AP Psych Unit 3 Vocab
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
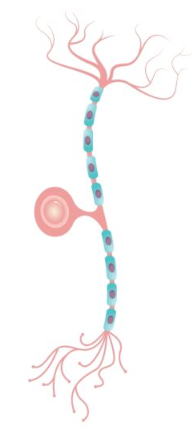
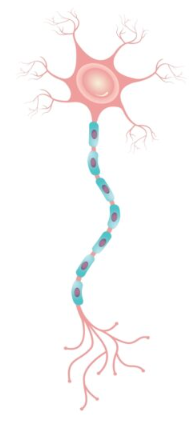
neuron
a nerve cell, the basic building blocks of the nervous system
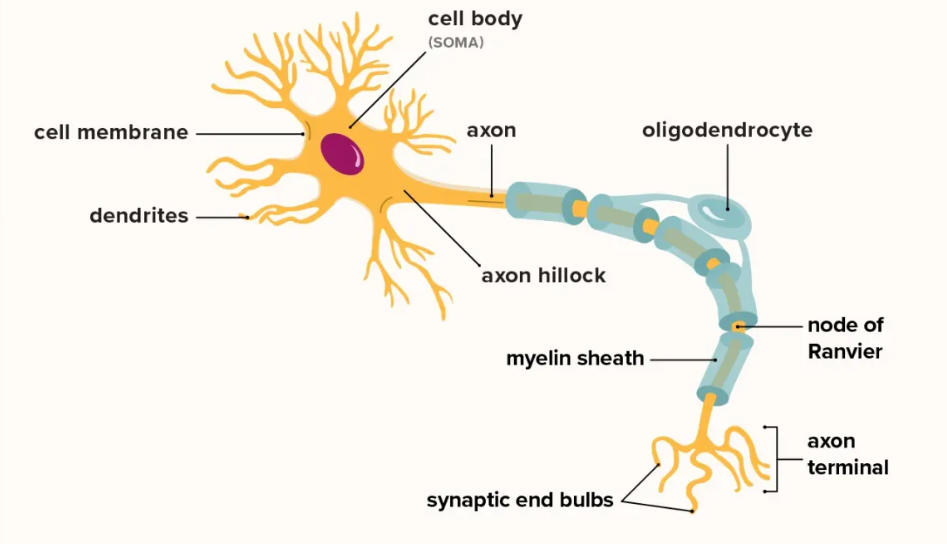
cell body
control center of neuron
integrates inputs from all dendrites
determines whether neuron should fire or not
dendrites
a neuron’s often bushy, branching extensions that receive and integrate messages, conducting impulses toward the cell body
input fibers that carry electrical signals into a neuron from connected cell
axon
the neuron extension that passes messages through its branches to other neurons or to muscles or glands
output fiber carries electrical signal from a neuron to a neighboring cell.
neurons have one each
larger than dendrites
divide into branches at end called terminals

myelin sheath
a layer of fatty tissue that encases the axons of some neurons
enables greater transmission speed of neural impulses as impulses jump from node to node
composed of glial cells (glove), support, nourish, protect neurons
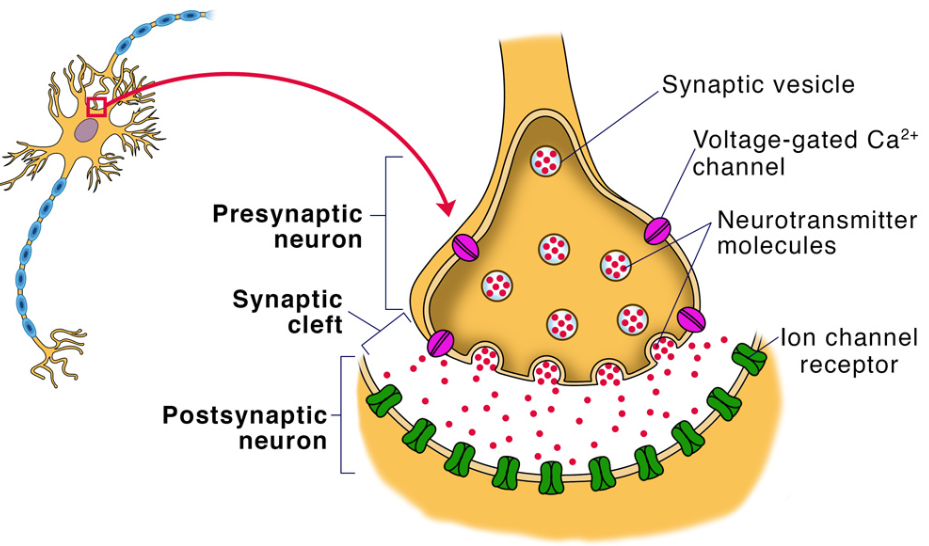
synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron.
The tiny gap at this junction is called the _____tic gap or _____tic cleft.
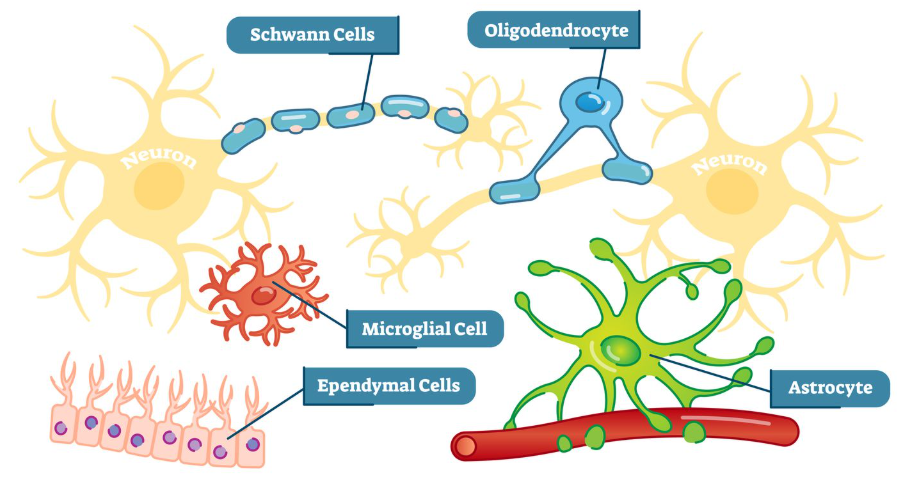
glial cells (glia)
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons
also plays a role in learning, thinking, and memory
afferent neurons
(sensory neurons)
communicate sense information from body to brain
efferent neurons
(motor neurons)
communicates instructions from brain to body (muscles)
interneurons
communicate messages between motor and sensory neurons (reflex arc)
once info reaches brain, it takes message and sends it along
mallet test!
action potential
a neural impulse
brief charge that travels down the axon as it becomes depolarized
travels down to terminal where it causes neuro transmitters that bind to specific receptor sites on receiving neurons to fire
refractory period
in neural processing, a brief resting pause that occurs after a neuron has fired’ subsequent action potentials cannot occur until the axon returns to its resting state
return to state of resting slightly negative charge (polarization)
no amount of stimulation can cause the neurons to fire again in this stage.
absolute refractory phase is followed by relative refractory phase in which neuron needs more stimulation to fire again
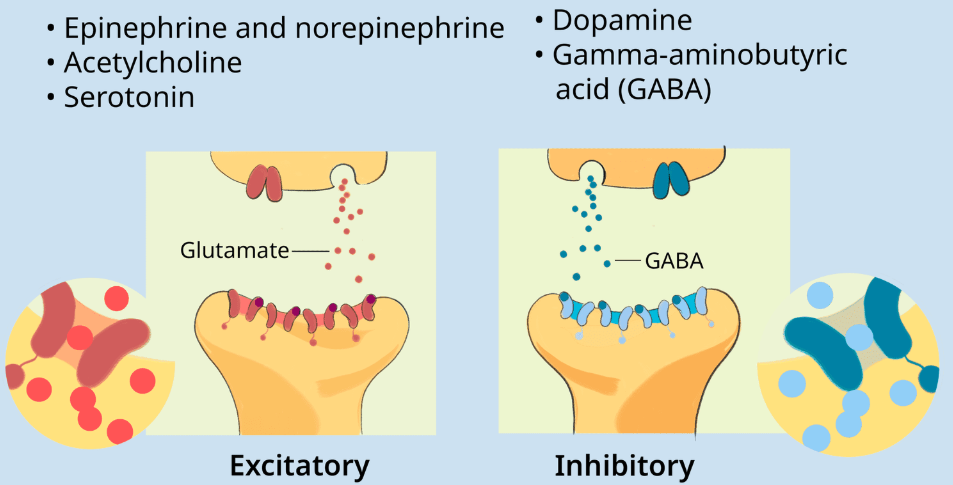
neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that traverse the synapse and bind to receptors sites on the next neuron like keys in a lock, influencing whether that neuron will generate a neural impulse
inhibitory inhibits the nerve cell from firing
excitatory excites the nerve cell into firing
causes neural firing to remain steady or even increase
agonist
a molecule that increases a neurotransmitter’s action or blocks reuptake

antagonist
a molecule that inhibits neurotransmitter activity at the post synaptic terminal by binding to receptor sites
serotonin
affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
undersupply linked to depression. some drugs that raise these levels are used to treat depression
prozac and ecstasy work by boosting its effects
dopamine
influence movement, learning, attention, and emotion
particularly in basal ganglia
undersupply linked to tremors and decreased mobility in Parkinson’s disease
oversupply linked to Tourrete's and schizophrenia
acetylcholine
facilitates muscle movement
also enables muscle action, learning, and memory
Alzheimer's associated with loss of it in neurons that connect with hippocampus
nicotine is an agonist (mimics it), thats why cigarettes boost arousal and concentration
norepinephrine (noradrenalin)
regulates alertness and arousal
too much=mania, too little=depression
puts the body on "red alert" during stressful or exciting situations
coke and amphetamines boost levels
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
a major inhibitory neurotransmitter
undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, and insomnia
glutamate
most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter
plays significant role in learning and memory
oversupply can overstimulate the brain producing migraines or seizures
endorphins
"morphine within"
natural opiate-like neurotransmitter linked to pain control and pleasure
exercise linked to raising levels of this
oversupply with opiate drugs can suppress the body’s natural supply of this
reuptake
a neurotransmitter’s reabsorption by the sending neuron
central nervous system (CNS)
made up of two major components: brain and spine
receives, processes, interprets, and stores incoming sensory info.
sends out messages for muscles, glands, and internal organs.
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
consists of nerves/tissue outside brain and spinal cord
two categories: somatic and autonomic nervous systems.
somatic nervous system
(skeletal)
consists of nerves that are connected to sensory receptors and to skeletal muscles that permit voluntary action
muscles, joints, skin
associated with all body movement
autonomic nervous system
controls autonomic functions of the body
controls fight or flight response
autonomic: sympathetic nervous system
mobilizes body to respond to stress
accelerates some functions (heart, b.p.) but conserves resources (digestion slows)
autonomic: parasympathetic nervous system
responsible for slowing down body after stress response
endocrine system
system of glands that secrete hormones that affect many different biological functions in body
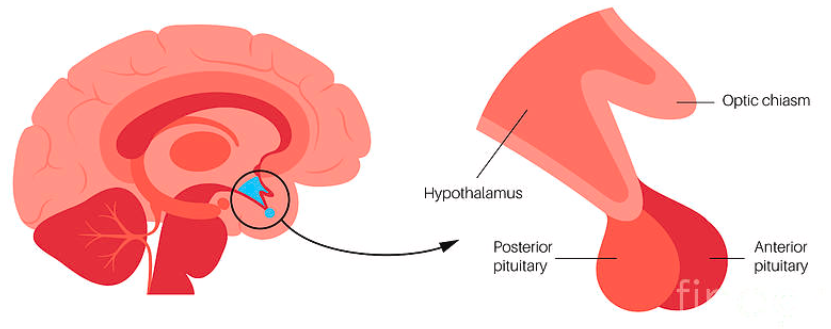
controlled by hypothalamus
pituitary gland, adrenal gland, thyroid gland, pancreas, pineal, ovary/testis.
pituitary gland
the endocrine system’s most influential gland
under the influence of the hypothalamus
regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands
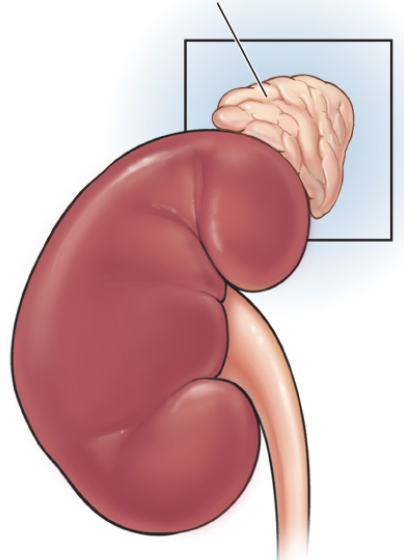
adrenal gland
releases epinephrine and cortisol during the flight or fight response
thyroid gland
releases thyroxine which helps regulate metabolism, heart function, and body temperature
overactive can lead to weight loss
Grave’s Disease
underactive can lead to weight gain
pancreas
releases insulin which helps us use and store glucose for energy
pineal
releases melatonin to induce sleep
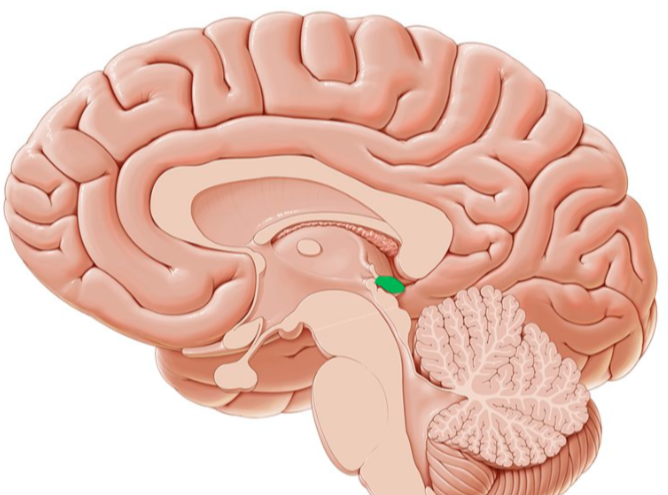
ovary/testis
release estrogen and testosterone respectively, both of which are involved in physical and sexual/reproductive development
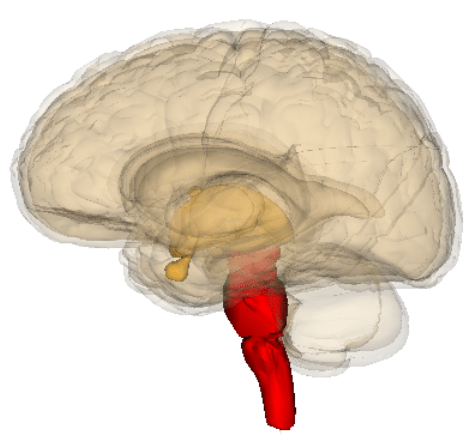
brain stem
the oldest part and central core of the brain
begins where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull
responsible for automatic survival functions
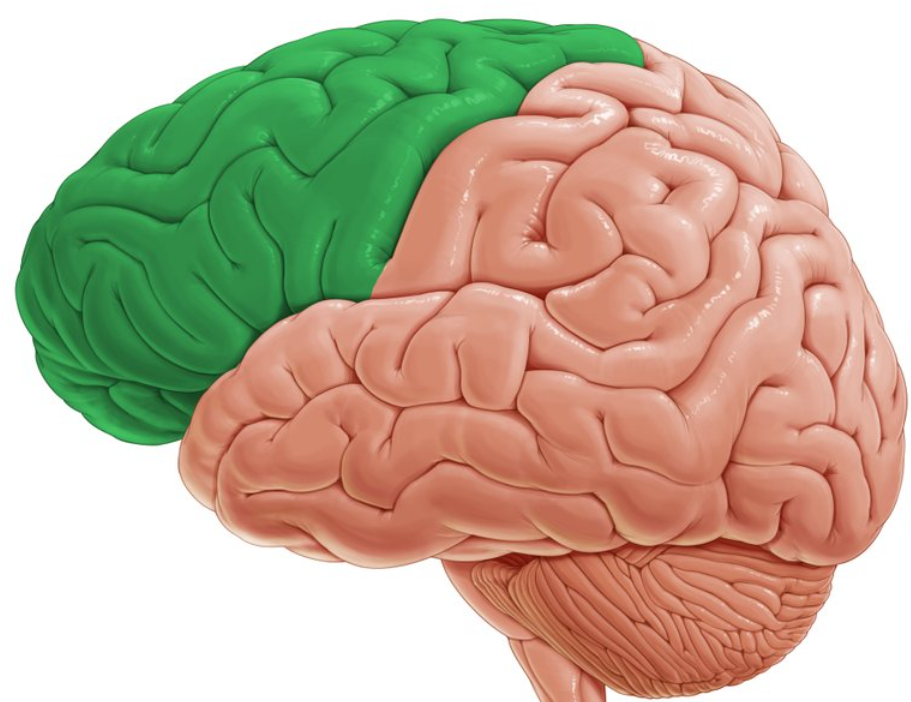
frontal lobes
the most recently evolved part of the brain
responsible for speaking, motor movements, short and long term planning, decision and judgement making
parietal lobes
large area, 1/2 of brain
goal oriented behavior, future planning
believed responsible for abstract thought and emotional control
contains Broca's area: controls muscles involved in speech
thin,vertical strip at back of cortex, motor cortex: sends signals to our muscles; involuntary movement
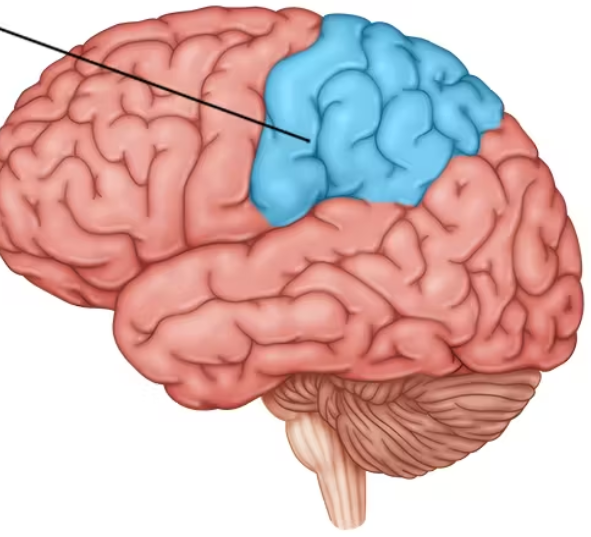
occipital lobes
located at the very back of brain, farthest from eyes
however, one major function is to interpret messages from eyes into visual cortex.
impulses from right half of each retina are processed in the visual cortex of the left side, and vice-versa.
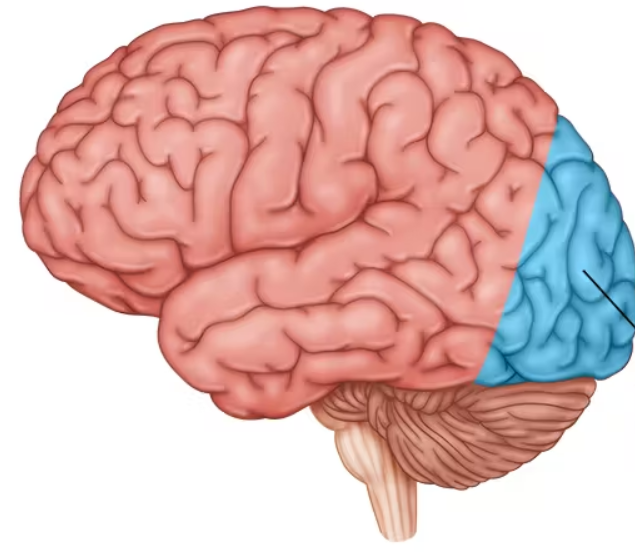
temporal lobes
processes sound sensed by ears
sound waves processed, turned into neural impulses and interpreted in auditory cortex.
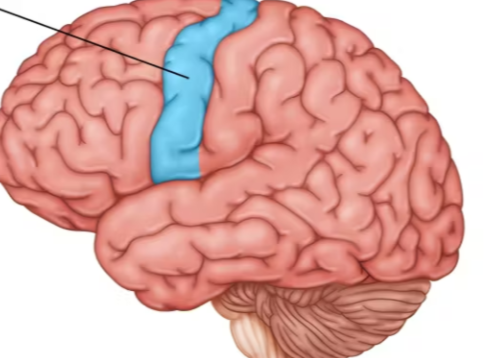
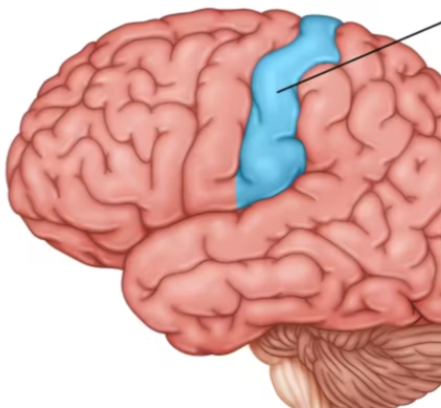
motor cortex
an area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements
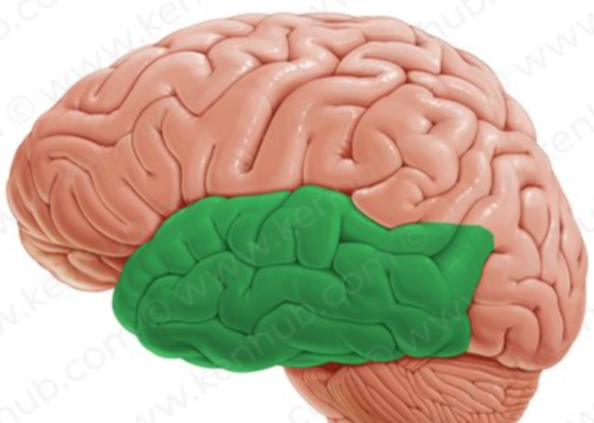
somatosensory cortex
an area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations
medulla
the base of the brainstem
controls heartbeat and breathing
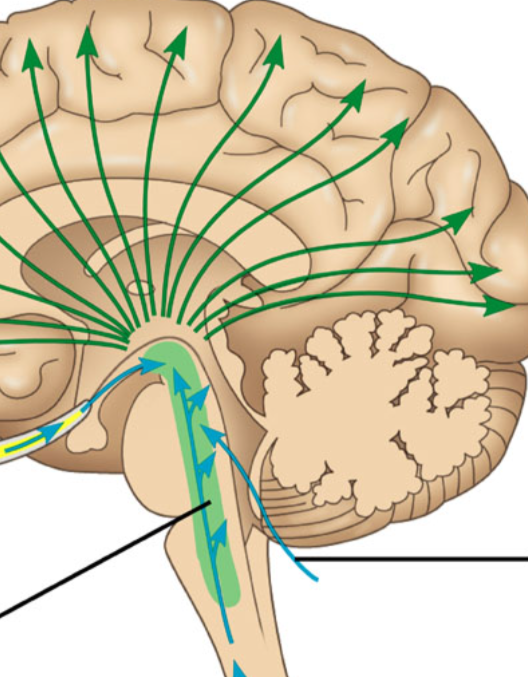
reticular formation
a nerve network that travels through the brainstorm into the thalamus and plays an important role in controlling arousal
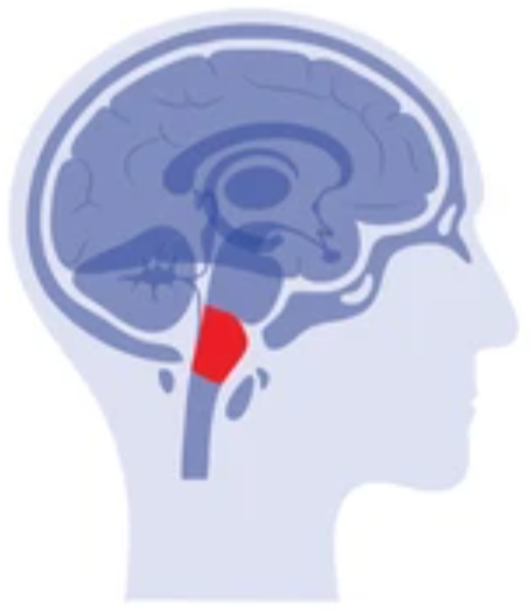
thalamus
the brain’s sensory control center
located on top of the brainstem
directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex
transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
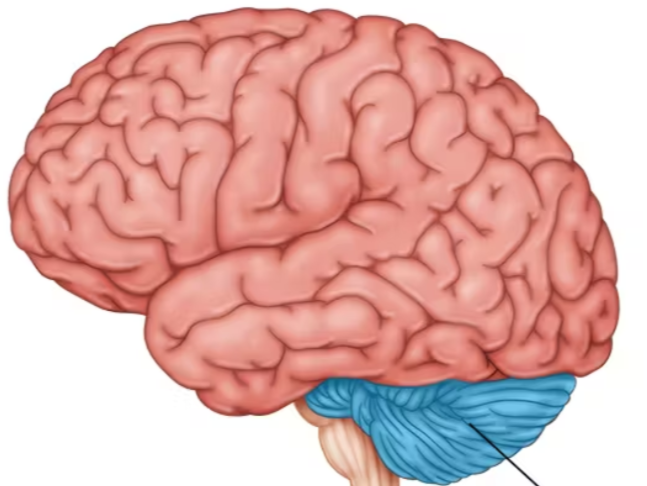
cerebellum
the “little brain” at the rear of the brainstorm
functions include processing sensory input, coordinating movement output and balance, and enabling nonverbal learning and memory
limbic system
neural system located below the cerebral hemispheres
associated with emotions and drives
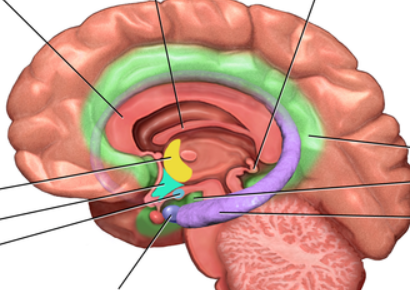
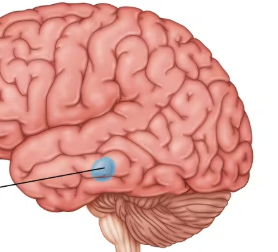
amygdala (limbic system)
two lima-bean-sized neural clusters in the limbic system
linked to emotion
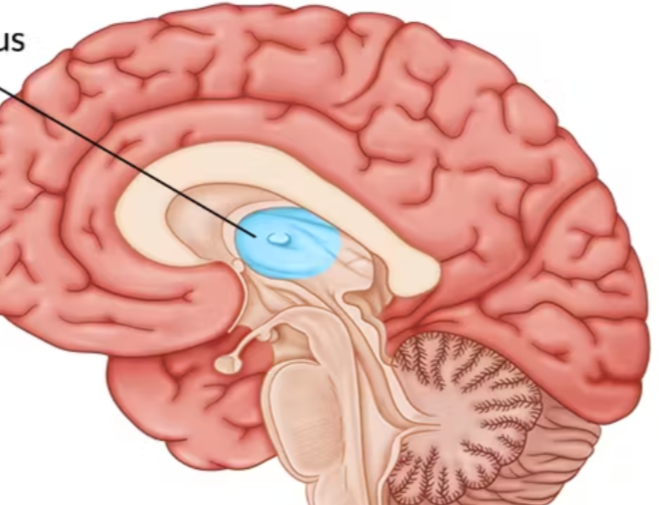
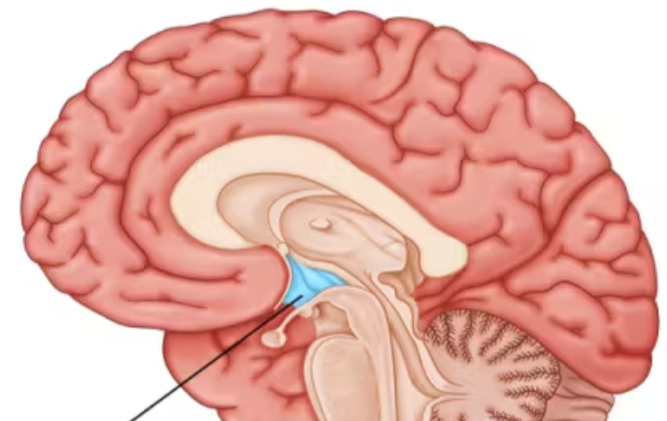
hypothalamus (limbic system)
directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temp)
helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland
linked to emotion and reward
hippocampus (limbic system)
a neural center located in the limbic system
helps process for storage explicit (conscious) memories of facts and events
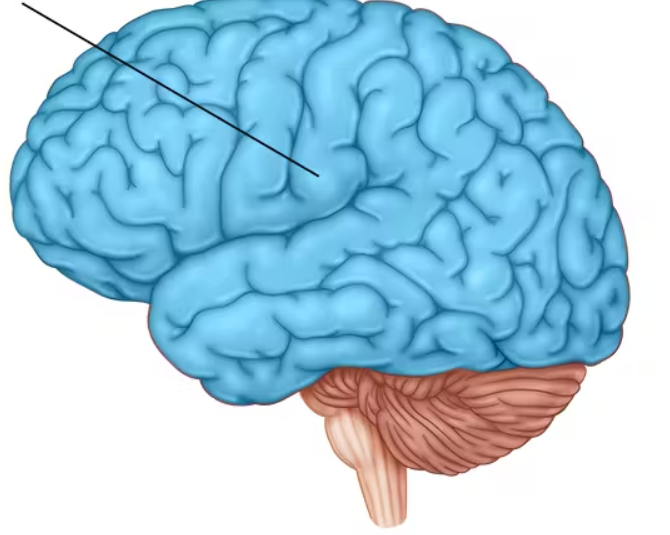
cerebral cortex
the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemisphere
the body’s ultimate control and information-processing center
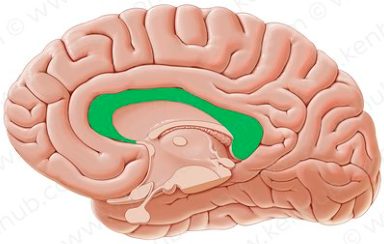
corpus callosum
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
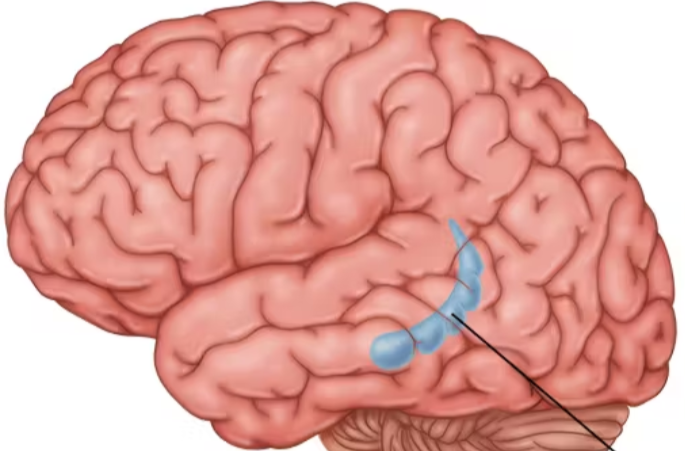
pons
helps coordinate movement and control sleep
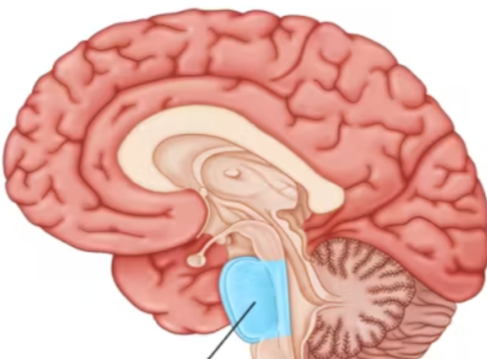
hormones
chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands, travel through the bloodstream, and affect other tissues
lesion
tissue destruction
a brain _____ is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue
EEG (electroencephalogram)
an amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity sweeping across the brain’s surface
these waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp
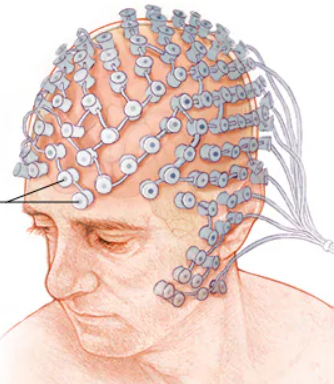
MEG (magnetoencephalography)
brain imaging technique that measures magnetic fields from the brain’s natural electrical activity
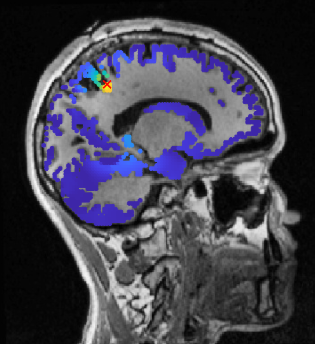
CT (computed tomography) scan, (AKA CAT scan)
a series of X-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by computer into a composite representation of a slice of the brain’s structure
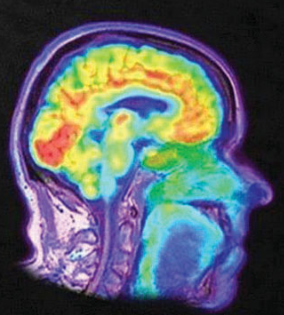
PET (positron emission tomography) scan
a visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task
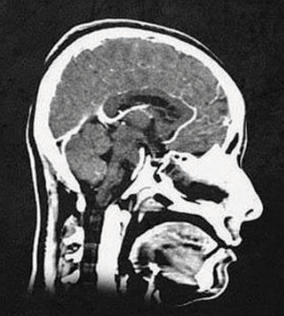
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissue
shows brain anatomy
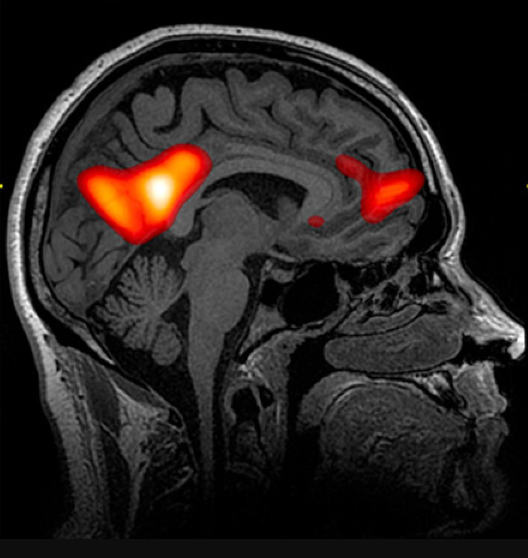
fMRI (functional MRI)
a technique for revealing bloodflow and brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans
shows brain function as well as structure
neural plasticity
brain undergoes billions of neural changes throughout the life span
both in functionality and structure
neurons in the brain adapt similarly to muscles in the body
neurogenesis
the formation of new neurons
parallel processing
processing many aspects of a problem simultaneously
generally used to process well-learned info or to solve easy problems
sequential processing
processing one aspect of a problem at a time
generally used to process new info or to solve difficult problems
monozygotic (identical) twins
develops from a single fertilized egg that splits in two, creating two genetically identical organisms
dizygotic (fraternal) twins
develops from separate fertilized eggs and genetically no closer than ordinary brothers and sisters but share a prenatal environment
epigenetics
“above” or “in addition to” genetics
the study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change