Med Imaging- Lungs Pt. 2
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
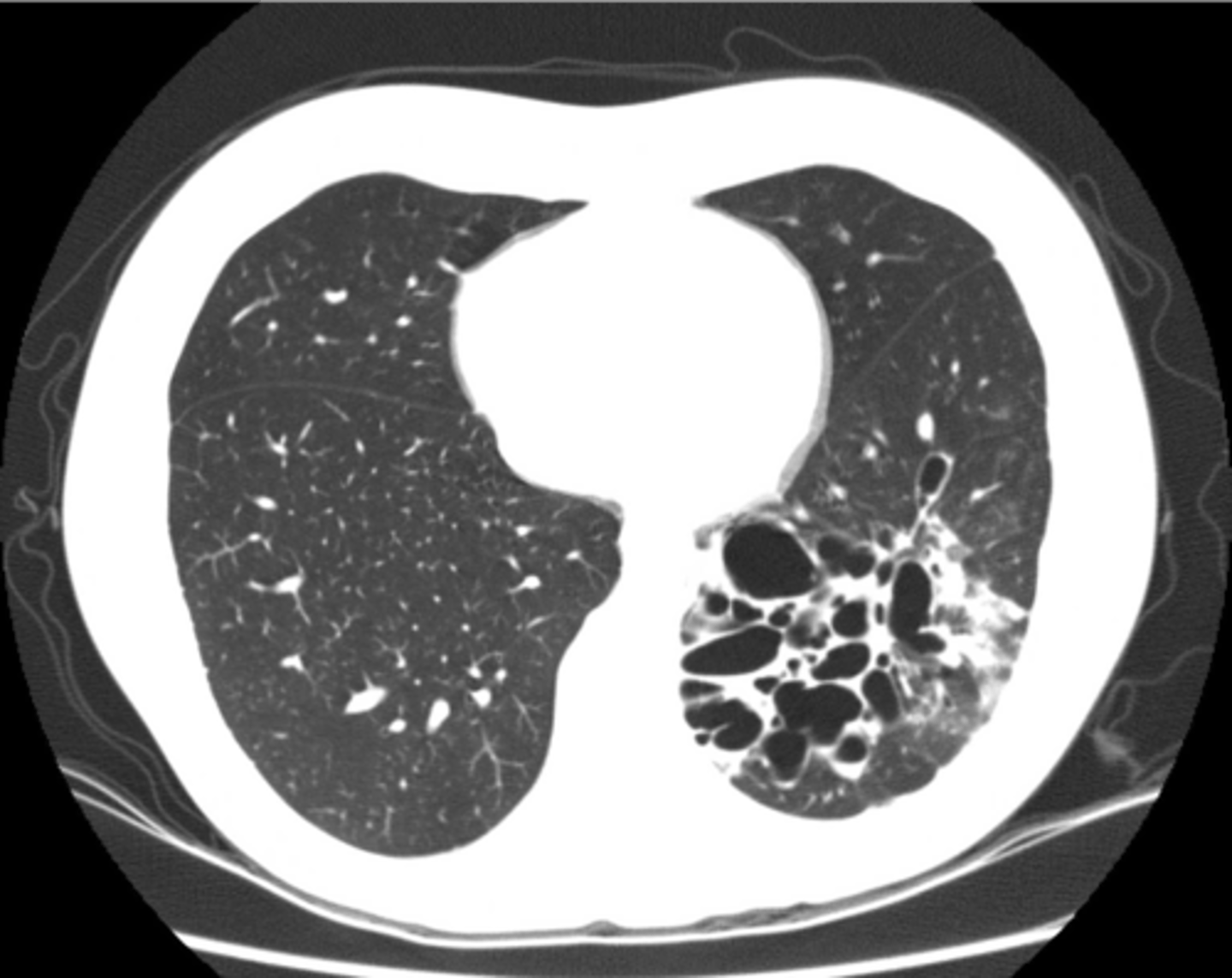
Walls of the bronchi thickened by inflammation or infection, may be diffuse or focal
Bronchiectasis
CXR in affected individuals is often normal or shows non-specific findings
Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis
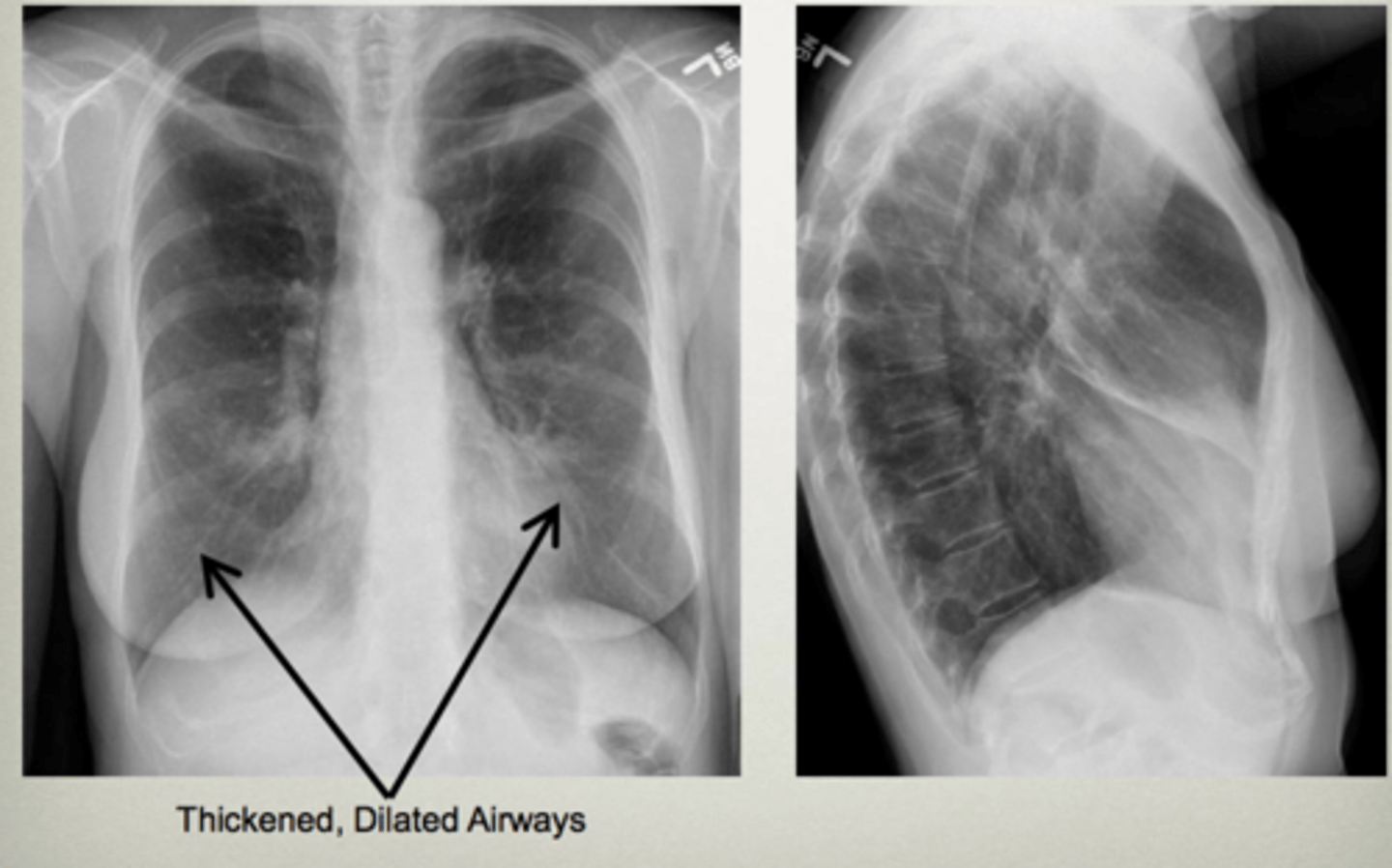
Tram track lines
Bronchiectasis
Condition that can cause bronchiectasis
Cystic fibrosis
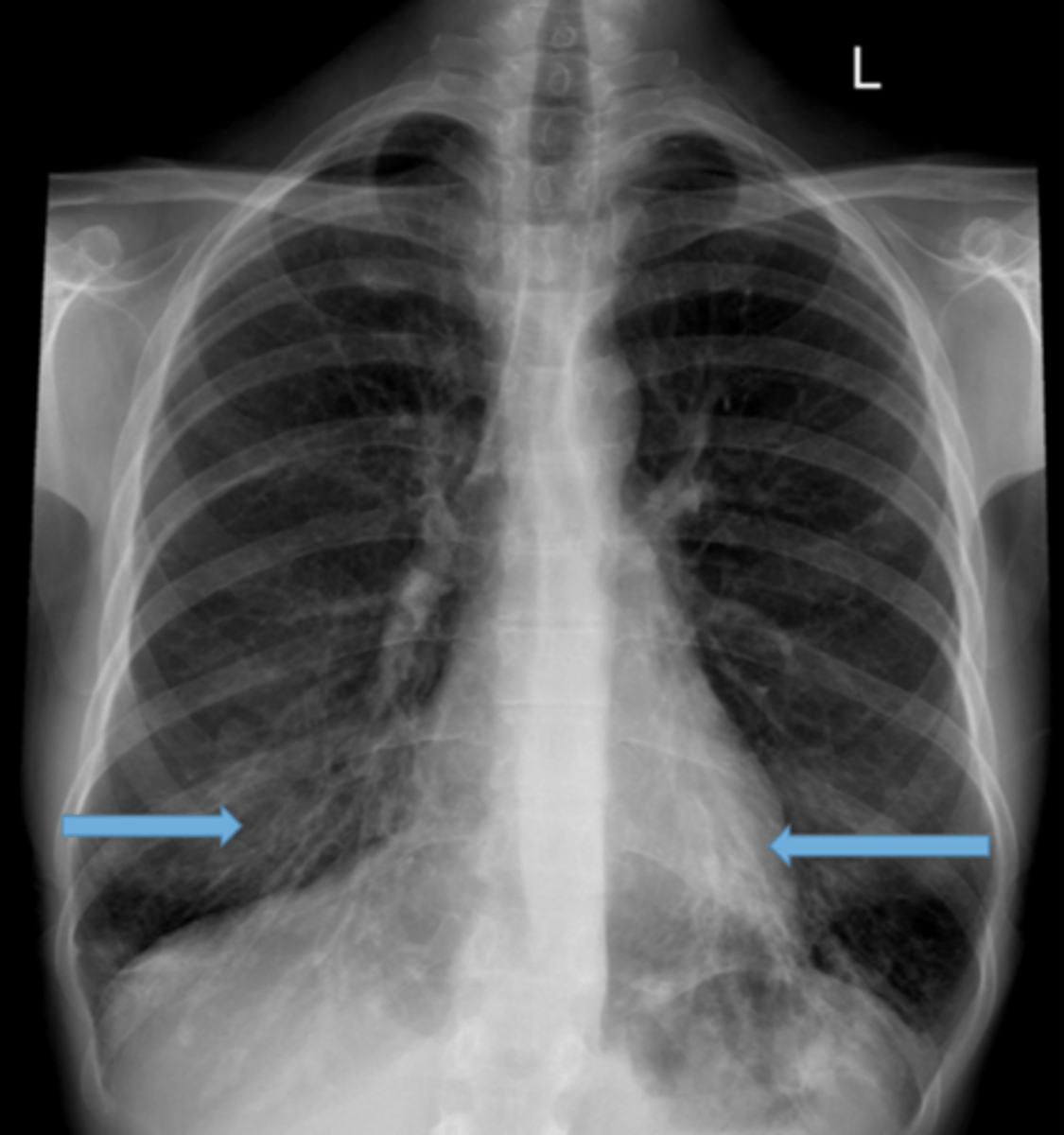
Lung tissues with air space but no alveoli thats less than 1 cm in diameter
Bleb
Lung tissues with air space but no alveoli thats greater than 1 cm in diameter
Bullae
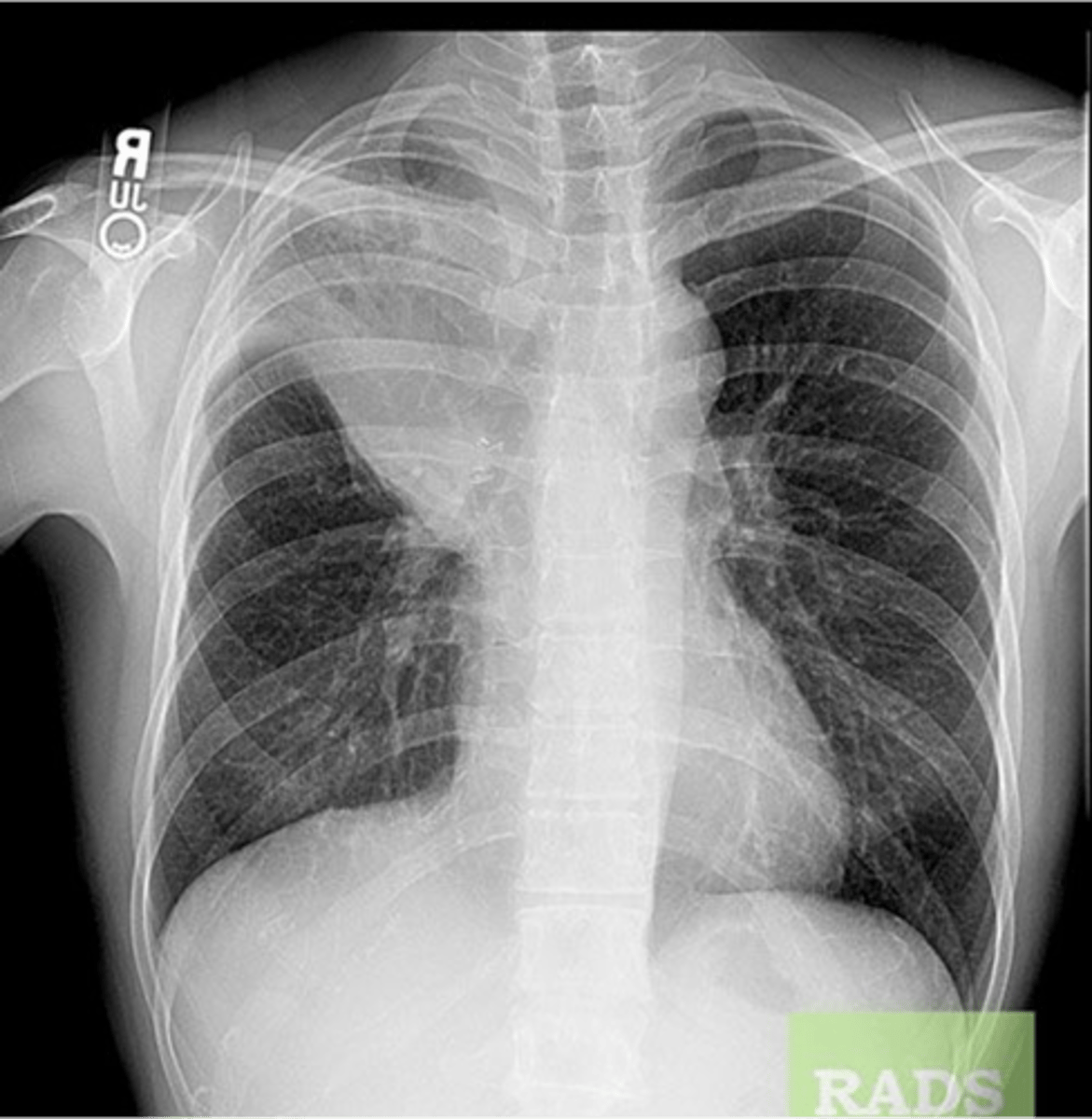
RUL bullae
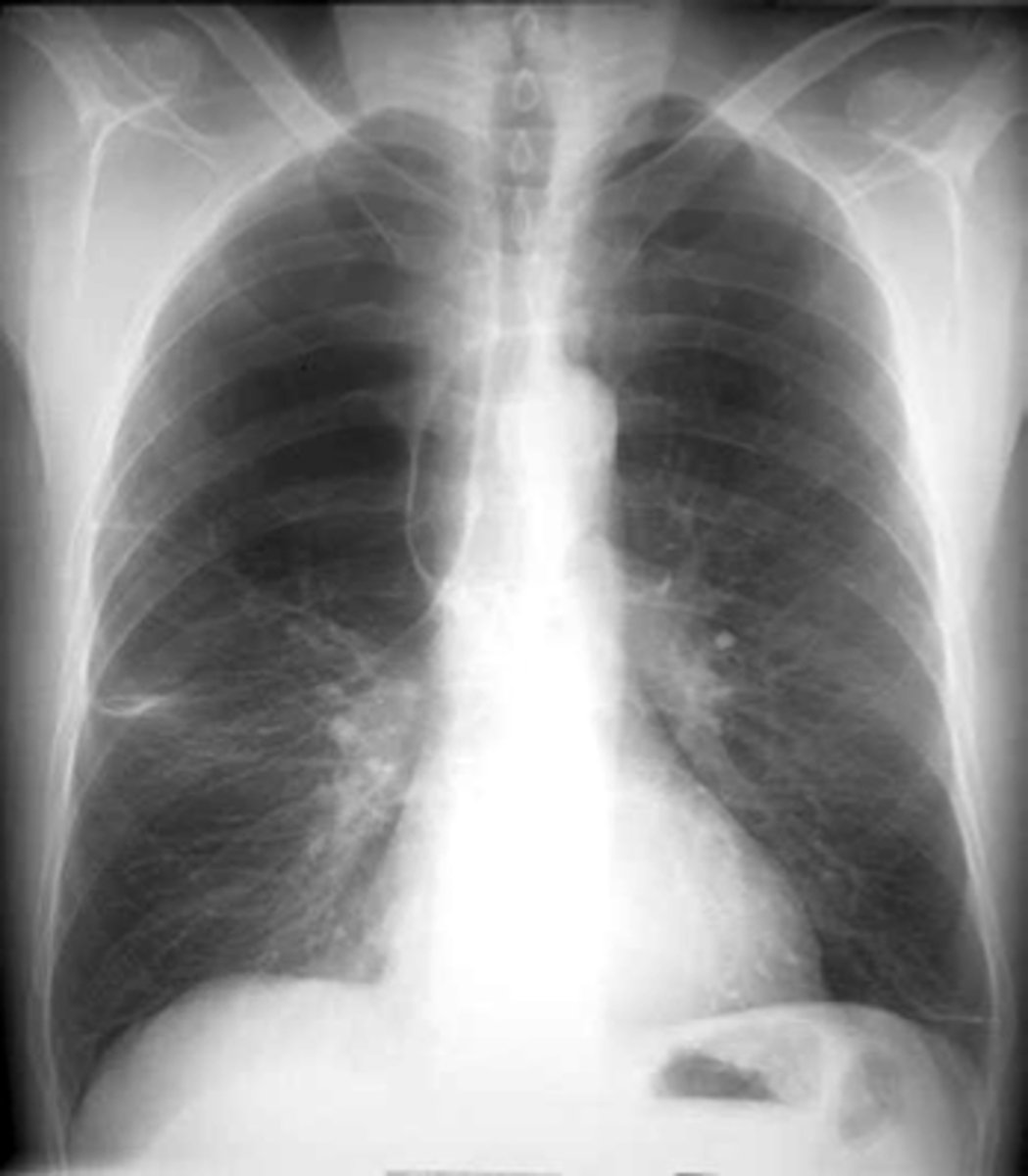
Flattening of hemidiaphragms
& blunting of costophrenic angles, Increased AP diameter (barrel chest), bullae or large air cavities indicates
hyperinflation
COPD/Emphysema
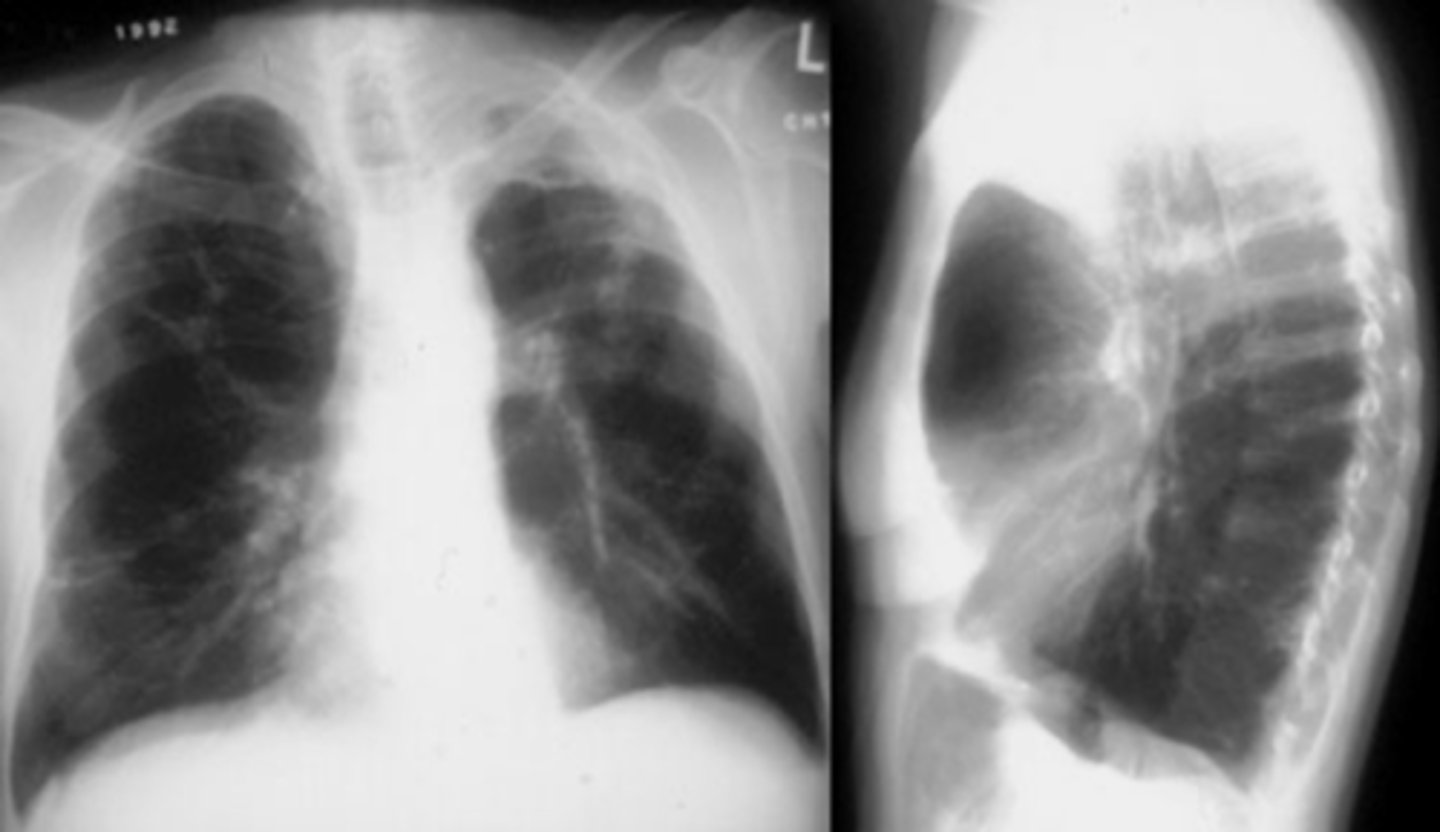
COPD/Emphysema
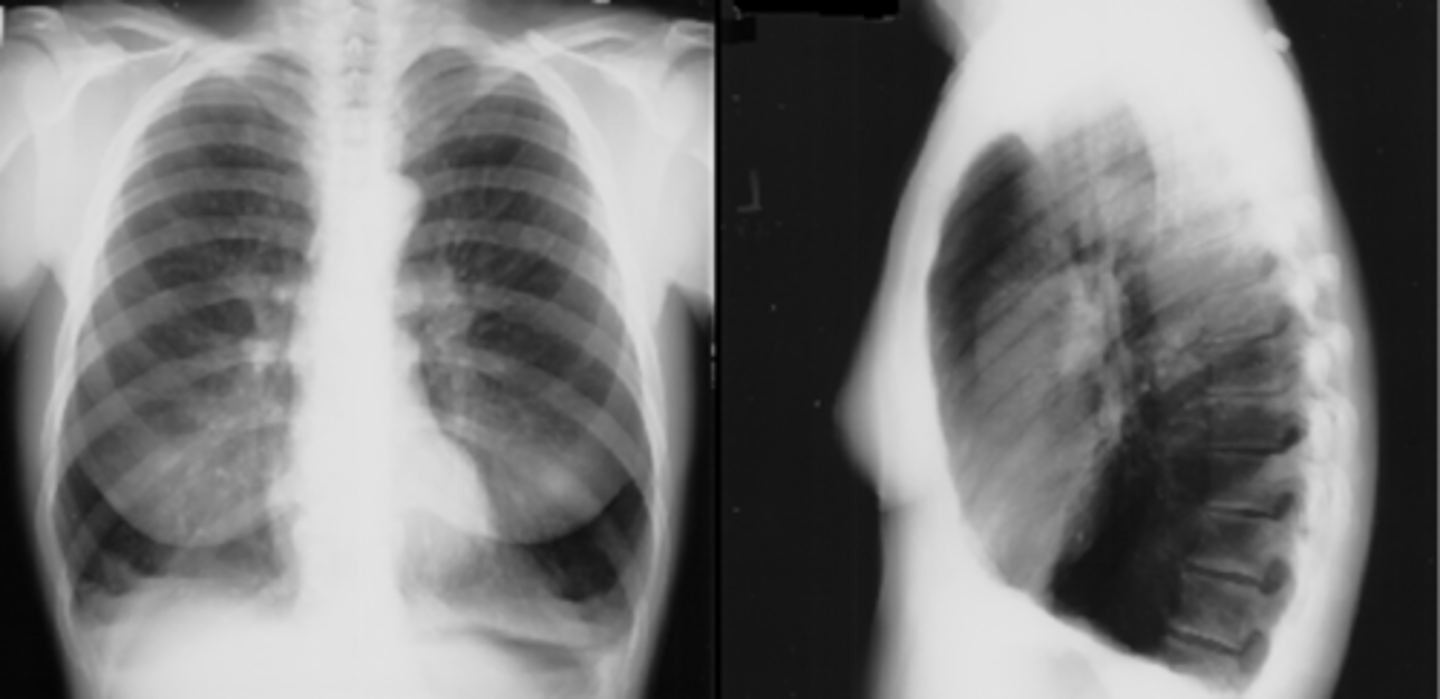
Occurs when alveoli become deflated (complete or partial collapse) or possibly filled with alveolar fluid
Atelectasis
Atelectasis
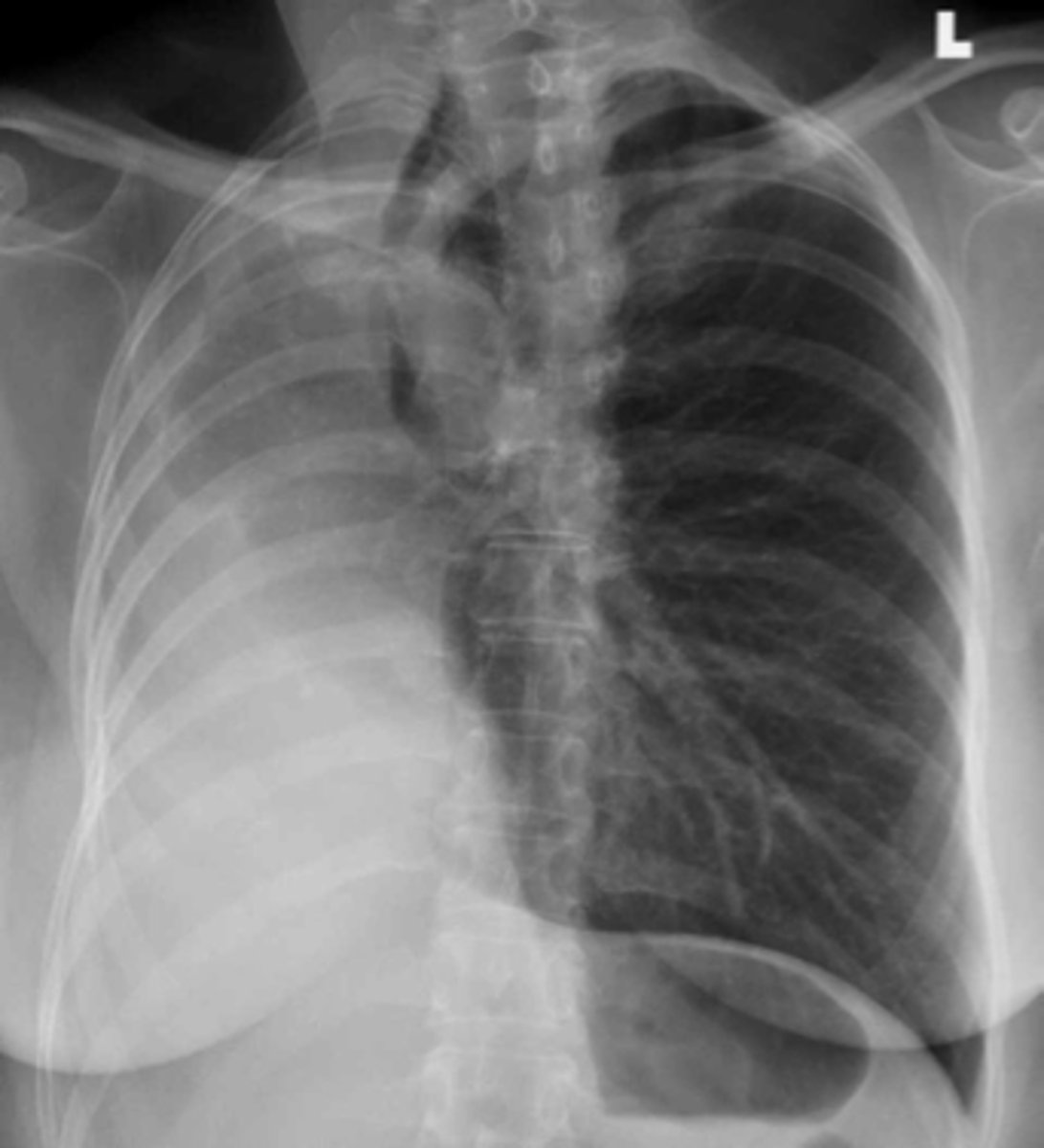
Atelectasis (RUL)
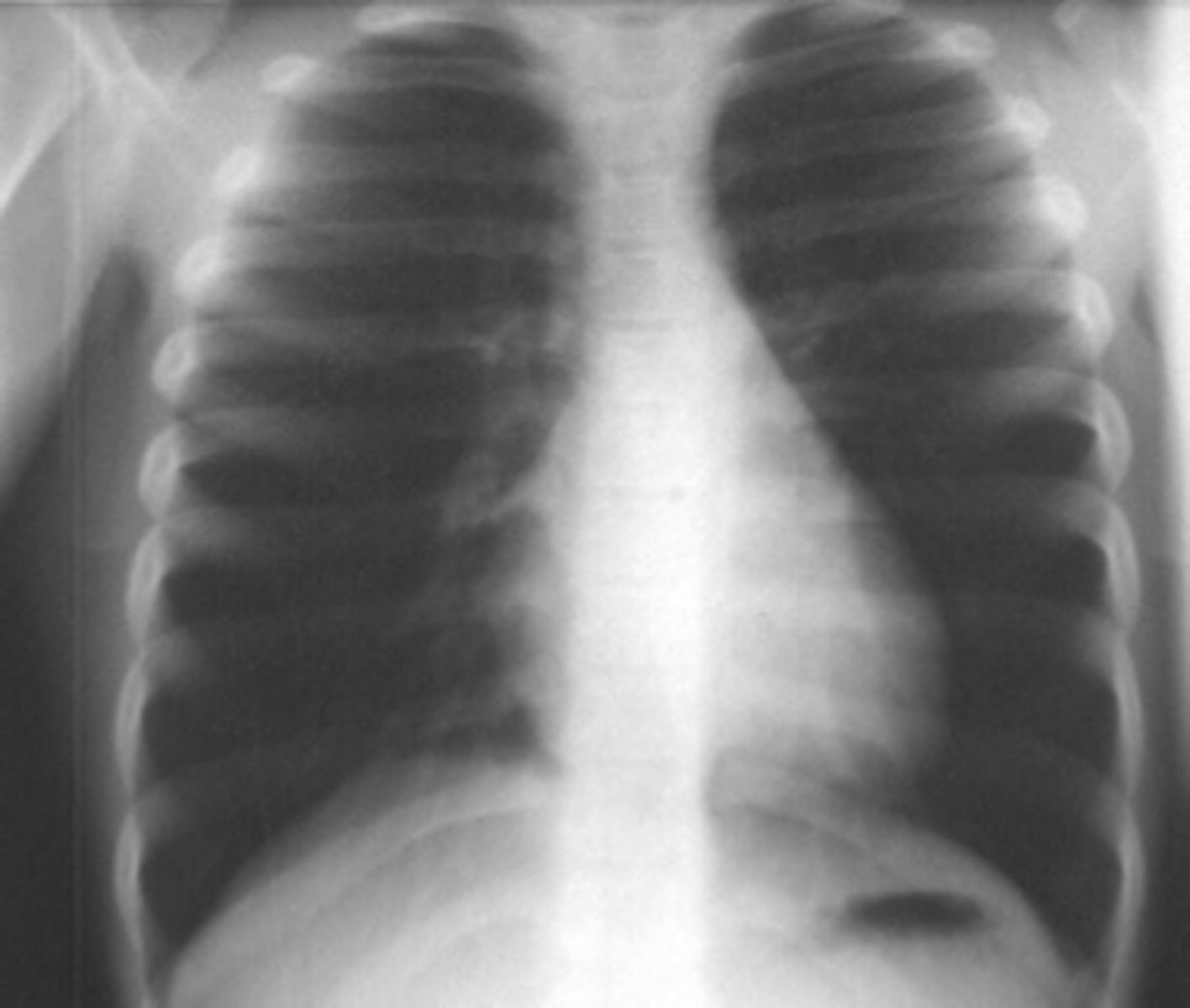
Linear atelectasis (often seen post-op)
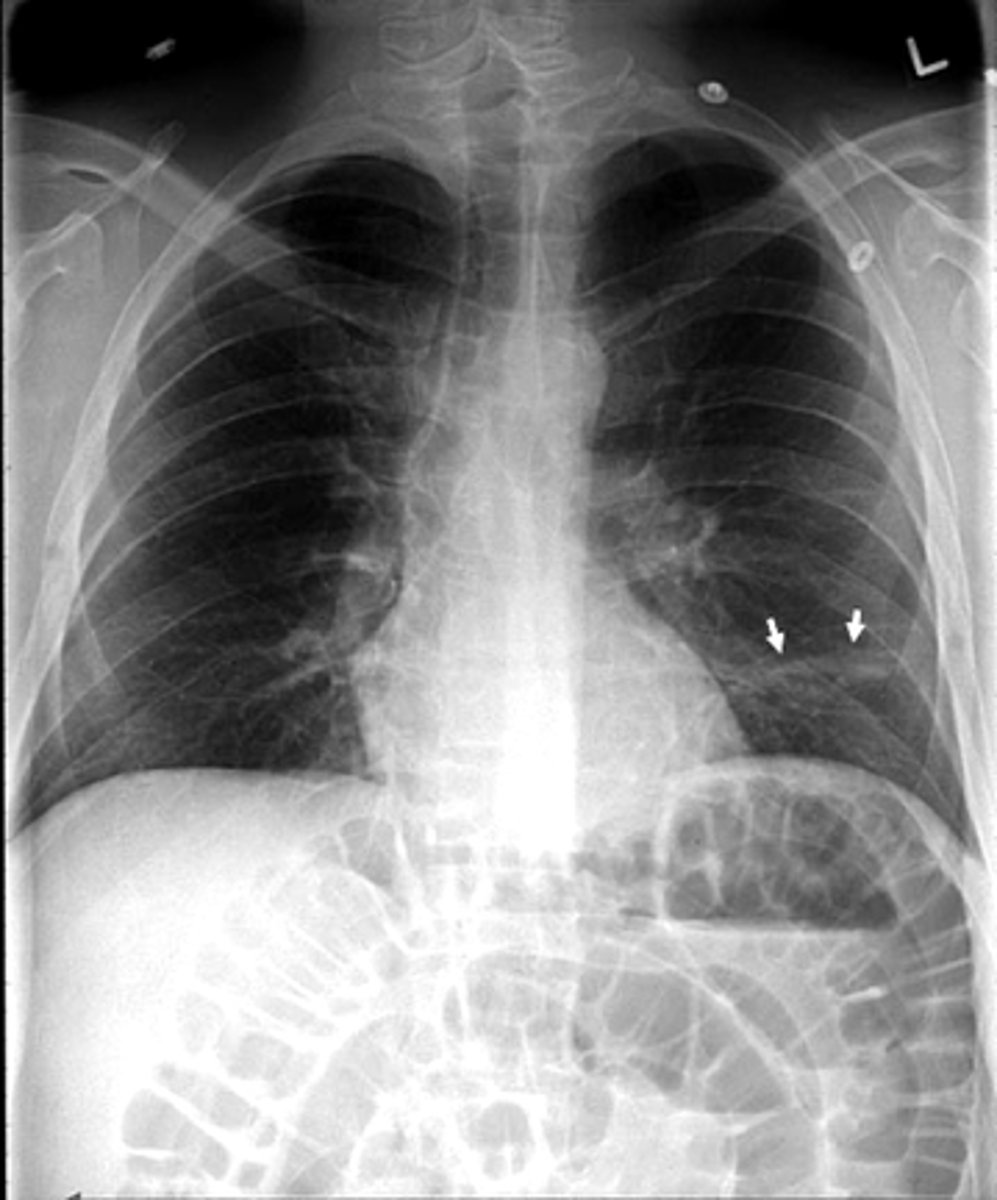
Asthma (hyperinflation with tram lines)
asthma
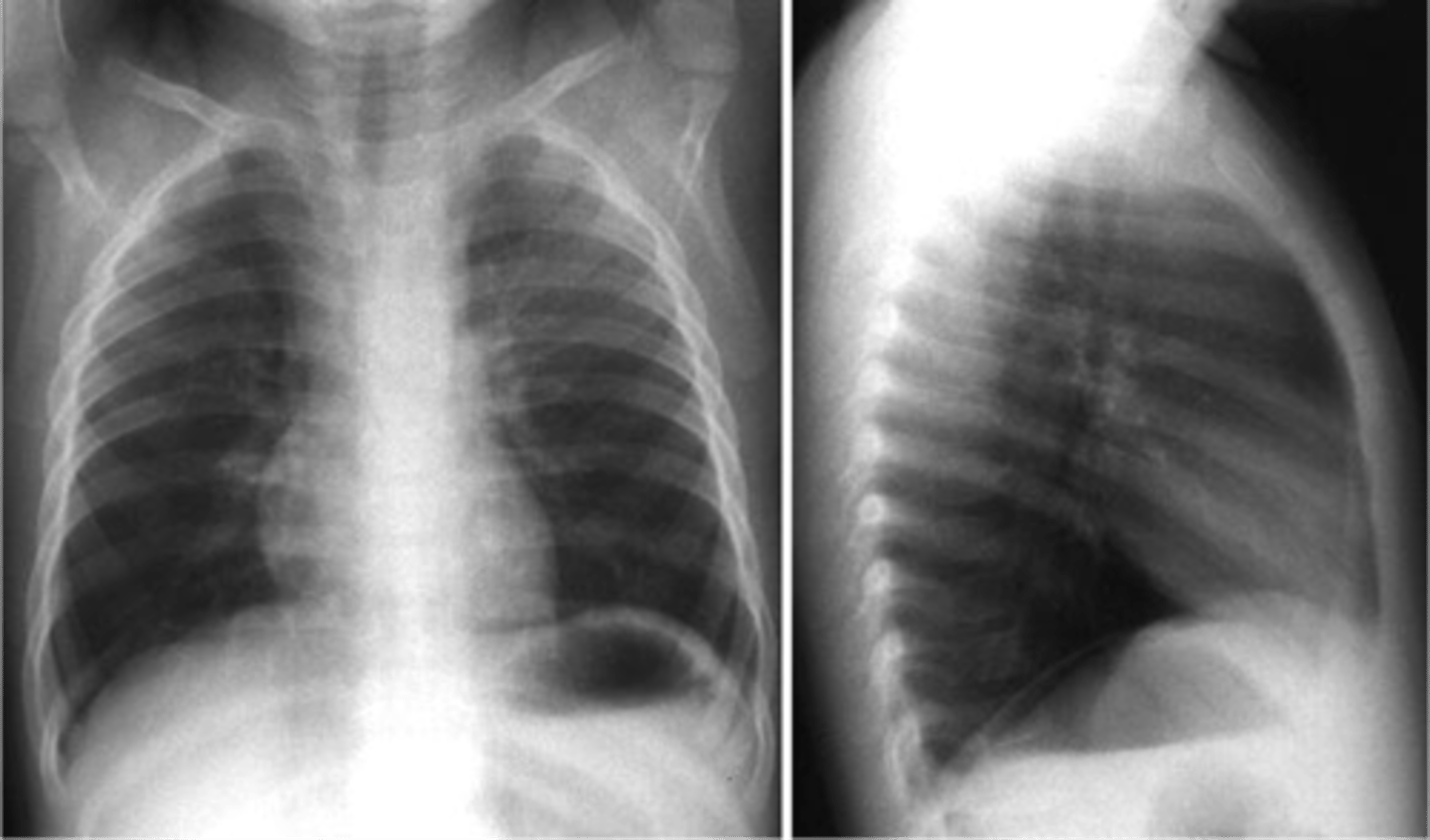
Air in the pleural space that causes collapse of the lung usually seen in the apices if pt is upright
Pneumothorax
Pneumothorax (apices)
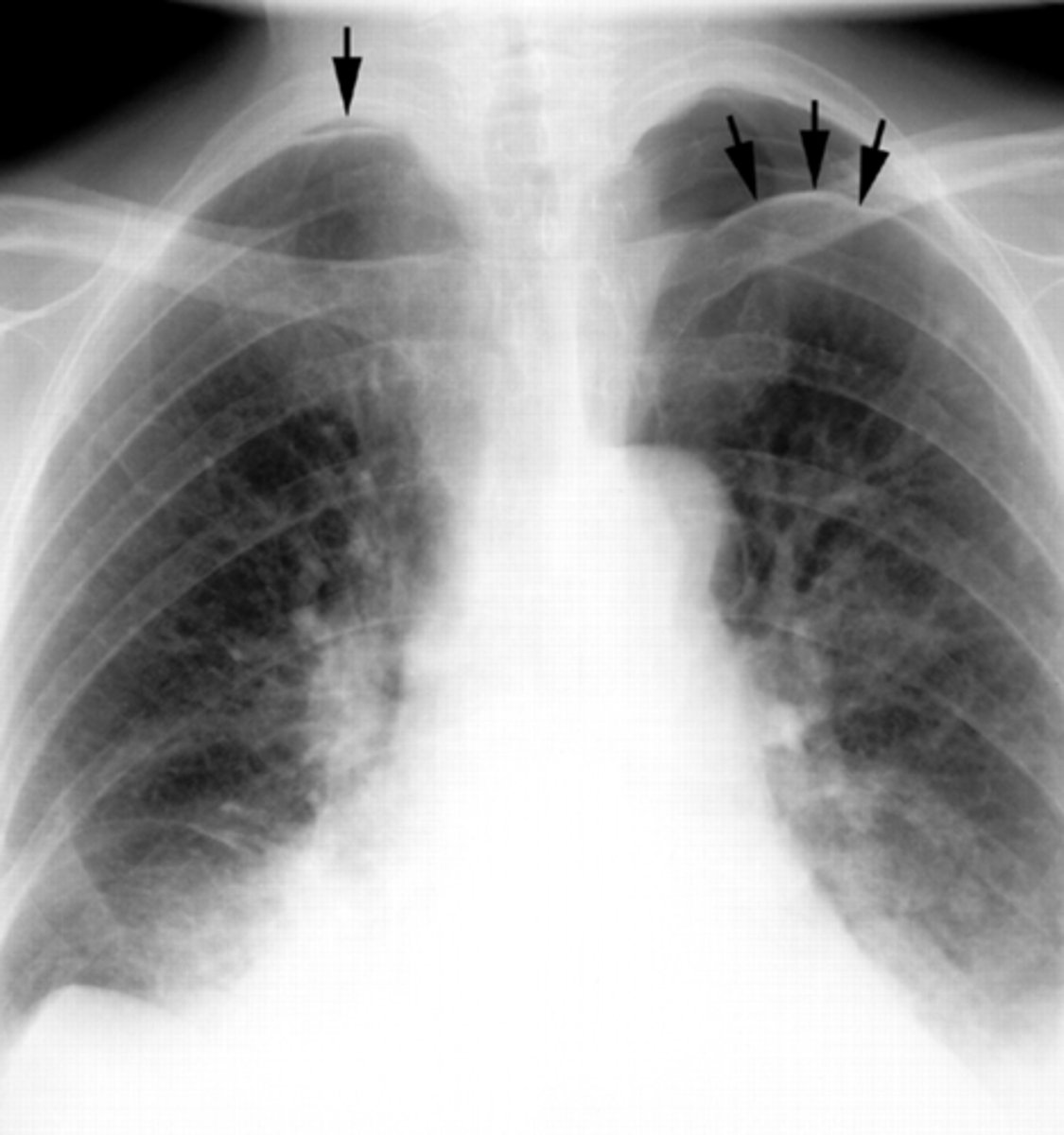
Pneumothorax (moderate, non tension)
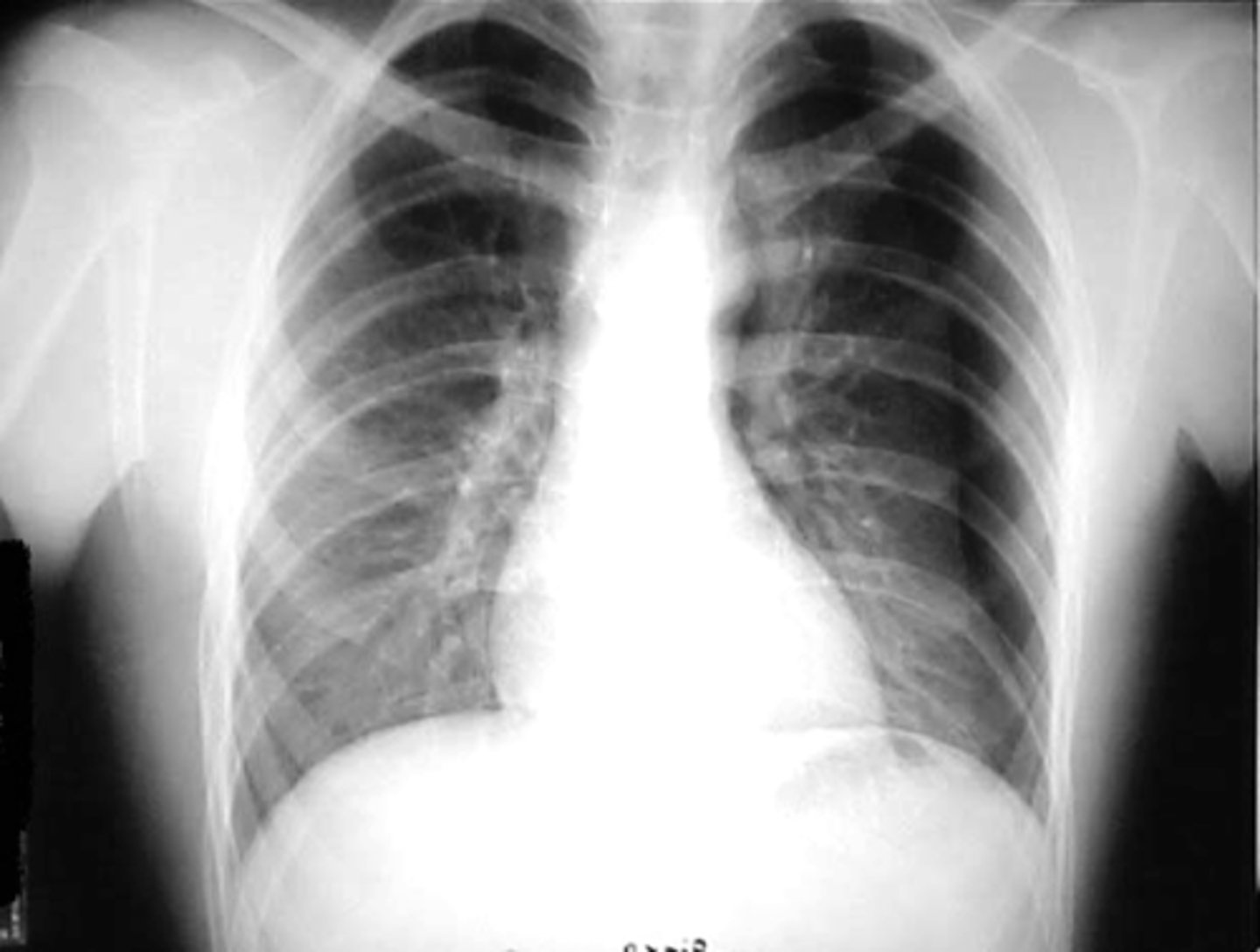
Tension pneumothorax
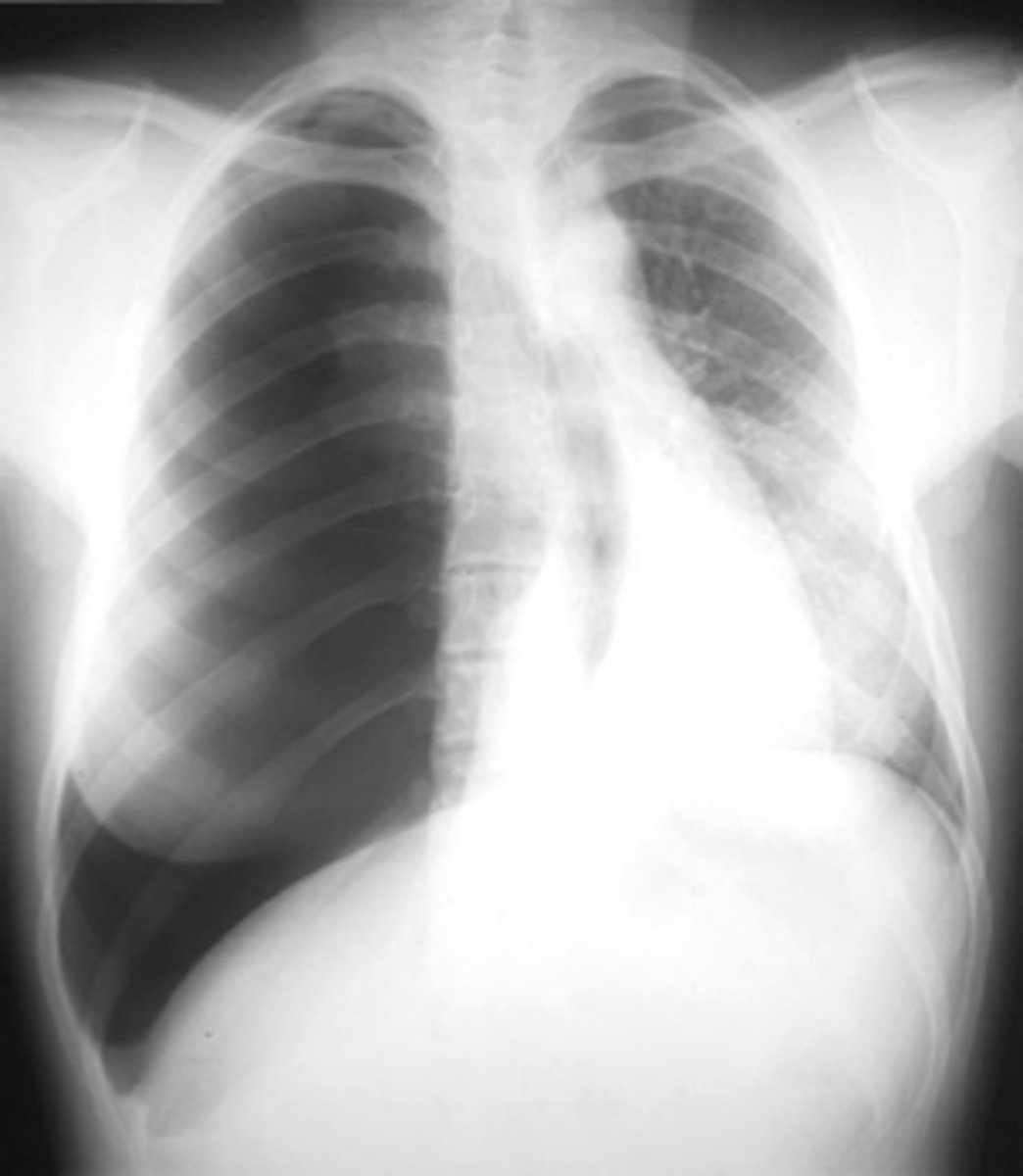
Hemopnuemothorax
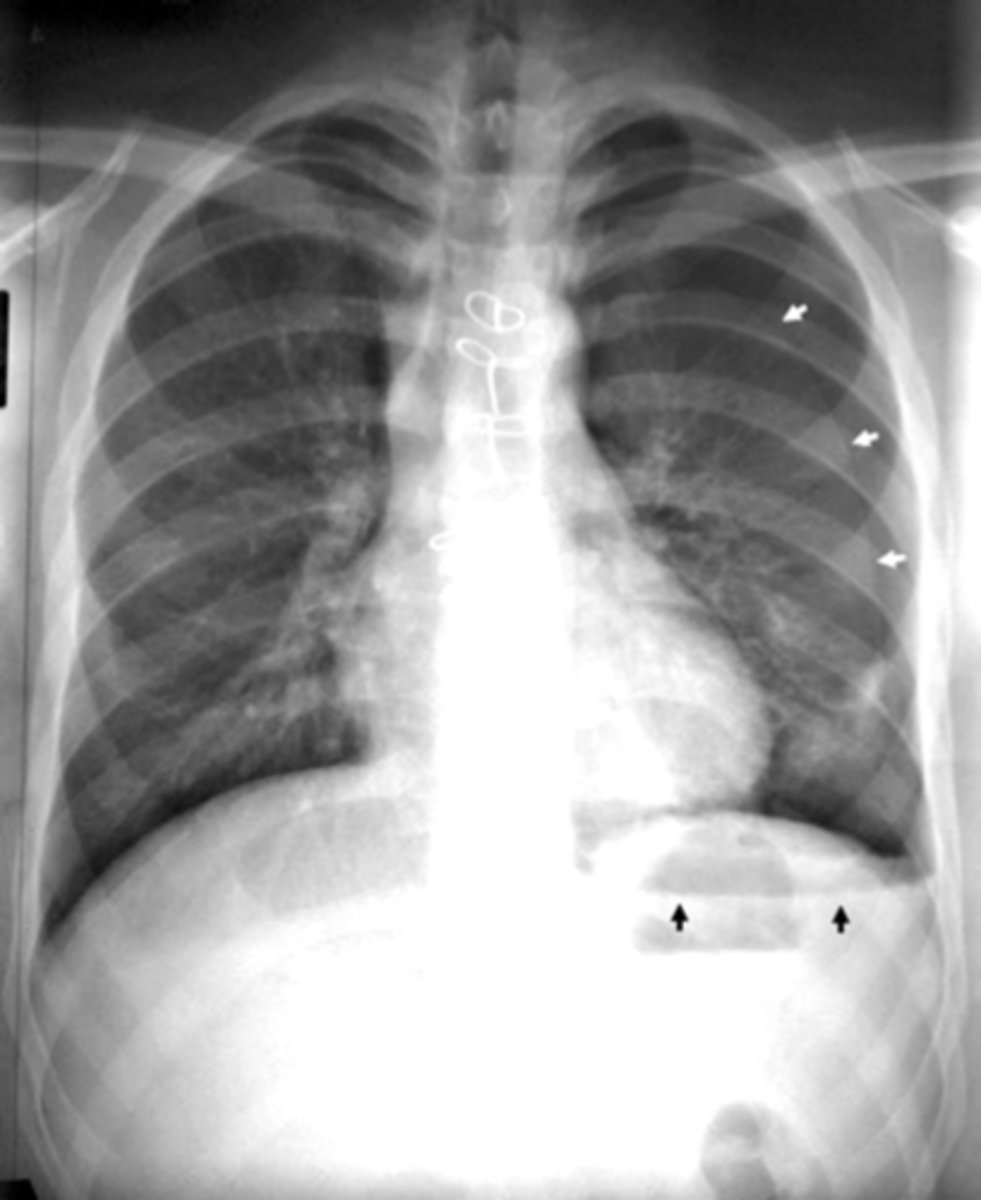
Pneumomediastinum (mediastinal emphysema)
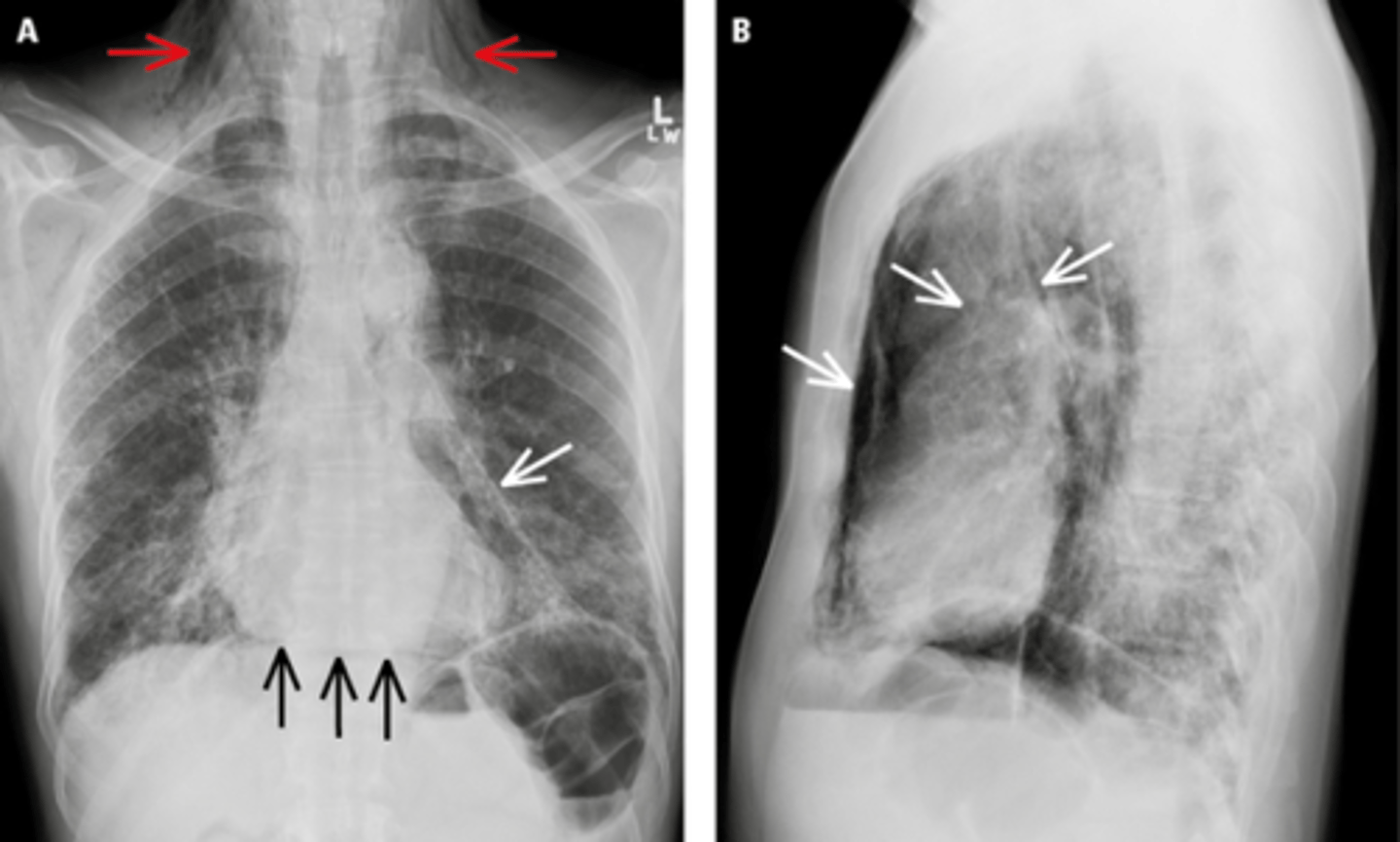
Pneumomediastinum
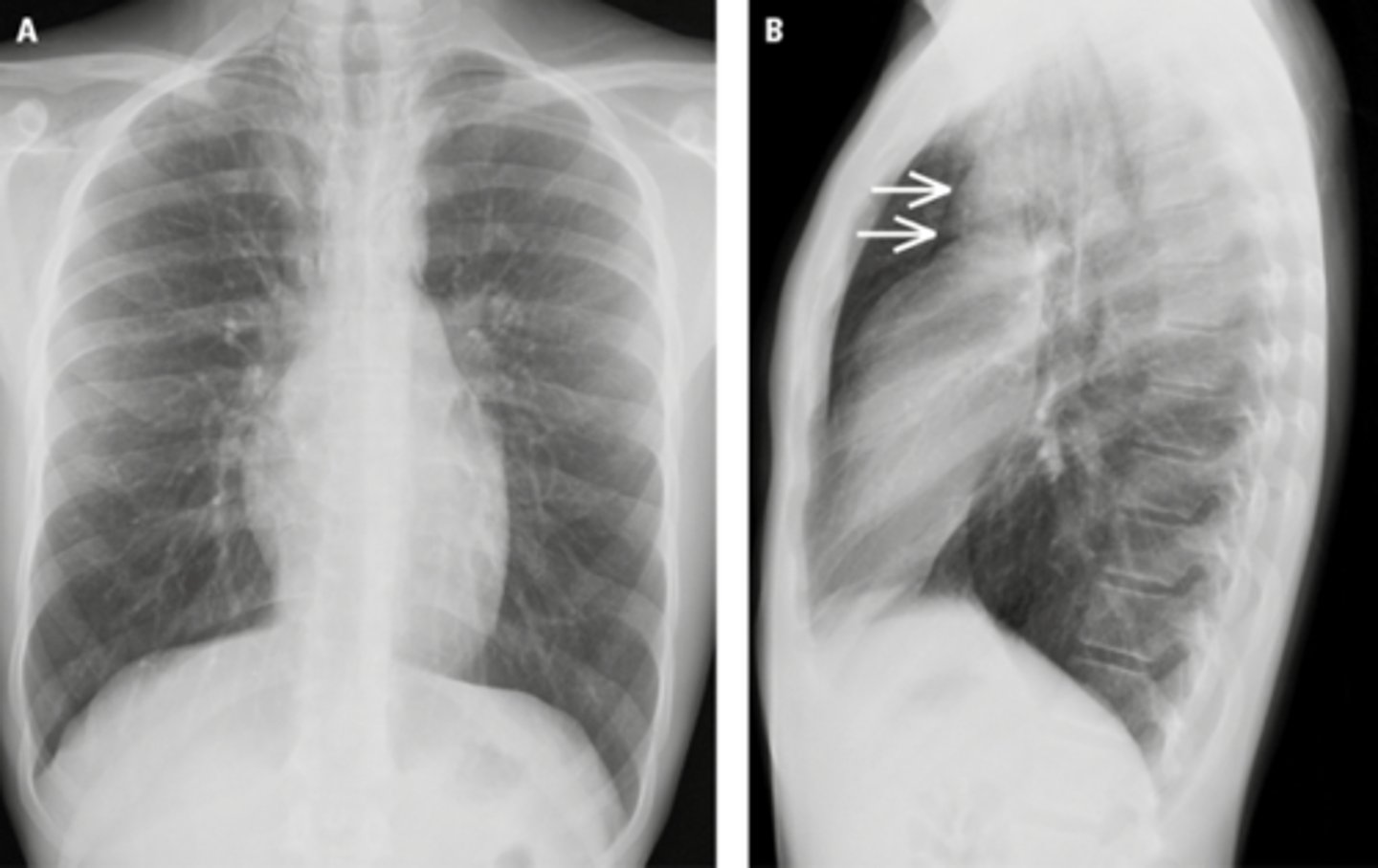
Pleural effusion
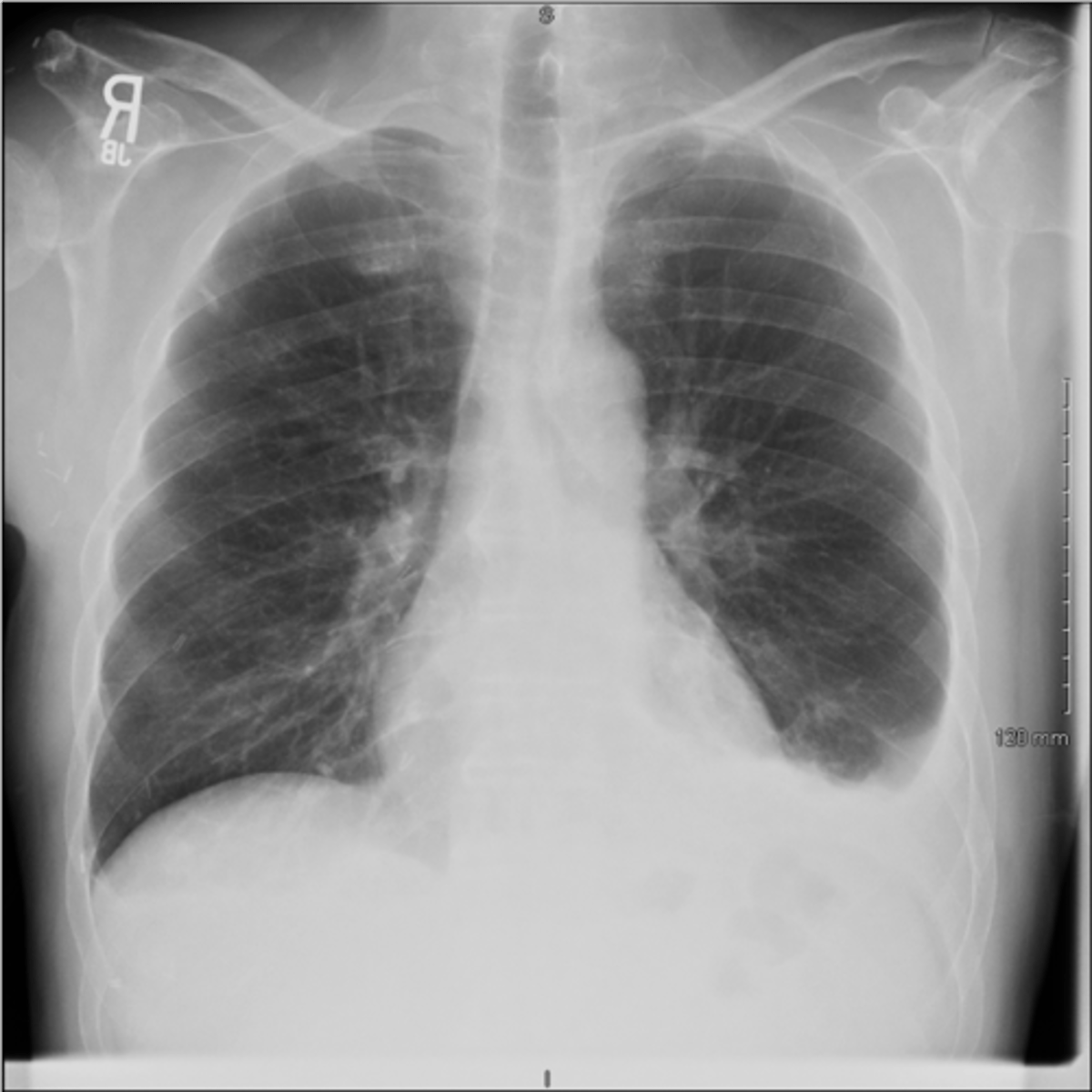
Pleural effusion
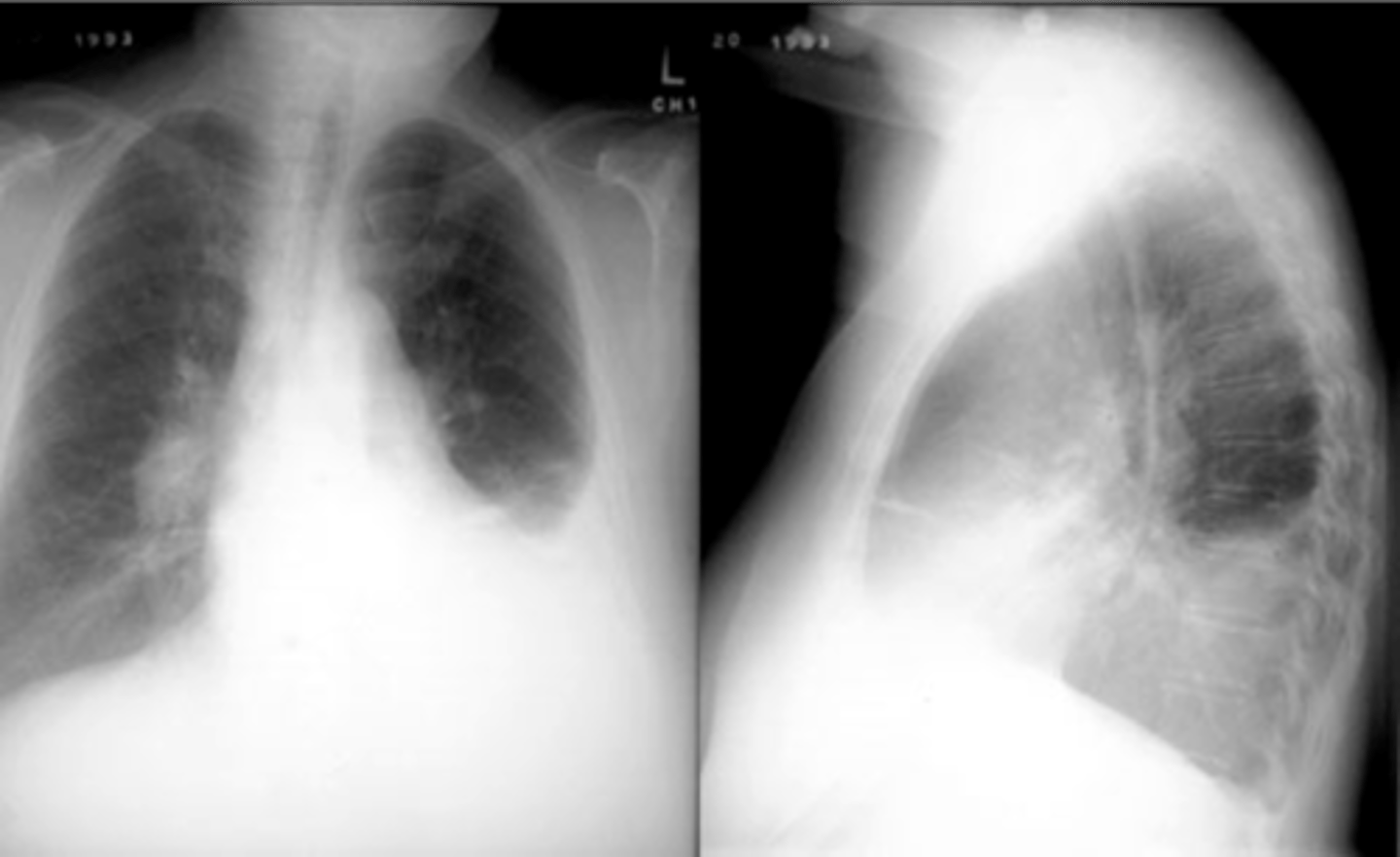
Pleural effusion (right sided)
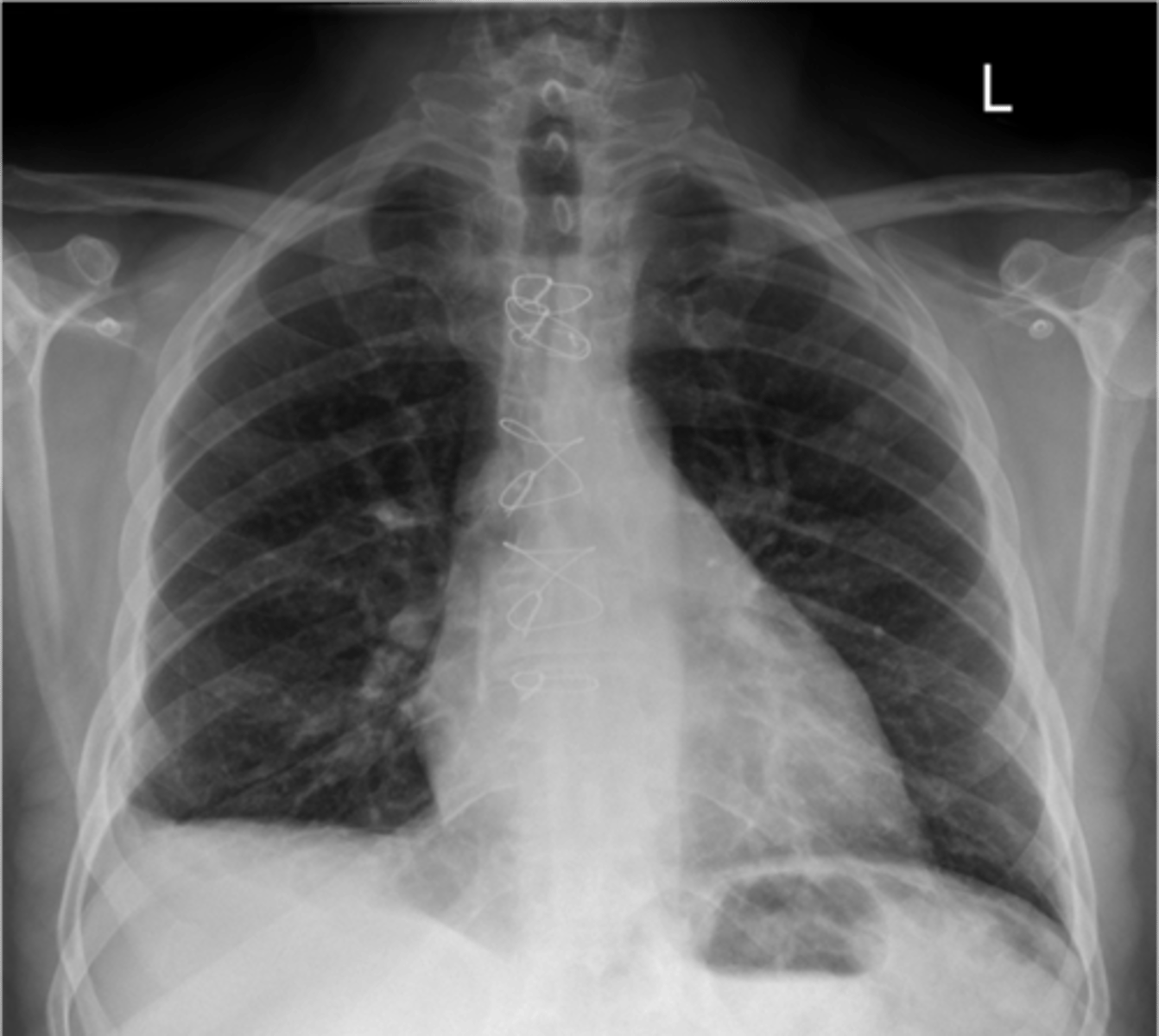
Empyema
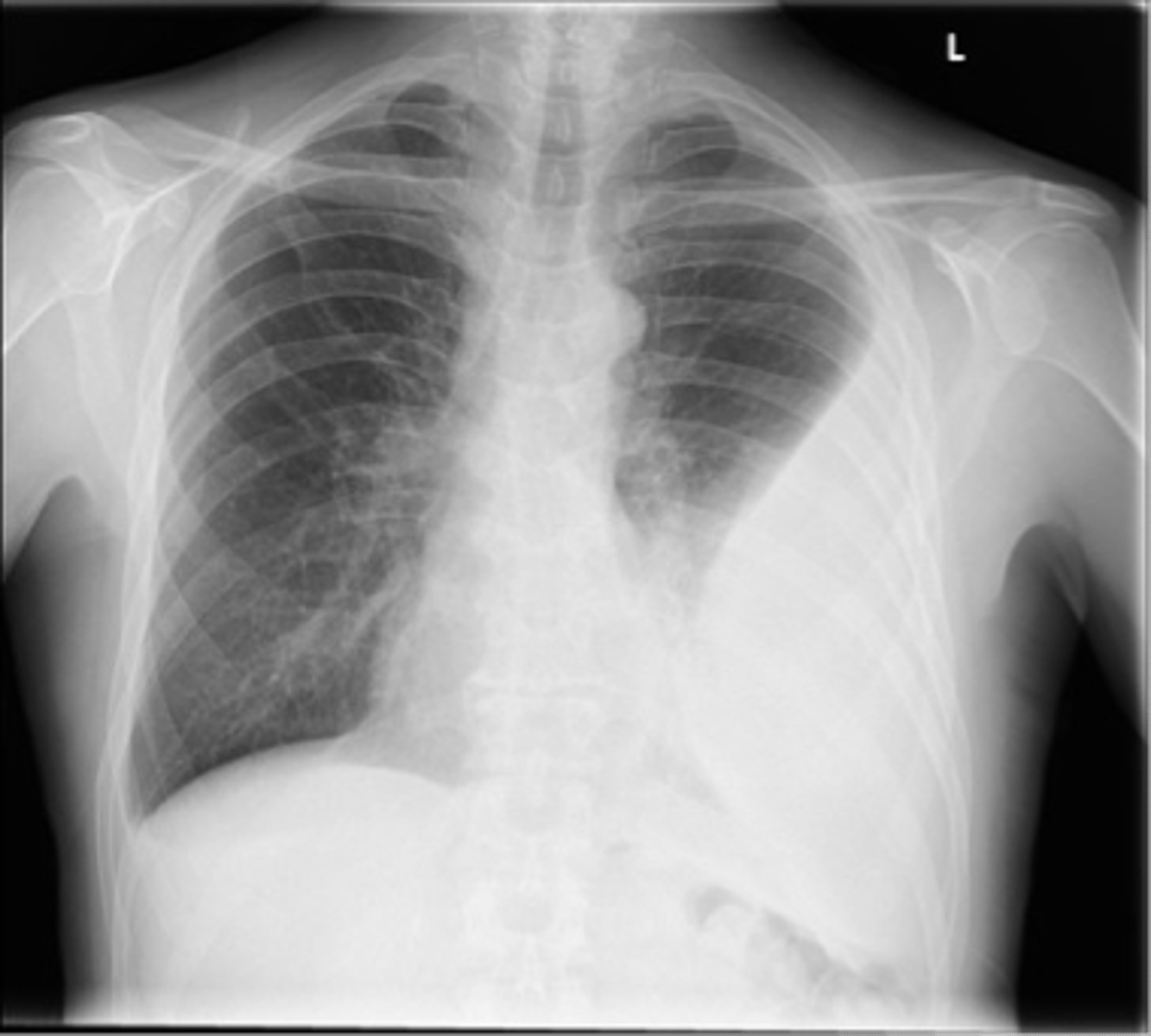
Empyema
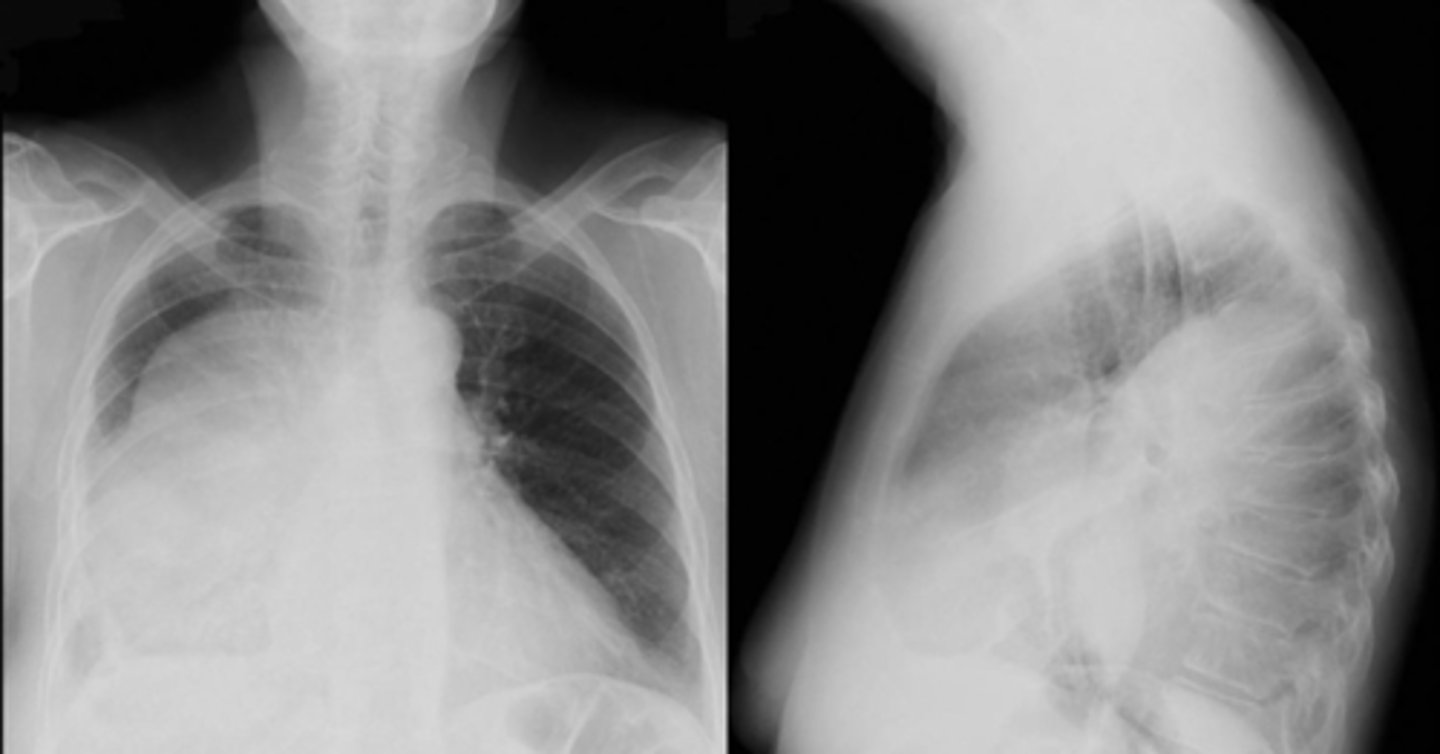
Pleural classifications and masses
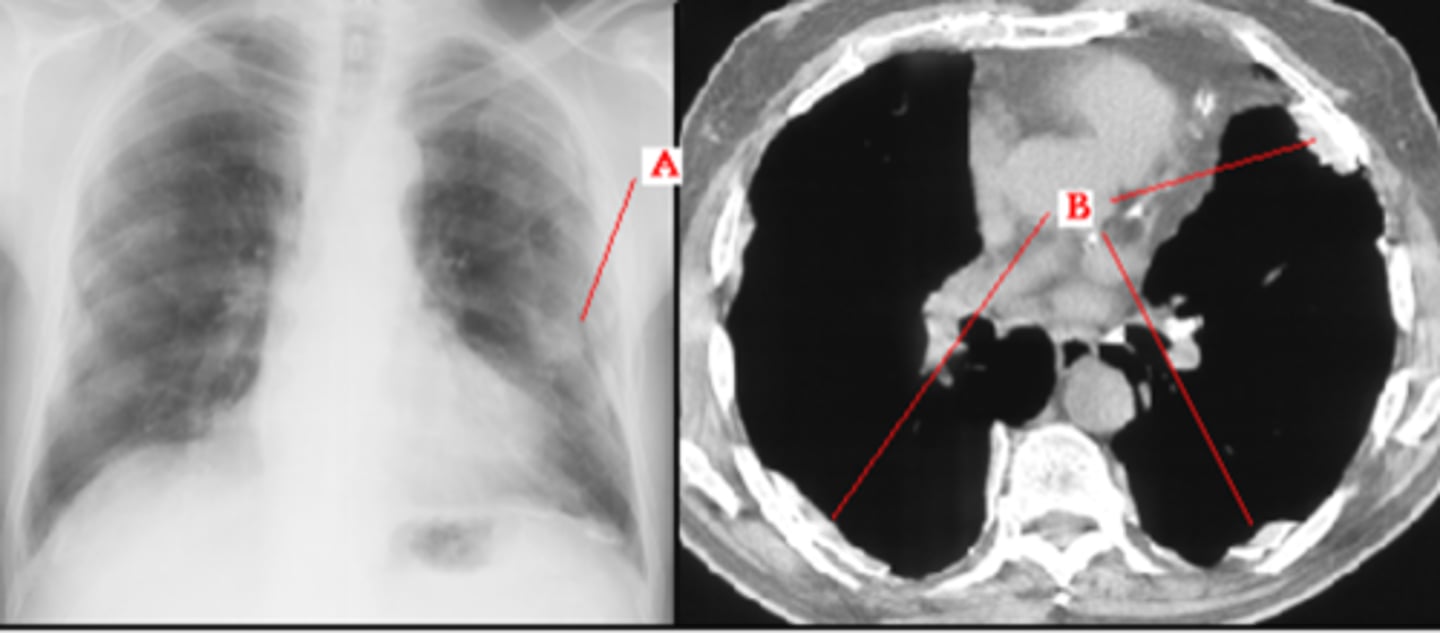
Diaphragmatic rupture
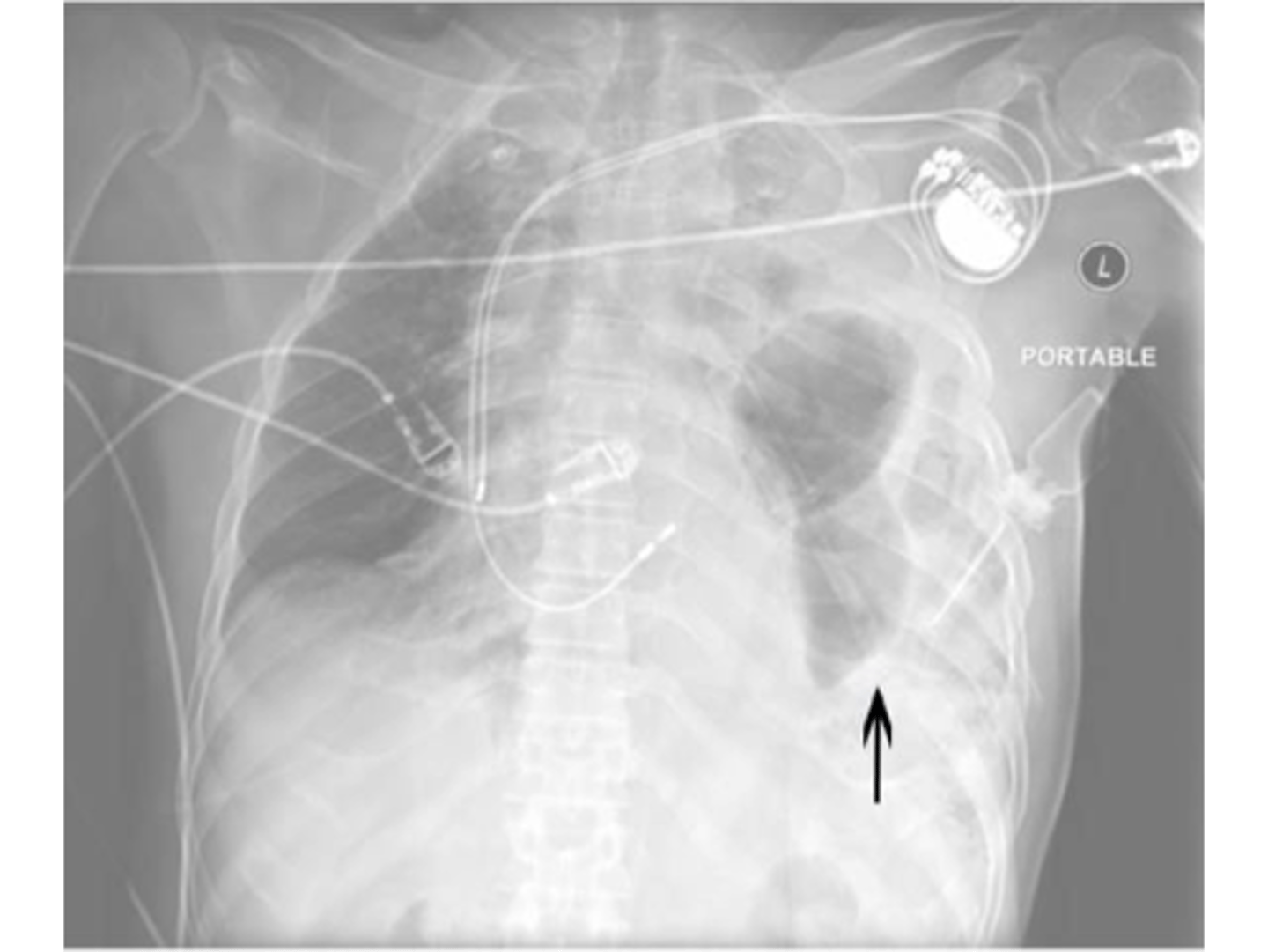
Diaphragmatic rupture
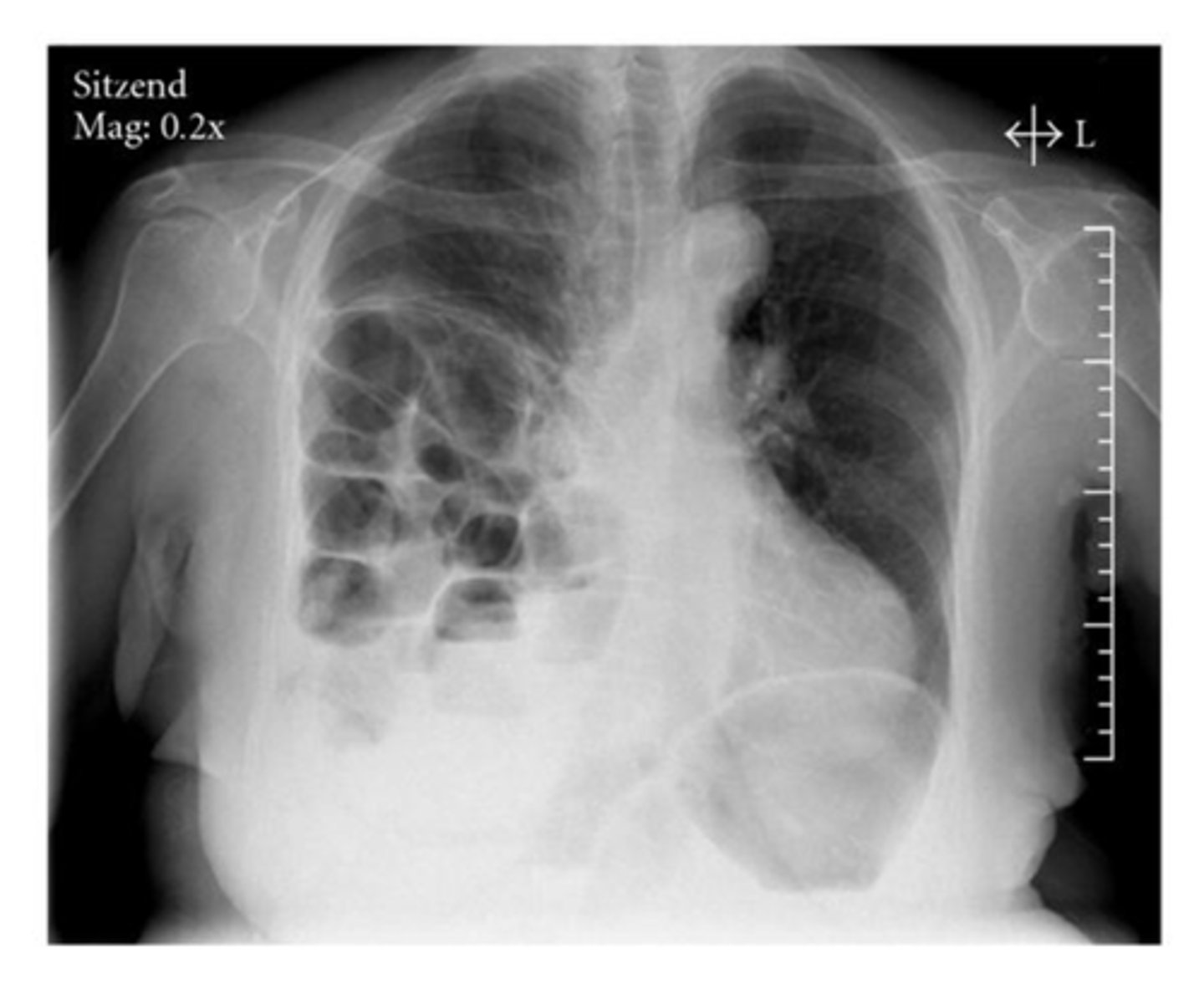
Diaphragmatic hernia
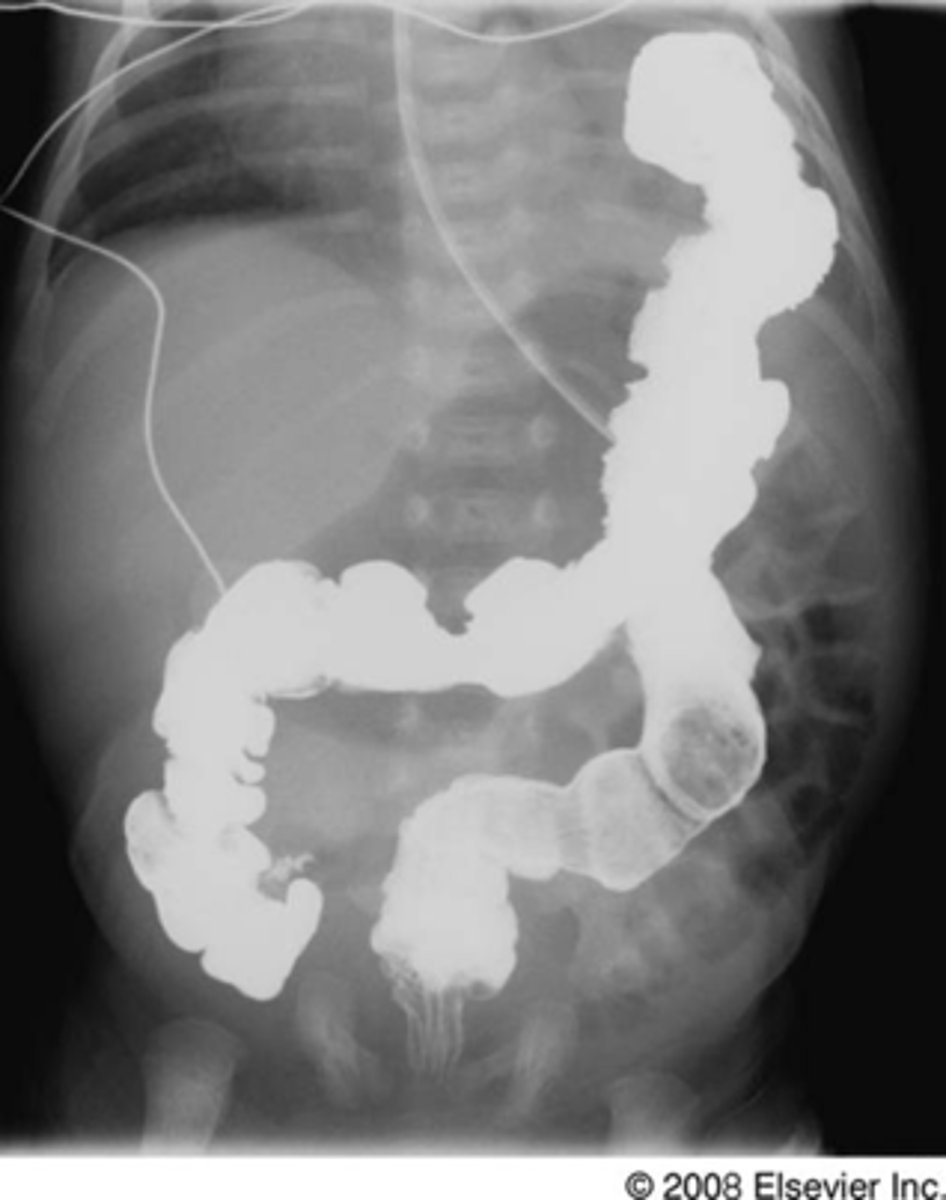
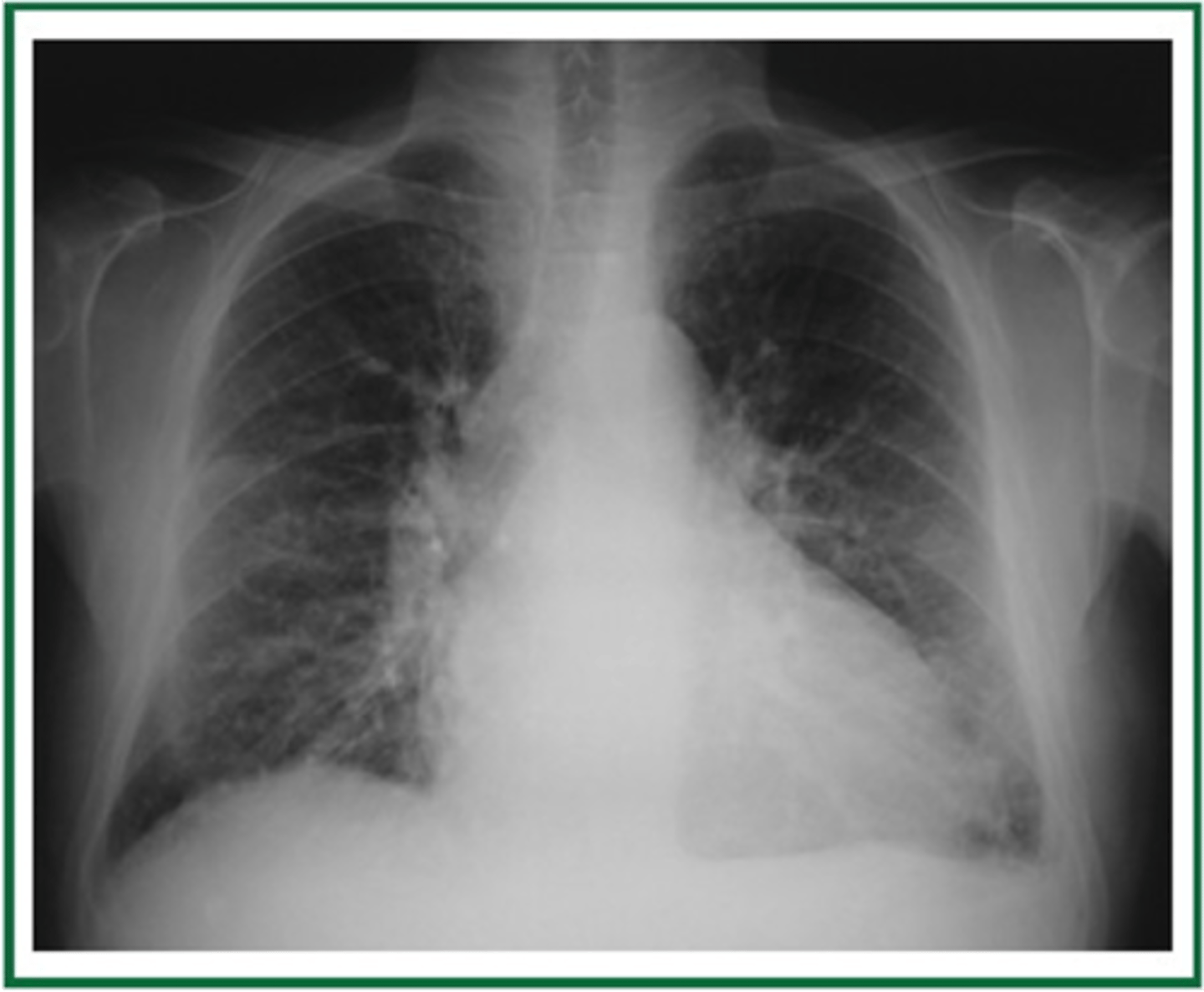
congestive heart failure
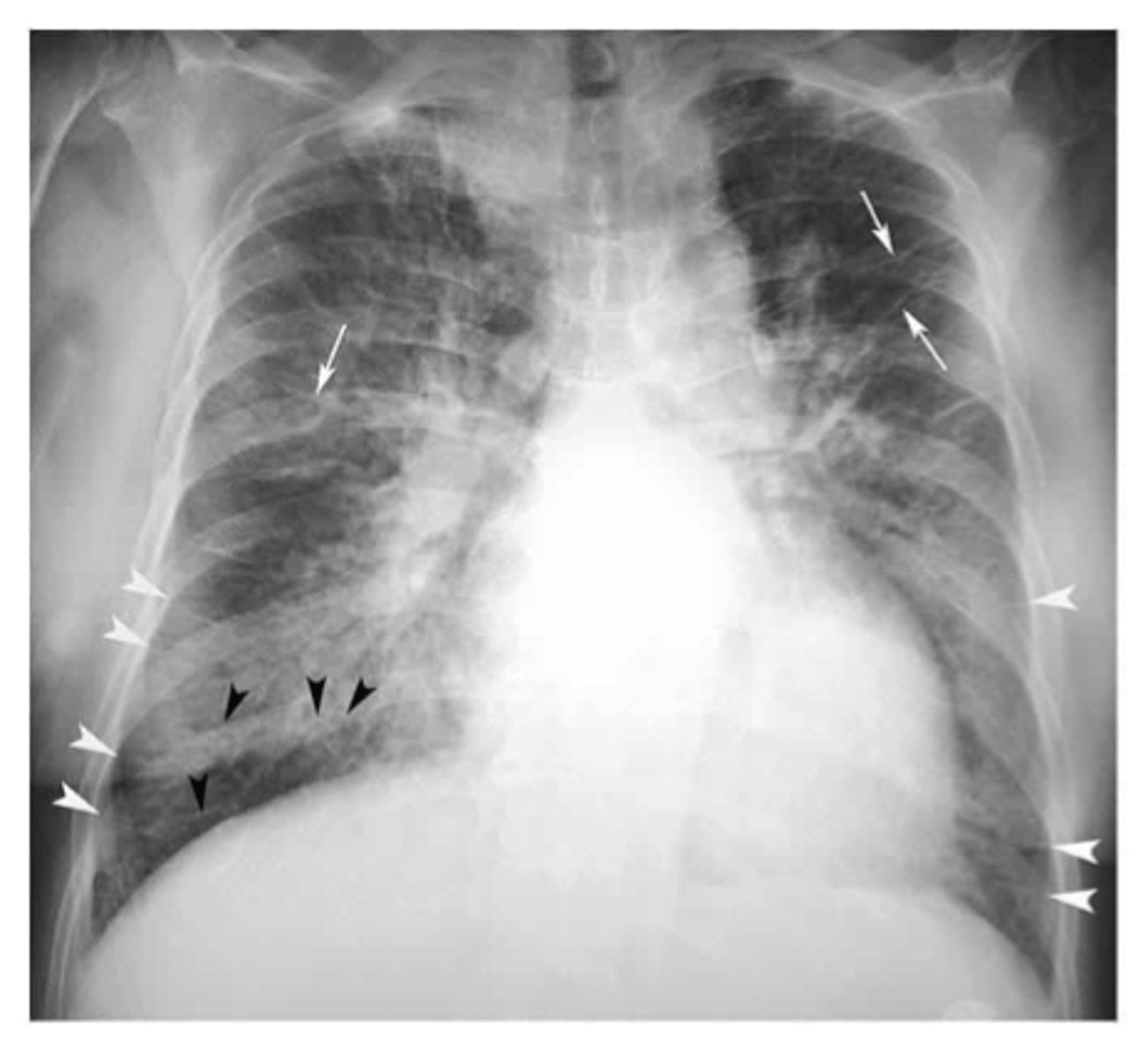
congestive heart failure
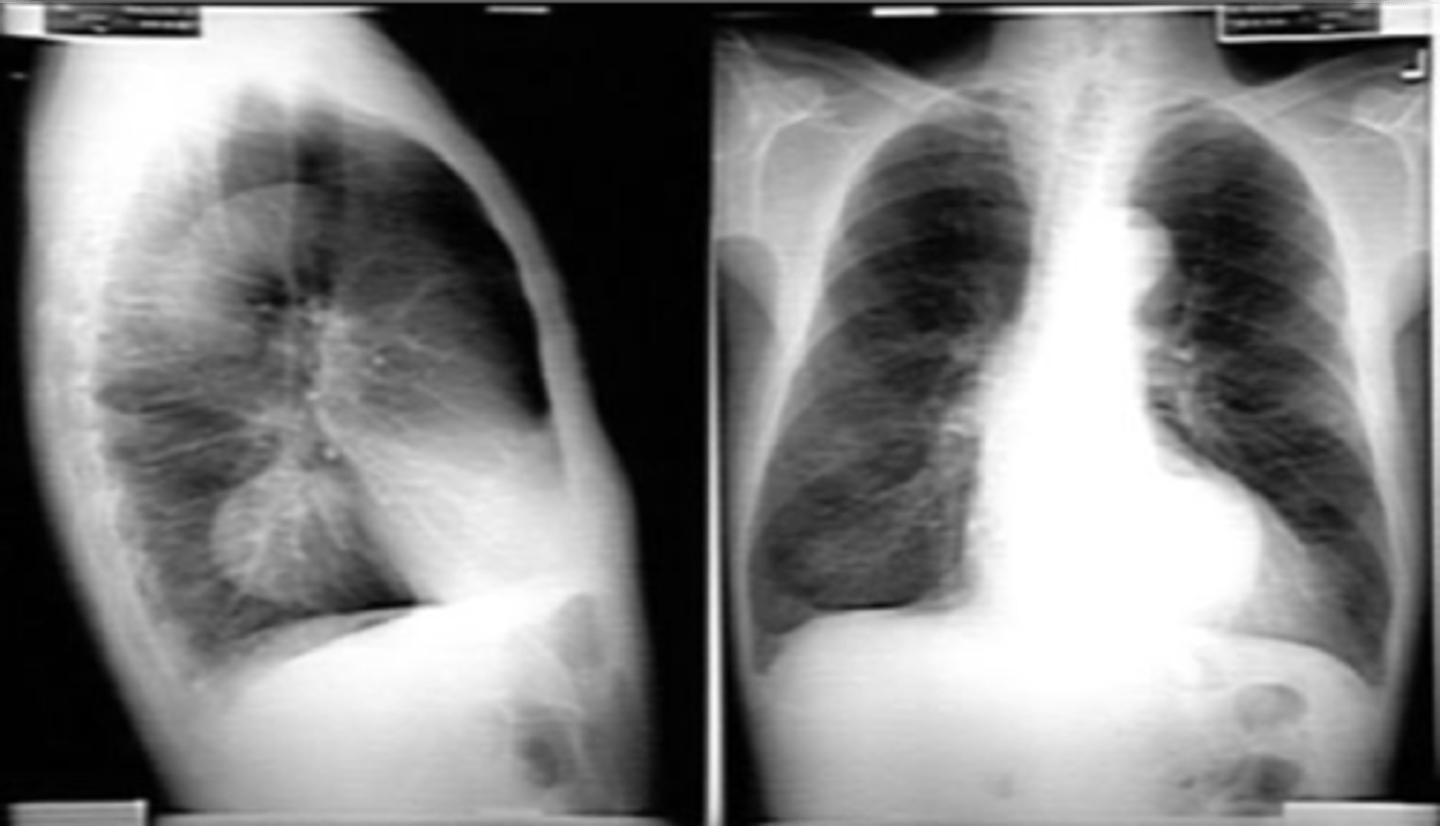
Most common anterior mediastinal mass
Thymoma
Most frequent cause of a middle mediastinal mass
Enlarged lymph nodes
Middle mediastinal masses
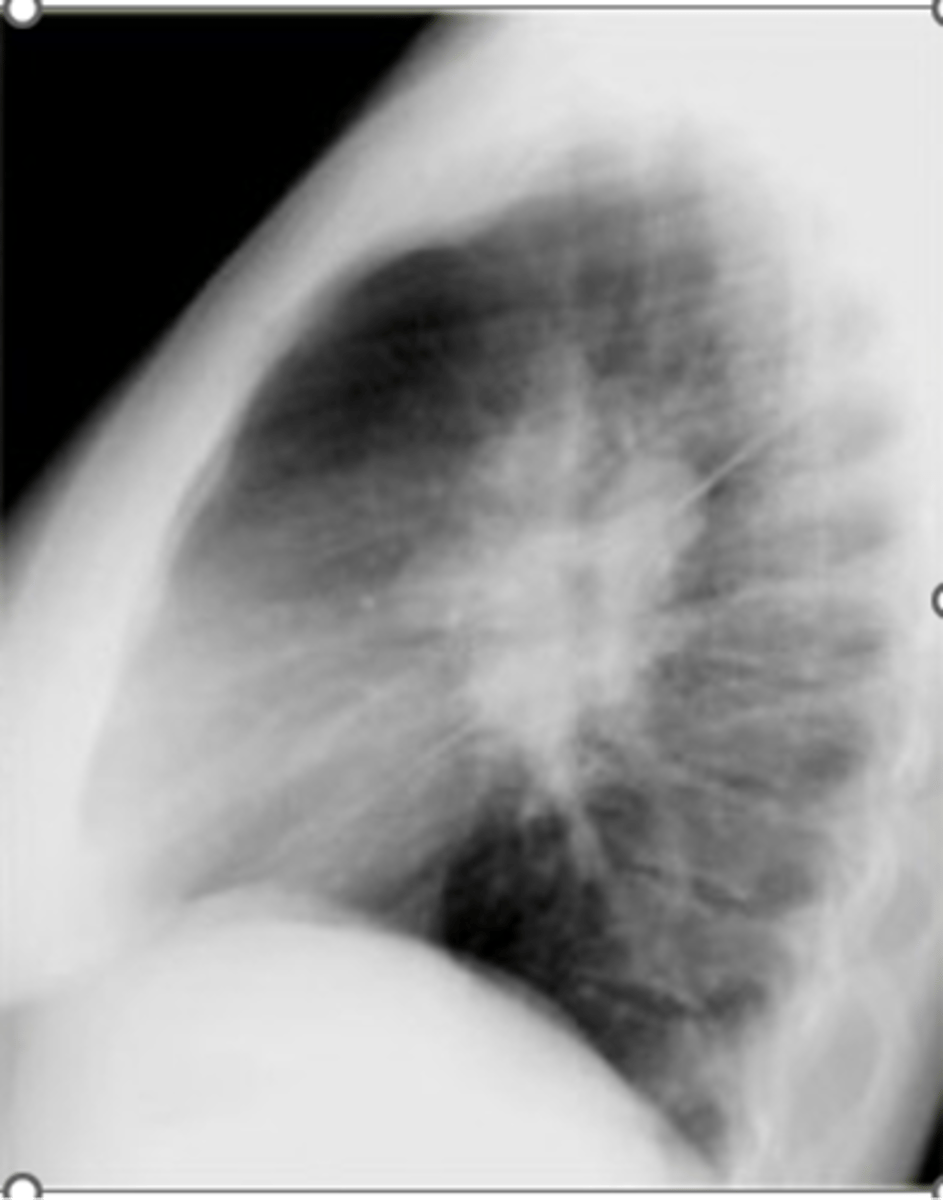
Posterior mediastinal masses
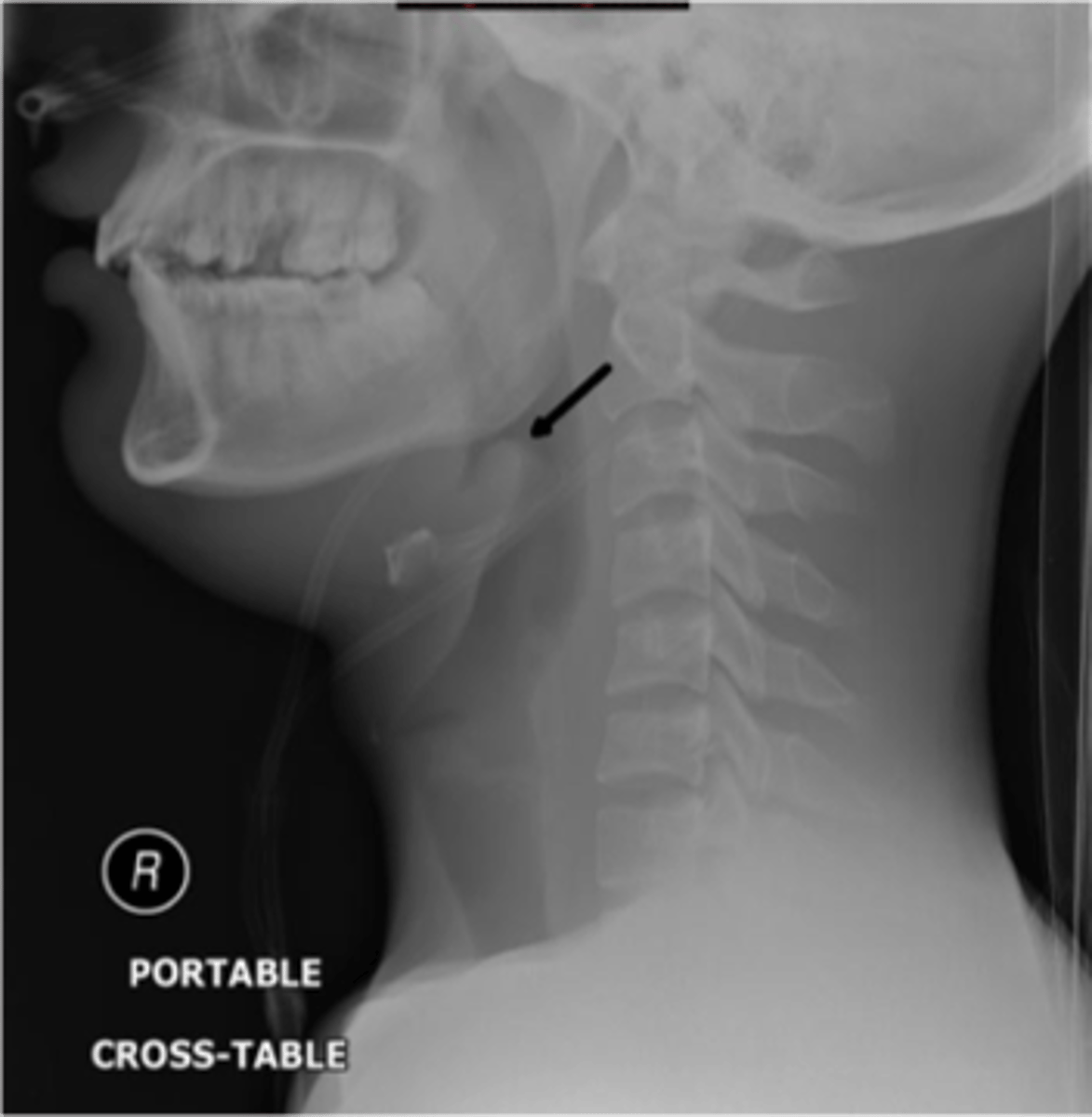
Epiglottitis (thumb sign)
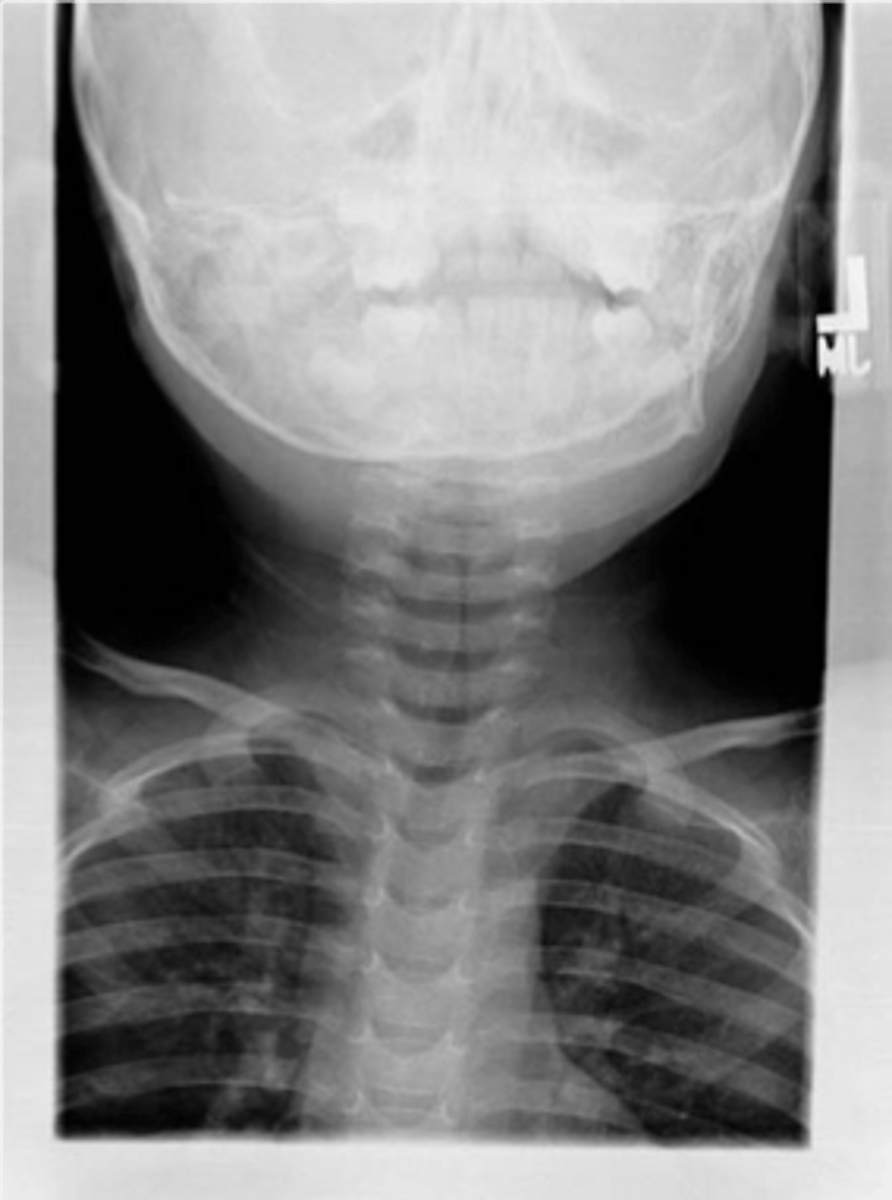
steeple sign (croup)
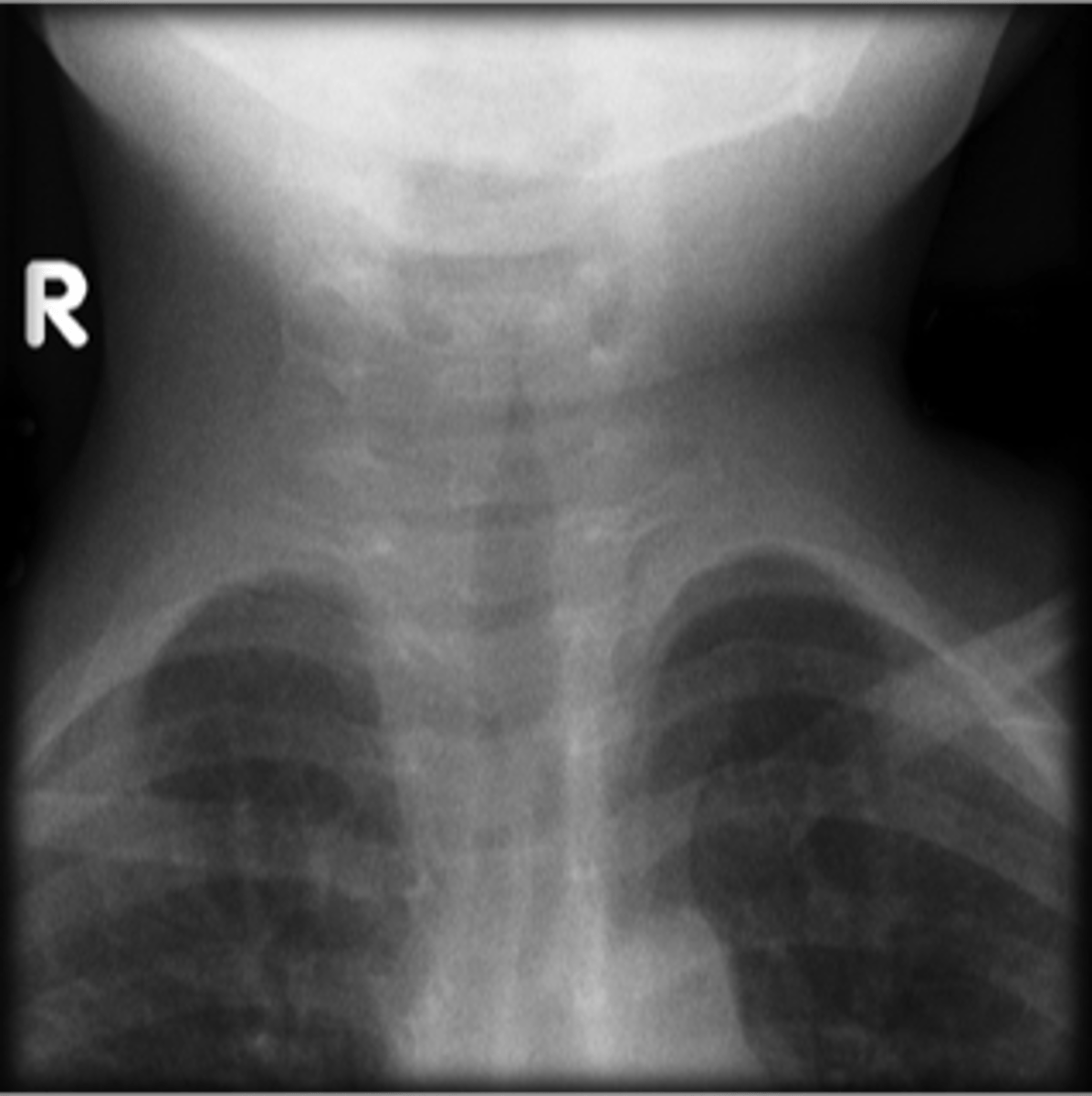
steeple sign (croup)
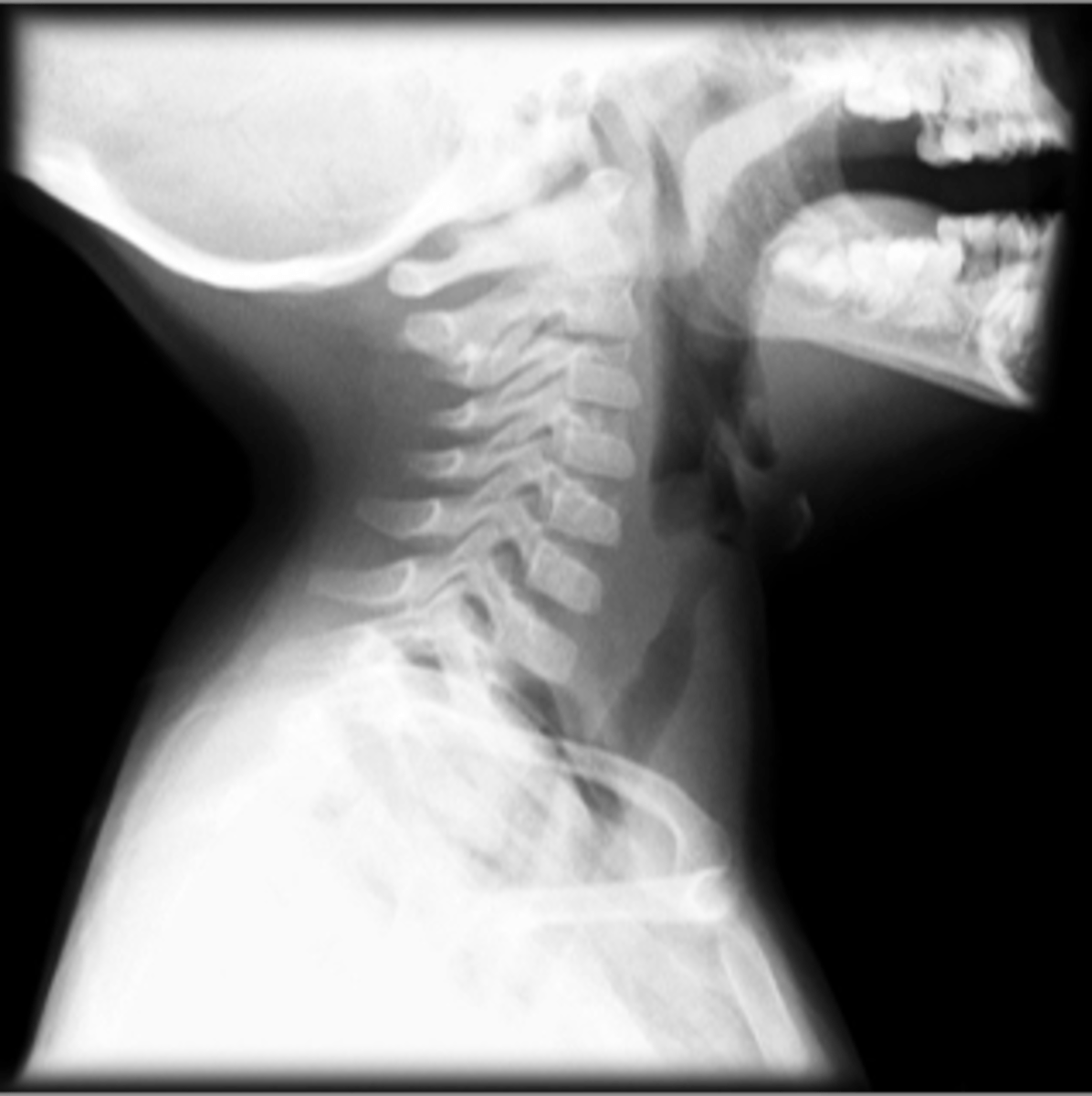
Croup
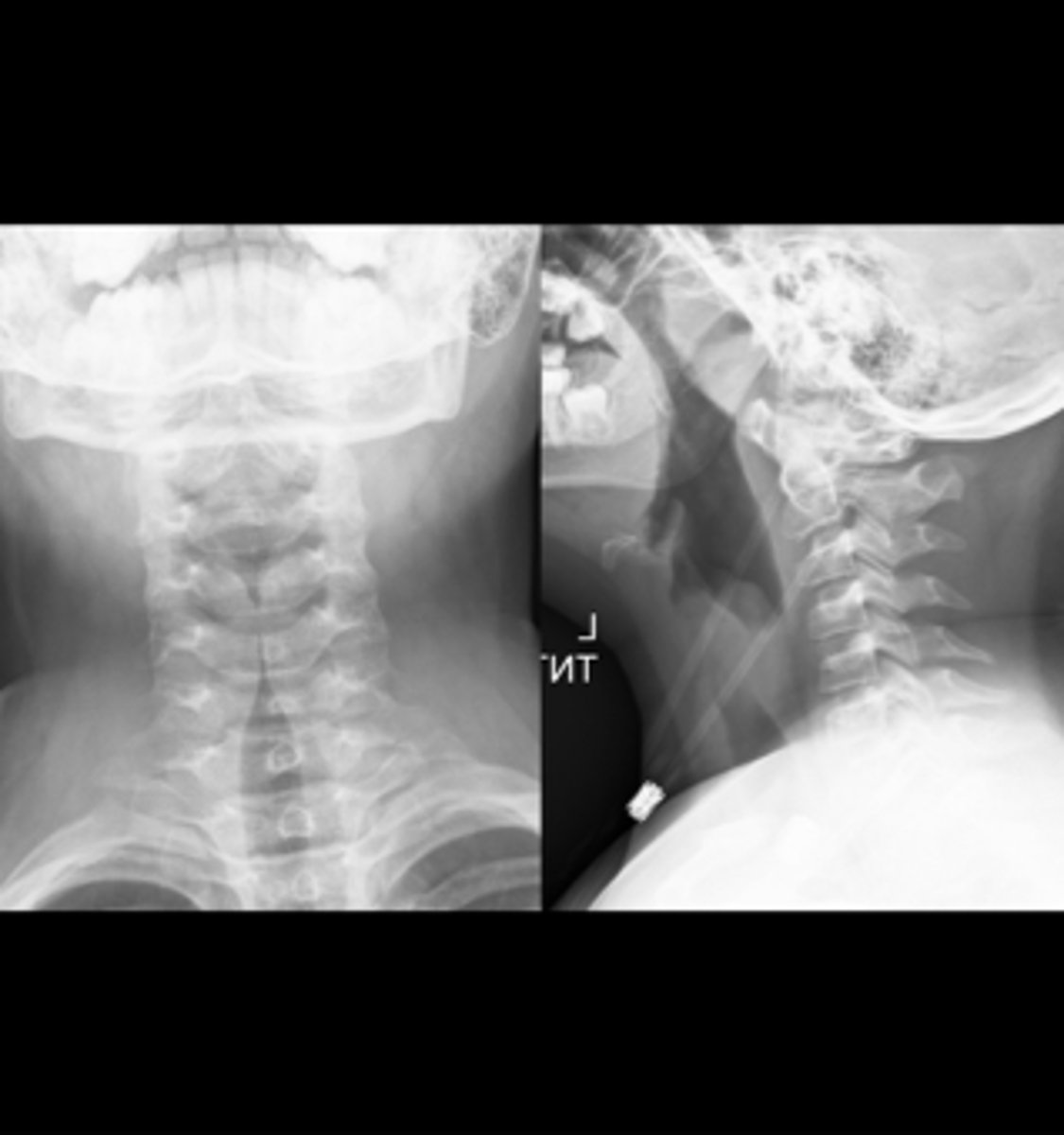
Right sided atelectasis
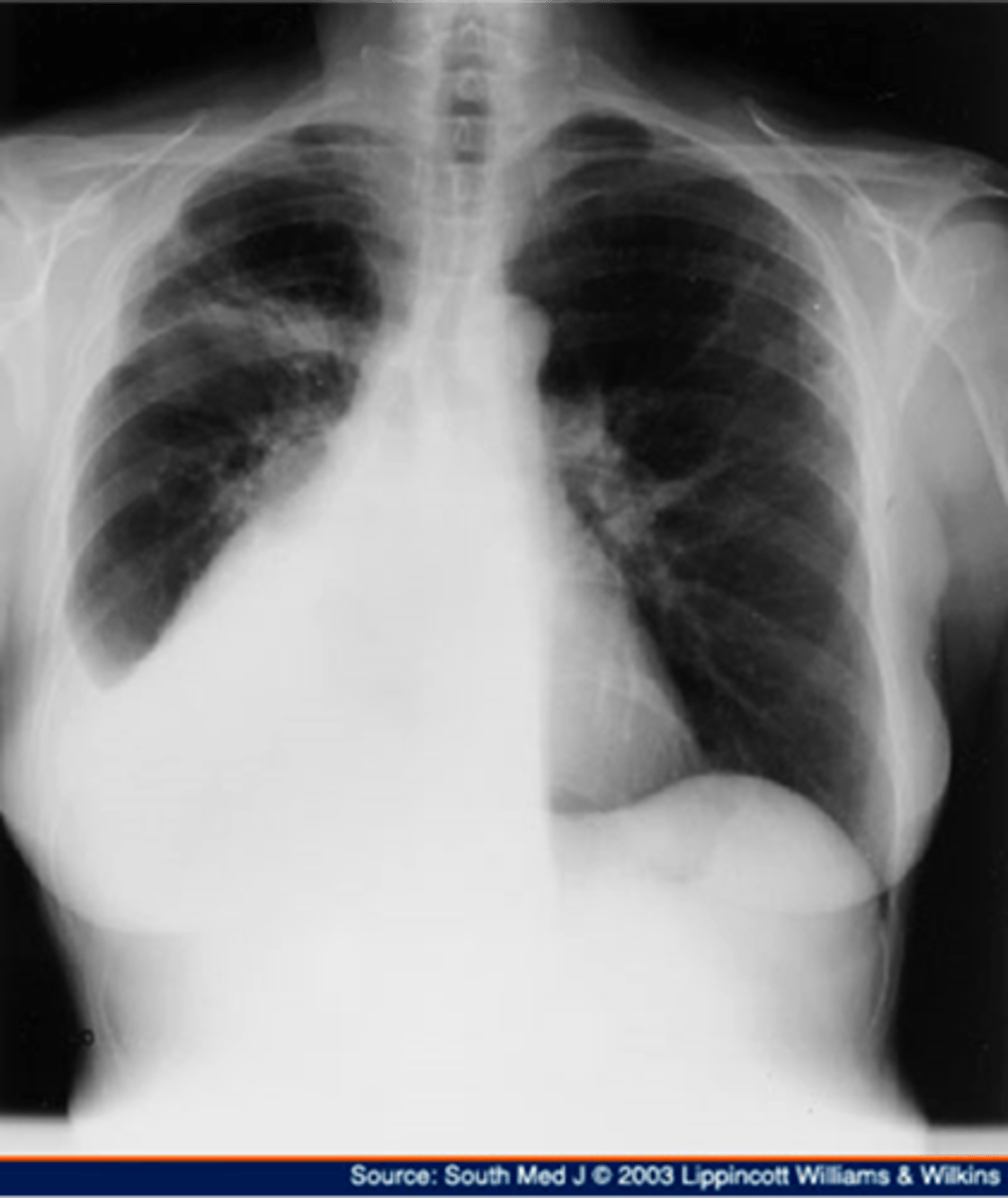
Right sided non tension pneumothorax
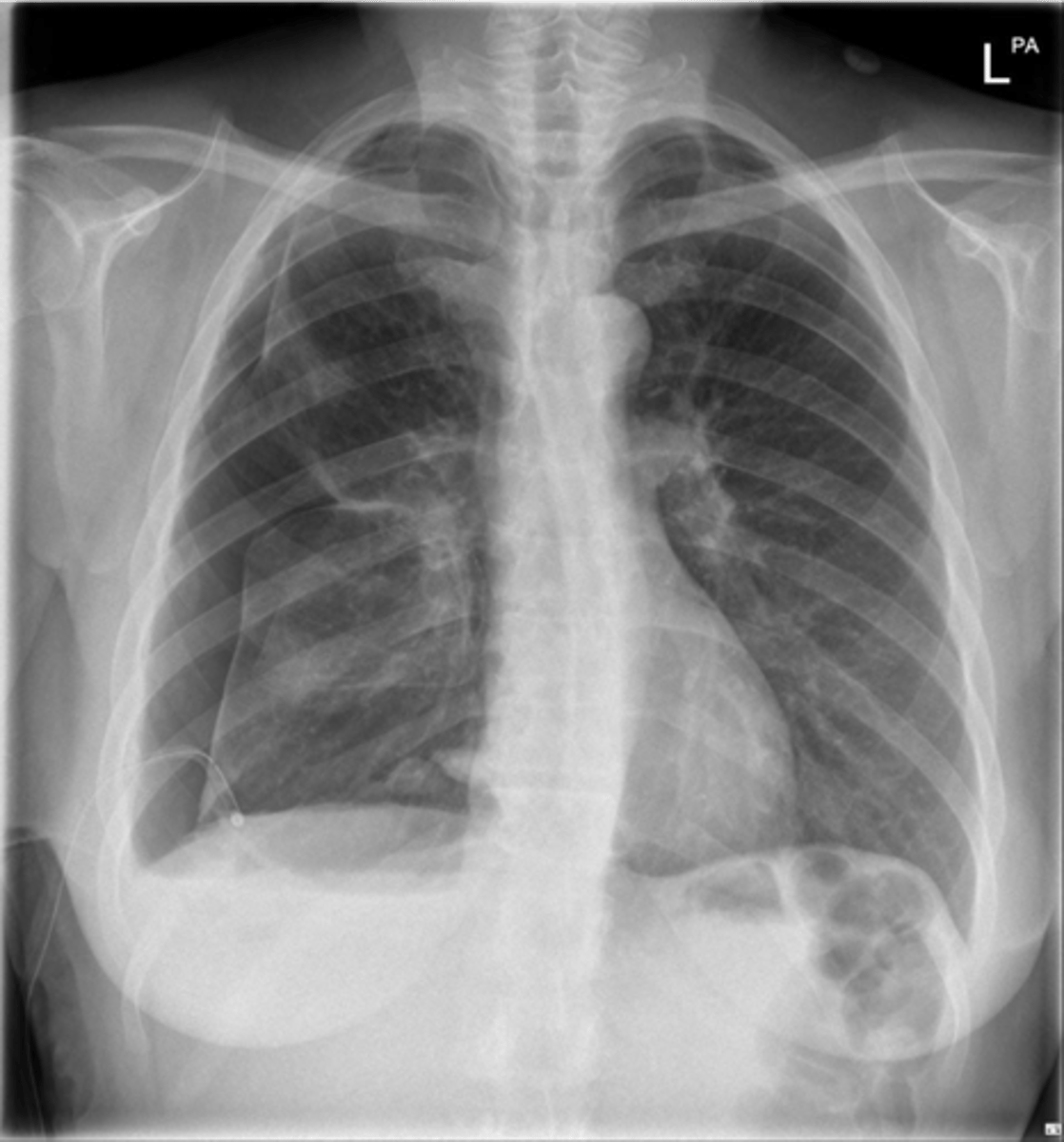
Atelectasis (right)
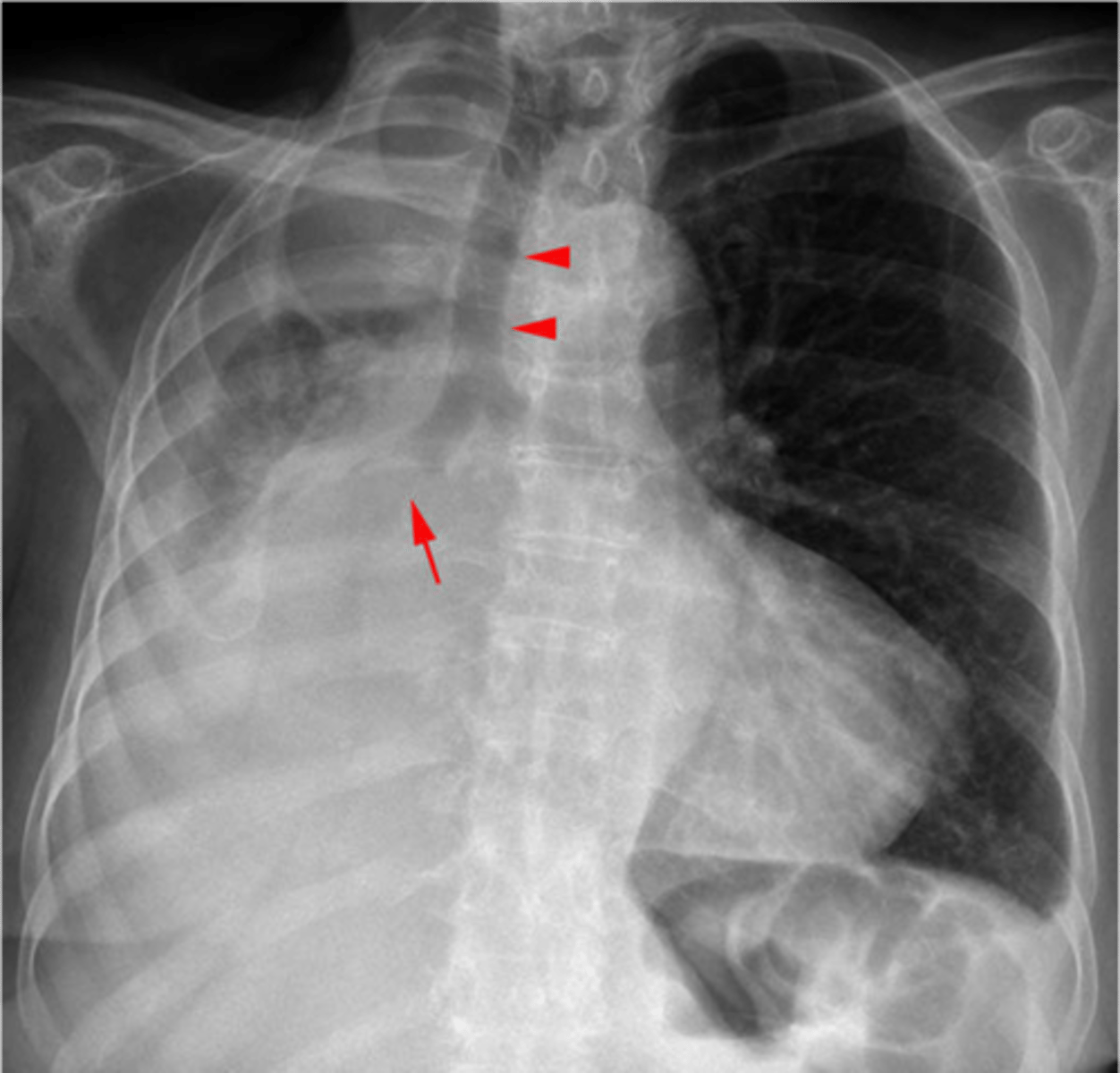
Bullae RUL
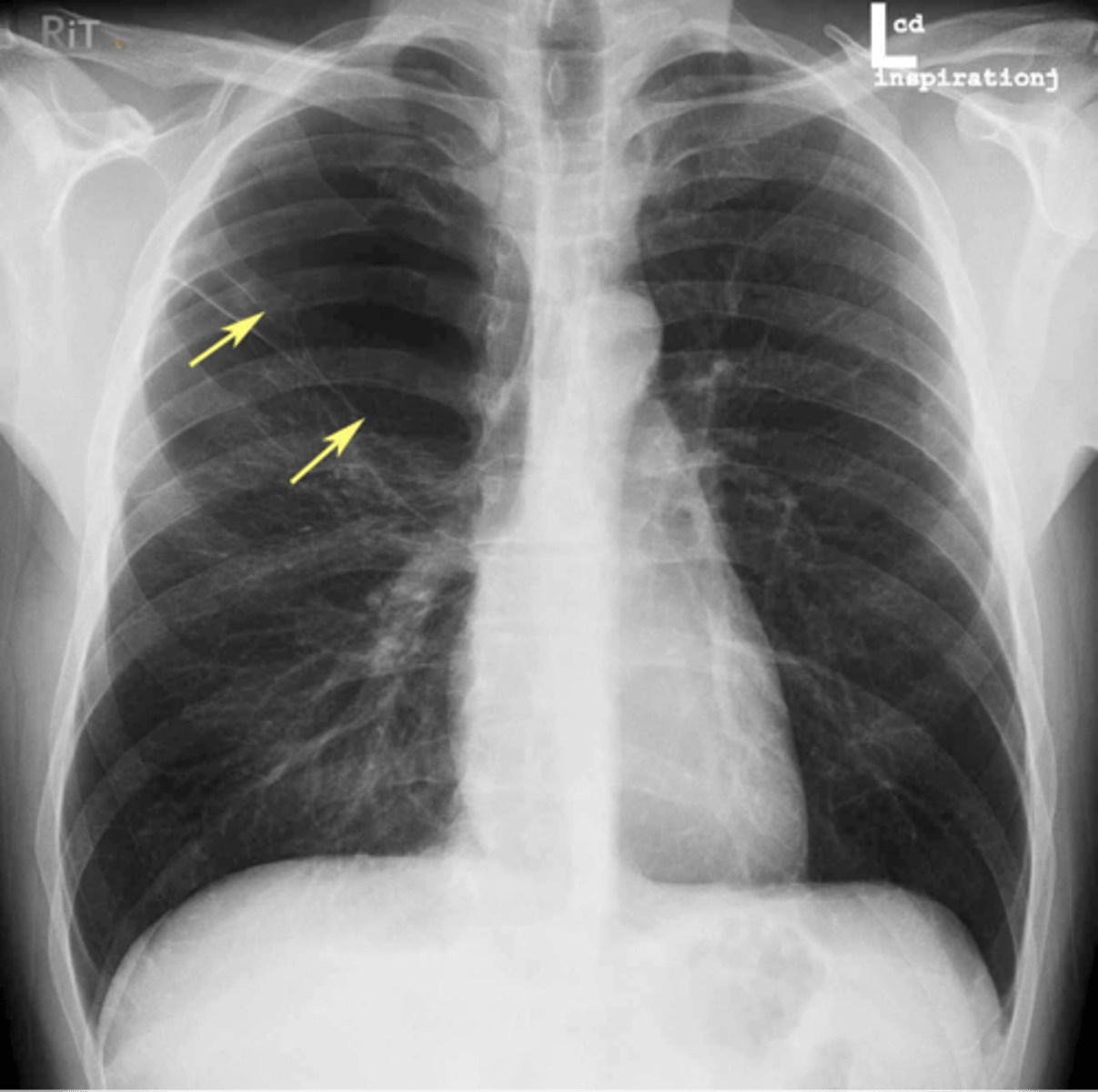
Atelectasis LLL
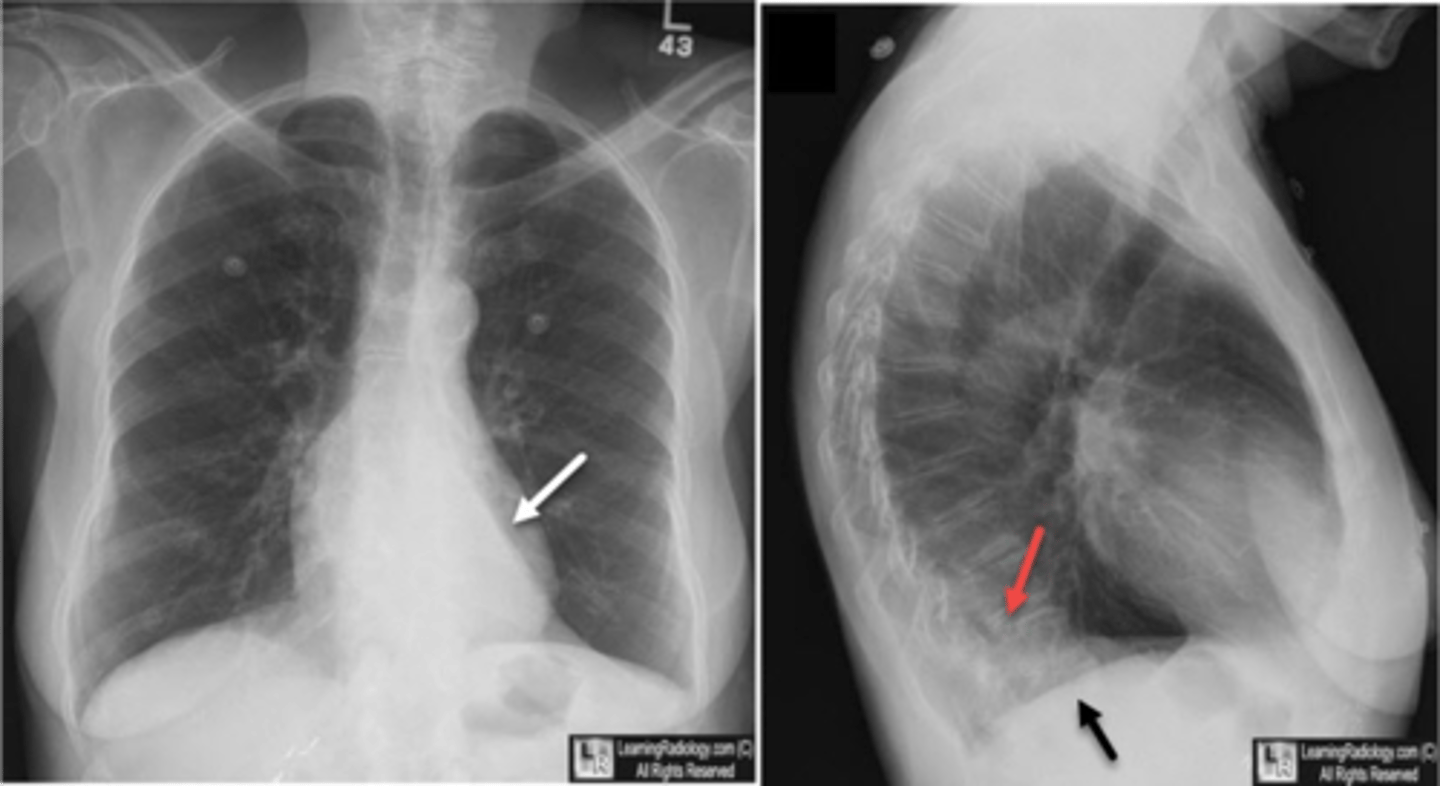
CHF - severe alveolar infiltrate
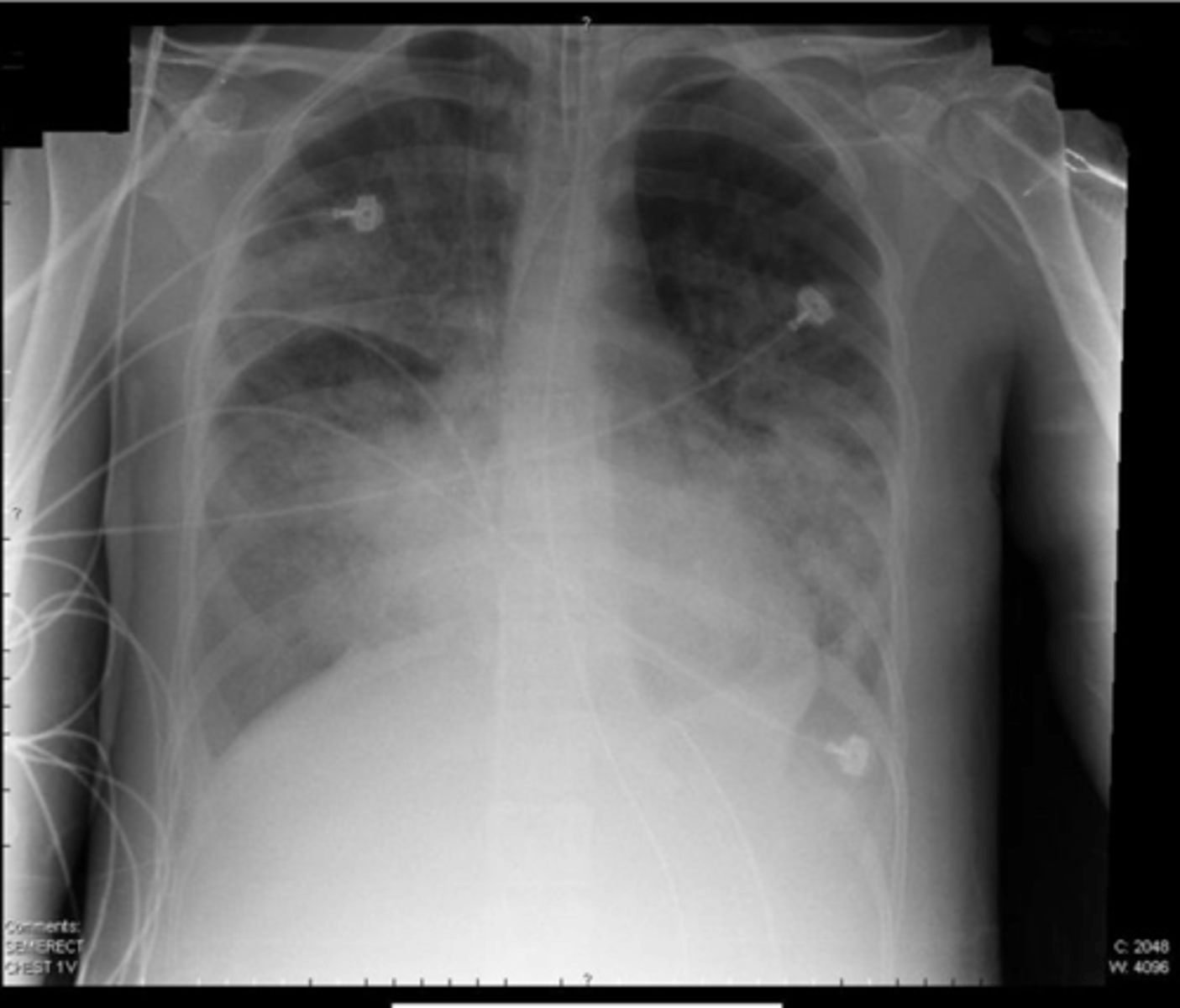
Tension pneumothorax (right)
Steeple sign- group