3. Circulation
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
1
New cards
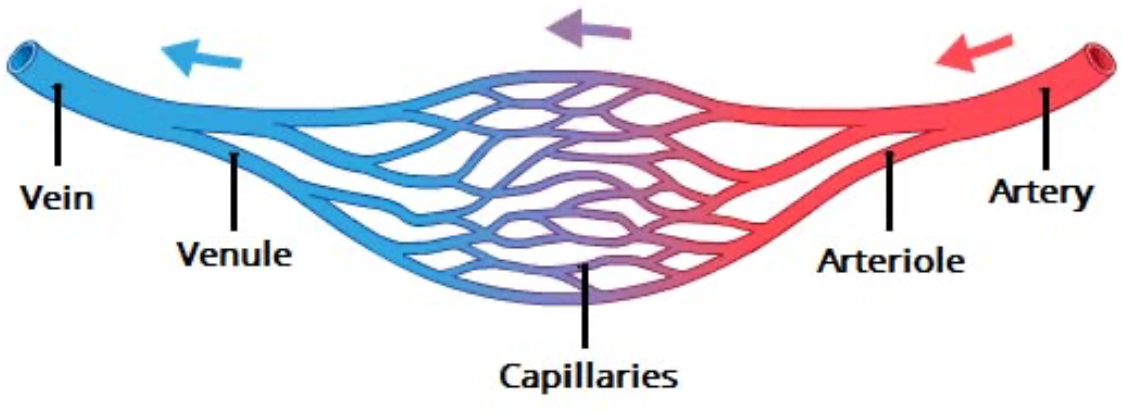
Circulation overview (describe flow of blood through relevant structures)
Artery > arteriole > capillary > venule > vein
2
New cards
What are the layers of a blood vessel?
1. Tunica intima
2. Tunica media
3. Tunica externa
3
New cards
Tunica intima
* Made up of endothelium
* Minimizes friction
* Minimizes friction
4
New cards
Tunica media
* Muscular layer
* Smooth muscle
* Vasoconstriction: decrease in diameter
* Vasodilation: increase in diameter
* Smooth muscle
* Vasoconstriction: decrease in diameter
* Vasodilation: increase in diameter
5
New cards
Tunica externa
* Loosely woven collagen fibers
* Contain vasa vasorum (delivers oxygen and nutrients to arterial and venous walls and removes waste)
* Contain vasa vasorum (delivers oxygen and nutrients to arterial and venous walls and removes waste)
6
New cards
Types of arteries
1. Elastic arteries
2. Muscular arteries
3. Arterioles
7
New cards
Elastic arteries
* More central
* Conducting arteries
* Presence of elastin allows for the stretching of artery
* Need to be able to withstand force because closer to the heart
* Continuous flow of blood
* Conducting arteries
* Presence of elastin allows for the stretching of artery
* Need to be able to withstand force because closer to the heart
* Continuous flow of blood
8
New cards
Muscular arteries
* More distal
* More active in vasoconstriction
* More active in vasoconstriction
9
New cards
Arterioles
Determines blood flow into capillaries
10
New cards
Capillaries (function, structural component)
* Responsible for exchange from blood to tissue and vice versa
* **Intercellular clefts** (gaps in junctions) to allow for **diffusion**
* **Intercellular clefts** (gaps in junctions) to allow for **diffusion**
11
New cards
Capillary bed
* 10-20 capillaries supplied from one arteriole
* Can be biased or flooded depending on local conditions
* Can be biased or flooded depending on local conditions
12
New cards
Types of capillaries
1. Continuous capillary
2. Fenestrated capillary
3. Sinusoid capillary
13
New cards
Continuous capillary
* Least permeable (hard for things to get out)
* Most common
* Abundant in skin, muscles, lungs, and CNS
* Most common
* Abundant in skin, muscles, lungs, and CNS
14
New cards
Fenestrated capillary
* Have **large fenestrations** (pores) that increase permeability
* Present in areas of __active filtration__ (e.g. kidney) or __absorption__ (e.g. small intestine), and areas of __endocrine hormone secretion__
* Present in areas of __active filtration__ (e.g. kidney) or __absorption__ (e.g. small intestine), and areas of __endocrine hormone secretion__
15
New cards
Sinusoid capillaries
* Most permeable
* Least common
* Present in liver, bone marrow, spleen, and adrenal medulla
* Large intercellular clefts and fenestrations, and few tight junctions
* Allow large molecules and even cells to pass
* Least common
* Present in liver, bone marrow, spleen, and adrenal medulla
* Large intercellular clefts and fenestrations, and few tight junctions
* Allow large molecules and even cells to pass
16
New cards
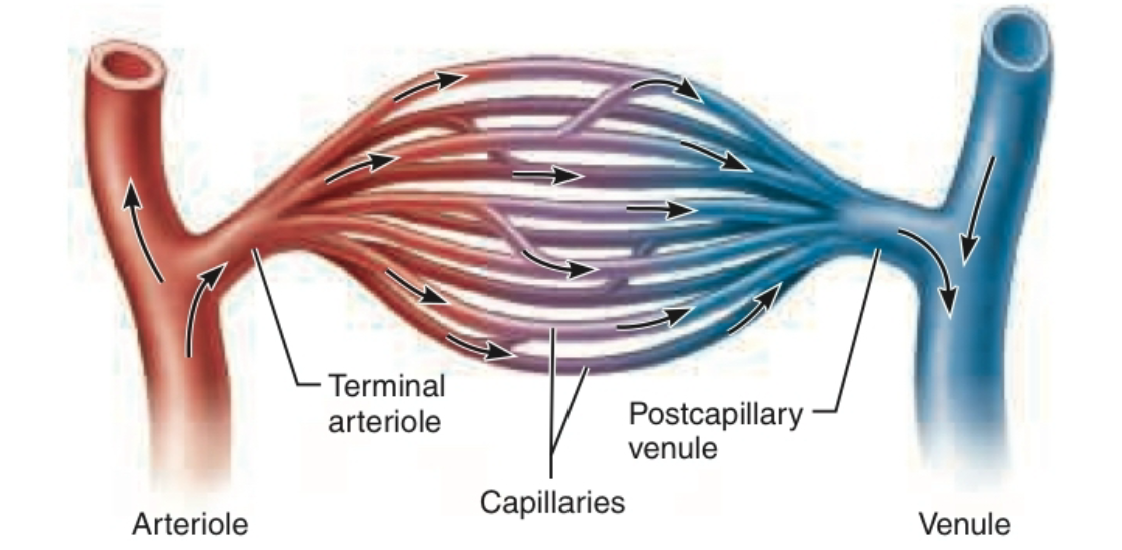
Arterioles dilated
Blood flows through capillaries
17
New cards
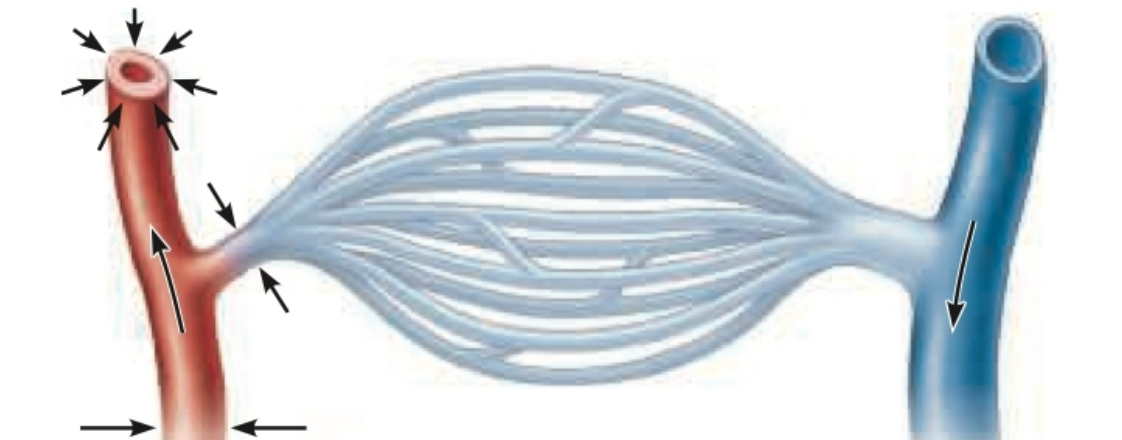
Arterioles constricted
Not as much blood flows into capillary bed

18
New cards
Intrinsic/local regulation of blood flow
* Metabolic control
* __Byproducts from usage__ (ex. exercise) cause vasodilation
* Low O2, increased H+ (lactic acid), nitric oxide
* __Byproducts of inflammation__ cause vasodilation
* __Byproducts from usage__ (ex. exercise) cause vasodilation
* Low O2, increased H+ (lactic acid), nitric oxide
* __Byproducts of inflammation__ cause vasodilation
19
New cards
Veins (structure, function)
* Relatively *little* smooth muscle
* Act as blood reservoir
* Contain up to 65% of blood in body
* Act as blood reservoir
* Contain up to 65% of blood in body
20
New cards
Pressure in veins (+ adaptation)
* Pressure in vein lower than in artery
* __Adaptation of valve__ (because not as much pressure to ensure correct blood flow like in arteries)
* Prevent back flow
* Resemble semilunar valve in heart
* __Adaptation of valve__ (because not as much pressure to ensure correct blood flow like in arteries)
* Prevent back flow
* Resemble semilunar valve in heart
21
New cards
Venous blood flow: muscular pump
* Another mechanism to **prevent back flow** in veins (in addition to valves)
* When contracting skeletal muscles press against vein, they __force open valves proximal__ to area of contraction
* Blood is propelled toward heart
* Backflowing blood __closes valves distal__ to area of contraction
* When contracting skeletal muscles press against vein, they __force open valves proximal__ to area of contraction
* Blood is propelled toward heart
* Backflowing blood __closes valves distal__ to area of contraction
22
New cards
Anastomosis/collateral circulation
The natural connection between two vessels
* Especially present in areas (like brain) where it is important for blood to reach
* Ensures that if one vessel were to get blocked/clot, blood could still get to that area of the body
* Especially present in areas (like brain) where it is important for blood to reach
* Ensures that if one vessel were to get blocked/clot, blood could still get to that area of the body
23
New cards
Anterior Cerebral Artery (ACA)
Supplies:
* Medial and superior parts of frontal lobe
* Anterior parietal lobe
* Medial and superior parts of frontal lobe
* Anterior parietal lobe
24
New cards
Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA)
Supplies:
* Lateral areas of frontal, temporal, and parietal lobes
**Most common artery involved in stroke**
* Lateral areas of frontal, temporal, and parietal lobes
**Most common artery involved in stroke**
25
New cards
Posterior Cerebral Artery (PCA)
Supplies:
* Occipital lobe
* Inferior part of temporal lobe
* Various deep structures including thalamus and posterior limb of internal capsule
* Occipital lobe
* Inferior part of temporal lobe
* Various deep structures including thalamus and posterior limb of internal capsule
26
New cards
Bonus exam question: compare and contrast ACA, MCA, and PCA strokes + which is most common
\
* ACA
* Personality changes (frontal lobe)
* Contralateral hemiplegia and hemisensory loss
* MCA
* **Most common**
* Contralateral vision changes
* One-sided paralysis
* Hemisensory loss
* Language impairment (typically with left-sided stroke)
* PCA
* Thalamic syndrome possible (losing temperature and pain regulation)
* Vision and eyes impacted
* Generally, stroke has contralateral effects on body (stroke in left hemisphere likely to effect right side of body, and vice versa)
* Reason for unilateral weakness following stroke
* ACA
* Personality changes (frontal lobe)
* Contralateral hemiplegia and hemisensory loss
* MCA
* **Most common**
* Contralateral vision changes
* One-sided paralysis
* Hemisensory loss
* Language impairment (typically with left-sided stroke)
* PCA
* Thalamic syndrome possible (losing temperature and pain regulation)
* Vision and eyes impacted
* Generally, stroke has contralateral effects on body (stroke in left hemisphere likely to effect right side of body, and vice versa)
* Reason for unilateral weakness following stroke
Explore top notes
Explore top flashcards
3. Circulation
Updated 972d ago3. Circulation
Updated 972d ago