Econ Unit 3 (Profit, Production, Costs, Markets & Perfect Competition)
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
marginal utility turns negative
total utility begins to decrease when
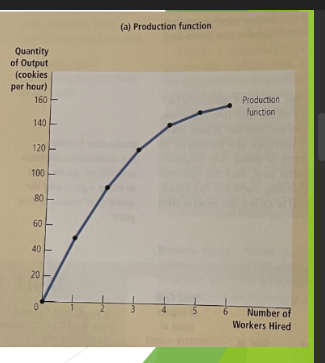
production function
shows the relationship between the quantity of inputs used to make a good and the quantity of output for that good
land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship, sometimes technology
factors of production
total product
the total amount of final output produced by a firm using given inputs in a given period of time
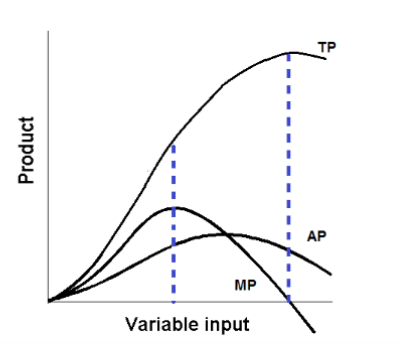
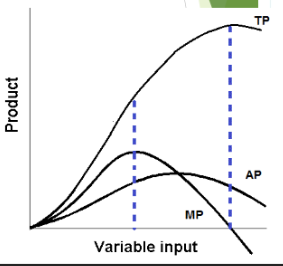
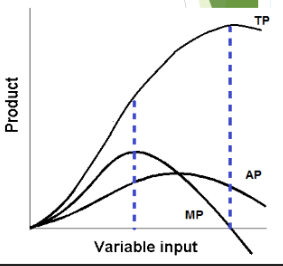
marginal product
increase in the quantity of output that arises from one additional unit of that input (ex: the additional number of strawberries harvested by a farmer who plants additional seeds OR the additional revenue a bowling alley receives if it builds extra lanes)
marginal product = 0
total product is maximized when
MP of capital
the additional output that results from adding one unit of _____ (additional pizza oven)
MP of labor
the additional output resulting from hiring another worker
MP of land
the additional output gained from adding another unit of ____ (a farmer who purchased a field next to their existing property)
MP of raw materials
a rechargeable battery manufacturer who purchased a cache of lithium or cobalt
law of diminishing marginal returns
as you add more of a single input (like labor or capital) to a fixed production process, the resulting increase in output will eventually get smaller. While initial investments usually boost production significantly, you will eventually reach a point where each new unit of input yields less additional "marginal" product, and could eventually lead to a decrease in total output
average product = total product / units of variable factor input
the average of the total product per unit of input
increasing at an increasing rate
if MP is increasing, TP is
decreasing
If MP is negative, TP is
crosses AP curve
the AP is maximized when MP
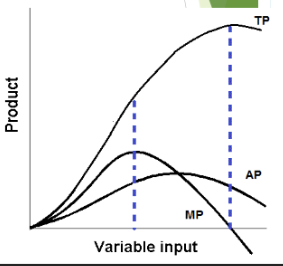
pulls AP up
when MP is higher than AP, it
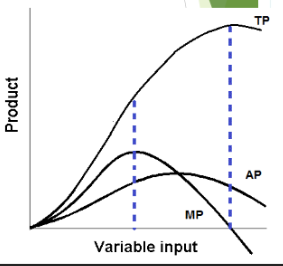
pulls AP down
when MP is less than AP, it

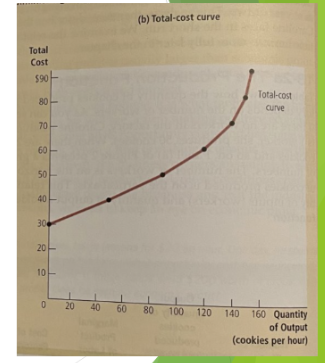
total cost curve
gets steeper as the amount produced rises. when the kitchen is crowded with lots of workers, producing an additional pizza requires a lot of additional labor and is therefore very costly
marginal cost
a representation of the costs incurred when additional units of a product are produced
short-run production costs
the period of time during which at least some factors of production are fixed, labor is typically variable
long-run production costs
the period of time during which all factors are variable, all costs are variable in this time
explicit costs
out-of-pocket costs, payments that are actually made, wages that a firm pays its employees or rent that a firm pays for its office
implicit costs
represent the opportunity cost of using resources already owned by the firm
economic profit
TR-TC, includes both explicit and implicit costs
TR-TC
economic profit
accounting profit
a cash concept, TR-explicit costs = the difference between dollars brought in and dollars paid out
economic profit
even though a business pays income taxes based on its accounting profit, whether or not it is economically successful depends on its ____________
TR - explicit costs
accounting profit
fixed inputs
can’t easily be increased or decreased in a short period of time, fixed inputs define the firm’s maximum output capacity
variable inputs
can easily be increased or decreased in a short period of time
optimal output rule
a business’s profit is maximized when it produces a quantity of output where the marginal revenue = marginal cost
MR = MC
optimal output rule
total cost - fixed cost
variable costs
average total cost
the total cost per unit of output, inclusive of both fixed and variable costs, is the per-unit cost of producing a product
total cost / quantity of output
average total cost
average variable cost
the variable cost per unit incurred by a business across a given period
total variable cost / quantity of output
average variable cost
average fixed cost
the fixed costs incurred by a company that remain constant irrespective of output, expressed on a per-unit basis
total fixed cost / production output
average fixed cost
costs fall
when workers are more productive,
diminishing marginal returns
when MC shifts up, this is when the firm is experiencing
ATC decreases
when MC is lower than ATC,
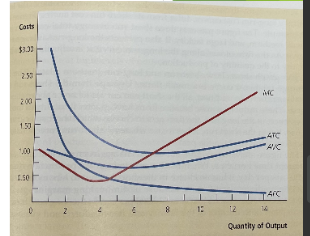
MC and ATC cross
ATC is at its lowest when
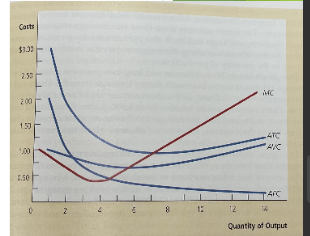
ATC rises
When MC is higher than ATC,
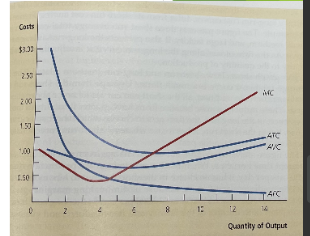
marginal cost
there is no relationship between average fixed cost and
downward
average fixed cost always trends
lower fixed cost per unit of output
as production volume increases, the same fixed cost is spread across a larger number of units, resulting in a
quantity increases
total fixed cost does not change as
quantity increases
total variable cost increases as (labor costs go up)
TFC
the gap between TC and TVC is
total fixed costs
TC does not begin at zero because even with no output there are still (rent)
TFC
The TC curve intersects the vertical axis at the level of
minimum efficient scale
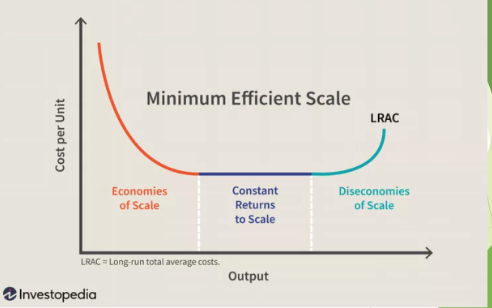
economies of scale
when long-run average total cost declines as a quantity of output increases, happens because higher production levels allows specialization among workers
increasing returns to scale
means that a company increases all its inputs (like labor and capital) by a certain percentage, the resulting output increases by a proportionally larger percentage
lower average costs per unit produced
increasing returns to scale: producing at a larger scale leads to greater efficiency and
constant returns to scale
when long-run average total cost stays the same as the quantity of output changes
diseconomies of scale
when long-run average total cost rises as the quantity of output increases
coordination problems
diseconomies of scale can happen because of
minimum efficient scale
the lowest point on a cost curve at which a company can produce its product at a competitive price, smallest output level at which long-run average total cost is minimized
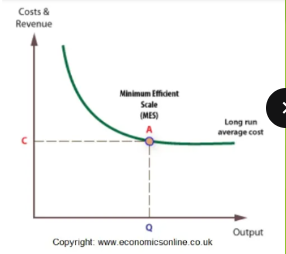
economies of scale
at the MES point, the company can achieve the ___________ necessary for it to compete effectively in its industry
minimum efficient scale will be
the higher a firm’s fixed costs are, the higher its
long-run average total cost
if a firm is experiencing economies of scale, what will decrease as output increases
market
a group of buyers and sellers of a particular good or service
competitive market
many buyers and sellers, not controlled by any one person or firm, a narrow range of prices are established that buyers and sellers act upon
perfect competition
products are the same, numerous buyers and sellers so that each has no influence over price, buyers and sellers are price takers, all firms charge about the same price, free entry into and out of the market
must accept the price for its output
a perfectly competitive firm can sell any number of units at exactly the same price,
quantity to produce
a perfectly competitive firm will determine its total revenue, total costs, and level of profits by deciding the
profit = total revenue - total cost
price equation 1
profit = quantity(price-average total cost)
profit equation 2
the supply curve
for a perfectly competitive firm, marginal costs curve is
the demand curve
for a perfectly competitive firm, marginal revenue curve is
a firm produces where MR = MC
profit maximization rule
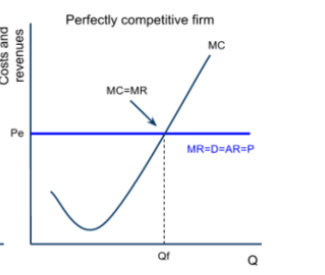
it can sell however much it wants
why is the firm’s demand curve perfectly elastic
price x quantity
total revenue =
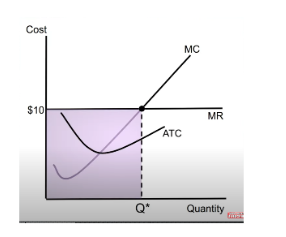
ATC x quantity
total cost =
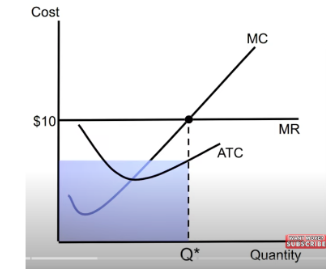
profit
difference between TR & TC is
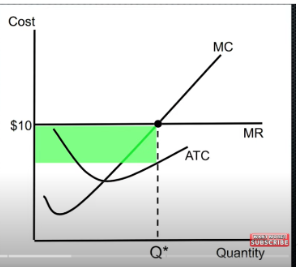
short-run shutdown
not producing anything during a specific time period because of market conditions
short-run shutdown
still has to pay fixed costs
short-run shutdown
if a farmer decides to not plant for one season, the fixed cost of land is a sunk cost
short-run shutdown
the farmer should ignore the sunk costs when deciding how much to produce
lowest point on ATC, lowest point on AVC
break even point/price = ______________, shut down point/price = ___________
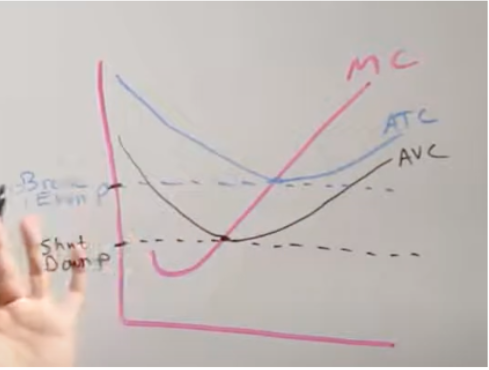
short-run shutdown
loses all revenue from the sale of its product
short-run shutdown
saves the variable costs of making its products
price < AVC
shut down if
P > ATC
if a price is greater than average total cost, then a firm is making economic profits
long-run exit
will save variable AND fixed costs
long-run exit
revenue it would receive from producing is less than total costs
MC = MR
in a short-run market supply with a fixed number of firms, for any given price, each firm supplies a quantity of output so that its
QS
to derive market supply curve, we add the ______ by each firm in the market
the same cost curves
in a long run market supply with entry and exit we will assume all current and potential firms had
profit is positive
if price is above ATC, (encourages new firms to enter)
profit is negative
if price is less than ATC, (encourages some firms to exit)
the quantity produced by each existing firm will decrease
Assume that all firms in a perfectly competitive market currently earn positive economic profits. What will happen in the long run if all firms face constant returns to scale in production