5 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
organelle
small units that are enclosed by a separate membrane located in the cell, prokaryotes don't have any
Ribosomes aren't ______
paramecium, amoeba
The most common protozoa (which include protists) are: (2)
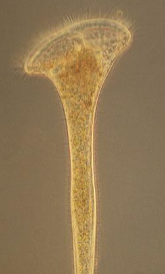
Stentor
This protozoa > protist has animal like instincts and will attack their food source
Golgi apparatus
This organelle receives, modifies, packages, & transports proteins. Replaces components of plasma membrane.
made of stacked cisternae (dictyosomes)
cis forming face
trans maturing face
dictyosomes
A stack of flattened cisternae in the golgi apparatus
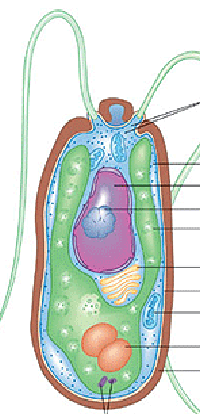
Chloroplast, starch vacuole
What two organelles differentiate algal cells from fungal or protozoan cells?
Protozoan cell
This type of cell doesn’t have a cell wall but it has a pellicle, outer surface layer of some _____ is sufficiently rigid to maintain a distinctive shape
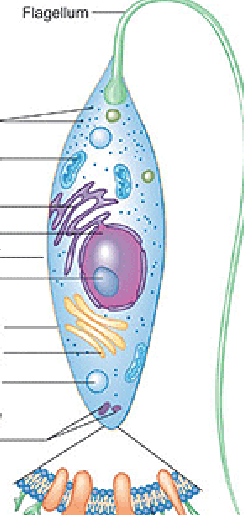
Euglena
Type of protist that posses plant and animal instincts
difference between paramecium and this organism, is that this organism has a chloroplast for photosynthesis
has flagella for movement unlike paramecium (cilia)
no cell wall but has pellicle
cytosol, organelles
The cytoplasm of eukaryotes consists of ___ and ____
chromatin
complex of DNA, histones, and other proteins
5 types of histones form nucleosomes: H1, H2A, H2B, H3, H4
condenses into chromosome during division
H1, H2A, H2B, H3, H4
these 5 histones form nucleosomes:
phagocytosis, clathrin dependent, caveolin dependent
What are the 3 types of endocytosis?
endosome
Clathrin-coated vesicles & some caveolin-coated vesicles deliver contents to ____ (organelles w/t hydrolytic enzymes)
eventually becomes a lysosome
nucleolus
Directs synthesis & processing of rRNA
directs assembly of rRNA to form a partial ribosomal subunits
ribosomes mature in cytosol
80s, 60s, 40s
The size of a eukaryotic ribosome ____
large subunit ____
small subunit ___
mitochondria
90% of energy is produced: contains its own ribosomes & DNA (may be circular)
enzymes of tricarboxylic acid cycle & those involved in catabolism of fatty acids
ATP generated in electron transport & oxidative phosphorylation
chloroplasts
Site of photosynthetic reactions
- The stroma (a matrix) is within inner membrane
DNA, ribosomes, & thylakoids (trapping of light energy to generate ATP, NADPH, & oxygen)
mycology
the study of fungi
yeast - always unicellular (can be hairy)
mold - multicellular, can be filamentous or fleshy (hairy)
mycoses
fungal infections: 200 of the 100,000 species are pathogenic to humans & animals
fungi
Nutritional type: chemoheterotroph
Multicellularity: all except yeast
Cellular arrangement: unicellular, filamentous, fleshy
food acquisition: absorptive
sexual & asexual spores
Rough ER
ribosomes attached; synthesis of secreted proteins by ER associated ribosomes
Ship to Golgi apparatus
Smooth ER
devoid of ribosomes, synthesis of lipids by ER associated enzymes
- Lipids: steroids or hormones
Filtration, gets rid of old products/ organelles
hyphae
strains on the mold with two distinct parts: vegetative & aerial
aerial hyphae
reproductive portion, breaks off & become a yeast cell & eventually becomes a mold
vegetative hyphae
strains on molds that obtain nutrients
thallus, mycelium
The fungal _____ (body) consists of hyphae; a mass of hyphae is a ______
Yeast
Unicellular fungi that produces by fission (divides symmetrically) or budding (divide asymmetrically)
1 ___ can produce up to 24 daughter cells
bud scar
In budding, this structure lets you know how many times a yeast cell has produced a daughter cell
fungal dimorphism
The ability of certain fungi to switch b/w two distinct morphologies: unicellular yeast form & multicellular filamentous form
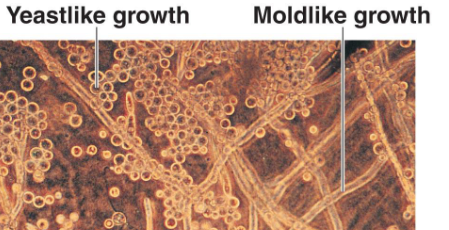
yeastlike
Pathogenic dimorphic fungi is _____ (shrink) at 37C & moldlike (elongate) at 25C
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S. cerevisiae)
This species of fungi makes beer, bread, wine, used to genetically engineer Hep. B vaccine
trichoderma
A genus of fungi used to commercially produce cellulase to remove plant cell walls to produce juice
Entomophaga
genus of fungi that works as biocontrol; kills gypsy moths that destroy trees in eastern US
Target moth at catepillar stage
paecilomyces
genus of fungi that kill termites
systemic, subcutaneous, cutaneous, superficial
What are the 4 categories of mycoses?
systemic mycoses
Type of mycoses deep within the body usually caused by soil fungi; inhalation of spores; lung infection spreads; not contagious
subcutaneous mycoses
type of mycoses beneath the skin; saprophytic soil fungi; direct implantation of spores of mycelia into a puncture wound
Ex: sporotrichosis, skin infection by fungus Sporothrix
cutaneous mycoses
type of mycoses: dermatophytes; affect hair, skin, & nails; human to human & secrete keratase
superficial mycoses
type of mycoses that is in the hair shafts; prevalent in the tropics
Candida albicans (C. albicans)
type of mycoses that results in skin infections, thrust, or vaginitis
Cryptococcus neoformans (C. neoformans)
Mycoses that cause meningoencephalitis
Histoplasmosis
An infection caused by Histoplasma capsulatum from absorbing or inhaling bird droppings
diagnosed from biopsy of lungs & is often misdiagnosed as cancer bc of white lesions in the lung tissue
Lung infection or pneumonia caused by breathing in spores
infection can be mild to severe & can lead to meningitis
Pneumocystis jirovecii
Fungus that causes pneumocystosis: lung infection primarily affecting individuals with weakened immune systems
Tinea corporis
Fungi that causes ringworm on the scalp
tinea pedis
type of fungi that causes athlete’s foot and jock itch
onychomycosis
fungal infection of the nail unit, encompass dermatophytes, yeast, & saprophytic mold infection
Thickening & discoloration of the nail
tinea versicolor
fungal skin infection caused by yeast Malassezia; result in discolored patches of skin bc it affects pigmentation of the skin
coccidioidomycosis
Infection caused by Coccidiodes immitis; also known as “Valley Fever”
cough, fever, rash on trunk, headache, joint pains that occurs 1-3 weeks after exposure
clears up if you have good immune system
Common in Utah, California, Arizona, Nevada, MX & lives in soil < highest cases in Cali & Arizona
treated with Amphotericin B or ketoconazole
25k-100k cases each year
Sprototrichosis
fungal infection caused by Sporothrix schenckii a dimorphic fungus
“Rose-handler’s disease” < often seen in gardeners/ farmers
cats key source of transmission
yeast like cells on cytologic exam are diagnostic
prototheca
Algae rarely infects humans, the biggest threat is food poisoning caused by agal toxins
Exception: ______ which produces toxins
diatoms
Type of algae with pectin & silica cell walls (high boiling point); unicellular or filamentous
chlorophyll a & c, carotene, xanthophylls (yellow color)
store oil by capturing light energy & converting it to oil
fossilized ____ form oil deposits
produce domoic acid
domoic acid intoxication
has caused outbreaks in those who eat mussels (diarrhea & memory loss) & killed hundreds of marine birds & sea lions in California (genus: Pseudo-nitzschia)
neurotoxin caused by diatoms that accumulate in shellfish
Dinoflagellates
Type of algae whose plasma membrane is made of cellulose; unicellular & stores starch
chlorophyll a & c, carotene, xanthophylls
some are symbionts in marine animals
neurotoxins cause paralytic shellfish poisoning
Gymnodinium breve
Species of dinoflagellate that cause red tide algae bloom (can look red, green, gold, brown)
secretes brevetoxin (can be deadly, no treatment)
massive fish kills & deadly to whales
Brevetoxin
toxin secreted by Gymnodinium breve that causes tingling sensations in mouth + extremities, heat or chills, bradycardia, diarrhea
meningoencephalitis
inflammation of both brain & meninges
fetal cases caused by amoebic meningoencephalitis (Balamuthia & Naegleria fowleri species)
enter body when water splashed into upper nasal tract & into brain via olfactory cranial nerves
found in 70% of lake reservoirs in the US
Malaria
Caused by plasmodium (protozoal) parasites: P. vivax (most common) & P. falciparum (most deadly)
symptoms: relapsing fever, shaking chills, prostration, anemia, enlarged spleen, vomiting, cough, joint pain, abdominal pain, jaundice
infects 300 million a year & 1 million deaths
Plasmodium vivax
The most common type of malaria infection
Plasmodium falciparum
the most deadly type of malaria infection
helminths
Parasitic worms with digestive, nervous, & complex reproductive system
Egg > larva > adult
monoecious (hermaphroditic)
dioecious
monoecious
Hermaphroditic helminths with a male & female reproductive systems in one animal; doesn’t require mate
Ex: Tapeworm
dioecious
reproduction in helminths that requires a male & female to mate
Ex: hookworm & pinworm
scolex
mouth of the tapeworm that attaches to the intestine
Enterobius vermicularis
Pinworm
female crawls out of anus at night to lay eggs
cause intense itching & irritability (generally not dangerous)
eggs spread easily to clothing, bedding, etc
estimates that 12% of US population is infested
Necator americanus
Hookworm
Eggs hatch in soil
Larvae penetrates intact skin (through hair follicles)
Enter capillaries, migrates to lungs
Leaves bloodstream to enter alveoli, crawls up respiratory tree to back of throat
Swallowed & uses hooks to latch on to intestinal lining
Causes blood loss, abdominal discomfort, & anemia, especially in children
Adult worms 0.5-1 inches. Lay eggs that come out in stool starting life cycle over again.