HP LEC 9: Cutaneous Sensations/ Eyes and Vision
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
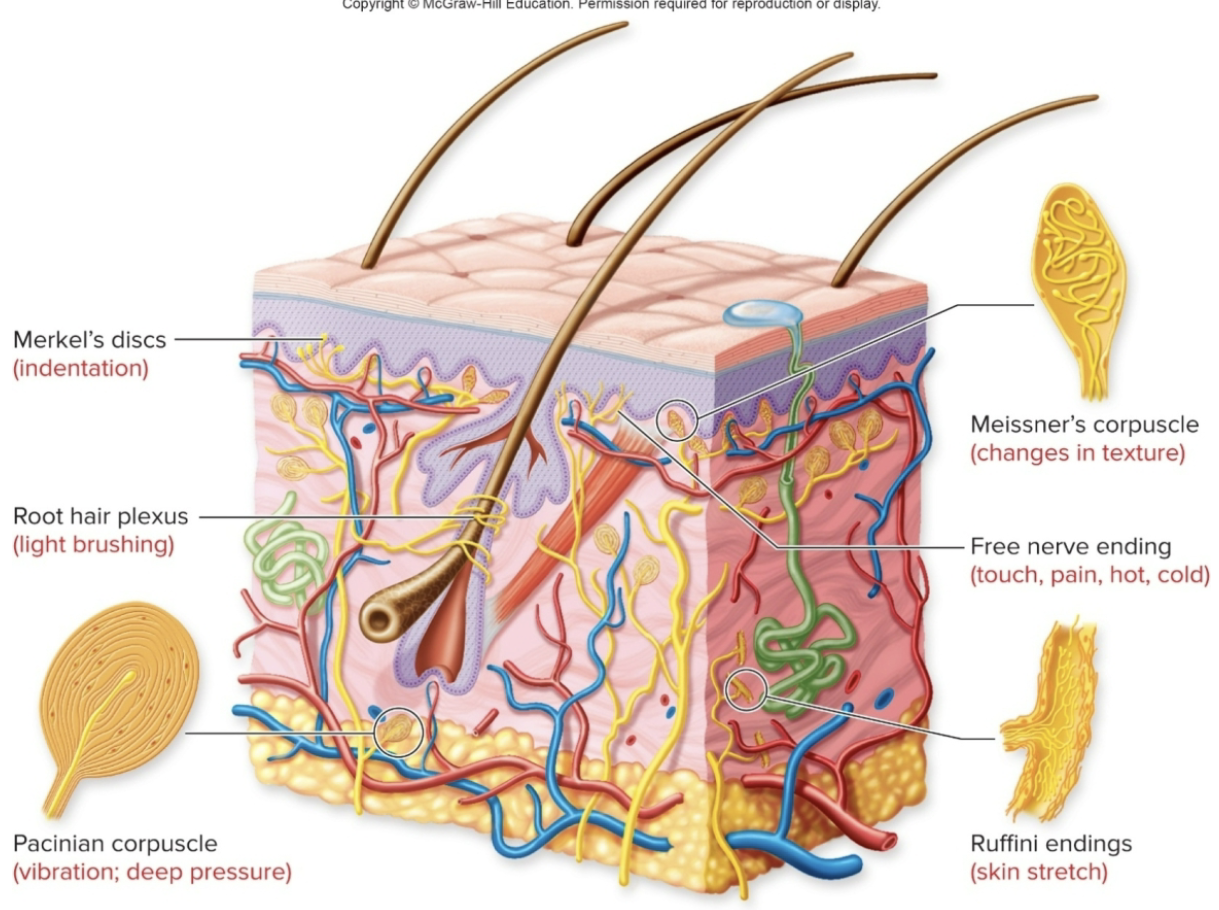
Cutaneous Receptors
Pain, cold, and heat receptors are naked dendrites of sensory neurons
Free nerve endings
Touch and pressure receptors have special structures around their dendrites
Merkel’s disks
Meissner’s corpuscles
Pacinian corpuscles
Ruffini corpuscles
Cultaneous Receptors: Cold Receptors- (location, what is it stimulated by, what can it also respond to, temp range)
Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) Channel
a) there are MANY more receptors that respond to cold than hot
b) located close to the epidermis
c) stimulated by cold and inhibited by warm
d) some cold receptors also respond to menthol
e) the temperature range of response is 8 to 28 degrees C
Cultaneous Receptors: Warm Receptors- (location, stimulated)
Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) Channel
a) located deeper in the dermis
b) excited by warming & inhibiting by cooling
c) different from receptors that detect painful heat
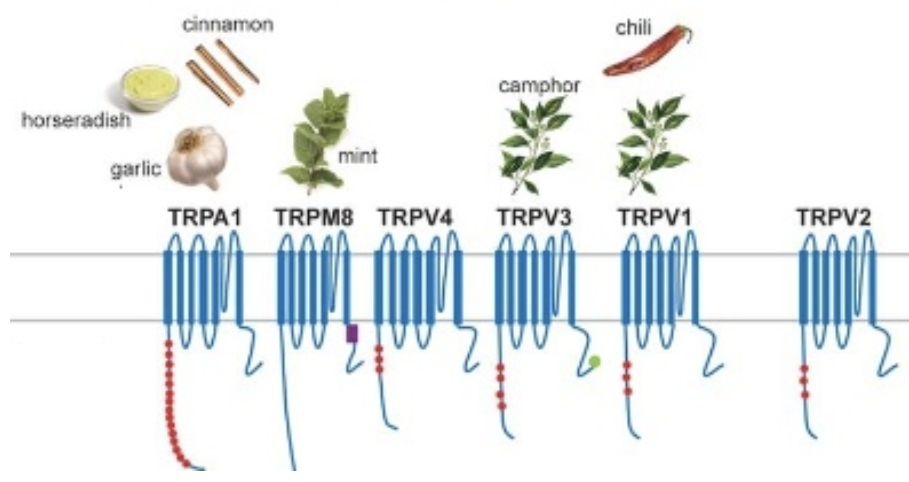
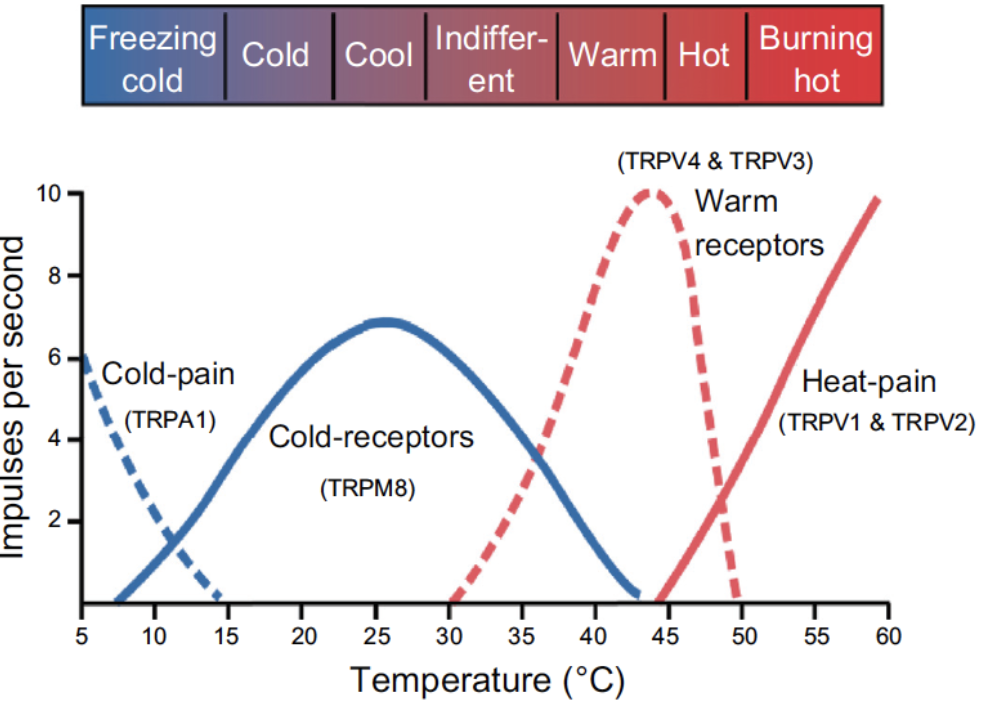
Cultaneous Receptors: Hot Receptors- (location, , activated)
Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) Channel
a) the pain experienced by a hot stimulus is sensed by a special nociceptor called a capsaicin receptor
b) also a receptor for the chemical found in chili peppers (capsaicin)
c) activated at 43 degrees C or higher
Noiceptors- Pain Receptors (different types, activation)
a) Nociceptors can be myelinated or unmyelinated
sudden, sharp pain is transmitted by myelinated neurons
dull, persistent pain is transmitted by UNmyelinated neurons
b) Nociceptors may be activated by chemicals released by damaged tissues, such as ATP, or by pH change or mechanical stimulus
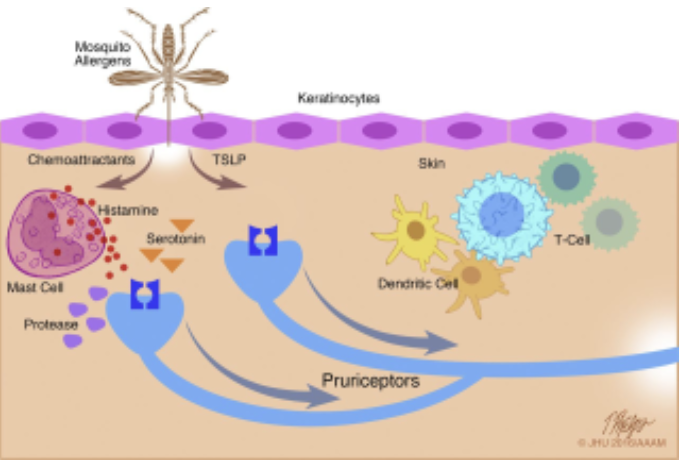
Itch Sensation
acute itch: stimulated by histamine release from mast cells and basophils
chronic itch: stimulated by other chemicals and does not respond to antihistamines
receptors stimulate Unmyelinated sensory axons to the spinal cord
Neural Pathway for Somesthetic sensations- Tract: Dorsal Column- Medial Leminscus (origin)
Dorsal Column- Medial Leminscus (origin)
peripheral afferent neurons; ascends on ipsilateral side of spinal cord but crosses over in medulla
Dorsal Column- Medial Leminscus (Termination)
Dorsal Column- Medial Leminscus (Termination)
Nucleus gracilis and nucleus cuneatus of medulla; eventually thalamus, then cerebral cortex
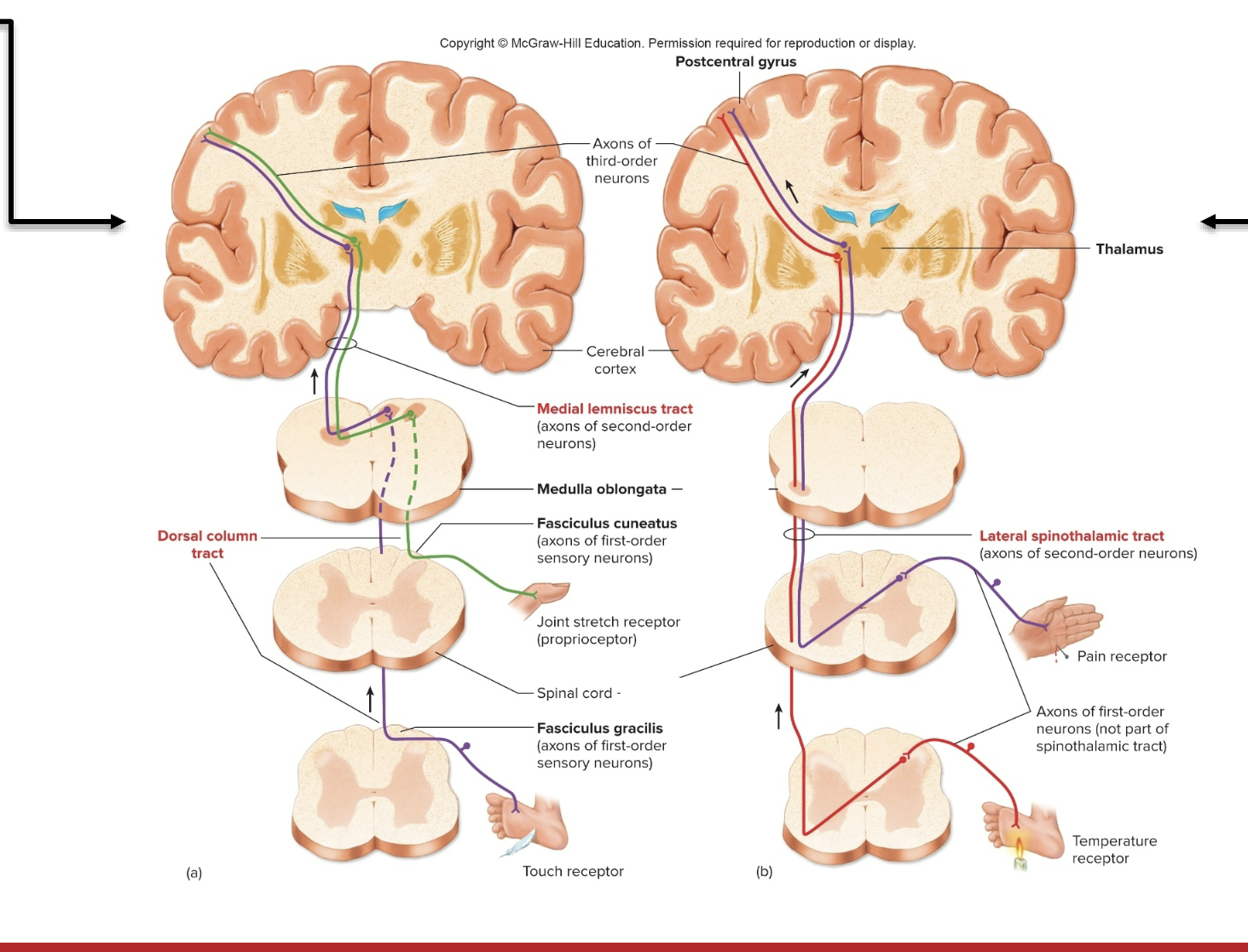
Dorsal Column- Medial Leminscus (Function)
Dorsal Column- Medial Leminscus (Function)
conducts sensory impulses from skin, muscles, tendons, and joints, which are interpreted as sensations of cutaneous touch and pressure, and body position
Neural Pathway for Somesthetic sensations- Tract: Anterolateral Spinothalamic (origin)
Anterolateral Spinothalamic (origin)
posterior horn on ONE side of cord but crosses to opposite side
Anterolateral Spinothalamic (Termination)
Anterolateral Spinothalamic (Termination)
thalamus, then cerebral cortex
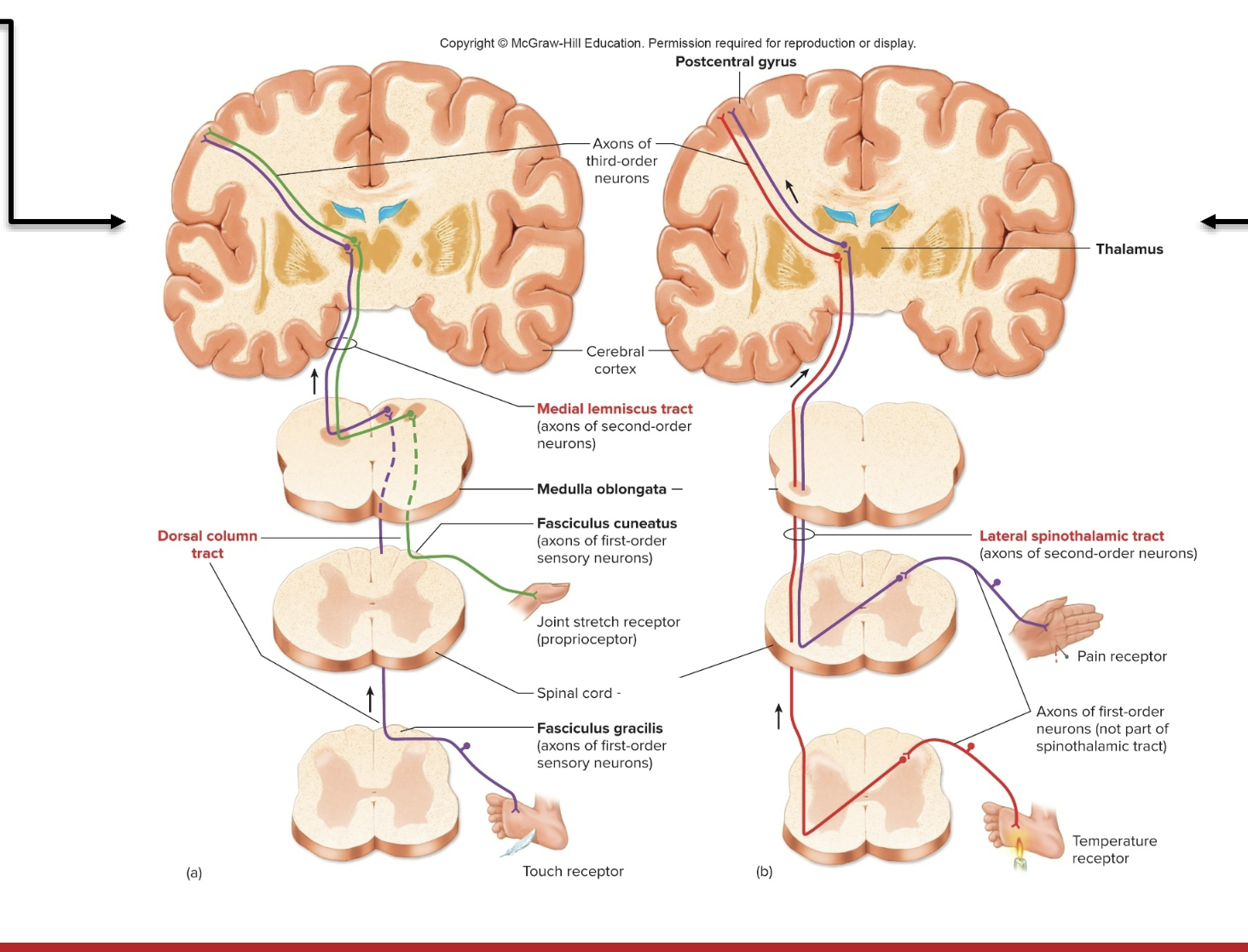
Anterolateral Spinothalamic (Function)
Anterolateral Spinothalamic (Function)
conducts pain and temperature impulses that are interpreted within cerebral cortex
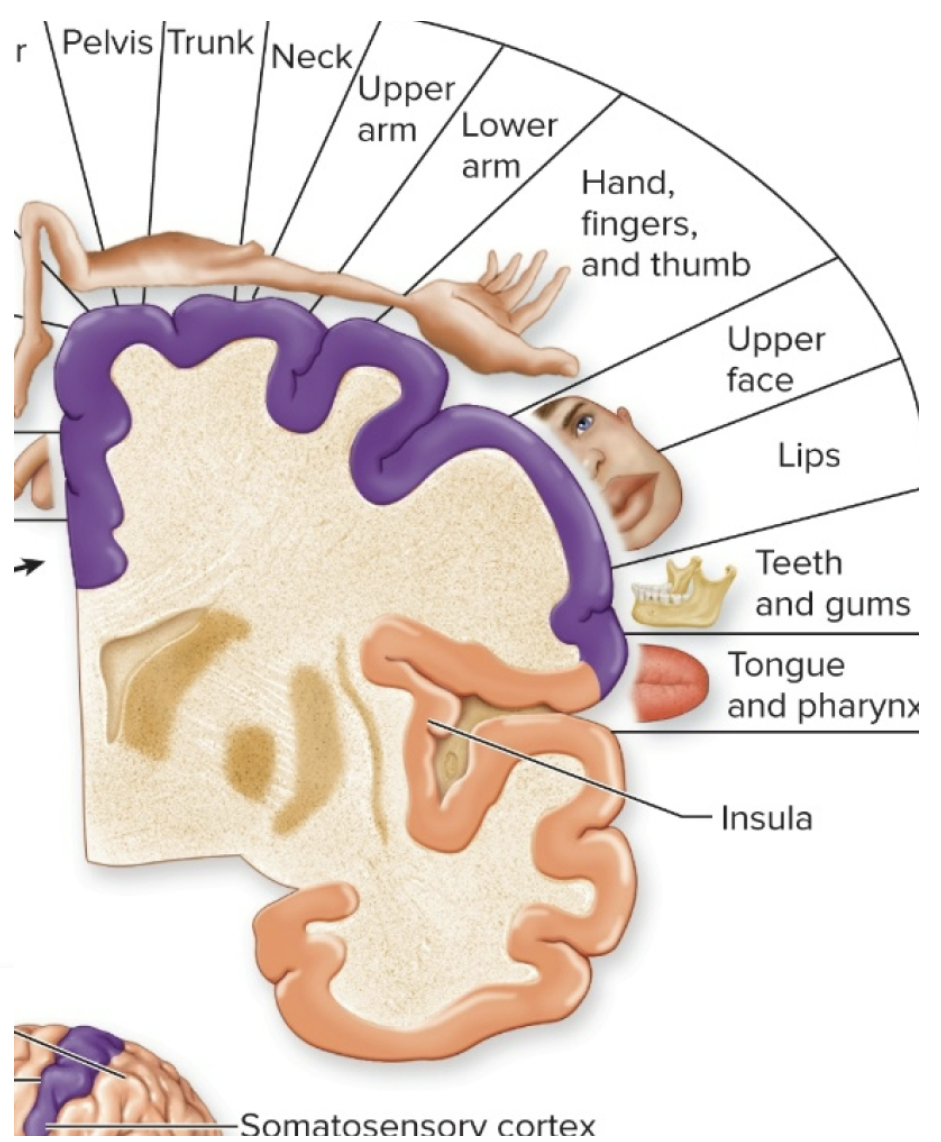
Receptive Fields and Sensory Acuity
Receptive Field: the area of skin that when stimulated, changes the firing rate of a neuron
a) size of a receptive field depends on the density of receptors in that region of skin
b) there are few receptors in the back and legs, so the RF are large
c) there are many receptors in the fingertips, so the RF are small
d) the more receptors, the smaller the field, the larger the area of the somatosensory cortex
e) a small receptive field = GREATER tactile acuity = sharpness of the sensation
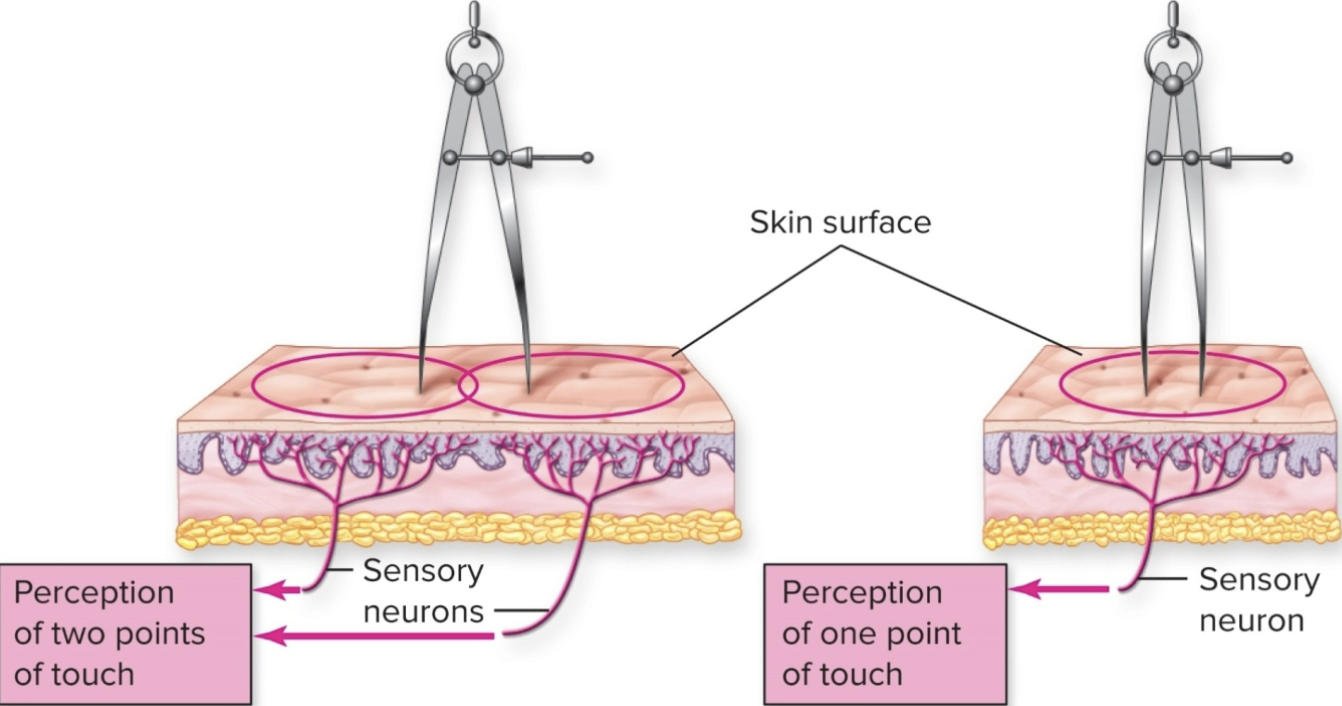
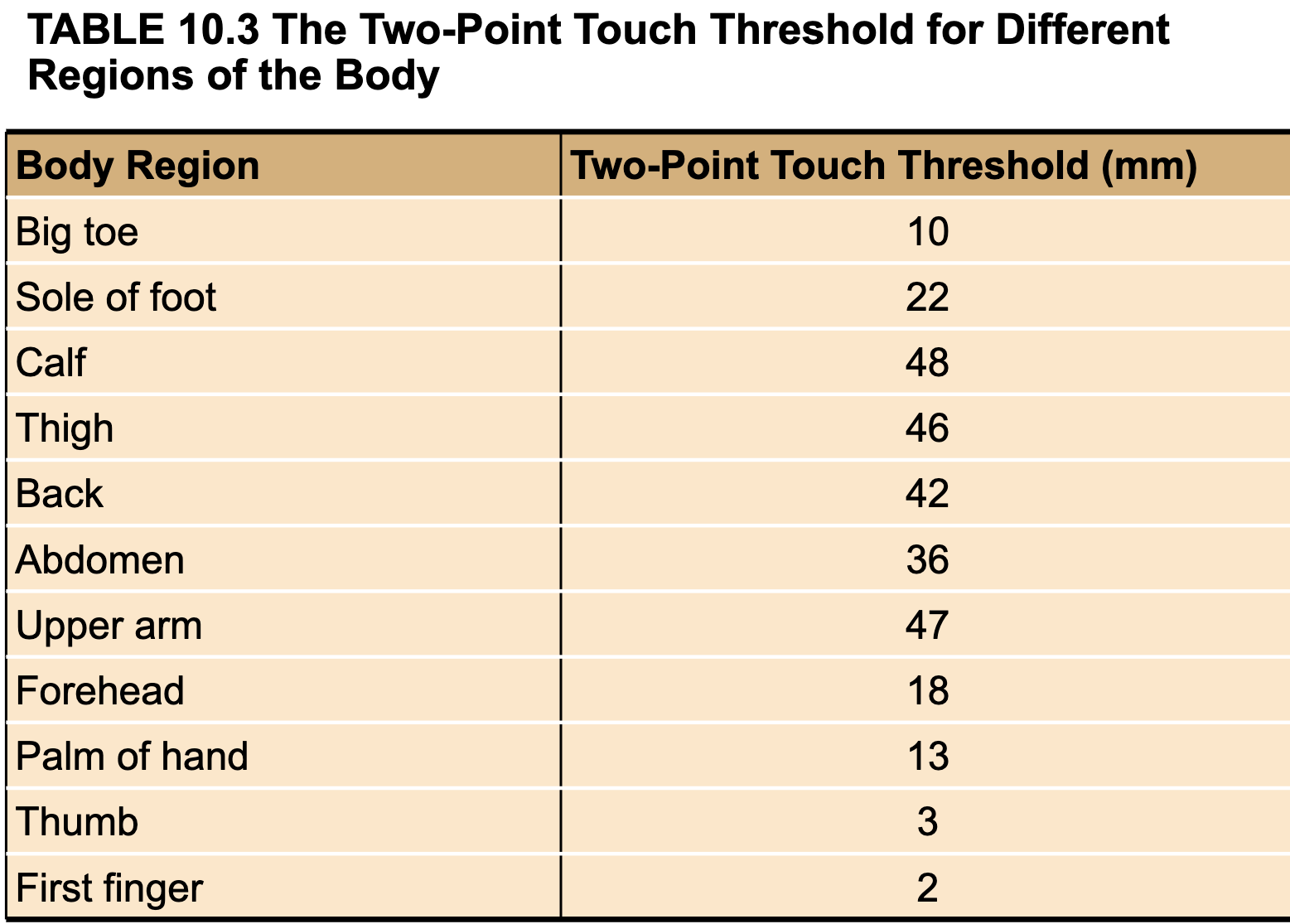
Two-point touch threshold ( RF is measured by by what, ex)
a) receptive fields can be measured by seeing at what distance a person can perceive TWO SEPERATE points of touch
b) measures tactile acuity
c) important in spacing the raised dots in braille symbols
Two-point touch threshold table
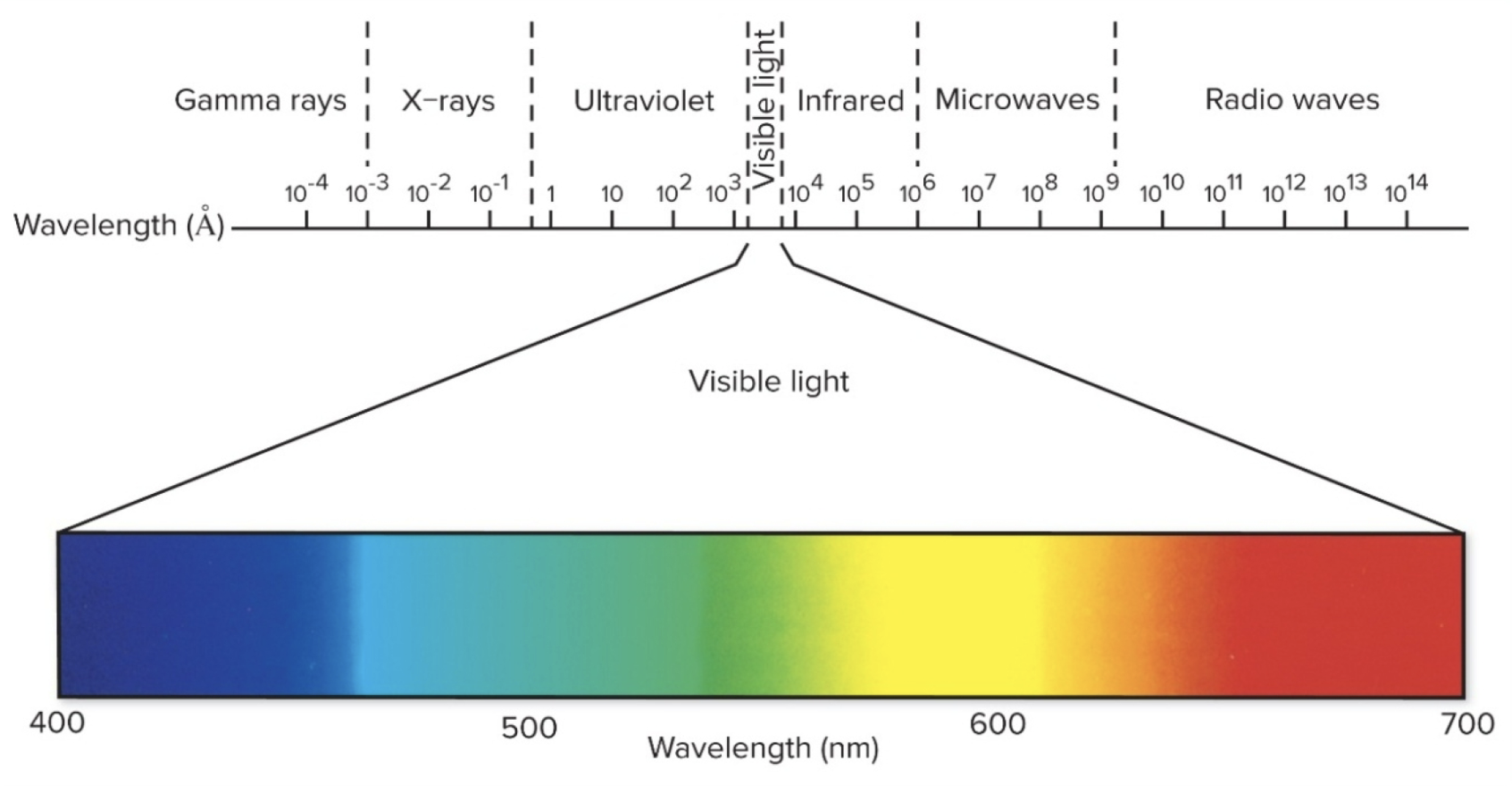
Intro to Vision (where does it come from?)
Vision comes from light energy transduced (converted) into nerve impulses
Only a limited part of the electromagnetic spectrum can excite photoreceptors in the eye
Structure of the Eye (5)
Sclera
Pupil
Lens
Retina
Fovea-Macula
sclera
tough outer layer of the eyeball (white part of eye)
cornea: the slight buldge in the sclera at the front of the eye
Cornea directs light rays into the eye and helps focus them on the retina
Pupil
the opening in the colored part of the eye (which is called the iris)
allows light to pass to the lens
black
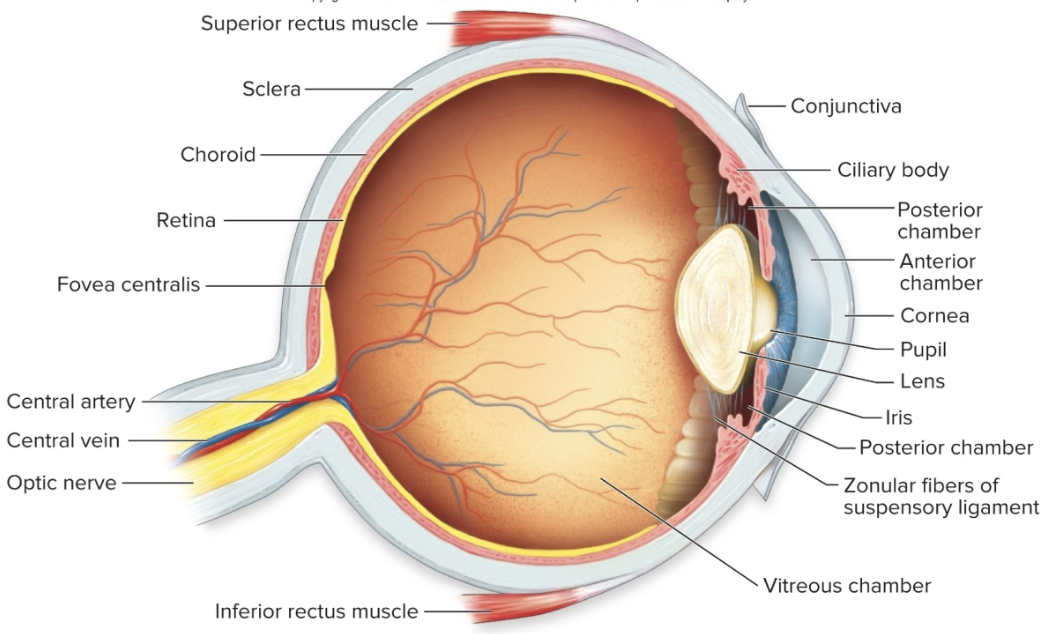
Lens
normally clear
located behind the iris
small muscles attached to the lens can change its shape- which allows the eye to focus on near or far objects
Retina
thin nerve tissue
that lines the back of the eye
detects light entering the eye and converts it into electrical impulses
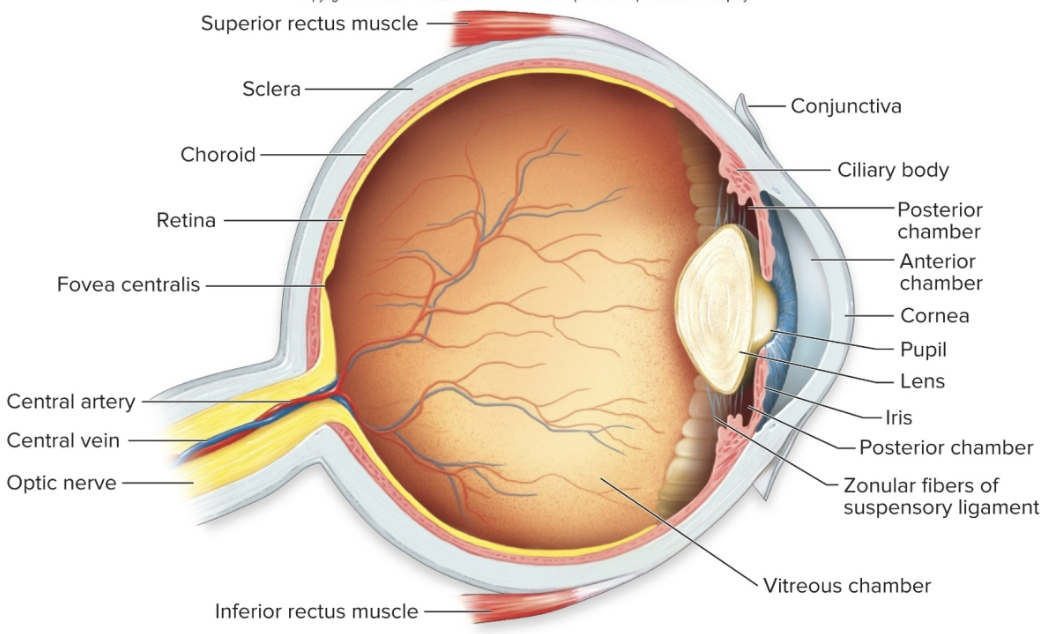
Fovea-Macula
is the part of the retina that provides the sharp, detailed central vision that allows you to focus on what is directly in the line of sight
the rest of the retina provides side (peripheral) vision, which allows you to see shape but not fine details
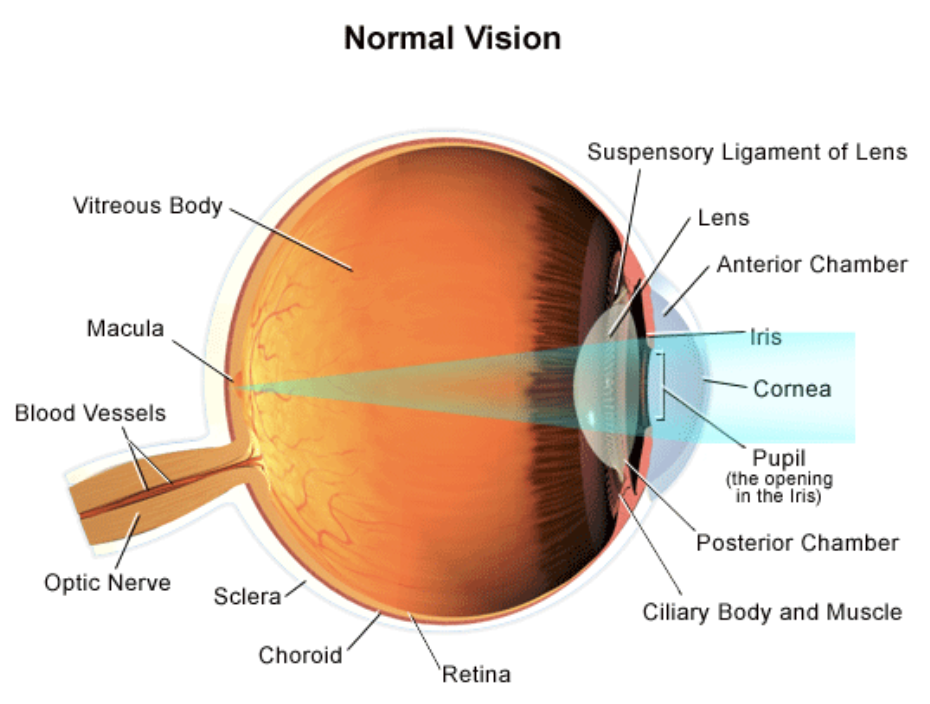
General Pathway of Light through the Eye
Light passes through the cornea and into the anterior chamber of the eye
Next, it passes through the pupil, which can change shape (due to the pigmented iris muscle) to allow more or less light in
Then it passes through the lens, which can change shape to focus the image
Then it passes through the posterior chamber and vitreous body
Finally, it hits the retina, where photorecptors are found
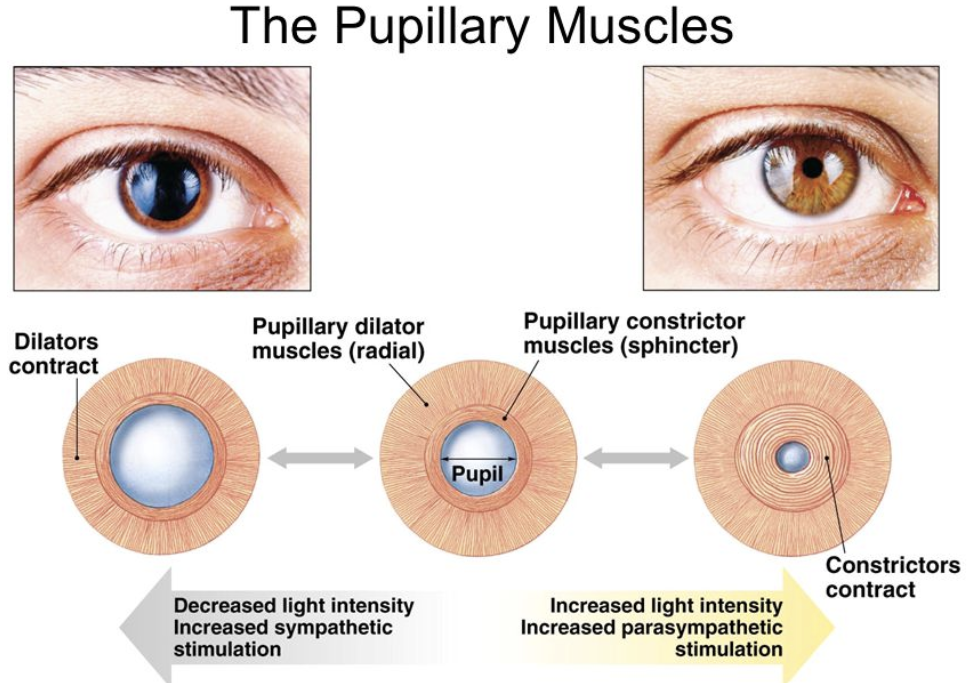
Structures of the Eye: Pupil & Iris
The iris sphincter muscle (pupillary sphincter, pupillary dilator)- can increase or decrease the diameter of the pupil
Constriction: contraction of pupillary sphincter via parasympathetic stimulation
Dilation: contraction of pupillary dilator via sympathetic stimulation
The iris also has a pigmented epithelium for eye color
Intro to the Retina (thickeness, what does it consist of)
The retina is approx 0.55 mm thick and lines the back of the eye. Retina consist of:
single cell pigmented epithelium
rods & cones: photoreceptor neurons
layer of other neurons
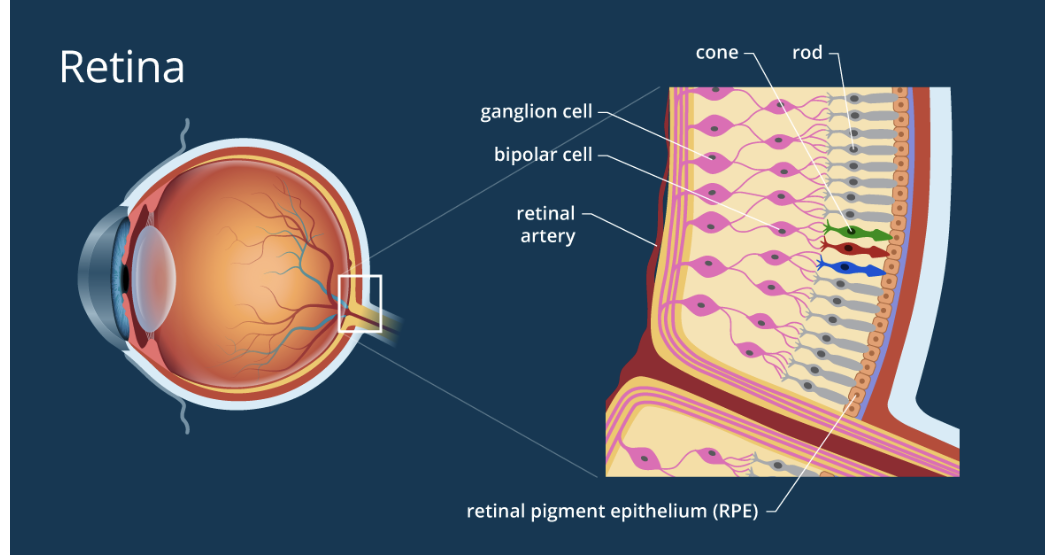
Intro to Retina (photosensors, ganglion cells)
2) the photosensors(rods & cones) lie outermost in the retina against the pigmented epithelium
3) The ganglion cells (the output neurons of the retina) lie innermost in the retina “closest” to the lens and the front of the eye
4) the optic nerve contains the ganglion cell axons running to the brain
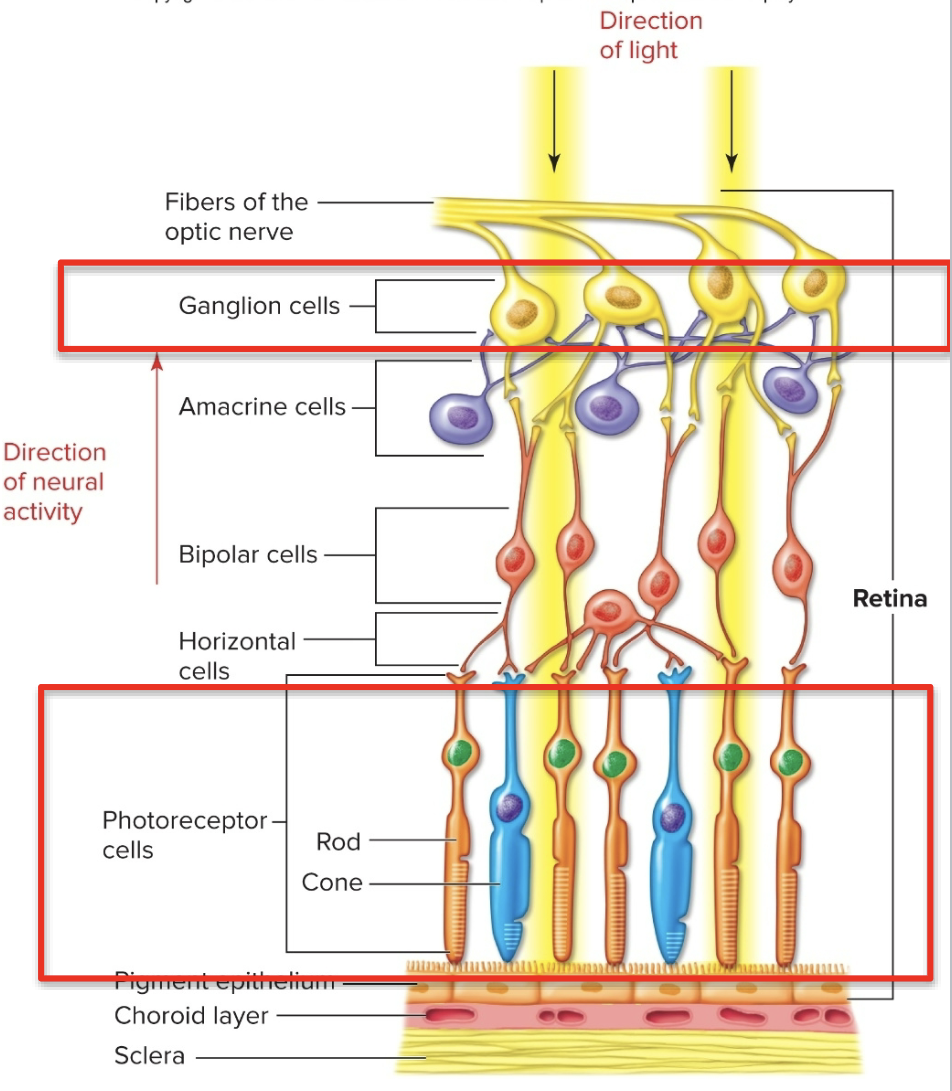
Layers of Retina: Rods & Cones
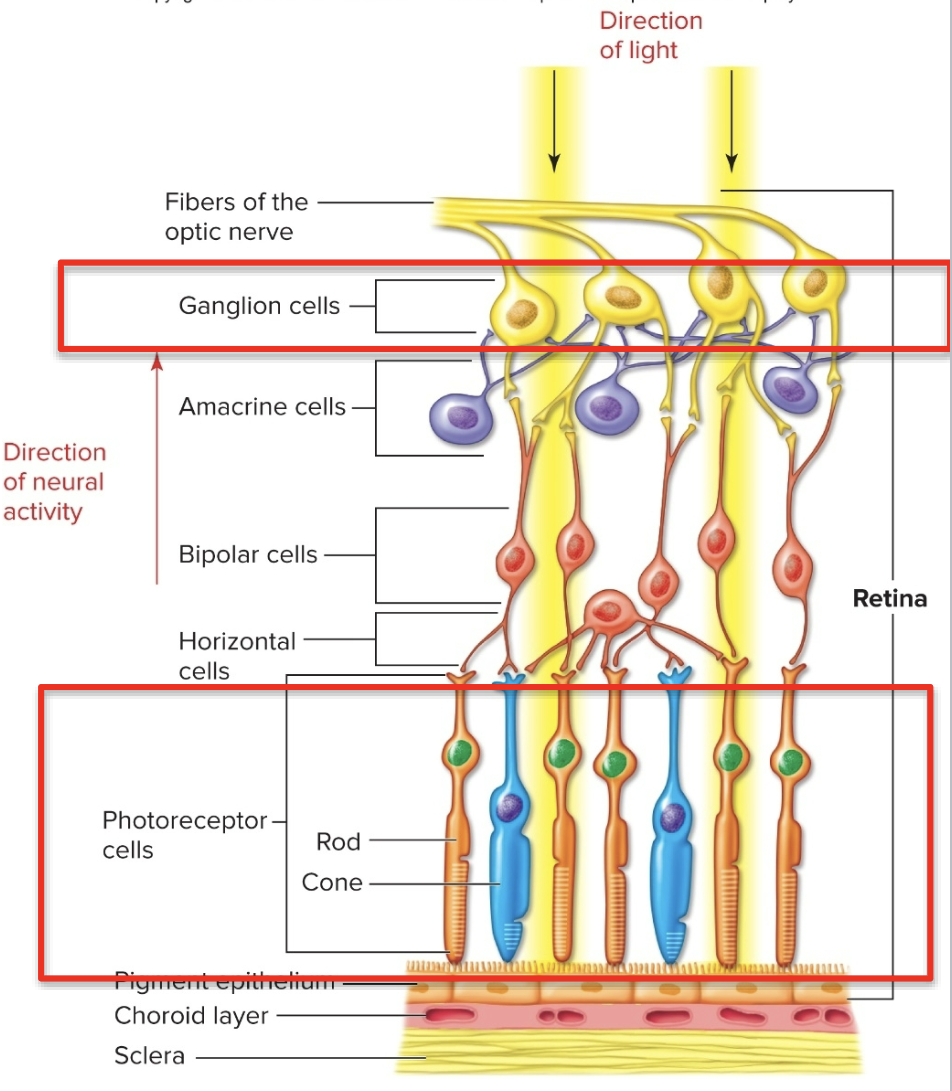
Rods & Cones
Photoreceptors (rods & cones) are in the inner layer- toward the vitreous body, back of the eye
they synapse on a middle layer of bipolar cells, which synapse on the outer layer of ganglion cells
there are also horizontal cells and amacrine cells within the layers
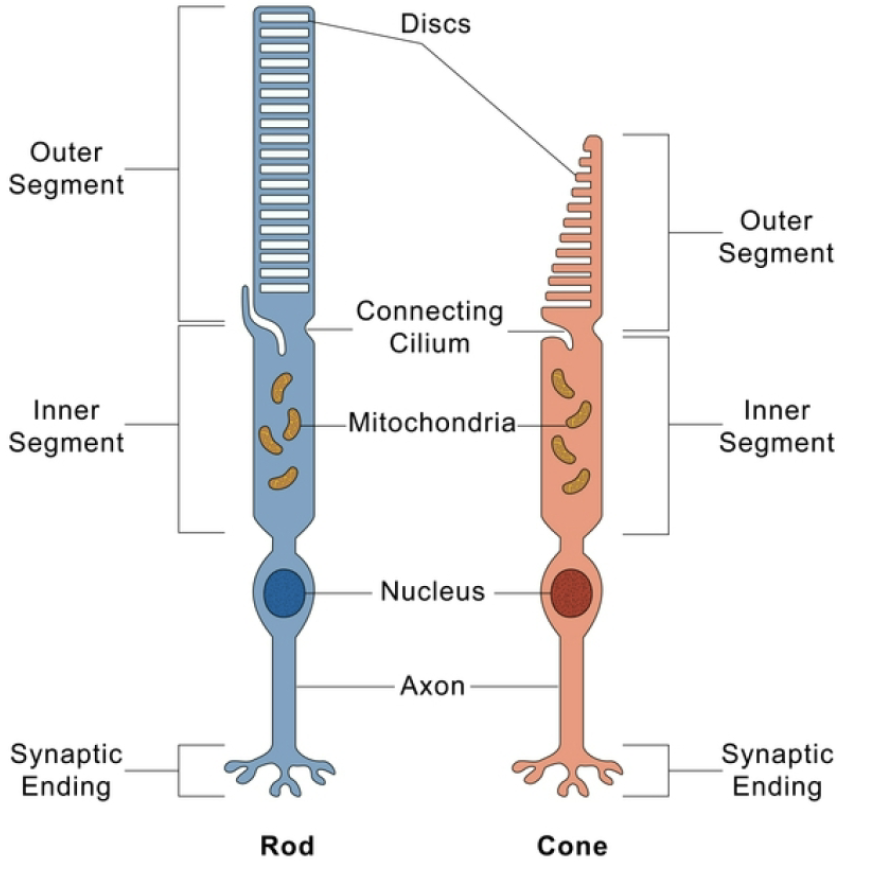
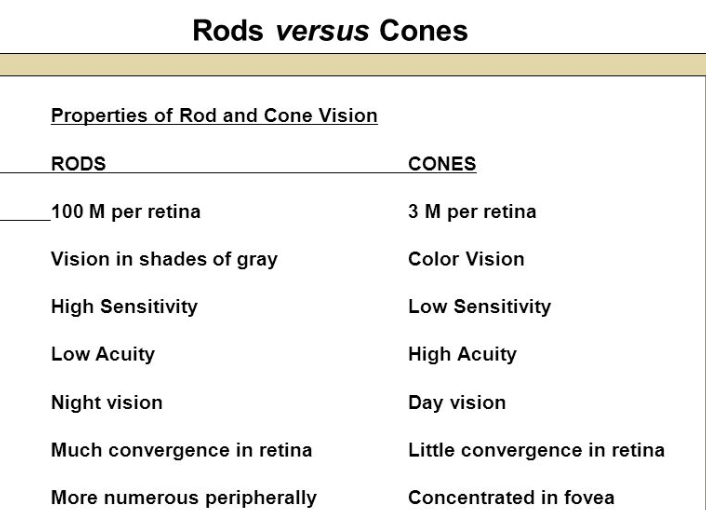
Rods
100 M per retina
Vision in shades of gray
High sensitivity
Low Acuity
Night vision
Much convergence in retina
more numerous peripherally
Cones
3 M per retina
Color Vision
Low sensitivity
high acuity
day vision
little convergence in retina
concentrated in fovea
Electrical Activity of the Rods - “On pathway”
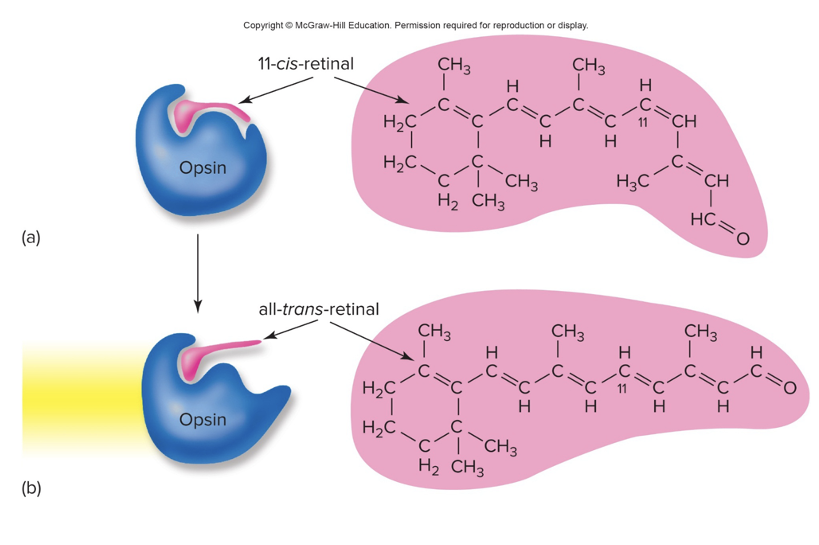
contain the pigment rhodopsin- rhodopsin is EXTREMLY sensitive to light- when rhodopsin is exposed to light, it immediately photobleaches
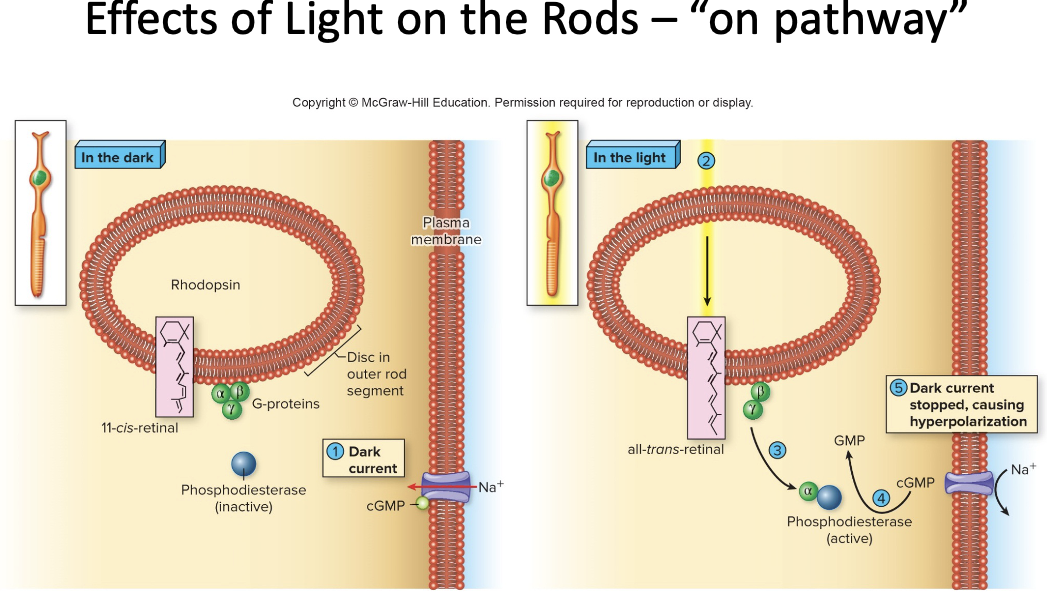
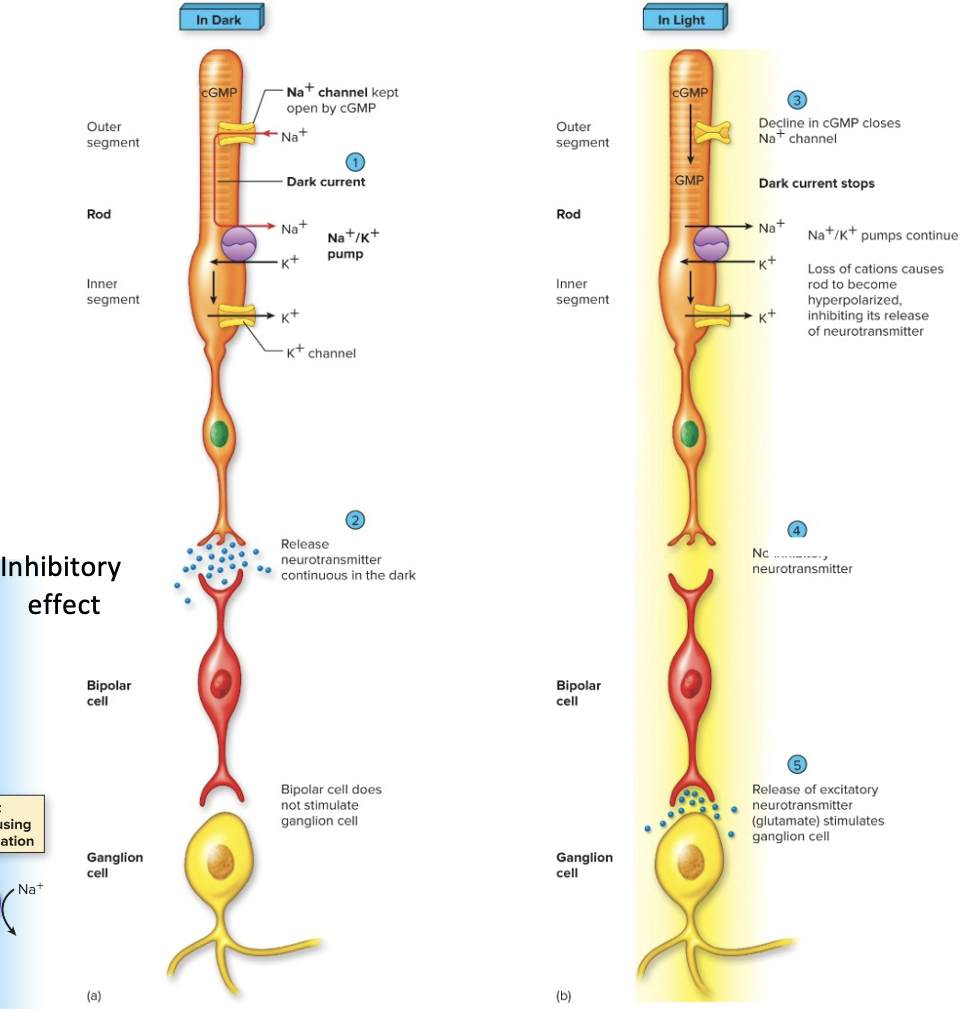
Effects of Light on the Retina- “On pathway”
When Light Hits Photoreceptors
a) dissociation of rhodopsin activates a G protein/2nd messenger system, which CLOSES Na+ channels
G-proteins are called transducins
activation of the enzyme phosphodiesterase converts cGMP to GMP
this closes Na+ channels
b) photoreceptors are hyperpolarized, and inhibition on bipolar cells is lifted
c) bipolar cells activate ganglion cells that transmit action potentials to the brain
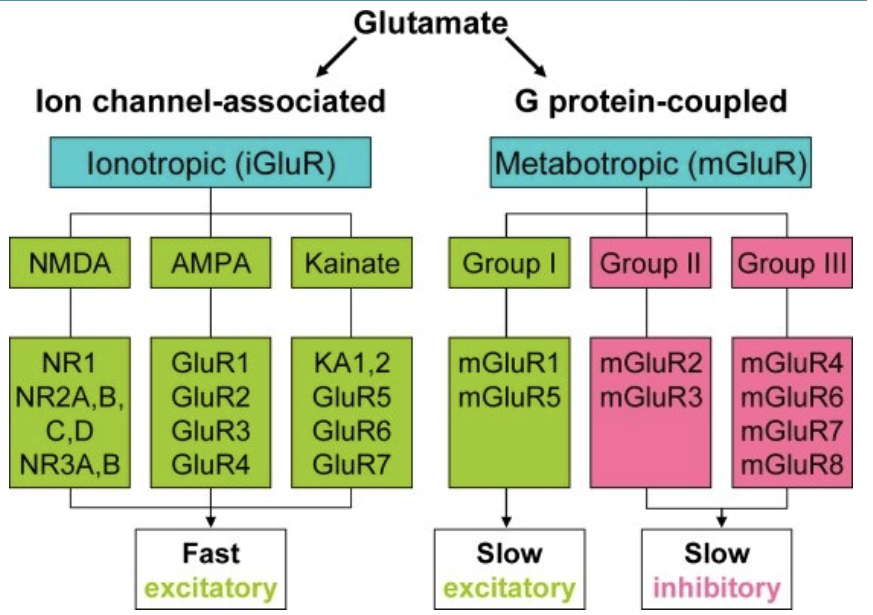
Glutamate Receptors (3 major classes)
AMPA receptors (iGluR- ligand)
NMDA receptors (iGluR- ligand and voltage)
Metabotrophic glutamate receptors
metabotrophic receptors act through a second messenger system to create slow, sustained effects on their targets
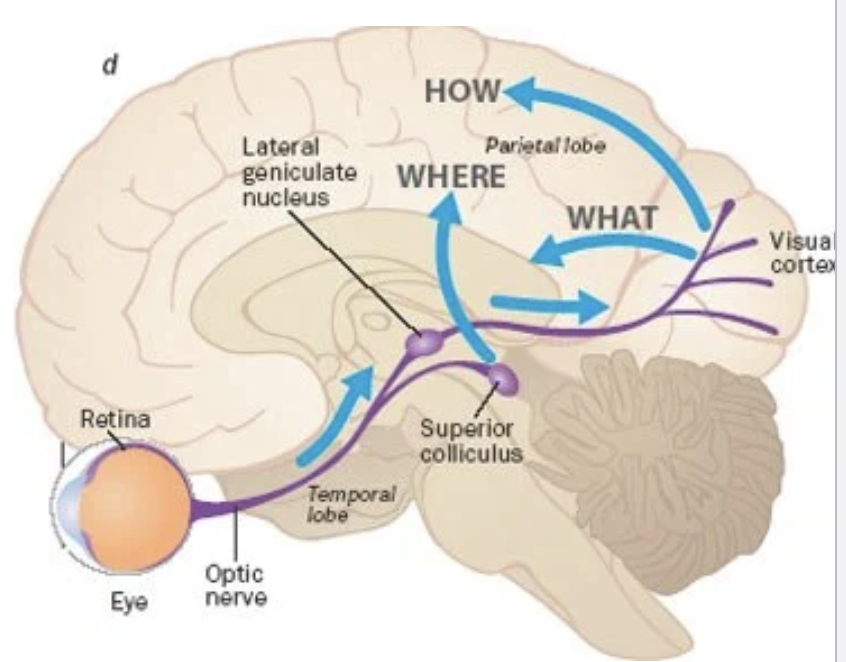
Neural Pathway for Vision (2 systems)
Geniculostriate System
Tectal System
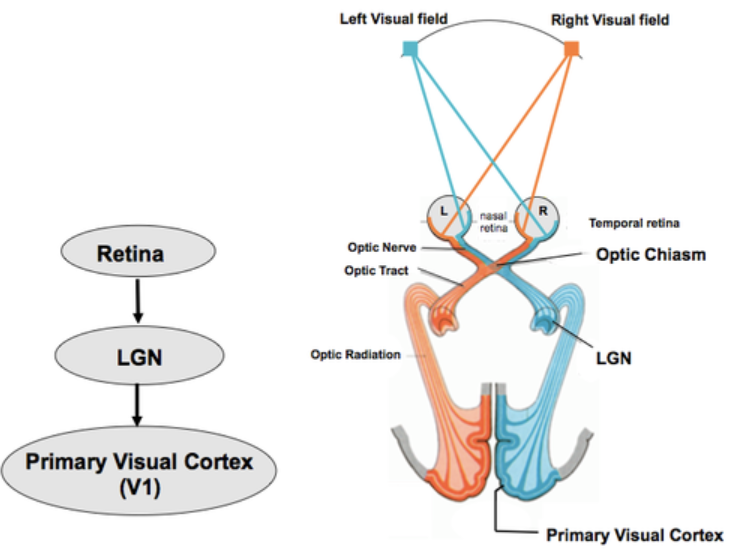
Geniculostraite System (what synapses on what, what kind of info does it carry?)
axons from ganglion cells synapse on the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus by way of the optic chiasma
information from the lateral portion of the retinas does not cross sides, but info from the medial portion does
neurons from the thalamus synapse on the visual cortex of the occipital lobe
carries info of “what” is seen
Tectal System (what synapses on what, what kind of info does it carrry?)
20 to 30% of the ganglion cell axons synapse on the superior colliculus of the midbrain, which helps with eye and body movements
carries info about “where” the object is