5.3 diffusion
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is the definition of diffusion?
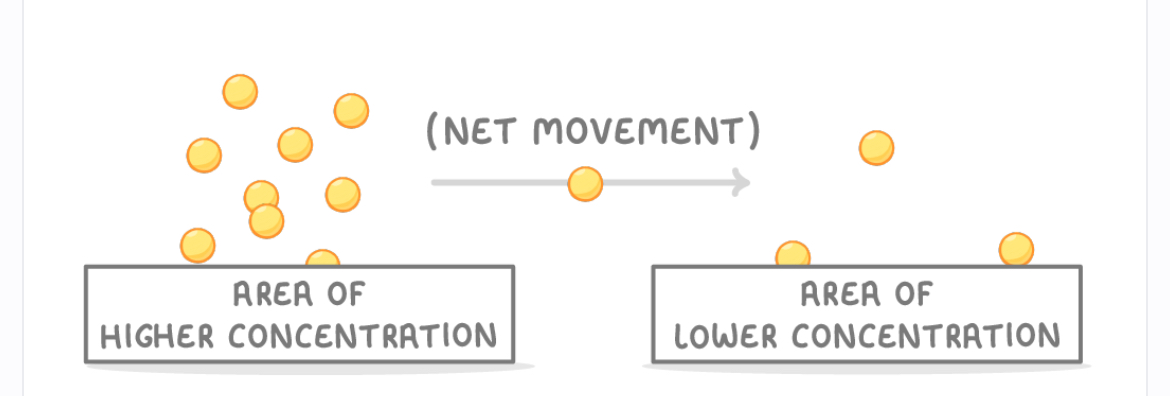
The net movement of particles, from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Is diffusion an active or passive process?
Diffusion is a passive process because it doesn’t require any energy from the cell.
Name two types of diffusion.
Simple diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
What is simple diffusion in the context of membranes?
Simple diffusion is the process in which molecules diffuse directly across membranes.
Explain why oxygen can enter cells via simple diffusion.
Oxygen can enter cells via simple diffusion because it is a small and non-polar molecule.
Explain why carrier and channel proteins are described as being specific.
Carrier and channel proteins are specific because they only allow specific molecule(s) to pass through them.
Explain how some large molecules can enter cells via facilitated diffusion.
Some large molecules can attach to carrier proteins, which causes them to change shape.
The carrier proteins release the molecules on the opposite side of the membrane.
Explain how ions enter cells via facilitated diffusion.
Ions pass through channel proteins in the cell membrane.
Name 5 factors that affect the rate of diffusion across a membrane.
Temperature
Concentration gradient
Thickness of membrane
Surface area
Number of carrier or channel proteins
Why does a higher temperature increase the rate of diffusion?
Higher temperature means particles have more (kinetic) energy.
So particles move around more quickly, and can diffuse more quickly.
How does the number of carrier proteins affect the rate of facilitated diffusion?
The more carrier proteins, the faster the rate of facilitated diffusion.
Why does a thin membrane increase the rate of diffusion?
A thin membrane means that particles do not have to travel as far, so they diffuse faster.