APHG Unit 6 - Urban Models + Types of Cities
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This flashcard set reviews all urban models such as the Burgess and Hoyt Sector Model, and types of cities such as primate and metacities. Please note that the first four models and most of the city types are guaranteed to be on the exam. you are EXPECTED to know these.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
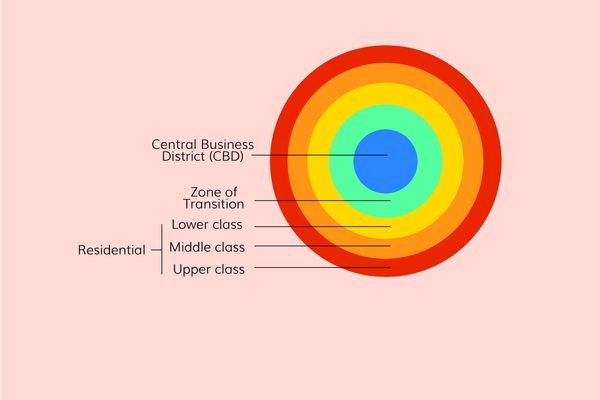
Concentric Zone Model / Burgess Model
City grows OUTWARDS
Central Business District → Factories → Low Class Residential (Zone of Transition) → Middle Class Residential → Upper Class Residential
Therefore, the further you are from the CBD the more land costs/wealthier you are
Outdated - predates the widespread use of cars
Think about Burgess + Bullseye
EXAMPLE- 1920s Chicago
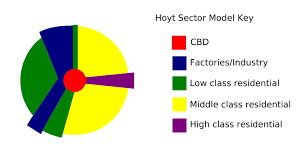
Sector Model (Hoyt)
Split into uneven pieces rather than being uniform circles
Different sectors grow outward from CBD along railroads, highways, etc.
Think about poorly cut pizza
EXAMPLE- Calgary- city in Canada, industrial zones grow alongside rail lines
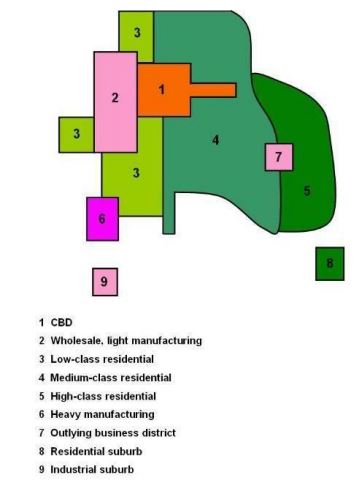
Multiple Nuclei Model (Harris & Ullman)
think MULTIPLE CBDs
Unlike previous two, not all activities revolve around the CBD
Odd shape
EXAMPLE-
New York City’s major CBDs include Midtown Manhattan, Lower Manhattan, Downtown Brooklyn, etc.
Atlanta’s major CBDs include Downtown, Midtown, and Buckhead
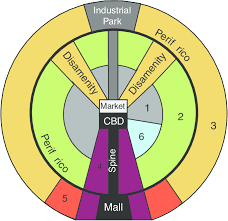
Latin American City Model (Griffin-Ford Model)
Has CBD with a spine
Includes disamenity zones/squatter settlements + a sector of elite housing.
Elite housing is located on the spine + near the CBD, squatter settlements are on the outskirts
EXAMPLE- Mexico City, Mexico or Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Primate City
A city that is significantly larger than any other city in the country and dominates economic, political, and cultural life. Primate cities often serve as the main hub for transportation and services.
EXAMPLE- Paris, France
Megacity
A metropolitan area with over 10 million inhabitants, characterized by high population density and significant economic influence.
EXAMPLE- Lagos, Mumbai
Metacity
A city with a population exceeding 20 million people, often facing challenges related to infrastructure, housing, and transportation.
EXAMPLE- Delhi, Shanghai
Edge City
A suburban area that has developed its own CBD, often with office spaces, retail centers, and entertainment facilities, distinct from traditional urban areas.
EXAMPLE- Tysons, Virginia
Squatter Settlement
A densely populated urban area that develops spontaneously, usually on the outskirts of cities, where residents lack legal claims to the land and often live in inadequate housing.
EXAMPLE- Kibera, Kenya
World City
A significant urban center that serves as a hub for global economic, cultural, and political activities, often influencing international relations and trade.
EXAMPLE- New York City, London
Rank-Size Rule
A statistical relationship that indicates that the size of a city or town is inversely proportional to its rank in the hierarchical order of cities, suggesting that the nth largest city is 1/n the size of the largest city. If the city does NOT follow RSR, it is likely a primate city.
RSR FORMULA- Pop. of largest city ÷ N (rank of city)
EXAMPLE- population- 10,000, rank 4. 10,000 ÷ 4 = 2,500
this is almost GUARANTEED to be on the exam!
Megalopolis
A large urban region formed by the merging of several metropolitan areas, characterized by high population density and economic interdependence.
EXAMPLE- BosWash corridor in the northeastern United States.