ARTH-153 Works (2)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
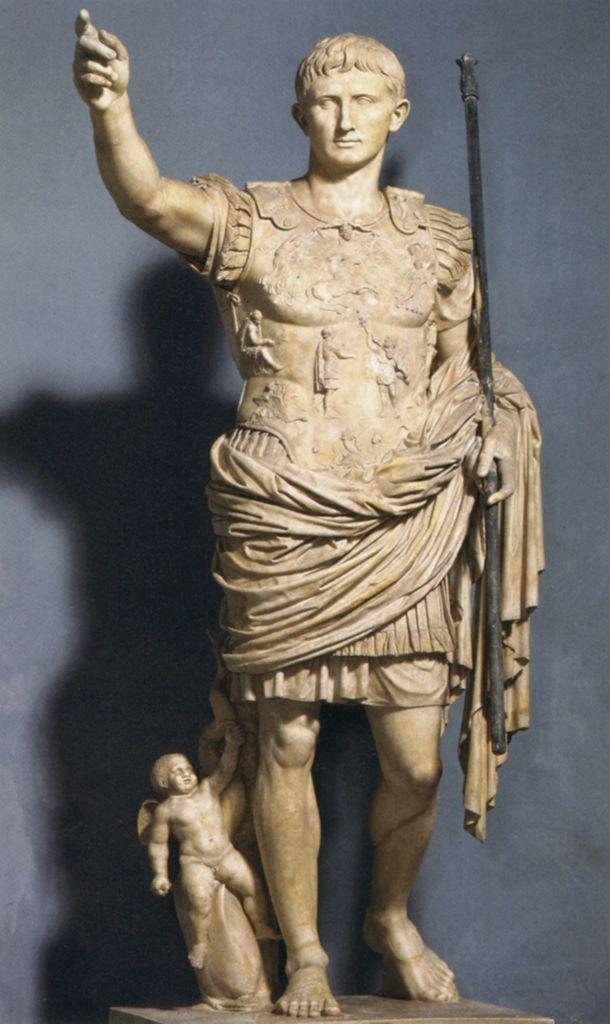

Portrait of Augustus as General
Copy of bronze original
ca. 20 bce
6’8” tall
Rome
Shows Roman interest in portraiture
Celebration of very specific, important individuals
Depicted with the bare feet of a god rather than wearing military boots
Suggests carved in deification
Depicted in contrapposto with idealized, youthful features
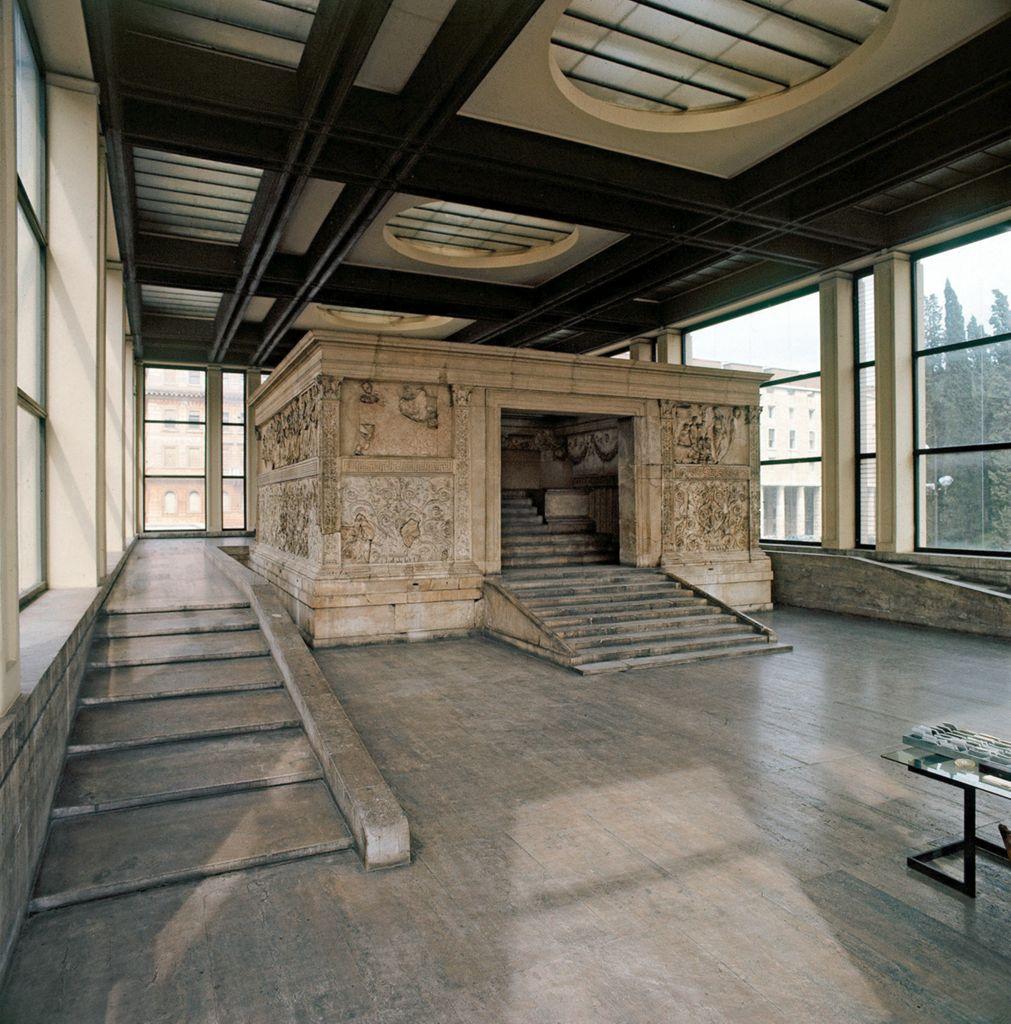

Ara Pacis Augustae (Altar of Augustan Peace)
Rome
13-9 bce
Carrara marble
Dedicated to Pax
Roman goddess of Peace
Layout:
Located on a podium, approached by a staircase, surrounded by an enclosure wall
Decorated with relief sculptures
Exterior divided into two large registers
Separated by a Greek key pattern
Lower register carved with vegetal, demonstrates abundance resulting from Augustan Peace
Upper register carved with historical & mythical propaganda that paints positive view of the emperor
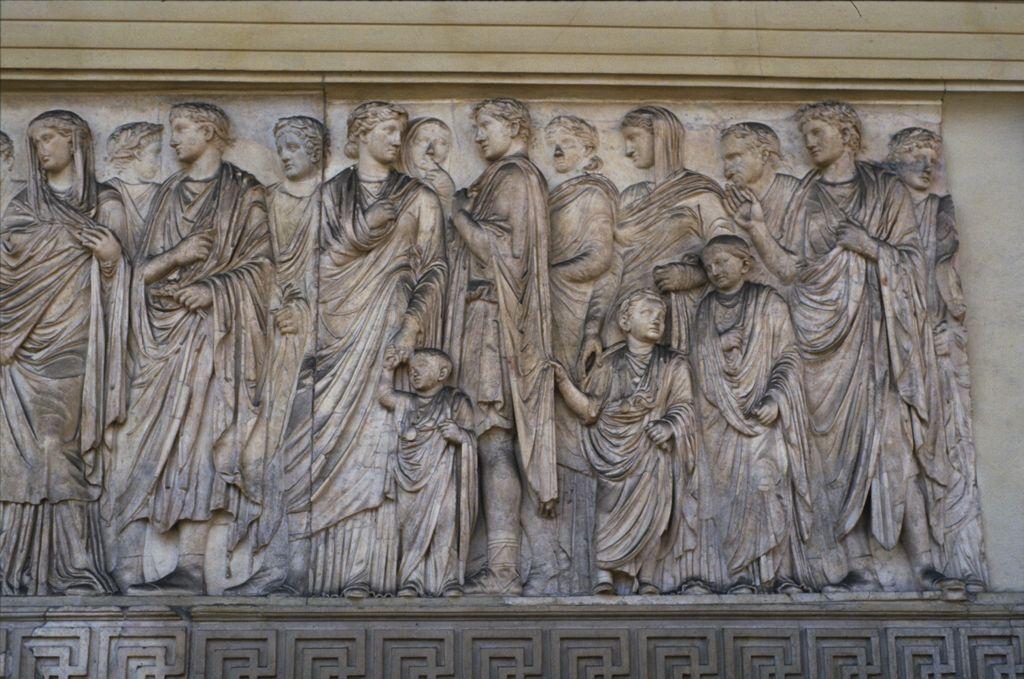

Imperial Family on Ara Pacis
Frieze on the Ara Pacis
Idealized naturalistic depiction of characters
Combines high & low relief to distinguish the foreground from the background
Each has distinct portrait features as opposed to the style of using anonymous figures
Domus Aurea (Golden House)
Built by Severus & Celer
Rome
ca. 64 ce
Belonged to Emperor Nero
Know for his cruel, extravagant behavior and excessive spending
Contrasted with the Republican-minded, modest home of Augustus
Built of confiscated land after the fire devastated Rome
Contained various paintings in different styles
A display of self-indulgence and greed overall
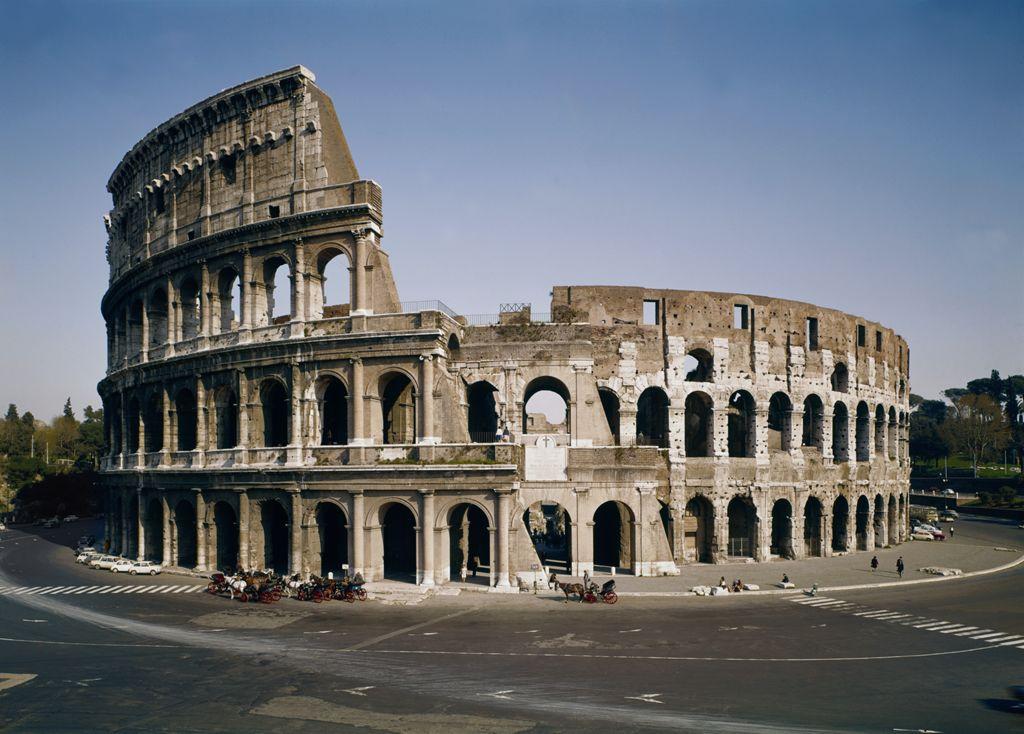

The Colosseum
a.k.a. The Flavian Amphitheater
Begun around 70 ce and completed in 80 ce
Built on the lands that Nero confiscated
Reclaiming the land for the people
Approximately 615 × 510 feet, 159 feet high
76 entrance doors to control the high foot traffic
Seating was ranked
Higher status closer to the arena floor
Mechanical awning partially protected seating during hot or rainy days
Below the floor was a system of passageways and rooms to hold gladiators and wild animals
Architectural Features:
Arcade - a covered walkway made of a series of arches supported by piers
Arches - a curved, symmetrical structure supported on either side by a post, pier, column, or wall, usually a supporting structure
Engaged Column - a column attached to a wall
Pilaster - a flat, rectangular vertical projection from a wall; usually has a base and a capital
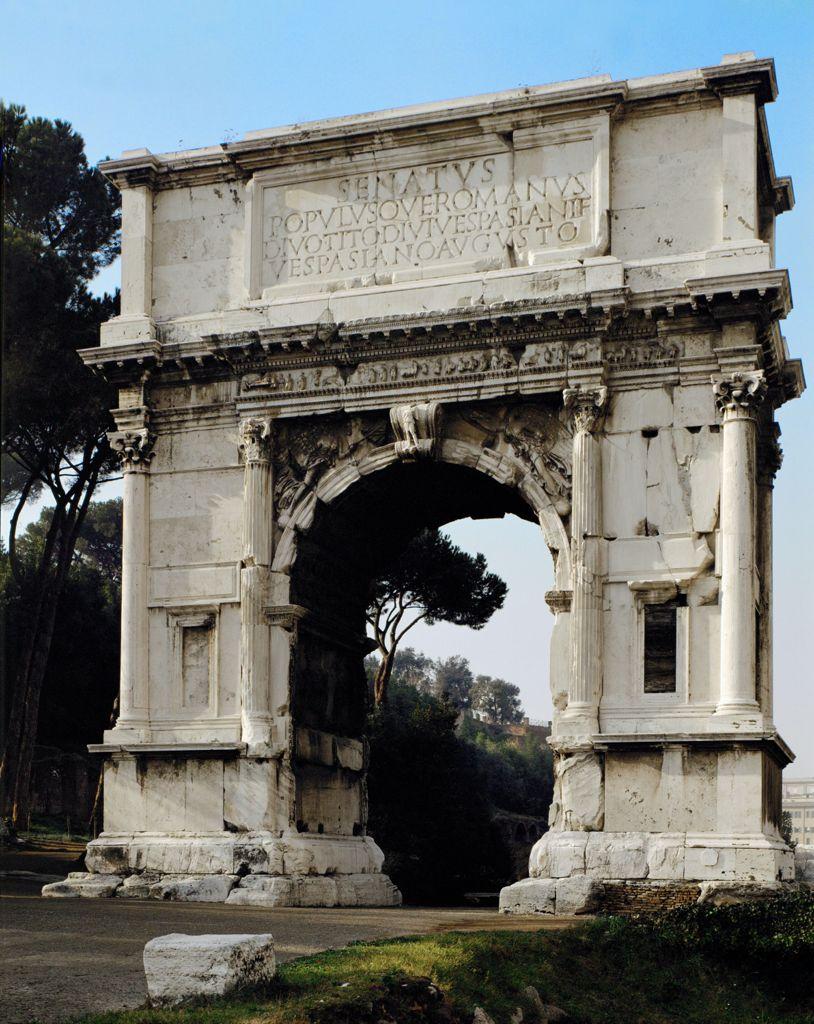

Arch of Titus
Rome
81 ce
50 feet high
Built with concrete and faced with marble
Example of a triumphal arch
a freestanding archway that often spans a road or marks an entrance decorated with relief carvings alluding to a historical, often military, victory
Served the sole function of being visual propaganda
Created after Titus’ death by his brother and successor to commemorate his victories in the Jewish Wars
Arch is located in along the route of major processions in the city
Ensures all future processions are literally in the shadow of Titus’ victory
Employs a combination of perspective, and high/low relief for 3D effect
Architectural Features:
Attic - on a facade or triumphal arch, the section above the frieze decorated with painting, sculpture, or an inscription
Spandrel - the almost triangular space between the outer curve of an arch, a wall, and the ceiling or framework
Barrel Vault - a semi-cylindrical ceiling the consists of a single curve
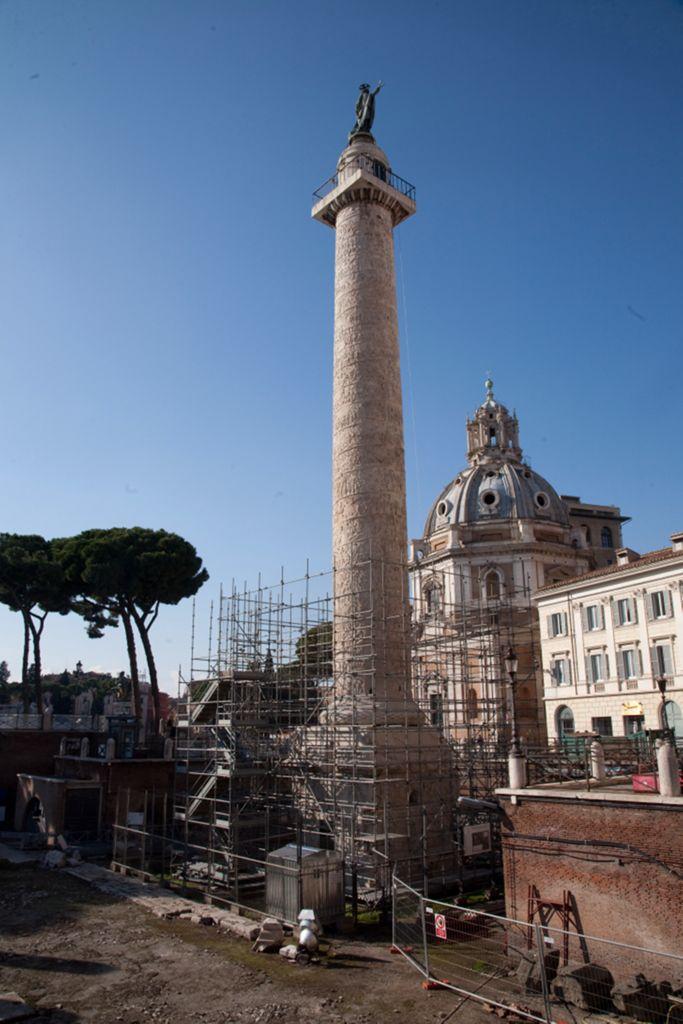

Column of Trajan
Rome
110 ce
128 feet high
Built to commemorate Trajan’s victorious Dacian campaigns
Relief sculpture on the column unfolds in a 625 foot spiral from the bottom to the top
Includes scenes of preparation for battle and construction of forts
Vivid battle scenes and numerous views of Trajan
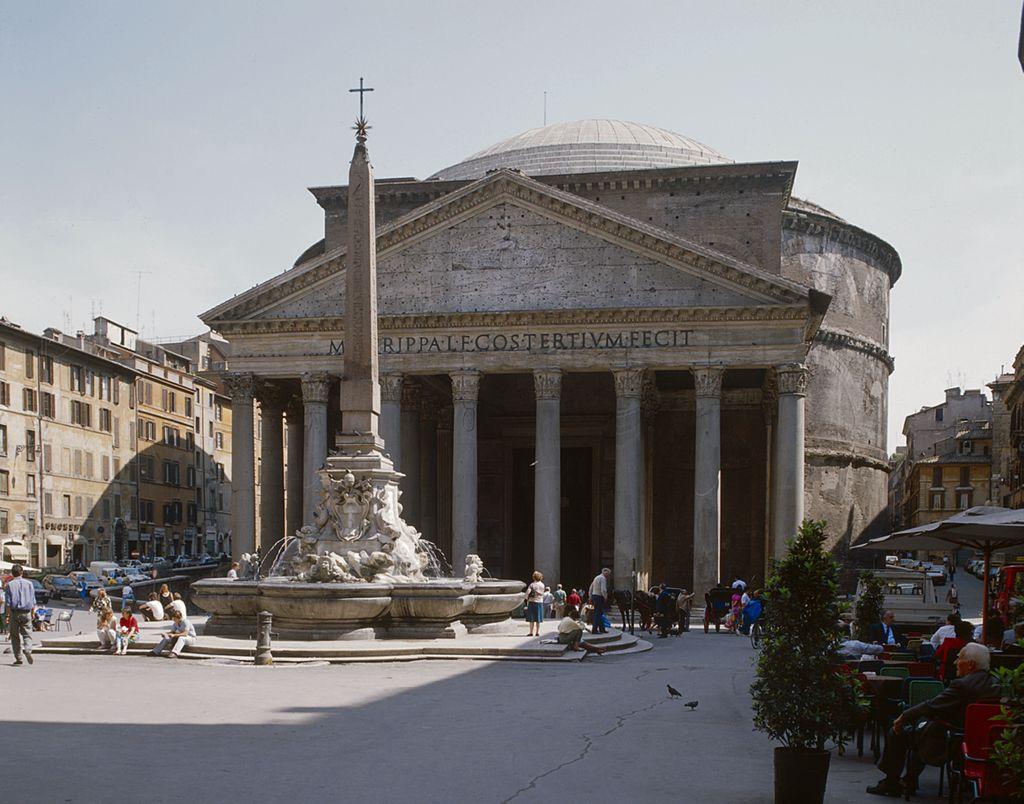

Pantheon
Rome
110-28 ce
Mixes Hadrian’s fondness for classical Greek architecture on the facade and the Roman engineering on the interior
Name stems from the phrase “every god”
Implies the temple was dedicated to all the gods of Rome
Some evidence suggests it was associated with the divine authority of the emperors
Architectural Features:
Drum - a wall, most often cylindrical, that supports a dome
Dome - a roof that projects upward in the shape of the top half of a sphere
Rotunda - a cylindrical building, or a cylinder-shaped room within a larger building
Oculus - a round, eye-like opening in a ceiling or roof
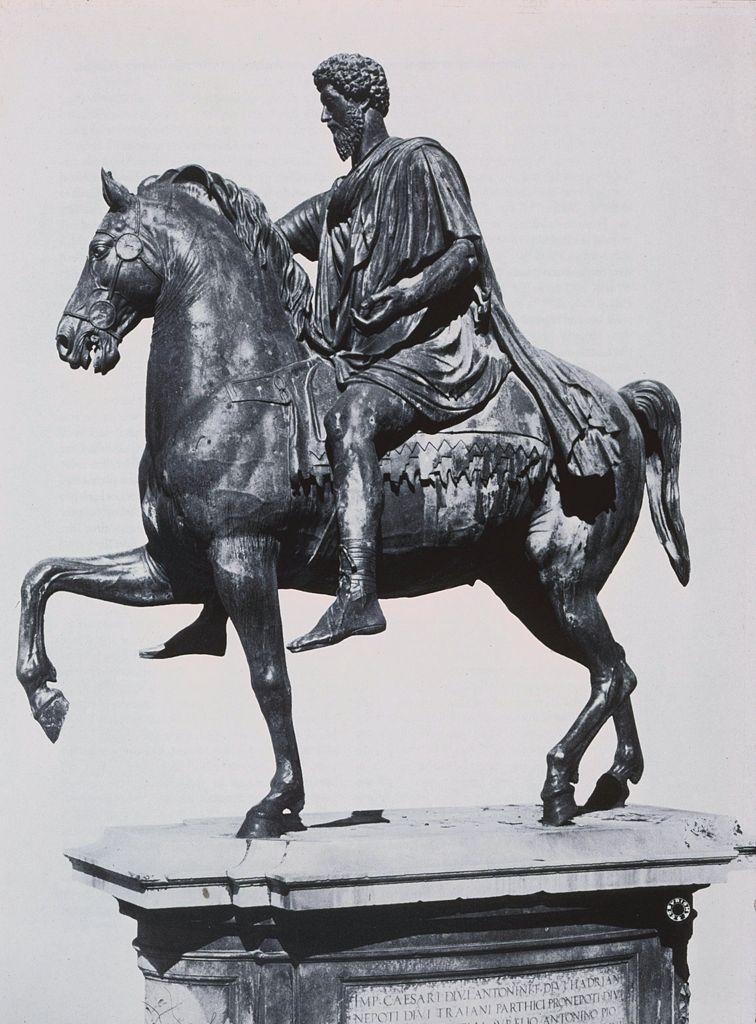

Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius
Rome
175 ce
Stands 11ft. 6in. high
Made of gilded bronze
Marcus Aurelius wears the tunic and cloak of the leader of the army but bears no weapons or armor
Depicted with one hand extended
Likely addressing a crowd
Scale demonstrates his power
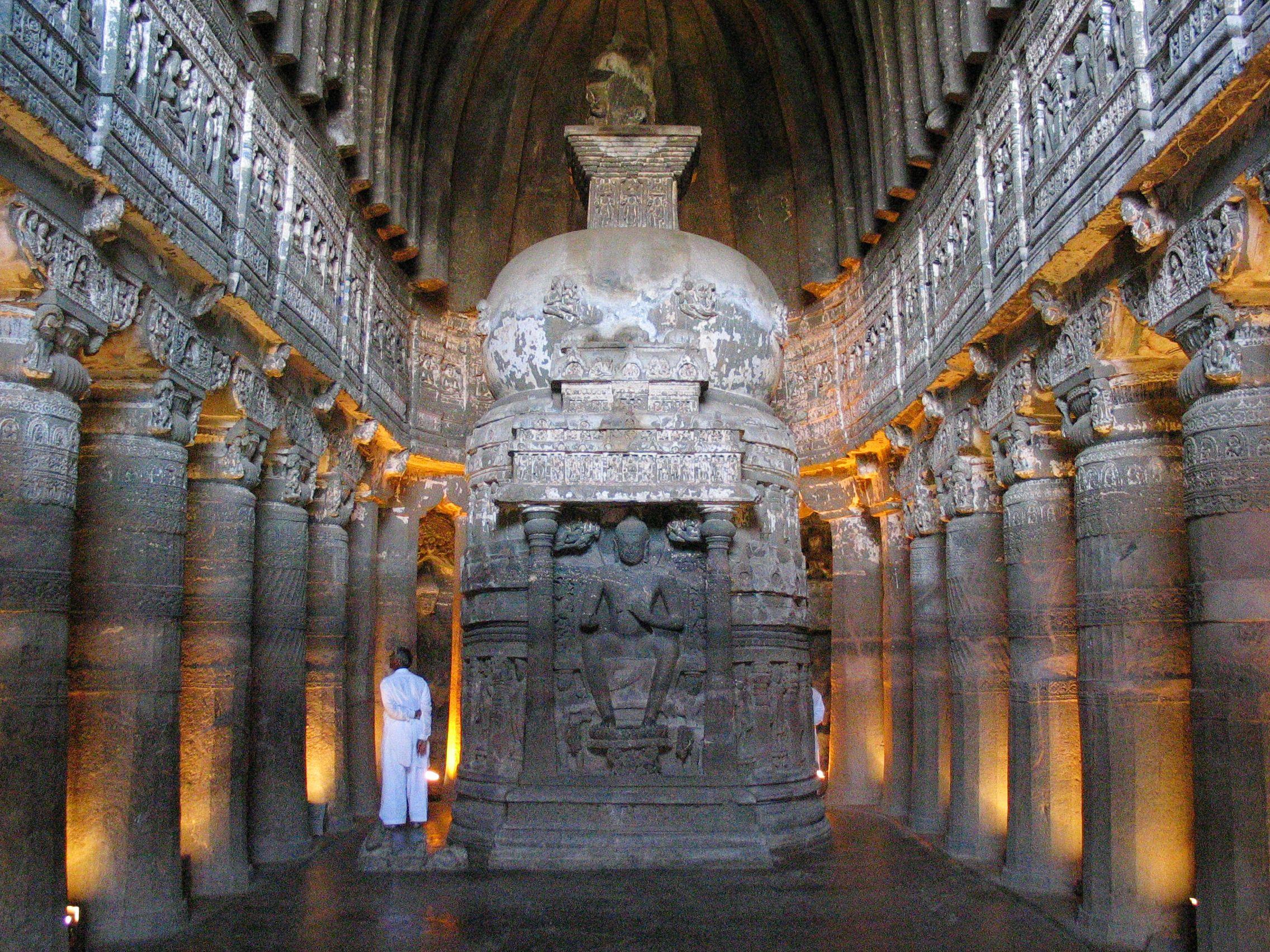
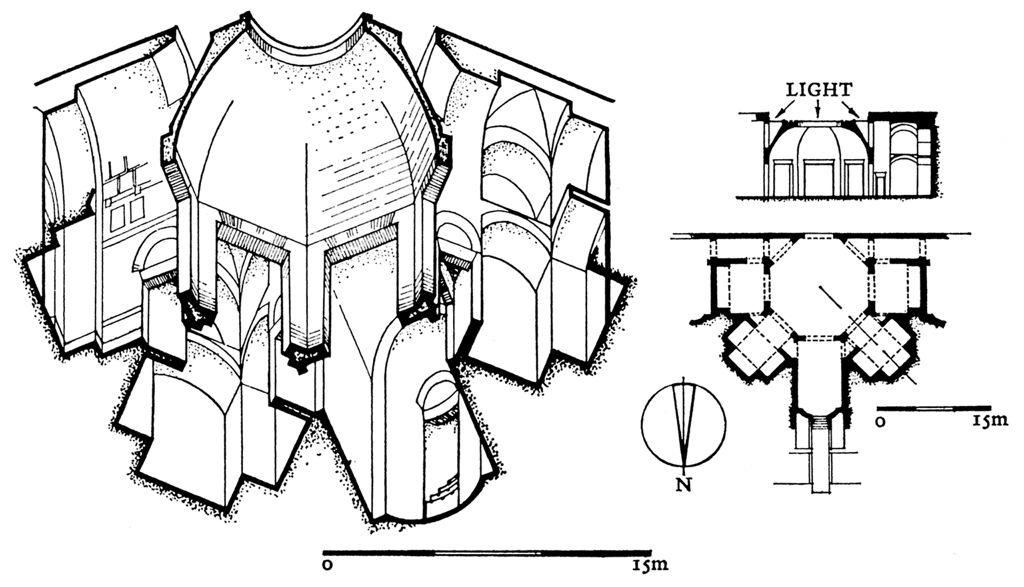
Buddhist Caves at Ajanta
Ajanta
100 bce - 500 ce
Traces of both Buddhist and Hindu faiths
Rock-cut Architecture - carving of rock out from where it naturally occurred
Two main types:
Viharas - a retreat for Buddhist monks and nuns
Chaitya - a Buddhist prayer hall with a stupa at one end
Teotihuacan Goddess Mural
Teotihuacan, Mexico
550-650 ce.
Public art here had a more geometric style than elsewhere in Mesoamerica
Used the true fresco technique
Painting directly on a wet plaster surface
Features:
Frontal pose
Water motifs
Greenstone mask with fanged teeth in place of face
Feathered headdress
Teotihuacan Pyramid of the Sun
Teotihuacan
150 ce.
200ft. tall and 700ft. wide
Base of approximately 12 acres
Once surrounded by a man-made canal
Important religious center
Temple of the Feathered Serpent
Teotihuacan
225 ce.
Smaller than the temple of sun and moon
Makes up for its size with elaborate sculptural decorations on its facade
Architectural profile called talud-tablero
Depicts a feathered serpent with seashells
Merges the land, sky, and water