BioE Lecture Notes 22 4/23/25
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Drugs
Used to inhibit certain CDKs and synchronize them
Checkpoint pathways
Comprised of event sensors, a signaling pathway, and an effector that halts cell cycle progression and activates repair pathways when needed
Cancer
Mutations in proto-oncogene and tumor suppressor genes that cause uncontrollable cell division
Genes promoting cell proliferation genes
Encodes proteins that promote cell division. Mutations cause proto-oncogenes (promotes cell division)
Antiproliferation genes
Encodes proteins involved in cell cycle checkpoints. Ex: Tumor suppressor genes (ex: p53 gene)
Meiosis
Restricted to the germ cells, where it is key to sexual reproduction. Germ cells undergo this process to produce haploid gametes (sperm and egg)
Meiosis I
Prophase I → Telophase I
Meiosis II
Prophase II → Telophase II. 4 nonidentical haploid daughter cells at the end.
Prophase I (early)
Synapsis and crossing over occurs.
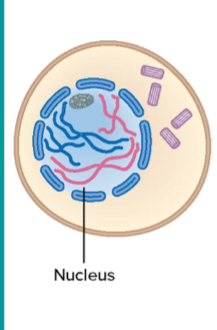
Prophase I (late)
Chromosomes condense, become visible. Spindle forms. Nuclear envelope fragments. Spindle fibers attach to each chromosome. Recombination between each homologous chromosome

Metaphase I
Paired homologous chromosomes align along the equator of the cell
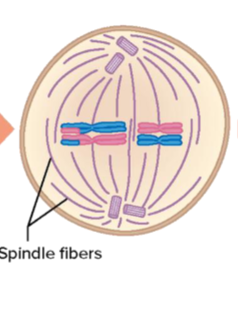
Anaphase I
Homologous chromosomes separate to opposite poles of the cell
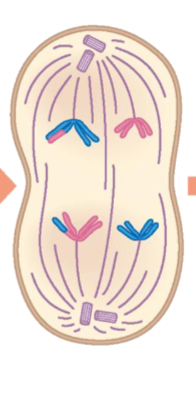
Telophase I
Nuclear envelopes partially assemble around chromosomes. Spindle disappears. Cytokinesis splits the cell into two.
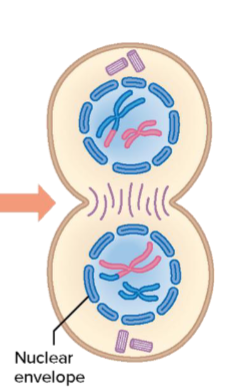
Prophase II
Nuclear envelop fragments. Spindle forms and fibers attach to both chromosomes
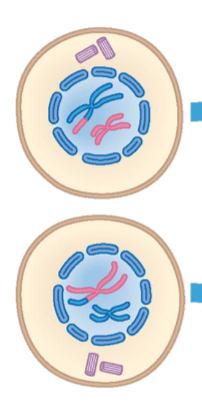
Metaphase II
Chromosomes attach align along equator of the cell
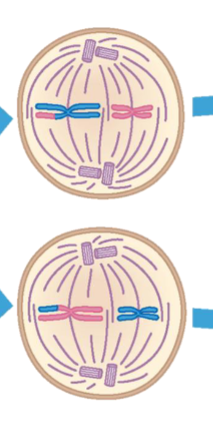
Anaphase II
Sister chromatids separate to opposite ends of the cell
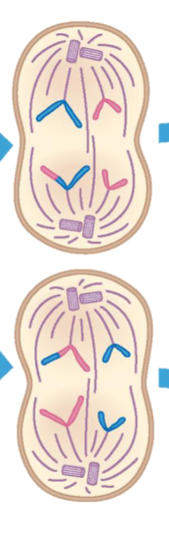
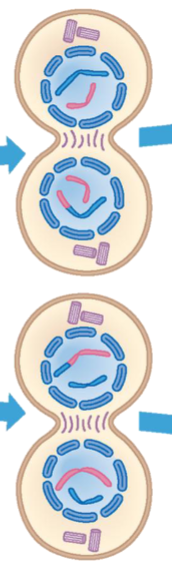
Telophase II
Nuclear envelopes assemble around two daughter nuclei. Chromosomes decondense. Spindle disappears. Cytokinesis divides cells.
G1 phase
Phase where the cell undergoes growth and DNA replication
Cyclin
Regulatory binding protein of the cell cycle
Asynchronous cell cultures
Cells are randomly distributed through the cell cycle
Prophase
Phase where chromosome condensation is initiated
Phase where centrosomes start moving to opposite poles of the cell
Cells where the nuclear envelope disintegrates
Cytokinesis
Meiosis involves one cycle of _______
Early development
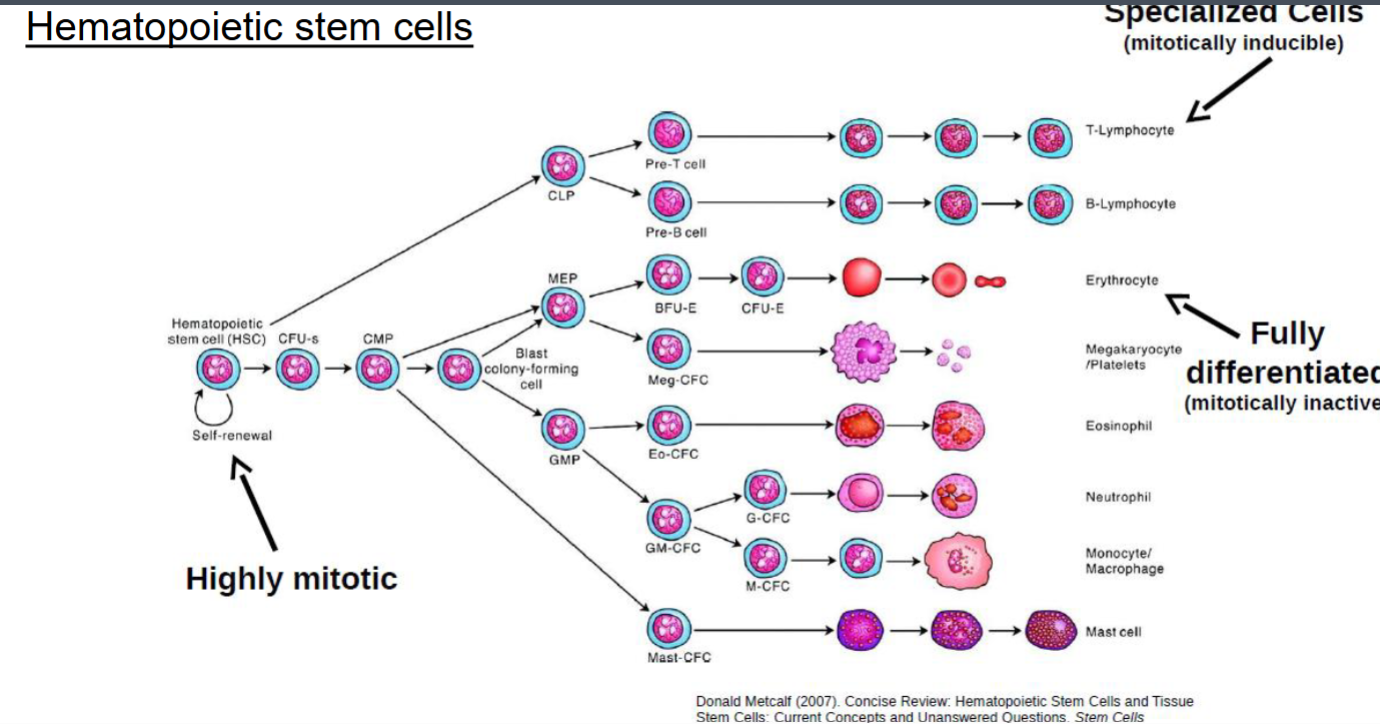
Characterized by the rapid proliferation of embryonic cells which differentiate to form specialized cells of adult tissues and organs. Ex: Hematopoietic stem cells.
Cell proliferation
Must balance cell death to maintain a constant number of cells in adult tissues and organs. Cells are lost throughout life.
Epithelial Cells
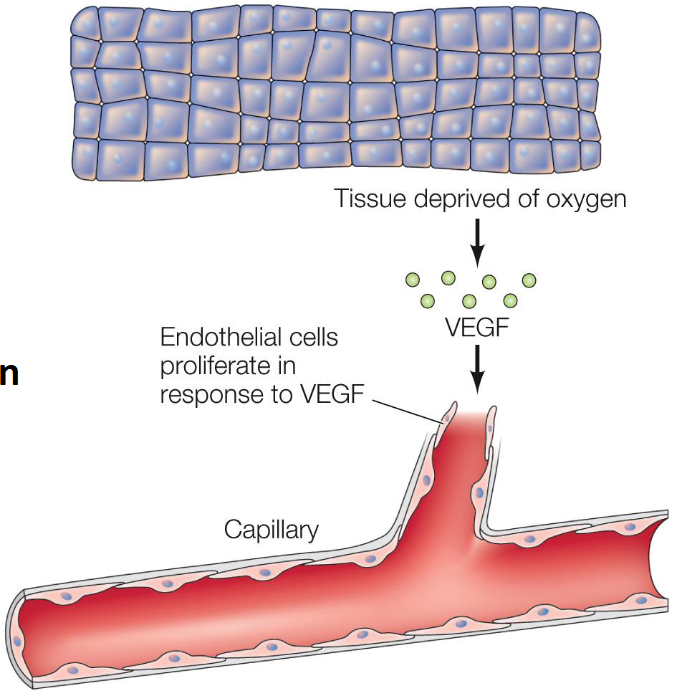
Are stimulated to proliferate by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)
Is secreted by cells deprived of oxygen, leading to the outgrowth capillaries into tissues lacking adequate blood supply.
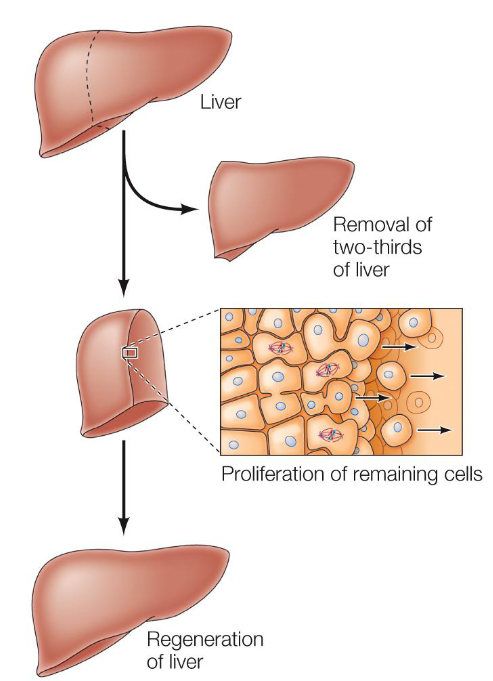
Proliferation of liver cells
Liver cells are arrested in G0 but resume proliferation to replace damaged tissue.
Most fully differentiated cells in adult animals, are no longer capable of cell division
Can be replaced by the proliferation of a subpopulation of less differentiated cells (stem cells) that are present in most adult tissues
Stem cells can proliferate and replace differentiated cells throughout an animal’s lifetime
All the different types of blood cells develop from hematopoietic stem cells in the blood marrow
Colon epithelial cells
Are renewed by the division of stem cells located at the bottom of the intestinal crypt.
Epidermal stem cells in the basal layer
Replace cells from the surface that are continually lost
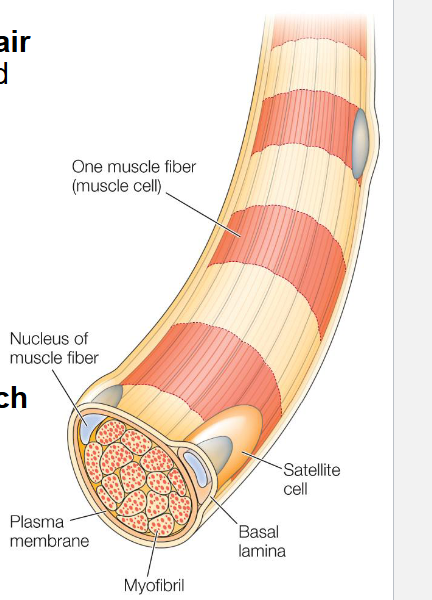
Skeletal muscles
Example of the role of stem cells in the repair of damaged tissue.
Normally a stable tissue with little cell turnover. It can regenerate rapidly in response to injury or exercise.
Regeneration is mediated by proliferation of satellite cells, the stem cells of adult muscle.
Embryonic stem cells
Stem cells of early embryos which have the ability to differentiate into all the cell types of adult organisms (pluripotency)
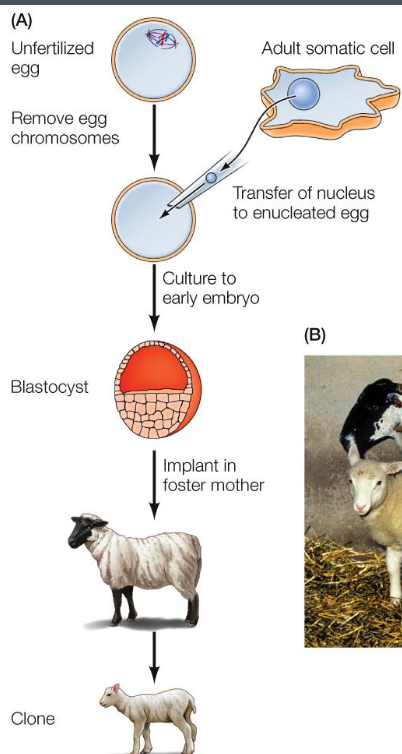
Ian Wilmut and gang
In 1997, initiated a new era of regenerative medicine by cloning Dolly the Sheep
Cloning of Dolly the sheep
Nucleus of a mammary epithelial cell that was transplanted into an unfertilized egg and implanted into a surrogate mother. (somatic cell nuclear transfer)
Adult somatic cells
Can be directly converted to pluripotent stem cells in culture. This circumvents the need to generate embryos and provide a direct mechanism for converting somatic cells to stem cells.
Method first reported by Kazutoshi Takahashi and Shinya Yamanaka in 2006. They got the Nobel Prize in 2012
Apoptosis (programmed cell death)
Mechanism by which damaged and potentially dangerous cells can be eliminated.
Virus-infected cells frequently undergo programmed cell death, preventing the production of new virus particles.
DNA damage can also induce apoptosis
Necrosis
Sudden cell death. Contents of the cell spread out causing inflammation.