Separation of Mixture
Mind Map: Separation of Mixtures Physically
Central Idea: Separation of Mixtures
- Separating mixtures into their individual components using physical methods.
Main Branches:
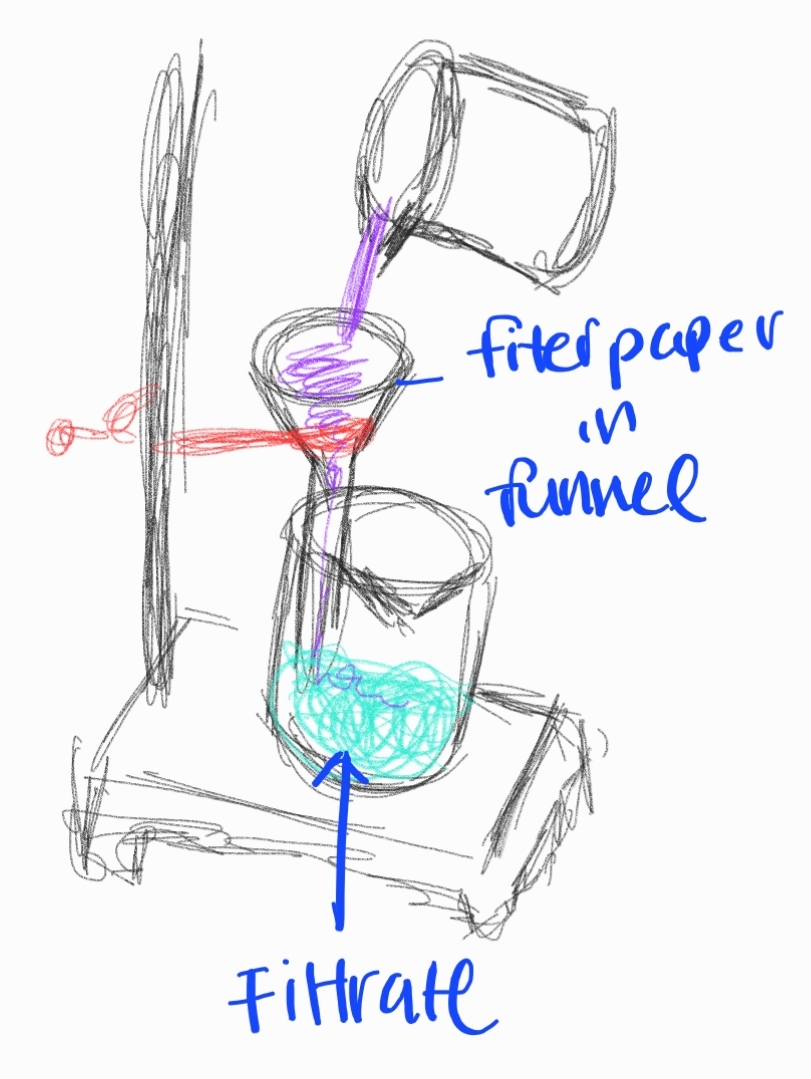
Filtration
Separating solid particles from a liquid or gas using a filter medium.
Sub-branches:
- Gravity Filtration
- Vacuum Filtration
- Hot Filtration
Distillation
- Separating a mixture of liquids based on their boiling points.
- Sub-branches:
- Simple Distillation
- Fractional Distillation: used to separate petroleum into simpler mixtures of LIQUID hydrocarbons
- process is dependent on the differences in the boiling points of the hydrocarbon fractions
Evaporation
- Separating a mixture of a solid dissolved in a liquid by heating and vaporizing the liquid.
- STRONG HEATING required → crucible used (usually made of porcelain)
- Sub-branches:
- Simple Evaporation
- Crystallization: separate a dissolved solid from its solvent
- concertation solution at HIGH temp and allow it to cool so the solute crystals of the solute form at the bottom of the vessel
- can add a single “seed crystal” of solute into a solution to initiate crystallization
- Separating a mixture of a solid dissolved in a liquid by heating and vaporizing the liquid.
Magnetic Separation
- Separating magnetic materials from non-magnetic materials using magnets.
- Sub-branches:
- Electromagnetic Separation
- High-Gradient Magnetic Separation
Centrifugation
- Separating components of a mixture based on their density using centrifugal force.
- Sub-branches:
- Sedimentation Centrifugation
- Differential Centrifugation
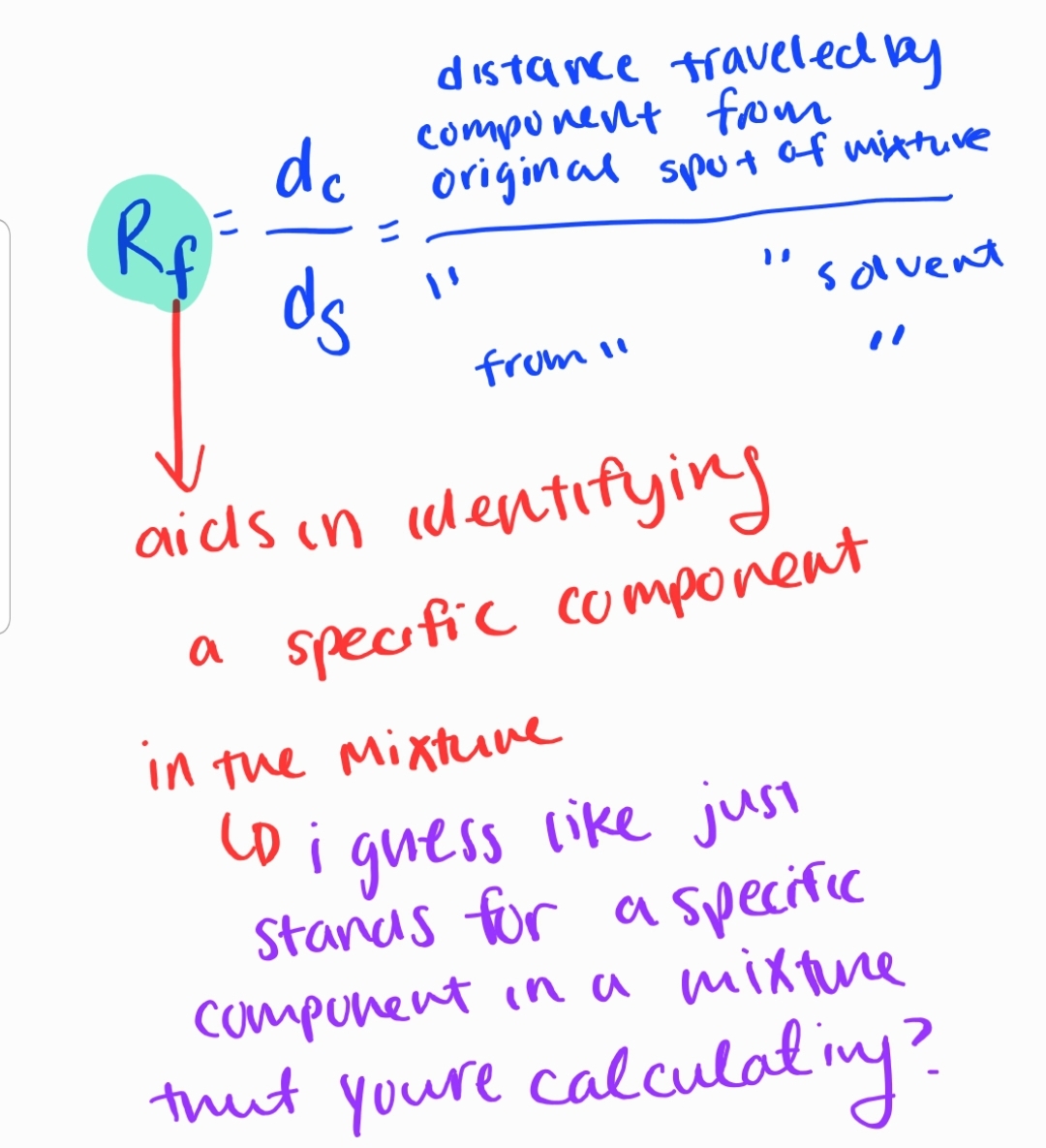
Chromatography: chroma= color graphein= to write
Separating mixtures based on the differential movement of components in a mobile phase.
Sub-branches:
- Paper Chromatography
- Thin-Layer Chromatography
Sieving
- Separating particles of different sizes using a sieve or mesh.
- Sub-branches:
- Wet Sieving
- Dry Sieving
- Decantation
- Separating a mixture of a liquid and solid by pouring off the liquid layer.
- Sub-branches:
- Gravity Decantation
- Centrifugal Decantation
- Sublimation
- Separating a mixture of a solid and a volatile substance by heating the mixture, causing the solid to directly vaporize.
- Sub-branches:
- Reverse Sublimation
- Freeze-Drying
- Extraction
- Separating a mixture by selectively dissolving one or more components into a solvent.
- Sub-branches:
- Liquid-Liquid Extraction
- Solid-Liquid Extraction
Note: This mind map provides an overview of various physical methods for separating mix