Anatomy of the Long Bone
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
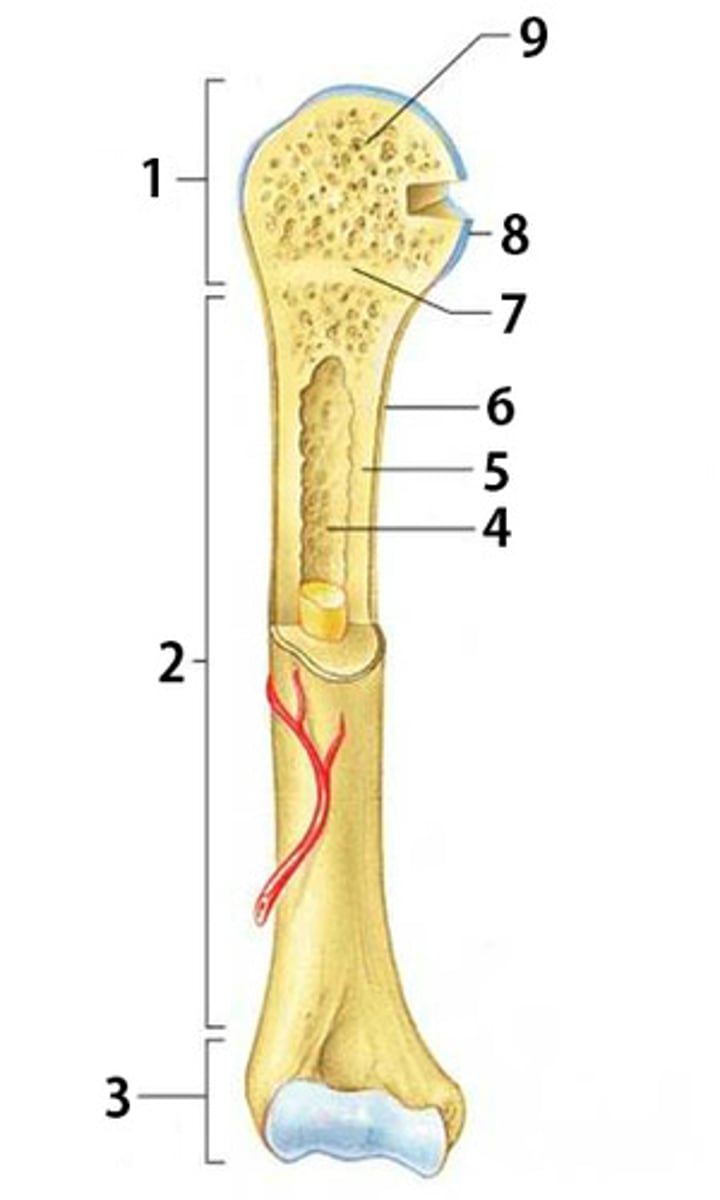
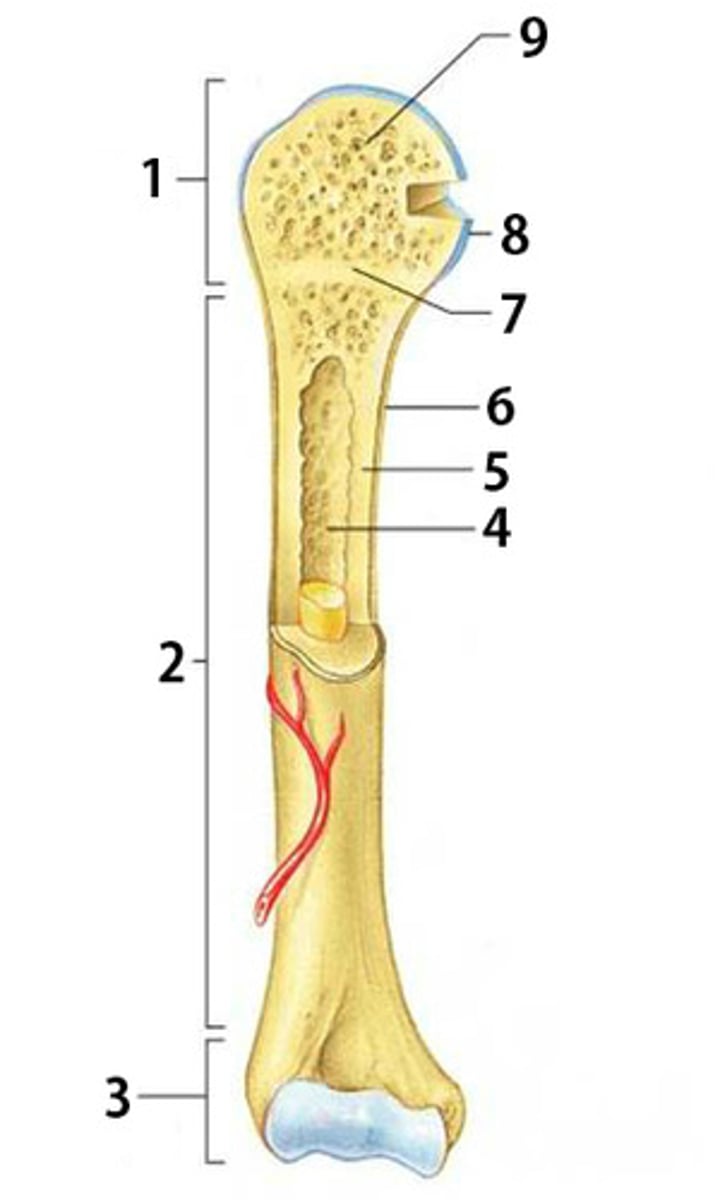
Proximal Epiphysis
1
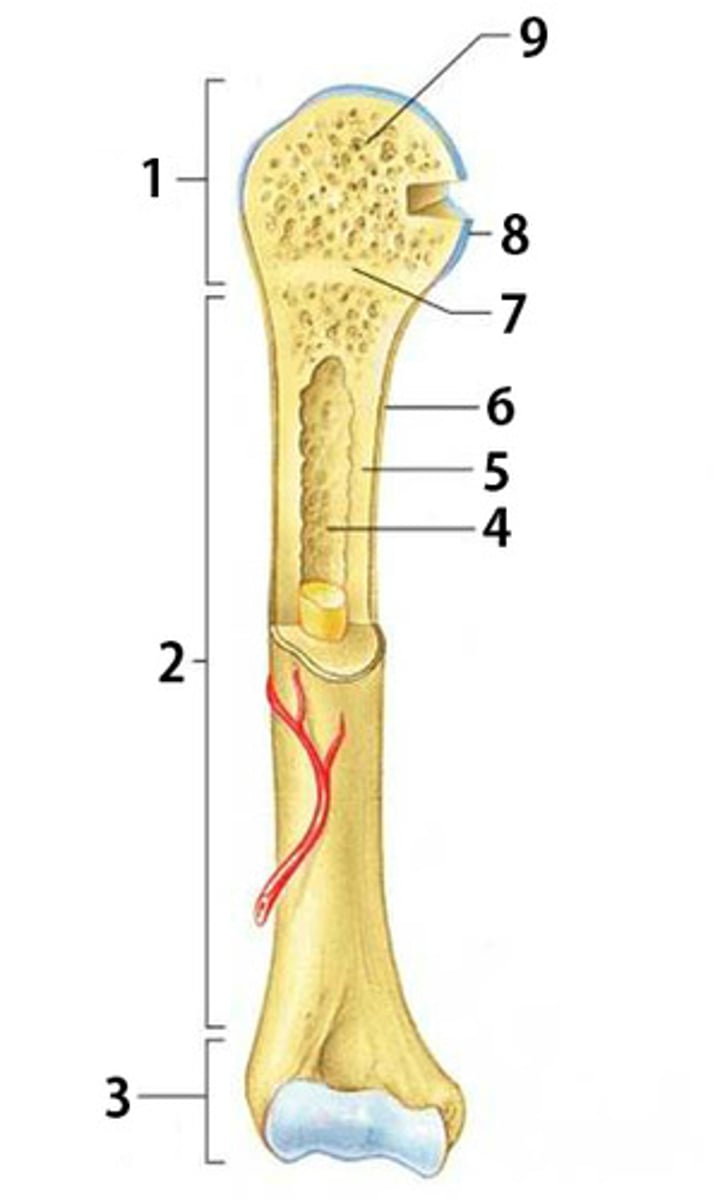
Proximal Epiphysis
The proximal and expanded end of a long bone. Made mostly of spongy bone and ends at the epiphyseal line
Diaphysis
2
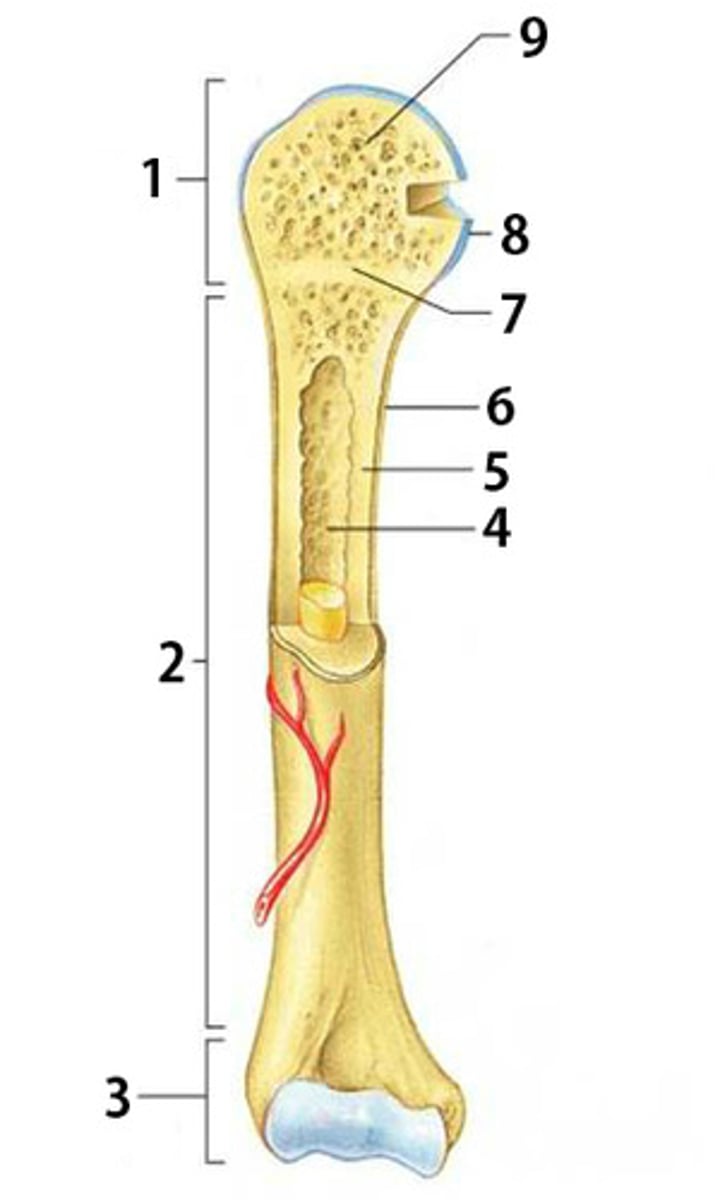
Diaphysis
The shaft of a long bone. Composed of compact bone.
Distal Epiphysis
3
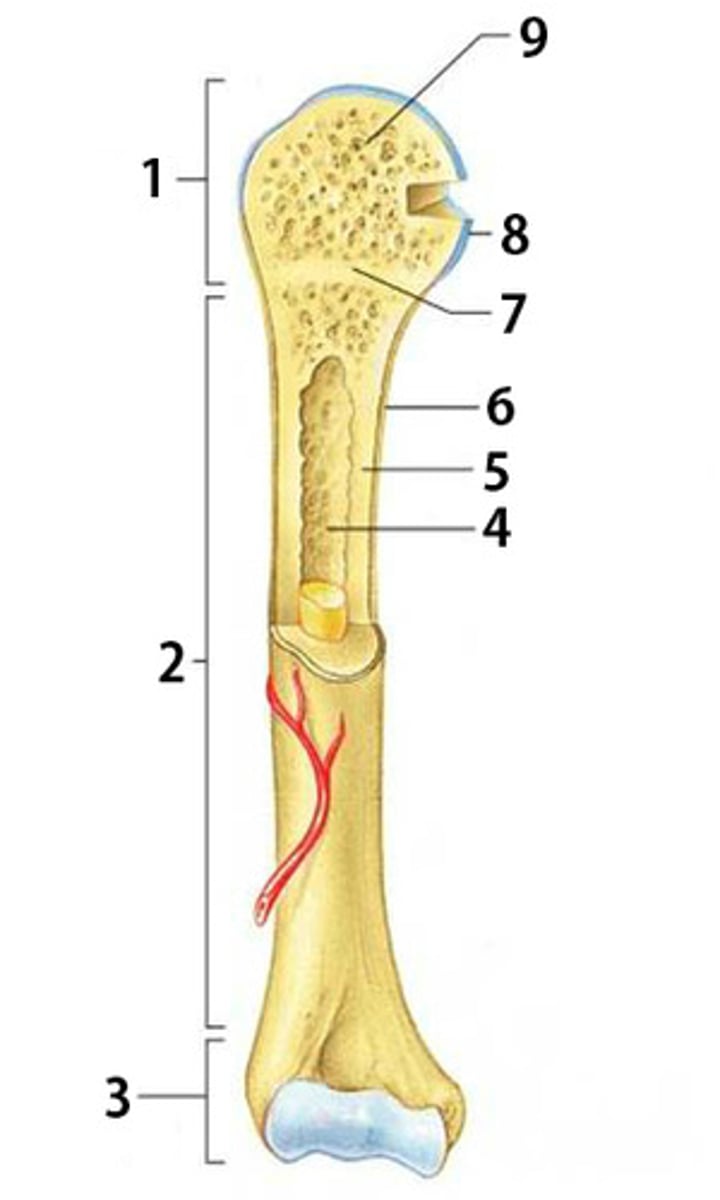
Distal Epiphysis
The distal and expanded end of a long bone. Made mostly of spongy bone and ends at the epiphyseal line.
Spongy Bone
9
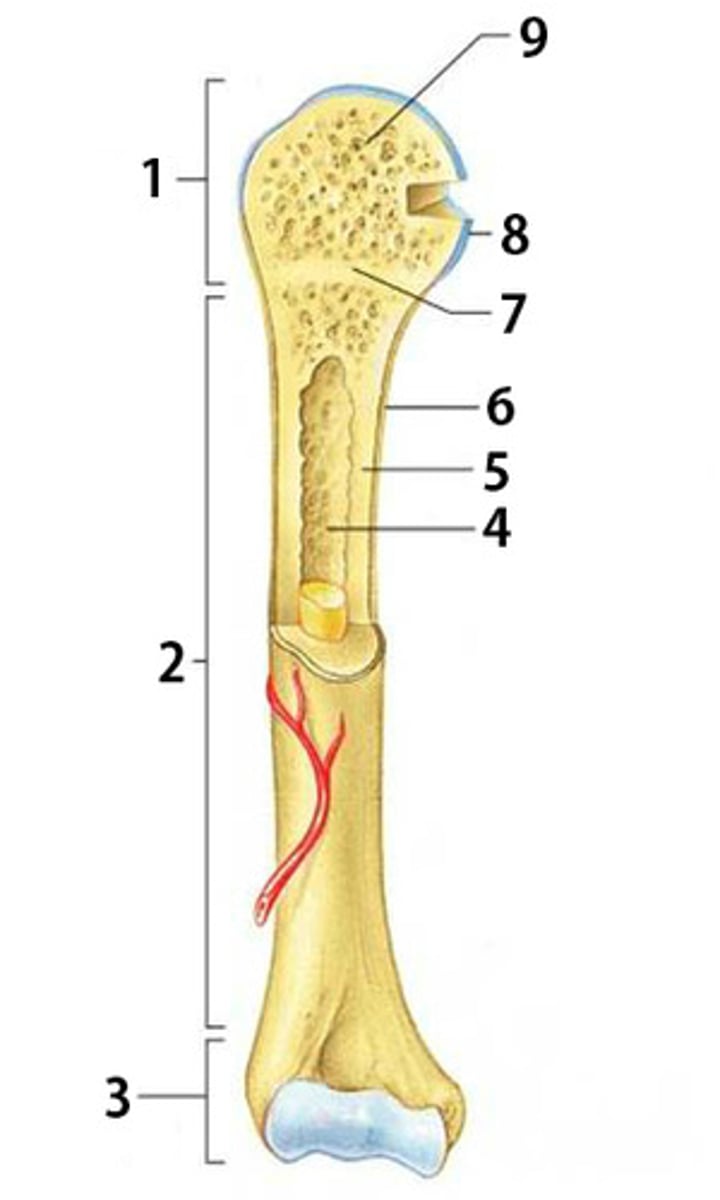
Spongy Bone
Light, porous bone enclosing numerous large spaces that give a honeycombed or spongy appearance. It is softer and weaker bone but highly flexible and vascular.
Articular Cartilage
8
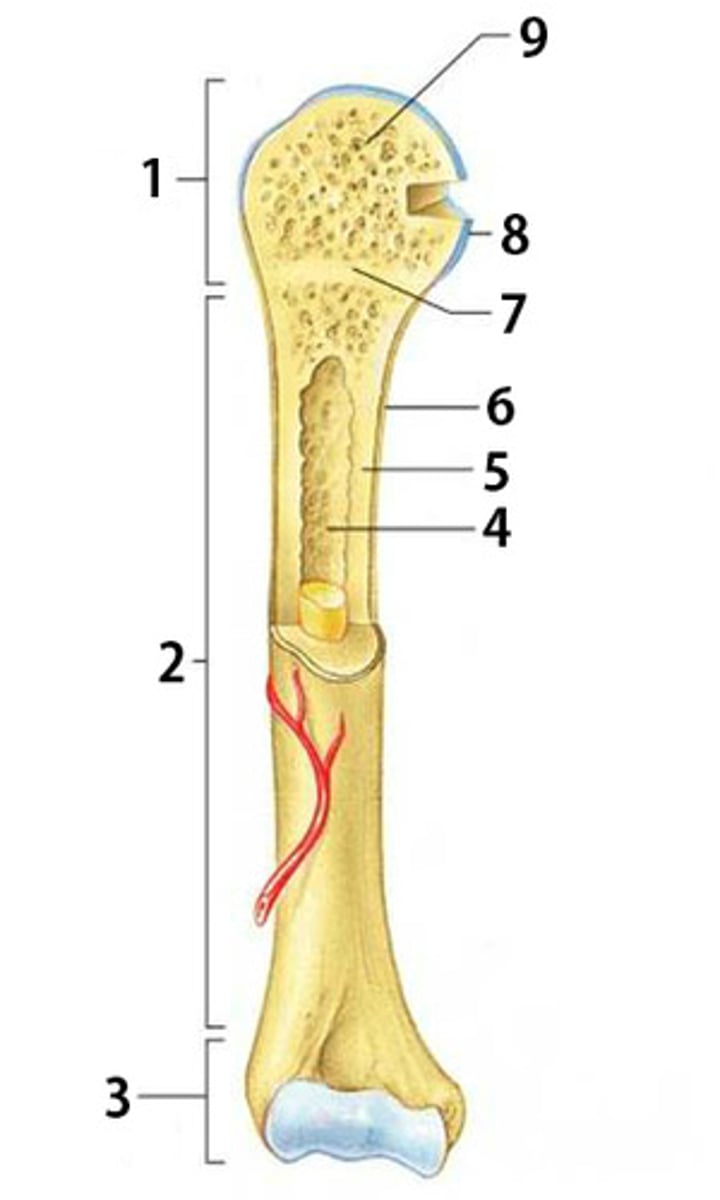
Articular Cartilage
The cartilage covering the articular surfaces of the bones forming a synovial joint
Epiphyseal Line
7
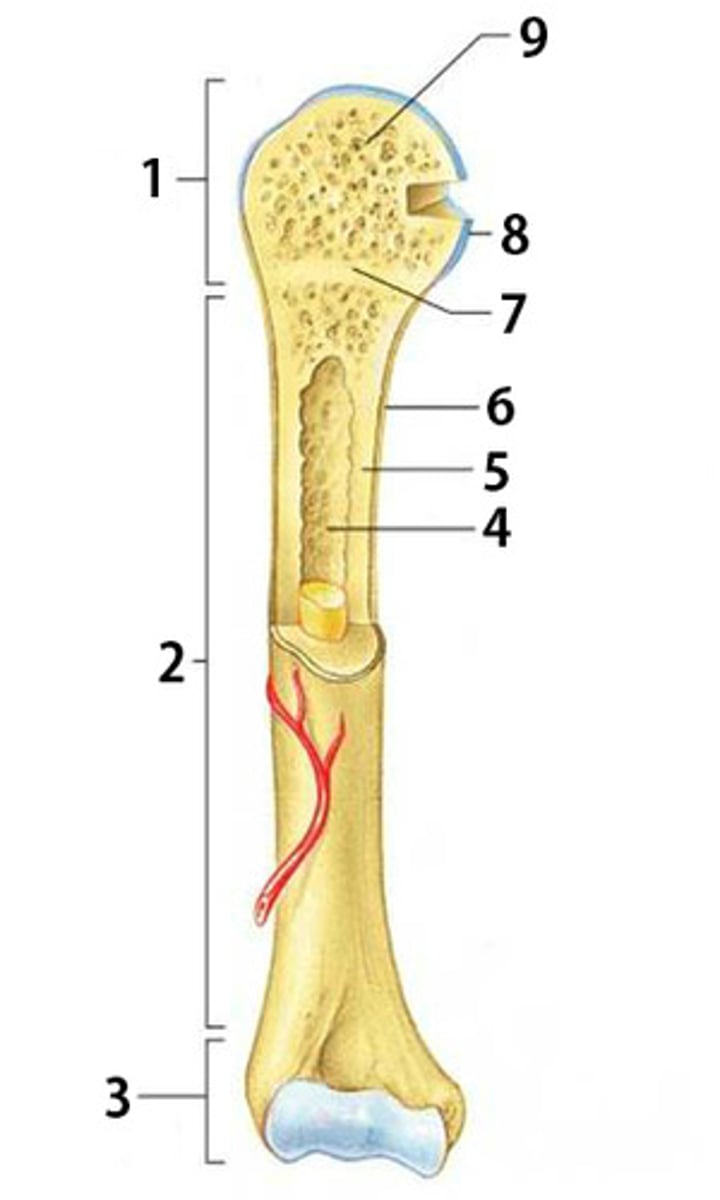
Epiphyseal Line
The line marking the site of the epiphyseal plate
Periosteum
6
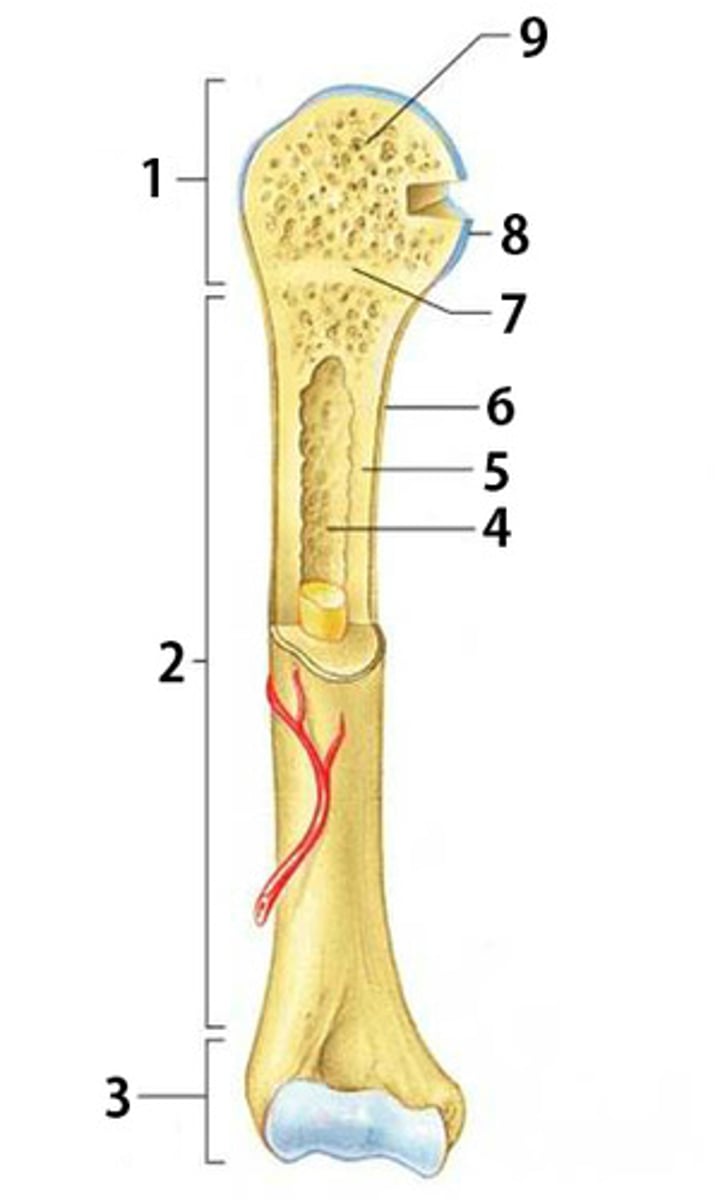
Periosteum
The dense fibrous connective tissue membrane covering the surface of bones except at the joints and serving as an attachment for muscles and tendons.
Compact Bone
5
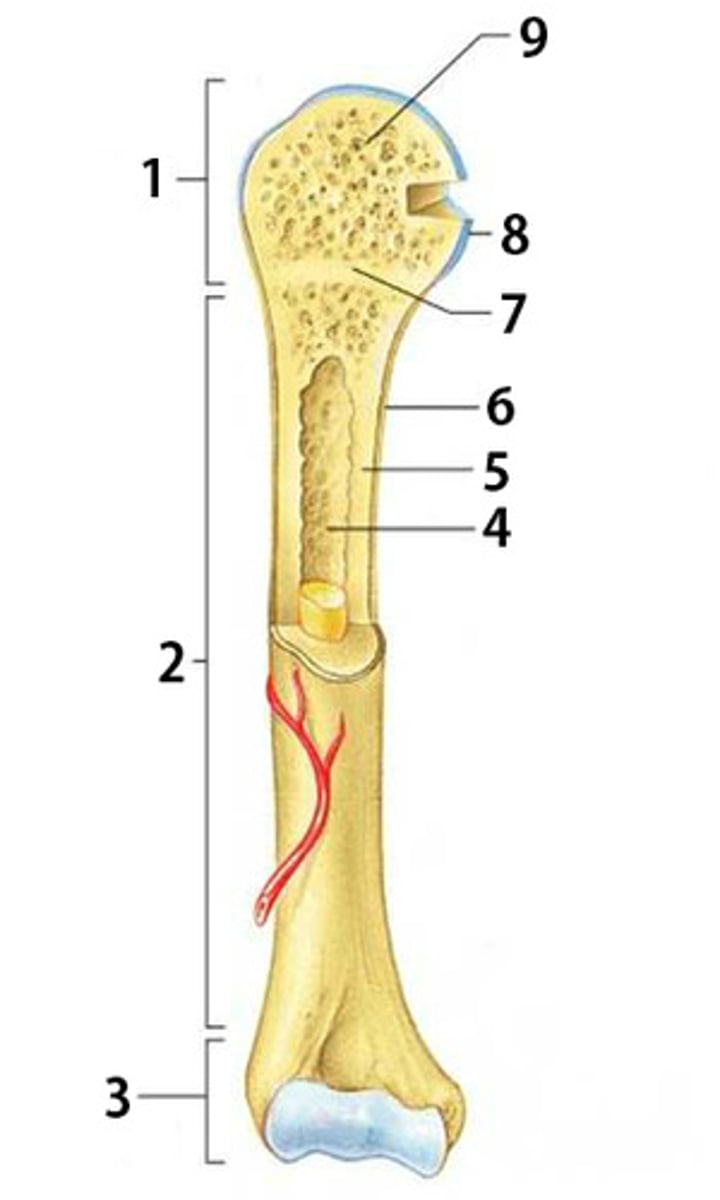
Compact Bone
Dense bone in which the bony matrix is solidly filled with organic ground substance and inorganic salts, leaving only tiny spaces (lacunae).
Medullary Cavity
5
Medullary Cavity
The central cavity of bone shafts where red bone marrow and/or yellow bone marrow (adipose tissue) is stored.
Bone Marrow
What is the yellow substance within #4?
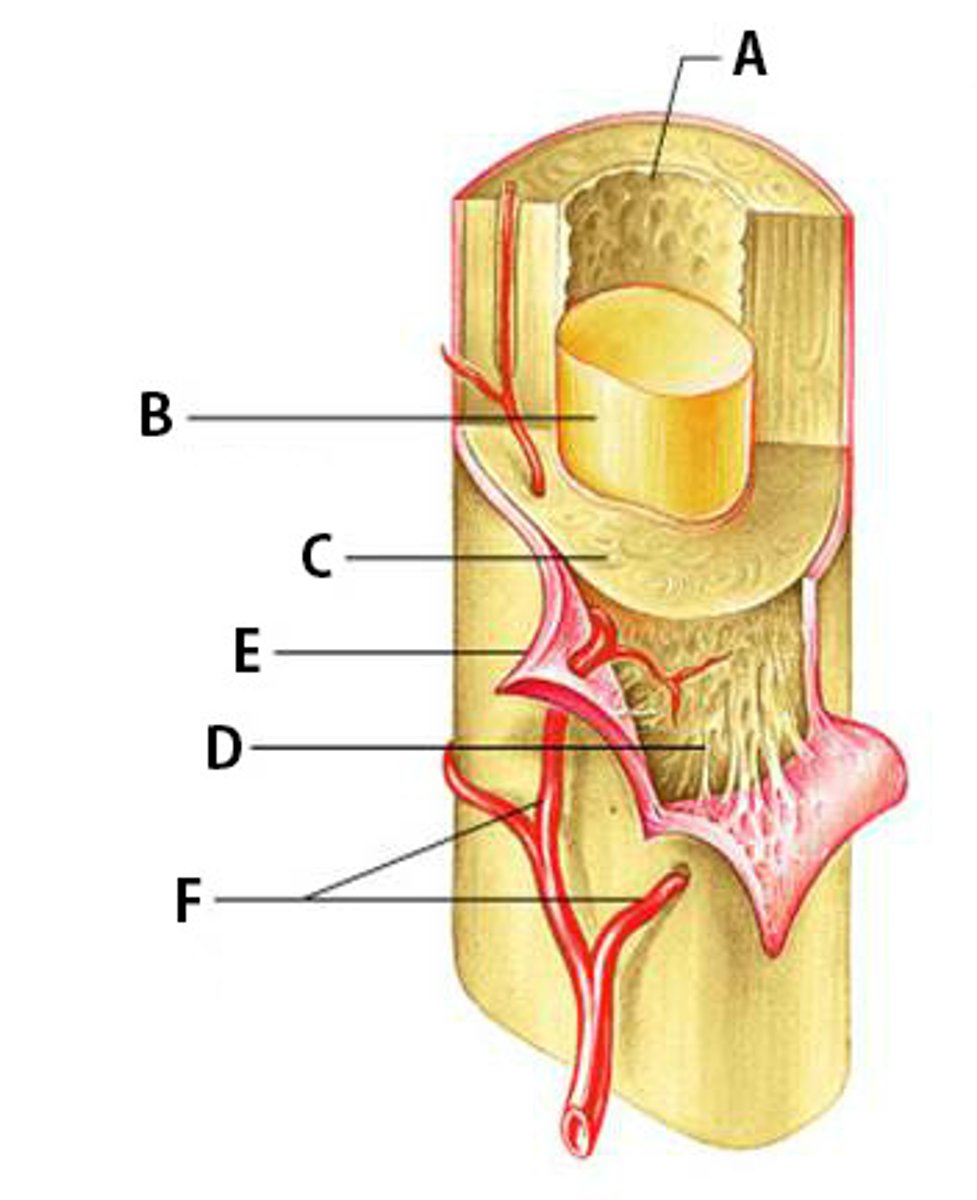
Bone Marrow
Flexible tissue in the interior of bones that produce red blood cells (described as red) or store fat (described as yellow).
Bone Marrow
B
Bone Marrow
Flexible tissue in the interior of bones that produce red blood cells (described as red) or store fat (described as yellow).
Compact Bone
C
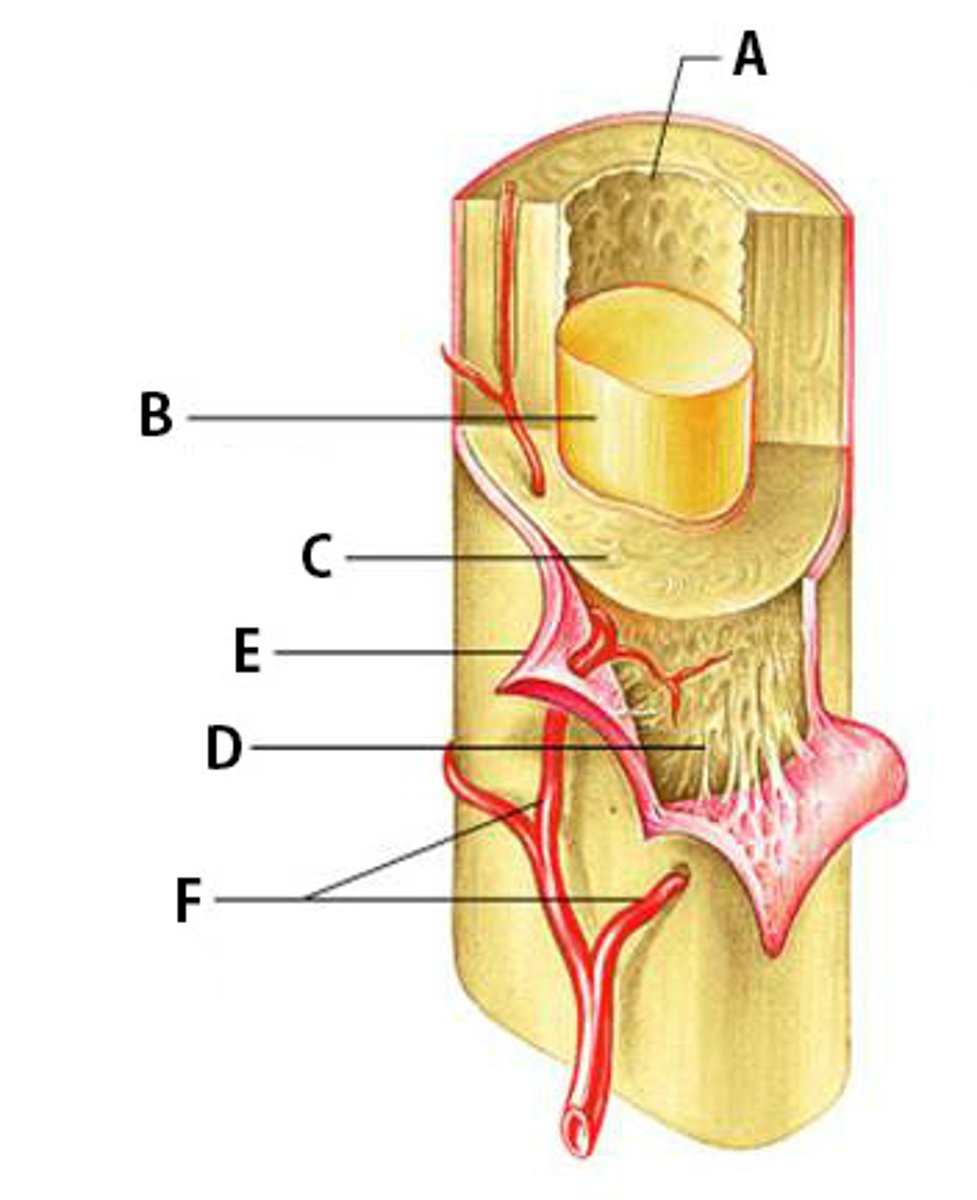
Compact Bone
Dense bone in which the bony matrix is solidly filled with organic ground substance and inorganic salts, leaving only tiny spaces (lacunae).
Periosteum
E
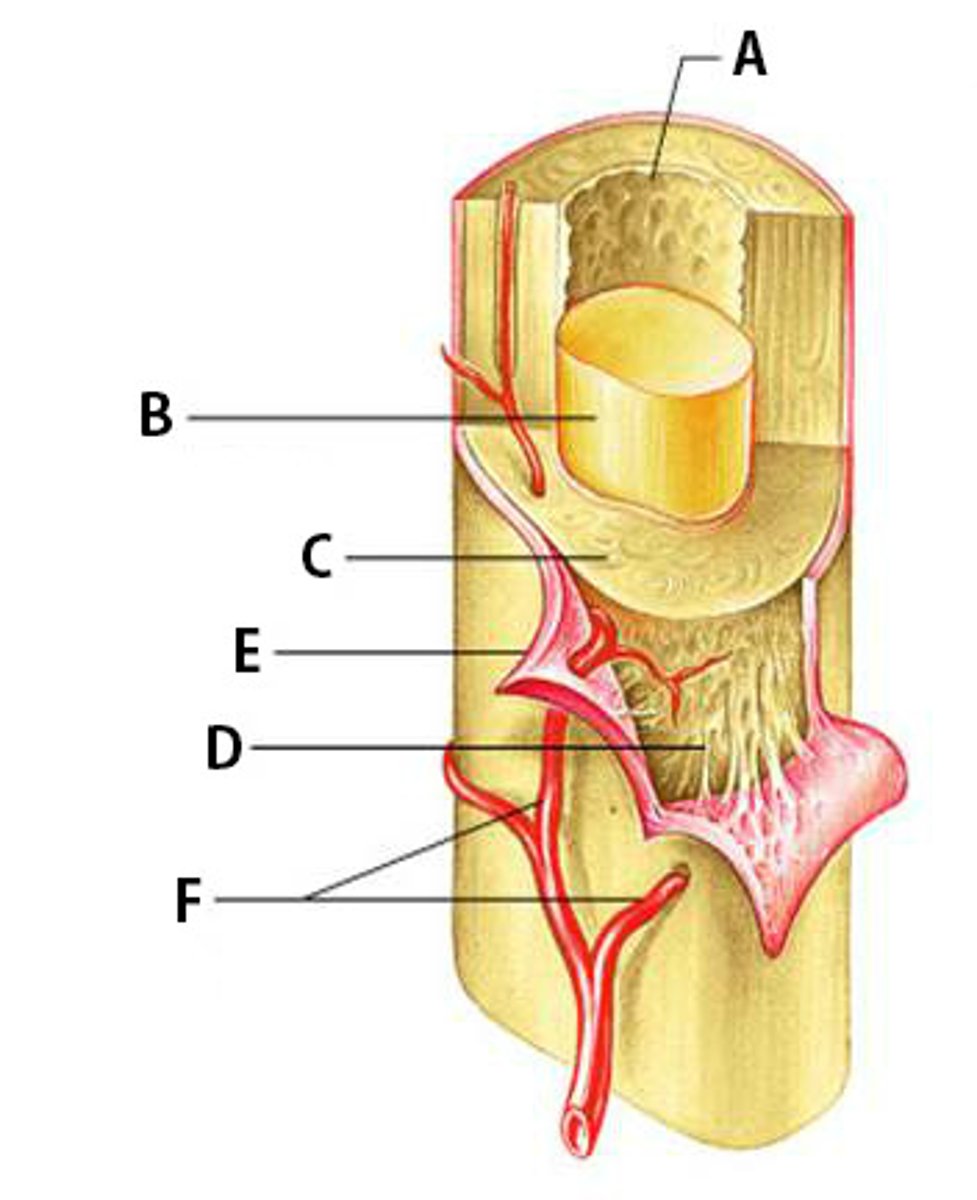
Periosteum
The dense fibrous connective tissue membrane covering the surface of bones except at the joints and serving as an attachment for muscles and tendons.
Nutrient Arteries
F
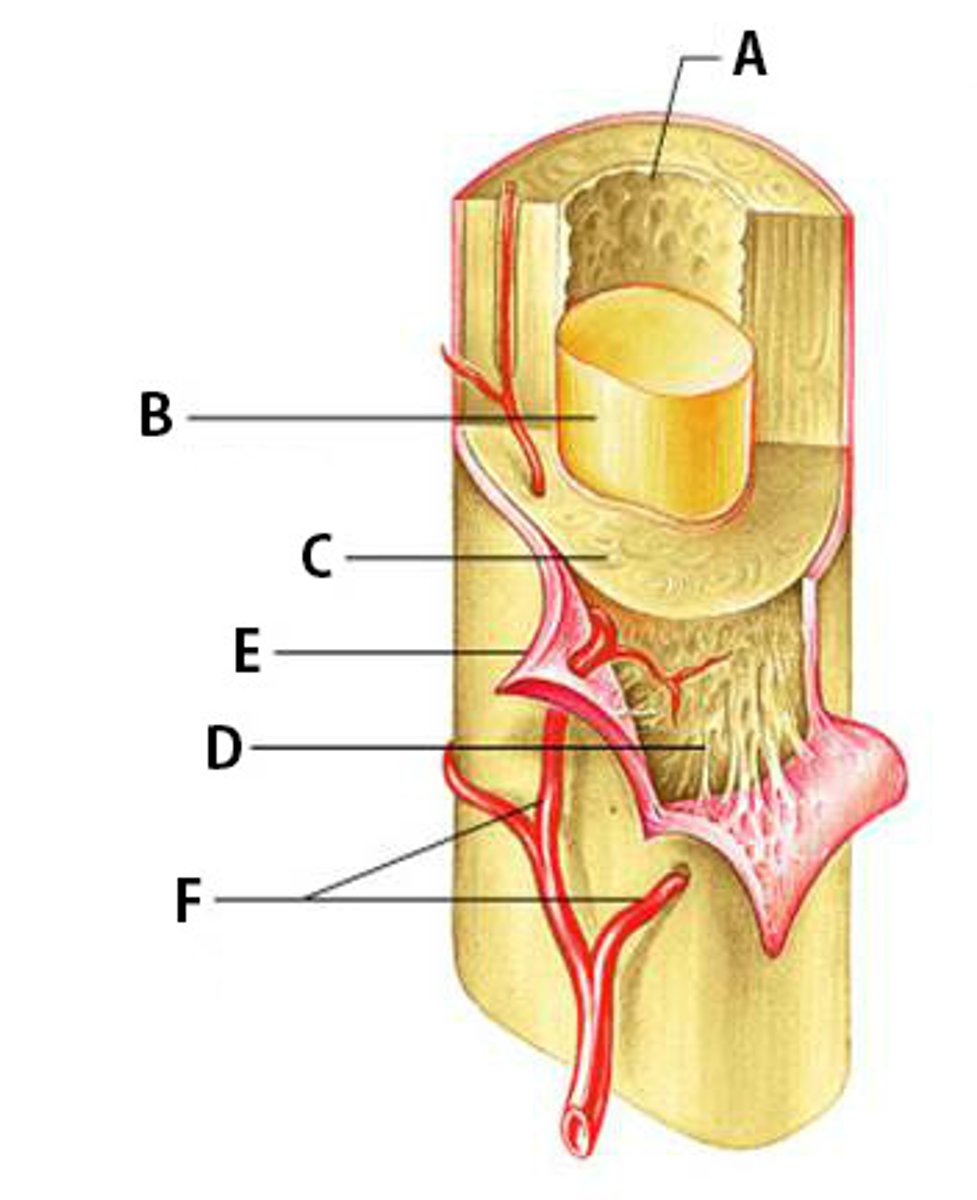
Nutrient Arteries
Arteries which bring nutrients.
Skeleton System Functions
-support: structural framework, points of attachment for tendons and muscles
-provides protection: internal organs (cranium, vertebrae, rib cage, pelvis)
-movement: muscle pull on bones, together bones and muscle produce movement
-mineral homeostasis: storage of Calcium and Phosphorus, body can draw on minerals when needed
-hematopoiesis: red bone marrow produces red/white blood cells/platelets (found in pelvis, ribs, sternum, humerus, femur)
-fat storage: yellow bone marrow → composed of adipose cells, long term place for storage of energy
Organization of Skeleton
appendicular and axial
Axial
skull, sternum, ribs, vertebral column
appendicular
upper extremities, lower extremities, shoulder girdle, pelvic girdle
long bones
longer than they are wide and work as levers (90) --> humerus, tibia
short bones
are cube shaped and have thin layer of compact bone, with inner spongy bone (30) --> wrist/ankles
flat bones
thin and usually curved, provide protection of organs (29) --> scapula, ribs
irregular bones
do not fit in any other category, shape usually has to do with specific function of the bone (53) --> vertebrae
sesamoid bones
bones that are embedded in tendons (4) --> patella
How do bones break
break/fracture because of stress on the bone (overtime or suddenly)
What type of cells are involved in healing a bone fracture?
-Phagocytes - cleans the bone fracture and kill germs, connective tissue
-Chondroblasts - makes soft callus, cartilage
-Osteoblast - makes hard callus, connective tissue
-Osteoclasts - dissolve hard callus, helps bone return to original shape, connective tissue
What is the role of blood in healing a bone fracture?
-Hematoma - blood clot formed around the bone
-Cleans the bone fracture
What is a hematoma?
-When a blood clot forms around break to help clean the area
-Happens a couple hours after bone is broken
What is the role of cartilage in the bone healing process?
Chondroblasts will form soft callus and then bone tissue follows to replace the soft callus
What is a soft callus?
-Provides stability at the fracture site for new blood vessels to form
-Made of collagen
-Created by chondroblasts
-Happens a couple weeks after the break
What is a hard callus?
-Formed into cartilage tissue then a bridge over the fracture site
-Phosphate and calcium
-Covers the fracture site
What is remodeling? When does it happen?
-Excess callus material is removed
-Osteoclasts break down old bone to replace it will new bone tissue
-3-6 month after depending on type of break
What role do osteoblasts play in bone healing?
-Cells that make bone tissues, produce bone cells (hard shell)
-Second to last stage of healing process
What role do osteoclasts play in bone healing?
-Breaks down the excess bone material made by hard callus
What is meant by setting the bone?
-Doctors make it so the bone will line it up correctly so it will heal in the right place
-Consequences if it is not set is the bone will heal in the wrong spot and be out of place
Why is immobilizing a break important?
-Casts and splints keep broken bones from moving so they heal and keep muscles from moving to reduce swelling when a cast would be too tight which would cause more swelling