Biomolecules 2 (CBol)
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Describe the key structural features of monosaccharides?
Monosaccharides are simple sugar units. They have the empirical formula (CH2O)n where n=3-7 carbons. They are poly-hydroxy aldehydes or ketones.
what are three examples of structural feature of monasaccharides?
3c triose, 5c pentose, 6c hexose
Define a glycosidic bond?
It is a covalent bond that forms between the anomeric carbon of one sugar molecule and a hydroxyl group -oh of another molecule. often another sugar. the bond is created through a condensation reaction. so water is released.
How is a glycosidic bond named? alpha or beta?
It is named alpha if the hydroxyl -oh group is in the alpha configuration, under the sea
what is an example of a beta glycosidic bond? and how would you name it?
Lactose. made up of a glucose and beta-galactose. beta(1-4)
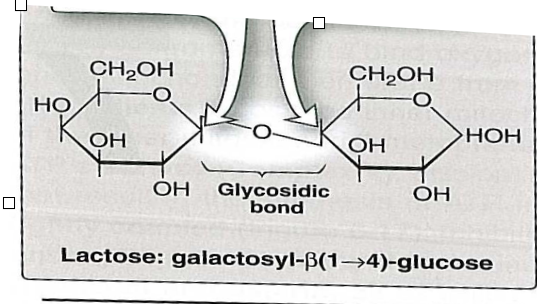
Can glycosidic bonds be only formed between two sugars? give examples.
no. purine and pyrimidine bases in nucleic acids, aromatic rings eg steroids, proteins glycoproteins and lipids glycolipids
what is an example of an alpha glycosidic bond? and how would you name it?
maltose. made up of glucose and glucose alpha(1-4)
what is the definition of a disaccharide?
It is a carbohydrate made up of two monosaccharide units.
give three examples of a disaccharide?
lactose, sucrose and maltose
Describe the structure of a polysaccharide? include carbon units
Polysaccharides are long chains of monosaccharide units linked by glycosidic bonds. n is 12 to hundreds. The links can be linear like cellulose or branched like amylopectin.
describe the function of the polysaccharides in animals.
storage in animals, eg glycogen. a homopolymer of glucose. branched every 12-14 residues (alpha 1-4, alpha 1-6)
describe the function of the polysaccharides in storage for plants
storage in plants eg starch. a homopolymer of glucose composed of amyloceptin branched every 24-30 residues (alpha 1-4, alpha 1-6) and amylose which is non branched helical structure (alpha1-4)
describe the function of the polysaccharides in structure in plants.
Cellulose for structure in plants. a homopolymer of glucose. long straight chains (beta 1-4)
what is the function of lipids? give three examples
To store energy in the body. structural components of cells and organelles. Involved in cellular signalling events eg steroids, postglandins and leukotrienes
Give four classifications of lipids.
fatty acids and their derivatives, lipids containing glycerol eg triglyceride and phospholipids. lipids not containing glycerol eg steroids and lipoproteins and lipopolysaccharides
Describe the structure of a saturated fatty acid
no double bonds, straight chains and packed tightly
describe the structure of an unsaturated fatty acid
one or more double bonds, kinked chains chains and not packed tightly
what is a polyunsaturated fat PUFA
A polyunsaturated fat is a type of fatty acid that contains more than one double bond in its hydrocarbon chain.
Describe the structure of phospholipids
They have a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
Describe the structure of sphingolipids
it is made up of sphingosine attached to a fatty acid via an amide bond to form a ceramide and they are attached to a polar head group