nuclear reactions test ⚛🧪⋆ ༘🔬₊
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
fusion
combining of lighter nuclei to make a heavier nucleus
where does fusion occur?
the sun
stars
fission
nucleus is bombarded by particles and split to create nuclei
where does fission occur
uranium 235 (unstable atoms)
nuclear power reactors
nuclear reactions
controlled chain reaction (def+example)
The rate of fission and conditions are carefully monitored
control rods in nuclear power plants
uncontrolled chain reaction (def+example)
The rate of fission and conditions happen too rapidly or without regulation
bombs
Fission releases…
an enormous amount of energy
The fission of 1 mol to uranium 235 produces about…
26 million times as much energy as the combustion of 1 mole of methane
Alpha particle
For decay
nucleus gives up 2 protons
nucleus gives up 2 neutrons
atomic number reduced by 2
mass number reduced by 4
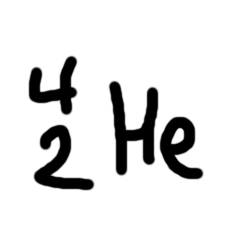
Beta particle - what happens for decay and capture
For decay
Nucleus gains 1 proton
Nucleus loses 1 neutron
Atomic no increased by 1
Mass no does not change
For capture
Nuclesu loses 1 proton
Nucleus gains 1 neutron
Atomic no decreased by 1
Mass does not change
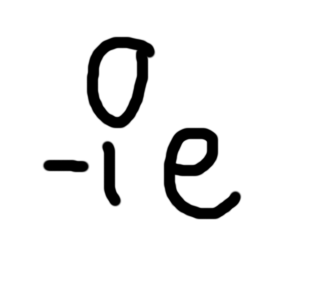
Gamma ray
high energy photon of light
0 charge
0 mass number
Positron
beta plus decay
proton turns into a neutron
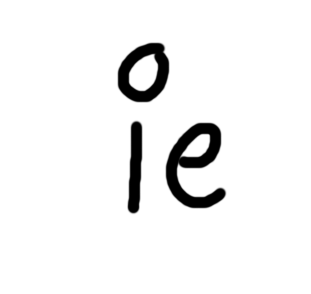
neutron
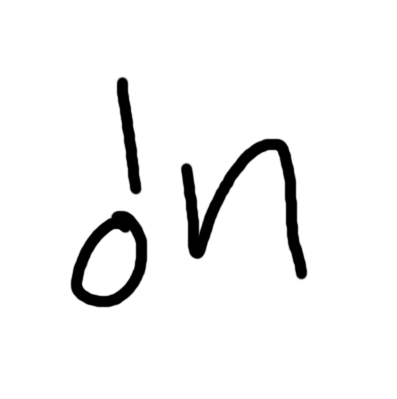
particle on the left
bombardment
capture
particle on the right
production
decay
rule for balancing nuclear equations
both the atomic number and mass number must be conserved on both sides
half life
time it takes for half of the radioactive substance to decay until its no longer radioactive (more stable)
bismuth can undergo _ to form _
alpha decay, thalium
left/final amt equation
initial(1/2)n
equation for n
ttotal/t1/2
t total equation
n * half life
nucleon
either a proton or neutron inside the nucleus
atomic number
number of protons in an atom
mass number
sum of protons and neutrons
isotope
different number of neutrons
advantages of fusion
low waste
abundant fuel
high energy yield
disadvantages of fusion
extreme conditions required
fission advantages
high tech for more advances
high energy output
fission dis advantages
produces waste
nuclear accidents
radioactive decay
unstable nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation
radiotracers
radioactive compounds used in the medical field to treat disease
chain reaction
single nuclear reaction causes subsequent nuclear reactions
critical mass
minimum amount of fissile material needed to sustain a nuclear chain reaction
e = mc2
formula to calculate energy released when mass is converted to energy
beneficial uses of nuclear radiation
food irradiation
medical
thickness gauging
nuclear power