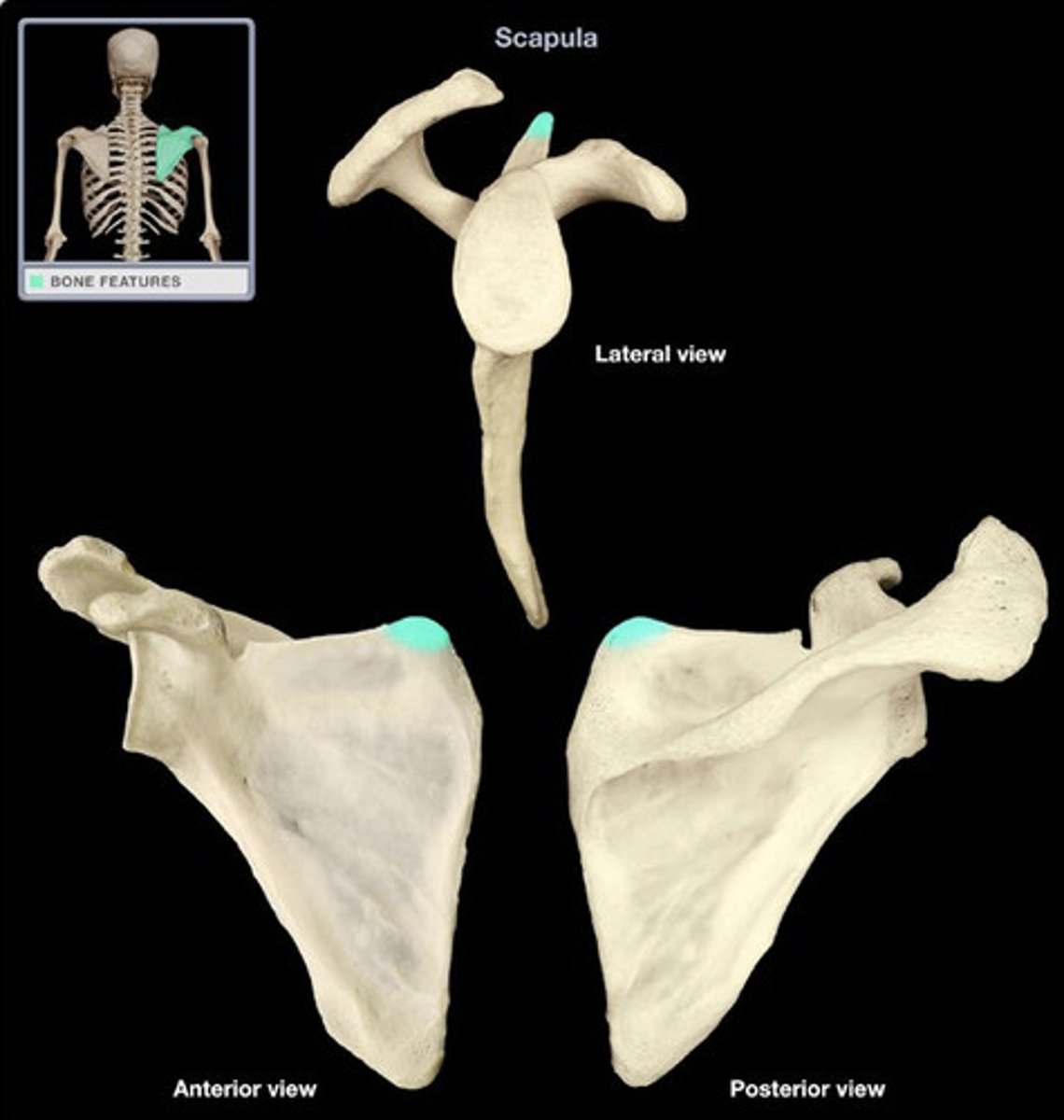
Superior Angle
The superior angle of the scapula or medial angle, is covered by the trapezius muscle. This angle is formed by the junction of the superior and medial borders of the scapula. ... The inferior angle is formed by the union of the medial and lateral borders of the scapula.
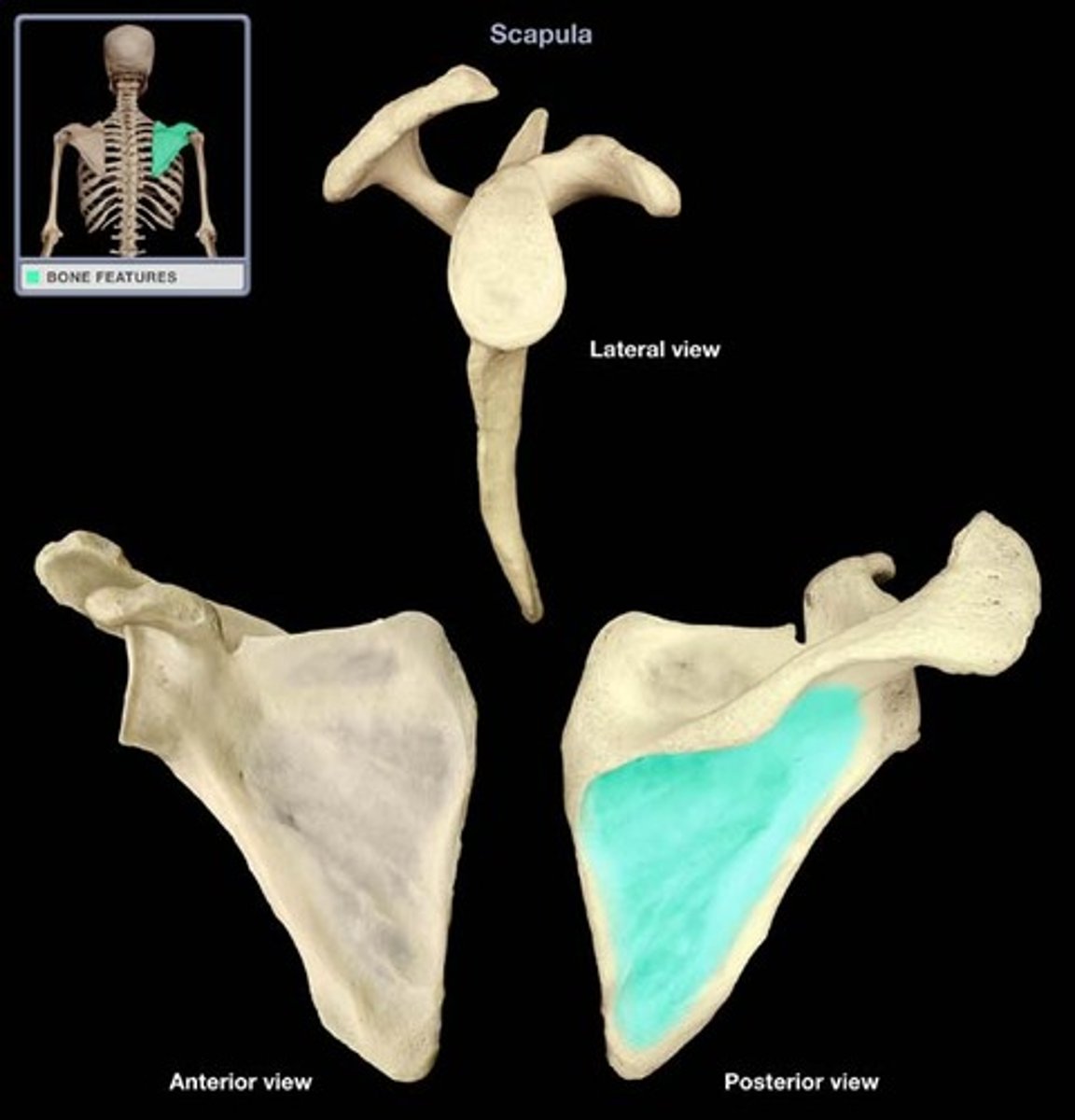
infraspinous fossa
The infraspinous fossa (of the scapula) is a structural feature on the scapula bone (also known as the shoulder blade or shoulder bone).
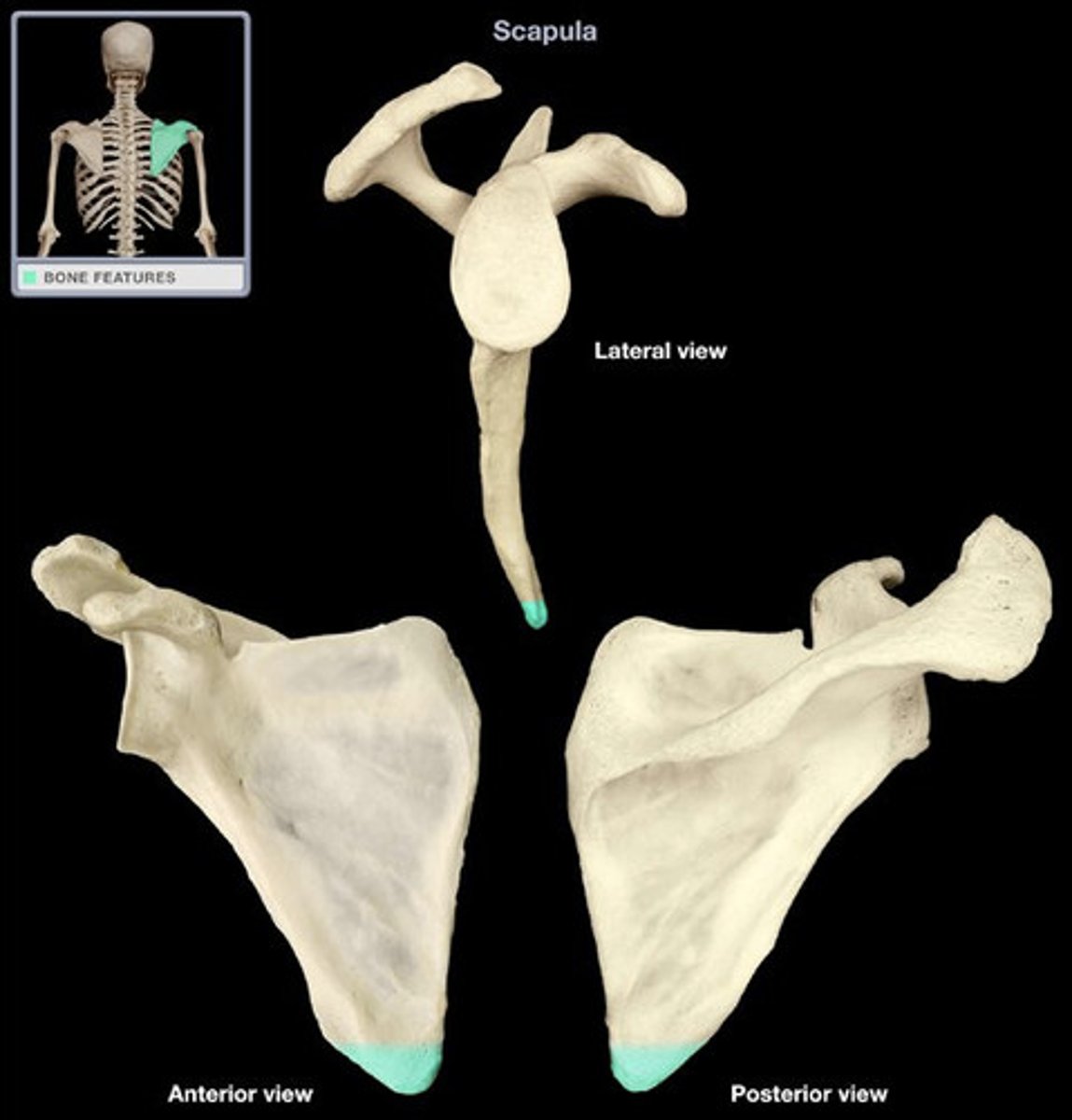
Inferior angle
The inferior angle of the scapula is the lowest part of the scapula and is covered by the latissimus dorsi muscle. It moves forwards round the chest when the arm is abducted. The inferior angle is formed by the union of the medial and lateral borders of the scapula.
Infraspinous tubercle
It is located inferior to the greater and lesser tubercles; it is a site of frequent fracture; fractures of the surgical neck of the humerus endanger the axillary