4. Small intestine
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Small intestine
Duodenum, jejunum, ileum
Physiologically similar between species
Digestion, absorption, endocrine, immune defence
Motility functions
Mixing chyme with digestive enzymes
Maximise contact with mucosa for absorption
Propelling chyme to large intestine
Names of 3 small intestine movements
Mixing contractions
Propulsive contractions
Migrating myoelectric complex
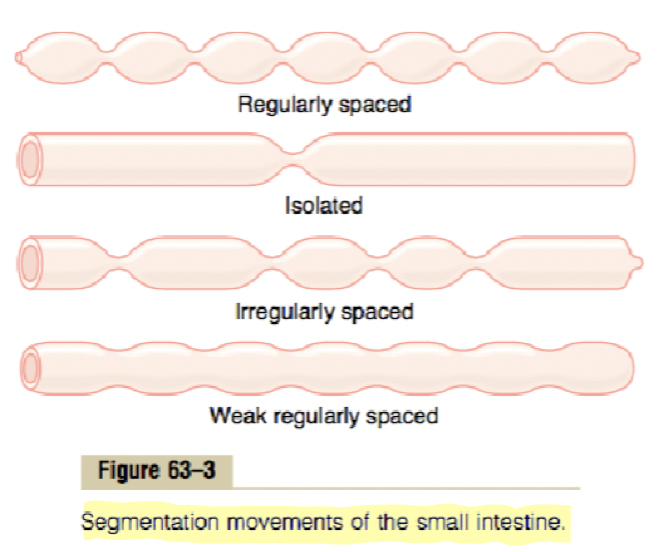
Mixing contractions (segmentation contractions)
During food intake
Triggered by chyme presence + wall stretching
Short and at regular intervals
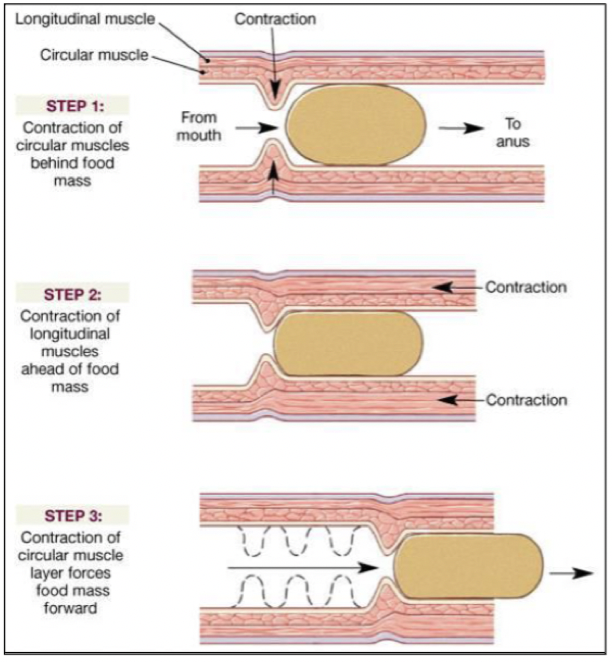
Propulsive contractions (peristalsis)
During food intake
Slow migration of contents to large intestine
Migrating myoelectric complex (MMC)
Cleans intestine during fasting
Moves undigested food and bacteria to large intestine
Motilin stimulates MMC via enteric + autonomous NS
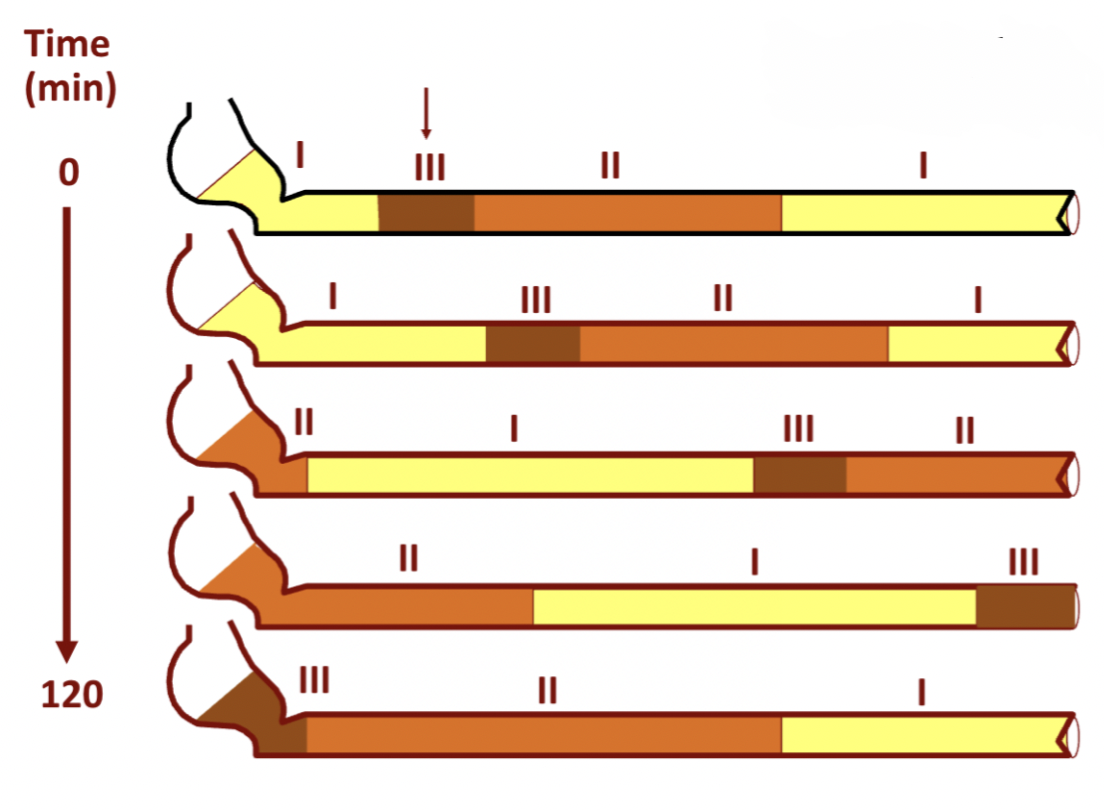
Phases of migrating myoelectric complex
Phase 1 - period of resting, no contractions
Phase 2 - increased frequency of action potentials + small intestine contractions, irregular mixing contractions
Phase 3 - peak electrical + mechanical activity, strong contractions for propulsion
Regulation of small intestine motility
Stimuli - wall stretching, gastroenteric reflex, parasympathetic (Ach increase motility), sympathetic (decreases motility)
Hormonal - increases (gastrin, CCK, insulin, motilin, serotonin…), decreases (secretin, glucagon…)
What are pancreatic secretions produced by in the small intestine
Acinar and centroacinar (duct) cells
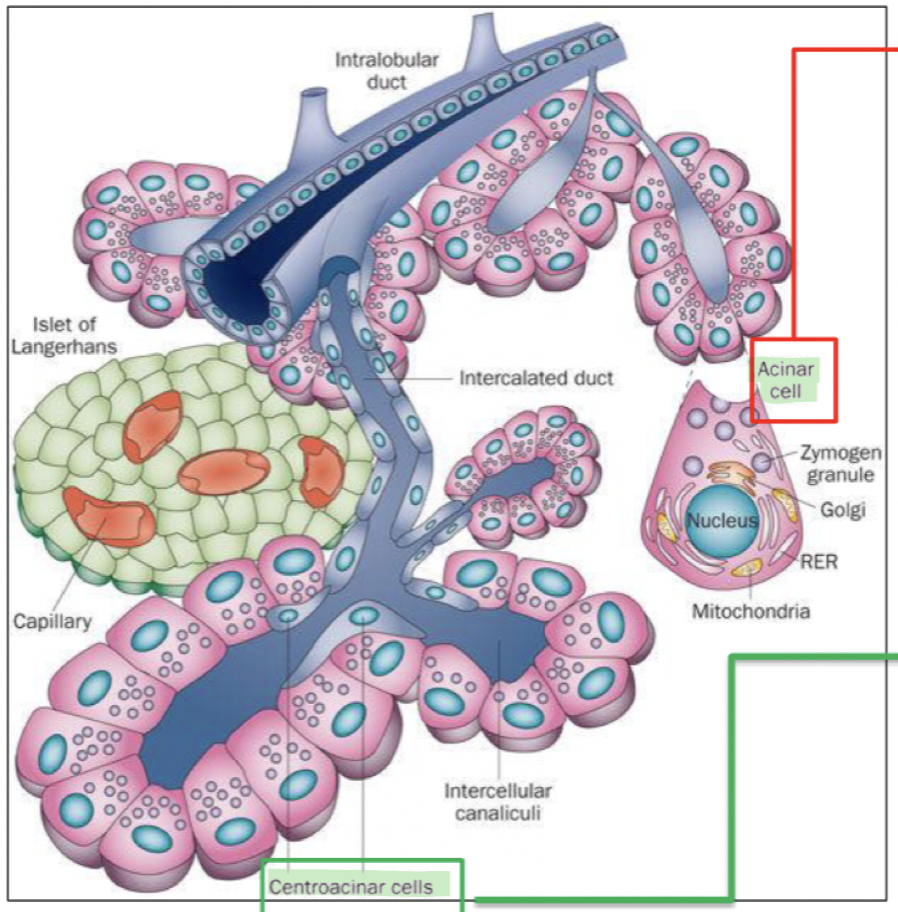
What do pancreatic secretions contain
Water + ions (Na+, K+)
Bicarbonate (HCO3-) - neutralise acid, inhibit pepsin, pH for pancreatic enzymes
Digestive enzymes - protein dig (trypsin, chymotrypsin), carb dig (pancreatic amylase), fats dig (pancreatic lipase, phospholipase), nuclease (deoxyribonuclease, ribonuclease)
Activation of pancreatic secretions
Enterokinase in duodenum activates trypsinogen into trypsin which then activates other enzymes
Regulation of pancreatic secretions
Acetylcholine - vagus nerve to acini cells
Cholecystokinin - duodenal/jejunal mucosa to stimulate acini cells to secrete dig enzymes
Secretin - duodenal/jejunal mucosa to stimulate duct cells to secrete bicarbonate and water
Phases of regulation of pancreatic secretions
Cephalic + gastric phase - stimulated by Ach, enzyme secretion (no fluid)
Intestinal phase - major, by CCK + secretin
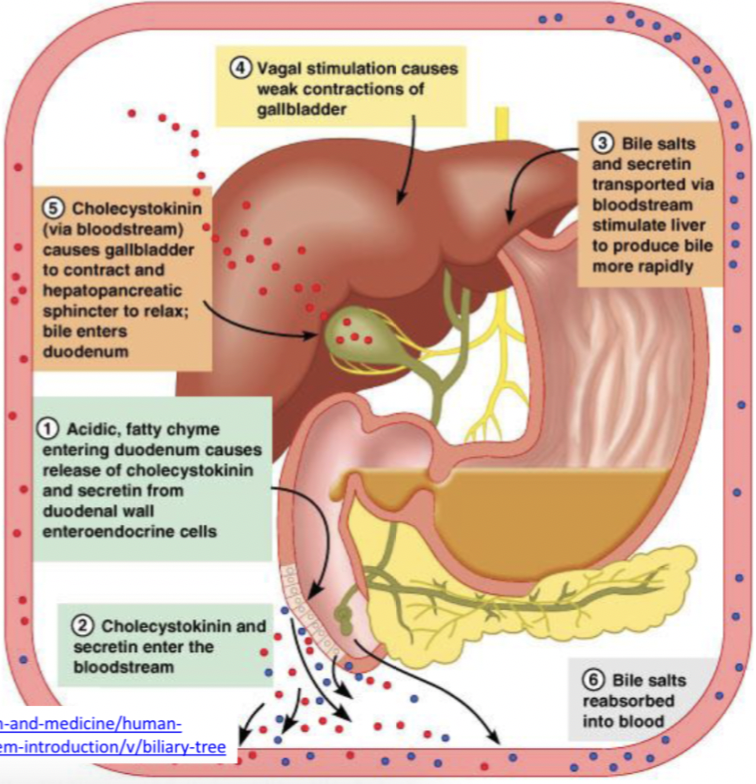
Bile secretion
Produced in liver by hepatocytes, stored in gall bladder
Functions - Fat digestion + absorption (bile salt emulsify fat, lipase digestion) and excretion (excretion of bilirubin and excess cholesterol)
Composition of bile secretion
Water, bile salts, bilirubin, cholesterol, fatty acids, lecithin, Na+, K+, Cl+, HCO3-
Enterohepatic circulation
Bile salts are recycled
Primary bile salts → produced in liver
Secondary bile salts → modified by intestinal bacteria
Bile flow
Hepatic duct → common bile duct → gall bladder
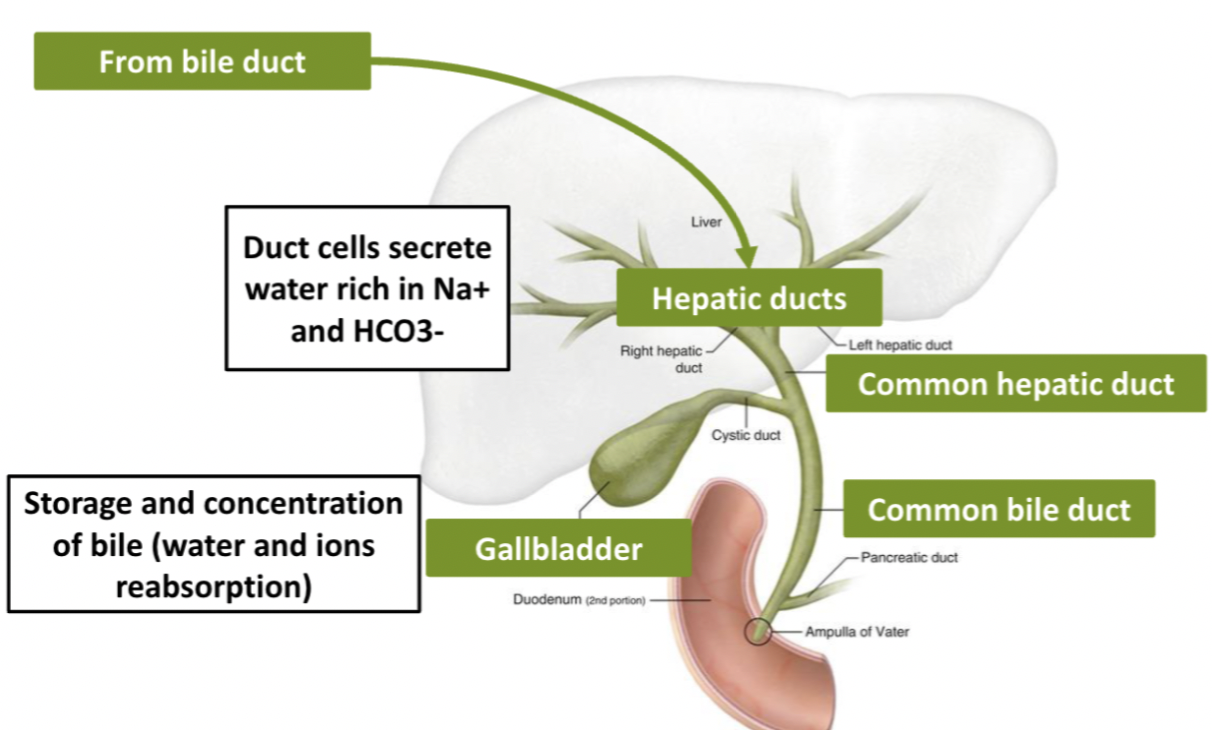
Bile salts
Precursor - cholesterol
Emulsificaiton - large fat droplets into smaller ones
Fat absorption - micelles (bile salts surround fat droplets) → micelles deliver to intestinal cells
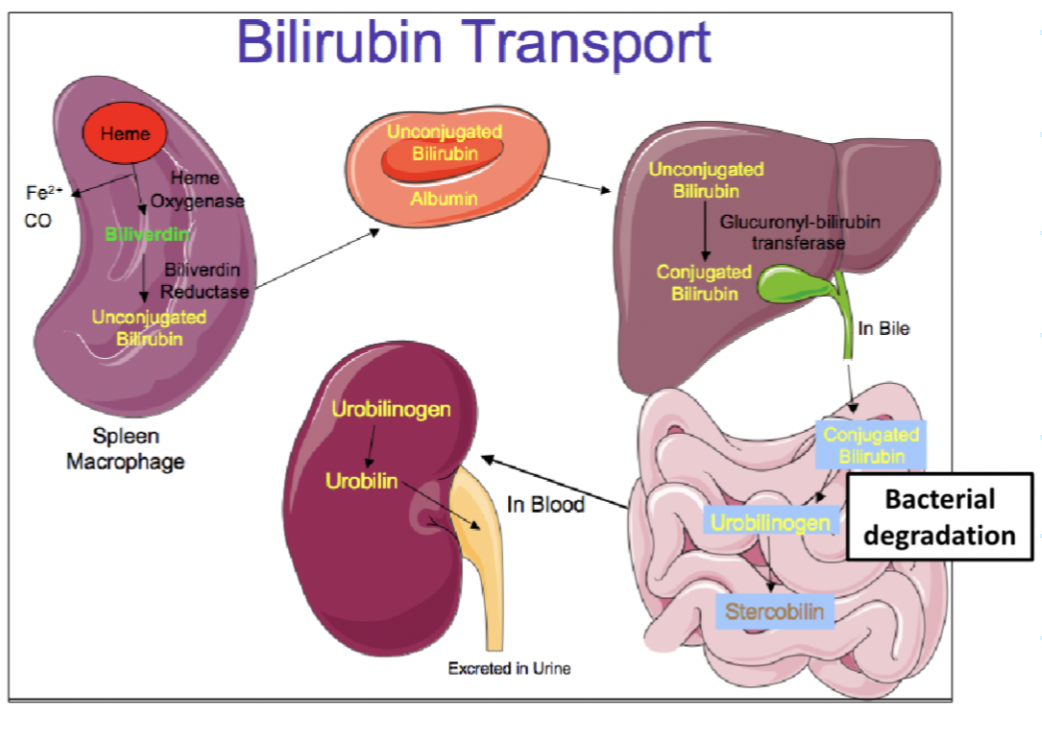
Bilirubin
Yellow brown colour to urine, feces and bruises
Hemoglobin breakdown (degragation of heme group)
Excess bilirubin leads to jaundice
Bilirubin metabolism
Biliverdin → unconjugated bilirubin (not water soluble)
Unconjugated bilirubin bound to albumin to transport to liver
Unconjugated bilirubin + glucoronic acid → conjugated bilirubin
Now water soluble and secreted in bile
Regulation of bile secretion
CCK (gall bladder contractions)
Secretin (bile secretion)
Bile salt recycling
Vagal stimulation