Topic 4- Stimulants and alohol
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
stimulents and aclhoh
- Cocaine
- (Amphetamines)
- Caffeine
- Nicotine
- Alcohol
cocaine
- Typically snorted in powder form or smoked in its free-base form (crack)
- Reaches peak in blood at 30-60 min- snort
- Easily penetrates the blood-brain barrier – lipophilic molecule
- Biological Half-Life: 30-90 minutes- more quicliy if regular user
when dose cocain recah half life
Reaches peak in blood at 30-60 min- snort
- Biological Half-Life: 30-90 minutes- more quicliy if regular user
short etrm effects of coke
• Cocaine is a stimulant, it increases:
• Euphoria
• Energy
• Confidence
• Talkativeness
• Activity
• Alertness
• Attention
Action of Cocaine at Mono-aminergic Synapses
Any snapsis that use monoamines synapsis
Monamines are senertionin dopime and nerodreadlin
Also have reuptake chanles – a way for the presynaptic chanle to recycle and put back inro vesicals
- Reduces nerotransmitters in the clesft
- Rcycles and reuses
Coke blacks the reuptake chanles- nerotrasmitters dsonst get recycles so stays in clef and has higher concentarrtion
so it keeps it there for longer
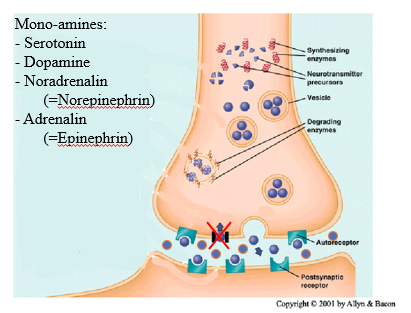
activity at neroadrenergic synaps supress
arousal and plato
monoemgic sysnas
seritoninn
dopimine
neroadrmilin
Sympathetic Nervous System
used by the sypathatic nerous system- narro the blood vesivals so cant be dilated so they cant go to the peinous/ clit
coke can cause sexual dysfunctio
Cocaine Long-Term Effects
• The lack of reuptake results in depletion of monoamines (serotonin, noradrenaline,…)
ð “crash” into depression after several hours
• The concentration of nerotransmitters in the presynaptic because of the lack of reuptaking witch causes crashes/ binges so takes a long time recovery
• This is usually remedied by taking more cocaine.
ð 2-3 day cocaine “binges”
• Destruction of the nasal septum- regular user
• Causes vaisal constriction highest concentration is in the nose – not enough oxygen, no glucus- so the ceels start dying
• Schizophrenia-like symptom:
ð Hallucinations
ð Delusions of Persecution
ð Mood Disturbances
ð Repetitive Behaviours
• Sexual dysfunction
• Tolerance for some of the “desired” effects, such as euphoria, confidence
Sensitisation for other effects, such as convulsiveness, stereotyped behaviour, addictiveness getting bad effect eler in the dosage
coke addictivennes
• Direct effect on Dopamine released in the N. Accumbens and Prefrontal Cortex
• Therefore Direct activation of the “seeking” or “reward” pathway
• Strong “psychological” addictiveness, much less physical addictiveness
Dopine is part to the addict8ivness not the positive side effects more likely the nerodarenalin
Action of Amphetamines at Mono-aminergic Synapses
work on same synapsis and reuptake channles as cokain
slightly diffrent properties on how they affect the diffren monamines and synapsis
they revers the uptake chenles
push the NT out of the reuptake dont need action potental
ritalin (methylyphendate)
acts simmilarliy to come by blocking the monoamine reuptake trasbporte
the relice is much more gradua
dose nit have the sme immidate effcets as coke
effcetive tratmet to ADHD
Caffeine
• Typically ingested in coffee or soft drinks
• Concentration peaks after ~40 minutes
• Easily passes through the blood-brain barrier
• Biological Half-Life: 3.5-5 hours (longer in children)
• Lethal dose: 100 cups of coffee (10g of caffeine)
Caffeine’s Short-Term effects
• Psychostimulant:
• Increases alertness and wakefulness
• Induces clear thinking
• Induces restlessness
• Difficulty with fine movements
• Increases cardiac contractions
Constricts blood vessels
Caffeine’s Side effects
• Anxiety
• Insomnia
• Change in mood
• Hypertension
• High blood pressure make worse
Caffeine Physiological Action
• Blocks adenosine receptors
• Adenosine is involved in inducing sleep
• vasodilation- signial in the blood vecies- bllod vescle contract= higher blood pressure
- Stimulates adrenaline release from adrenal medulla
Caffeine Long-term effects
mostly slep deprivation
some of it effects can be counterd by using more cafine to wake up in the moreing
Caffeine Addictiveness
• Clear physical dependence. Withdrawal symptoms include:
• Headaches (vasodilation)
• Sleepiness
• Irritability
• Difficulty concentrating
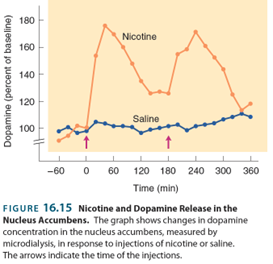
• Psychological dependence: it increases dopamine release in the n. Accumbens
nictine
• From the tobacco leaf:
• Typically smoked or vaped – tyaked by lungs
• Sometimes chewed
• Within 7 sec of a puff, 25% of the nicotine in the smoke has already crossed the blood-brain barrier!
Biological Half-Life of 2 hours in the chronic smoker
Nicotine Short Term effects
• Induces vomiting- affcet the brain stem area thet induces noausia
• Reduces muscle tone (relaxes)
• Reduces weight gain
Increases heart rate and blood pressure
Nicotine Physiological Action
• Binds to nicotinic Acetylcholine receptors
agonist at the synapsis
symils parsypthetic and sypathetic
sympathetic wins- stronger tone
• Nicotinic receptors are involved in stimulation of sympathetic nervous system, including release of adrenaline from the adrenal gland
Nicotinic receptors are also found in the brain
Nicotine Long-term effects
• Body easily develops tolerance
• Possibly wears out the heart more quickly
• Major problems are from other components of tobacco (and cigarette smoke), which can cause cancer, cardiovascular disease, ect
• Long term consequences of smoking in in the smoke rather than the nicotine- however there isn’t much LT consequences to the nicotine and vaping
Nicotine Addictiveness
• A large component of physical dependence: Withdrawal symptoms include:
• Craving
• Irritability
• Increased appetite
• Insomnia
• Although controversial, possibly the most addictive drug from a psychological point of view (effect on dopamine in n. Accumbens)
nictine of dopimine- nucals sucumbas
From the physical aspects are strong
Debate about the psychological addiction
Harder to self administer coke than nicotine- rats
Humans- highly addictive 70% addicted to smokers , 30% who do heroine – relaps within a year
Easy to relaps
Alcohol
• Usually ingested (mostly as drinks)
• Reaches max. blood concentration in 30-90 minutes
• Easily crosses the blood-brain barrier (soluble in both water and lipids)
• Mostly eliminated through the liver, which breaks it down at a steady rate
• Half life depends on the molecule
Alcohol Short Term effects
• Low dose
• Mild euphoria
• Anxiolytic effect (lowers anxiety)
• Higher dose: intoxication
• Slower reflexes
• Incoordination
• Sedation
• Memory problems
• Dilation of blood vessels (heat loss)- acholo coat
• Diuretic (more urination)
Alcohol Physiological Action
• Agonist of GABA-A receptors (increases inhibitory processes)- mimic/ increase effect of GABA( inhinitory system)
controls behvior
• Antagonist of NMDA (group of glutamate receprtes) receptors (suppresses excitatory processes)- involved in meoemary formation- blocking prevents the making of meoemoys meomemory loss long term
• And several other effects…
• Intracts with lots of different things
Alcohol Long-term effects
• Cirrhosis of the liver: liver failure
• Brain damage (especially hippocampus: Korsakoff’s syndrome)- perminalt cant make LTM
• Foetal alcohol syndrome- when pregnant
Alcohol Addictiveness: Pysical dependace
• Tolerance is induced even from one night drinking and results in mild withdrawal symptoms (hangover)
• After chronic use, there are very strong withdrawal symptoms (Delirium Tremens); this can be fatal- delirous tremmer- go into seasures
the bodys mechnisusm for getting back to homeostatus for gabab a- goes down so the body make not enoug Gaba making the circtes not be able to be inhabitted causing seasures
Alcohol addictivenss:Psychological dependence:
• It increases dopamine release in the n. Accumbens (as do other NMDA receptor antagonists)
• Strong heritable component to alcoholism