FMLec | M5: Food Preservation, Food Safety, & Food Plant Sanitation
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Give 6 aspects of food preservation, food safety, & food plant sanitation
Traditional food preservation (methods)
Novel techniques in food preservation
GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices)
HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point)
Food defense
Risk assessment
Enumerate 6 traditional food preservation methods
chembio moralodry
Chemicals
Chemical preservatives
Biocontrol
LAB
Bacteriocins
Phages
Modified atmosphere
Hypobaric storage
Vacuum packaging
Radiation
EMR
UV rad
Ionizing rad
Radiation treatments
Raddapertization
Radicidization
Radurization
Low & high-temperature
Drying
_ is a traditional food preservation method that involves the use of compounds that can prevent or delay food spoilage, e.g., generally recognized as safe (GRAS) food additives
Chemical preservatives
Enumerate 9 common chemical preservatives / GRAS (as traditional food preservation method)
psb psn nsi
Propionic acid (propionates)
Sorbic acid (sorbates)
Benzoic acid (benzoates)
Parabens
Sulfur dioxide
Nitrates & nitrites
NaCl
Sugar
Indirect antimicrobials
_ is a chemical preservative highly specific against molds (fungistatic)
Contains acids or calcium & sodium (Ca, Na) salts (0.32% max)
e.g., bread (“rope inhibitor”), cakes, cheese (Swiss), low-acid food
Results in weakened transmembrane gradient due to lower intracellular pH from proton leakage, consequently inhibiting AA transport
Propionic acid (propionates)
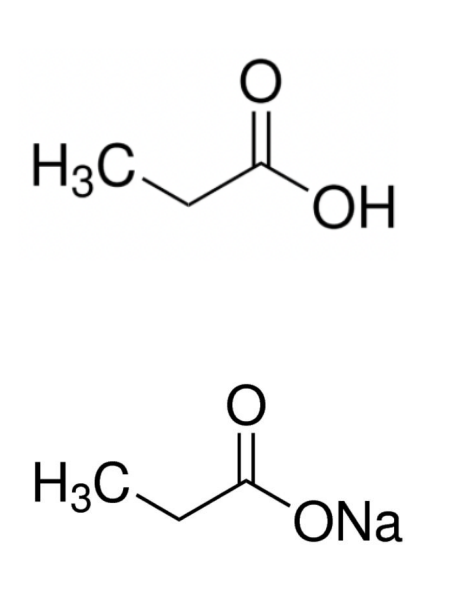
Explain preservation mechanism of propionic acid / propionates
Results in weakened transmembrane gradient due to lower intracellular pH from proton leakage, inhibiting AA transport
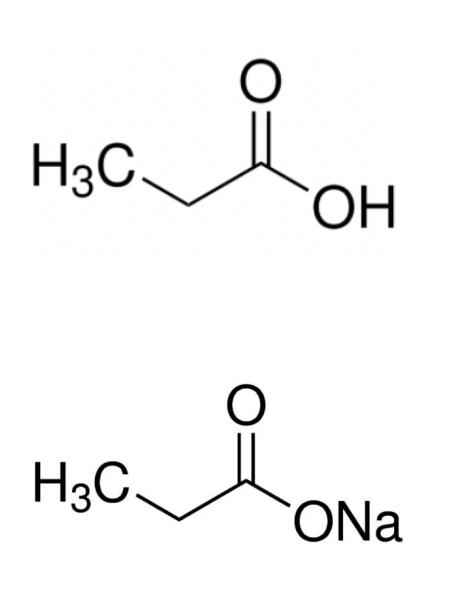
Propionates usually contain acids or calcium & sodium (Ca, Na) salts at _% max concentration
0.32%
_ is a chemical preservative considered to be primary fungal inhibitors and inhibitors of bacteria, including S. aureus, Salmonella, coliforms
Contain 0.2% max conc of calcium, sodium, potassium (CaNaK) salts
Preserves hard cheese, syrups, salad dressings, jellies, cakes hssjc
More effective in acidic foods > neutral foods
Weakened transmembrane gradient due to lower intracellular pH from proton leakage, inhibiting AA transport
Sorbic acid (sorbate)
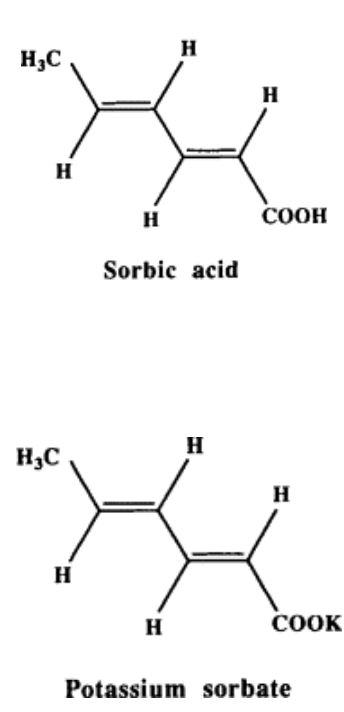
_ is a chemical preservative known to be primary fungal inhibitors and inhibits bacteria, including _
Sorbic acid (sorbate)
S. aureus, Salmonella, coliforms
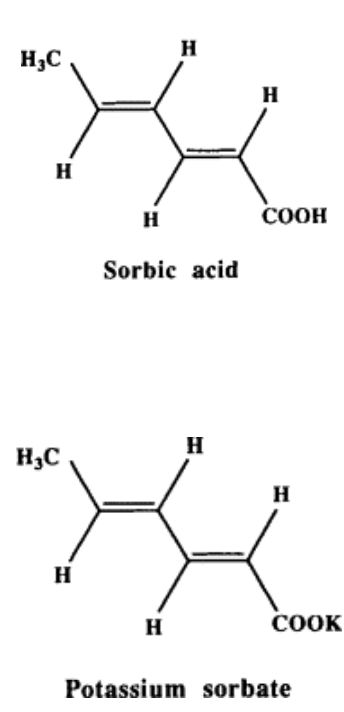
Chemical preservative that preserves ff. food
Bread (“rope inhibitor")
Cake
Cheese (Swiss)
Low-acid food
Propionic acid (propionate)
Sorbic acid (sorbates) contain _ salts
0.2 % max concentration of Ca, Na, K salts
_ is a chemical preservative highly specific against molds (fungistatic) and contains acids or calcium & sodium salts (0.32% max)
Propionic acid (propionates)
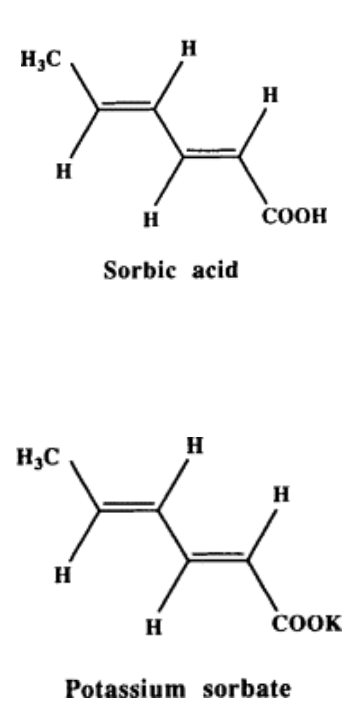
Chemical preservative that preserves ff. food
Hard cheese
Syrups
Salad dressings
Jellies
Cakes
Sorbic acid (sorbates)
T/F: Sorbates has the same preservation mechanisms as propionates and benzoates
TRUE
Weakened transmembrane gradient from lower intracellular pH due to proton leakage, inhibiting AA transport
T/F: Sorbates are more effective in preserving neutral foods than acidic foods
FALSE
Sorbates are more effective in preserving acidic foods > neutral foods
T/F: Benzoates inhibit both bacteria and fungi at 30 ppm
FALSE
Fungi = 30 - 500 ppm
Bacteria = 50 - 500 ppm
_ is a chemical preservative that acts as fungal inhibitor at 30 ppm but can inhibit bacteria at 50 - 500 ppm
Most active at lowest pH values of foods (0.1% max)
Essentially ineffective at neutral values
e.g., margarine, apple cider, soft drinks, tomato catsup, salad dressings masts
Weakened transmembrane gradient due to lower intracellular pH from proton leakage, inhibiting AA transport
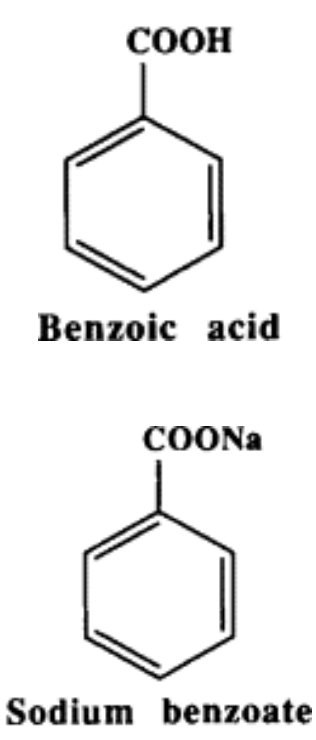
Benzoic acid (benzoates)
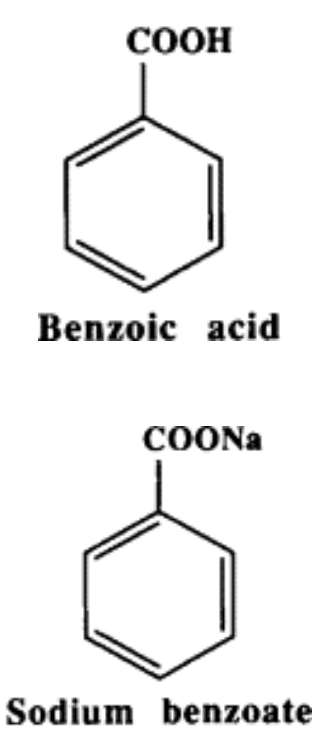
T/F: Benzoates are more effective at preserving foods with neutral pH values than acidic ones
FALSE
Benzoates are most active at lowest pH of foods (0.1% max), while essentially ineffective at neutral values
Chemical preservative that preserves ff. food
Apple cider
Soft drinks
Margarine
Tomato catsup
Salad dressings
Benzoic acid (benzoates)
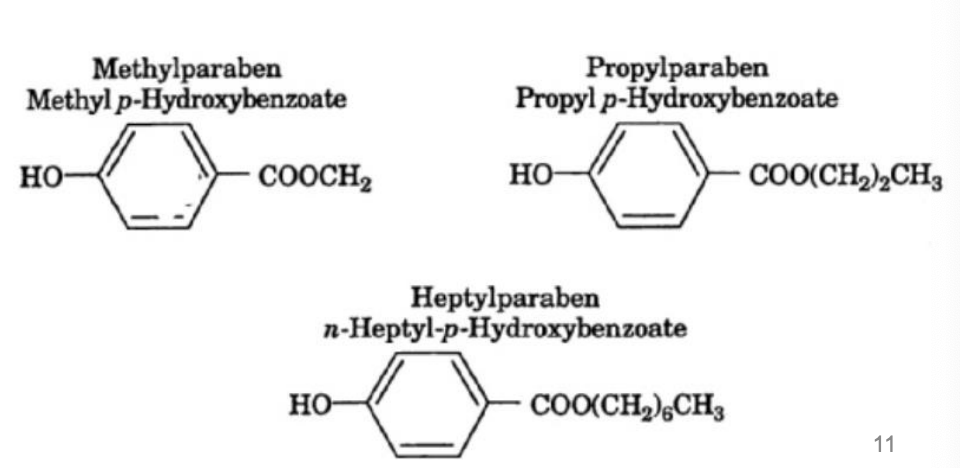
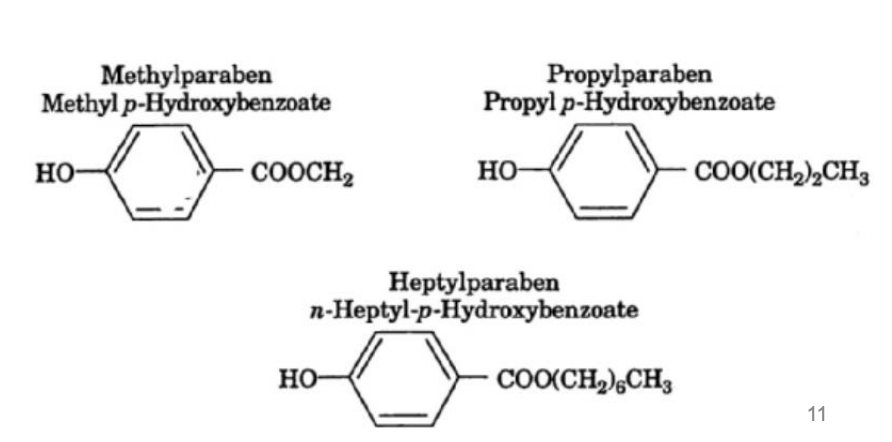
_ is a chemical preservative that serves as a bacteria & fungal inhibitor at 0.1% max
Less sensitive to pH than benzoates
e.g., bakery products, soft drinks, pickles, salad dressings bsps
Parabens
T/F: Benzoates are less sensitive to pH than parabens
FALSE
Parabens are less sensitive to pH than benzoates
Chemical preservative that preserves ff. food
Bakery products
Soft drinks
Pickles
Salad dressings
Parabens
Bacteriostatic vs. Bactericidal vs. Bacteriolytic
Bacteriostatic = inhibits but does not kill them
Bactericidal = kills without lysing them
Bacteriolytic = kills by lysing them

_ is a chemical preservative that is bacteriostatic against Acetobacter & LAB at low pH
Yeasts & molds
Bactericidal at higher concentrations
e.g., dried fruits, lemon juice, molasses, wines, fruit juices dlmwf
MOA
Strong reducing power (reducing oxygen tension)
Enzyme inhibition
Sulfur dioxide (SO2)
Chemical preservative that preserves ff. food
Dried fruits
Lemon juice
Molasses
Wines
Fruit juices
Sulfur dioxide
T/F: Sulfur dioxide is bactericidal against Acetobacter & LAB at high pH
FALSE
Sulfur dioxide is bacteriostatic against Acetobacter & LAB at low pH
T/F: Sulfur dioxide can be bacteriolytic at higher concentrations
FALSE
Sulfur dioxide can be bactericidal at higher concentrations
Sulfur dioxide’s potential mode of action include _
Strong reducing power (reduction of oxygen tension)
Enzyme inhibition
_ is a chemical preservative used in curing meats
Inhibits some spoilage and food poisoning organisms
Stabilizes red meat color and contributes to flavor development
Have anti-botulinal & anti-clostridial effects
Nitrites & nitrates
_ is a chemical preservative with anti-clostridial & anti-botulinal effects; can inhibit some spoilage & food poisoning organisms
Nitrites & nitrates
_ is a chemical preservative with high salt concentrations and thus causes drying effect in both food & microorganisms
Preservation of fish & other meat products without refrigeration
Most nonmarine bacteria are inhibited by 20% or less conc
Some molds generally tolerate higher levels of this (bc they can tolerate lower Aw)
NaCl
T/F: Some molds generally tolerate higher levels of NaCl
TRUE
Most nonmarine bacteria can be inhibited by _ NaCl
≤ 20%
Chemical preservative that preserves ff. food
Fish, other meat products without refrigeration
NaCl
Chemical preservative that preserves ff. food
Cured meats
Red meats
Nitrites & nitrates
_ is a chemical preservative with the same MOA as NaCl
Bacteria is more susceptible to this than fungi
e.g., fruit preserves, candies, condensed milk fcc
Sugar
T/F: Higher concentrations of sugar is needed to preserve food than salts
TRUE
While sugar has the same MOA as NaCl (i.e., reducing Aw), it is less potent and thus higher concentrations would be needed for it to have the same effect
_ is a chemical preservative used in curing meats; stabilizes red meat color & contributes to flavor development
Nitrites & nitrates
Chemical preservative that preserves ff. food
Fruit preserves
Condensed milk
Candies
Sugar
_ are chemical preservatives considered multifunctional food additives because they have a different primary use but have antimicrobial effects, e.g., vanillin = flavoring, lauric acid = defoaming agent, BHA = antioxidant
Indirect antimicrobials
_ is a traditional food preservation method that refers to the inhibition or control of pathogens using 1 or more living organisms or their products (nonliving), e.g., LAB, bacteriocins, phages
Biocontrol
_ is a biocontrol agent that can perform _ antagonism & microbial interference (nonspecific inhibition / destruction)
Inhibits or kills closely related bacteria via phbpn
Produce antibiotics
H2O2 (ROS)
Bacteriocins
pH depression (low/acidic)
Nutrient depletion
LAB
T/F: While LAB can be used as biocontrol agent producing antibiotics, H2O2, bacteriocins, lower pH, & deplete nutrients, they can still be agents of spoilage
TRUE
LAB can inhibit or kill closely related bacteria via _
phbpn
Production of antibiotics
H2O2
Bacteriocins
pH depression
Nutrient depletion
T/F: LAB can perform antagonism and microbial interference (nonspecific inhibition/destruction)
TRUE
_ is a biocontrol agent that refers to ribosomally synthesized antimicrobial peptides rsap from bacteria that can kill or inhibit bacterial strains closely related (narrow-spectrum) or nonrelated (broad-spectrum) to bacterial producer
Bacteriocins

T/F: Narrow-spectrum antibiotics can only inhibit either Gram (+) or (-), while broad-spectrum can inhibit both and thus will have higher chances of inducing AMR
TRUE
BSA are more likely to induce AMR bc more types of bacteria will experience selection pressure and potentially evolve resistance mechanisms against this
T/F: Only Gram (+) bacteria produce bacteriocins
FALSE
Almost 99% of all bacteria can produce bacteriocins, both Gram (+) and (-)
T/F: Bacteriocins are ribosomally synthesized antimicrobial peptides used as biocontrol to kill or inhibit only closely related strains
FALSE
Bacteriocins are ribosomally synthesized antimicrobial peptides used as biocontrol to kill or inhibit both closely related (narrow-spectrum) or nonrelated (broad-spectrum) strains
_ is a biocontrol agent specific for given bacterial species and strains
Effective in destroying their host cells, e.g., L. monocytogenes, E. coli 0157:H7, Salmonella les
(Lytic) phages
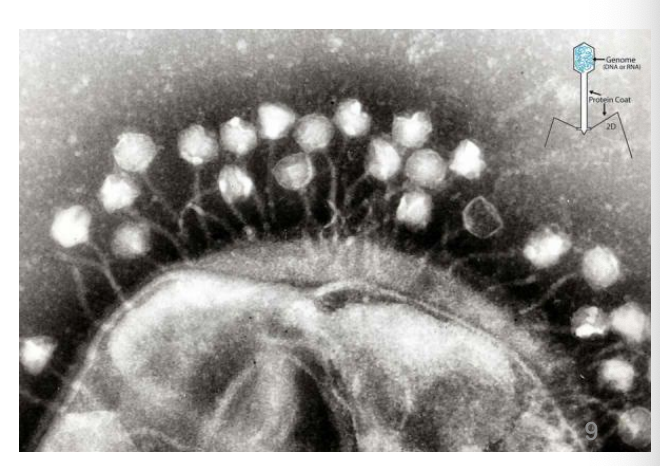
T/F: Phages are host-specific, meaning these are only effective against their host cells
TRUE
T/F: Plants can also be biocontrol agents
TRUE
Some plants release secondary metabolites, e.g., essential oils, that inhibit bacterial or fungal growth
T/F: Lytic phages are more useful in food preservation
TRUE
Bc the goal is to kill bacteria
T/F: Lysogenic phages can effectively destroy their hosts, including L. monocytogenes, E. coli 0517:H7, Salmonella
FALSE
Lytic phages are specific for given bacterial species & strains and can effectively destroy their host cells, including L. monocytogenes, E. coli 0517:H7, Salmonella
_ is a traditional food preservation method that alters gaseous environment on & around foods for purpose of extending their shelf-life; consists of various ways thru which CO2 is used as food preservative, e.g., hypobaric storage, vacuum packaging
Modified atmosphere
_ is a modified atmosphere tradtl food preservation method utilizing low pressure & temperature but high humidity lpt hh to reduce O2 concentrations (lowering Eh and thus aerobe growth)
Hypobaric storage
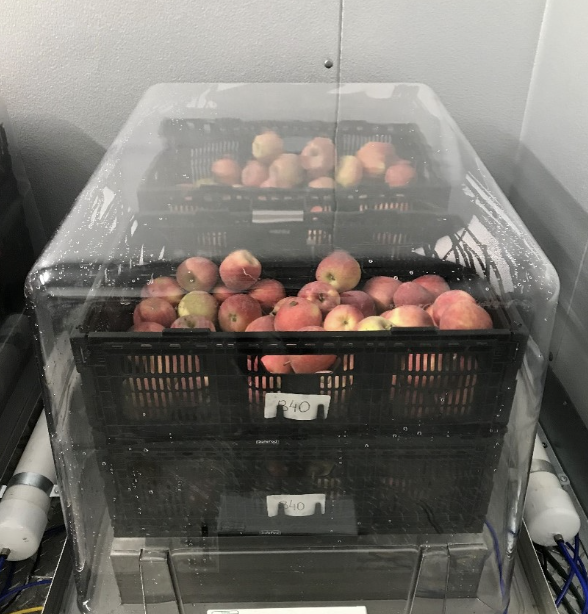

_ is a modified atmosphere tradtl fpm where air is evacuated from a gas-impermeable pouch followed by sealing, thus reducing O2 concentrations
Vacuum packaging

T/F: CO2 can also be used to increase CO2 concentration and reduce O2 concentration in food packaging for food preservation
TRUE
_ is a traditional food preservation method involving electromagnetic radiation (EMR) as the primary interest in food preservation; shorter wavelengths are most damaging to microorganisms
Radiation
T/F: EMR is of primary interest in food preservation, with longer wavelengths most damaging to microorganisms
FALSE
EMR is of primary interest in food preservation, with shorter wavelengths most damaging to microorganisms
The 2 most commonly used EMR for traditional food preservation are _
Ultraviolet (UV) light = nonionizing bactericidal agent (2600 Å Angstrom)
Ionizing radiation = cold sterilization; beta rays, gamma rays (cheapest), x-rays, microwaves bgxm
_ is an EMR tradtl fpm that refers to nonionizing bactericidal agent at 2600 A, causes lethal mutations and is mainly for surface applications (e.g., baked fruitcakes)
UV light
T/F: There should be a direct UV light exposure to kill microbes in food
TRUE
Remove cover of petri dish to directly expose E. coli colonies to UV and kill them
_ is an EMR tradtl fpm that contains enough energy to ionize molecules in their path; works via cold sterilization, e.g., beta rays, gamma rays (cheapest), x-rays, microwaves
Ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation, e.g., beta, gamma, x-ray, microwaves, is used as a traditional food preservation method via _, where food is sterilized (and endospores are eliminated at some point) without using heat
cold sterilization
T/F: Ionizing radiation contains enough energy to ionize molecules in their path and works via hot sterilization, including beta rays, gamma rays (cheapest), x-rays, microwaves
FALSE
Ionizing radiation contains enough energy to ionize molecules in their path and works via cold sterilization, including beta rays, gamma rays (cheapest), x-rays, microwaves
Enumerate & describe 3 radiation treatments of foods
Radappertization = equivalent to radiation sterilization or “commercial sterility”
Radicidation = reduction of viable specific non-spore forming vsnp pathogens to an undetectable level
Radurization = substantial reduction of viable specific spoilagen microbes vssm
T/F: Radicidation entails completely eliminating all viable, specific non-spore forming pathogens in food products
FALSE
Not necessarily. There could still be vsnp but are just kept at undetectable levels
T/F: The main difference between radurization and radicidation is that the former reduces viable specific spoilage microbes, while radicidation reduces viable, specific non-endospore forming pathogens to an undetectable level
TRUE
_ is a radiation treatment equivalent to radiation sterilization or “commercial sterility”
Radappertization
T/F: Radicidation refers to radiation treatment that reduces viable, specific endospore-forming pathogens to undetectable level
FALSE
Radicidation refers to radiation treatment that reduces viable, specific non-endospore-forming pathogens to undetectable level
Enumerate 3 factors affecting success of irradiation
Type, number, & age of organisms
Food composition & physical state
Oxygen
Bacteriocin vs. Antibiotics
Bacteriocin = primary metabolite; ribosomally synthesized antimicrobial peptide; produced during log phase
Antibiotic = secondary metabolite produced during stationary phase
T/F: Both microorganisms and food will have implications on use of irradiation as food preservation method
TRUE
Factors affecting success of irradiation: tfo
In terms of types, numbers, & age of organism (as factor affecting irradiation success), which of the ff. would be more resistant to effects of UV? gsm fhl
Gram (-) or Gram (+)?
Spore-former non-spore former?
Molds or yeasts?
Fungi or bacteria?
High or low density?
Lag or log?
Gram (+) = thicker peptidoglycan layer in cw
Spore-formers = thick, multilayered coats; DNA-protective proteins; low water content
Molds = produce spores highly resistant to environment stresses
Fungi = tougher cell walls made of chitin
High density = more would survive
Lag phase = bc it’s not actively dividing as opposed to log phase, where DNA is actively replicated and thus prone to DNA-damaging effects of UV
_ is a radiation treatment that reduces viable specific spoilage microbes
Radurization
T/F: Actively dividing microbial cells are more protected and resistant to UV than those not actively dividing
FALSE
Actively dividing ones will have DNA damaged from dimerization effects of UV light
In terms of food composition & physical state (as factor affecting irradiation success), which of the ff. would be more resistant to effects of UV? pdf
Protein-containing or non-protein-containing?
Dried or moist cells?
Frozen or nonfrozen cells?
Protein-containing = proteins have protective effects
Dried = moist cells have water on surface that absorbs UV and is thus more affected; water generates free radicals
Frozen = crystals have protective effect; enzymes are inactive
In terms of oxygen (as factor affecting irradiation success), which of the ff. would be more resistant to effects of UV? the pdf
Anaerobic or aerobic?
Anaerobic = their metabolic processes do not rely on O2 and thus less likely to undergo oxidative damage from UV exposure; also have physiological mechanisms to protect themselves from UV light
_ is traditional food preservation method relying on principle that rate of enzyme-catalyzed metabolic rxns are temperature-dependent; at above freezing temperature, microbial activities slow down; at subfreezing temperatures, these stop
Low-temperature fpm
Enumerate & explain temperature ranges of low-temp stored foods
Chilling temp
Between ref temp (5-7C) and ambient temp (10-15C)
e.g., Certain fruits & vegetables
Refrigerator temp
0-7C, but ideally not higher than 4.4C
e.g., Milk
Freezer temp
At or below -18 C
Free water freezes and forms ice crystal
e.g., Meat
_ is a radiation treatment that reduces viable, specific non-endospore forming pathogens to an undetectable level
Radicidation
Enumerate 2 basic ways of freezing (as low-temp tradtl fpm), differentiate
Quick/fast freezing
Reaches -20C within 30 mins
Via
Direct immersion or indirect contact of foods with refrigerant
Using air blasts of frigid air blown across foods being frozen
Favors small intracellular crystal formation, allowing the killing of more cells
Slow freezing
e.g., home freezer
Reaches desired temp within 3-72h
Favors large extracellular crystal formation
_ is a basic method of freezing that leads to formation of small intracellular crystals, killing more cells; reaches -20C within 30 mins; direct immersion or indirect contact; using air blasts of frigid air blow across food
Quick / fast freezing
Enumerate 6 effects of freezing on microorganisms
dvc pdm
Dehydration
Increase in viscosity of cellular matter
General alteration of colloidal state of cellular protoplasm
Concentration of cellular electrolytes
Loss of cytoplasmic gases (e.g., O2)
Changes in pH of cellular matter
Denaturation of cellular proteins
Metabolic injury to some microbial cells
_ is a freezing method that kills bacteria via cell membrane disruption, dehydration, and oxidative damage cdo, but also affects the texture, flavor, and other nutritional qualities of frozen product
Repeated freeze-thaw cycle
Repeated freeze-thaw cycle kills bacteria through _ but also affects texture, flavor, and other nutritional qualities of frozen product
cdo
Cell membrane disruption
Dehydration
Oxidative damage
Psychrophiles vs. Psychrotrophs
Psychrophiles
Cold-loving, thus have to be in an environment thats constantly cold
Can be killed by warming to moderate temp
Psychrotrophs / psychrotolerants
Can grow at 0C but have an optima of 20 - 40C
Cause spoilage of meat, vegetables, poultry mvp
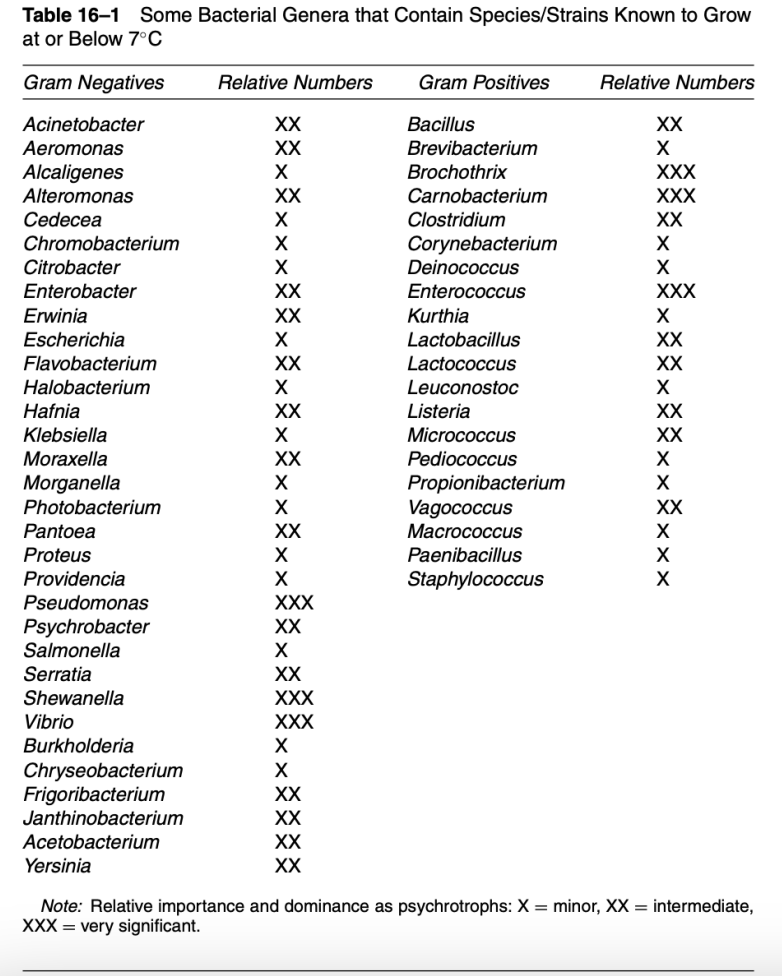
T/F: Generally, there are more psychrotrophs than psychrotolerants
FALSE
Psychrotrophs / Psychrotolerants > Psychrophiles
Gram(-) = Pseudomonas, Shewanella, Vibrio
Gram (+) = Brochotrix, Enterococcus
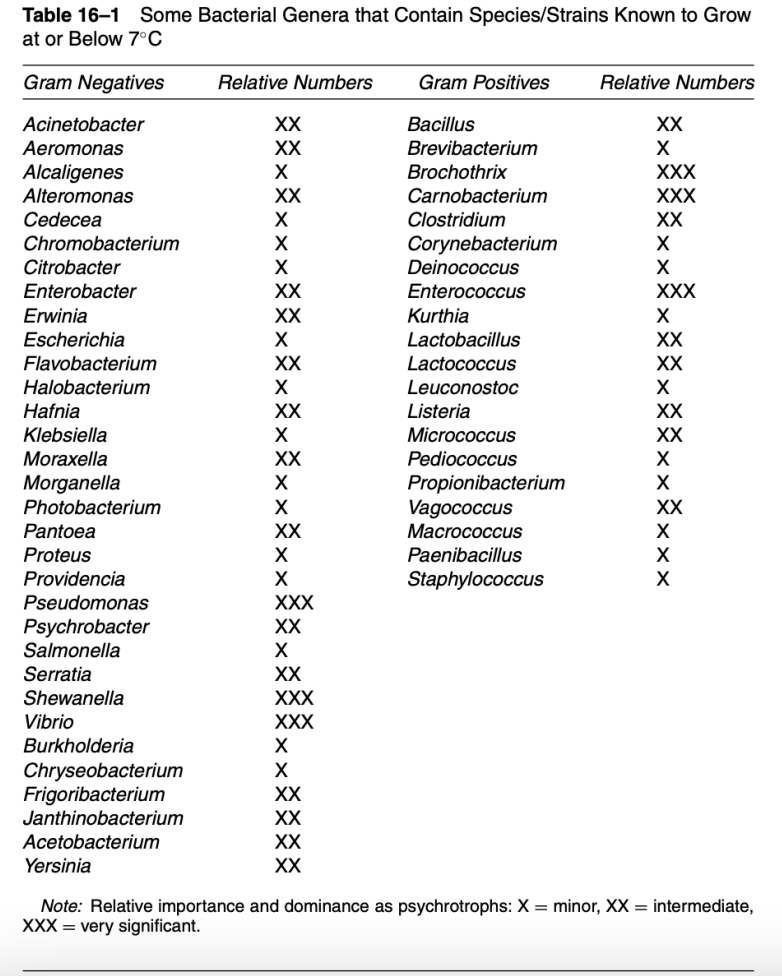
_ is basic method of freezing that forms large extracellular ice crystals; reaches desired temp within 3-72 hrs; e.g., home freezer
Slow freezing