ap chem ch. 9 IMFs
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
molecular particle diagram
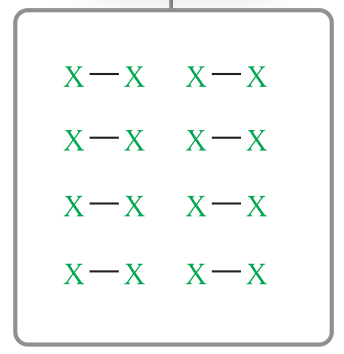
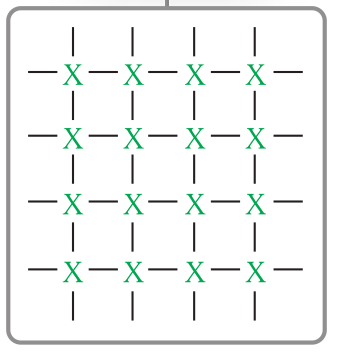
network covalent particle diagram
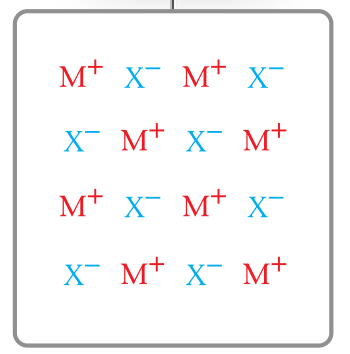
ionic particle diagram
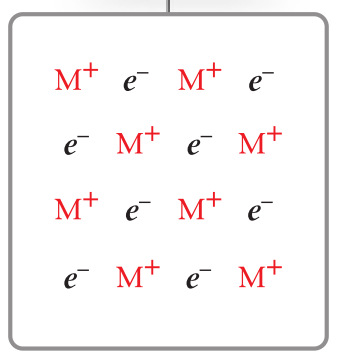
metallic particle diagram
network covalent characteristics
high melting points, insoluble, low electrical conductivity
ionic characteristics
high melting points, soluble, low electrical conductivity
metallic characteristics
moderately high melting points, insoluble, high electrical conductivity
molecular characteristics
low melting points, soluble if polar/insoluble if nonpolar, low electrical conductivity
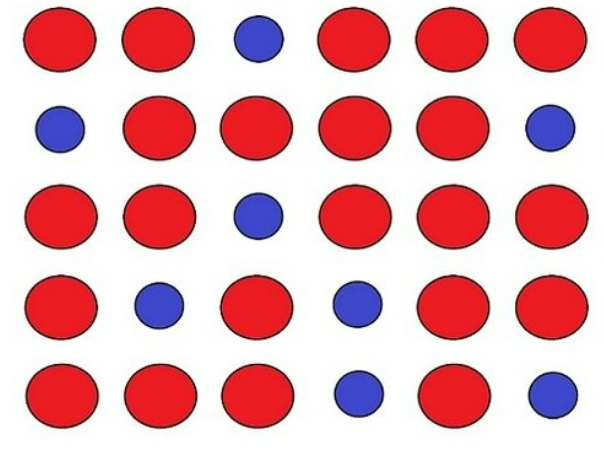
interstitial alloy
random extra atoms scattered throughout the mixture
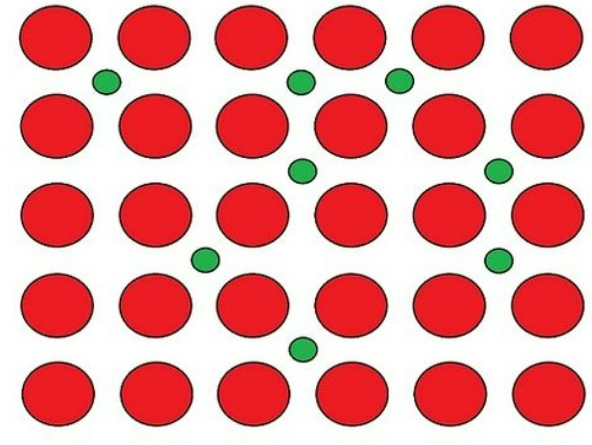
substitutional alloy
metal ion B replaces metal ion A
coulomb’s law
F = (kq1q2)/r2
vapor pressure
characteristic property—pressure of a vapor in equilibrium with a liquid
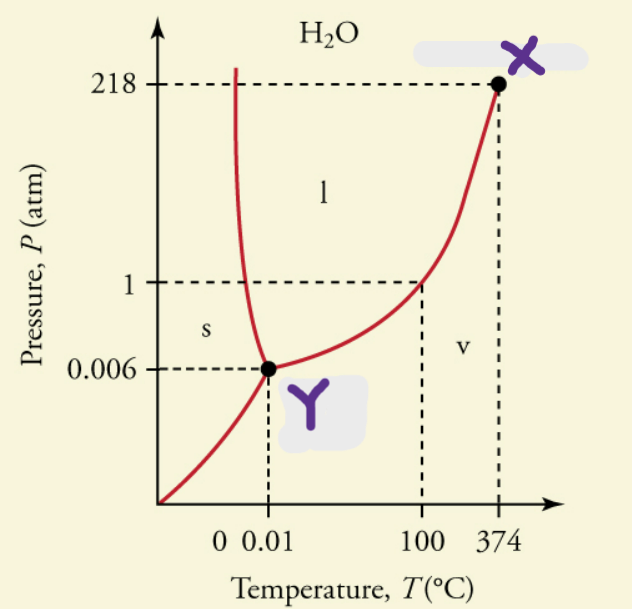
critical temperature
temperature above which a liquid of a pure substance cannot exist (X)
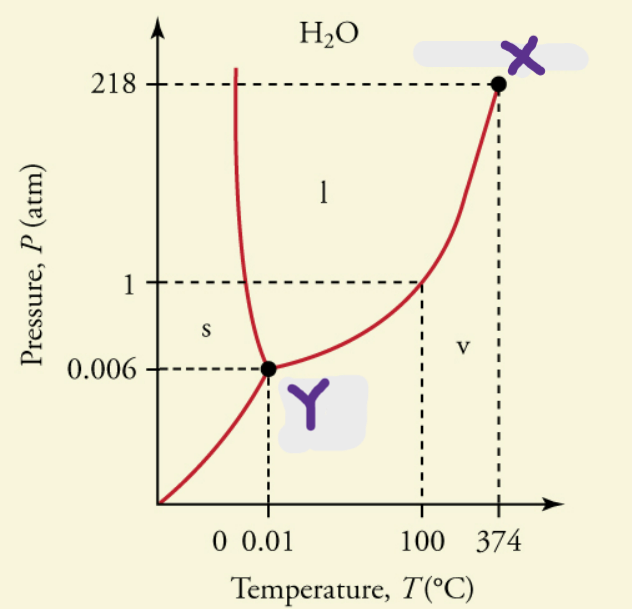
critical pressure
pressure that must be applied to cause condensation at a specific temperature; vapor pressure at critical temperature
triple point
point where all phases are in equilibrium with each other and all phases are present (Y)
sublimation
solid changes directly to vapor
deposition
vapor changes directly to solid
dipole forces
negative pole attracted to positive pole of a molecule
nonpolar molecule characteristics
electrons evenly distributed, no permanent pos/neg end, symmetrical
polar molecule characteristics
electrons unevenly distributed, permanent pos/neg ends, asymmetrical
electron sea model
positive ions anchored in a sea of electrons