UNL CHEM 109 EXAM 4
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Covalent Bonding
The sharing of a valence electron between atoms. They hold the atoms together by attracting the nuclei of both atoms
Ionic Bonding
The transfer of a valence electron from one atom to another. The atoms bond through electrostatic attraction between the anion and cation
lattice energy
The energy required to convert a mole of ionic solid to its constituent ions in the gas phase
Lattice Energy Formula
F ∝ charge / distance^2
F ∝ Q1 x Q2 / r^2
3 trends of Lattice energy
1) Larger ions = bigger distance = weaker attraction
2) Larger charge = stronger attraction
3) Stronger the attraction => larger the lattice energy
Is Ion Charge or Size more important in determining lattice energy
Ion charge
Born- Haber Cycle
A hypothetical series of reactions that represents the formation of an ionic compound from it's constituent elements
Born Haber Cycle Equation
∆Hf˚ = Δsub + Δdiss + IE + EA + ΔHlattꝋ
∆Hf˚ = enthalpy of formation
sub = sublimation
diss = dissolution
IE = ionization energy
EA = electron affinity
Lewis theory of bonding
a chemical bond involves atoms sharing electrons
Lewis Structure
A representation of covalent bonding in which shared electron pairs are shown as dashes between to atoms
Bond Length
The distance between the nuclei of 2 covalently bonded atoms in a molecule
Bond Length Trend
The higher the number of bonds in a molecule, the shorter the bond length
Two attractive forces in covalent bonds
1) The intramolecular bonding force that holds the atoms together in the molecule
2) The intermolecular forces between molecules
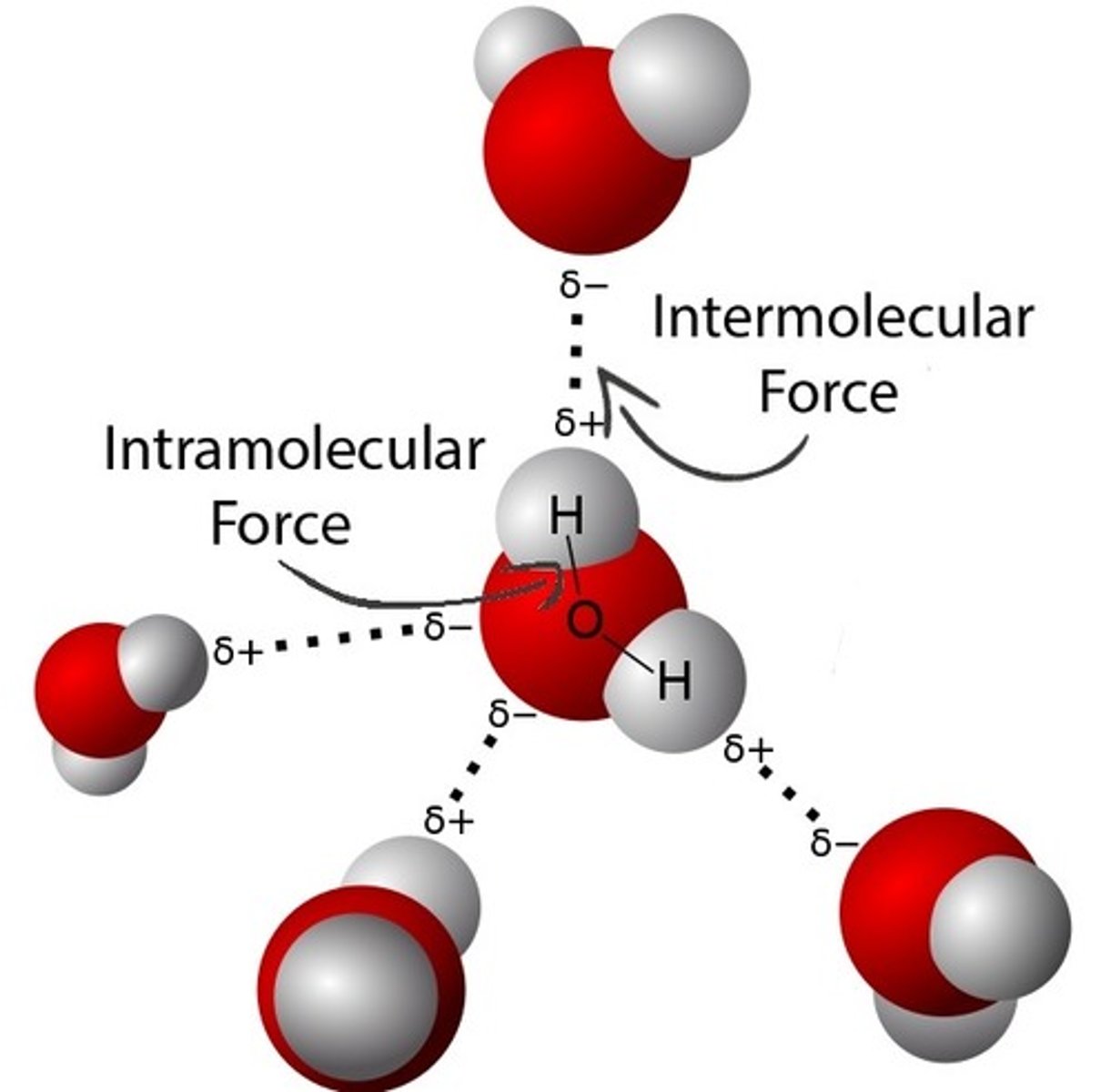
Are intermolecular bonds or intramolecular bonds stronger?
Intramolecular
3 characteristics of covalent compounds
- Usually gases, liquids or low melting solids
- Insoluble in water
- Non-conductive
Why are ionic compounds usually solid at room temperature?
Because the electrostatic attraction is usually very strong
3 characteristics of ionic compounds
- They have a high melting point
- Soluble
- Conductive
bond polarity
The extent to which electrons are equally shared between 2 atoms
polar bond
Where the valence electrons spend more time with one atom
non-polar bond
Where there is an equal sharing of valence electrons between two atoms
trend in electronegativity
Electronegativity increases to the right and up the periodic table
Electronegativity
the ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound
ionization energy
The energy required to remove an electron from an atom
Nonpolar bonds are
A bond between atoms whose electronegativities differ by less than 0.5
Polar bonds are
A bond between atoms who's electronegative differ by the range of0.5 to 2.0
Do ionic bonds or covalent bonds have higher bond polarity?
Ionic bonds
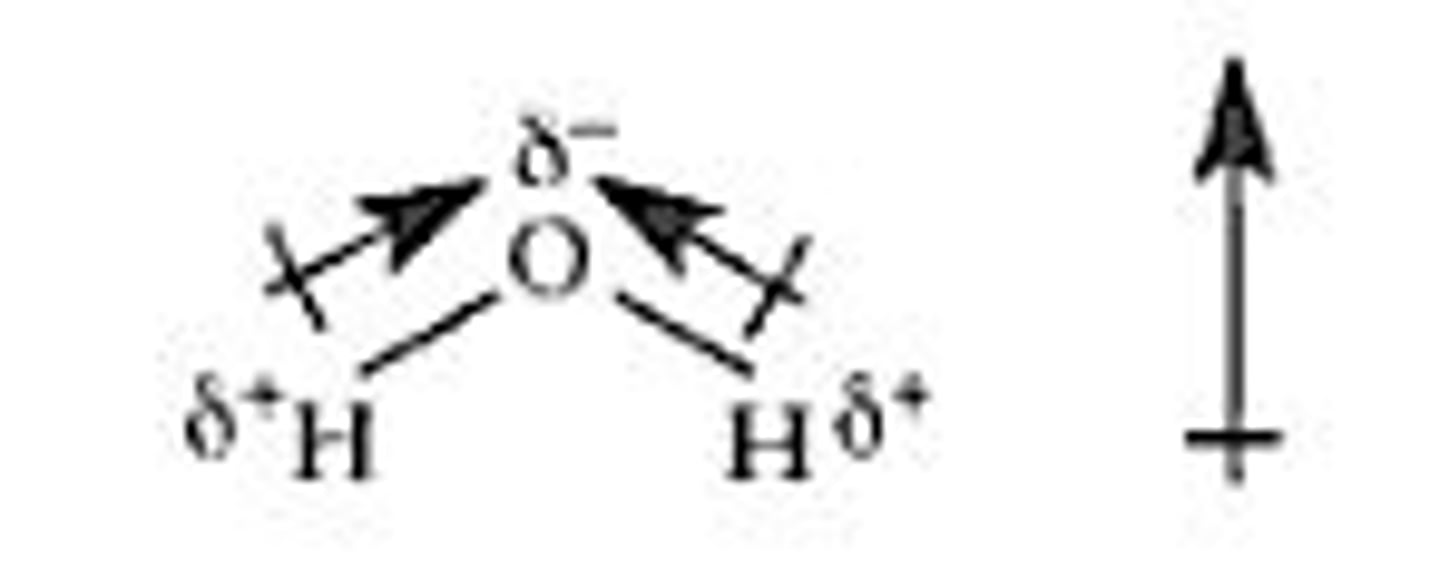
dipole moment
A quantitative measure of the polarity of a bond
How is dipole moment represented?
With an arrow extending from a plus sign, extending from the lower to the higher electronegativity
equation for a dipole moment
µ = Q x r
µ = Dipole moment (>0)
Q = the magnitude of partial charges
r = distance
units for a dipole moment
Debye units (D)
1 Debye unit =
3.336 x 10^-30 C.m
Formal Charge
The overall charge of a molcule
Formal Charge Formula
Formal charge = valence electrons -{bonds+dots}
Which lewis structures are preferred?
-most atoms without formal charge
-lowest magnitude of formal charges
-if there is a negative formal charge, its on the most electronegative atom
Resonance Structures
The different potential lewis structures of a molecule
Resonance Hybrid Structures
A combination of resonance structures that represent reality
Octet Rule
That most atoms want 8 valence electrons and they will react with other atoms to get them
3 exceptions to the octet rule
1) Free radicals - ions or molecules with an odd number of electrons
2) Electron deficient atoms that have less than 8 valence electrons
3) Expanded octet atoms have more than 8 valence electrons
characteristics of free radicals
They are extremely reactive and are excellent oxidizing agents because they accept electrons
What molecules can be electron deficient
Any molecule with boron as the central atom
What atoms can have an expanded octet
Any atom on the third row or below on a periodic table
Bond Enthalpy
The enthalpy change associated with breaking a particular bond in 1 mole of gaseous molecules
How do you measure the stability of a molecule
Using the average bond enthalpy
Bond Enthalpy Equation
∆H˚ = ∑(BE of reactants) - ∑(BE of products)
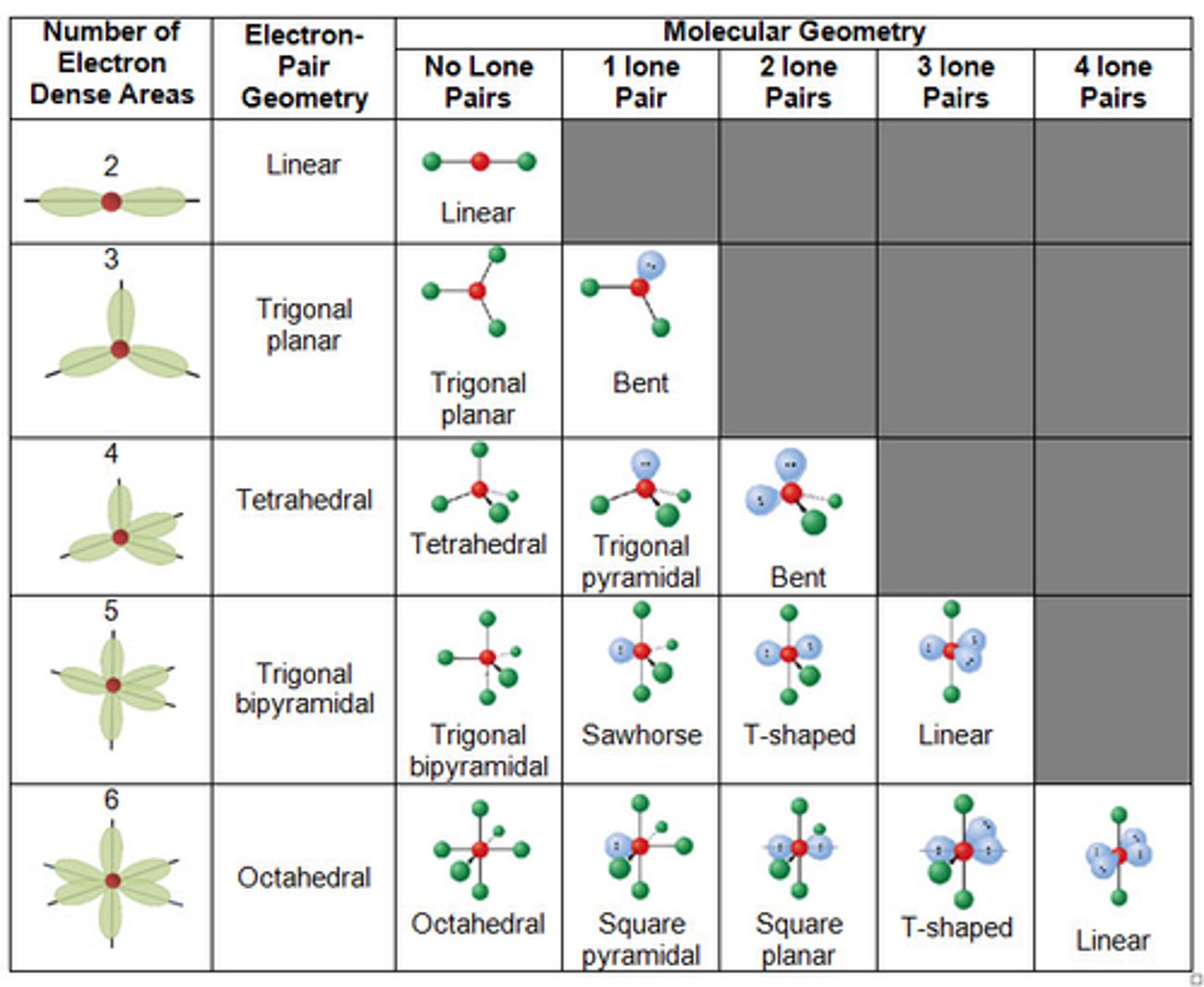
VSEPR
The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory
VSEPR theory
That molecules adopt the shape tat minimizes the electron pair repulsion
How to determine the molecular shape
The relative repulsion between electron pairs around the central atom
Molecular Geometry
More specific shape and based off lone pairs. Seesaw, T shape, Bent etc.
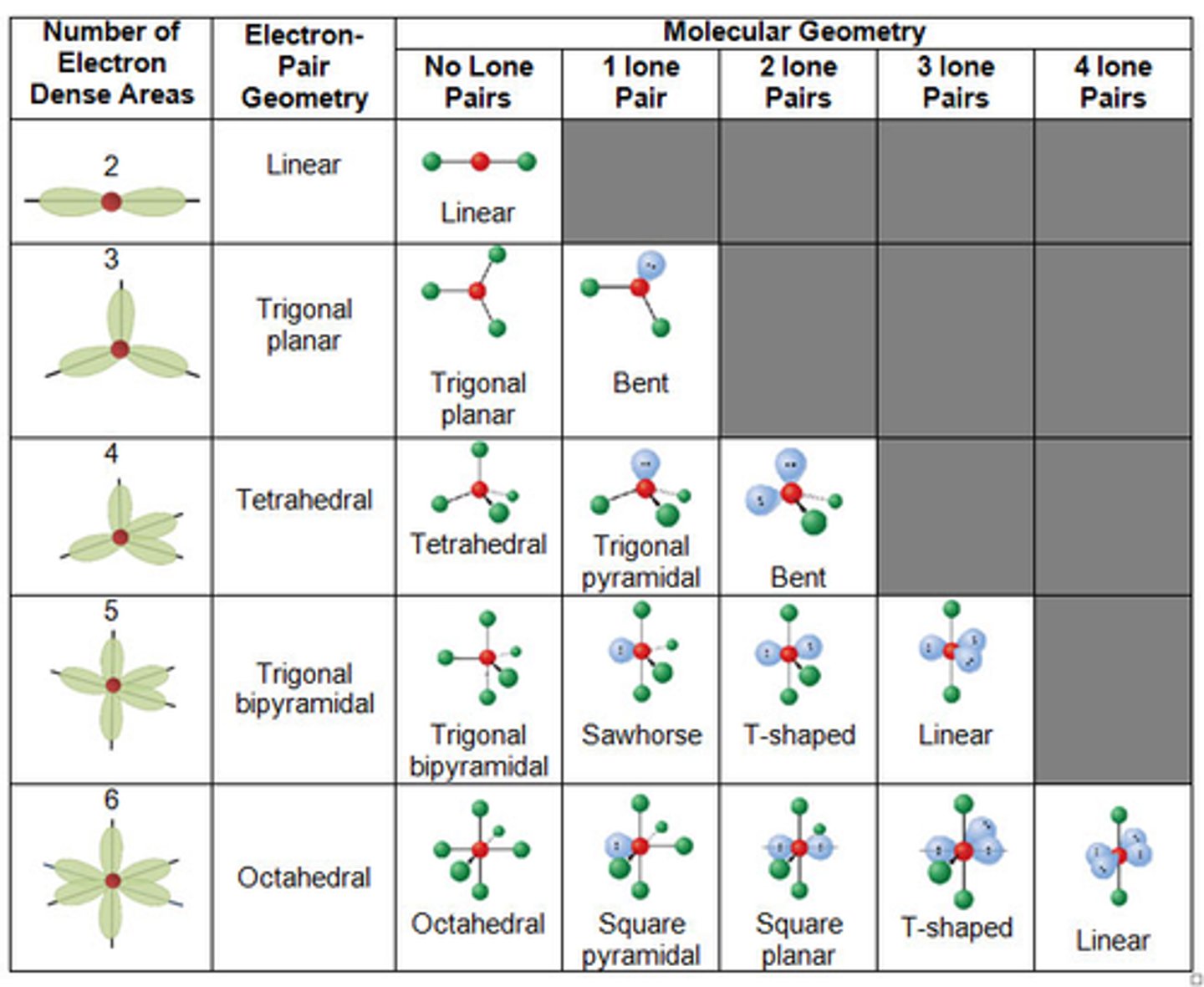
Electron Domain Geometry
The First Shape in the Group, the broad category. Linear, Trigonal Planar, Tetrahedral, Trigonal Bipyramidal, Octahedral
difference of 0-0.5 electronegativity
That the bond is non-polar
difference of 0.5-2 electronegativity
That the bond is polar
What does a difference of >2 in electronegativity mean between two bonded atoms
That the bond is ionic
Structural Isomers
Molecules that have the same chemical formula but different arrangements of atoms
valence bond theory
States that atoms share electrons when their atomic orbitals overlap. The two shared electrons in the overlapping orbitals must have opposite spin. Formation of a bond lowers the potential energy of the system and helps the atoms in the bond achieve higher stability.
What are the 2 downsides of the valence bond theory?
1) It gives us a visualization but doesn't describe bonding
2) It does not account for the shapes of most molecules
Hybridization
Where atomic orbitals mix together to form hybrid orbitals that arrange themselves in the same way as the repulsions in the VESP theory
Can double bonded molecules freely rotate? (pi bonds)
No, they are restricted in their position
cis-trans isomers
same covalently bonded atoms but differ in spatial arrangement . cis= both on top. trans= opposite sides
pure covalent bond
neutral atoms held together by equally shared electrons
polar covalent bond
A covalent bond in which electrons are not shared equally
ionic bond
Oppositely charged ions held together by electrostatic attraction
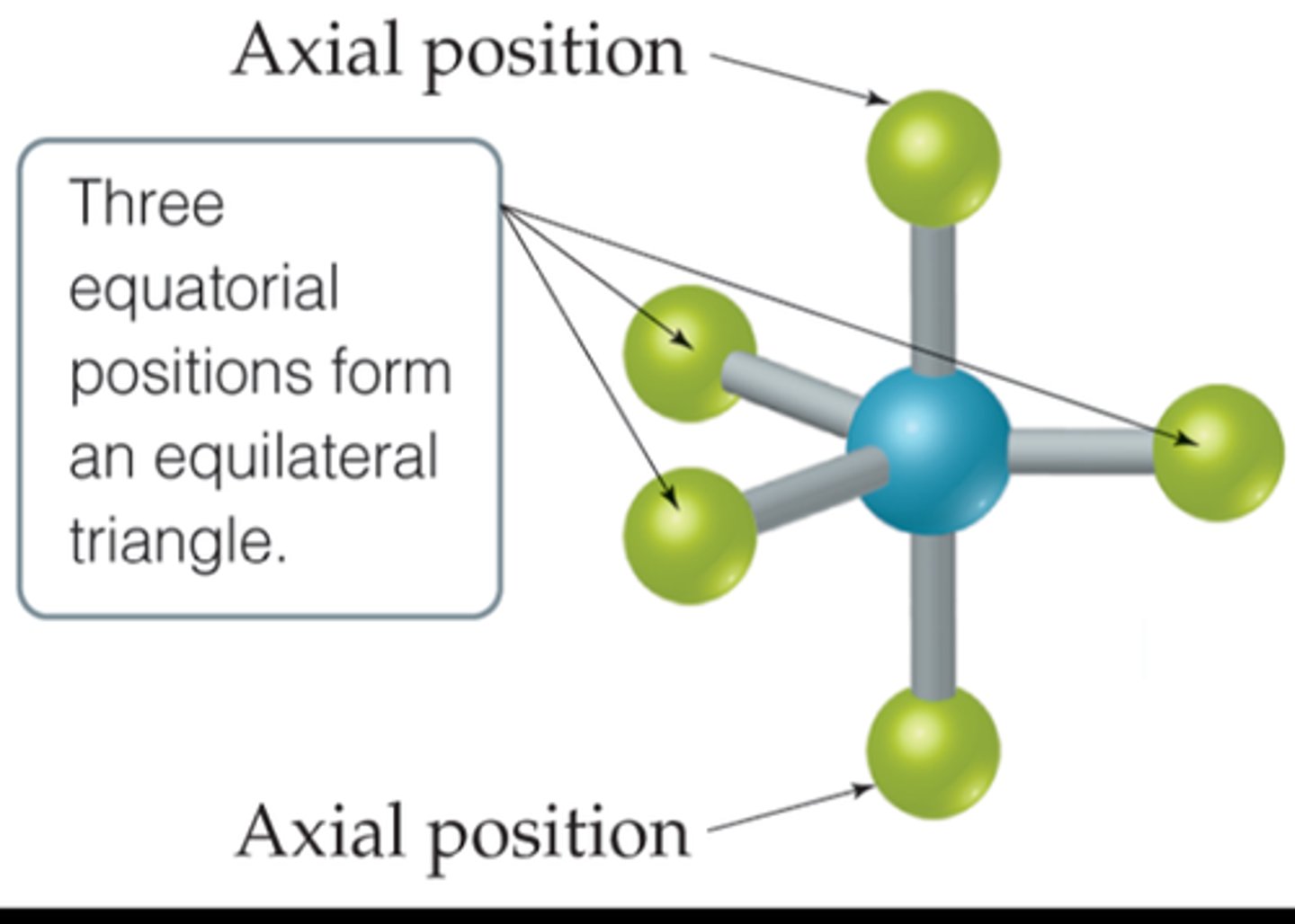
axial positions
The positions above and below the central atom
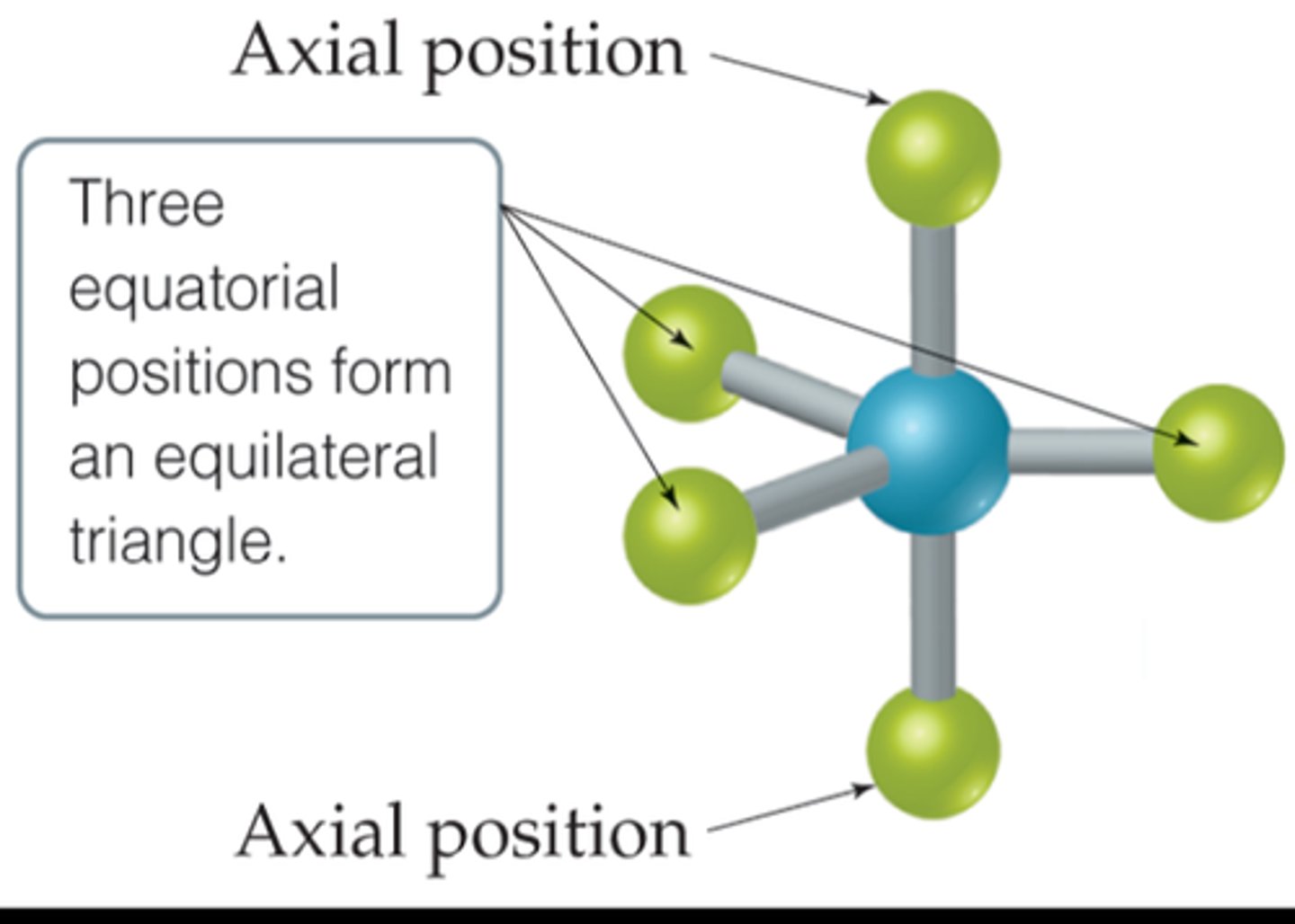
equatorial position
one of the three positions in a trigonal bipyramidal geometry with 120° angles between them; the axial positions are located at a 90° angle