A&P Practicum 6
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
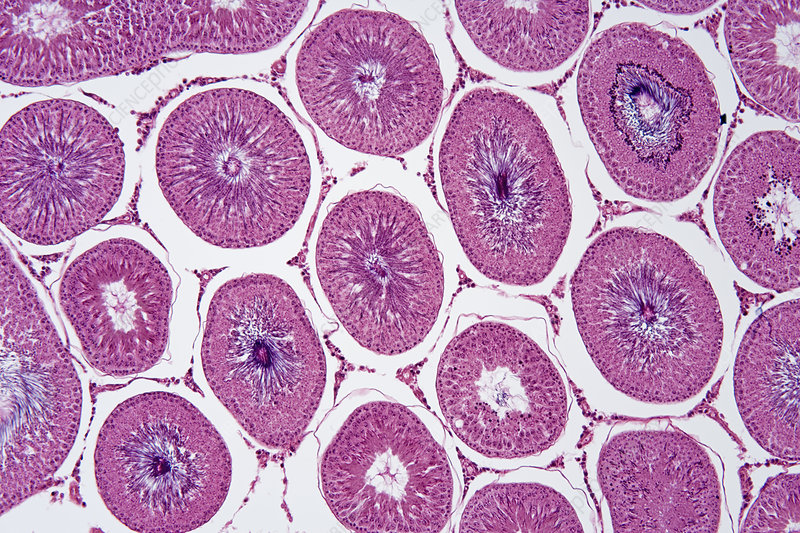
Seminiferous Tubules function
Site of germ cell development
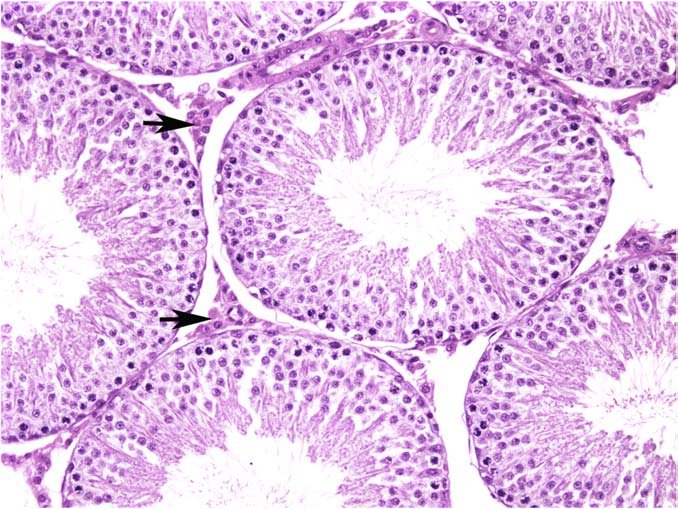
Leidig Cells function
AKA Interstitial cells. Secrete Testosterone
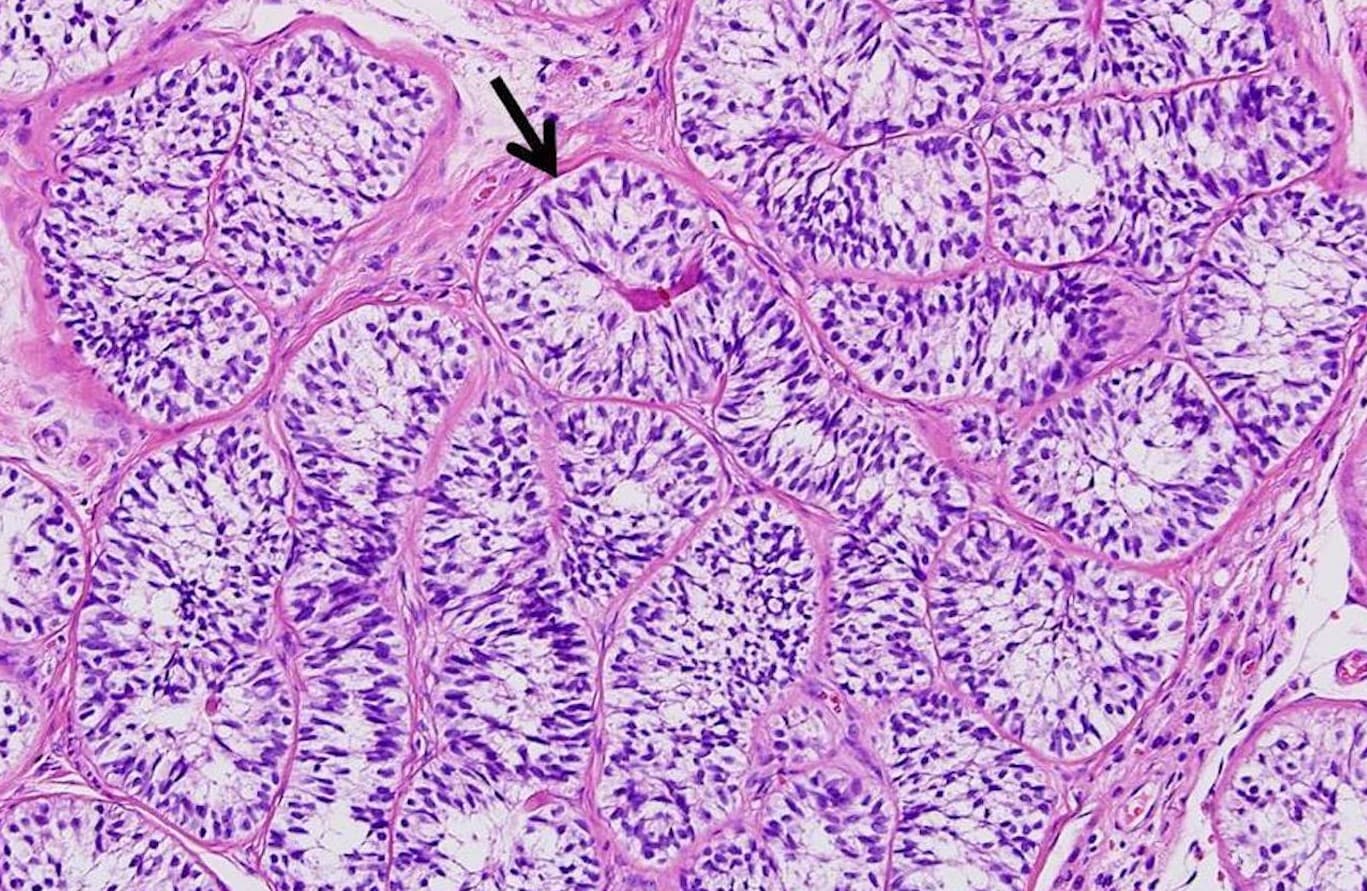
Sertoli Cells function
AKA Sustentacular cells. Supplies nutrients to developing sperm. Secrete inhibin
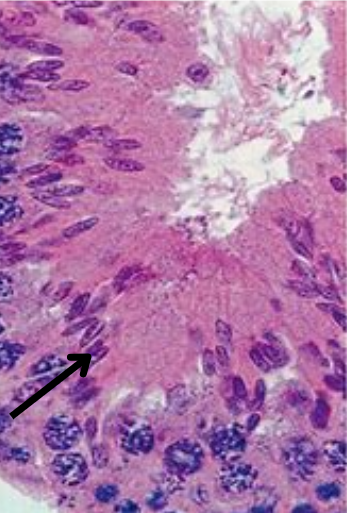
Spermatids function
Immature derivatives of germ cells. Develop and mature to become sperm
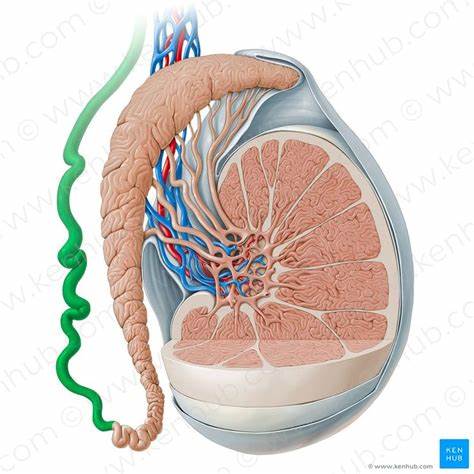
Testes features
Seminiferous tubules, Leidig cells, Sertoli cells, Spermatids
Ovary features
Primordial follicles, developing (primary and secondary) follicles, Tertiary (Grafian) follicle, corpus luteum
Primordial follicles function
Ova paused in meiosis, surrounded by a single layer of support cells.
Developing (primary and secondary) follicles function
Support cells become cuboidal and multiply as the ova continues through meiosis and the follicle gets larger
Tertiary (Grafian) follicle function
Largest developed follicle capable of undergoing ovulation
Corpus luteum function
Remnant of a follicle shortly after ovulation
Seminiferous tubules
Leidig cells
Sertoli cells
Spermatids
Primordial follicles
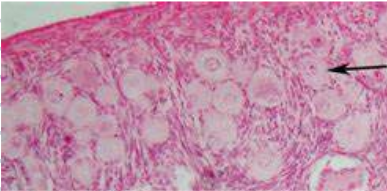
Developing (primary and secondary) follicles
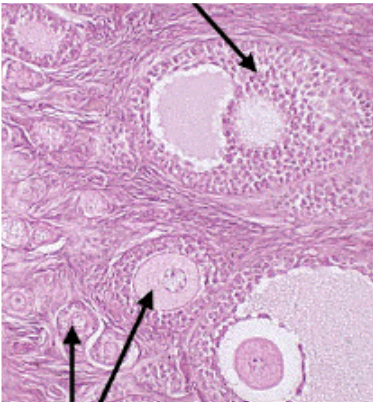
Tertiary (Grafian) follicles
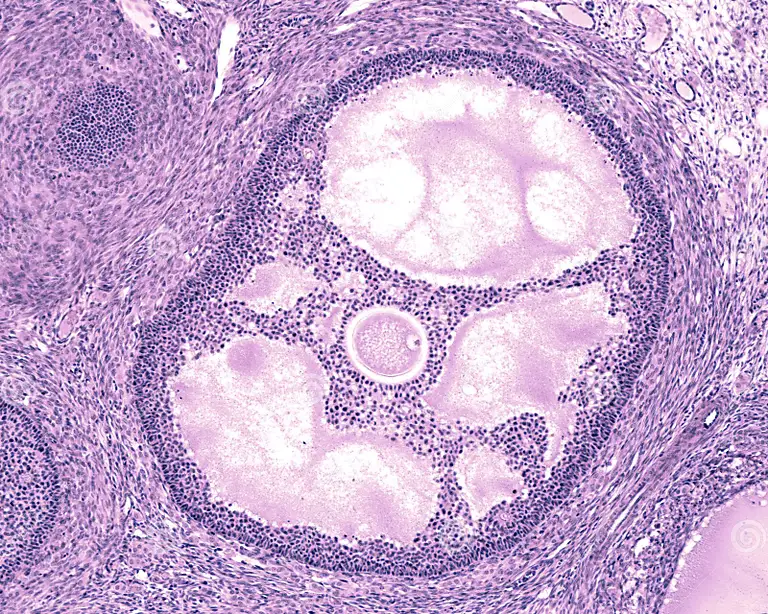
Corpus luteum
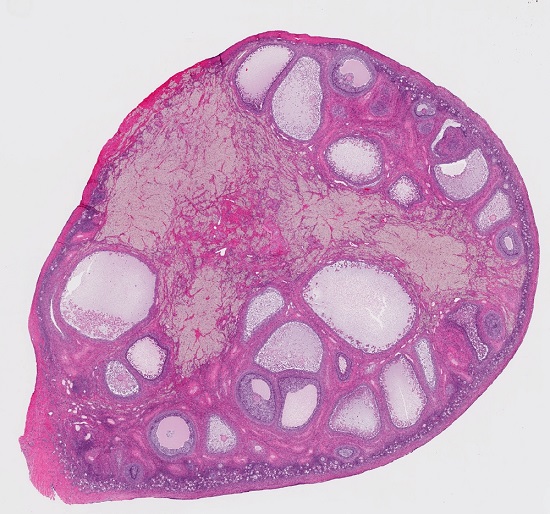
Testis function
Sperm production; secretes androgen hormones
Seminiferous Tubules function
within testis, site of sperm production
Epididymis function
site of sperm maturation between seminiferous tubules and ductus deferens
Ductus (vas) deferens function
transports sperm
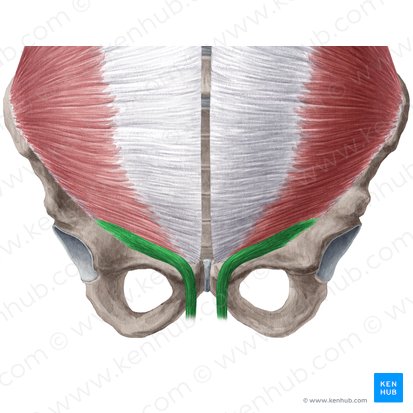
cremaster muscle function
elevates the scrotum
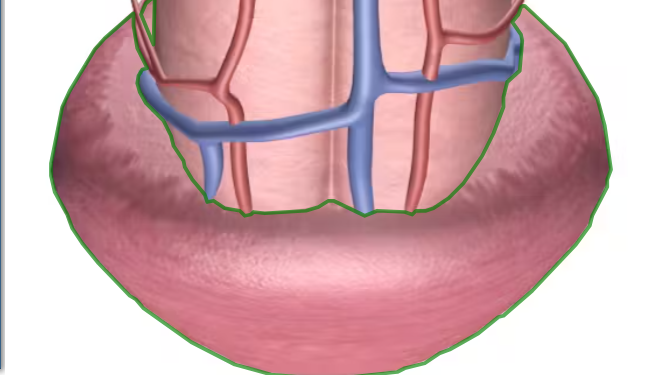
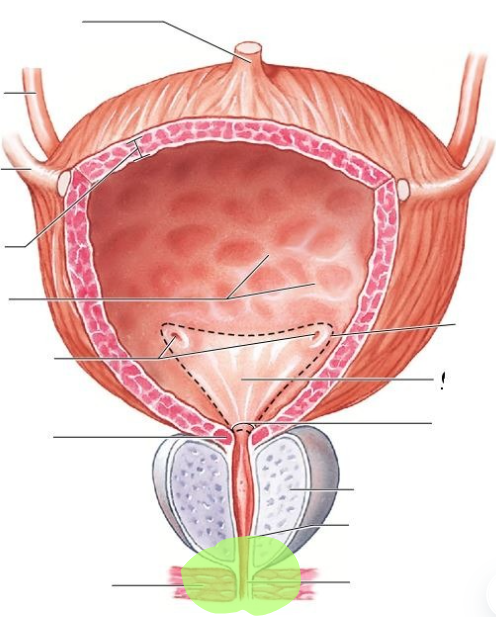
Penis features
glans penis, prepuce, corpora cavernosa, corpus spongiosum
male urethra
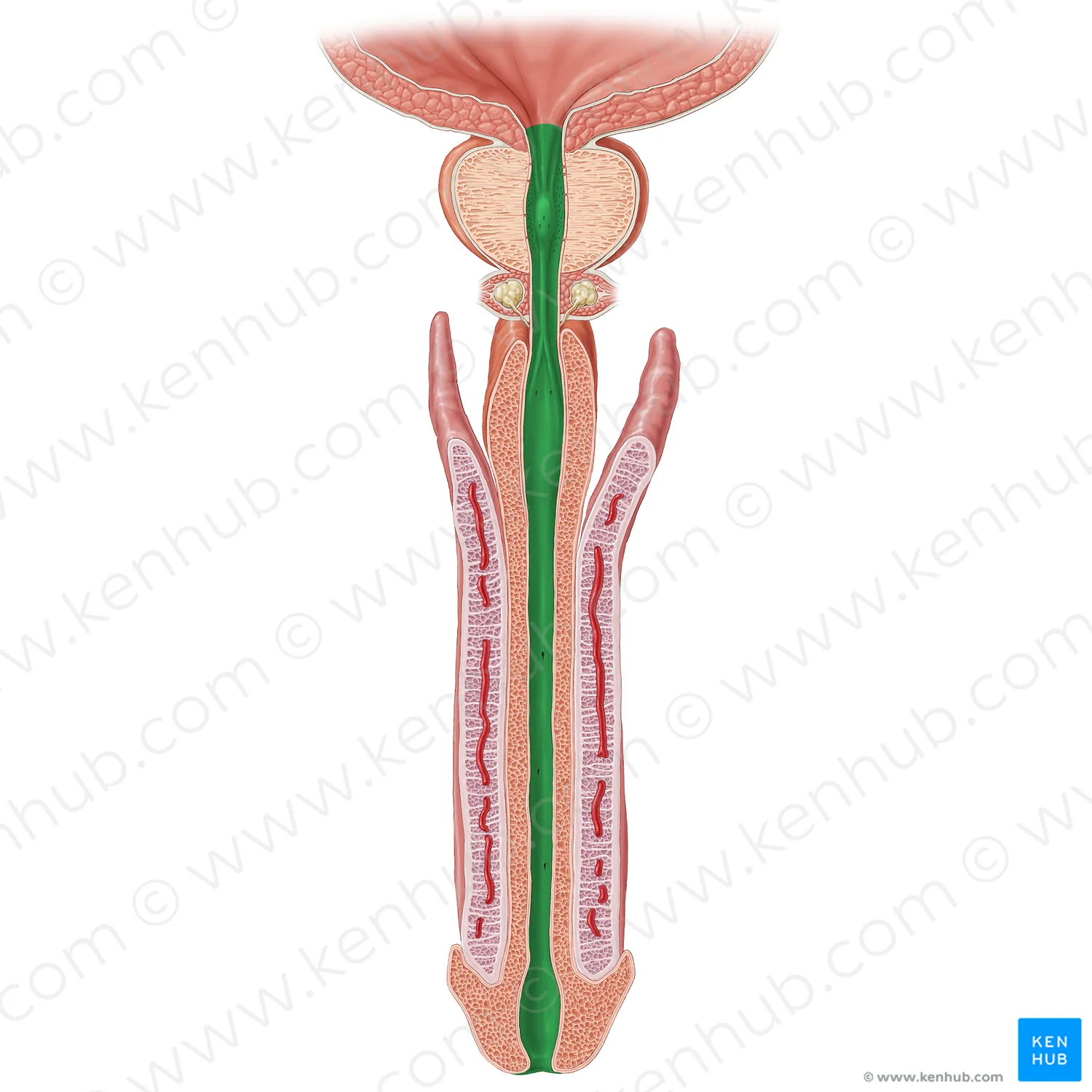
Scrotum features
testis, seminiferous tubules, epididymis
Spermatic cord features
ductus (vas) deferens, cremaster muscle
accessory glands features
seminal gland, prostate gland, bulbourethral gland
seminal gland function
secretes 60% of semen volume
prostate gland function
secretes 30 % of semen volume
bulbourethral gland function
secretes alkaline lubricating fluid
Testis
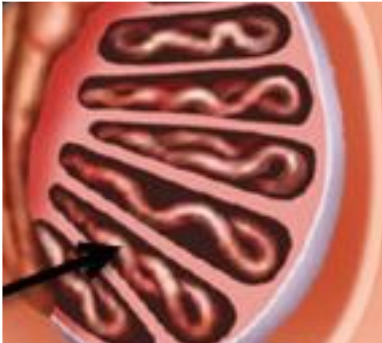
seminiferous tubule
epididymis
spermatic cord
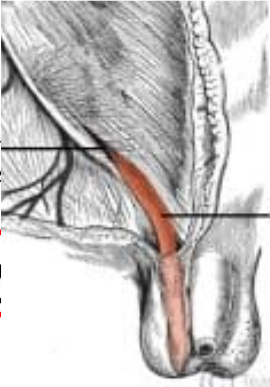
ductus (vas) deferens
cremaster muscle
glans penis
prepuce
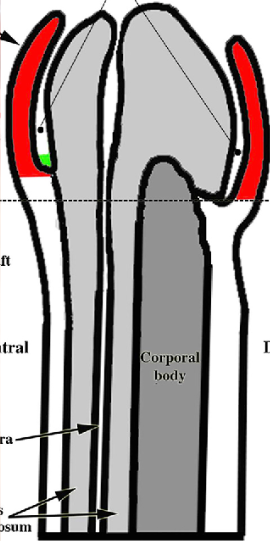
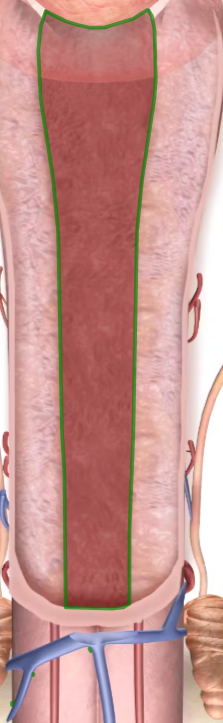
corpora cavernosa
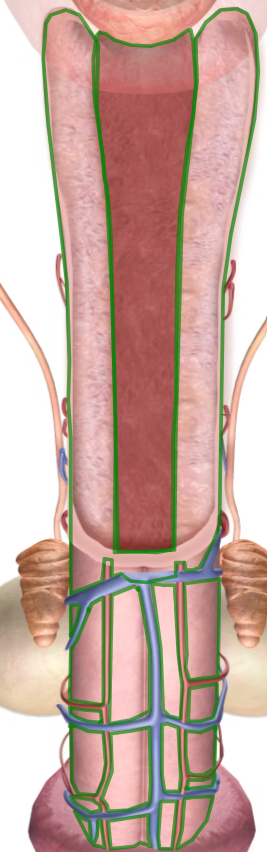
corpus spongiosum
female urethra
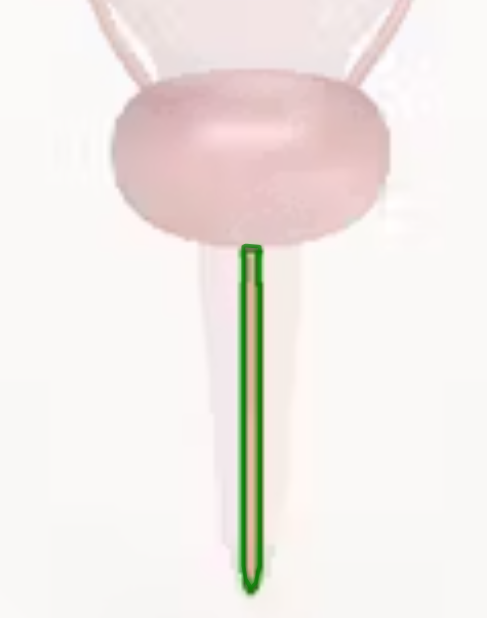

seminal gland
prostate gland
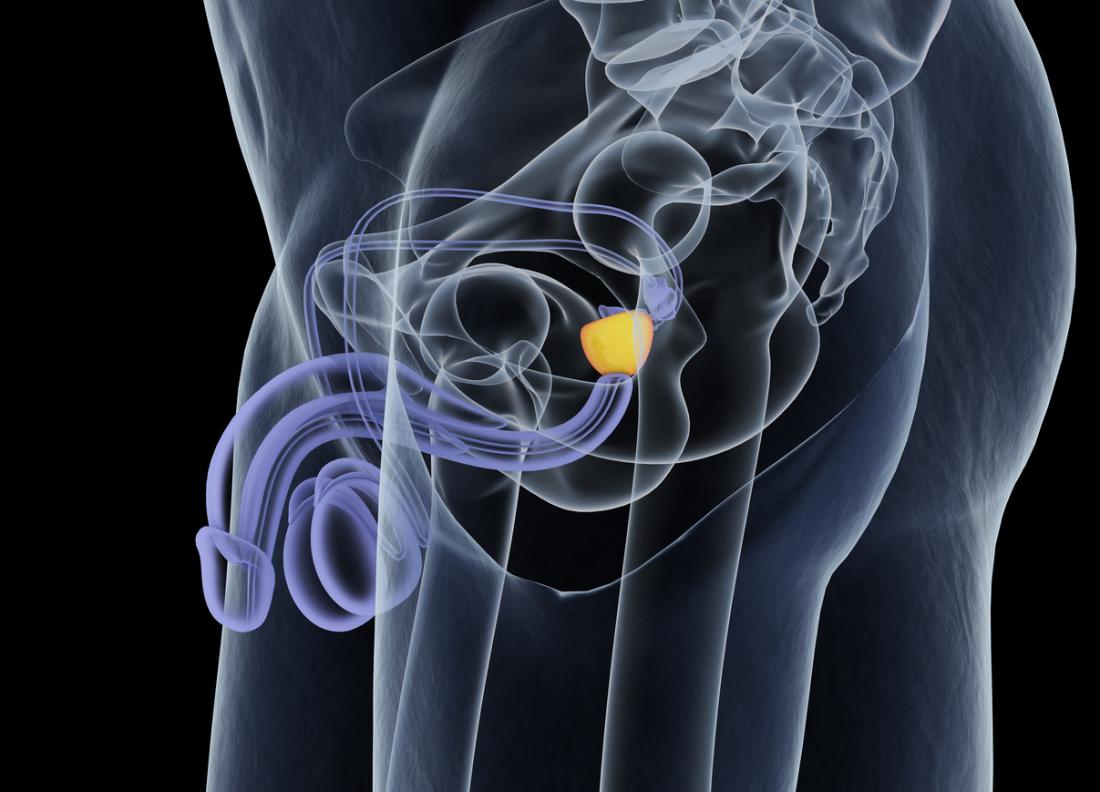
bulbourethral gland
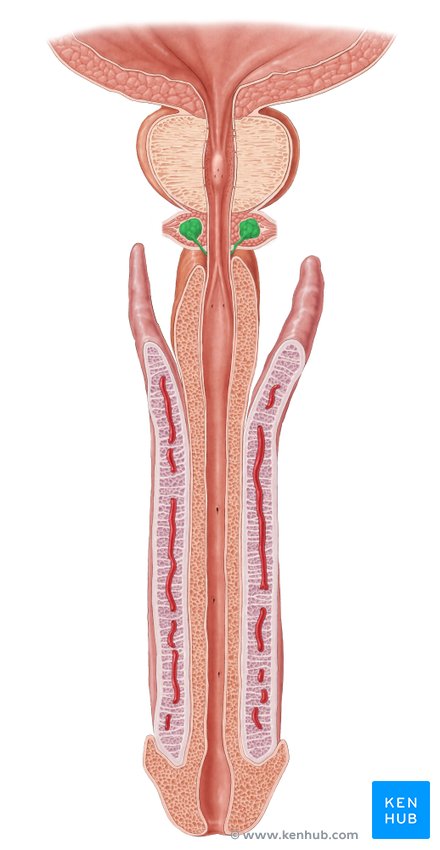
ovaries function
production of ova (eggs) and estrogens
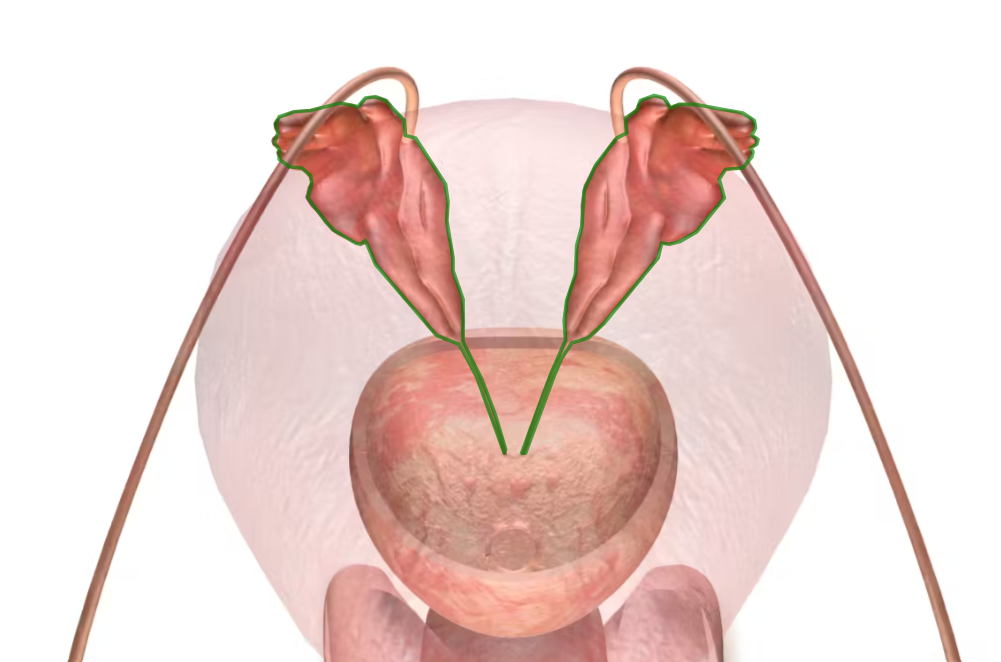
uterine (fallopian) tubes
connects ovary with the uterus
fimbriae
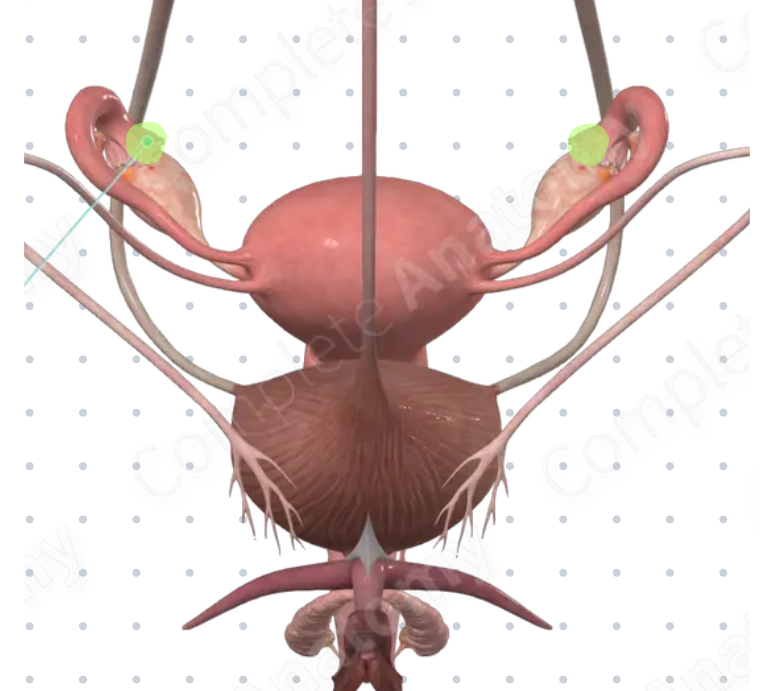
uterus function
site of implantation of fertilized ovum
cervix
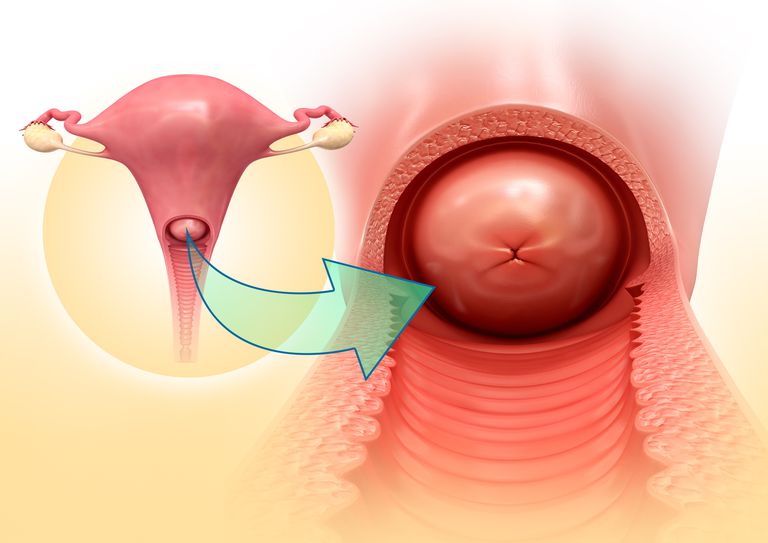
vagina function
muscular tube (birth canal)
ovaries

uterine tubes
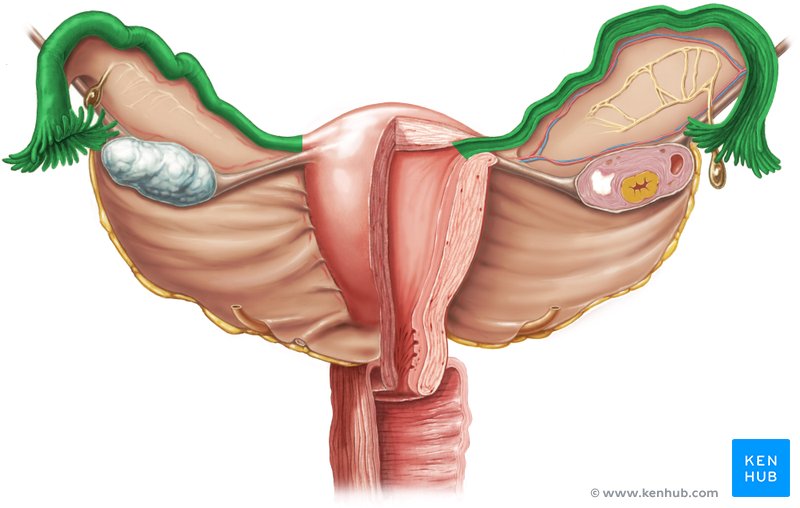
uterus

vulva function
external genitalia
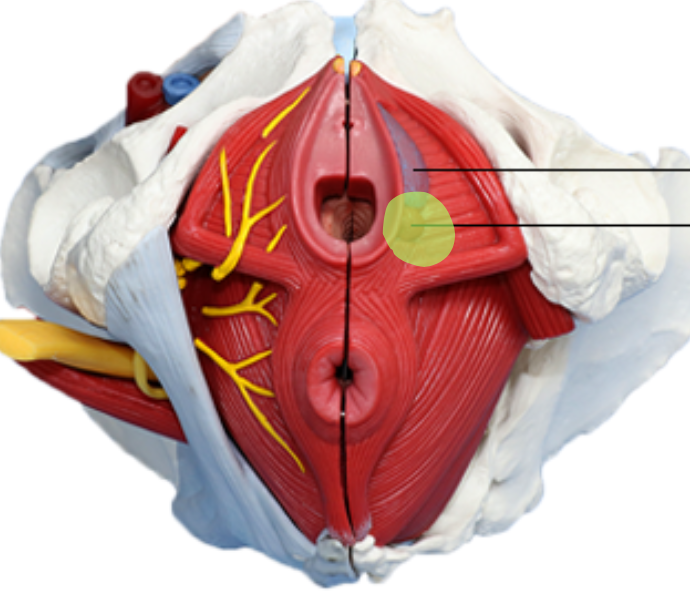
greater urethral orifice function
Bartholin’s glands, secrete lubricating fluid into the vagina
clitoris function
erectile tissue with sensory nerves
vulva

labia majora
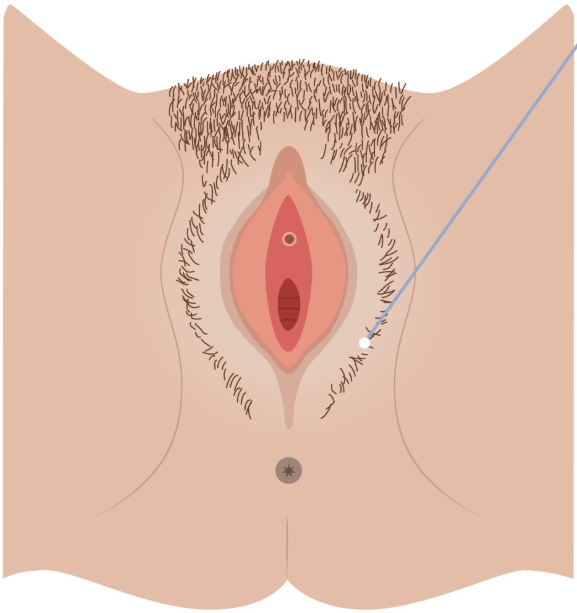
labia minora
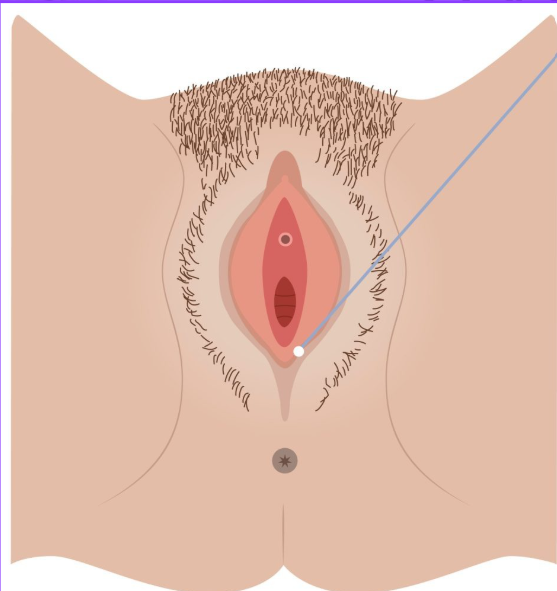
external urethral orifice
prepuce female
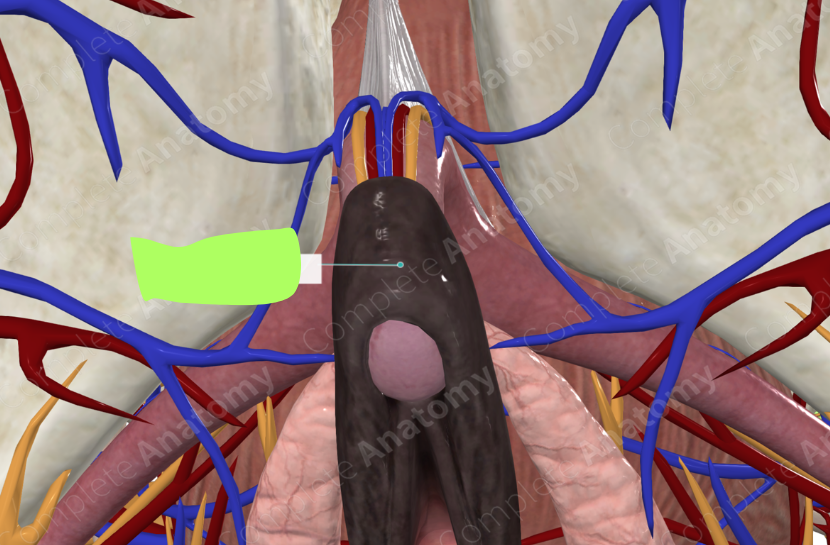
greater vestibular glands
hymen
clitoris
corpora cavernosa
bulbs of the vestibule
Testes and ovaries
Homologous structures that produce gametes
Skin of the scrotum and labia majora
Homologous structures that often develop coarse hair during puberty
Skin of penis shaft and labia minora
Homologous structures that do not develop coarse hair
Glans penis and glans clitoris
Homologous structures that is the tip of structure containing nerve endings
Prepuce and prepuce
Homologous structures that is the skin covering glans organ
Corpora cavernosa and corpora cavernosa
Homologous structures that are the two cylinders of erectile tissue
Corpus spongiosum and bulbs of vestibule
Homologous structures that are one tube of erectile tissue, divided in two for females