Exam 2 - Biochemistry
1/256
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch. 7-9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
257 Terms
Per glucose molecule, how many ATP are produced?
4
Per glucose molecule, what’s the net number of ATP produced?
2
D glucose + 2 ATP + 2 Pi + 2NAD+
2 pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2H+ + 2H2O
2 pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2H+ + 2H2O
D glucose + 2 ATP + 2 Pi + 2NAD+
Which glycolysis steps are irreversible?
1, 3, 10
Which glycolysis steps use up ATP?
1, 3
Which glycolysis step produces ATP?
7, 10
Purpose of Synthesis of Glucose 6 phosphate
increase reactivity of OH with phosphoryl group
Make glucose negative
Keep it in the cell
Enzyme (step 1 glycolysis_
hexokinase
Purpose of isomerization of G6P to F6P
Create primary OH for future phosphorylation
Enzyme (step 2 glycolysis)
Phosphoglucose isomerase
Phosphorylation of F6P purpose
Second phosphorylation makes negative on both halves of hexose when fragmented
Enzyme used for 3rd step glycolysis
Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)
Cleavage of F-1,6 bisphosphate purpose
Break into 2 3-carbon molecules
Enzyme for 4th step glycolysis
Aldolase
Conversion to DHAP to GAP purpose
Use both fragments for max energy yield
step 5 glycolysis enzyme
triose phosphate isomerase
Oxidation of GAP purpose
Create high E phosphoanhydride bond
Produce reduced coenzyme
Enzyme used in 6th step of glycolysis
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAP dehydrogenase)
Phosphoryl Transfer purpose
Create 2x ATP
Enzyme used in 7th step of glycolysis
Phosphoglycerate kinase
Phosphate transfer purpose
Generate higher E bond to produce another molecule of ATP
8th step of glycolysis enzyme
Phosphoglycerate mutase
Purpose of dehydration to phosphoenolpyruvate
Complete preparation of high E bond for ATP synthesis
Enzyme used in 9th step of glycolysis
Enolase
Why is PEP high energy?
Phosphoryl group traps the enol form, squashing the opportunity for tautomerization
Purpose of the synthesis of pyruvate and ATP
Synthesize ATP again
Enzyme used in 10th step of glycolysis
Pyruvate kinase
Irreversible steps of glycolysis
1, 3, 10
1ST STAGE of glycolysis
Phosphorylation and cleavage of glucose
2nd stage of glycolysis
Conversion of GAP to pyruvate, gaining 4 ATP
How many pyruvate are produced at the end of glycolysis?
2
The fate of pyruvate depends on:
its environmental condition
organism
If pyruvate is in an aerobic environment,
It is converted to acetyl coA and begins the TCA cycleIf
If pyruvate is in an anaerobic environment, the __________ is not possible and pyruvate is converted to a ______________ compound
Oxidation; reduced
What can be regenerated to keep glycolysis running for a short time?
NAD+
Homolactic fermentation is an example of what kind of process?
Anaerobic
Alcoholic fermentation is an example of what kind of process?
Anaerobic
Homolactic fermentation takes place where?
Muscles and red blood cells
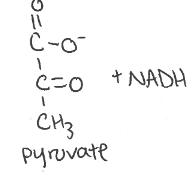
yield what
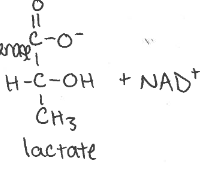
Enzyme used in homolactic fermentation
Lactate dehydrogenase
Alcoholic fermentation yields what from pyruvate?
CO2 + EtOH
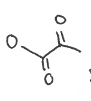
yields by which enzyme?
Losing what in the process
pyruvate decarboxylate, CO2
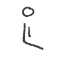
yields by which enzyme?
What is converted?
alcohol dehydrogenase
NADH + H+ —→ NAD+
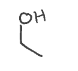
What mechanism is used to break C-C bond (pyruvate decarboxylase, alcoholic fermentation)?
TPP Mechanism
TPP Mechanism
Splits molecule between C=O and alpha carbon
The opposite reaction of glycolysis is considered?
Gluconeogenesis
Net Reaction of gluconeogenesis
2 pyruvate + 4 ATP + 2 GTP + 2NADH + 2H+ + 6H2O —> glucose + 4 ADP + 2GDP + 6 Pi + 2NAD+
2 pyruvate + 4 ATP + 2 GTP + 2NADH + 2H+ + 6H2O —>
glucose + 4 ADP + 2GDP + 6 Pi + 2NAD+
Why is gluconeogenesis more costly than glycolysis?
Far less favorable with a higher delta G
When does gluconeogenesis occur?
In the liver during fasting
Viable starting materials for gluconeogenesis
pyruvate
lactate
alpha- keto acids from amino acids
Gluconeogenesis must bypass ____ irreversible reactions
3
Most costly challenge of gluconeogenesis
Synthesis of PEP
PEP general synthesis from gluconeogenesis step 10
Pyruvate + CO2 + H2O —→ oxaloacetate —→ PEP
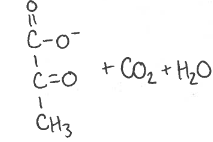
what is produced?
what enzyme facilitates this reaction?
What are any side reactions taking place?
(oxaloacetate)
pyruvate carboxylase
ATP —> ADP + Pi
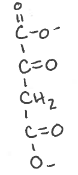
Oxaloacetate is membrane ________ because of _______
impermeable; 2- charge
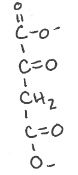
What is the yield?
What enzyme facilitates this reaction?
What are any side reactions taking place?
PEP carboxykinase
GTP —> GDP + Pi
Loss of CO2
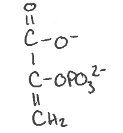
PEP carboxykinase is found where?
In the cytosol
Problem with 1st bypass reaction (gluconeogenesis)
Most organisms only have PEP carboxykinase in the cytoplasm but OAA can’t leave mitochondria
To move OAA to cytosol, what is used?
Malate shuttle
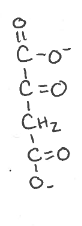
what reaction is this part of?
what is the yield?
what enzyme facilitates this reaction
what is a side reaction taking place?
Where does this reaction take place?
malate shuttle
malate dehydrogenase
NADH + H+ —> NAD+
Mitochrondria
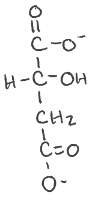
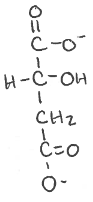
Where does this reaction go to?
What is the yield?
What enzyme?
What side reaction?
Cytosol
OAA
Malate dehydrogenase
NAD+ ——> NADH + H+
Malate shuttle provides _________ in cytosol for later reactions
NADH
2nd bypass reaction Step and reaction
“Step 3” —> F 1,6 BP to F6P
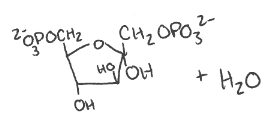
What is this reaction?
What is the yield?
What enzyme facilitates it?
Step 3 of gluconeogenesis
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
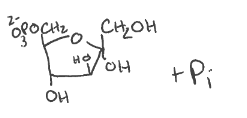
Difference between Step 3 of glycolysis and “Step 3” of gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis doesn’t generate ATP
Positive modulation
Increases the activity of a metabolic pathway
Citrate ________ modulates Step 3 of gluconeogenesis
Positively
AMP________ modulates Step 3 of gluconeogenesis
Negatively
Fructose 2,6-BP ________ modulates Step 3 of gluconeogenesis
Negatively
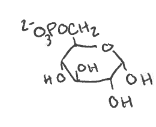
What reaction pathway is this from?
What is the yield?
What enzyme facilitates the result?
“1st” step of gluconeogenesis
Glucose-6-phosphatase
There is/isn’t ATP made in 3rd bypass reaction of gluconeogenesis
Isn’t
3rd bypass reaction and step 1 of gluconeogenesis
G6P to glucose
This many ATP and GTP were put into the first bypass reaction of gluconeogenesis
ATP 2
GTP 2
Where are 2 more ATP added for gluconeogenesis besides step 10?
Step 7
“Step 7” of gluconeogenesis net reaction
3 phosphoglycerate + ATP ←→ 1,3- BPG + ADP
How fast is allosteric ligand binding?
Fast (usec - msec)
How fast is covalent modification bonding, such as phosphorylation?
Medium (sec)H
How fast is a genetic/transcriptional regulatory mechanism?
Slow (hour to days)
Hexokinase has ______ isoforms
4
1, 2, and 3 isoforms of hexokinase are located?
Tissues, low levels of liver
Km hexokinase 1, 2, 3
0.1 mM for glucose
Activity of isoforms 1, 2, 3 Hexokinase is inhibited by?
G6P, preventing buildup of products
Isoform 4 of hexokinase is found where?
Liver and pancreas K
Km of hexokinase 4
10 mM
is Hexokinase 4 inhibited by G6P?
No
At high concentrations, glucose is diverted where by isoform 4 of hexokinase?
Storage
Most regulated step of glycolysis is
Step 3, enzyme phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK-1)
Inhibitors of PFK-1
ATP
Citrate
As the concentration of ATP gets high, it can act as an _______ for this enzyme.
inhibitor for PFK-1
Activators of PFK-1
AMP/ADP
F-2,6 BP
F 2,6 BP is controlled by
Hormone levels
Blood glucose concentration
Where is F-2,6 BP synthesized and by what?
In the liver by PFK-2
Bifunctional enzyme
Acts as kinase or phosphatase depending on how many of its own phosphoryl groups are added
Kinase
Transfers phosphoryl groups
Phosphatase
removes phosphate groups
How is PFK-2 modified?
Hormone signaling cascades
When PFK-2 is phosphorylated, it acts as a
phosphatase
When PFK-2 is dephosphorylated, it acts as a
kinase