chemistry- alkenes 🟣
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Describe alkenes
Unsaturated
Contain carbon-carbon double bond
Describe C=C double bond & arrangement of bonds
Consist of one sigma and one pi bond
Represents a region of higher localised electron density- attacked by electrophiles
The arrangment of bonds around the C=C is planar and has the bond angle 120º
Restricted rotation around the double bond- responsible for geometric isomerism
What are geometric isomers caused by
Molecules with a C=C with 2 different groups attached to each C of the C=C
What are optical isomers caused by
E-Z isomers
C atoms having 4 different groups attached leading to molecules that are non superimposable mirror images of each other
When does geometric isomerism occur
when there is a carbon-carbon double bond (due to restricted rotation around the double bond)
When the carbon atoms on both sides of the bond are attached to different groups
What are Z isomers
Both hydrogen atoms/higher mass groups are on the same side of the molecule
Zame Zide
What are E isomers
Both hydrogen atoms/higher mass groups are on opposite sides of the molecule
Why are alkenes non polar
No dipole moment, no significant difference in electronegativity between carbon and hydrogen
Why are alkenes insoluble in water
Water is a polar substance and alkenes are non polar
Why does melting and boiling points of alkenes increase with chain length
Mr increases
more points of contact between molecules
So vdw forces (IMF) between molecules is stronger
Why do Z isomers have a higher boiling point than E isomers
Z isomers are polar molecules (net dipole moment)
E isomers are non polar molecules
Permanent dipole-dipole interactions (IMF) between the molecules is stronger than the weaker vdw forces
Why do E isomers have a higher melting point than Z isomers
molecules of the E isomer can ‘pack’ more closely and therefore have more points of contact than the Z isomer
What are addition reactions
A reaction where 2 molecules react together to produce one
What is the intermediate formed in electrophilic addition reactions called
Carbocation intermediate- positive charge on carbon atom
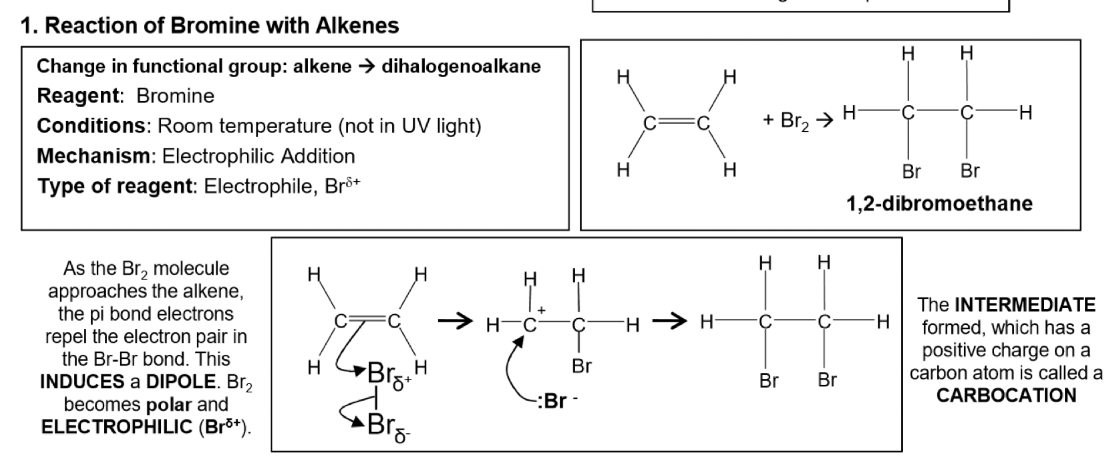
Electrophilic addition reaction of bromine with ethene- description and equation and mechanism
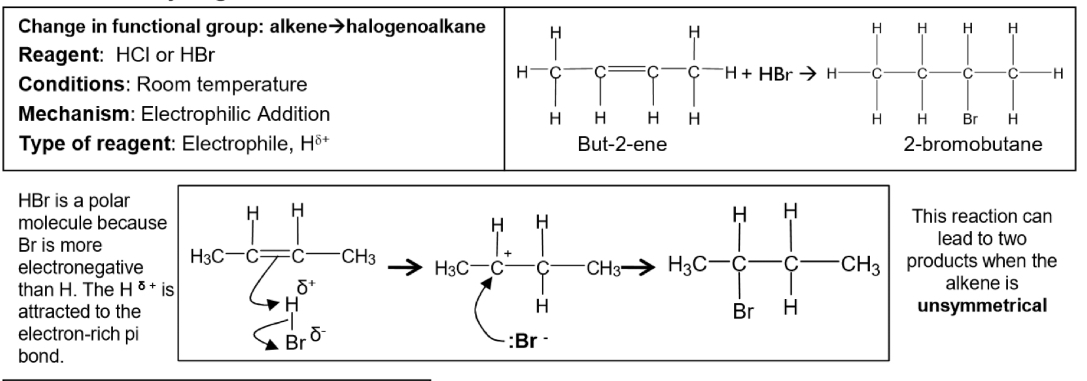
Electrophilic addition reaction of hydrogen bromide with But-2-ene- description and equation and mechanism
What happens if the alkene is unsymmetrical in electrophilic addition of HBr to but-1-ene
The addition of hydrogen bromide can lead to 2 isomeric products
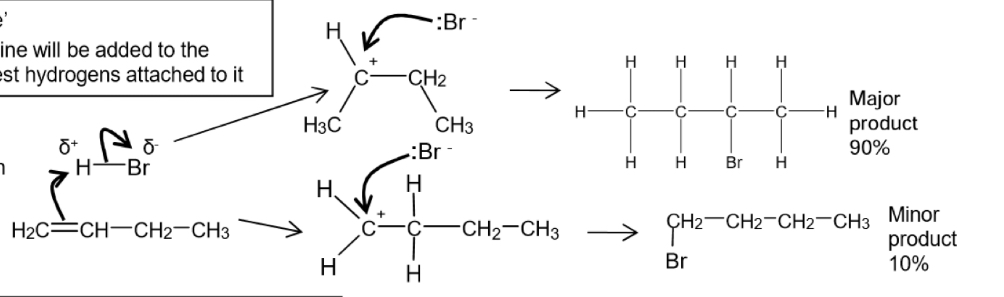
What is Markownikoffs rule
The halogen atom will be added to the carbon with the fewest hydrogens attached to it
Reaction mechanism for propene and hydrogen bromide
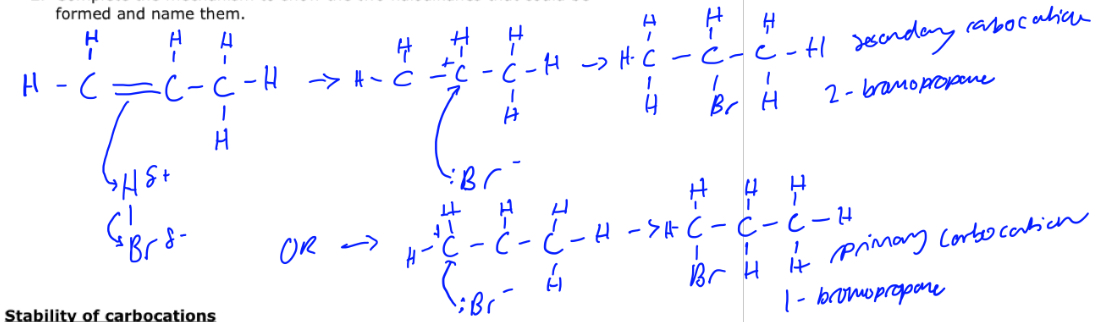
How is the major product formed in electrophilic addition to alkenes
Via the more stable carbocation intermediate
Why are carbocation intermediates more stable
the methyl groups on either side of the positive carbon are electron releasing and reduce the charge on the ion which stabilises it
What is the order of stability for carbocations
Tertiary > secondary > primary
What to do for exam answers relating to stability of carbocations?

Conditions and equations for electrophilic addition of sulfuric acid with alkenes
What is the overall role of sulfuric acid?
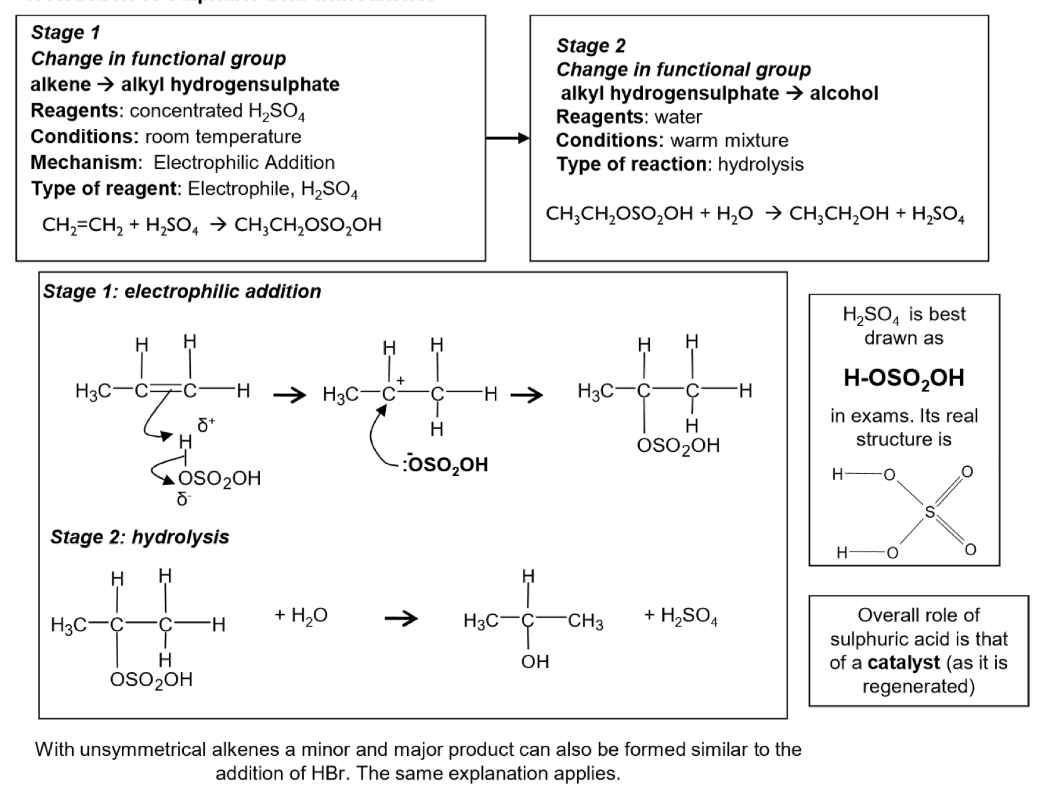
How are alkenes converted to alcohols industrially
Hydration
reacted with water in the presence of an acid catalyst
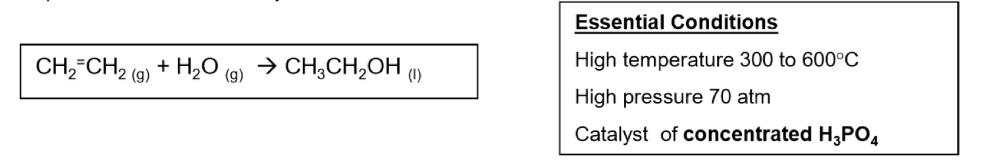
Hydration of ethene conditions and equation
Test for alkenes/double bond(s) in a molecule
Bromine water turns colourless
Process where addition polymers are formed from alkenes
Addition polymerisation
Equations for addition polymerisation of ethene and propene
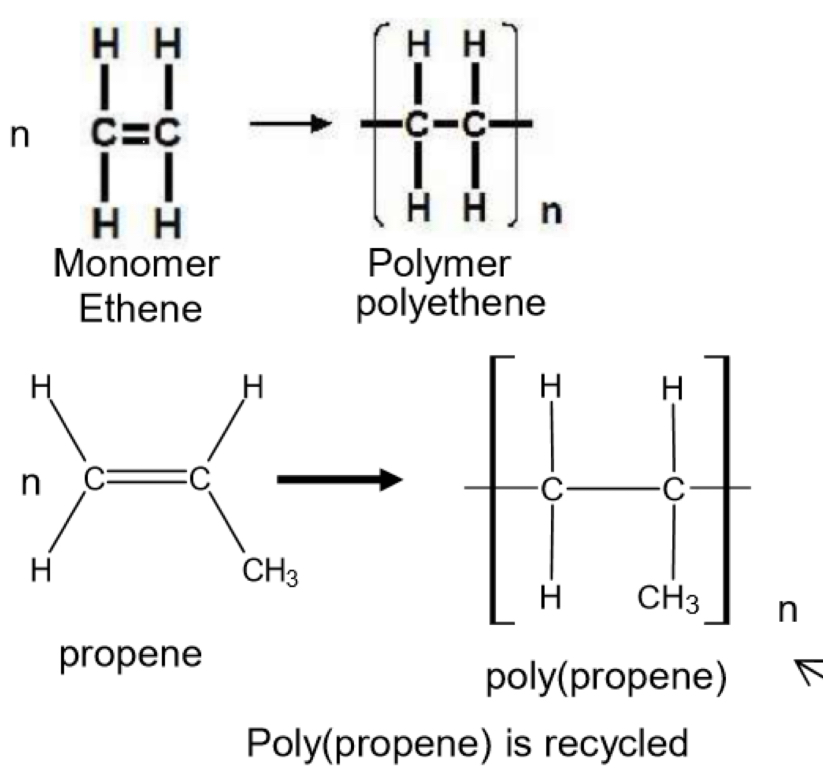
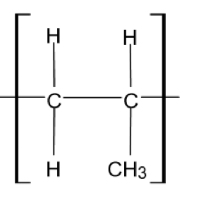
One repeating unit in addition polymerisation
No n
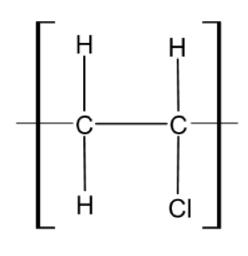
properties of poly(chloroethene) in its pure form and if plasticiser added
Waterproof, electrical insulator, doesnt react with acids
Rigid plastic due to strong intermolecular bonding between polymer chains which prevents them moving over each other
Used to make uPVC window frame coverings and guttering
If plasticiser is added the intermolecular forces are weakened which allows the chains to move more easily resulting in more flexibility in the polymer
In this form PVC is used to make insulation on electrical wires and waterproof clothing