MCB - Proteins, Carbs, Lipids, Nucleic acids
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Glucose linear structure
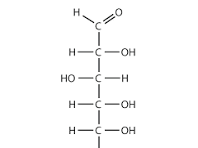
aldoses
Galactose Linear structure
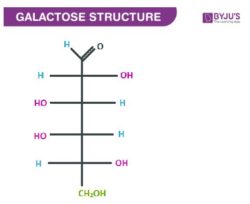
aldose
Fructose linear structure
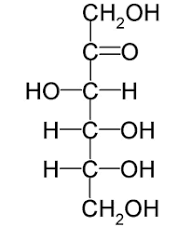
ketone
ring structure of glucose
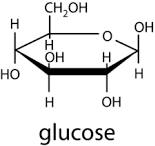
Beta glucose
Dehydration synthesis linkage for maltose
1(OH) - 4(H) glycosidic linkage
Dehydration synthesis linkage for fructose
1-2 glycosidic linkage
Glycerol linear structure
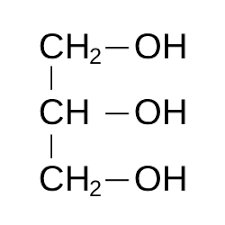
it is an alcohol
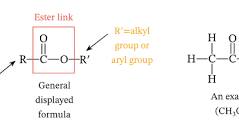
linkage between fatty acid and glycerol
ester linkage
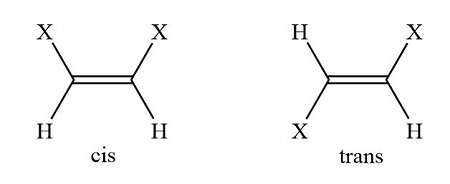
cis vs trans double bond
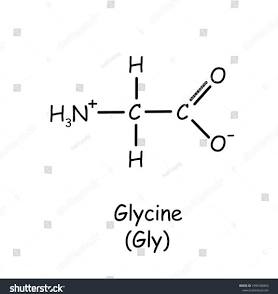
2 non polar amino acids (glycine and Alanine)
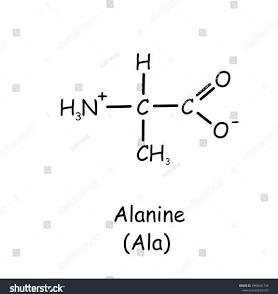
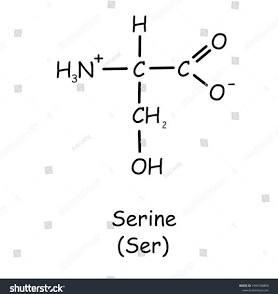
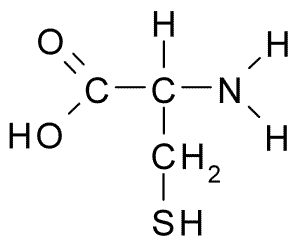
2 polar amino acids (serine and cysteine)
2 electrically charged amino acids (aspartic acid and lysine)
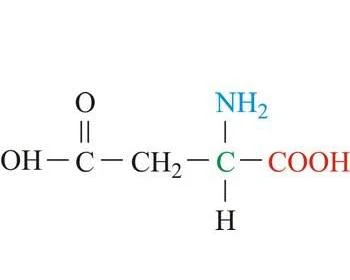
(acidic)
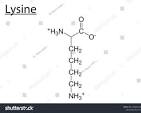
(basic)
what glucose is in cellulose and what is the chain
beta glucose - alternating
Polysaccharide for structure
chitin
cellulose
What is starch made out of
alpha glucose
Storage polysaccharides
glycogen
starch
polymers with alpha glucose are
helical
polymers with beta glucose are
straight
Between cellulose strands what hold them together
hydrogen bonds
Structure of Chitin
on 5 Carbon of glucose there is
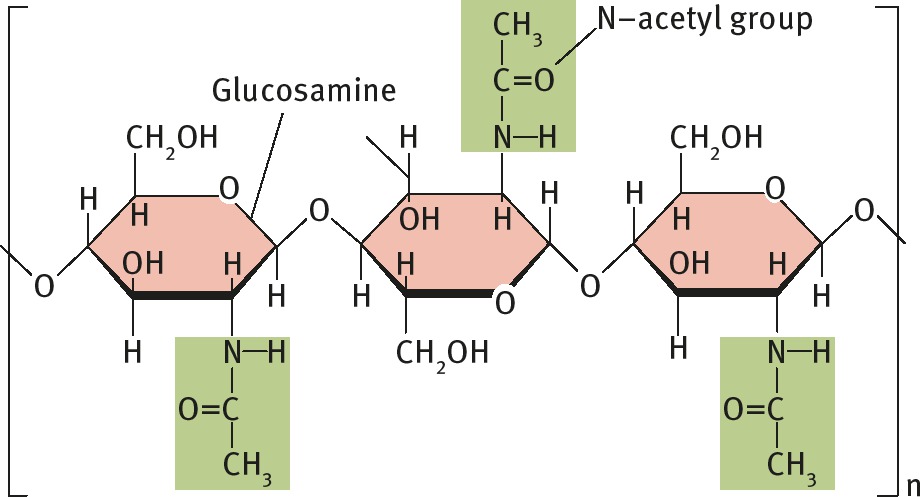
what is a saturated fatty acid
maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible and NO DOUBLE BONDS
solid bonds
stacked/solid at room temp
what are unsaturated fatty acids
have one or more double bonds
liquid at room temp
what fat can your body not break down
trans fats
what does omega-3 mean
3 - where the double bond occurs and where the piece that breaks off will happen
omega-3s are the perfect size because it doesn’t waste energy
function of fats
energy storage
list the 4 parts of a phospholipid
2 fatty acids - glycerol - 3rd carbon on glycerol is flipped up - phosphate group - caped with Choline
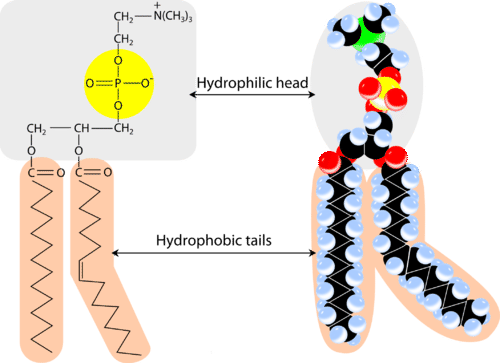
what are sterioids
lipids - carbon skeleton of 4 FUSED RINGS
what is cholesterol
a steroid that is a component in animal cell membranes
what are waxes
long chains - bonded with organic acids
ester group found in the middle
what reaction happens with enzymes
hydrolysis
what do bases and acids do with hydrogen ions
base - pick up H
acid - gives away H
Two types of proteins
globular and fibrous
What is the Quaternary structure
When 2+ polypeptide chains form one macromole
subunits come together
In denaturing (temp, pH changes) what order to bonds break
hydrogen bonds
then secondary structure
then disulfide bridges
what are Chaperonin proteins
They are hollow with a “cap” an d help proteins fold faster and last I'm not perfect conditions
DNA
two strands
helical
deoxyribonucleic acid (take away oxygen)
RNA
single strand
ribonucleic acid (look at sugar on carbon 2)
3 types of RNA
mRNA, rRNA, tRNA
what is a nucelosidee
the portion of a nucleotide without the phosphate group
DNA/RNA pairings
A-T (or U for RNA)
C-G
draw a nucleotide
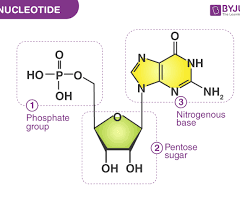
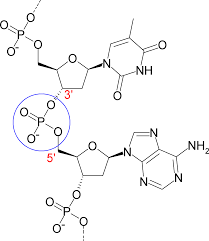
How do nucleotides attatch
5’ to 3’
What is the importance of each carbon on pentose
C1 - attaches to nitrogenous base
C2 - whether it has oxygen (RNA vs DNA)
C3 - attaches next nucleotide
C4 - n/a
C5 - bonds phosphate group
How are the two strands in DNA situated
the 2 strands are antiparallel
What are the Pyrimidines and how many rings do they have
C, T, U have 1 ring
What are the Purines an show many rings do they have
A, G have 2 rings
What is the sugar in DNA and RNA
DNA - deoxyribose
RNA - ribose
for dehydration synthesis, what molecules come off of each part of a nucleotide
and OH group comes off of 3’
an H group comes of of 5’ (from the phosphate group)
What is a Phophodiester bond
How many bods does A-T make an dhow many bodny does G-C make
A-T (or U) = 2 hydrogen bonds
G-C = 3 hydrogen bonds