heart
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
heart
transport pump made of cardiac muscle tissue that delivers nutrients and waste via blood. O, glucose, CO2
lungs
located laterally to heart
heart location
base is ventral to heart, apex points to sternum laterally, dorsal to sternum
auscultation
listening to heart via stethoscope
pericardium
double walled sac enclosing heart. fibrous and serous layer
fibrous pericardium
dense connective tissue that anchors and protects heart. also prevents over filling of the heart
serous pericardium
inner layer of pericardium with two membranes parietal and visceral layer
parietal layer
lines internal fibrous pericardium
epicardium
visceral layer of serous pericardium that is intimately attached to heart, outermost layer of the heart wall
pericardial cavity
surrounds the heart and contains serous fluid that lubricates heart
pericarditis
inflammation of pericardium, decreased serous fluid production causes rubbing and pain beneath sternum. auscultate friction rub
cardiac tamponade
increased fluid or blood in pericardial cavity that compresses heart
heart wall
very vascular and made of 3 layers: epicardium, myocardium, endocardium
epicardium
most superficial, outermost layer of heart. visceral layer of serous pericardium
myocardium
middle, muscular layer (cardiac muscle) of heart. contracts. anchored by crisscrossing connective tissue fibers
myocardium
fibrous skeleton of heart, prevents stretching over time, limits spread of action potential across heart to specific pathways
endocardium
glistening inner layer of heart. made on squamous endothelium, continuous with blood vessels leaving heart
superior chambers
left and right atrium, separated by interatrial septum
inferior chambers
left and right ventricle separated by interventricular septum
coronary sulcus
separates atria from ventricles, atrioventricular groove
interventricular sulci
grooves with blood vessels along septum between ventricles. anterior and posterior
atria
receiving blood chambers with thinner walls. posterior surface is smooth, anterior surface is muscle bundles
auricles
appendages that increase atrial volume
pectinate muscles
prominent muscular ridges along the inner surface of the auricle and across the adjacent anterior atrial wall
crista terminalis
C-shaped ridge landmark used to locate veins entering right atrium
fossa ovalis
remnant of foramen ovale of fetal heart
right atrium
the right upper chamber of the heart that receives blood from the superior and inferior vena cava, coronary sinus
superior vena cava
receives blood superior to diaphragm
inferior vena cava
receives blood inferior to diaphragm
coronary sinus
receives blood from myocardium, coronary veins join together to form this, drains directly into right atrium
left atrium
chamber that receives oxygenated blood from the 4 pulmonary veins and lungs
ventricles
largest part of heart that discharges blood from heart. contains trabeculae carneae and papillary muscles
right ventricle
pumps deoxygenated blood to pulmonary trunk and arteries- lungs. thinner walled w larger cavity
left ventricle
pumps oxygenated blood to aorta- body. thicker walled w smaller cavity
trabeculae carneae
irregular ridges of muscle on ventricular walls
papillary muscles
conelike muscle bundles projecting into ventricular cavity, anchor chordae tendineae
heart pathway
two side by side pumps that create two circuits- pulmonary and systemic circuits
pulmonary circuit
right ventricle is pump- short low pressure. blood to and from lungs, gas exchange
systemic circuit
left ventricle is pump- long high pressure. provide oxygen rich blood and returns oxygen poor CO2 rich blood to heart
pulmonary circuit pathway
O poor CO2 rich blood from vena cava. right atrium to right ventricle to pulmonary trunk to lungs (O rich CO2 poor) to left heart
systemic circuit pathway
O rich CO2 poor blood from pulmonary vein to left atrium to left ventricle to aorta to body tissues to systemic veins to vena cava to right atrium
blood pathway
veins carry blood to heart, arteries carry blood away from heart. heart to arteries to arterioles to capillaries (gas and nutrient exchange) to venules to veins to heart
coronary circulation
circulation of blood to myocardium, myocardium is too thick for diffusion, blood in chambers does NOT supply myocardium
coronary arteries
the two arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle, emerge from aorta
left coronary artery
supplies blood to the left ventricle, left atrium, and interventricular septum. 2 branches: anterior interventricular artery and circumflex artery
anterior interventricular artery
supplies blood to anterior interventricular septum
circumflex artery
supplies left atrium and posterior wall of left ventricle
right coronary artery
supplies right atrium and most of right ventricle. 2 branches: marginal artery and posterior interventricular artery
marginal artery
supplies oxygenated blood to lateral wall of right ventricle
posterior interventricular artery
supplies the posterior surface of the left and right ventricles and apex of heart
arterioles
small vessels that receive blood from the arteries, greatest effect of blood pressure
coronary blood vessels
these branch into myocardium, blood flows during relaxation, decrease in contraction, compressed by myocardium, entrances blocked by open valves
cardiac veins
these empty into coronary sinus which then empties into right atrium. great, middle, and small
atrioventricular valves
these separate atria and ventricle, prevents backflow of blood into atria while ventricles are contracting
right av valve
tricuspid valve, 3 cusps that are flaps of endocardium with connective tissue
left av valve
bicuspid valve, 2 cusps, mitral valve
both valves
these are one way and are anchored to ventricular wall with papillary muscles and chordae tendinae
semilunar valves
half moon, controls blood flow out of ventricles and into arteries. ventricular pressure forces valves open, backflow of blood closes valves
pulmonary valve
right semilunar valve, blood from right ventricle flows through this into lung circuit
aortic valve
left semilunar valve, blood from left ventricle flows through this into systemic circulation
incompetent valve
heart has to re pump same blood over and over, can be replaced surgically- synthetic, pig heart, cadavers
murmur sound
sound of blood being shot backward
stenosis
valve is stiff from scar tissue from endocarditis or calcium deposits, heart works harder and may cause the heart to weaken
cardiac muscle cells
striated, paler, branched, shorter than skeletal. 1-2 central nuclei. intercalated discs- desmosomes, gap junctions prevent separation of adjacent cells
functional syncytium
mass of merging cells that function as a unit. ions pass so myocardium contracts in unison
mitochondria
cardiac muscle has large ____ and a high resistance to fatigue. also has less elaborate sarcoplasmic reticulum
cardiac contraction
some myocardial cells can initiate depolarization automatically, self excitable. heart dose this as a unit
250 ms
length of cardiac muscles absolute refractory period (where Na channels are open) and the contraction duration
skeletal muscles contraction
1-2 ms refractory period. 20-100 ms period of contraction
contraction
1. voltage, Na channels open, depolarization -90mV to +30mV. 2. action potential travels through t tubules, sr releases Ca ions. 3. cross bridge activation
Ca
10-20% for muscle contraction is extracellular. stimulates of 80% release from sr. action potential opens slow channels
action potential
1. Na dependent membrane depolarization 2. Ca channels open 3. Ca from sr released 4. Ca channels close 5. K flows outward, restores resting membrane potential
200 ms
duration of cardiac muscle action potential and contraction
skeletal duration
1-5 ms for action potential. 15-100 for contraction
cardiac muscle
more dependent on aerobic respiration, cannot contract for long periods in anaerobic conditions. better at using different nutrients
oxygen
the most important factor for myocardium
intrinsic cardiac conduction system
cardiac muscle can initiate depolarization and distribute impulses throughout heart, may still beat even when disconnected from nerves
coordinated contraction
the heart can do this because of the gap junctions at intercalated disc and function syncytium
autorhythmic cells
are also called pacemakers because they set the rate of the heartbeat. continually depolarize and slowly approach threshold
autorhythmic cells
these initiate action potential through rest of myocardium
autorhythmic cell location
these are found at the sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node and bundle, right and left bundle branches, and purkinje fibers
sa node
on right atrial wall, generates impulses 75 times per min. fastest depolarization rate
sa node
pacemaker, produces sinus rhythm, determines heart rate
av node
receives wave of depolarization through internodal pathway from sa node. located in interatrial septum by tricuspid valve. impulse is delayed- allows atria to contract
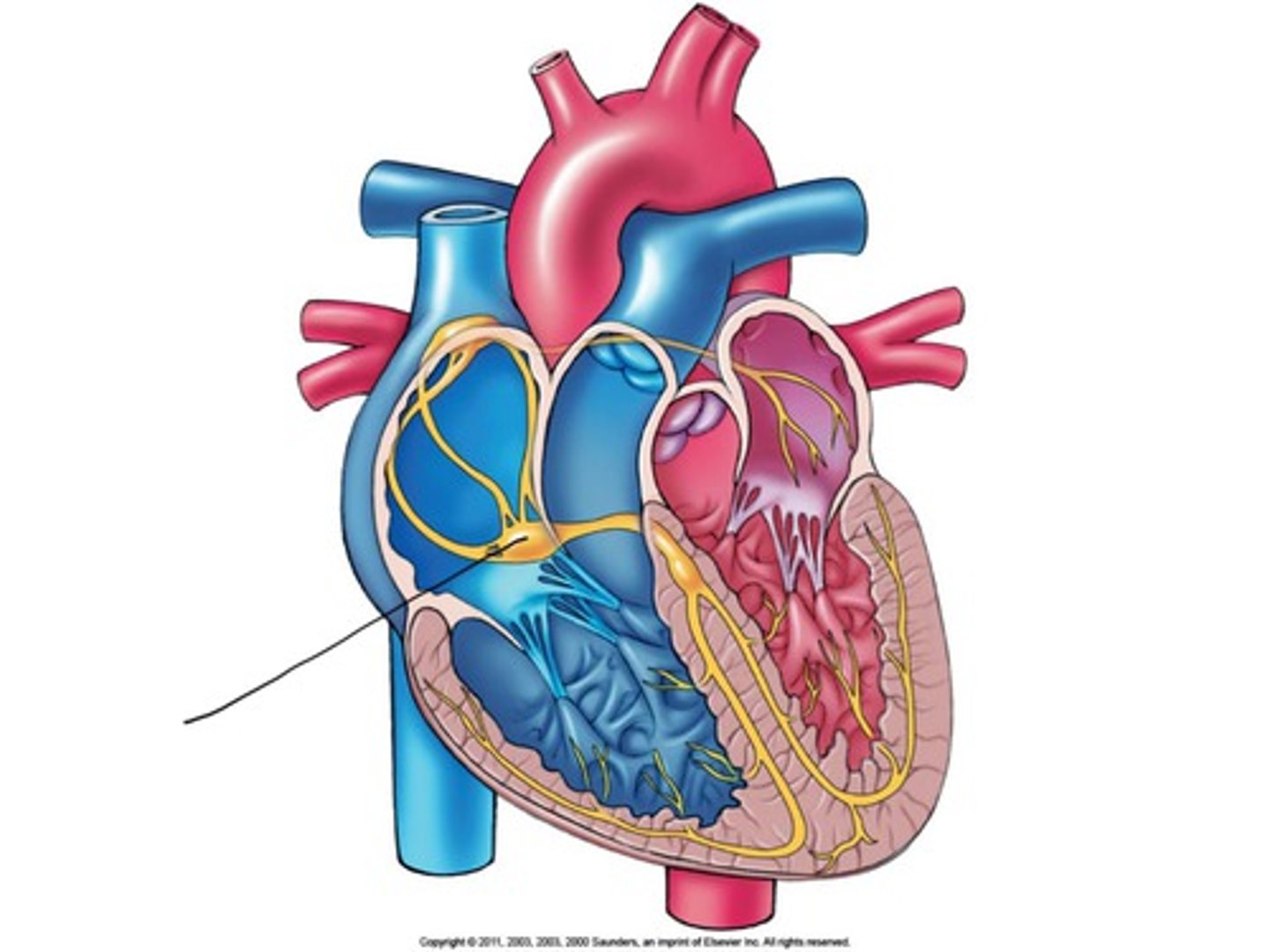
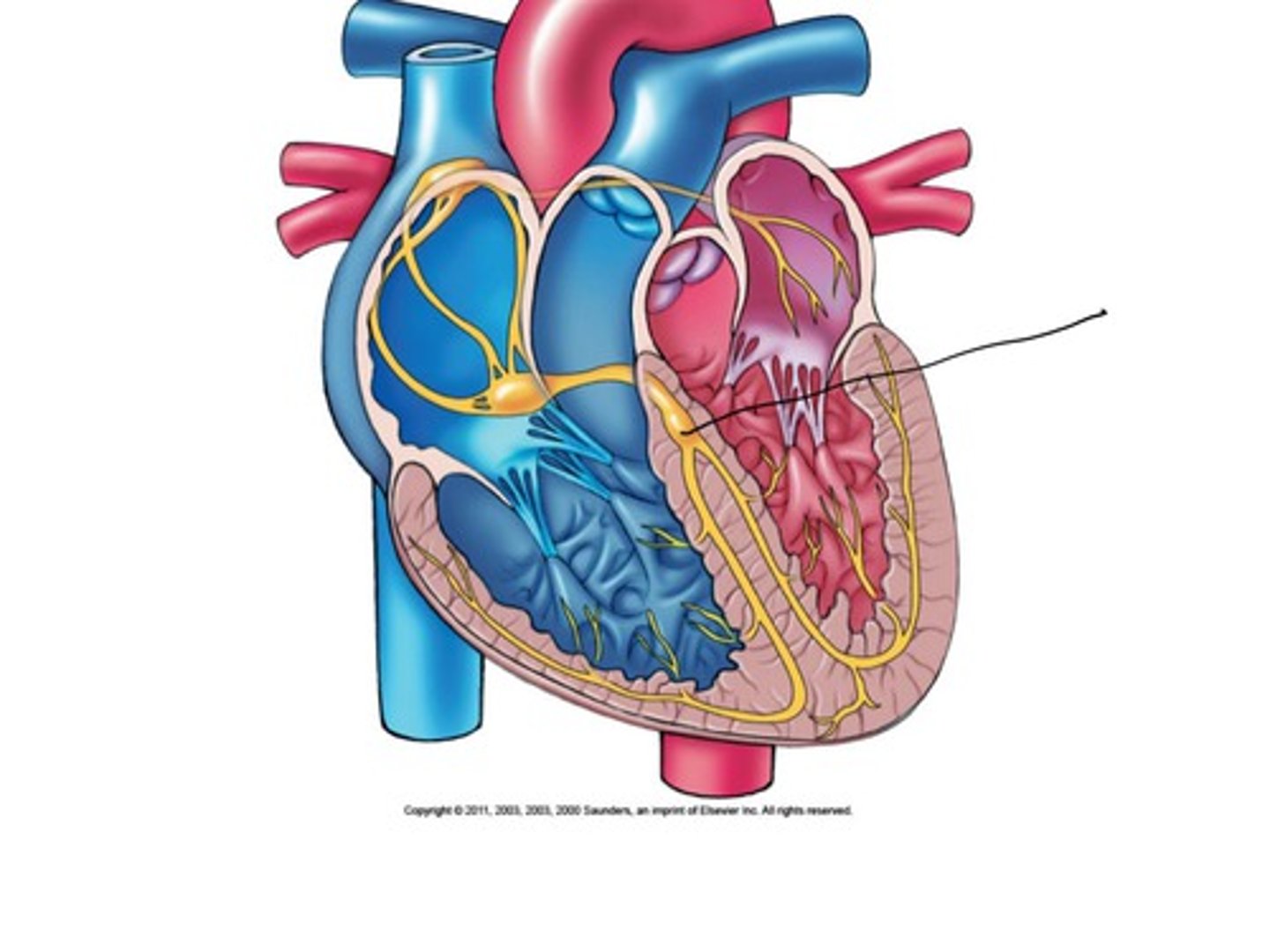
av bundle
bundle of his, located on superior interventricular septum. the only electrical connection between atria and ventricles
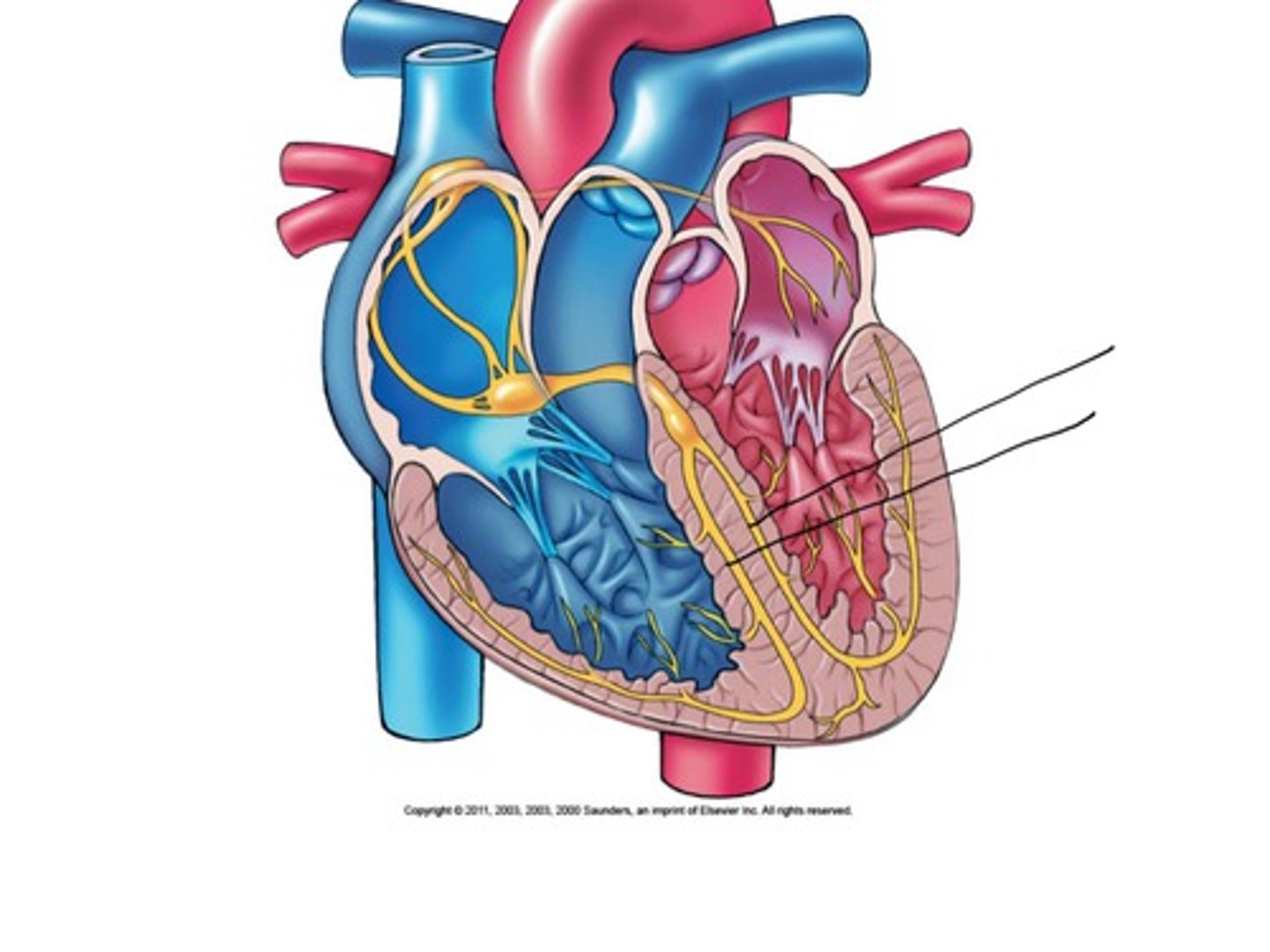
bundle branches
branches of the AV bundle that divide to the right and left sides of the interventricular septum, travel towards apex
purkinje fibers
fibers in the ventricles that transmit impulses to the right and left ventricles, causing them to contract
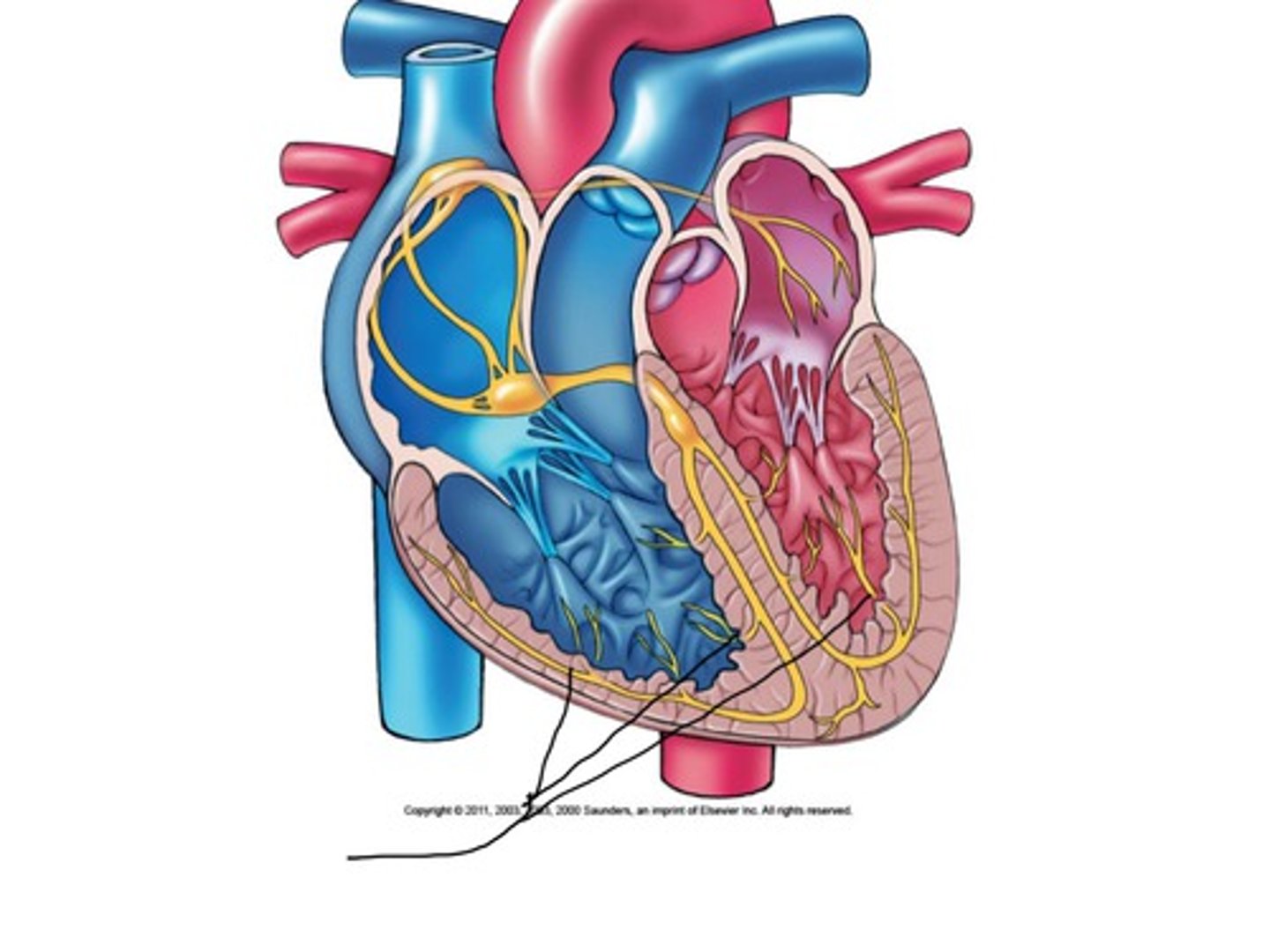
purkinje fibers
penetrate myocardium and are more elaborate in left ventricle. directly supply papillary muscles and allows them to contract before the ventricles
arrhythmias
irregular heart rhythms; uncoordinated atrial and ventricular contractions
ectopic focus
defective sa node, abnormal pacemaker, av node may take over- junctional rhythm
extrasystole
premature contraction, atria or ventricle contracts before sa node initiates impulse
heart block
damaged AV node releases the ventricles from control of the SA node; result is a slower heart rate as ventricles contract at their own rate. partial or total
sympathetic
increases heart rate, medulla oblongata
parasympathetic
decreases heart rate, vagus nerve x
electrocardiogram
recording of the electrical activity of heart, composite of all action potentials. recoded on electrocardiograph
lead
electrodes that detect electrical current, limb leads I, II, III, up to 12
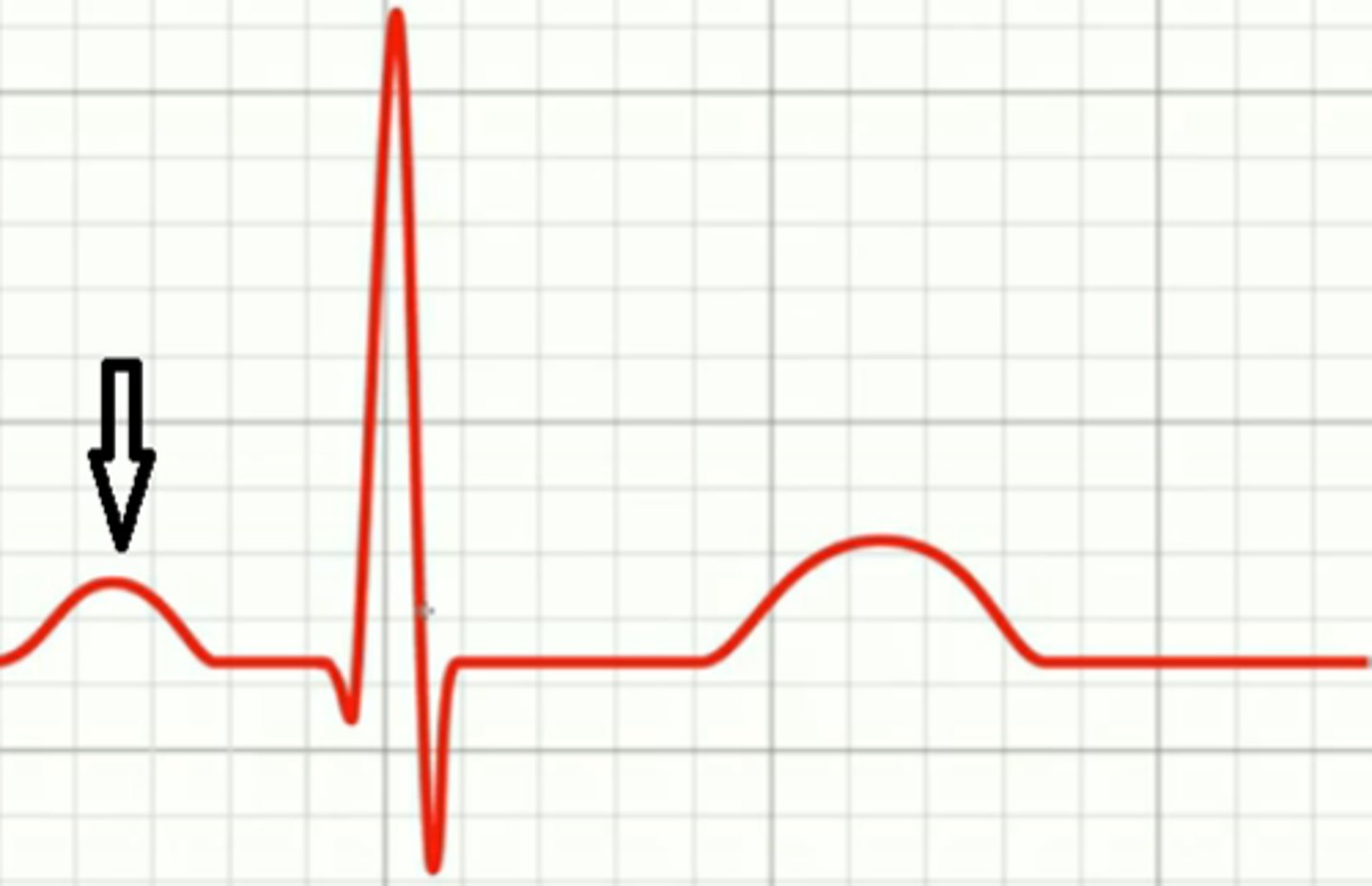
p wave
first deflection, depolarization from sa node through atria, atria contracts shortly after
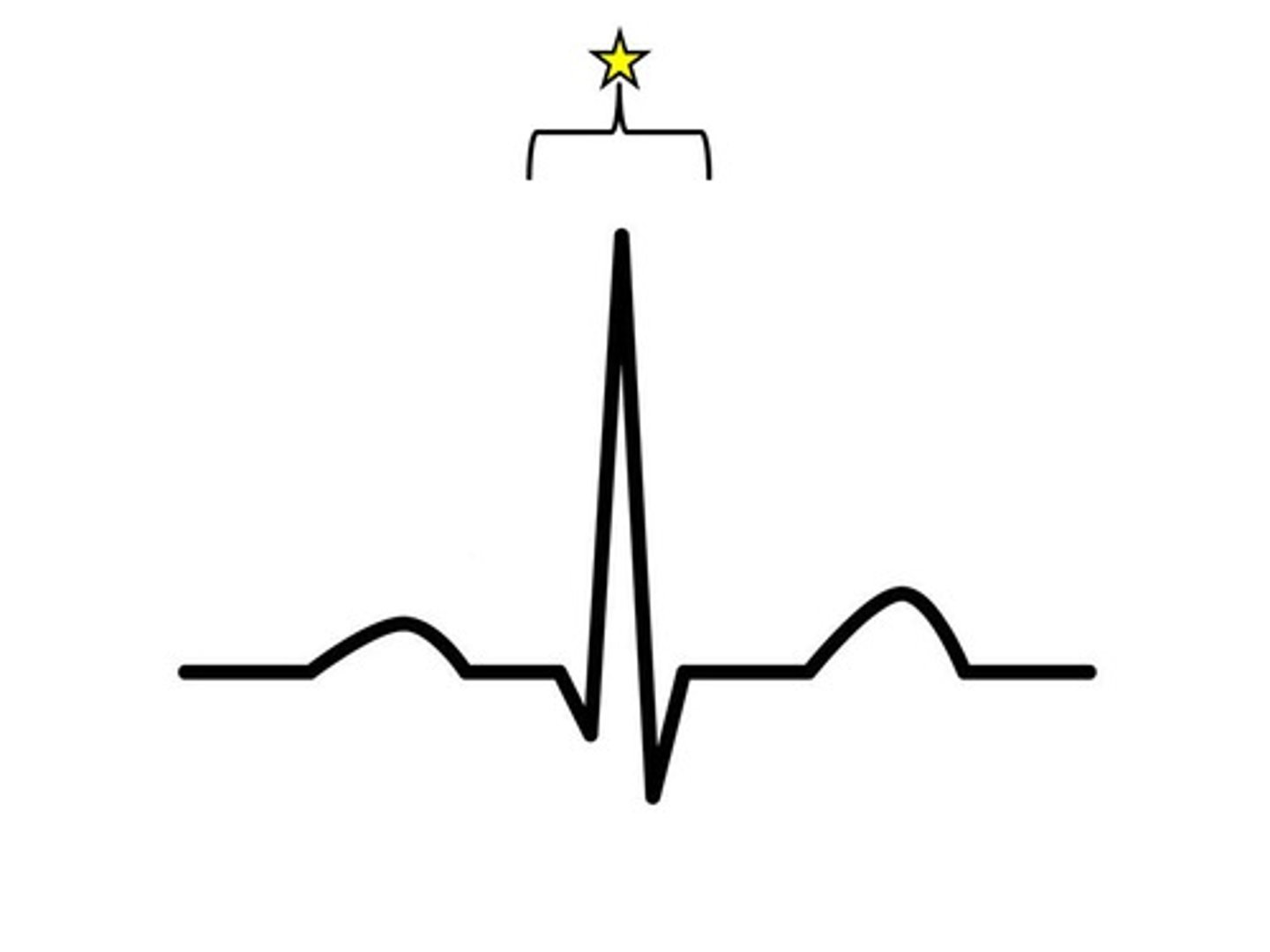
qrs complex
largest deflection, depolarization of ventricles, ventricles contract shortly after
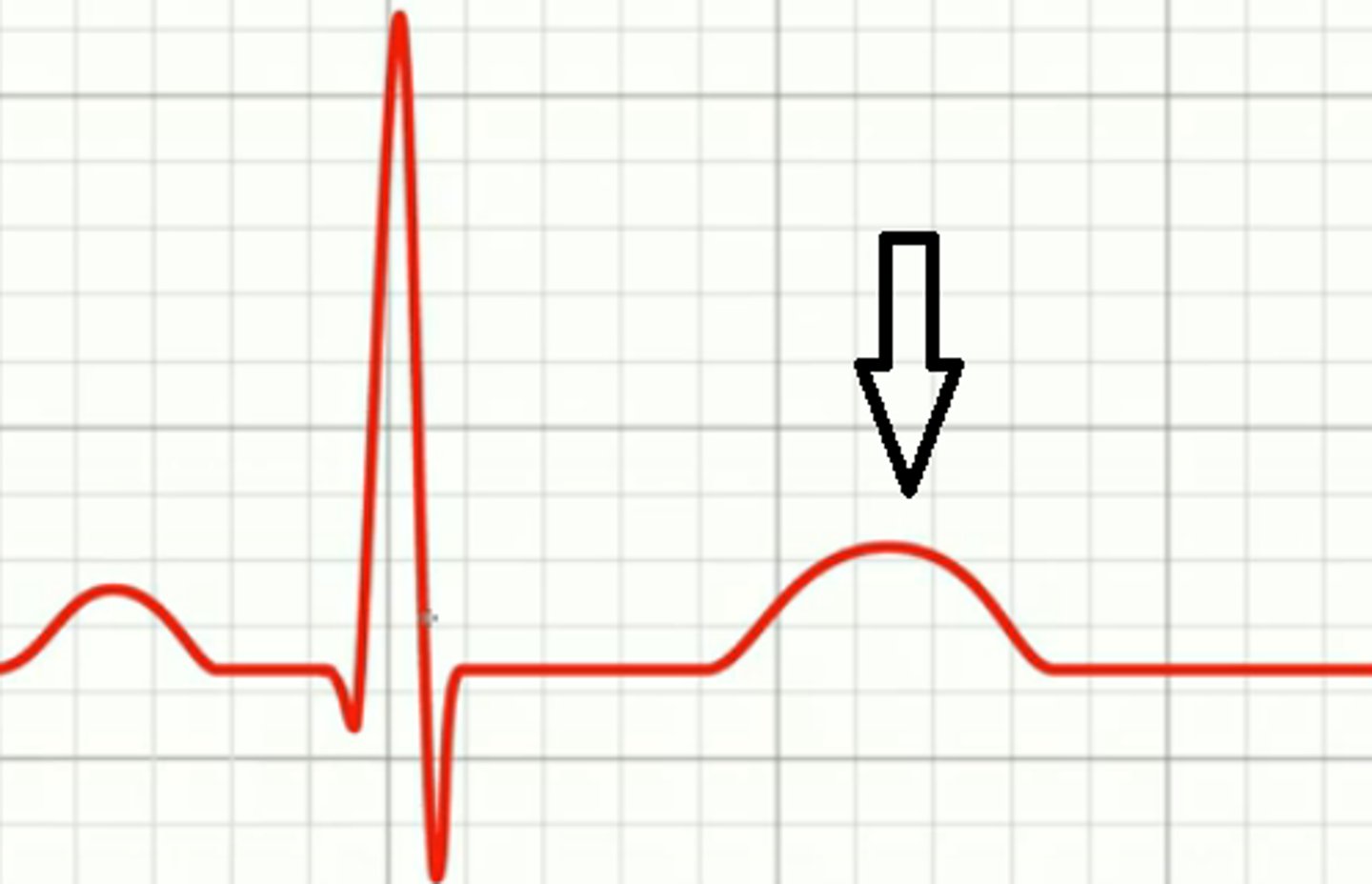
t wave
follows qrs complex, represents repolarization of ventricles
p q interval
beginning of atrial contraction to beginning of ventricular excitation, atrial depolarization through rest of conduction system