LIVER
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
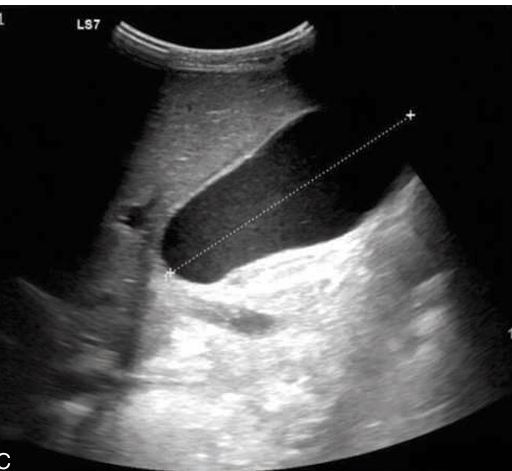
Size of the liver in the sagittal plane ~15 cm
Parenchyma ~ homogeneous
Liver texture > right kidney; <pancreas, <spleen
Presence of hepatic vascular structures, ligaments, fissures
Surface ~ smooth
Normal liver
Greatest transverse diameter of liver:
21 to 22.5 cm
Greatest vertical height of liver:
13 to 17.5 cm
Anteroposterior depth of liver: (in sag)
10 to 12.5 cm
Weight of the liver:
1200 to 1600 g (in adults) (2.65 to 3.53 lbs)
causes
Obesity
Excessive alcohol intake
Poorly controlled hyperlipidemia
Diabetes
Excess corticosteroids
Pregnancy
Total parenteral hyperalimentation
Severe hepatitis
Glycogen storage disease
Cystic fibrosis
Pharmaceutical
fatty liver causes
Most of the liver is covered by peritoneum, but a large area rests directly on the diaphragm; this is called the
bare area
the liver is covered by a thin connective tissue layer called
Glisson’s capsule.
space between the liver and right kidney
morrisons pouch
separates the left and right lobe of the liver
The main lobar fissure
This is the fetal remnant of the umbilical vein.
Ligamentum Teres
Liver cells (hepatocytes) produce bile.
Bile flows from liver cells into tiny bile ducts called bile canaliculi.
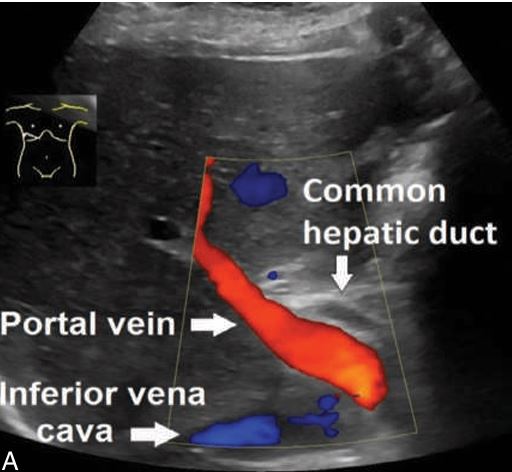
The bile moves through larger bile ducts and eventually to the common hepatic duct.
From the common hepatic duct, bile travels to the gallbladder for storage.
When you eat, the gallbladder releases bile into the small intestine (via the common bile duct) to help digest fats.
Bile Production and Transport
Blood from your intestines, which may contain toxins (like alcohol or drugs), travels to the liver through the portal vein.
The liver filters the blood to remove toxins.
Some toxins are turned into less harmful substances.
These filtered toxins are either:
Excreted in bile, which goes to the intestines and leaves the body in stool.
Excreted in urine, passed through the kidneys, and leaves the body in urine.
Toxin and Harmful Substance Removal
Portal Vein:
Main Function: Carries about 70% to 80% of the blood to the liver.
Source: It collects blood from the gastrointestinal tract (from the esophagus to the middle of the anal canal), spleen, pancreas, and gallbladder.
How It Works: This blood is rich in nutrients (but low in oxygen).
The portal vein divides into two branches: the right portal vein (supplying the right lobe) and the left portal vein (supplying the left lobe).
Hepatic Artery:
Main Function: Carries about 20% to 30% of the blood to the liver, and this blood is oxygenated.
Source: The hepatic artery originates from the celiac trunk (a branch of the aorta) and supplies oxygen to the liver tissue.
Blood Drainage from the Liver:
Hepatic Veins:
The liver processes the blood, and the clean, filtered blood needs to exit the liver.
How It Drains: Blood passes from the liver sinusoids (small blood vessels in the liver) into the hepatic veins.
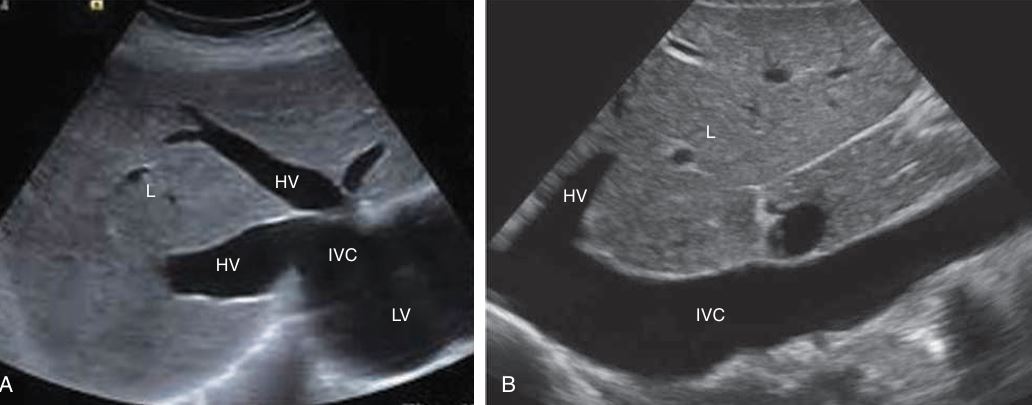
The hepatic veins drain the blood into the inferior vena cava, which is the large vein that carries the blood back to the heart.
There are three main hepatic veins:
Right Hepatic Vein: Drains blood from the right lobe of the liver.
Middle Hepatic Vein: Drains blood from the middle part of the liver (separates the right and left lobes).
Left Hepatic Vein: Drains blood from the left lobe of the liver.
Liver blood supply
This is the remnant of the ductus venosus, a fetal shunt that allowed blood to bypass the liver and flow directly into the inferior vena cava
Ligamentum Venosum
The liver occupies
Blood Supply to the Liver:
Portal Vein:
Main Function: Carries about 70% to 80% of the blood to the liver.
Source: It collects blood from the gastrointestinal tract (from the esophagus to the middle of the anal canal), spleen, pancreas, and gallbladder.
How It Works: This blood is rich in nutrients (but low in oxygen).
The portal vein divides into two branches: the right portal vein (supplying the right lobe) and the left portal vein (supplying the left lobe).
Hepatic Artery:
Main Function: Carries about 20% to 30% of the blood to the liver, and this blood is oxygenated.
Source: The hepatic artery originates from the celiac trunk (a branch of the aorta) and supplies oxygen to the liver tissue.
So, the liver gets blood from two main sources:
The portal vein (for nutrients from the digestive organs),
The hepatic artery (for oxygen).
Blood Drainage from the Liver:
Hepatic Veins:
The liver processes the blood, and the clean, filtered blood needs to exit the liver.
How It Drains: Blood passes from the liver sinusoids (small blood vessels in the liver) into the hepatic veins.
The hepatic veins drain the blood into the inferior vena cava, which is the large vein that carries the blood back to the heart.
There are three main hepatic veins:
Right Hepatic Vein: Drains blood from the right lobe of the liver.
Middle Hepatic Vein: Drains blood from the middle part of the liver (separates the right and left lobes).
Left Hepatic Vein: Drains blood from the left lobe of the liver.
right hypochondrium, the greater part of the epigastrium, and the left hypochondrium
Hepatomegaly is present when the liver measurement exceeds
20 cm
Cirrhosis may be classified as micronodular the measurements are
nodules 0.1 to 1 cm in diameter
Cirrhosis may be classified as macronodular the measurements are
nodules up to 5 cm in diameter
The normal portal vein waveform is______ and varies with the patient’s respiration and cardiac pulsation. The flow should be smooth and laminar.
monophasic with low velocity (15 to 18 cm/sec)
The normal diameter of the portal vein is
1.0 to 1.2 cm
peribilary cysts range in size ____ from _____.
0.2 to 2.5 cm
Of patients with polycystic liver disease, 60% have associated polycystic renal disease. The cysts are small, less than ______
2 to 3 cm
In Cavernous Hemangioma the appearance is typically a homogeneous, hyperechoic mass that is usually_______ in size with acoustic enhancement
less than 3 cm
Focal Nodular Hyperplasia. Bands of fibrous tissue separate the multiple nodules. The size of the mass is usually
less than 5 cm in diameter.
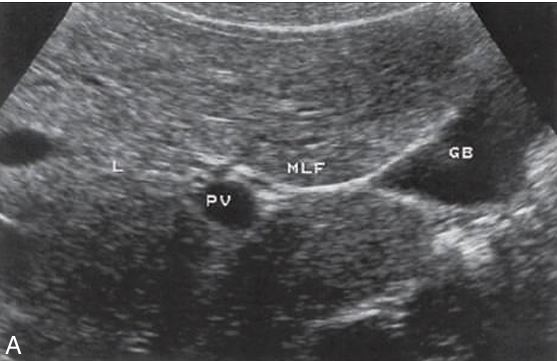
what fissure is showing
Main lobar fssure
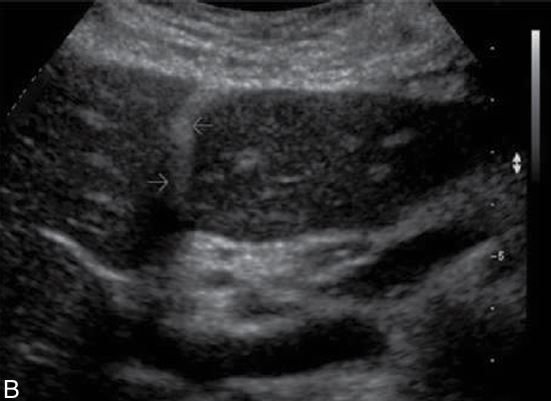
what ligament is showing
falciform ligament
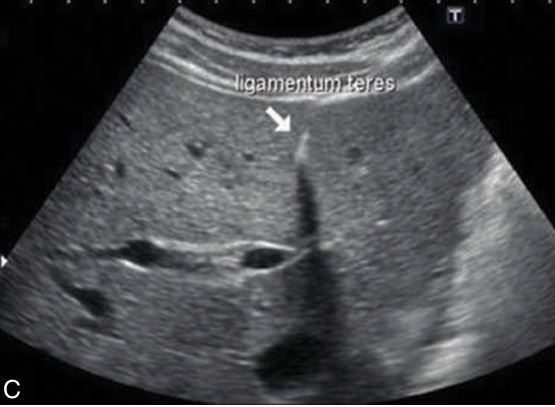
what ligament is showing
ligamentum teres
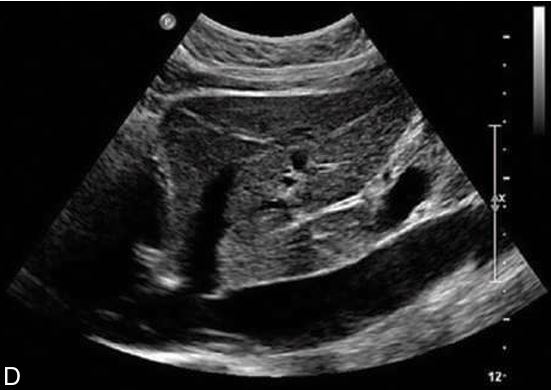
what ligament is showing
ligamentum venosum
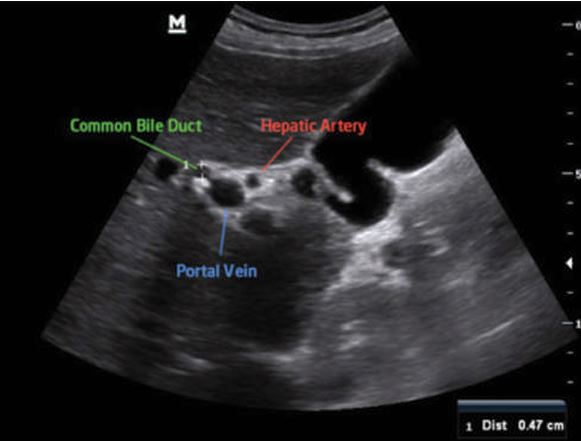
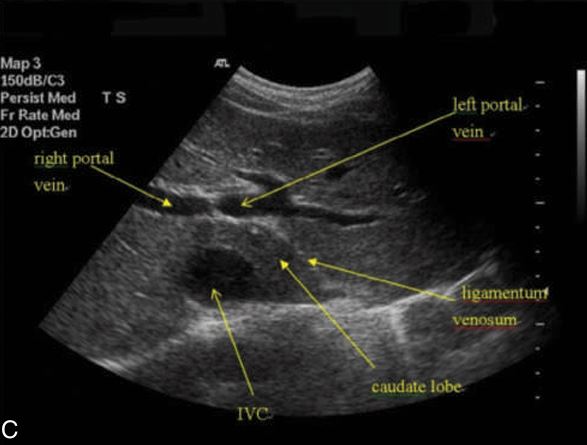
this is showing what?
the portal triad
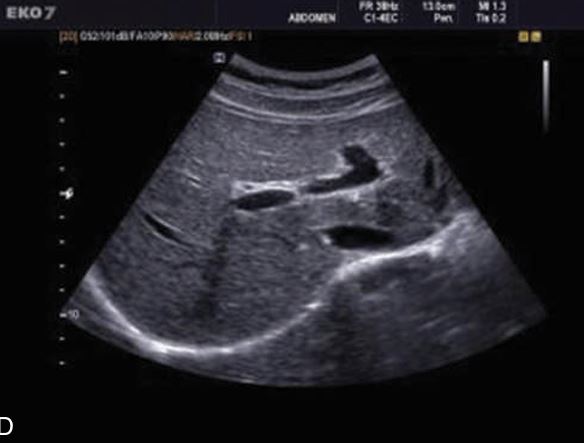
what vessels are connecting
Left portal vein and right portal vein
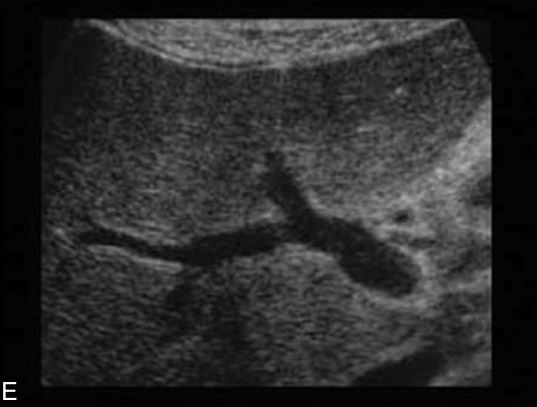
what is showing here
right anterior portal vein , and right posterior portal vein
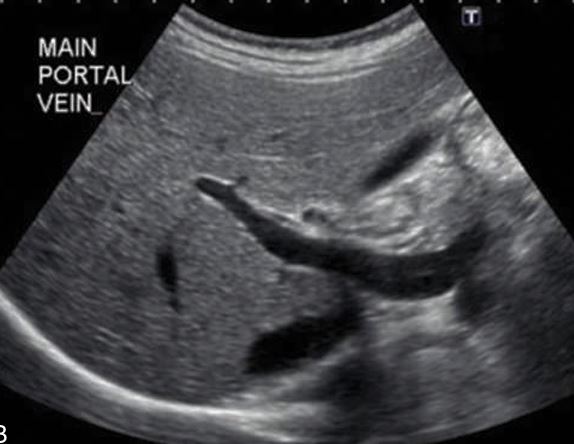
what portal vein is this
main portal vein because you see it opening on bottom, and its echogenic borders
choose 2 (just a pic)
2
what animal sign is this
mickey mouse
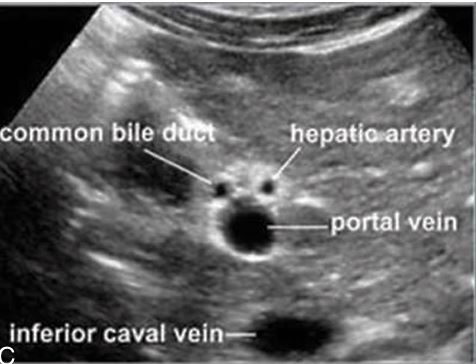
what is the arrow pointing to?
hepatic artery
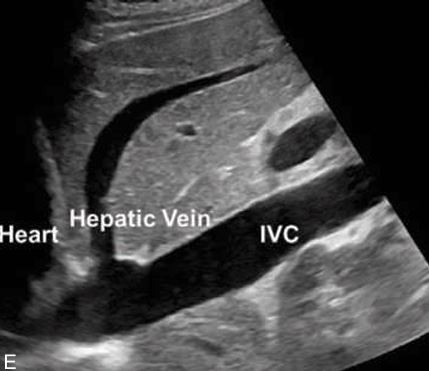
is this left or right hepatic vein
left hepatic vein
what is shown here
TRANS - 3 hepatic veins, rt , mid , and left
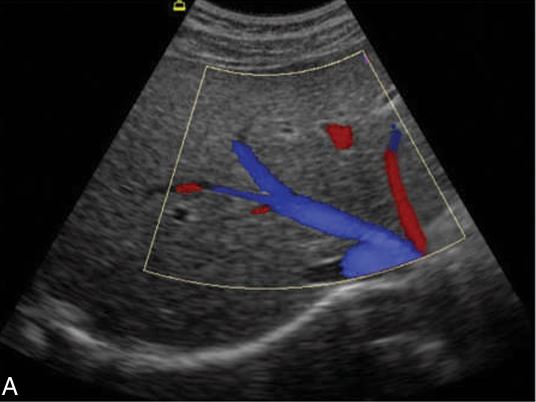
why is the color blue
because hepatic veins bring blood back to IVC , draining the blood
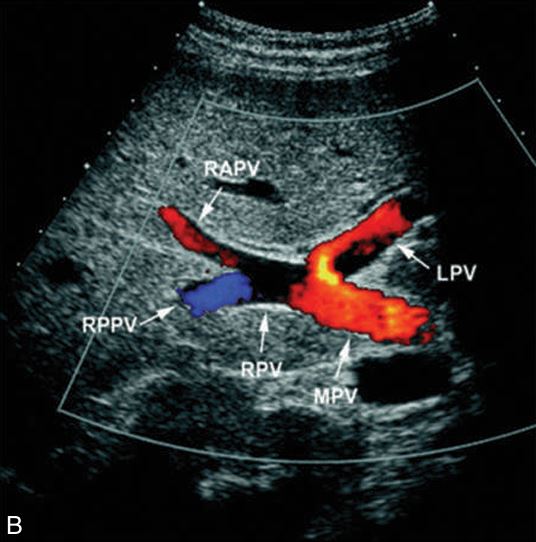
theses are what
the branches of portal veins that separate the lobe
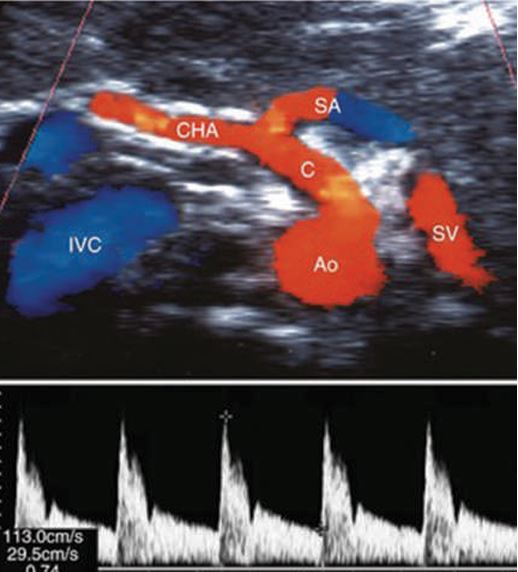
what sign is this
seagull sign
how else can u scan the MPV?
intercostally
what plane is this?
SAG of liver/kidney interface
what plane is this
SAG of LT LOBE and AORTA
what plane and what vessel is this (1)
SAG - showing RIGHT PORTAL VEIN
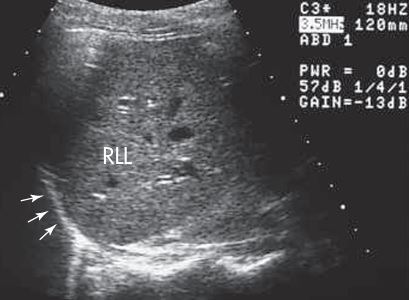
what plane and what are the arrows pointing to
SAG image - diaphragm/ pleural space
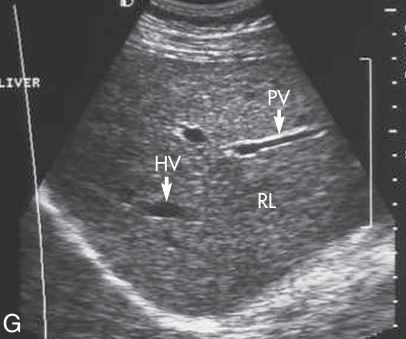
what plane is this
SAG of HV, PV, and right lobe
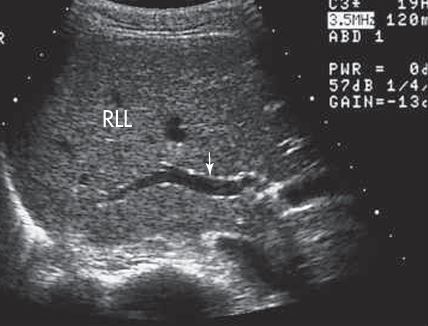
what plane and what vessel is showing
SAG plane andRT PORTAL VEIN???
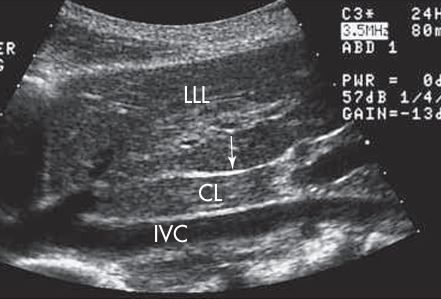
what plane is this
SAG - showing ivc with caudate lobe
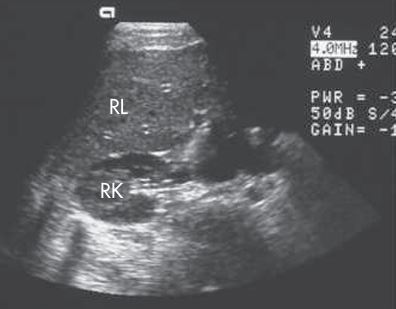
what plane is this
TRANS - lobe and kidney
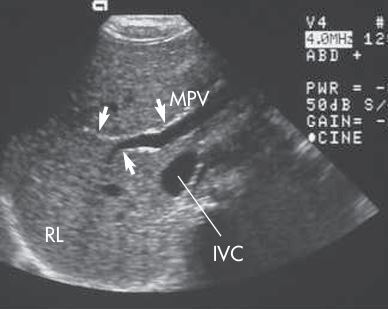
what plane is this
trans - main portal vein (MPV), right portal vein with branches (RPV), and IVC.
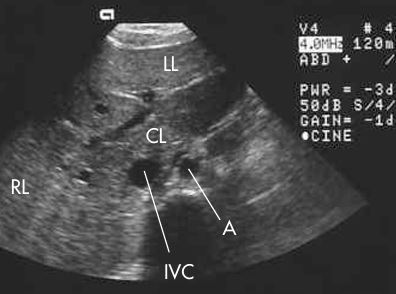
what plane is this
TRANS - CL, IVC, AO, RT AND LT LOBE
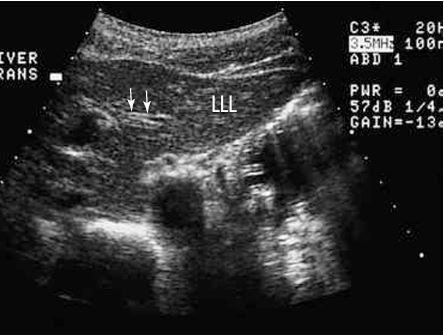
what plane and what arrows are pointing to?
TRANS - ligamentum venosum
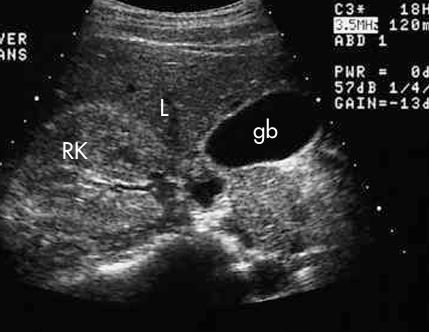
what plane and what is showing
TRANS - RT kidney, GB, and Liver
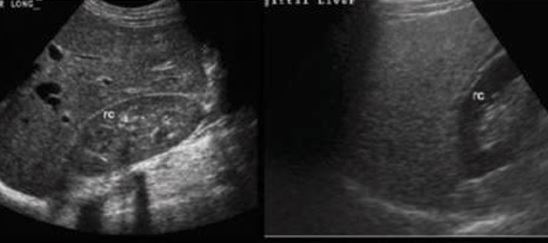
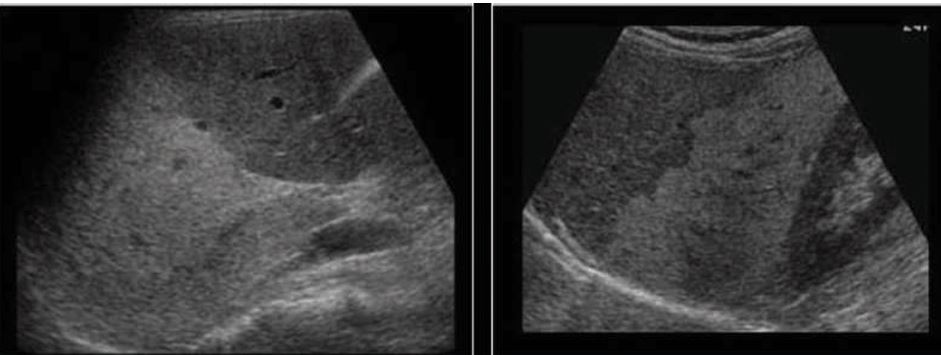
what does right image show
fatty liver compared to normal liver (left image)
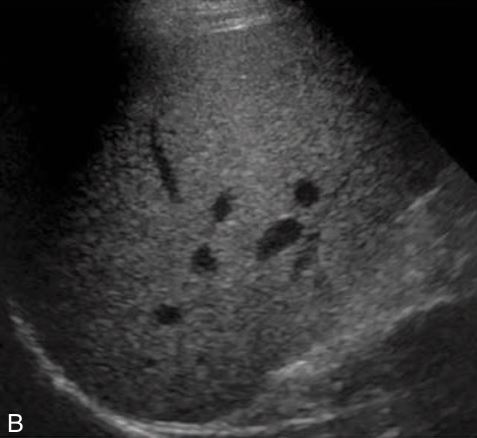
what form of fatty liver is this
mild form of fatty liver

what form of faty live is this
moderate form of fatty liver
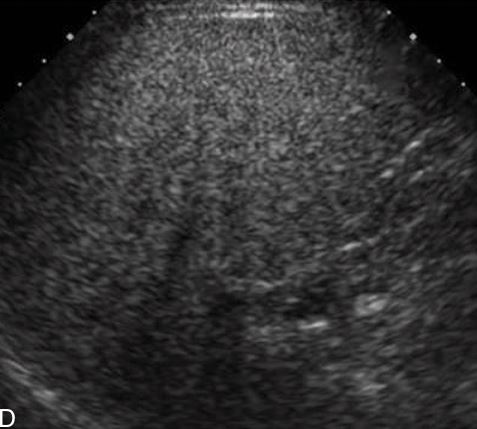
what form of fatty live is this
severe form of fatty liver
a condition with mass-like hypoechoic areas in typical locations in a liver that is otherwise increased in echogenicity.
The most common areas are anterior to the gallbladder or the portal vein and the periportal region of the medial segment of the left lobe of the liver
Focal sparing
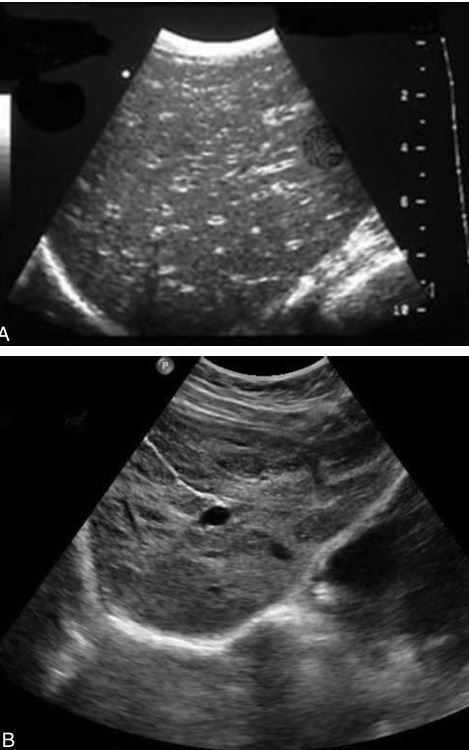
what is this showing
“starry sky” AKA Acute hepatitis
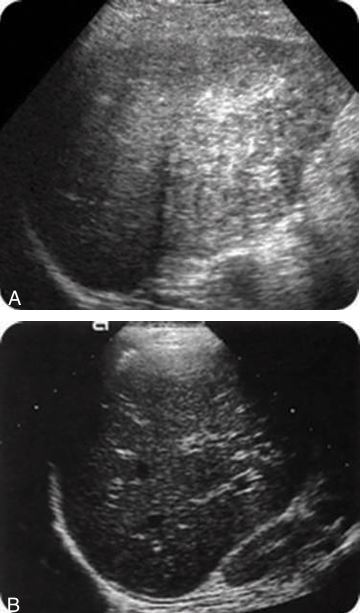
what is this showing?
The liver parenchyma is coarse with decreased brightness of the portal triads, but the degree of attenuation is not as great as is seen in fatty infiltration.
The liver does not increase in size with chronic hepatitis. Fibrosis may be evident, which may produce “soft shadowing” posteriorly
chronic hepatitis
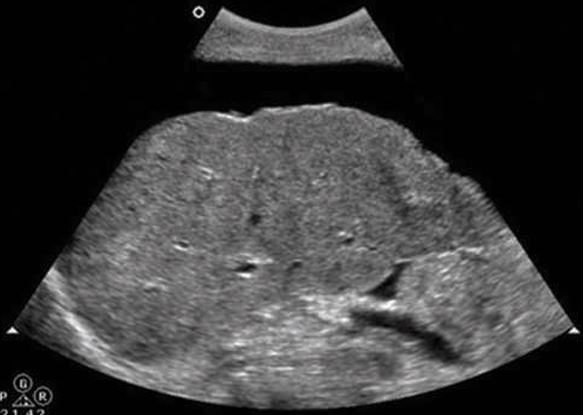
when cirrhosis happens, the liver is enlarged at first
Hepatomegaly with ascites
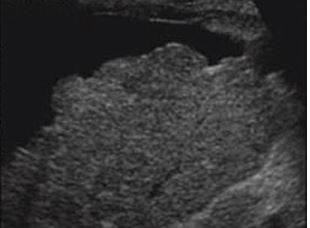
what is this?
cirrhotic liver
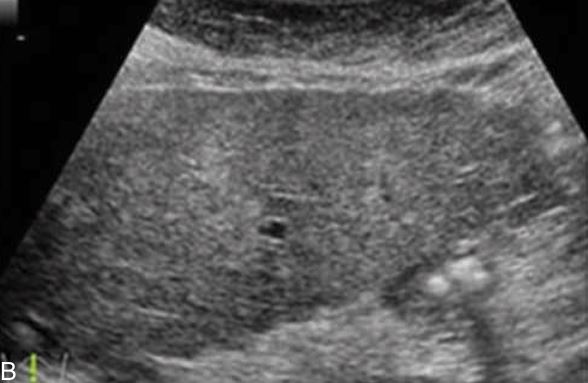
Hepatomegaly with some liver nodularity is noted
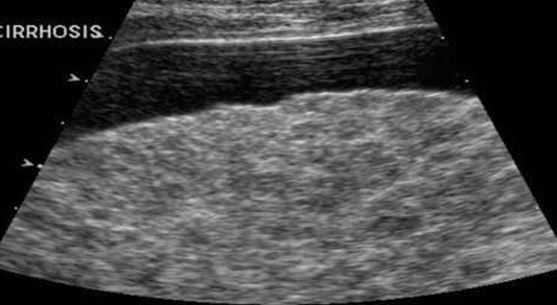
what plane is this
trans - The ascites demarks the surface liver nodularity
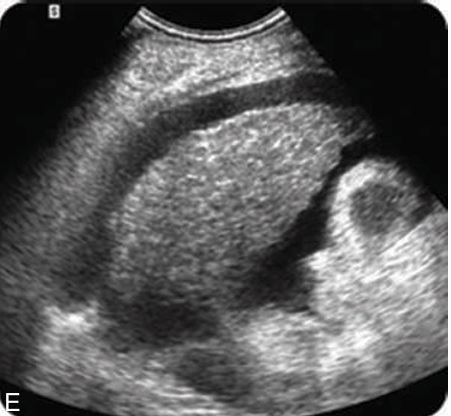
Shrunken liver with ascites
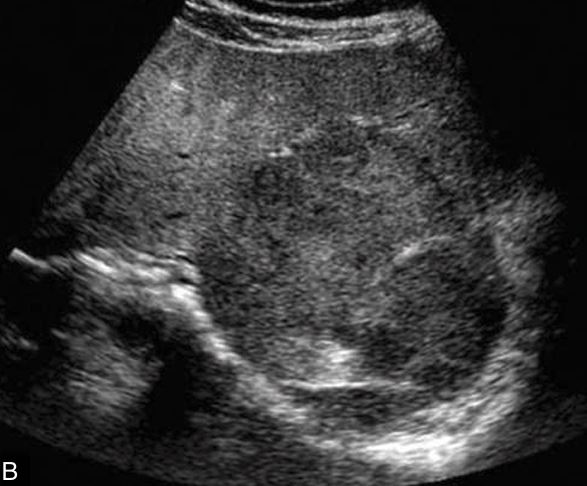
presents with hepatomegaly, increased echogenicity, and slightly increased attenuation (similar to diffuse fatty infiltration).
The disease is associated with hepatic adenomas, focal nodular hyperplasia, and hepatomegaly.
The adenoma presents as a well-demarcated, round, homogeneous, echogenic tumors.
Glycogen storage disease
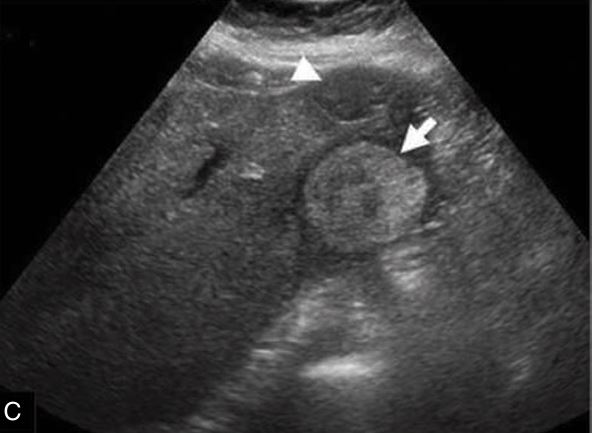
If the tumor is large, it may be slightly inhomogeneous
hepatic adenoma
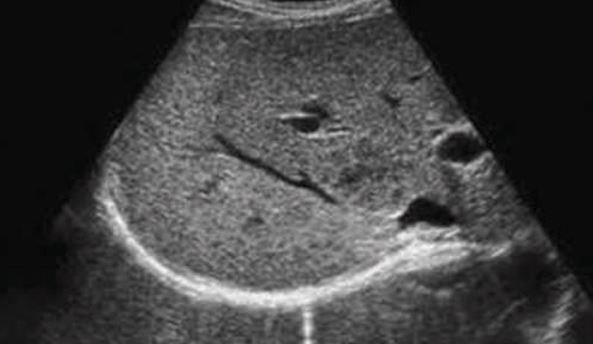
Hepatomegaly with slightly increased echogenicity throughout the liver parenchyma.
Hemochromatosis.
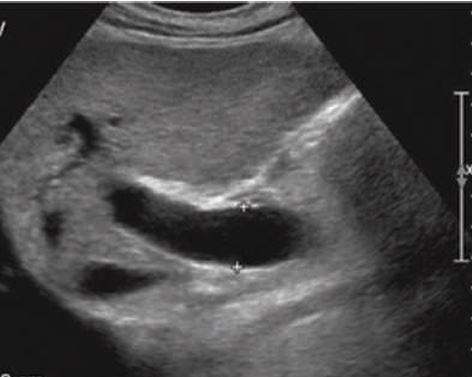
The dilated venous structures near the superior mesenteric-splenic vein confluence, the main portal vein, and the gastric veins should be evaluated.
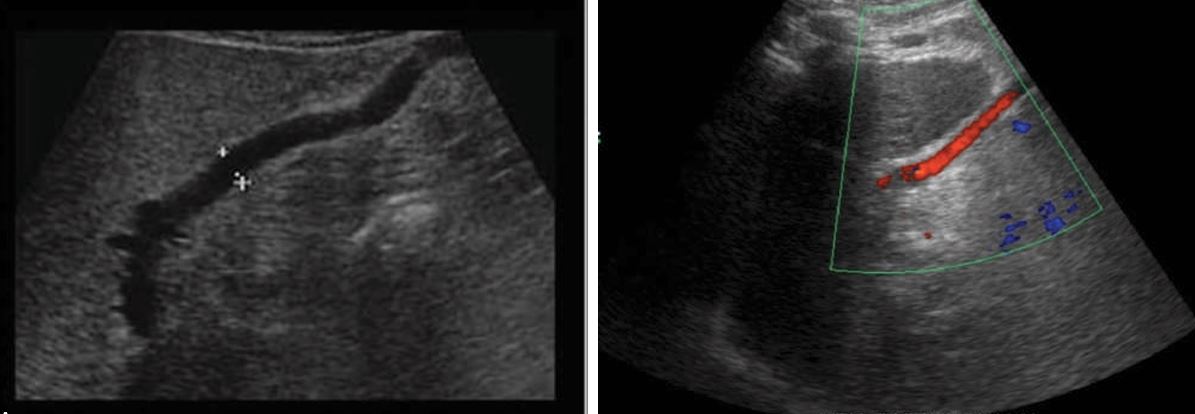
The umbilical vein may become recanalized secondary to
portal hypertension
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS)
normal flow from the portal vein to the inferior vena cava without evidence of thrombus. APV, Anterior portal vein; MPV, main portal vein
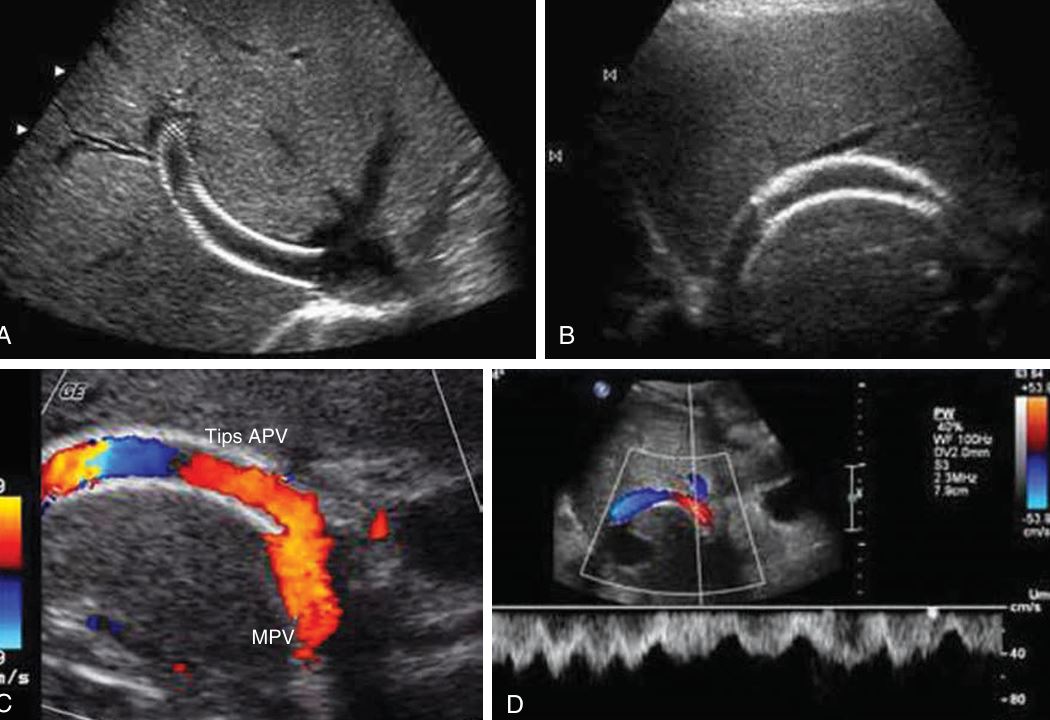
thrombus in right hepatic vein
budd chiari syndrome
thrombus in rt and mid hepatic vein (image 2)
budd chiari syndrome (image 2)
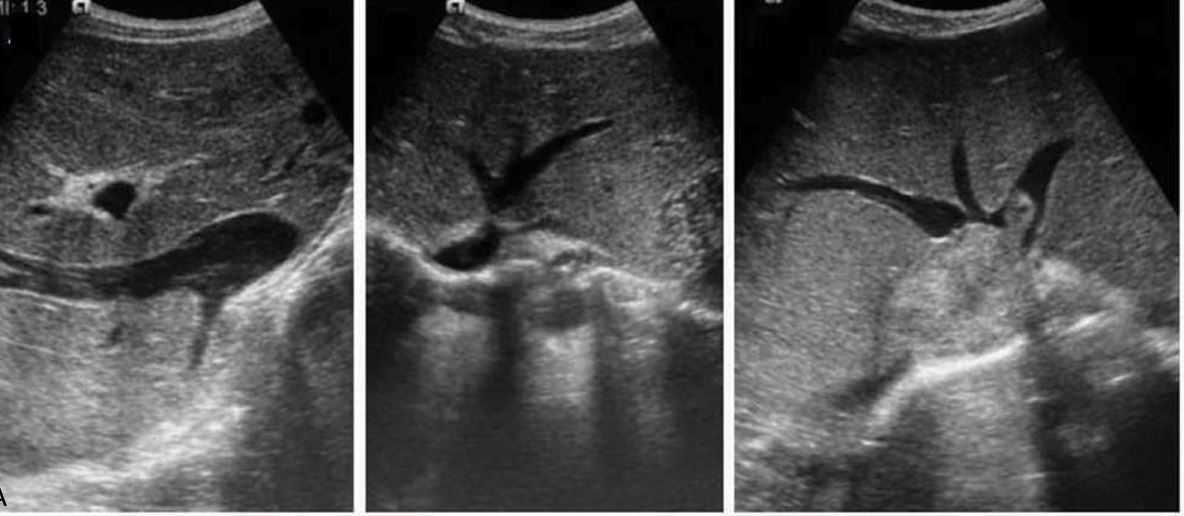
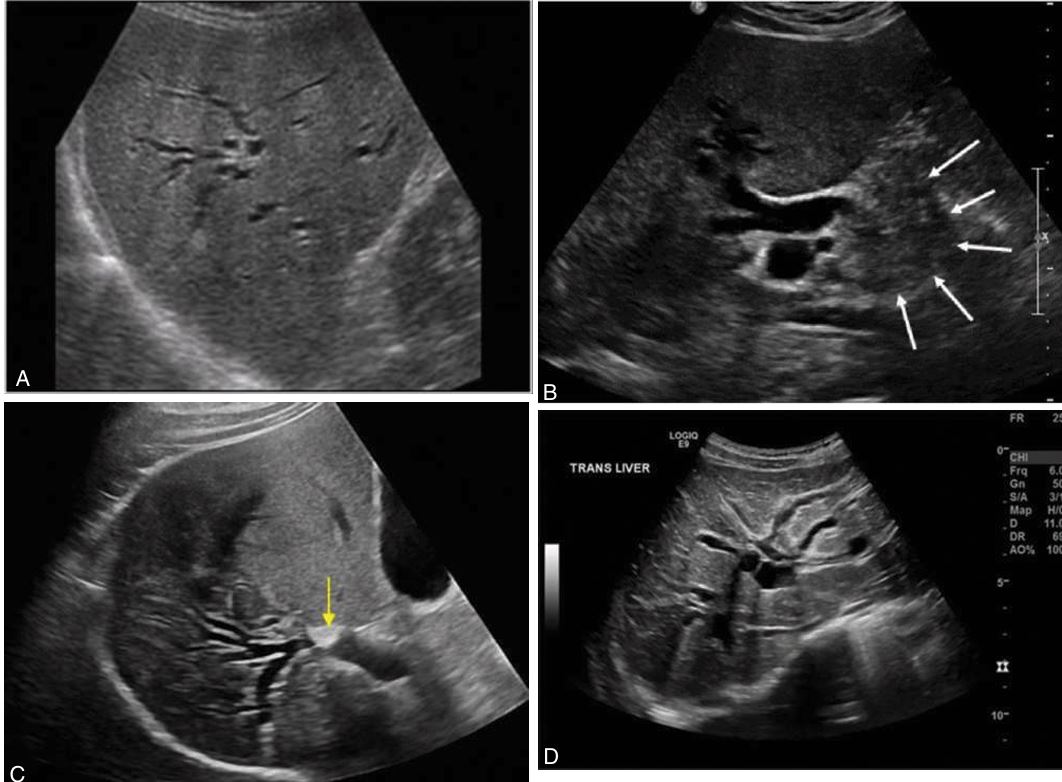
thrombosis of the right, middle, and left hepatic veins.(im 3)
In Budd-Chiari syndrome(image 3)
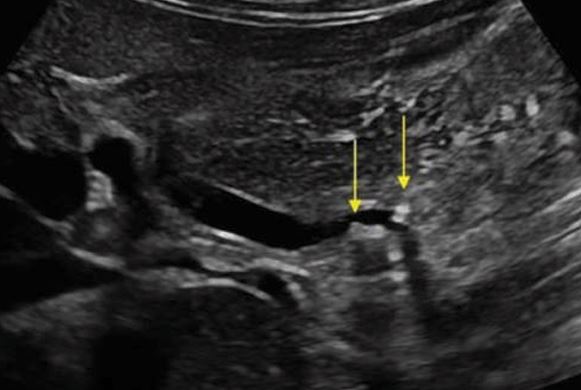
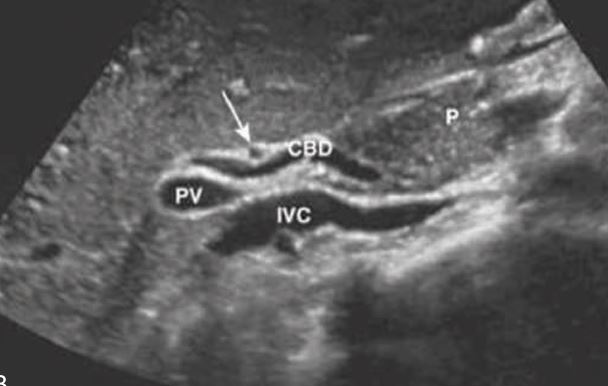
gallstones in CBD
may be caused by stones in the common duct, an extrahepatic mass in the porta hepatis, or stricture of the common duct. On ultrasound examination, the dilated intrahepatic ducts are seen in the periphery of the liver.
A biliary obstruction distal to the cystic duct
An extrahepatic mass, such as a tumor in the head of the pancreas
extrahepatic mass may cause this
hydrops of GB
An extrahepatic mass, such as a tumor in the head of the pancreas may cause
intrahepatic biliary duct dilation
The inferior vena cava (IVC) and hepatic veins (HV) are dilated
congestive liver failure
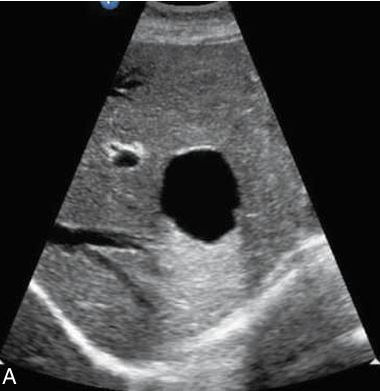
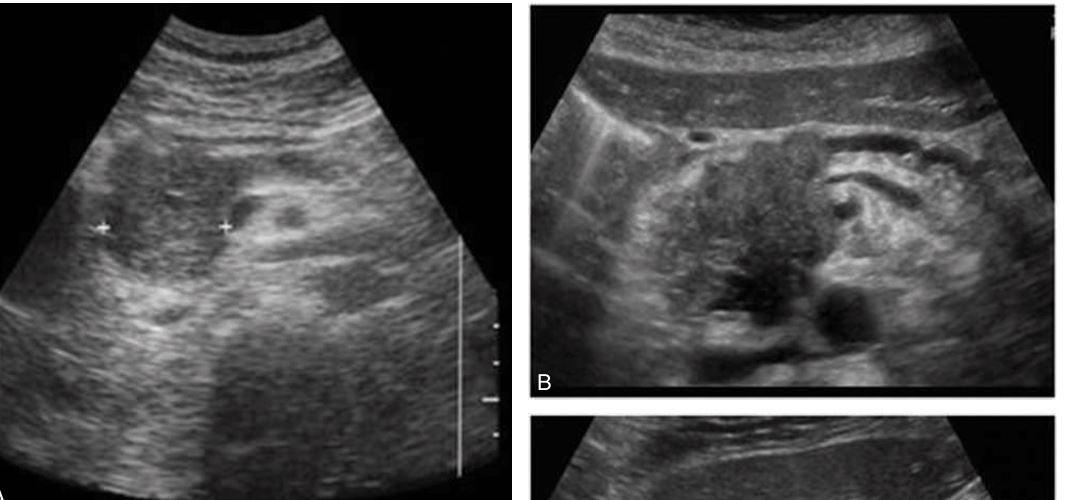
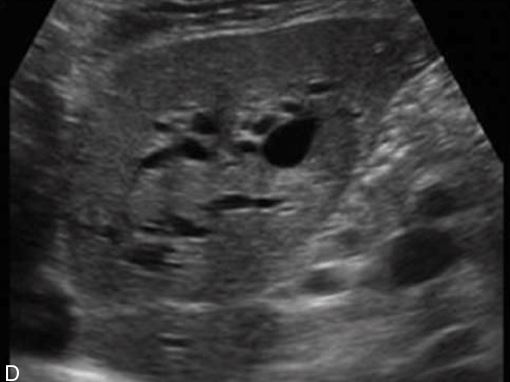
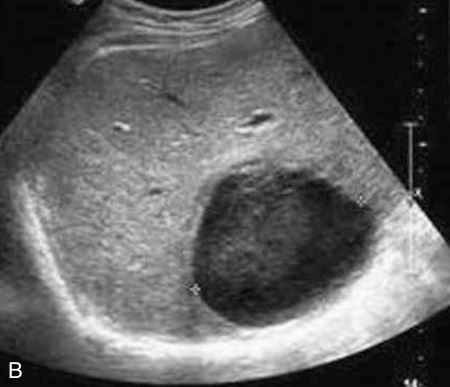
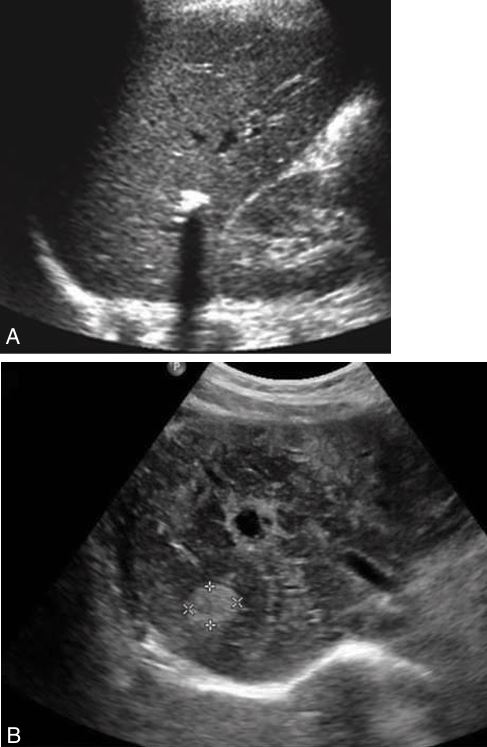
in the left lobe of the liver shows increased through-transmission and well-defined borders.
Solitary hepatic cyst
Liver cyst appears complex secondary to the hemorrhage
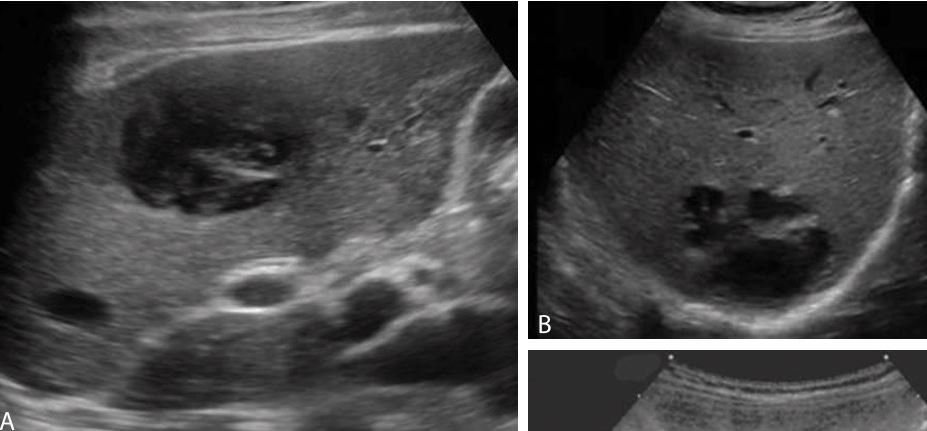
located centrally within the porta hepatis at the junction of the right and left hepatic ducts. They are seen as discrete, clustered tubular-appearing cysts with thin septae that parallel the bile ducts and portal veins in the central area of the liver.
Peribiliary cysts
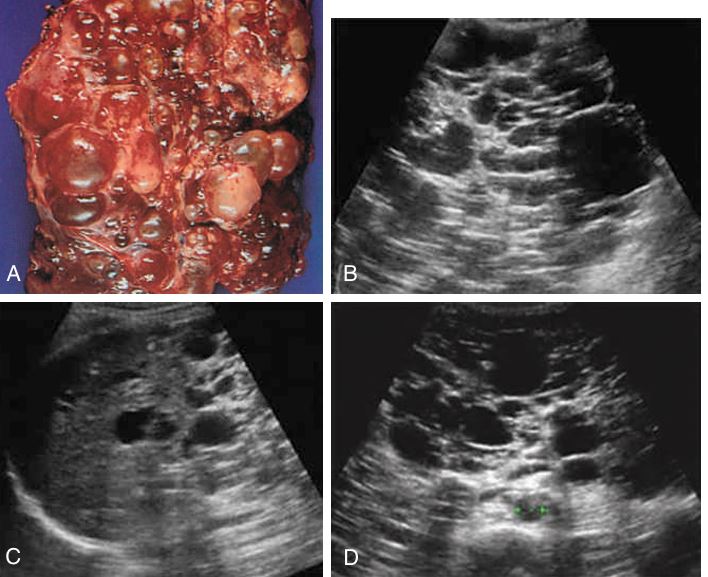
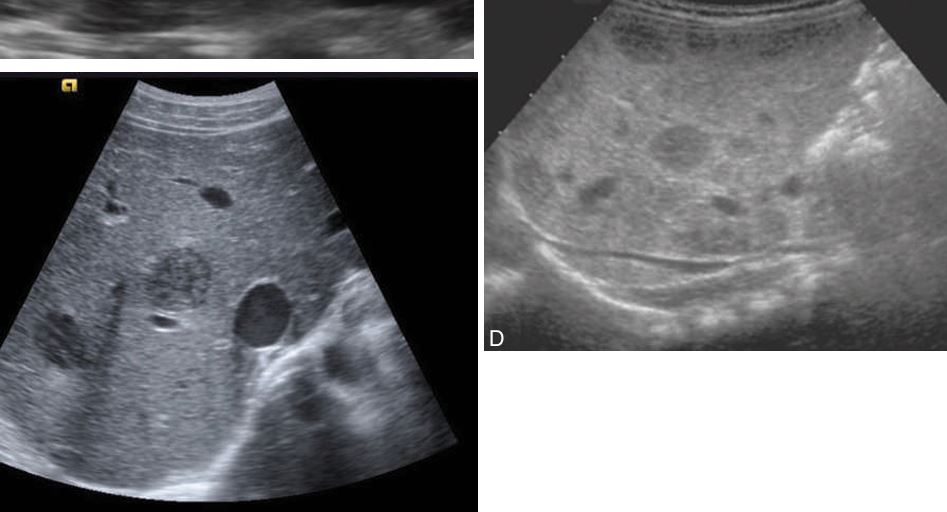
numerous large cysts throughout the liver parenchyma. Images of a liver parenchyma filled with multiple cystic lesions
Polycystic liver disease.
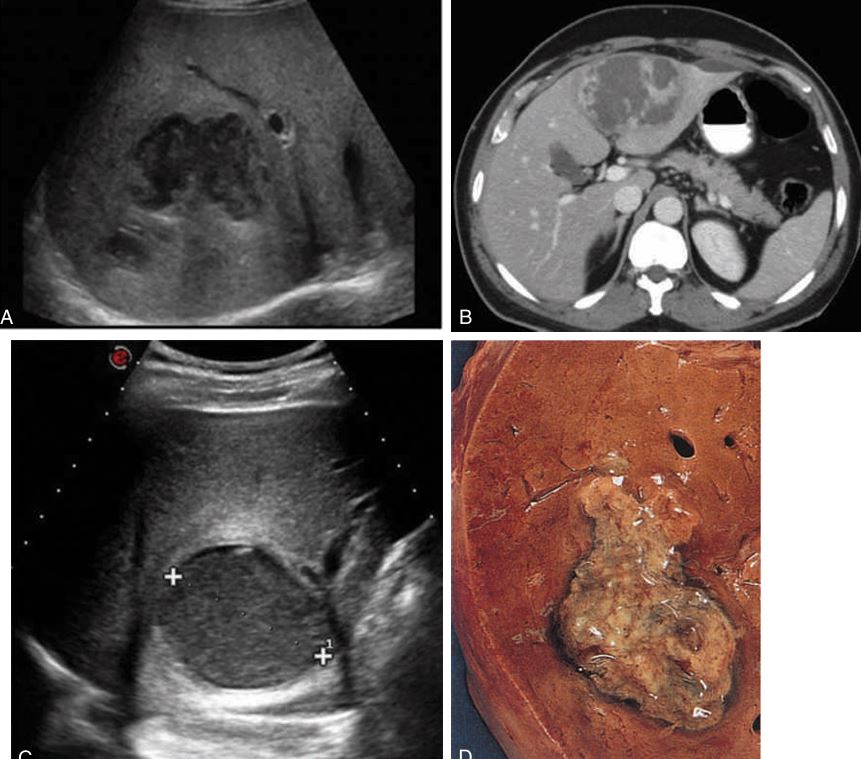
The right central lobe of the liver is the most common site for a ____________ to occur.
hypoechoic with round or ovoid margins and acoustic enhancement, or it may be complex, with some debris along the posterior margin and irregular walls.
Pyogenic abscess
as multiple small hypoechoic masses with echogenic central cores, referred to as bull’s-eye or target lesions.
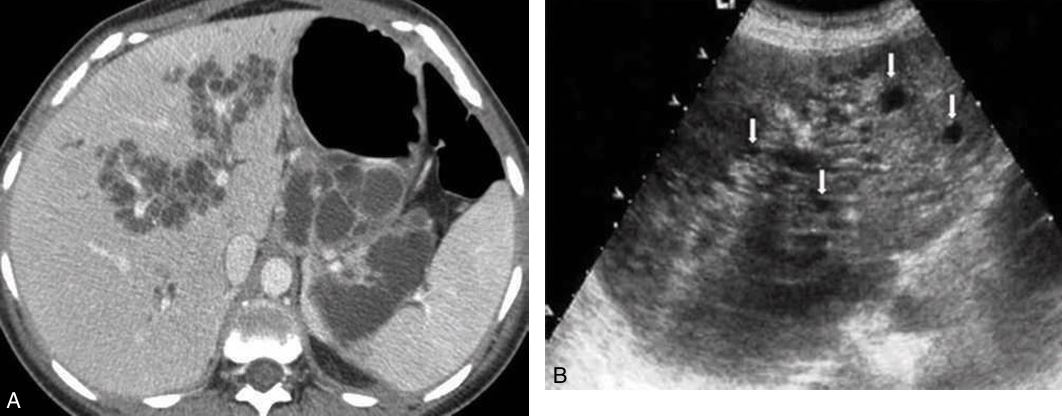
Candidiasis
a poorly marginated, hypoechoic mass is seen with posterior enhancement. Calcification may be present with posterior shadowing
Chronic granulomatous disease
may be round or oval and lack notable defined wall echoes
Gross pathology: the intracavitary lesion is filled with yellow necrotic material and does not contain pus
The amebic abscess
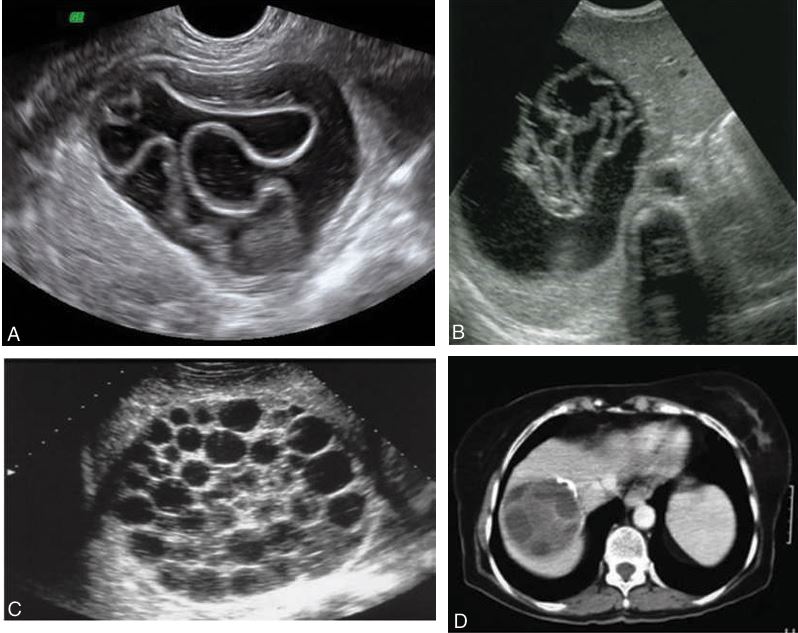
may be oval or spherical, with regularity of the walls. Calcifications may occur. (C) Septations are frequent and include honeycomb appearance with fluid collections; “water lily” sign, which shows a detachment and collapse of the germinal layer, or “cyst within a cyst” (D)
Echinococcal cyst
the most common organism causing infection in patients with AIDS. _____
affects patients undergoing bone marrow and organ transplantation or patients receiving chemotherapy.
Pneumocystic carinii
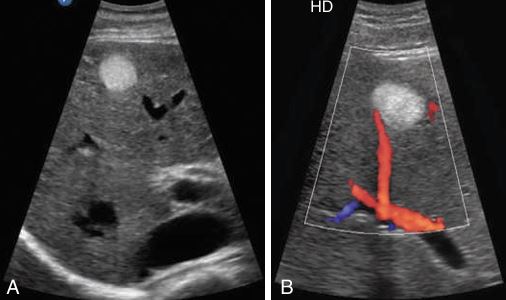
the most common benign neoplasm of the liver
The appearance is typically a homogeneous, hyperechoic mass that is usually less than 3 cm in size.
This sponge like tumor consisting of large, blood-filled cystic spaces is found more frequently in females.
Patients are usually asymptomatic, although a small percentage may bleed, causing right upper quadrant pain.
enlarge slowly and undergo degeneration, fibrosis, and calcification.
found in the subcapsular hepatic parenchyma or in the posterior right lobe more than the left lobe of the liver.
Cavernous Hemangioma
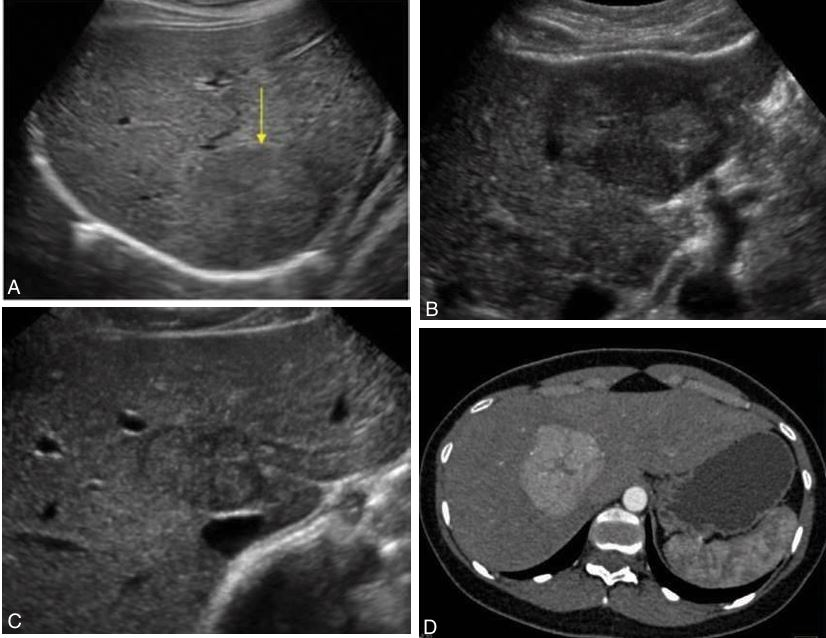
benign,
most affected young women
Focal nodular hyperplasia
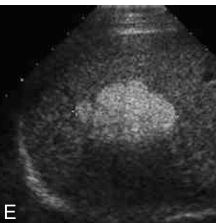
Hepatic adenoma. This lesion is usually hyperechoic with a central hypoechoic area caused by hemorrhage.
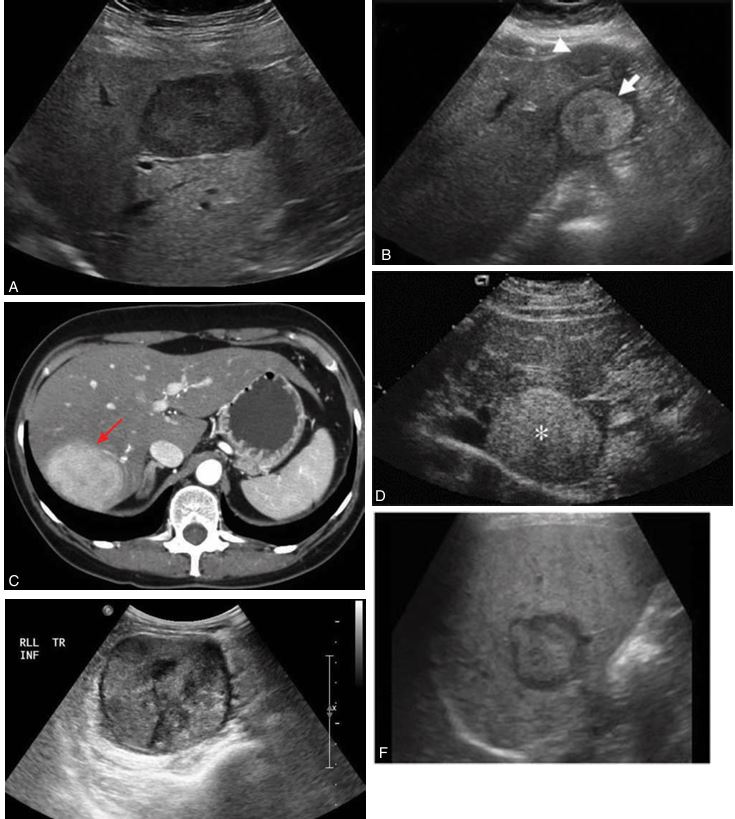
The echogenicity of a hepatic adenoma may be hyperechoic, hypoechoic, isoechoic, or mixed. This lesion is usually hyperechoic with a central hypoechoic area caused by hemorrhage. Echogenicity examples: (A) hypoechoic, (B) hyperechoic with hypoechoic central hemorrhage, (C) computed tomographic image of adenoma, (D) hyperechoic, (E) mixed, and (F) hyperechoic with central hemorrhage.
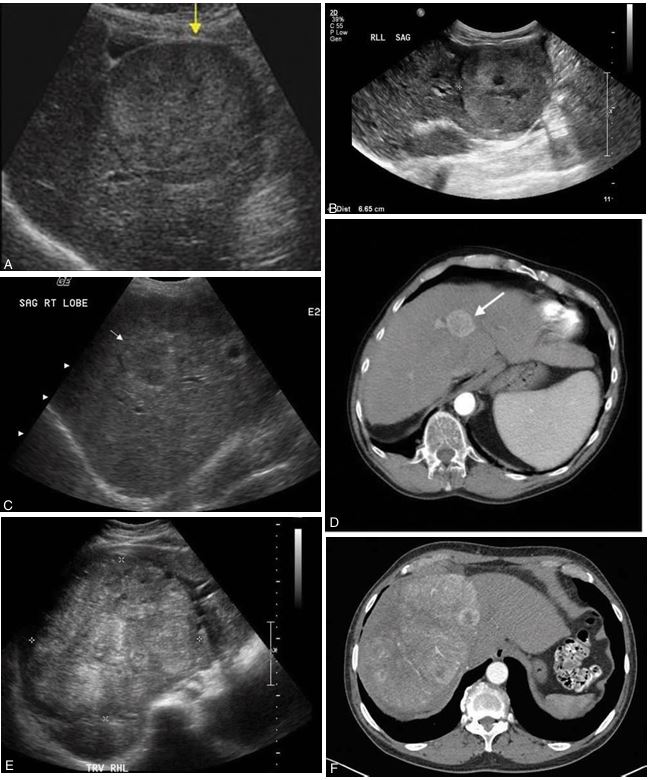
ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES
Hepatocellular carcinoma
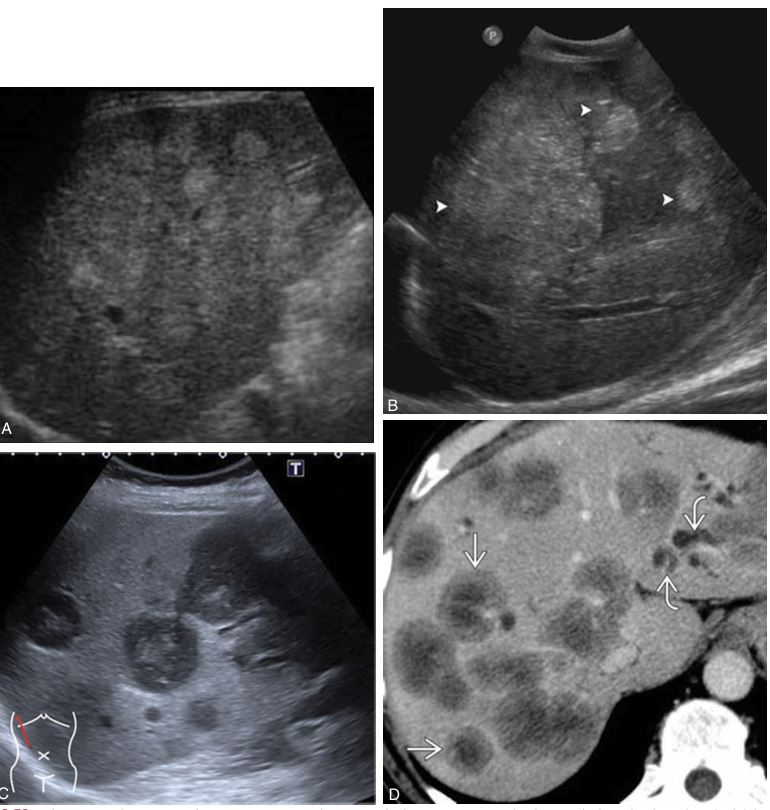
is typical to have multiple nodes throughout both lobes of the liver.
metastatic tumor
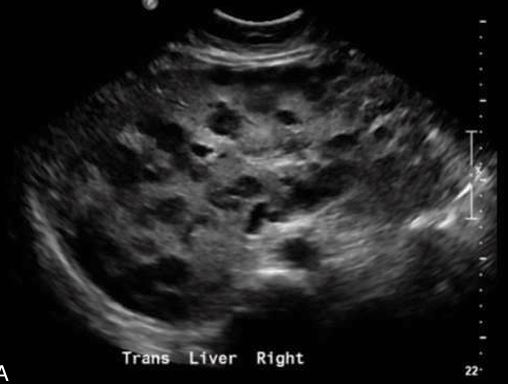
shows up as diffuse parenchymal changes in the liver
Hodgkin lymphoma
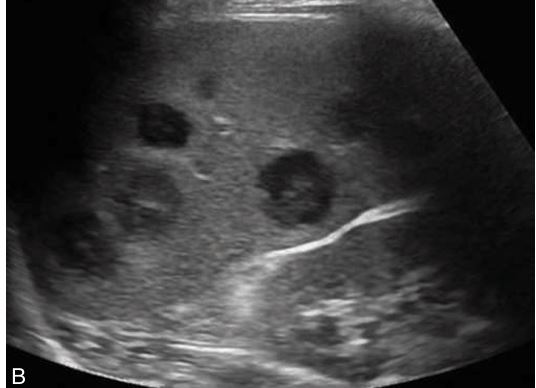
may appear with target hypoechoic mass lesions.
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
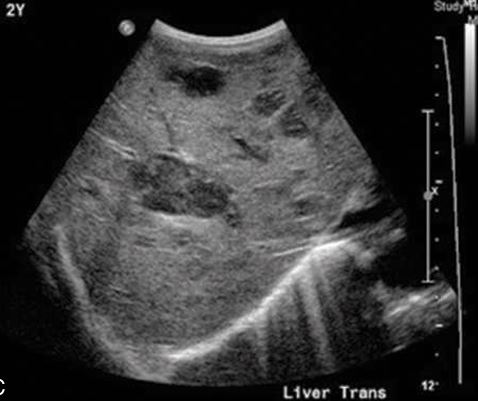
lesions may appear intrahepatic and lucent
Burkitt lymphoma