Environmental Science Chapter 3
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
4 interacting spheres
-hydrosphere
-atmosphere
-biosphere
-geosphere/lithosphere
hydrosphere
the watery areas of the earth, including oceans, lakes, rivers, and other bodies of water. most of it is found on the surface
atmosphere
the gases that surround Earth, primarily made up of nitrogen and oxygen
biosphere
the portion of the Earth where life is found.
extends high into he air and below the surface into oceans
geosphere/lithosphere
is made up of rocks, minerals, and soil
it includes all of the layers of the Earth's interior
cryosphere
a portion of the hydrosphere that is frozen, made primarily of glaciers and sea ice. this is also monitored to collect data about climate change
ecology
the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment. It is a multidisciplinary science, and is closely linked to other disciplines such as biology, meteorology, chemistry, engineering, geology, physics, and mathematics
organism
one individual living thing
population
group of organisms of one species in one place at one time
community
interacting populations (many species together in one place)
ecosystem
all biotic and abiotic factors in a certain area
ecologists
collect the qualitative data (observations of organisms)and the quantitve data (measurements)
biome
all the ecosystems in a portion of the world with a specific climate
a niche
the unique role of a species within an ecosystem
fundamental niche
the role an organism can occupy without competition.
realized niche
the smaller niche an organism occupied because of competition
habitat
where an organism lives
tolerance
the ability of an organism to survive in changing conditions, such as temperature
specialists
organisms that have limited tolerance and can only withstand small changes in their environments
generalists
organisms that adapt easily to changes in their niche due to large ranges of tolerance
autotrophs
obtain energy from the sun or chemical compounds
heterotrophs
depend on autotrophs for energy
herbivores
eat plants
carnivores
eat meat
omnivores
eat plants AND meat
scavengers
eat animals that have already died. they keep organisms from covering the ground while decomposing
decomposers
break down dead and decaying matter into simpler molecules that can be absorbed
food chains
show the feeding relationships of the organisms
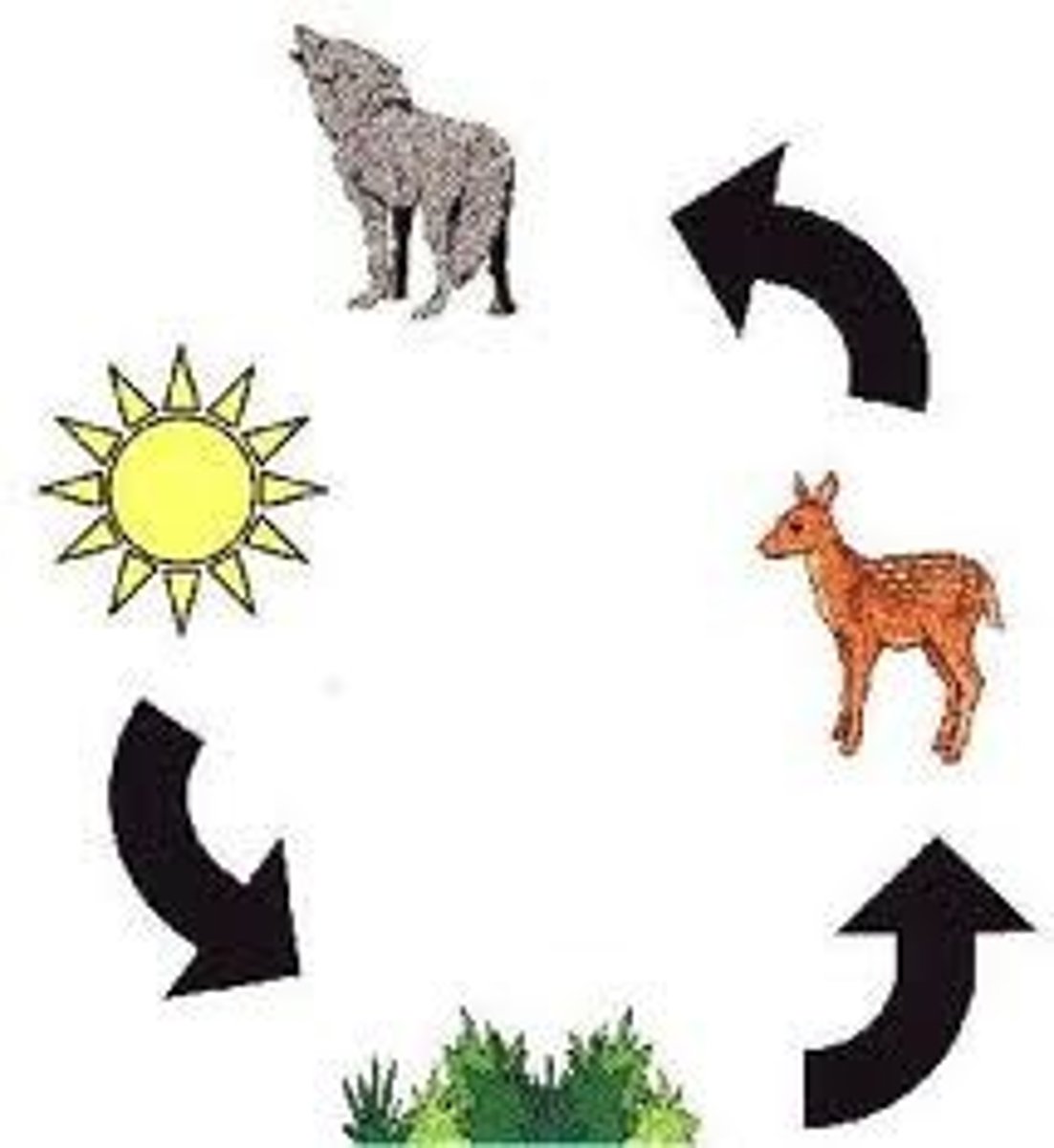
food webs
show many overlapping food chains. decomposers and scavengers are found at every point in the food web if an organism dies
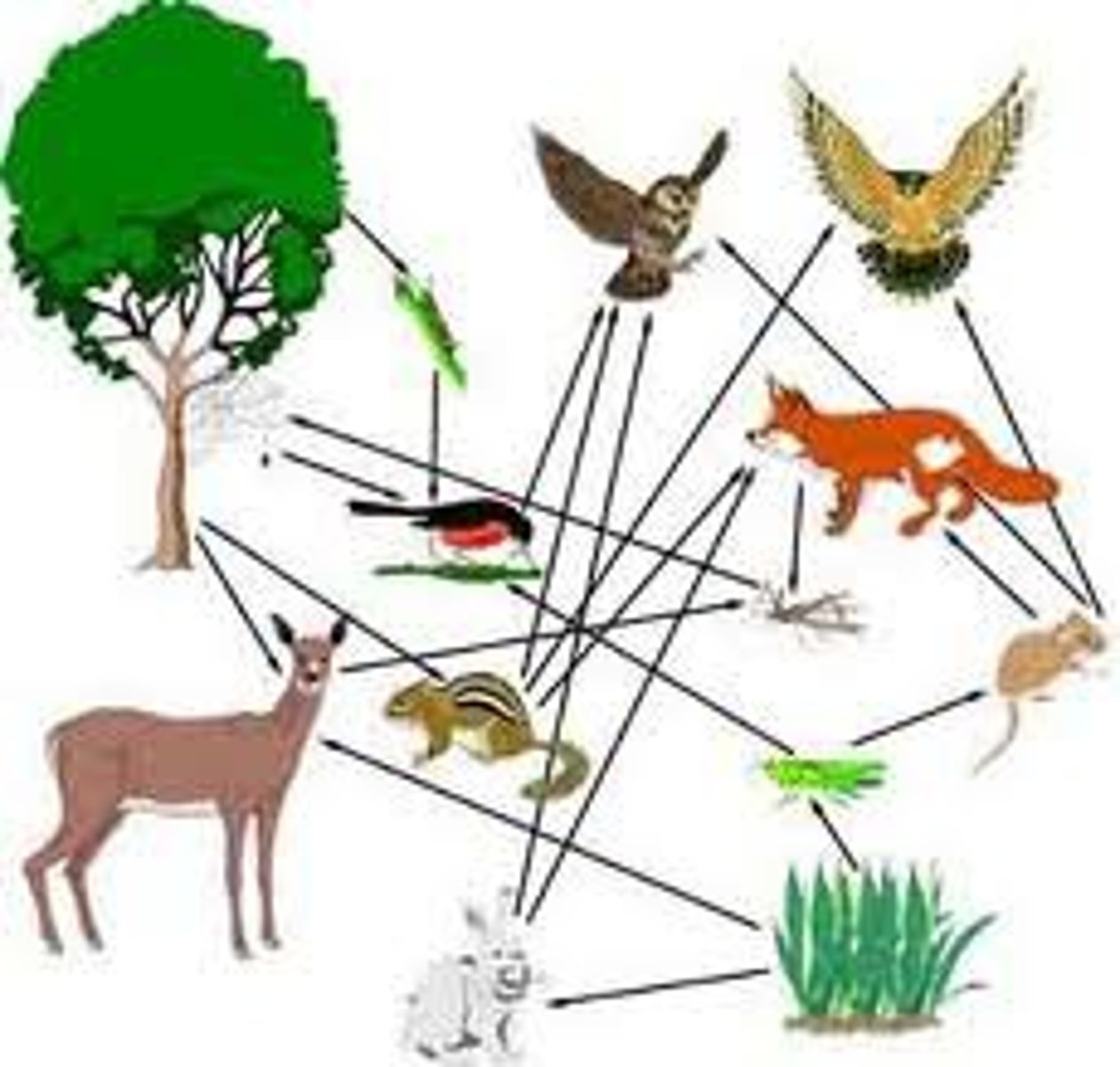
arrows in food chains/webs
show the transfer of energy
examples of atmosphere
ozone, wind, oxygen
examples of biosphere
bacteria, plants, animals
examples of geosphere/lithosphere
rocks, mountains, bricks
examples of hydrosphere
snow, oceans, stream, water vapor, rivers