Med Imaging- Lungs Pt. 1
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Alveolar spaces are filled with some material such as blood, pus, fluid, or cells
Alveolar (localized)
tissue outside of the alveoli are affected
Interstitial (diffuse)
Alveolar infiltrates are either
fluffy or complete consolidations
Air bronchogram
Air bronchogram sign
air filled bronchi become visible against a background of dense lung tissue
Kerley A lines
periphery (interstitial infiltrate)
Kerly B lines
base (interstitial infiltrate)
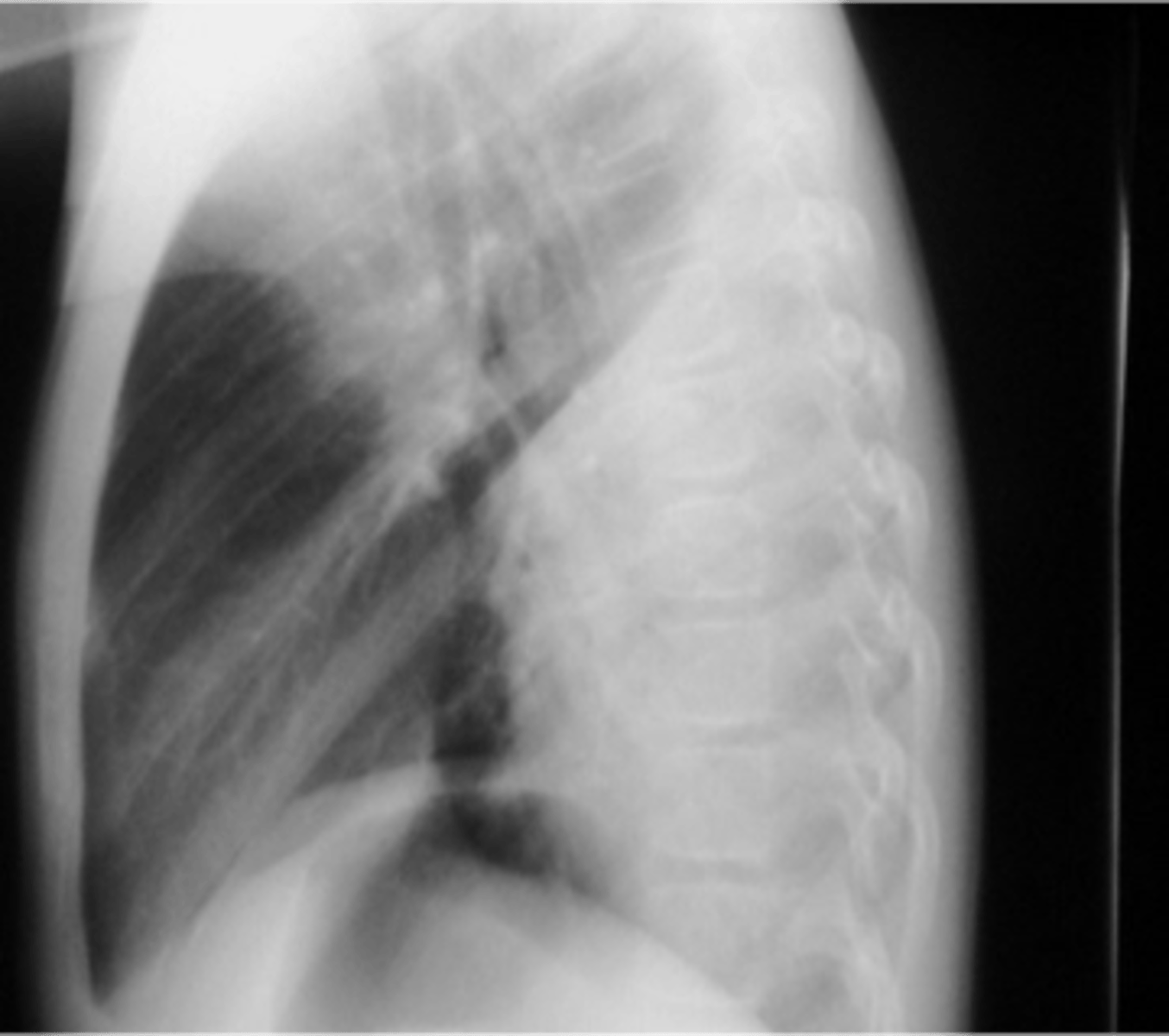
vertebral bodies are lighter (white) than normal on lateral x-ray view
spine sign
Aspiration pneumonia shows as an
alveolar infiltrate
Enlargement of hilar or mediastinal lymph nodes is present in
primary active TB
calcified nodes are associated with
TB
less than 3cm, calcified, round well defined borders, solid-no cavity
Benign solitary pulmonary nodule
great than 3 cm, not calcified, irregular shape, cavitated, growth in past 2 years
malignant solitary pulmonary nodule
most common type of lung cancer and usually occur peripherally
Adenocarcinomas
what lung cancer usually occurs centrally and tend to cavitate
squamous cell carcinomas
what lung cancer often presents as an indistinct hilar or perihilar mass
small cell carcinomas
what lung cancer occurs peripherally or centrally and grow rapidly with early metastases- poor prognosis
non-small cell carcinomas
Arise in the superior sulcus of the lung as an apical soft tissue mass
lung cancer- pancoast tumor
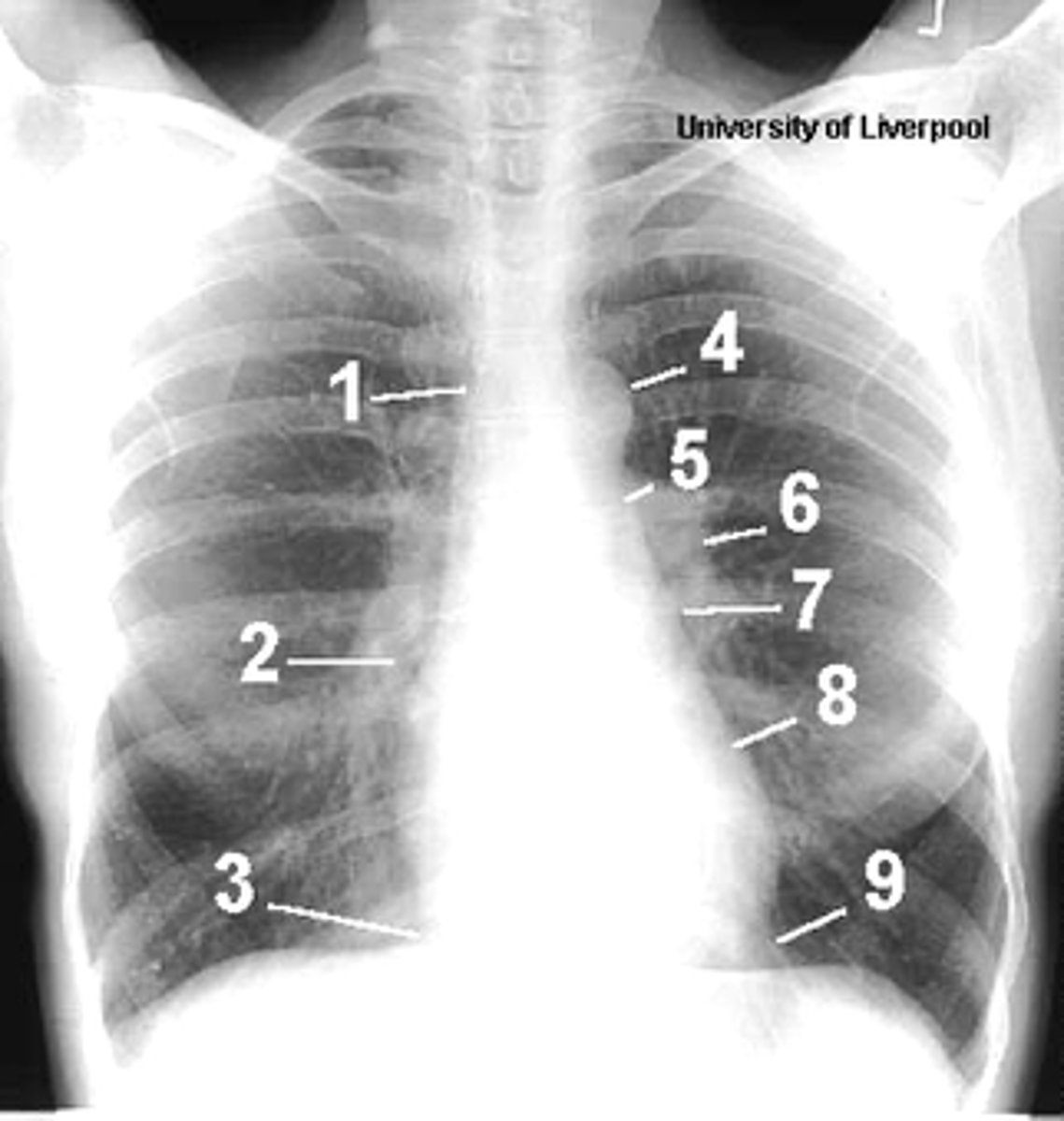
1
superior vena cava
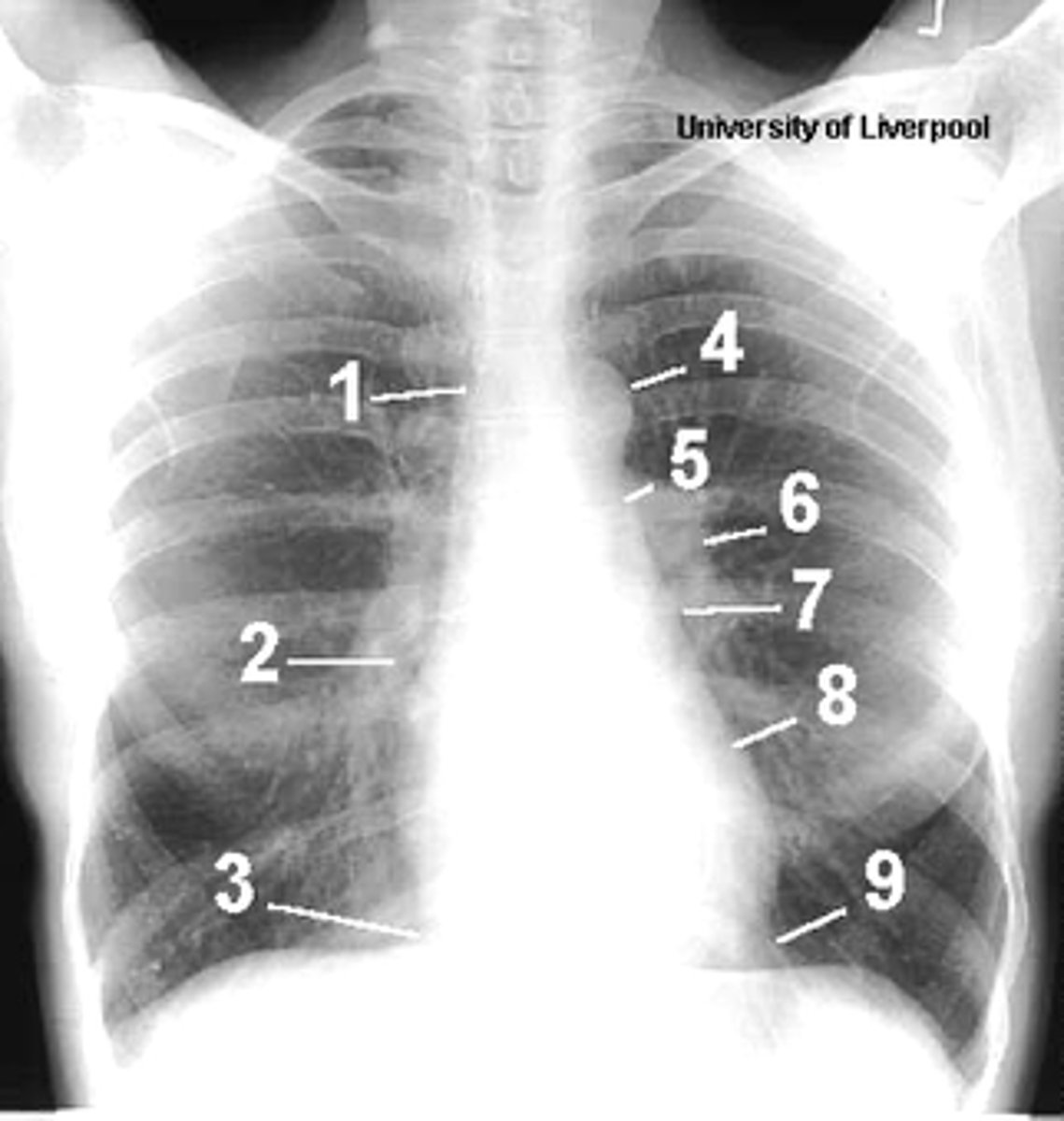
2
right atrium
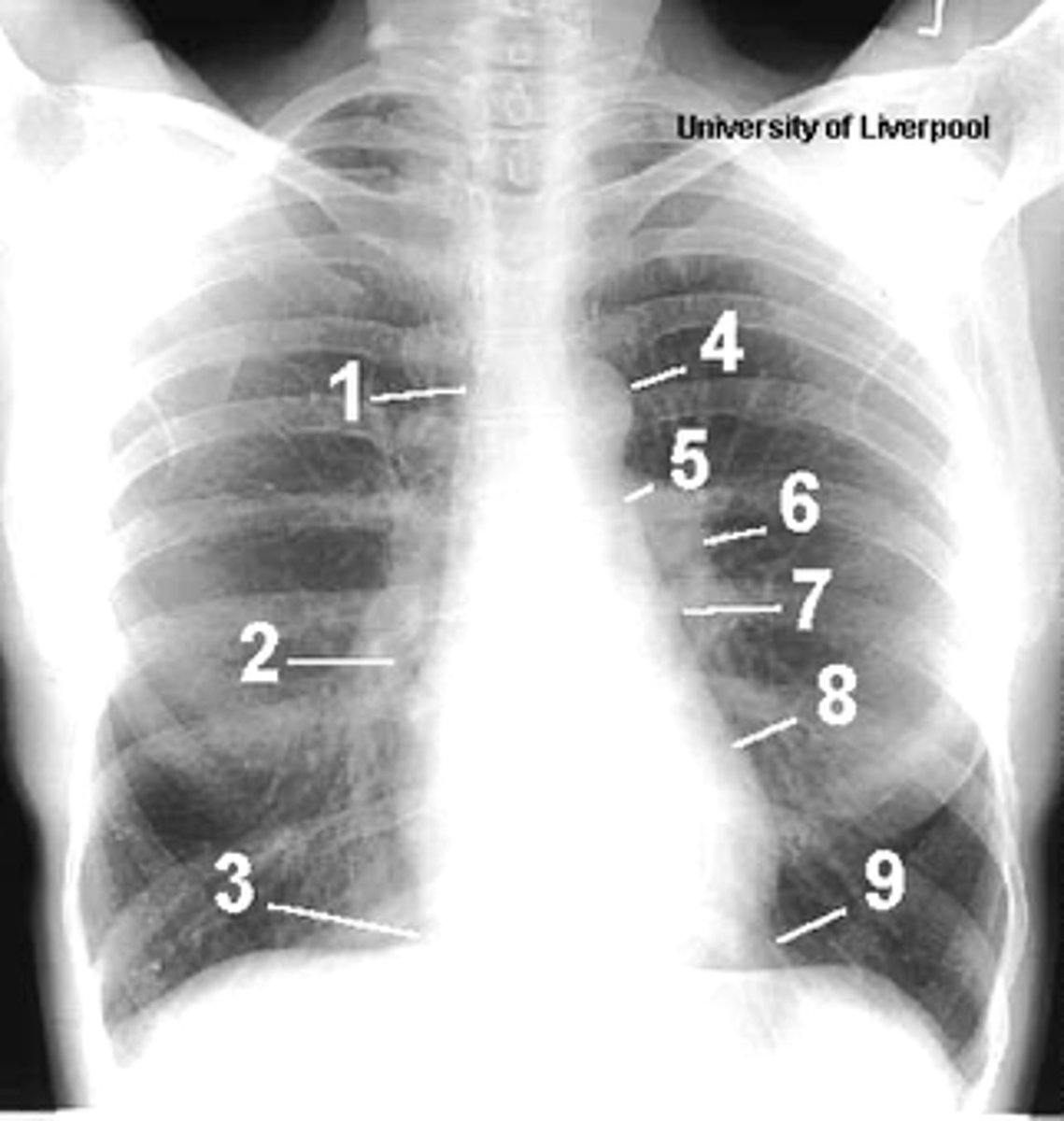
3
inferior vena cava
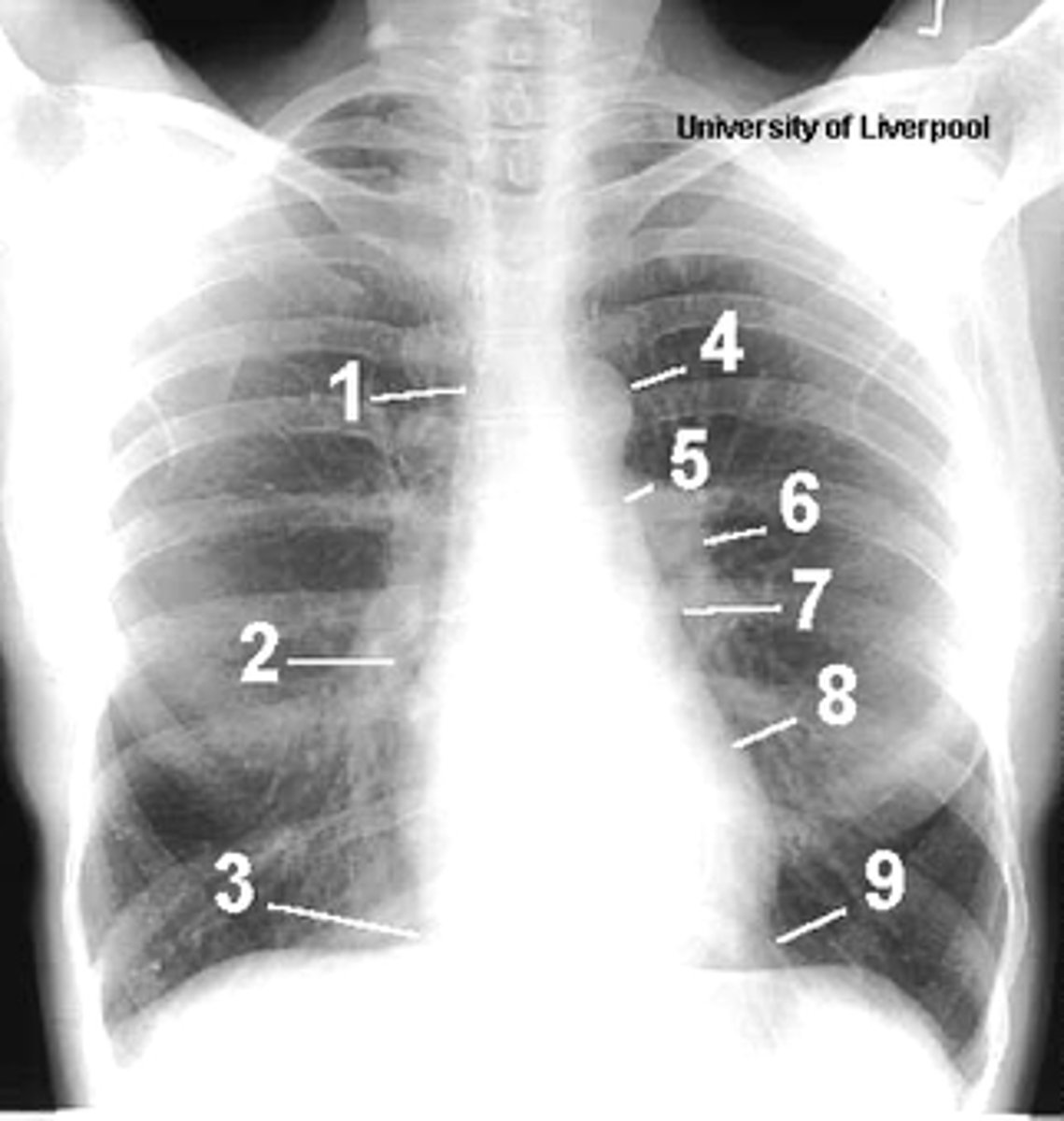
4
aortic arch or knob
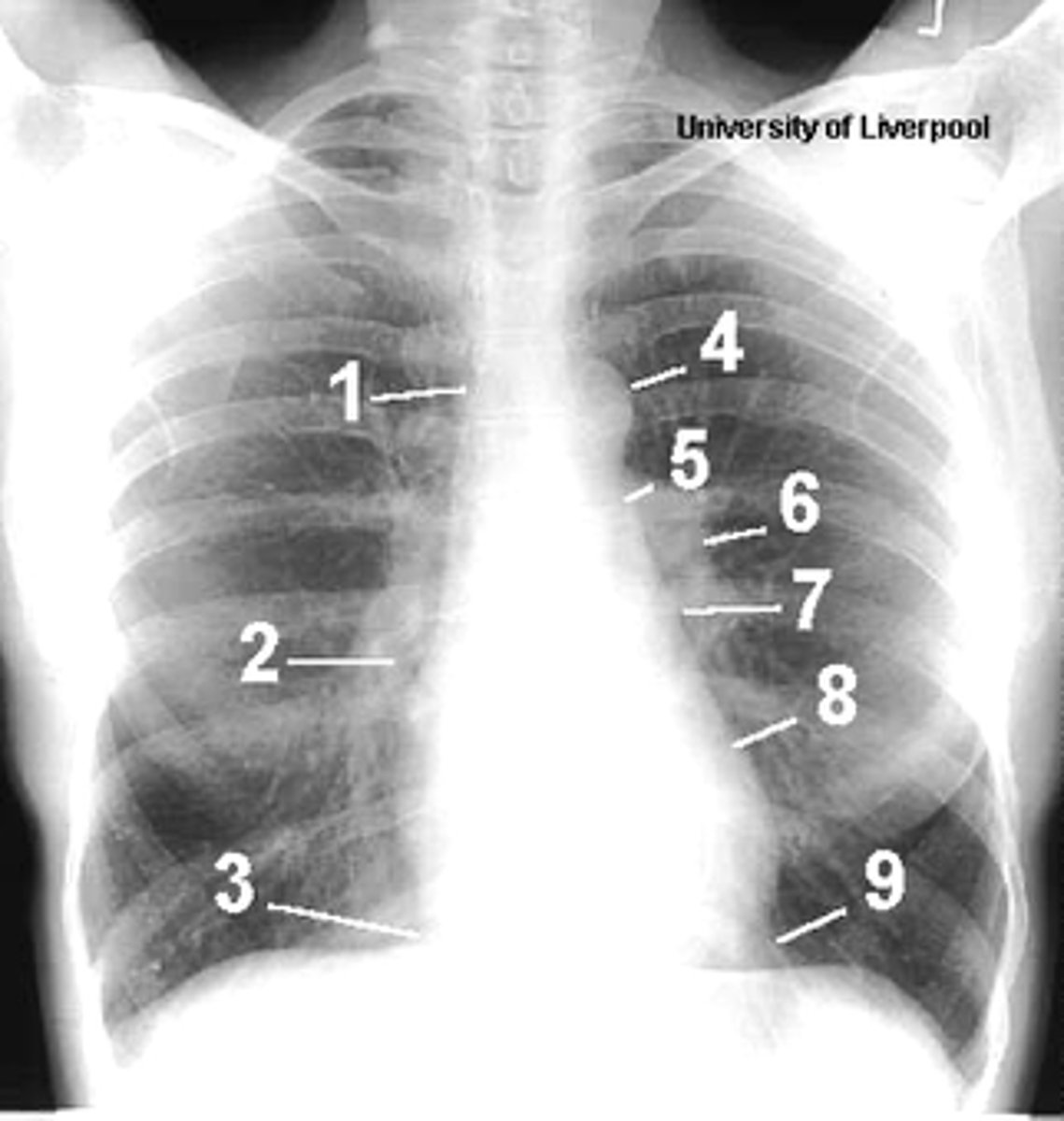
5
left pulmonary trunk
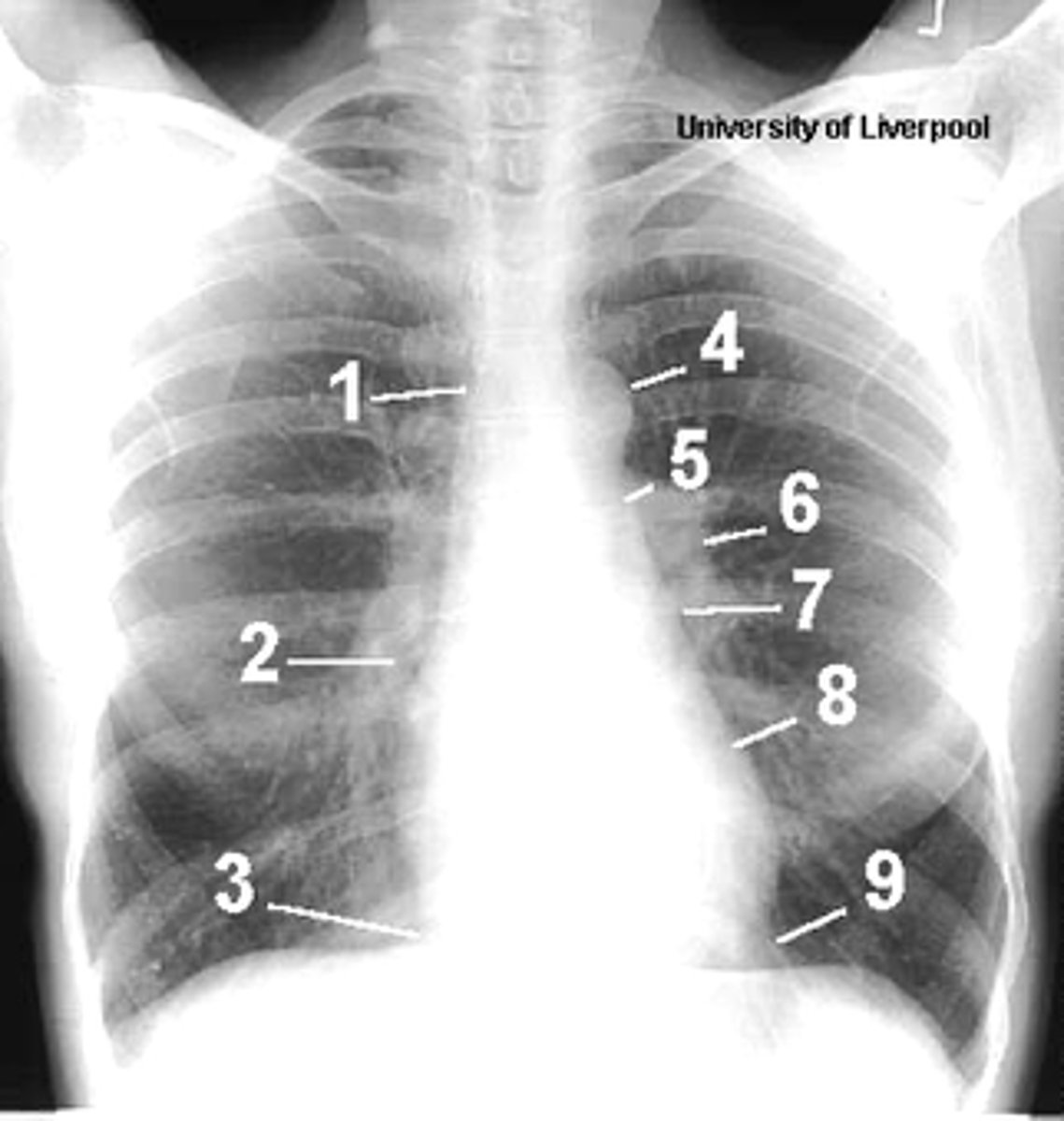
6
left pulmonary artery
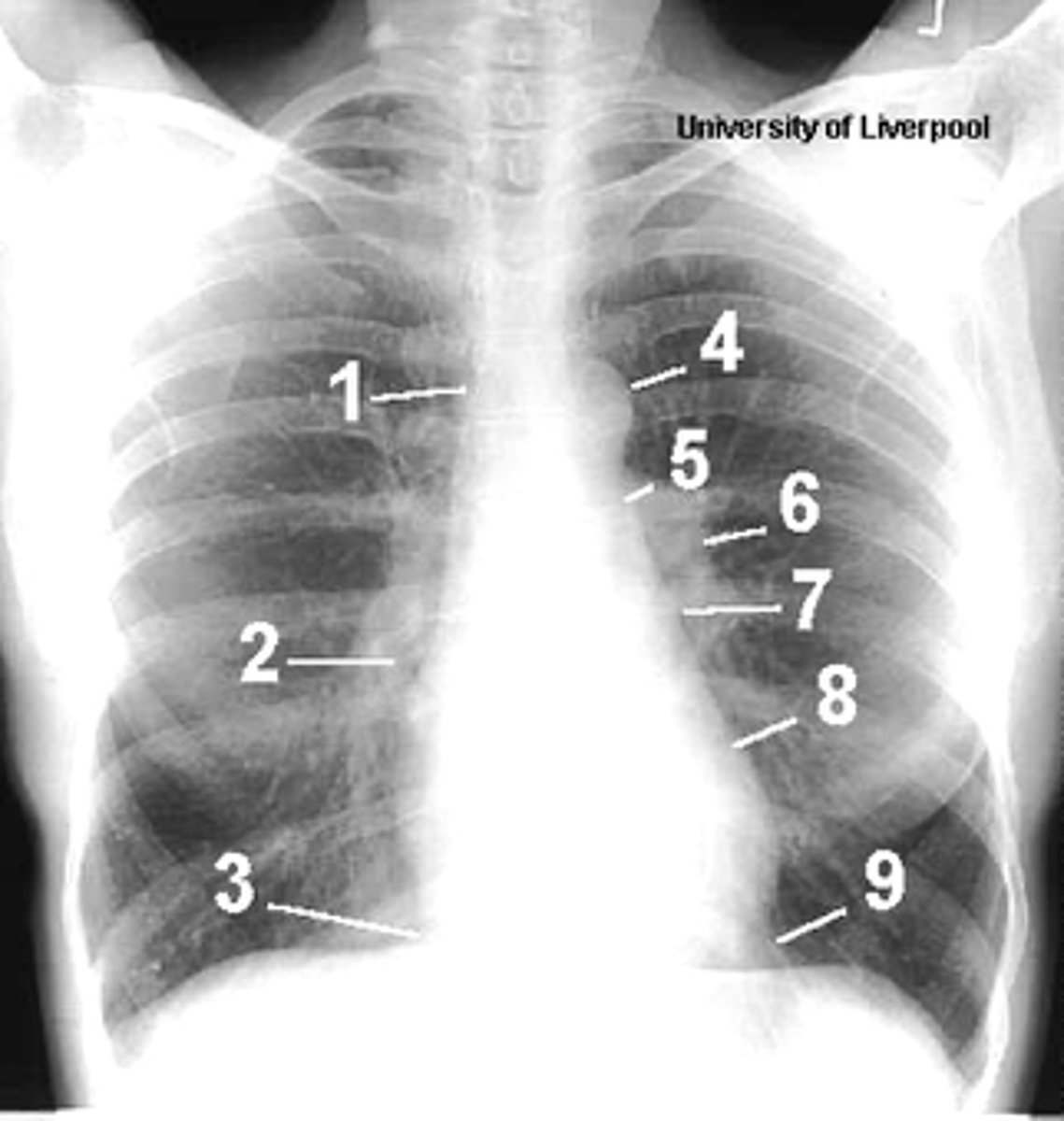
7
left atrium
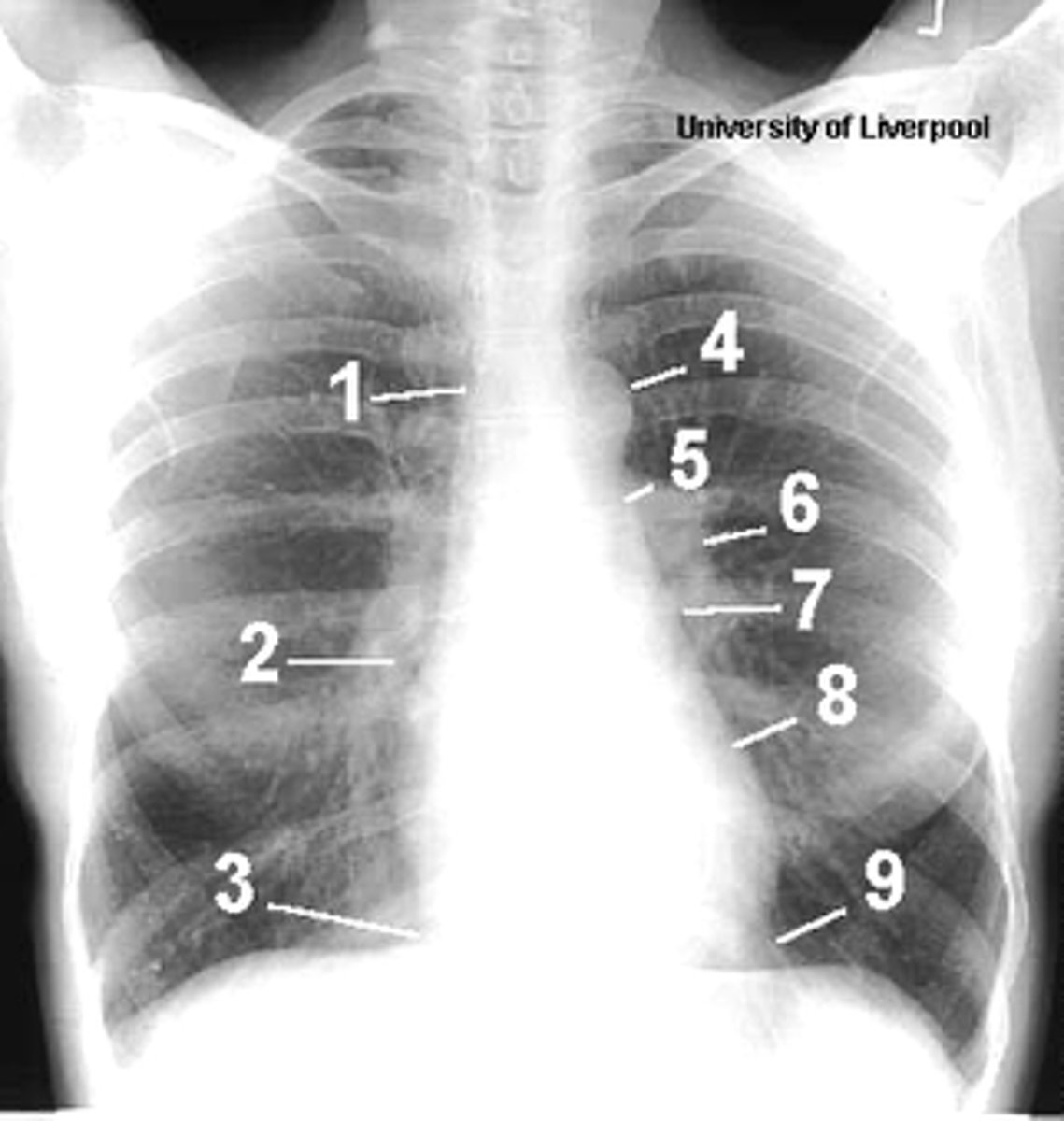
8
left ventricle
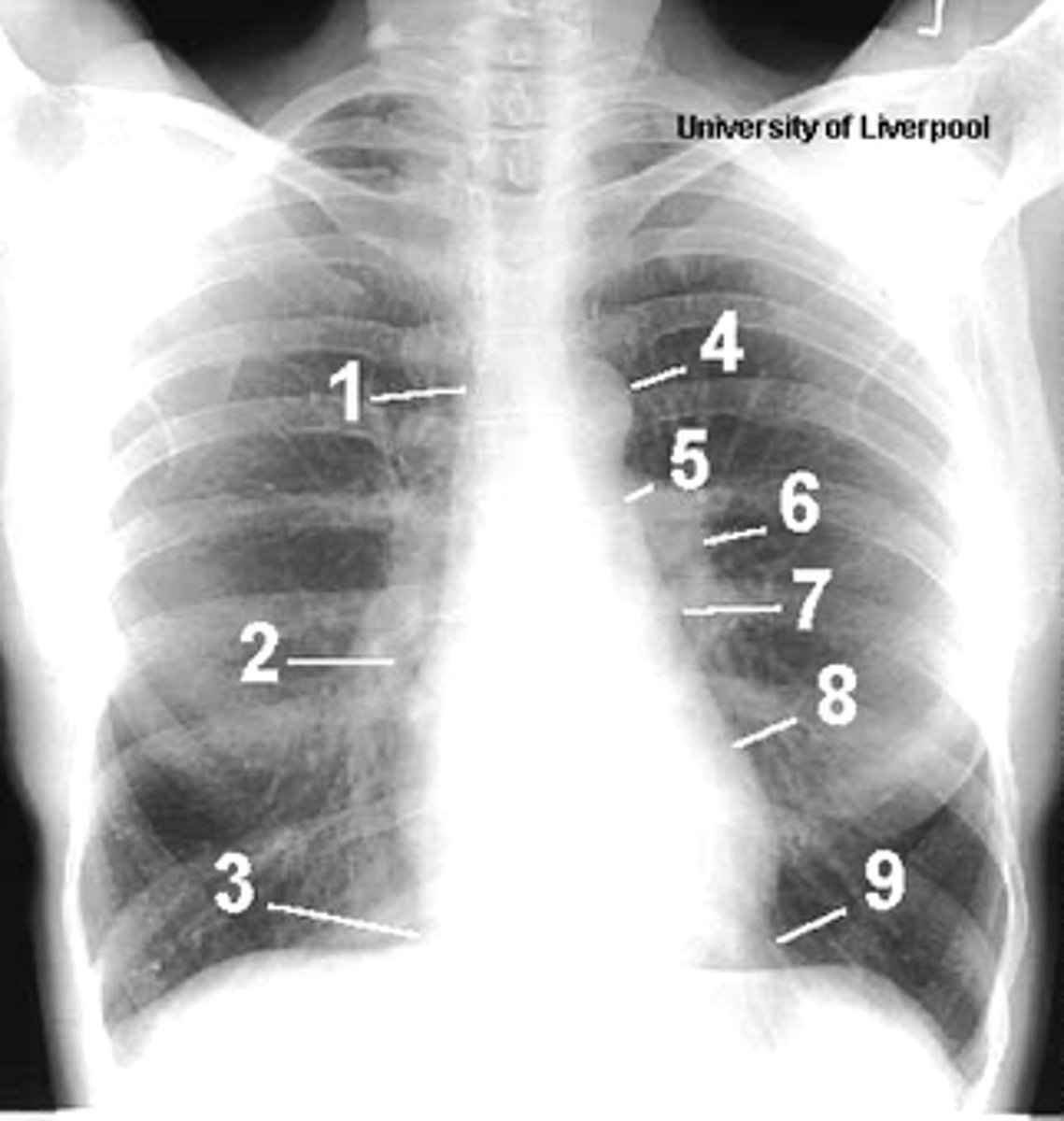
9
left cardiophrenic angle
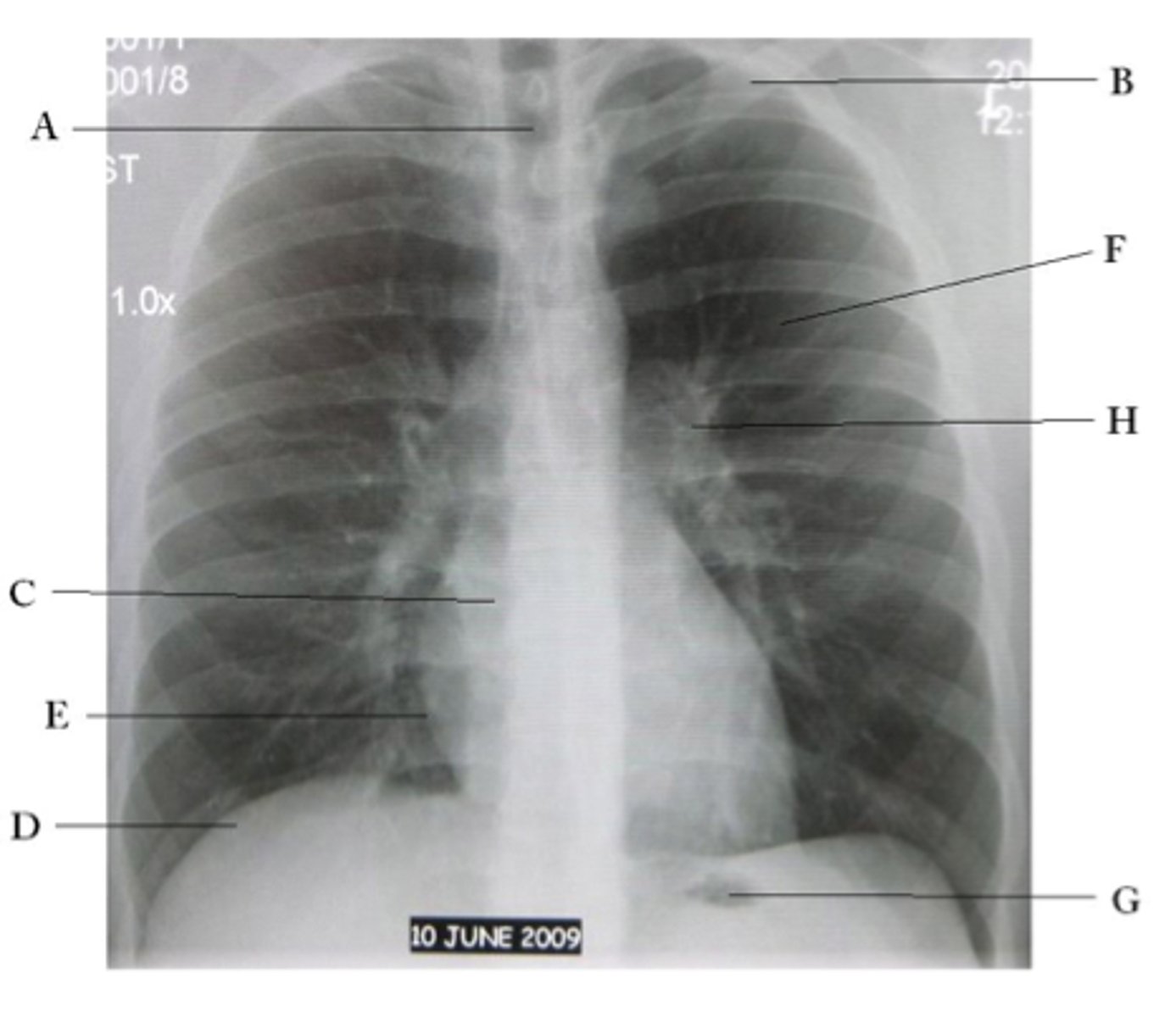
A
trachea
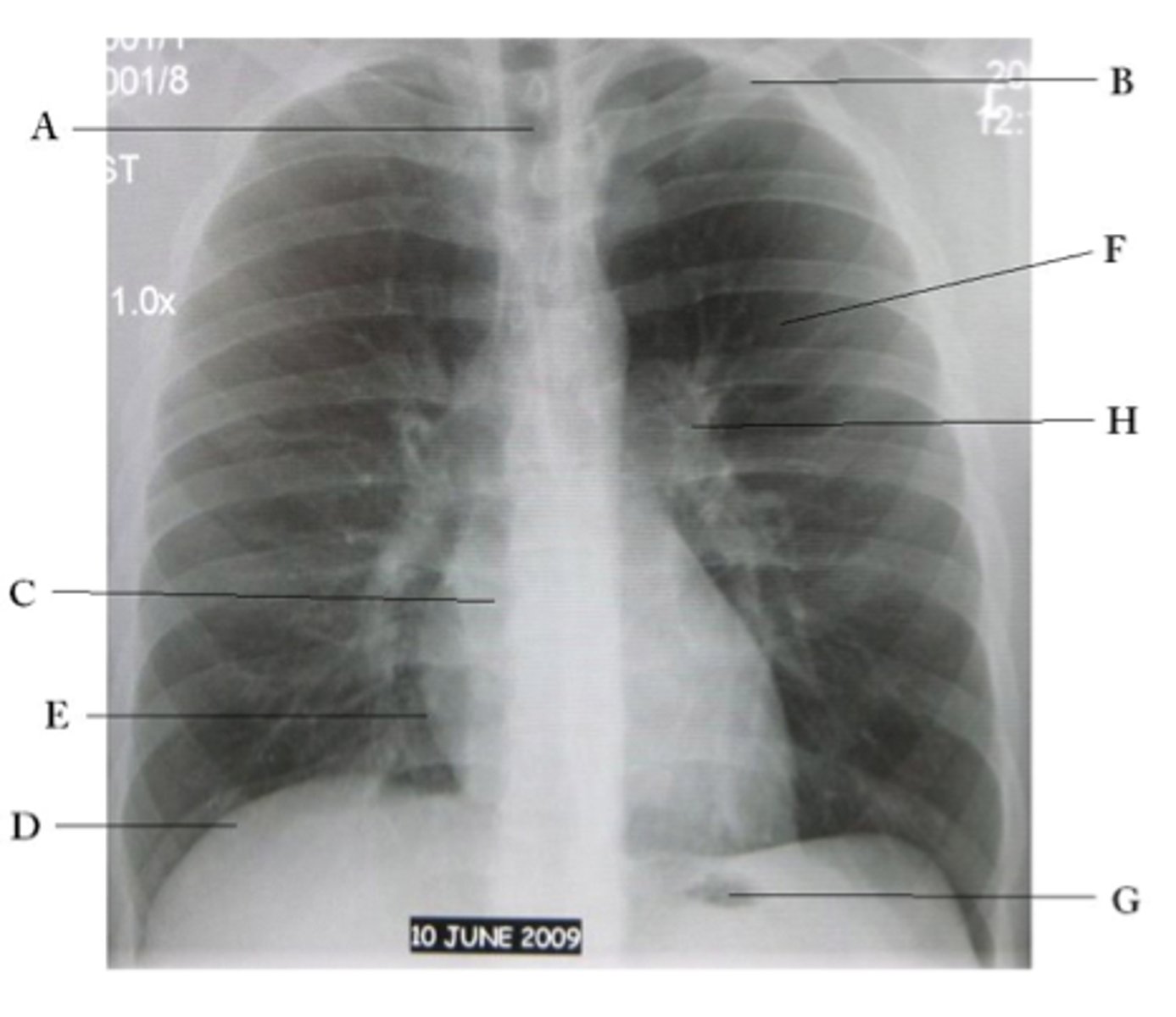
B
Clavicle
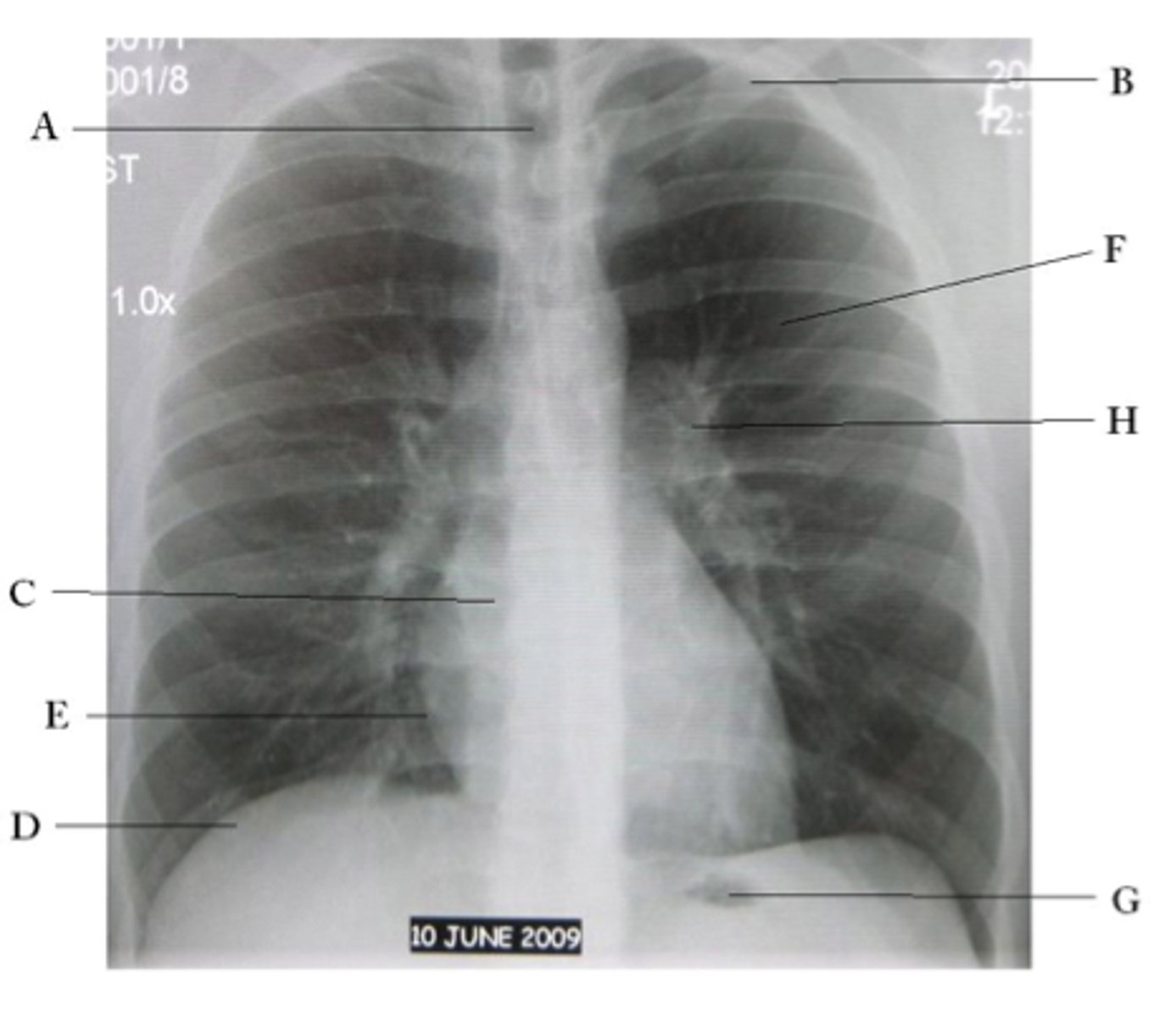
C
Right atrium
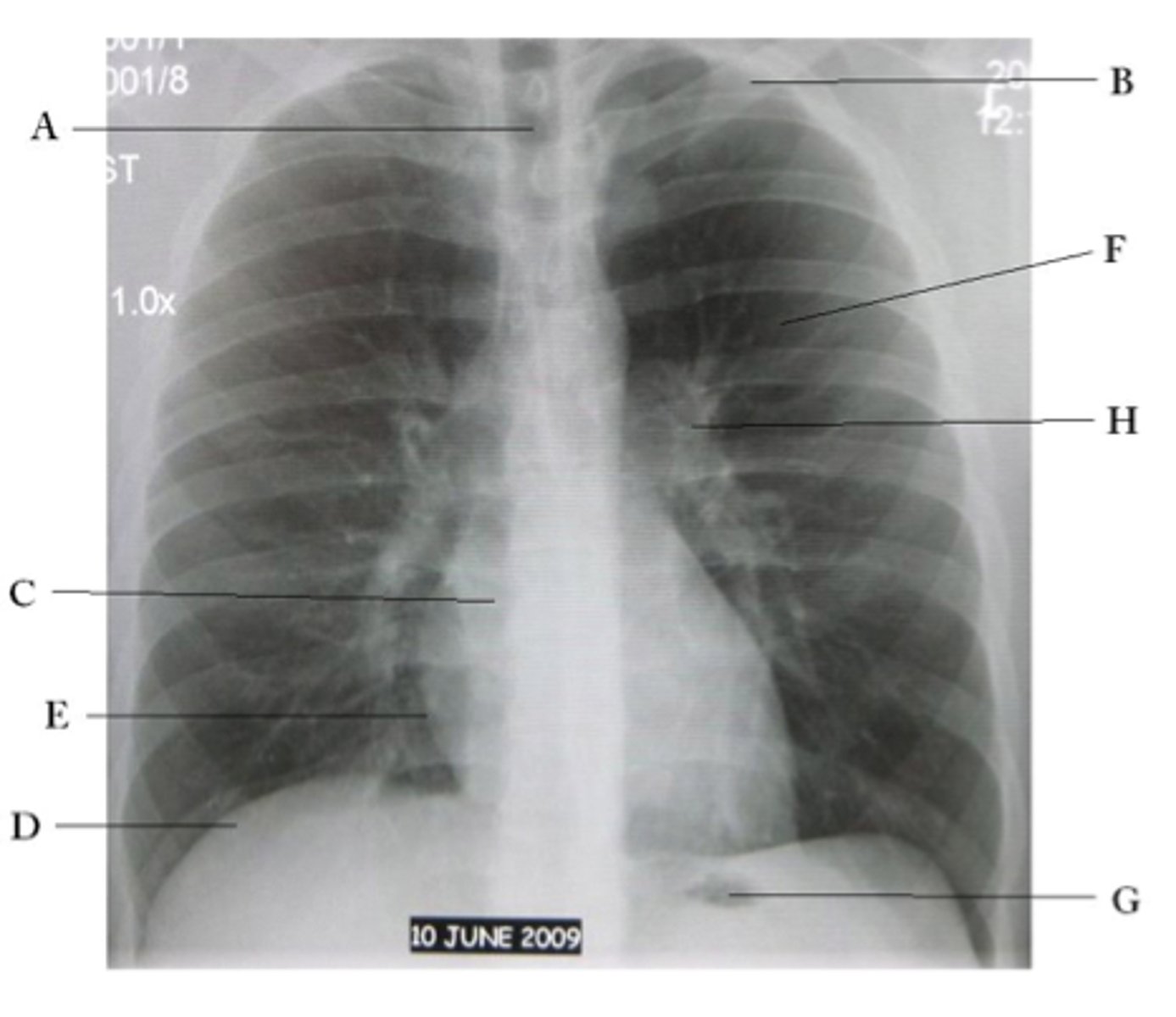
D
Diaphragm
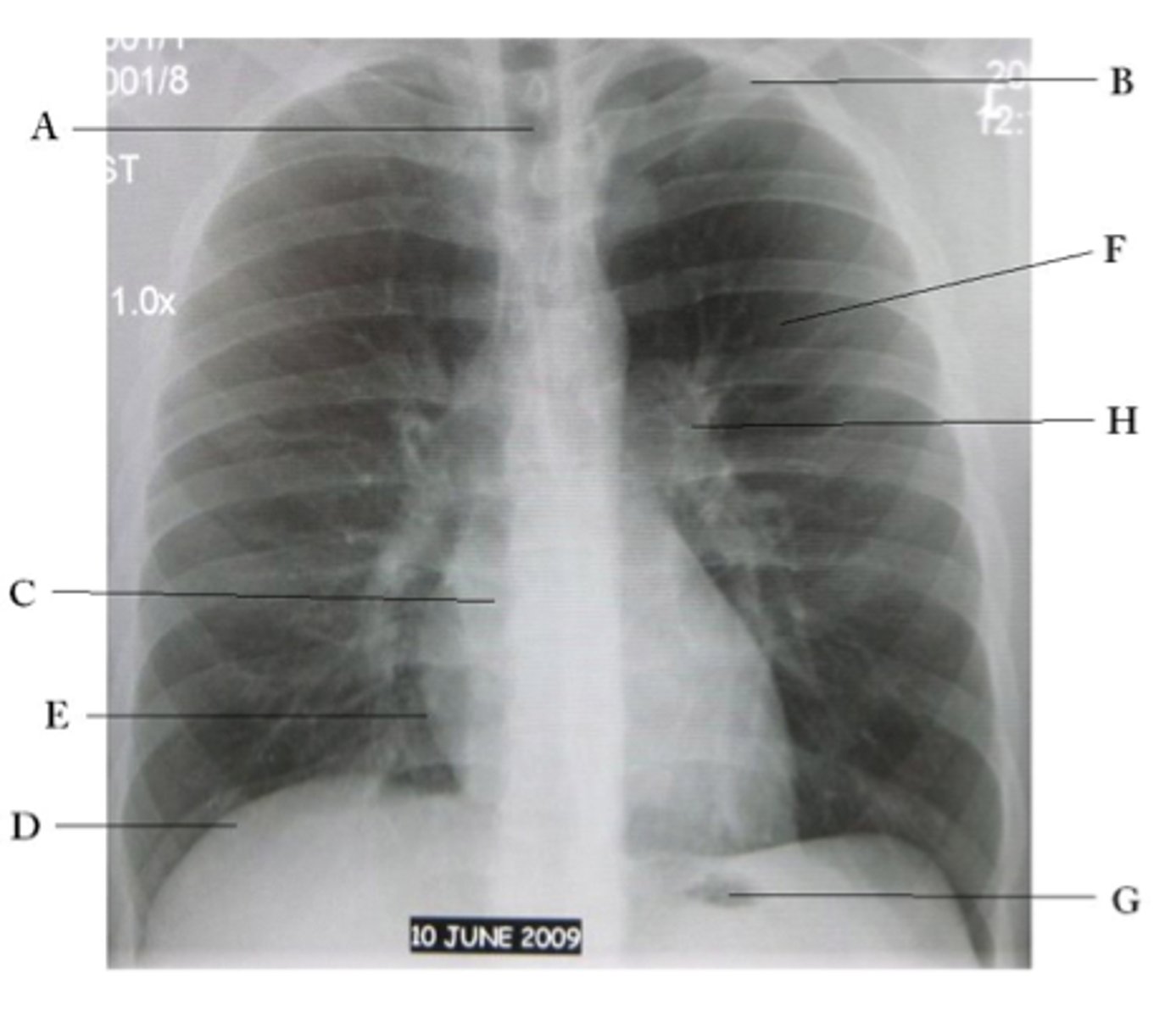
E
Cardiophrenic angle
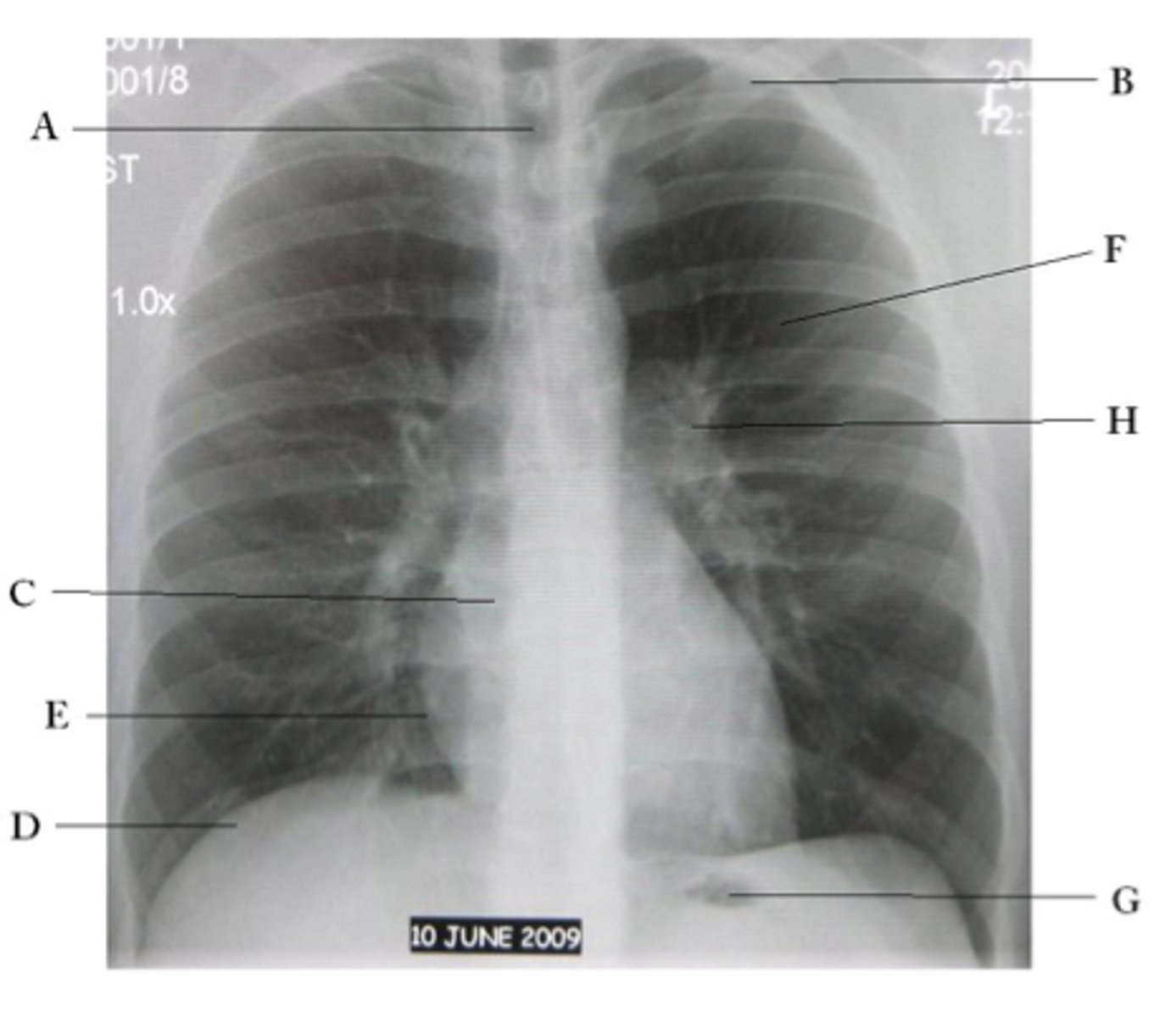
F
left upper lobe
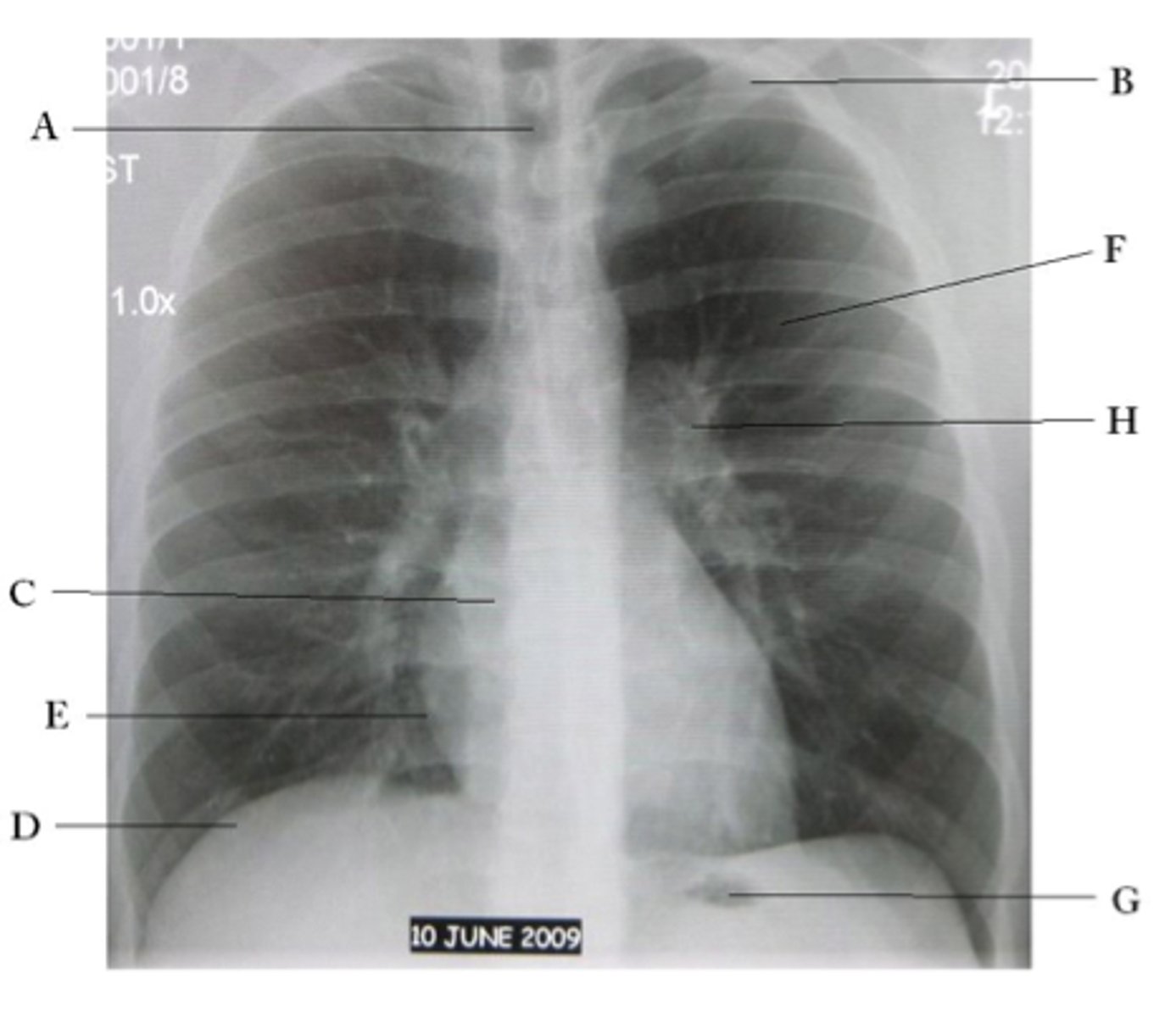
G
gastric bubble
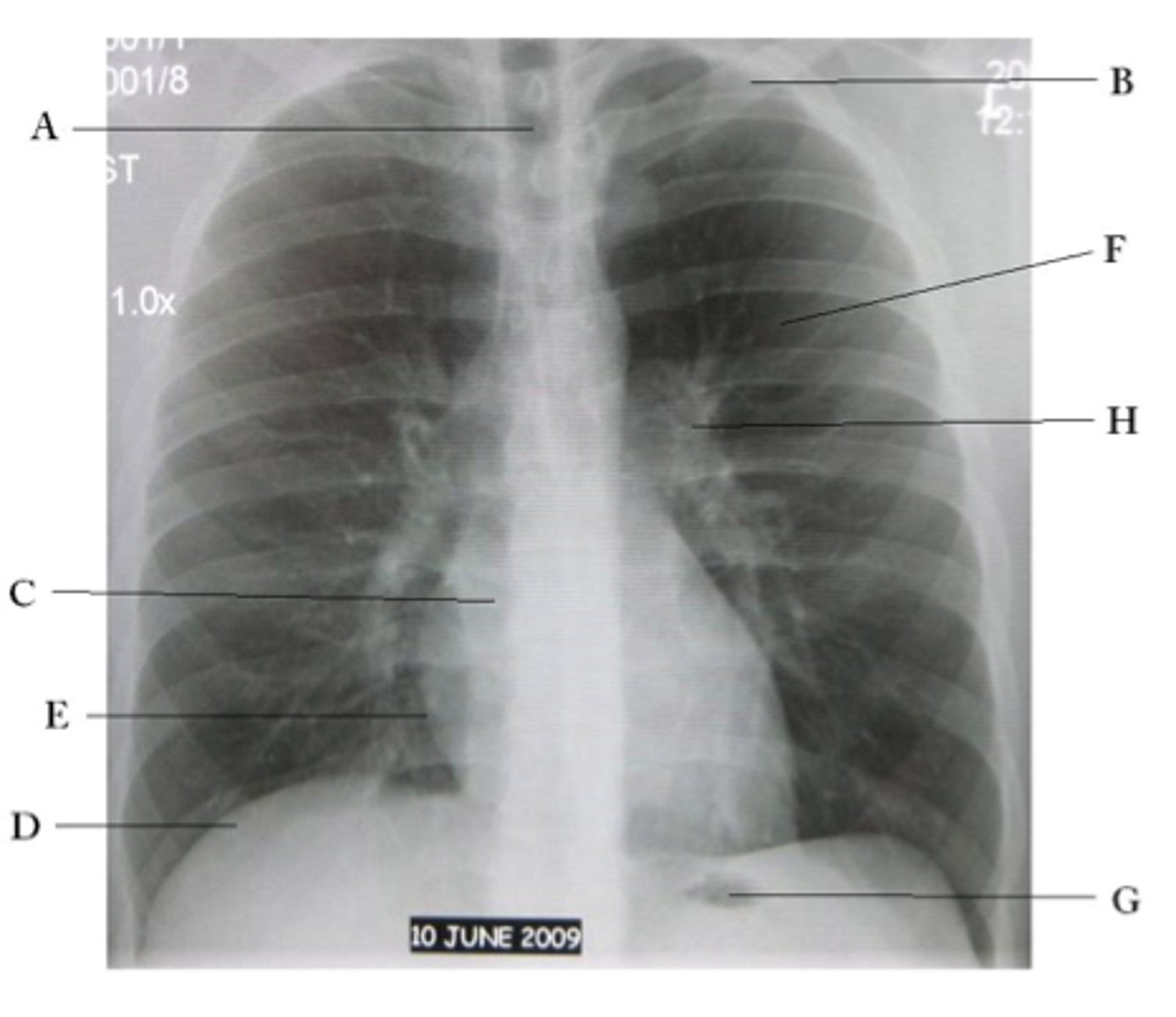
H
Left hilum
Reticular interstitial infiltrate (fine)
Reticular interstitial infiltrate (coarse)
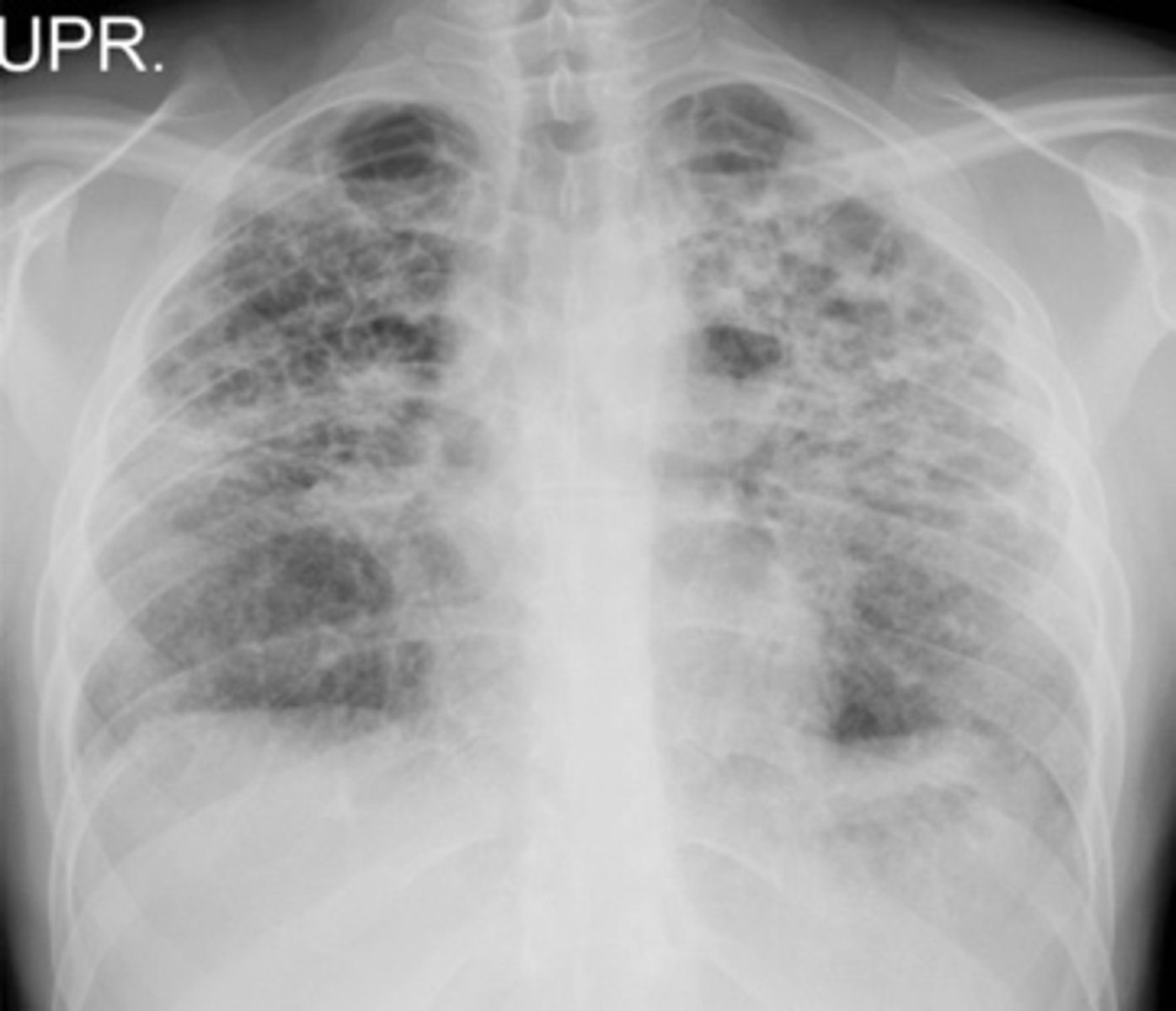
Nodular Interstital infiltrate
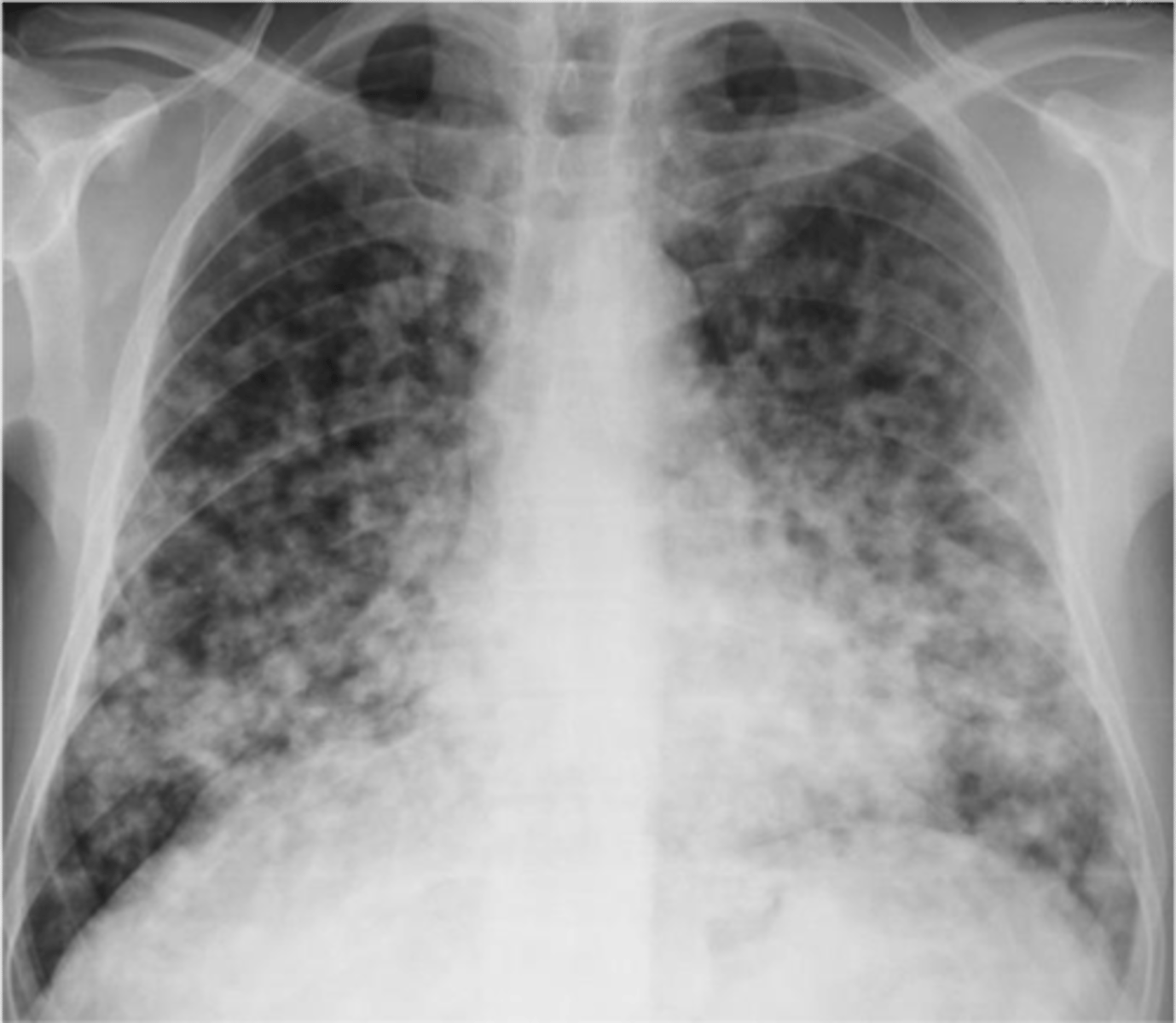
Reticulonodular interstitial infiltrate
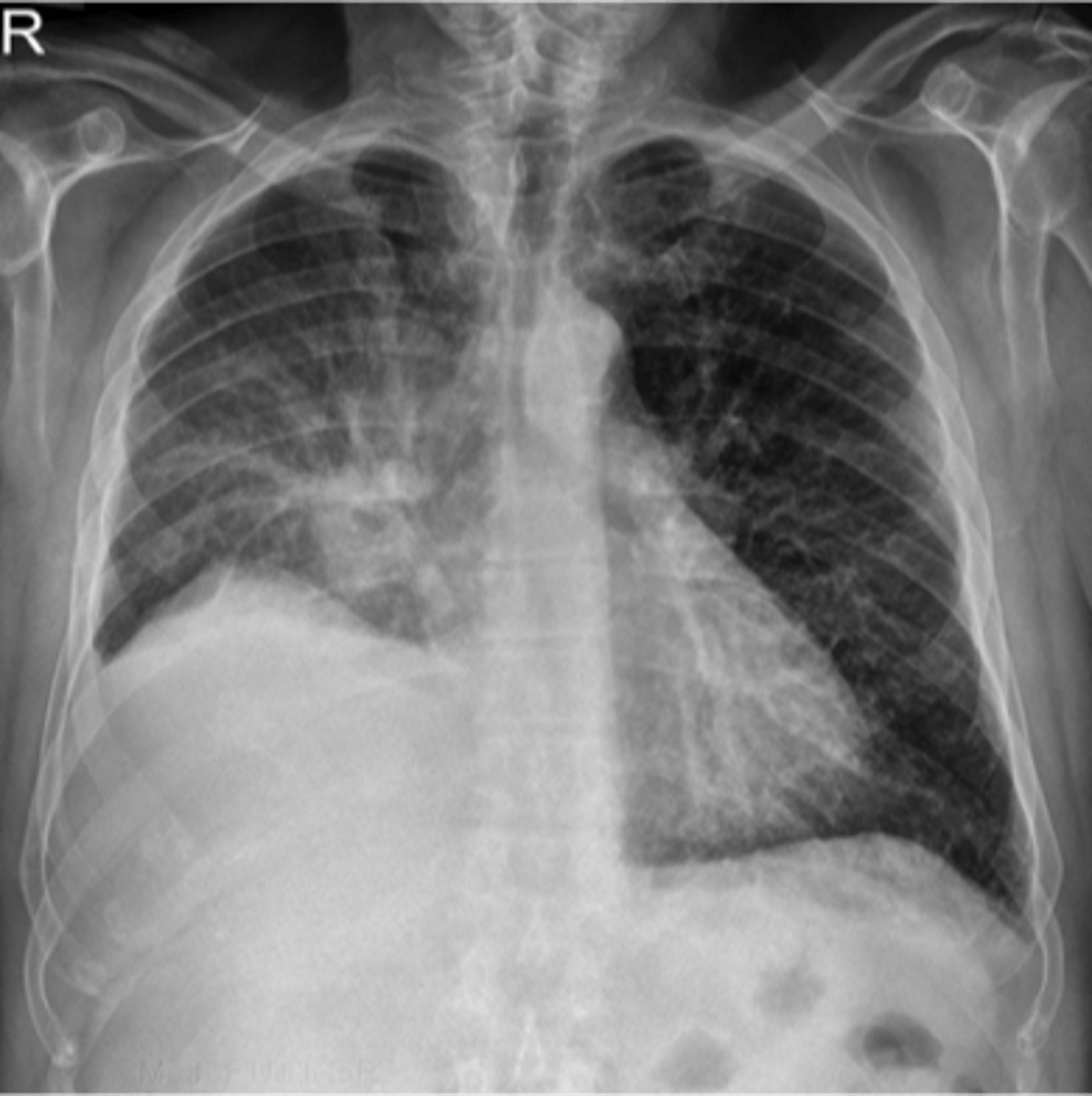
community acquired pneumonia
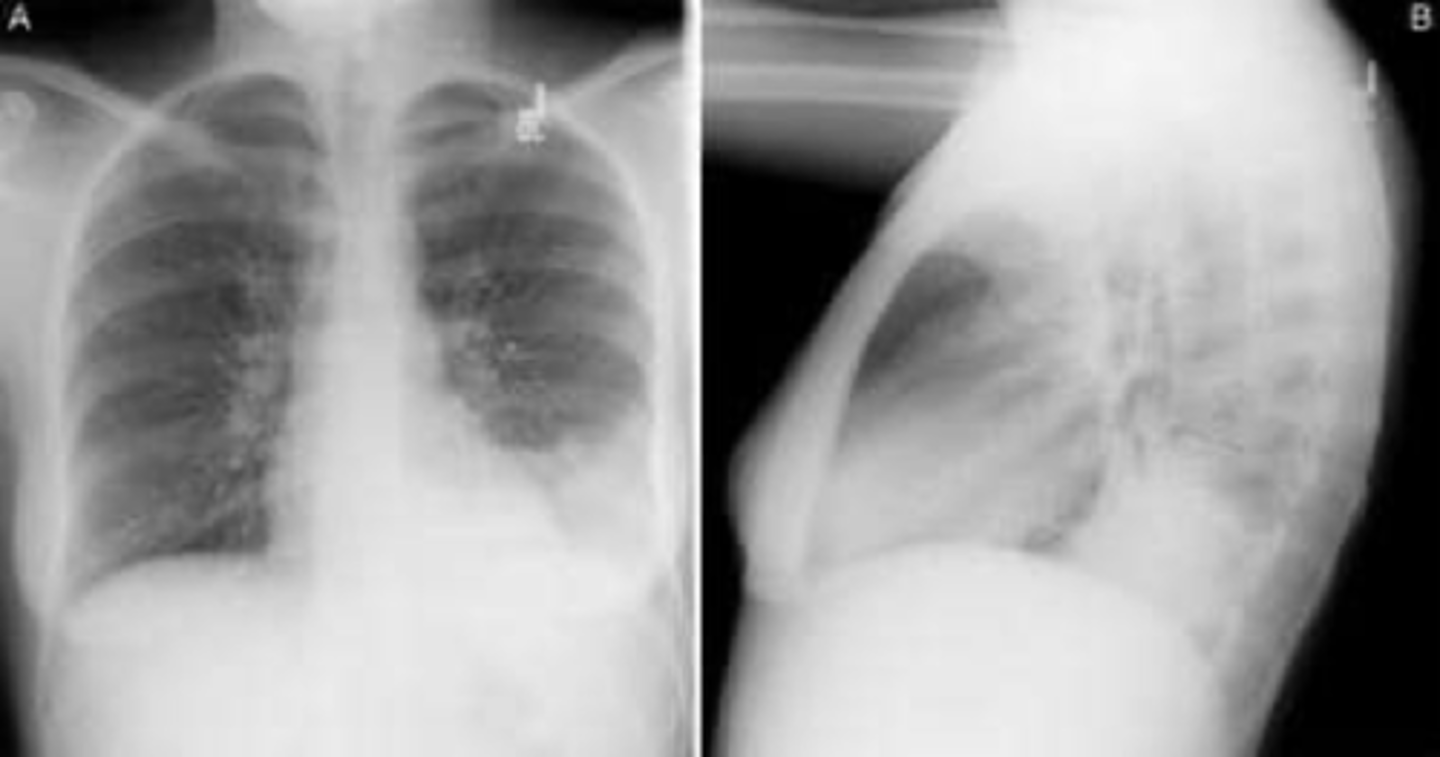
Silhouette sign
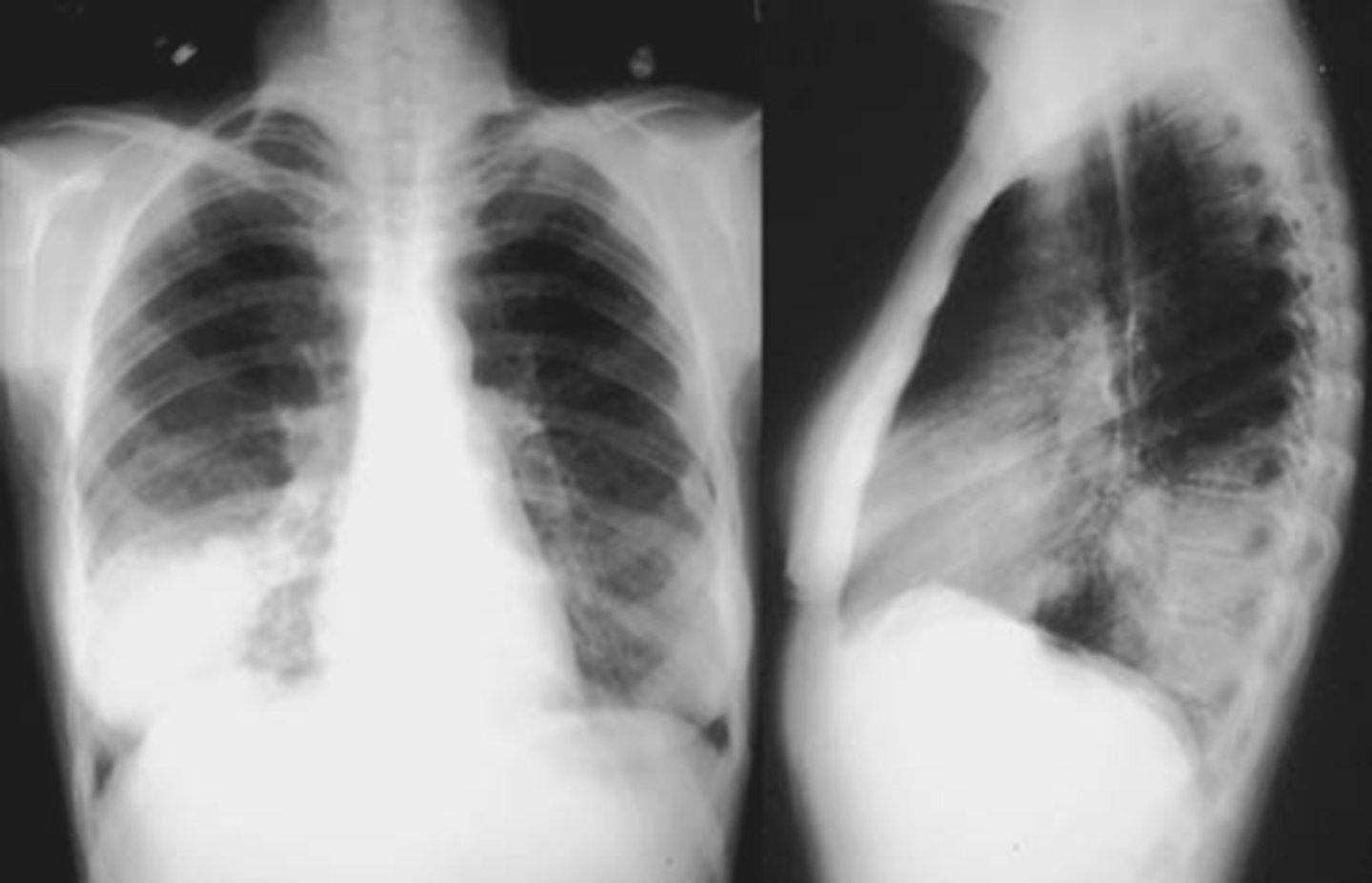
spine sign
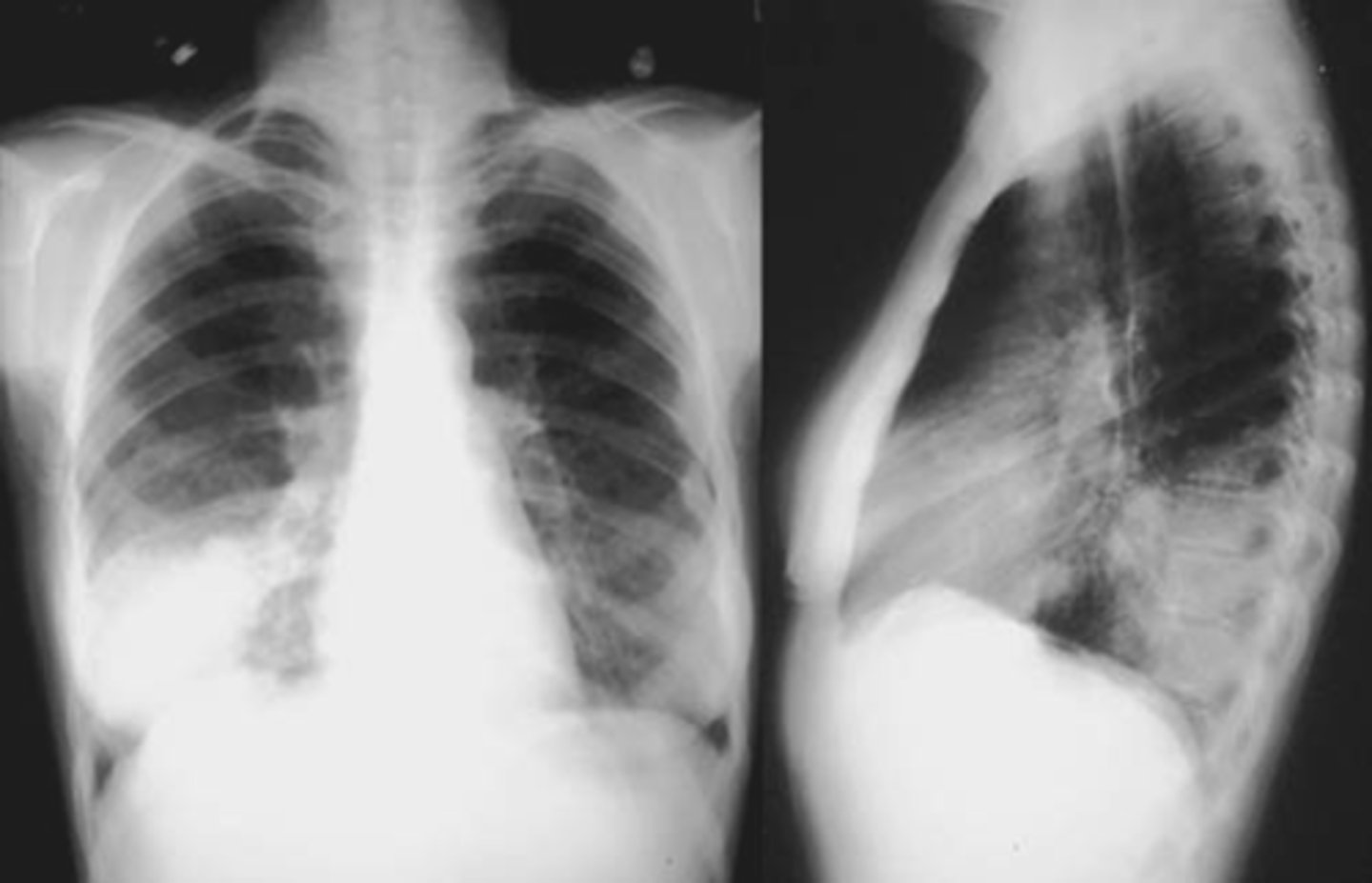
CAP- interstitial
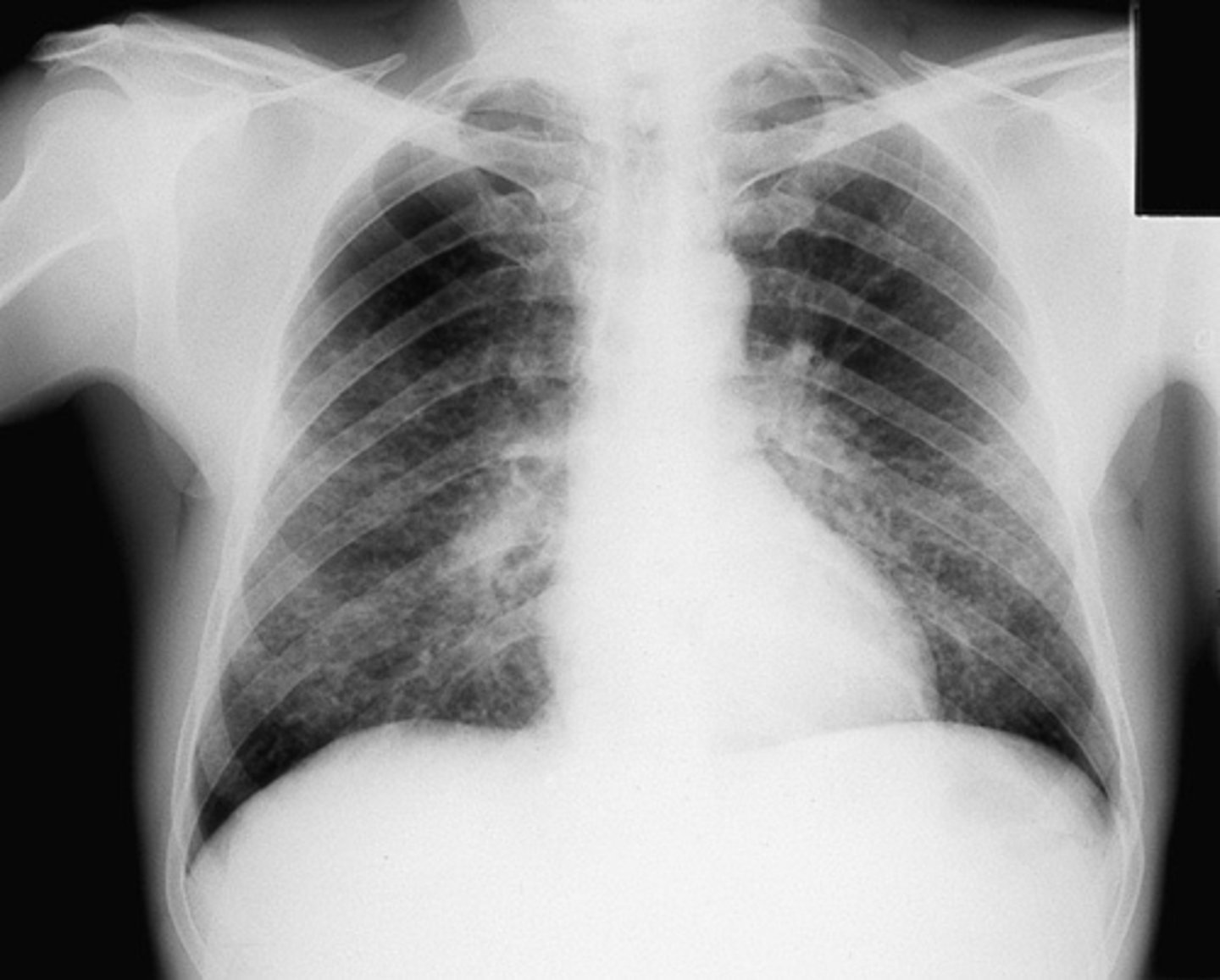
CAP- round
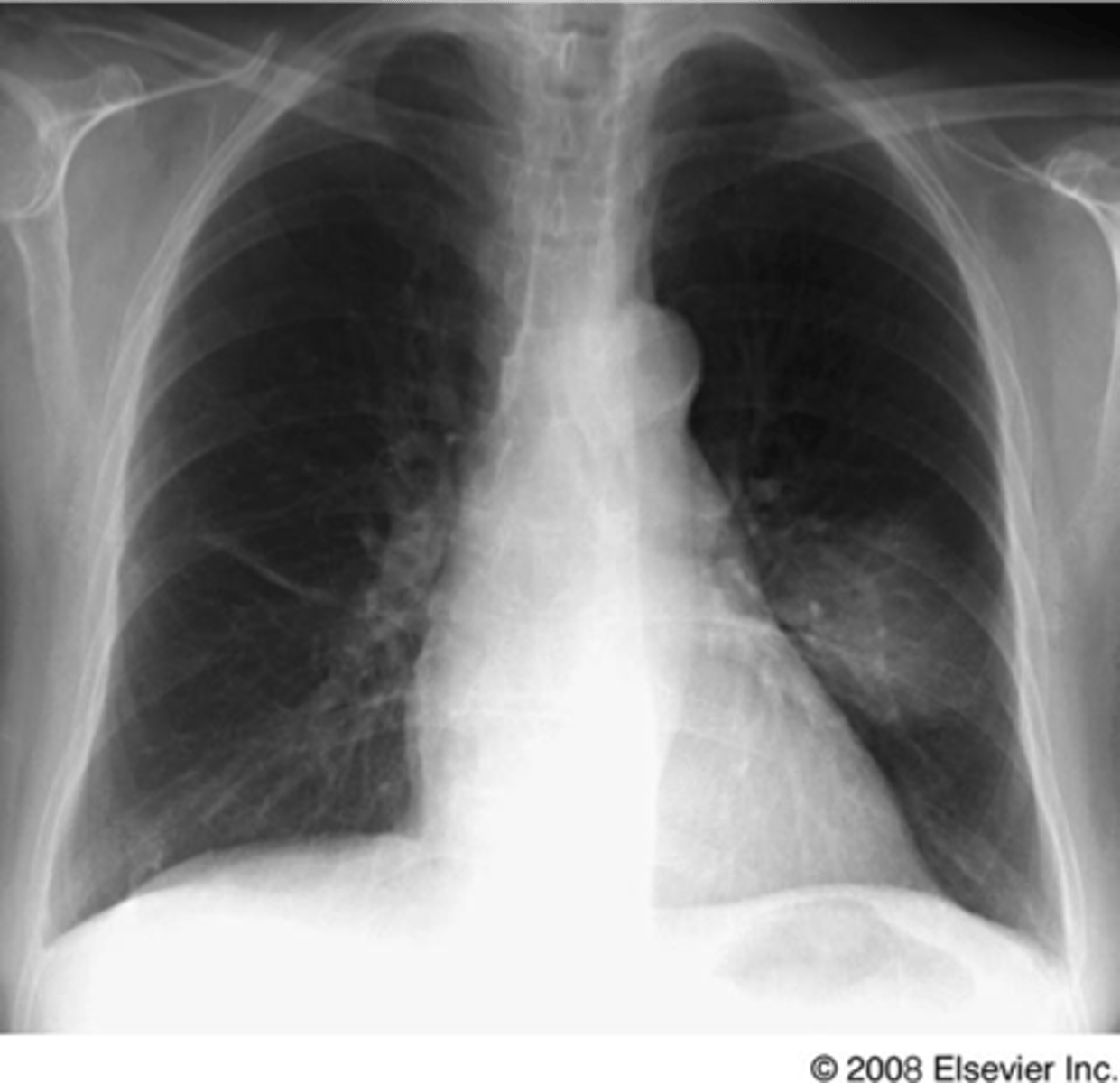
Aspiration pneumonia
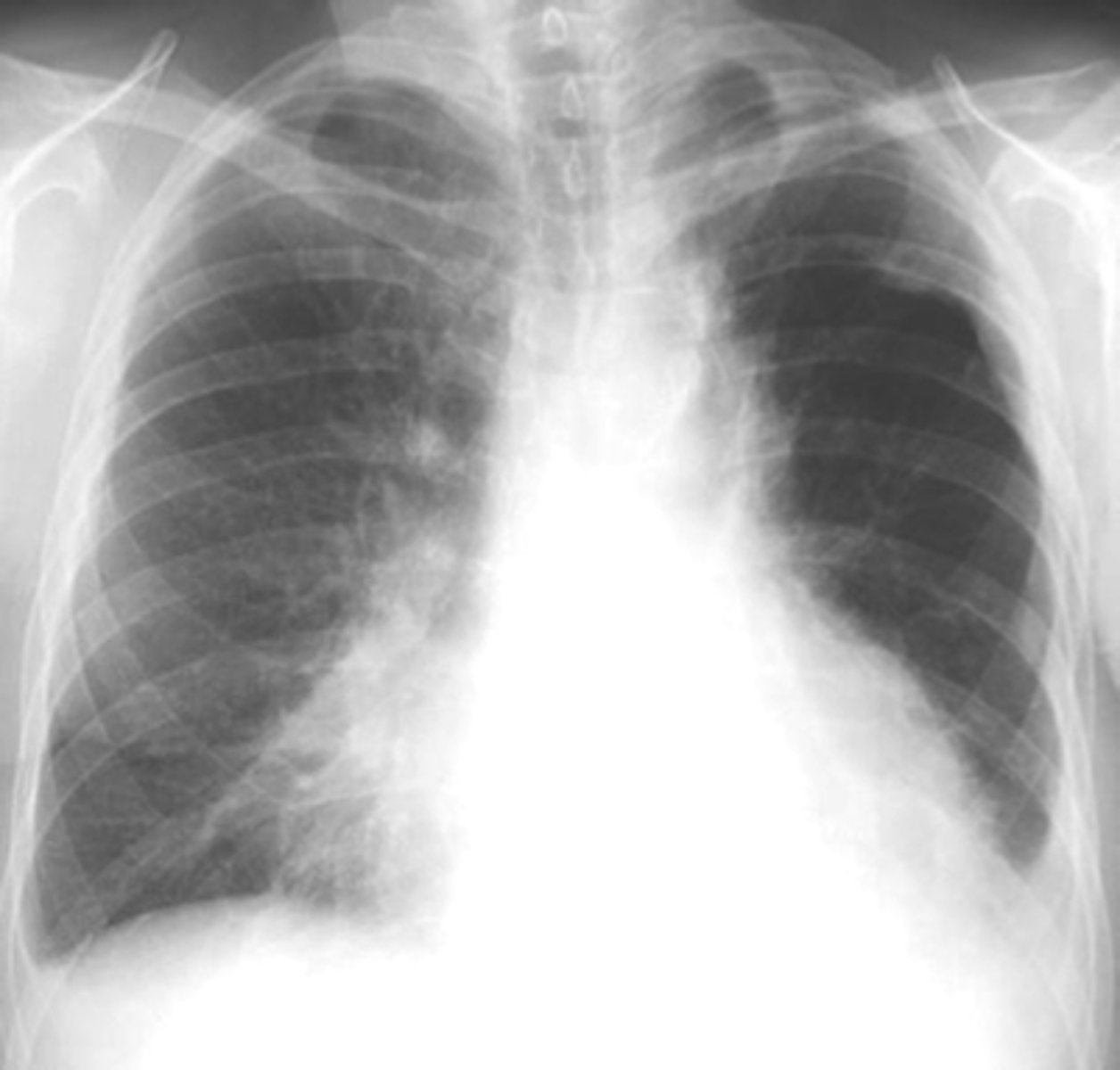
lung abscess
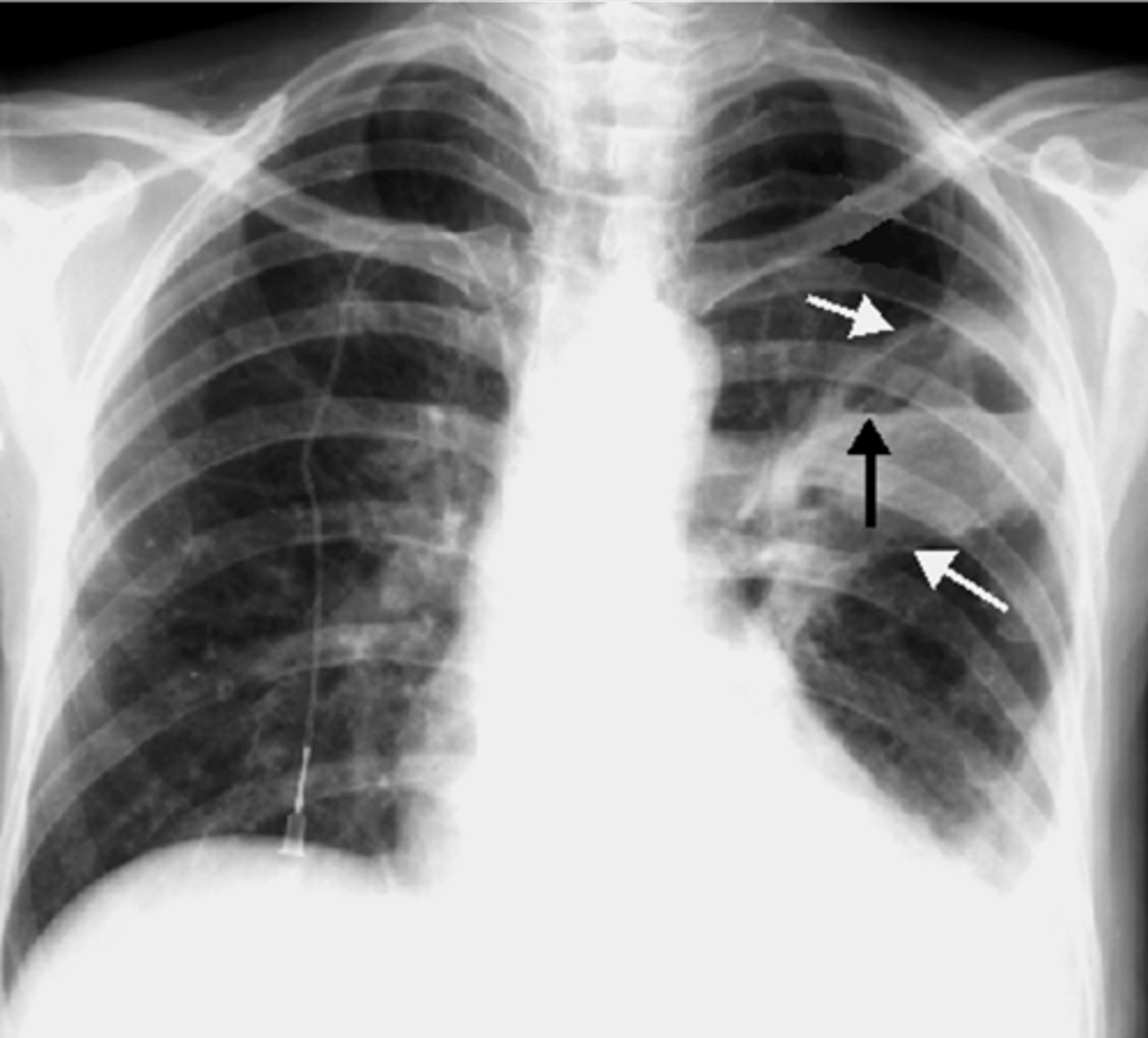
ARDS
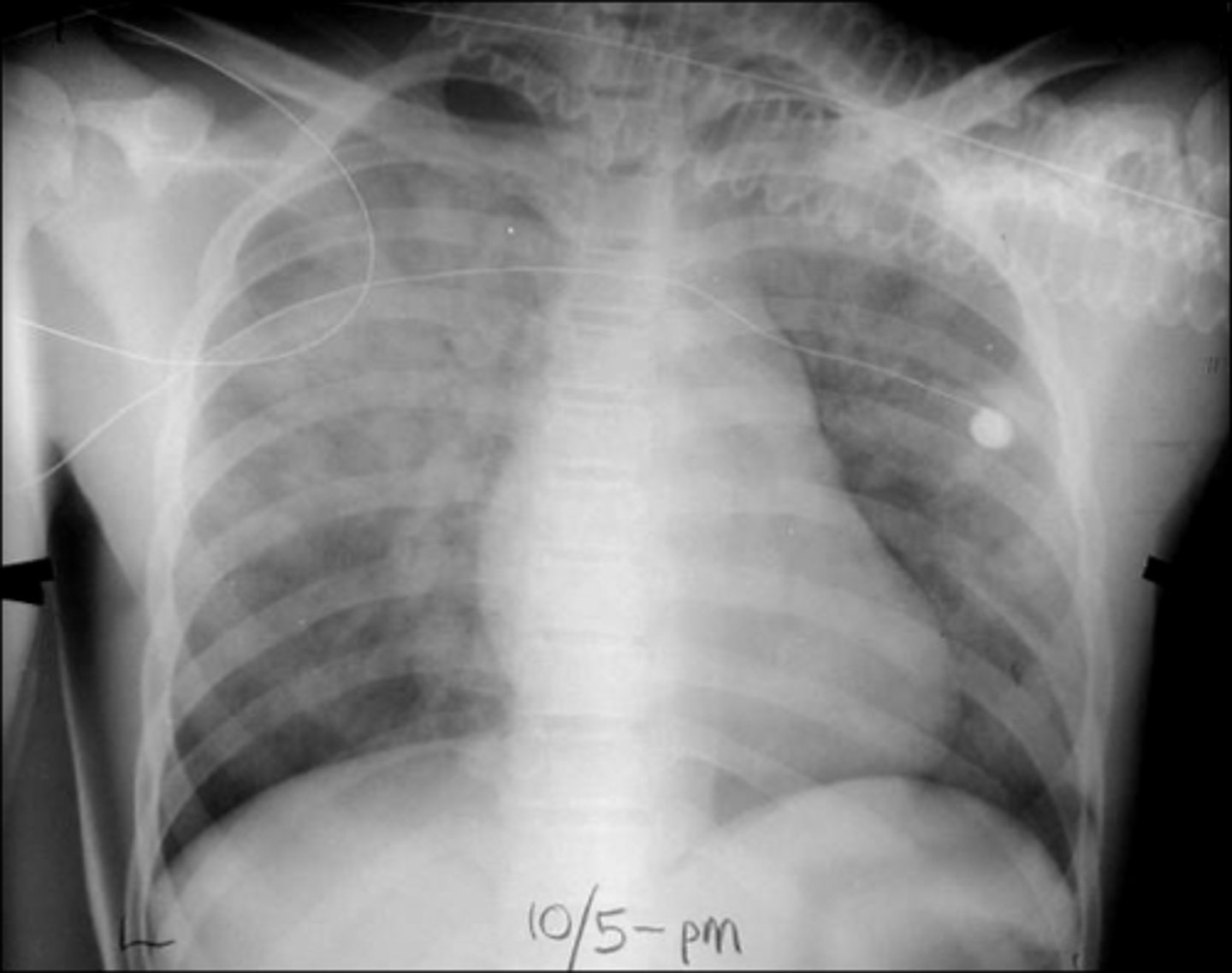
ARDS
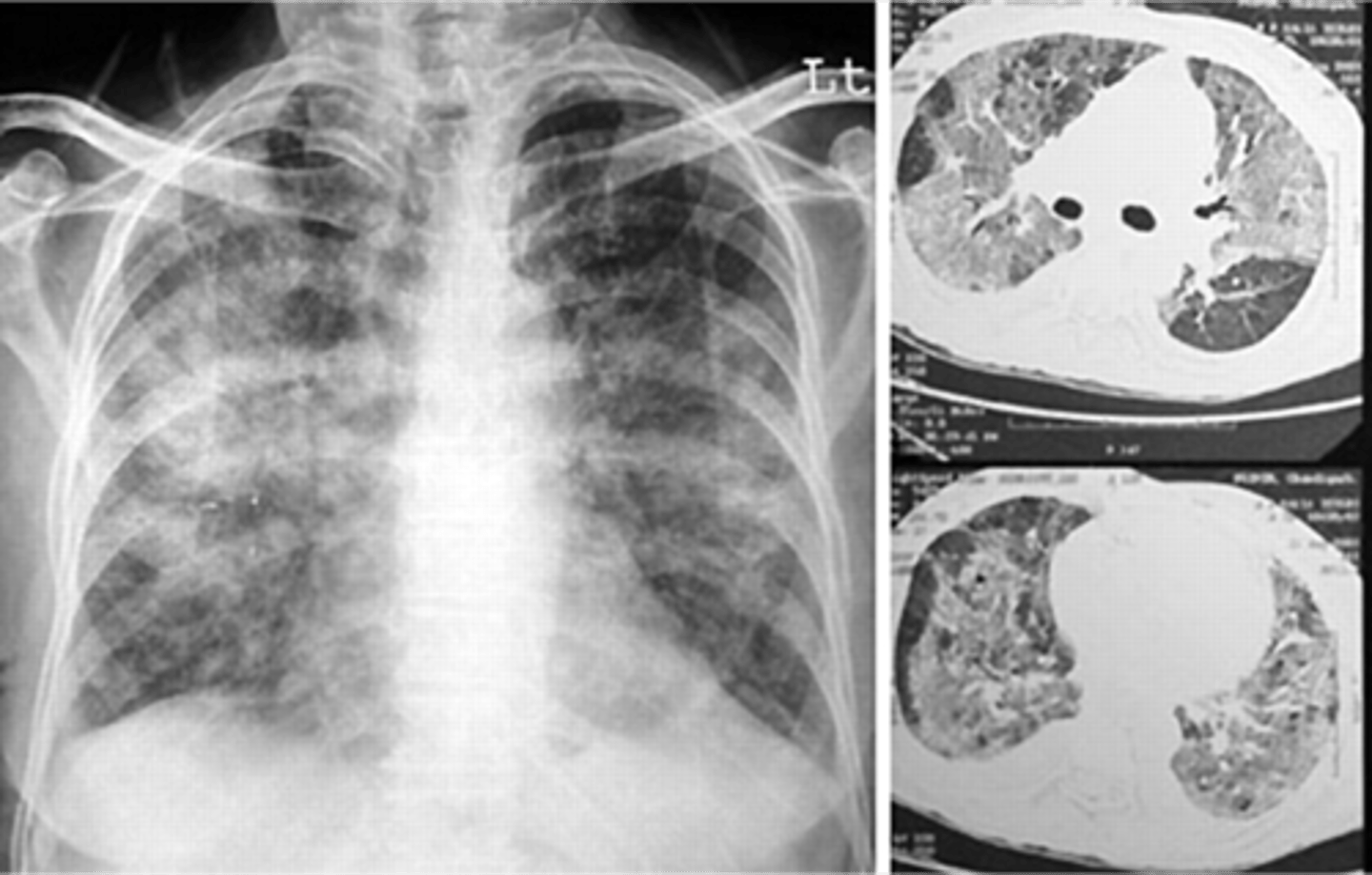
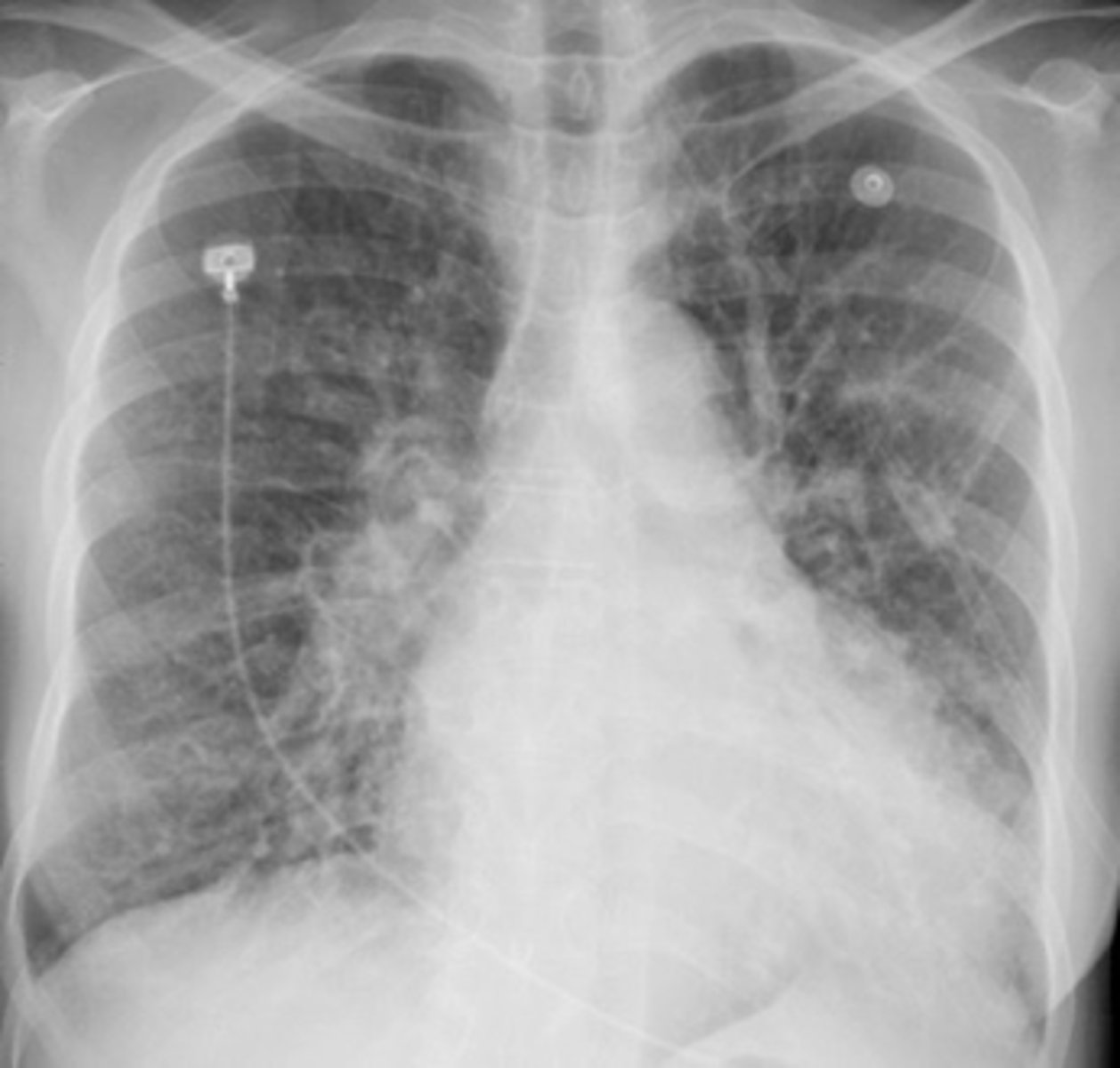
Solitary pulmonary nodule
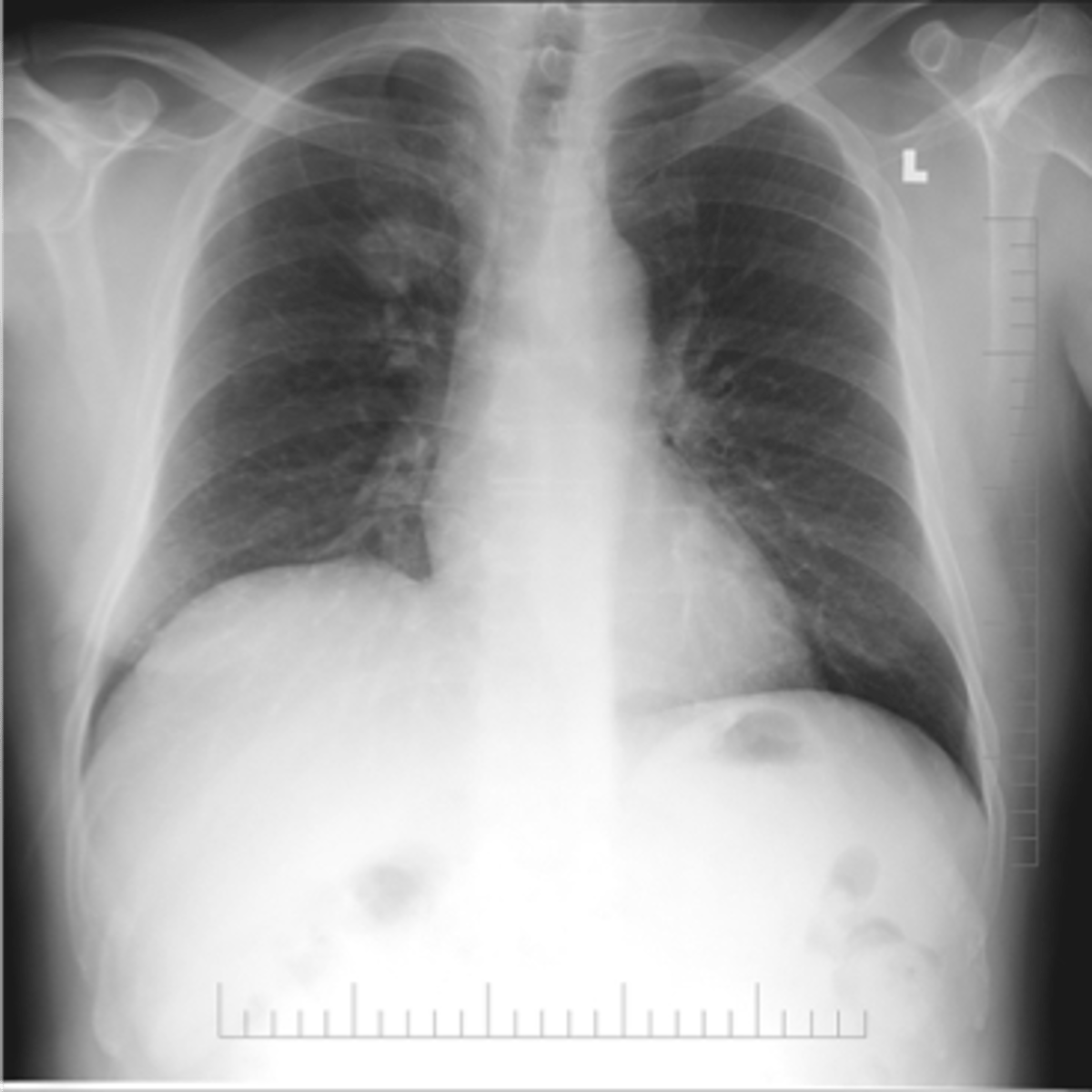
Lung cancer- adenocarcinoma
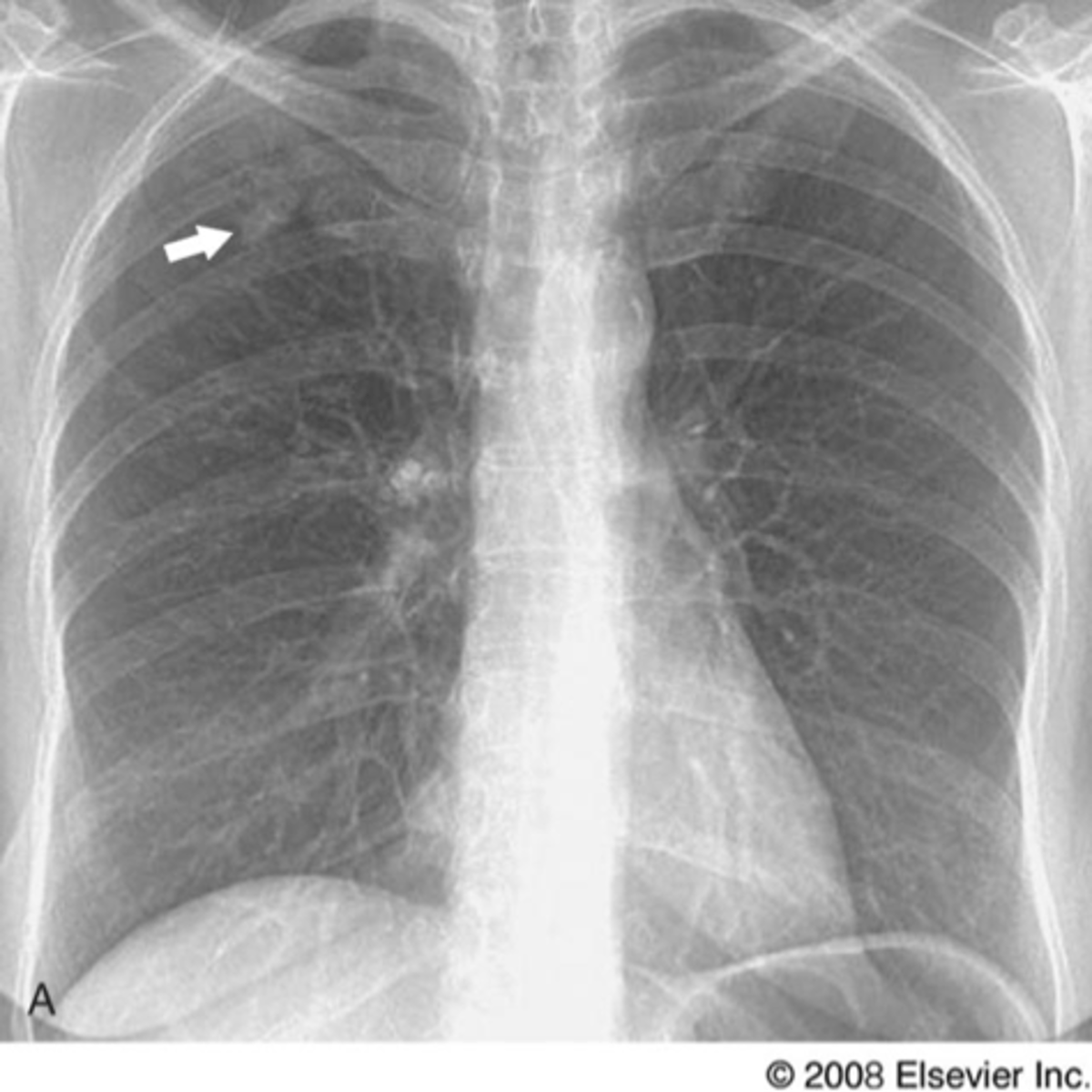
Lung cancer- squamous cell carcinoma
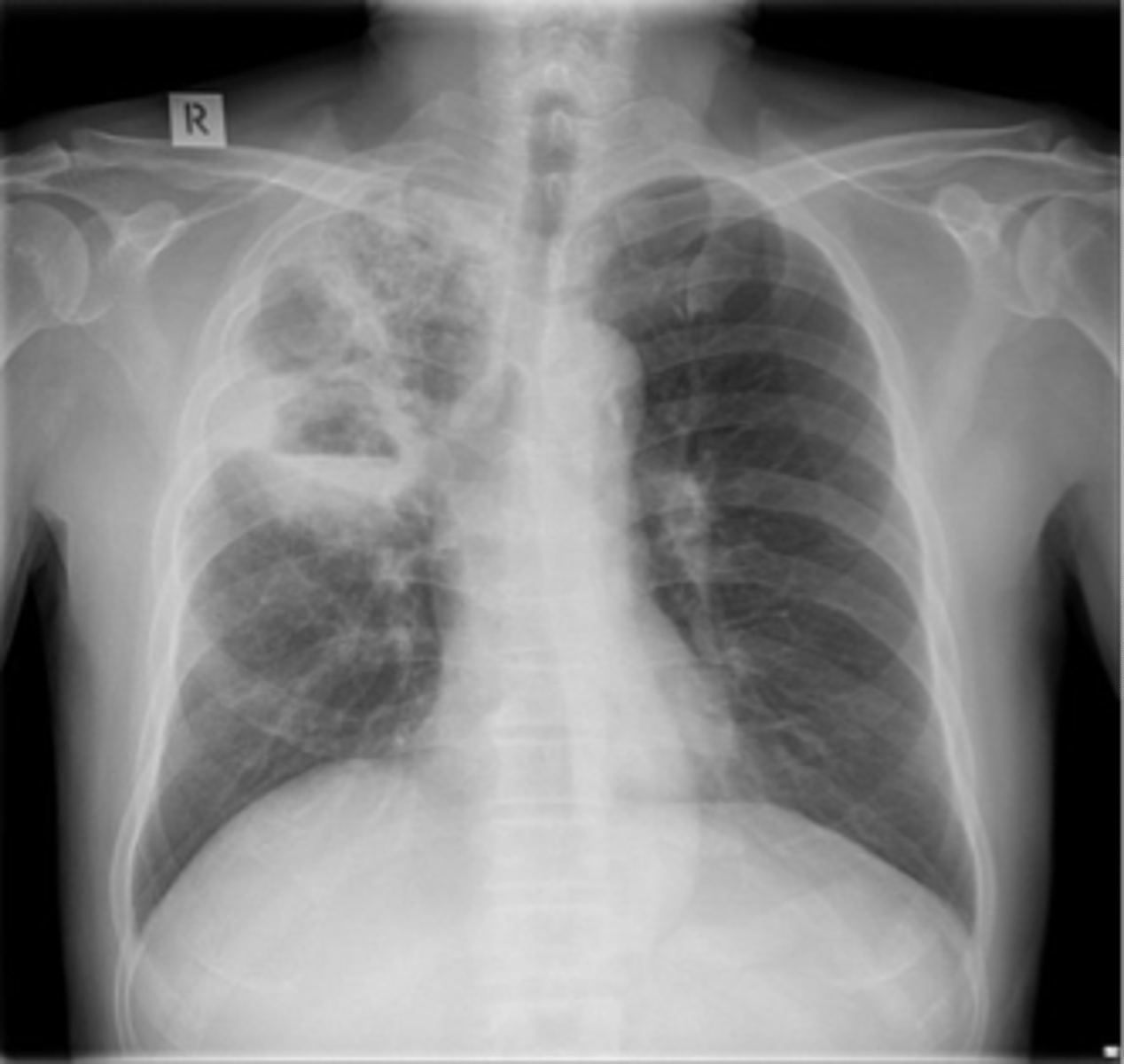
Lung cancer- non small cell carcinoma
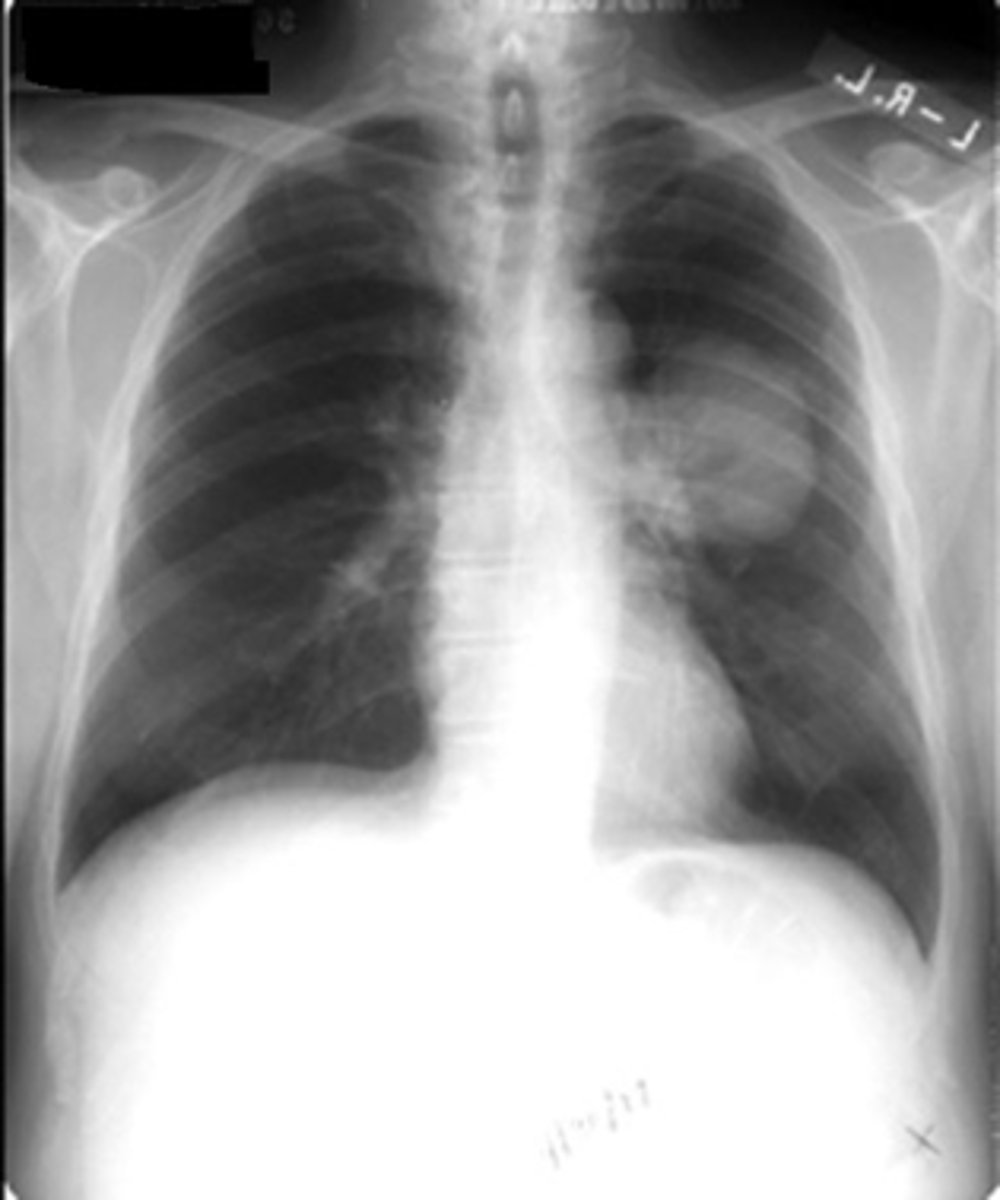
Pancoast tumor
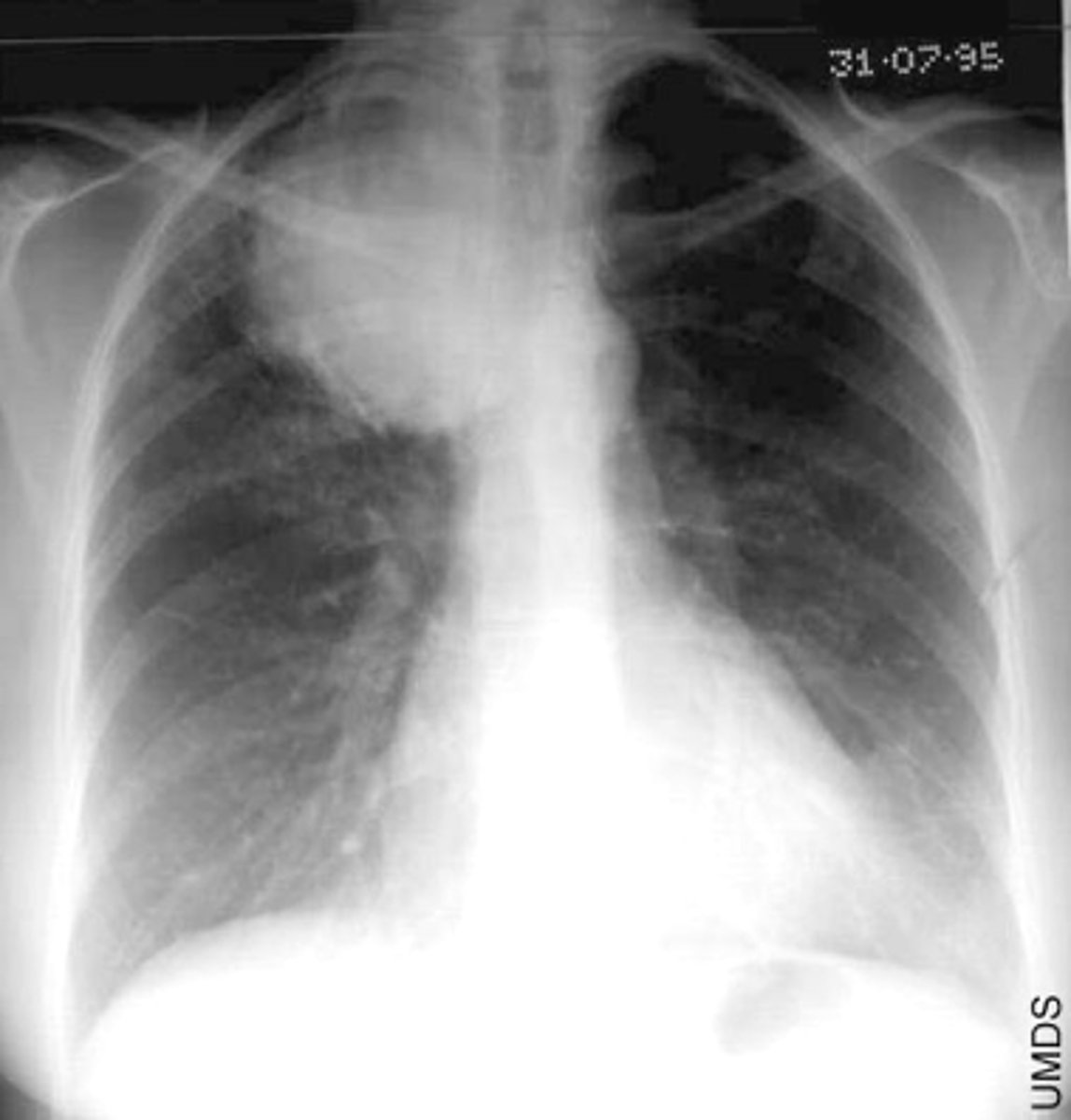
Lung cancer- metastatic disease
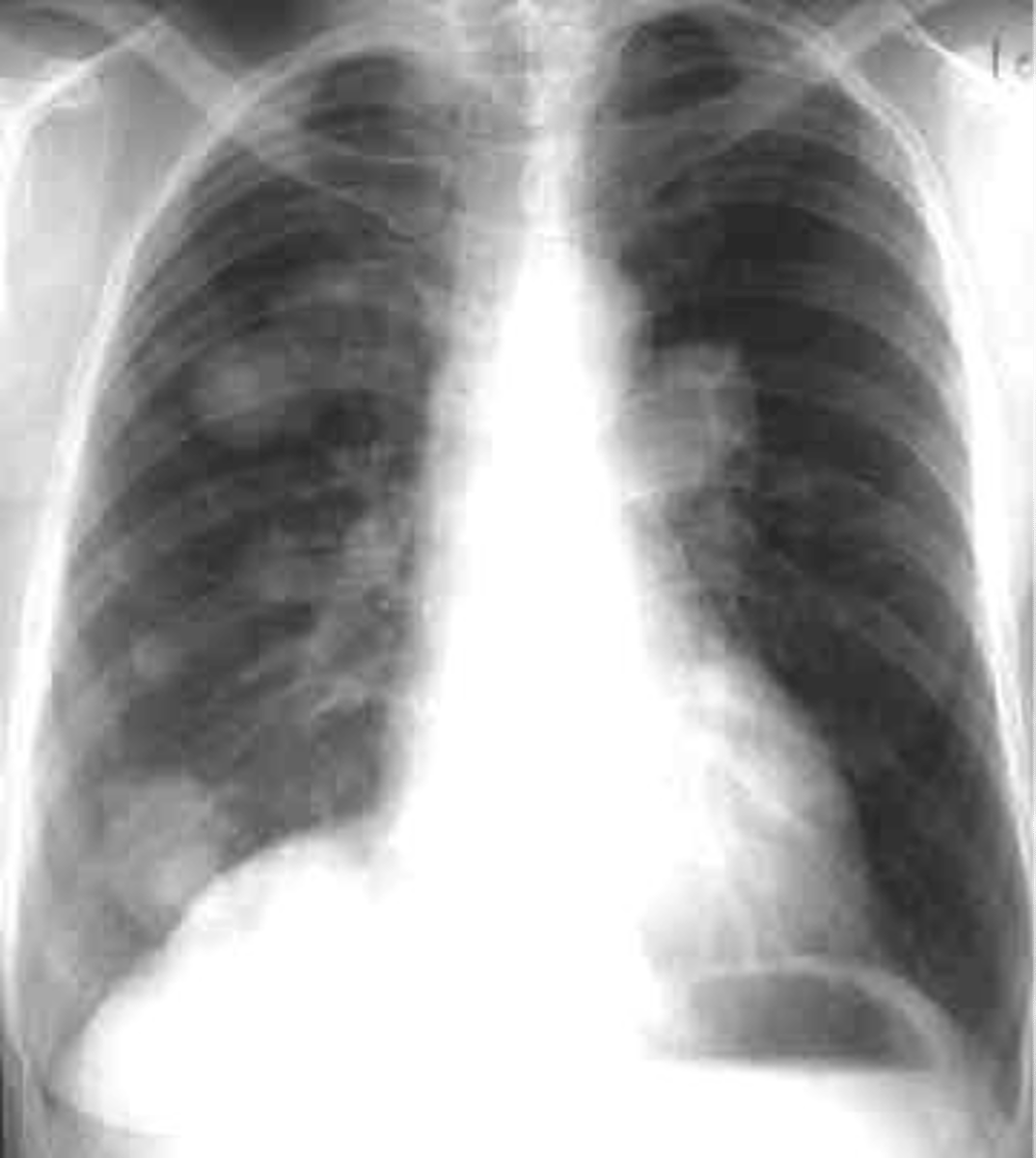
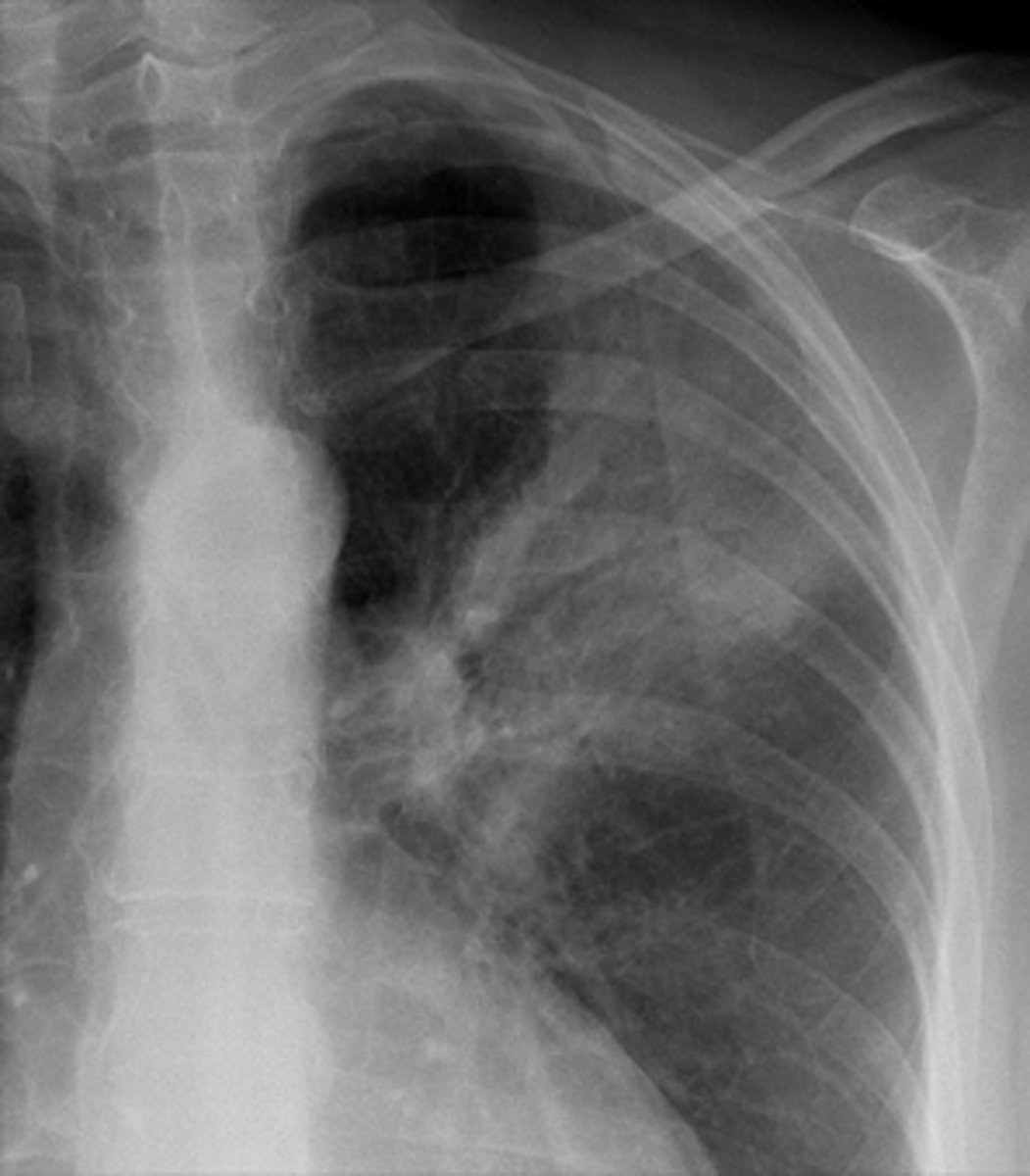
Silhouette sign right cardiac border- RML infiltrate
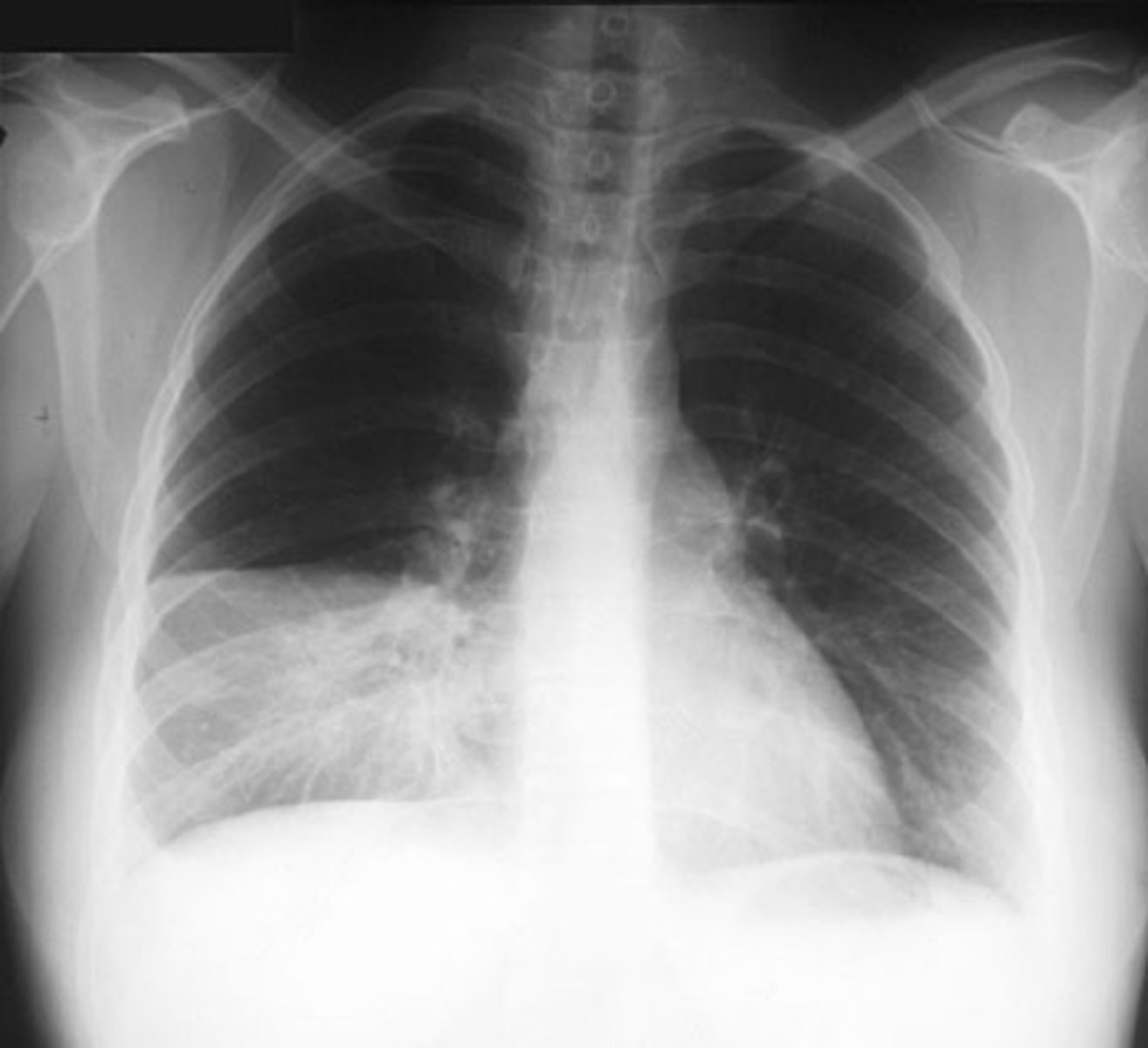
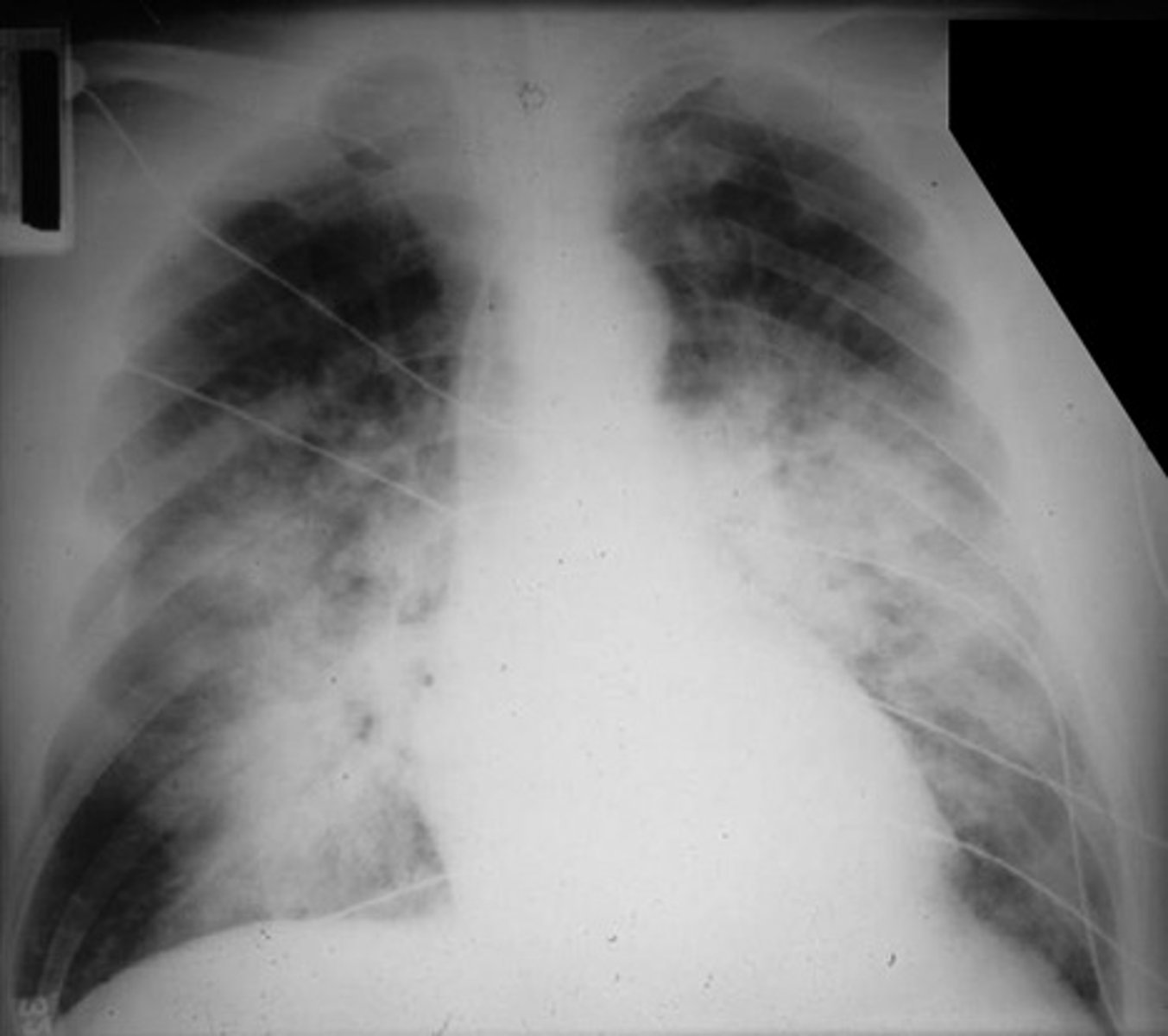
Bilateral interstitial infiltrates
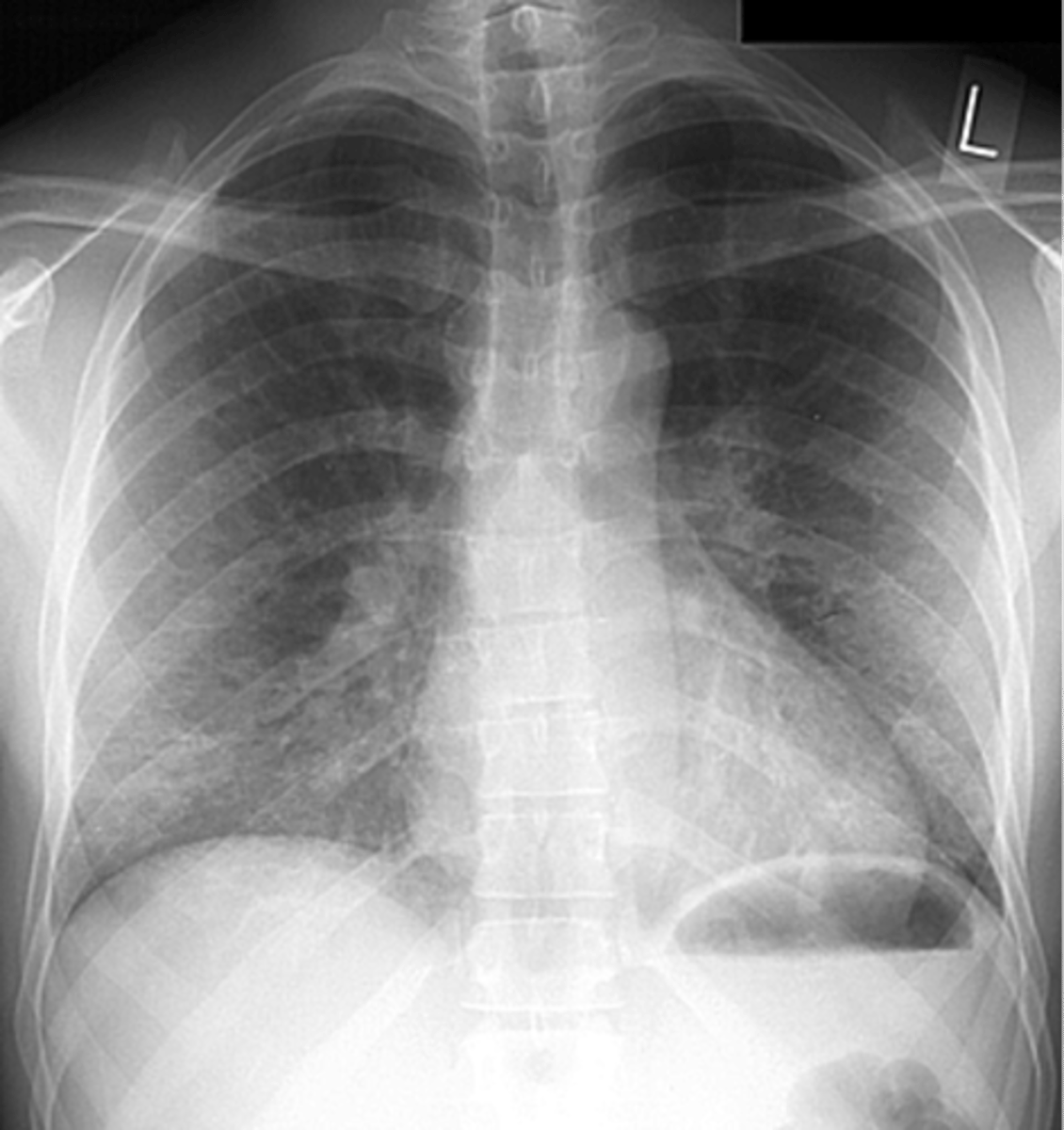
squamous cell carcinoma
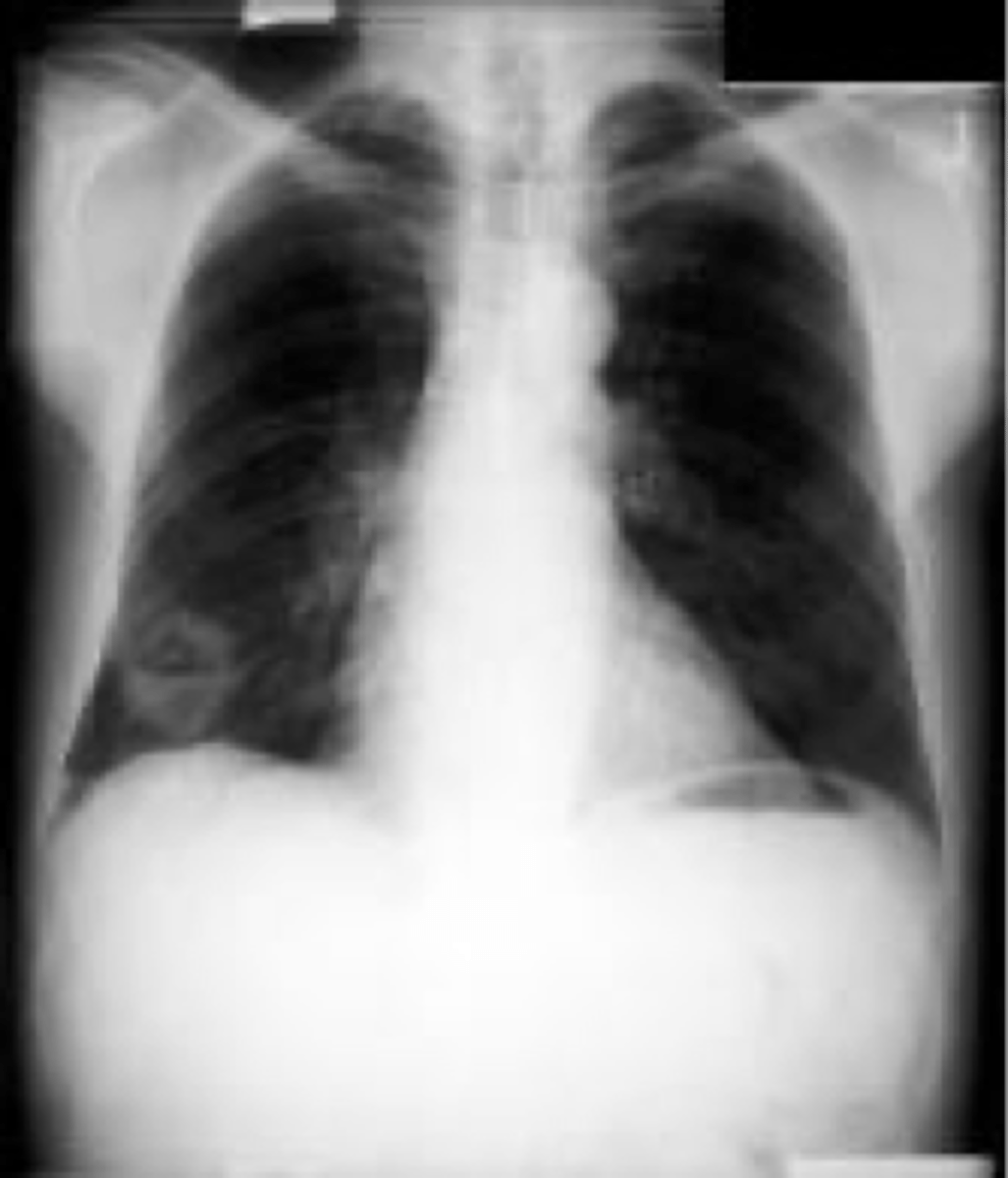
Bilateral pleural effusion
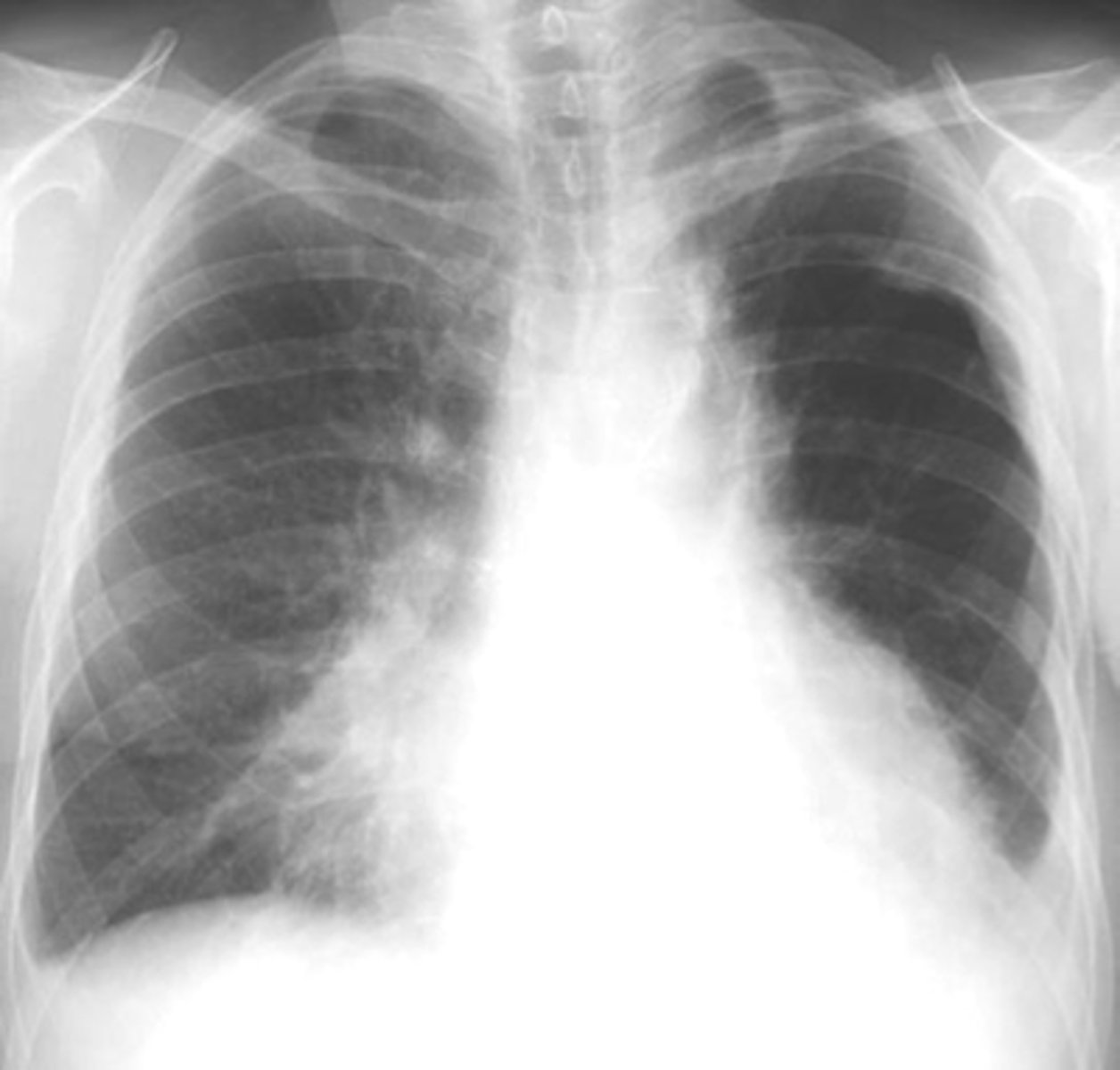
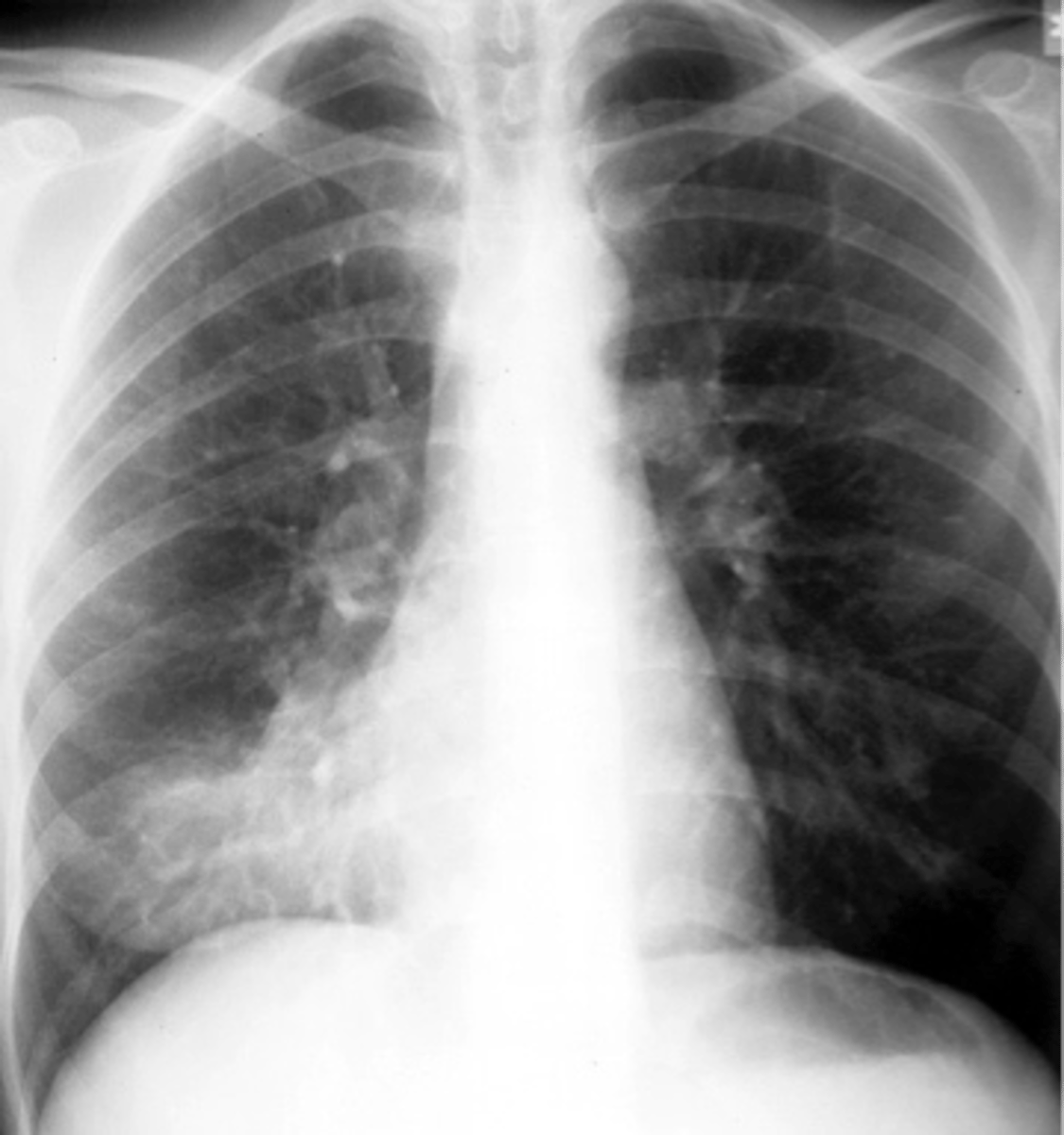
air bronchogram- alveolar consolidation LUL
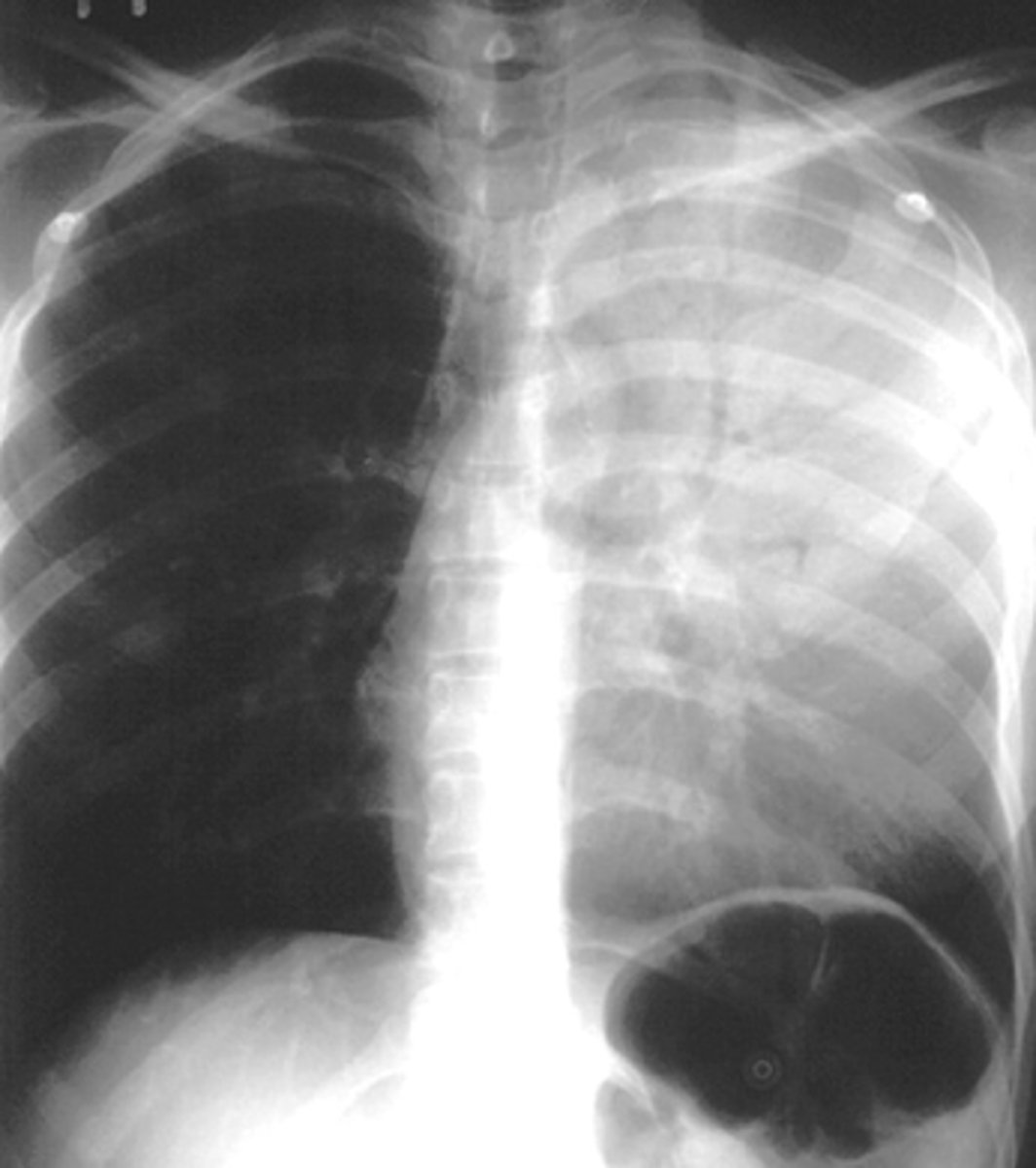
Multiple nodules- metastatic
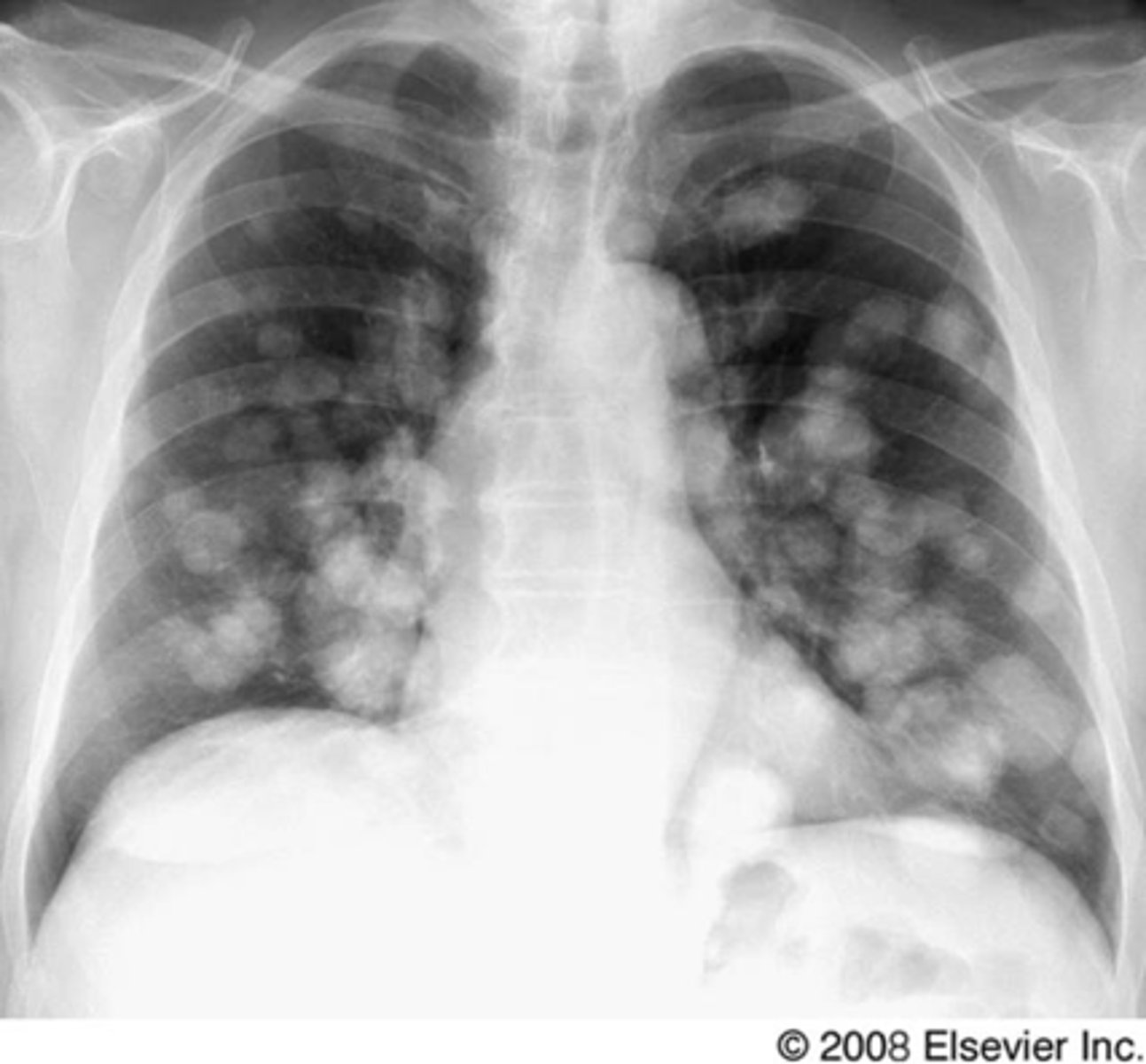
Nodule
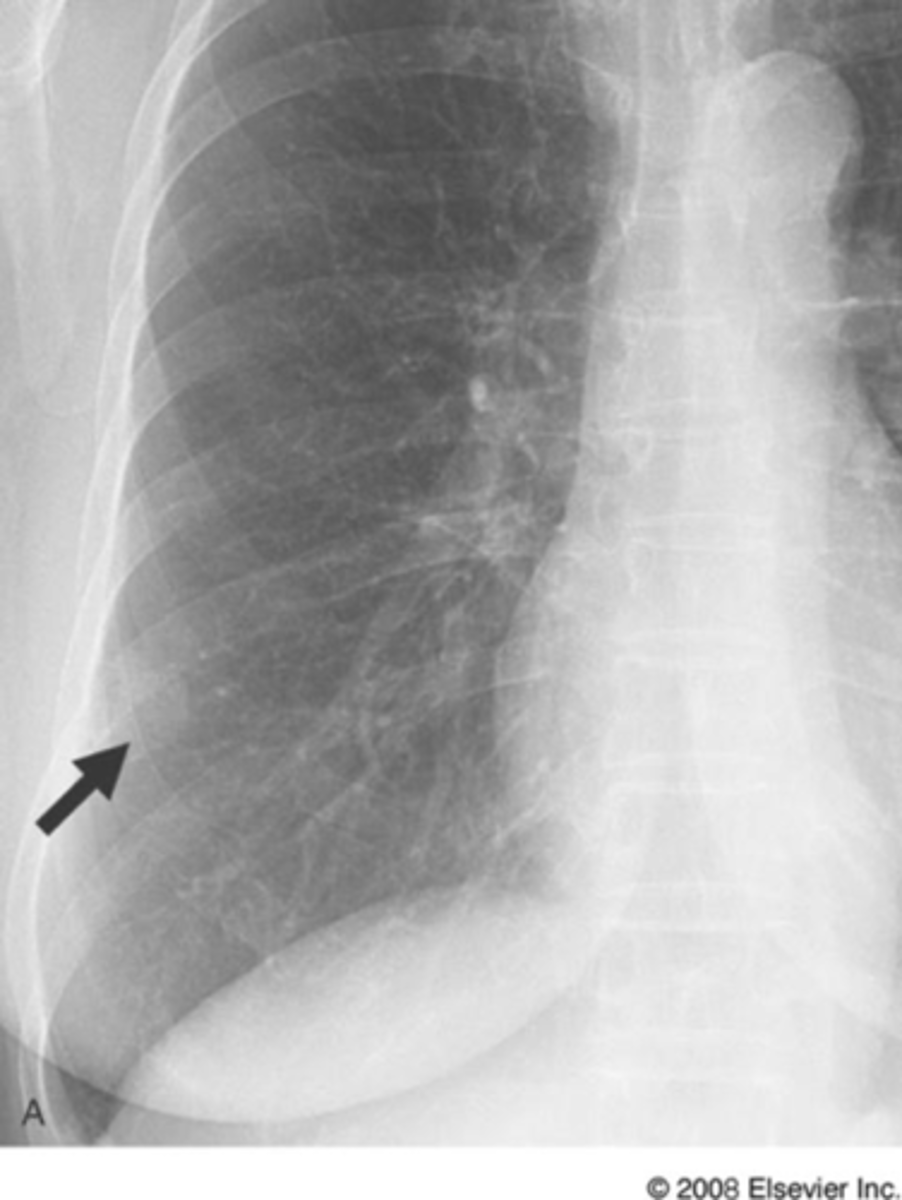
Silhouette sign right cardiac border, RML