BIO 203: Ch. 4
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What is a prokaryote?
Single cell, lacks organelles, cell walls contain peptidoglycan, divide by binary fission
What is a eukaryote?
More than cell, contains organelles, cell walls are chemically simple, divide by mitosis
What are the basic shapes of bacteria?
Coccus (spherical), bacillus (rod), spiral (spirillum, vibrio, spirochete)
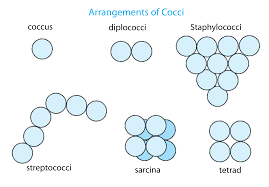
Arrangements of coccus bacteria?
Diplococci, streptococci, tetra, sarcinae, staphylococci
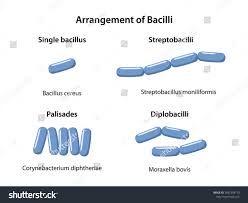
Arrangements of bacillus?
single, streptobacilli, palisades, diplobacilli
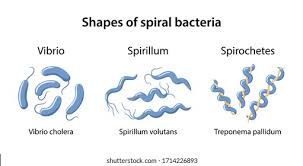
Arrangements for spiral?
What is the glycocalyx?
In prokaryotic bacteria, it is the outermost, viscous, gel-like layer composed primarily of polysaccharides
What are the two main forms of the glycocalyx?
Capsule: neatly organized, and tightly bound layer of polysaccharides adhered to cell wall
Slime layer: unorganized and loose layer of polysaccharides, glycoproteins, and/or glycolipids
What are the functions of the glycocalyx?
Protection and adhesion
What is the flagella?
Filament made of chains
Attached to the hook
Anchored to the wall and membrane by basal body
What are the arrangements of bacterial flagella?
a. peritrichous (lots all around)
b. monotrichous and polar (one at one end)
c. lophotrichous and polar (multiple at one end)
d. amphitrichous and polar (one at each end)
Function of flagella?
Motility (run or tumble)
What is chemotaxis?
move away or toward stimuli
What is a stimulus?
An attractant or repellent
What is phototaxis?
Movement away or toward a light source
What are axial filaments?
Also called endoflagella and causes cell to move in spiral motion (ex. spirochete)
What are fimbriae?
Hairlike appendages that are shorter, thinner, and straighter than the flagellum that adhere
What are pili?
Longer than fimbriae and only one (or two) per cell that facilitate transfer of DNA from one cell to another
What is a hypotonic environment?
More solutes inside cell than out → water rushes in to cell →cell explodes
What is a hypertonic environment?
Less solutes inside the cell than outside → water rushes out → cell shrivels up
What does a gram-positive bacterial cell wall have?
Multiple layers of peptidoglycan
What does a gram - negative bacterial cell wall have?
Only a single layer of peptidoglycan with an outer membrane
What are acid fast cell walls?
Have a thick peptidoglycan layer with a waxy lipid layer
What is the plasma membrane?
Viscous structure where proteins can move to function
What is simple diffusion?
Movement of solute from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
What is facilitated diffusion?
Solute combines with a transporter protein in the membrane (water channels)
What is active transport?
Requires a transporter protein and ATP
What is group translocation?
Requires a transporter protein and PEP (prokaryotes)
What is the cytoplasm in a bacteria?
Thick, aqueous, transparent, and elastic and accommodates the nucleoid, ribosomes, and inclusions
What does a bacterial chromosome look like?
Single, long circularly arranged thread of double - stranded DNA
What is plasmid?
Circular, double - stranded DNA that is transferred between cells (can be lost and not cause harm to cell)
What do ribosomes do?
SIte of protein synthesis and contains 2 subunits that contain rRNA and protein. (Prokaryotic: 70S = 50S + 30S)
What are endospores?
Gram + bacteria in adverse circumstances
What is sporulation?
Endospore formation
What is germination
Return to vegetative state
What is flagellum/a?
few and long projections
What is cilium/a?
numerous and short projections
How are flagella and cilia formed?
Anchored to plasma membrane via basal body, consists of 9 pairs and 2 array, moves in a wavelike manner
What is the glycocalyx?
Sticky carbs extending from animal plasma membrane bonded to proteins and lipids and helps to strengthen cell surface and adhesion
What is the function of plasma membrane?
Selective permeability and endocytosis
What is phagocytosis?
Pseudopods extend and engulf particles
What is pinocytosis?
Membrane folds inward, bringing fluid an dissolved substances
What is the cytoplasm?
Substance inside plasma and outside nucleus
What is cytosol?
Fluid portion of cytoplasm
What is the cytoskeleton?
Microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules
What is the nucleus?
Contains chromosomes (DNA)
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
Rough ER + ribosomes = Protein synthesis, smooth ER is continuous with nucleus and deals with lipids
Eukaryotic ribosomes subunits?
have two subunits (80S = 60S + 40S)
What is the golgi complex?
Major collection and dispatch station of protein products received from ER
What is a Lysosome?
Digestive enzymes that breakdown molecules
What is a vacuole?
Some provide storage or bring food into cells
What is the mitochondria?
Involved in producing energy and cellular respiration