Topic 1 - System fundamentals - 1.2 System design basics
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Hardware
The physical elements of a computer system

Software
The programs and other operating information used by a computer.

Peripheral
A device that is able to be attached to and used with a computer, though not an integral part of it.
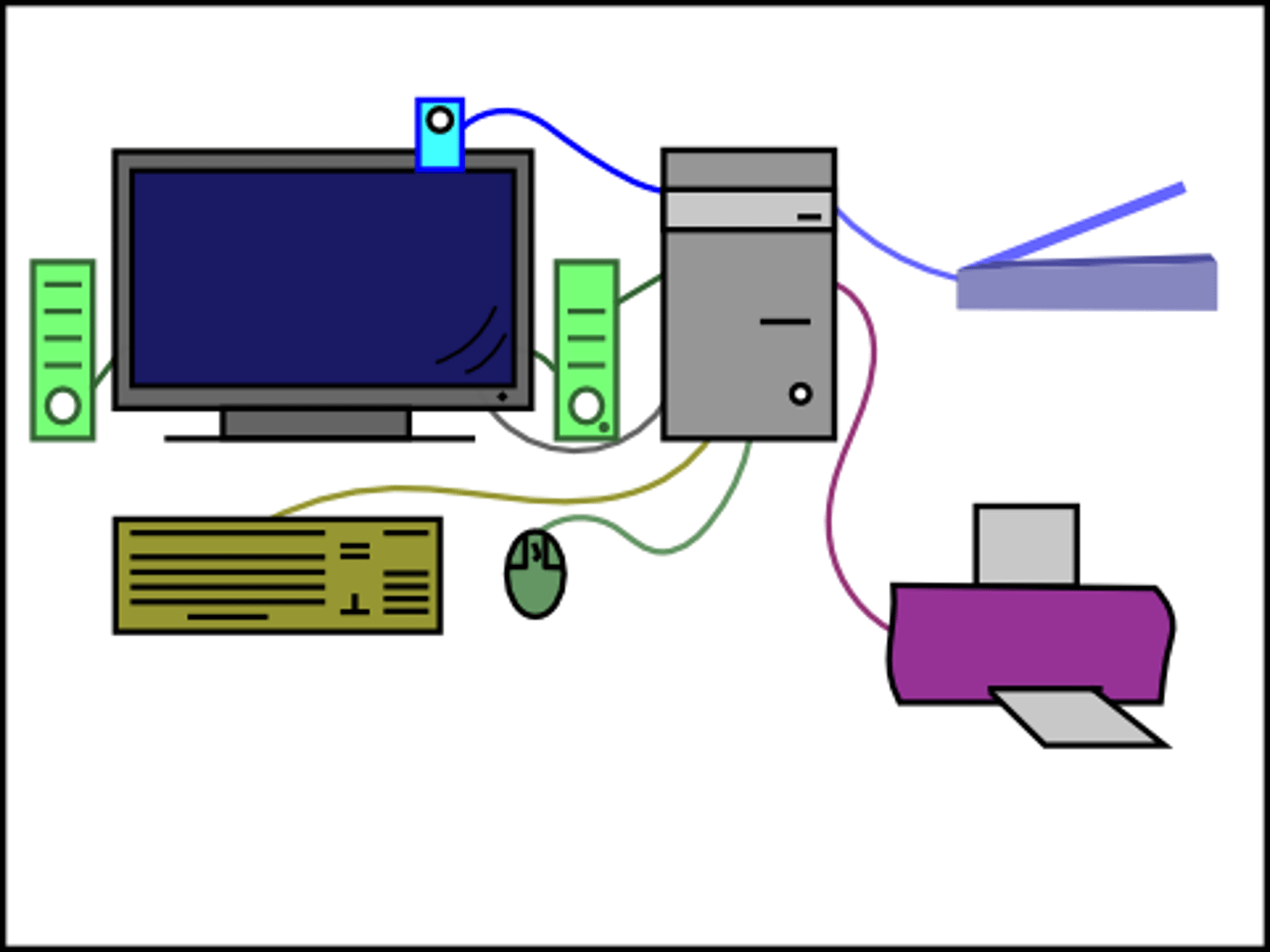
Network
This is a group of two or more computer systems linked together.
Human resources
The personnel of a business or organization.

Client
This is a piece of computer hardware or software that accesses a service made available by a server.
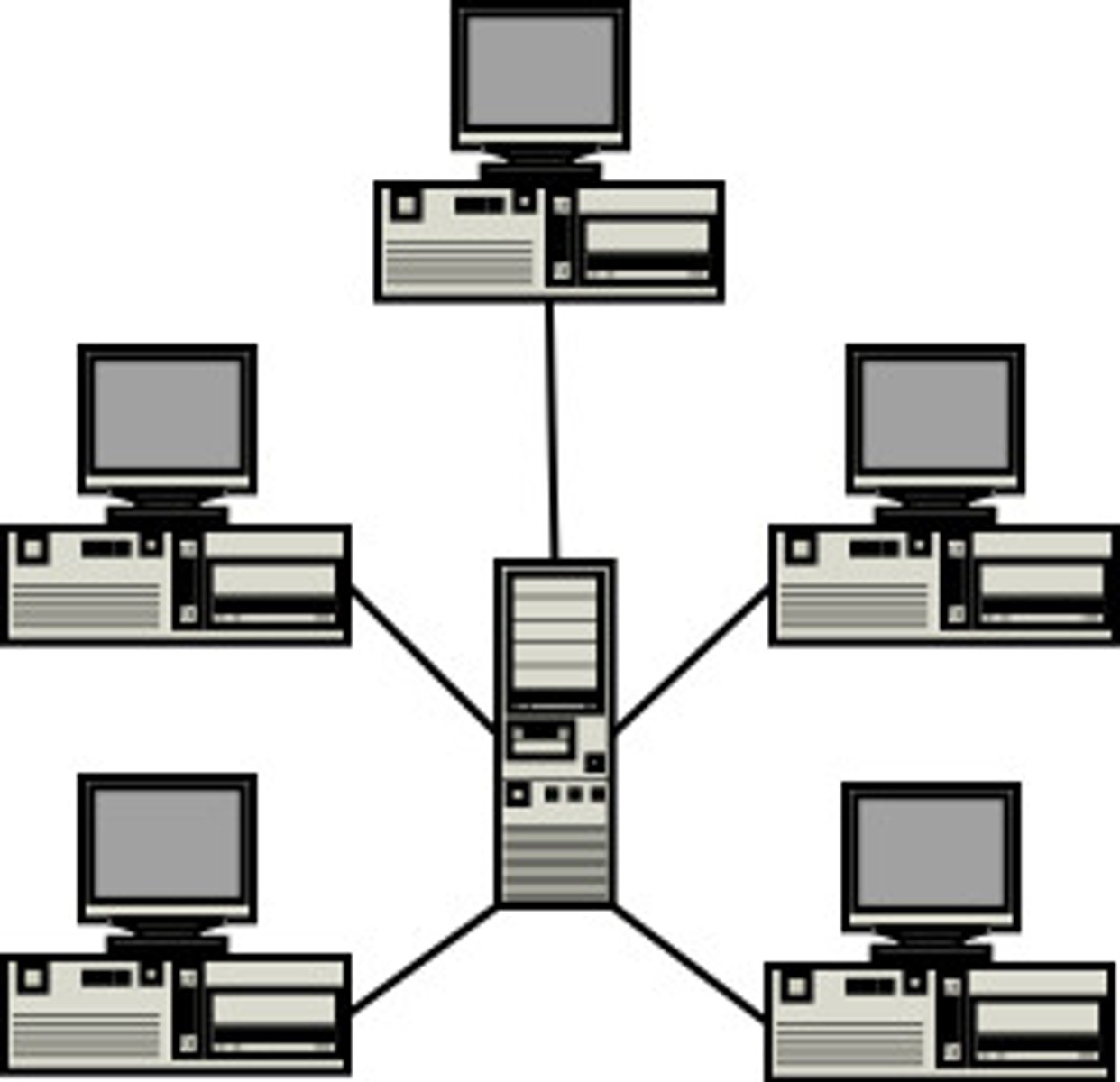
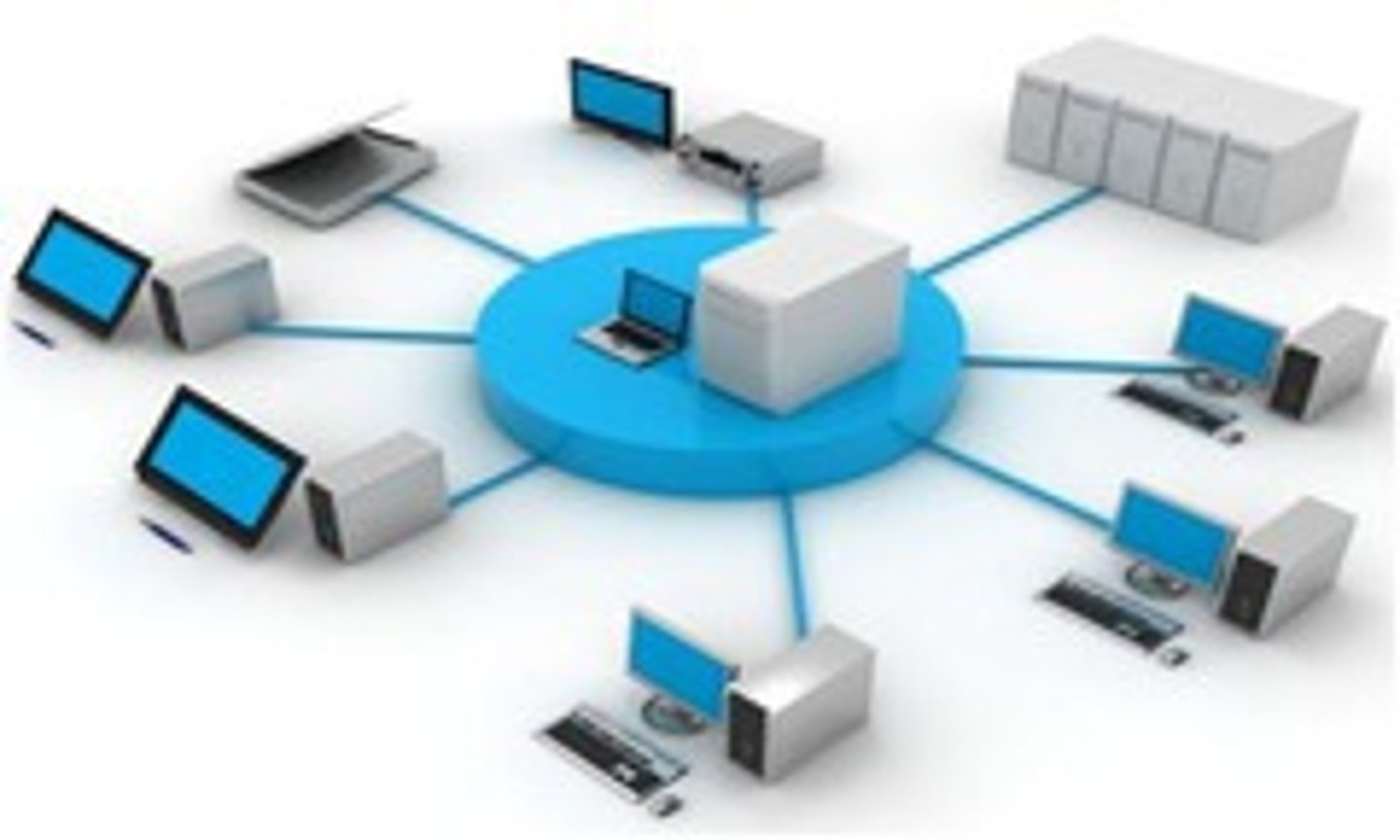
Server
A computer or computer program which manages access to a centralized resource or service in a network.

email server
An application that receives incoming e-mail from local users (people within the same domain) and remote senders and forwards outgoing e-mail for delivery
DNS server
This is the Internet's system for converting alphabetic names into numeric IP addresses.
Router
This is a device that forwards data packets between networks.

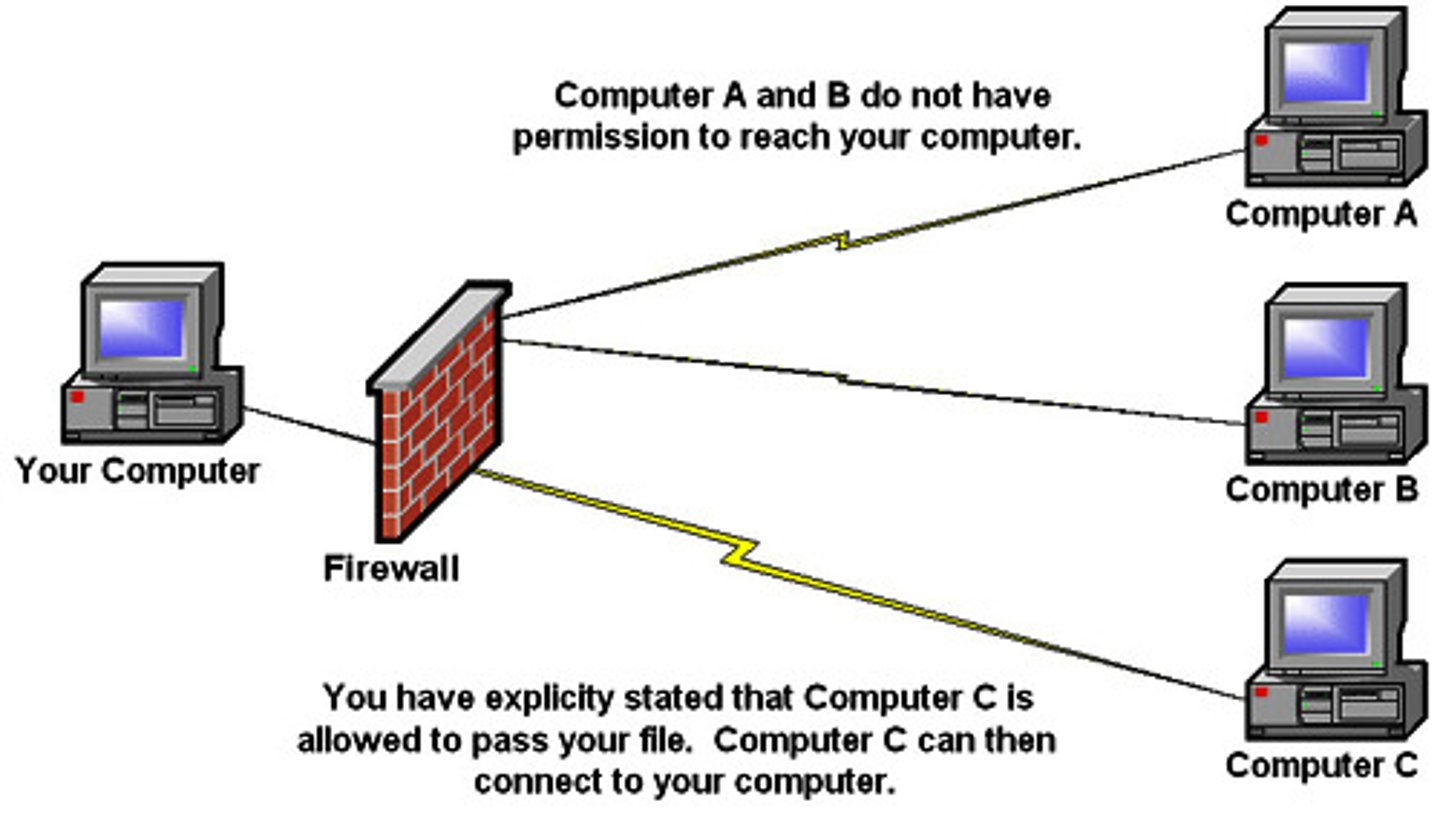
Firewall
This is a network security system, either hardware- or software-based, that controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on a set of rules.
End user
The person who actually uses a particular product.

Stakeholder
A person or group that has an investment, share, or interest in something, as a business or industry

Survey
To ask (many people) a question or a series of questions in order to gather information about what most people do or think about something.

Interview
A meeting of people face to face, especially for consultation.

Direct observation
The action or process of closely observing or monitoring something or someone.

Flow chart
A graphical representation of a computer program in relation to its sequence of functions
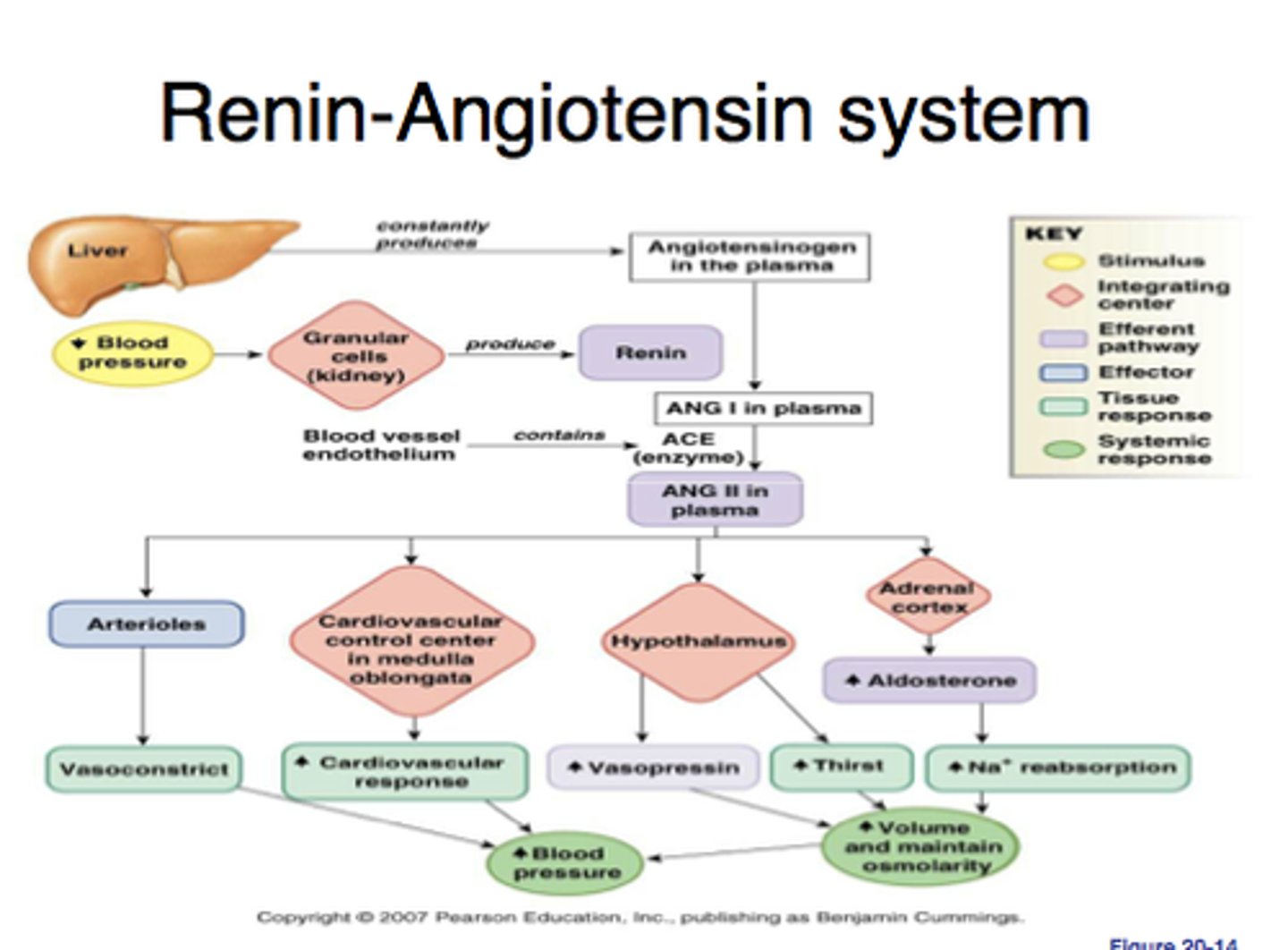
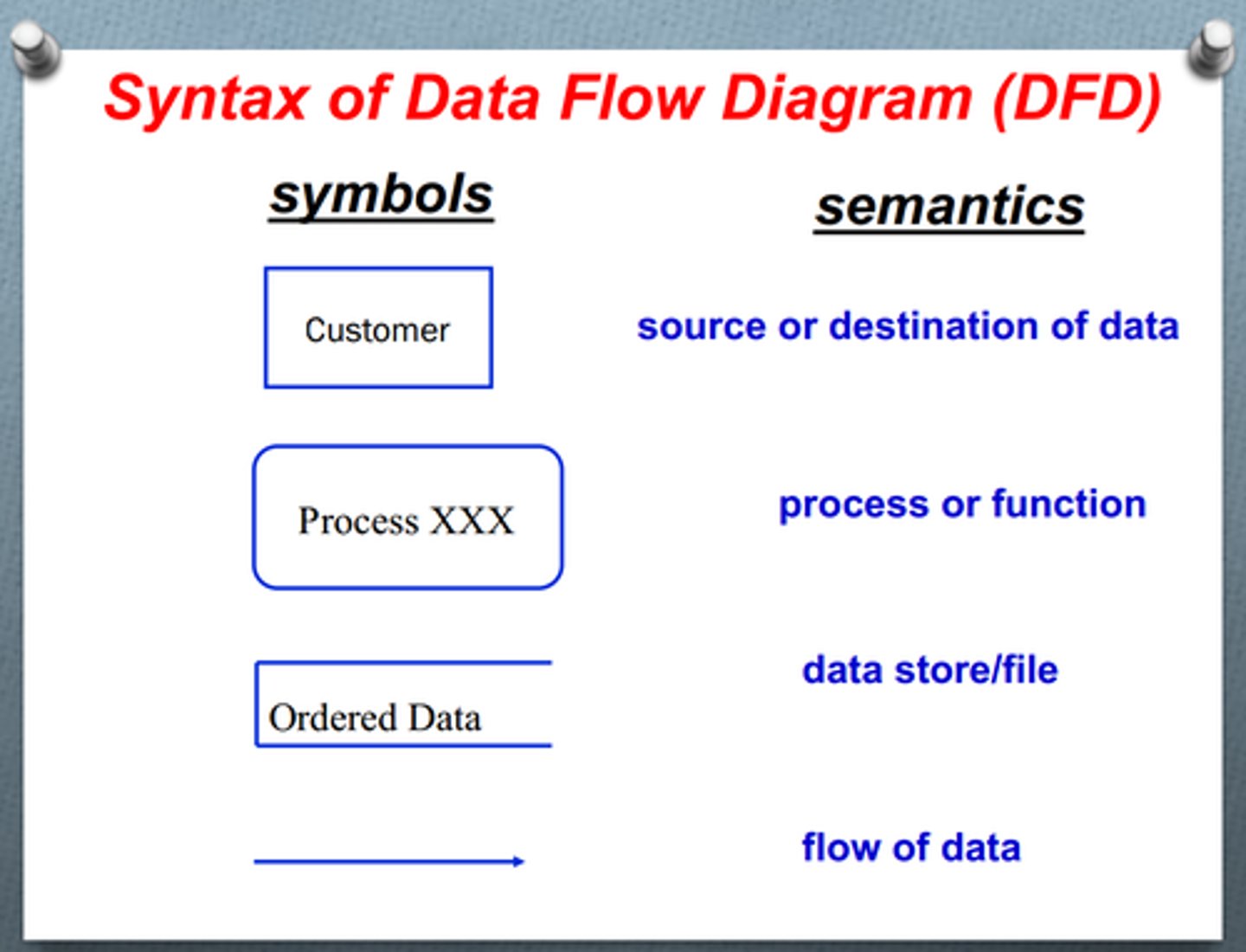
Data Flow Diagram
This is a graphical representation of the "flow" of data through an information system, modelling its process aspects.
Structure Chart
In software engineering and organizational theory, this is a chart which shows the breakdown of a system to its lowest manageable levels.
Prototype
A first or preliminary version of a device or vehicle from which other forms are developed.
System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
This is a framework defining tasks performed at each step in the software development process.
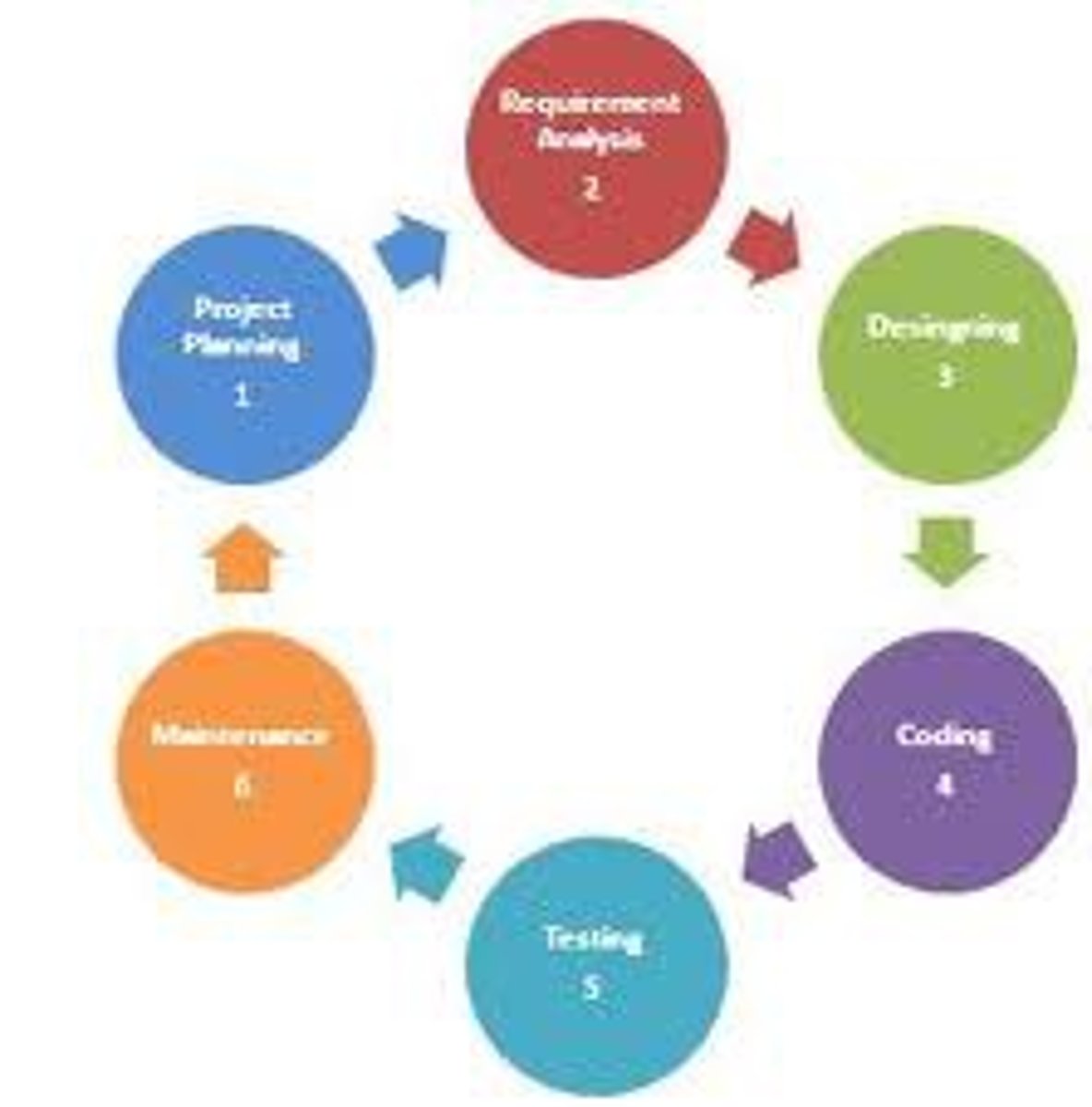
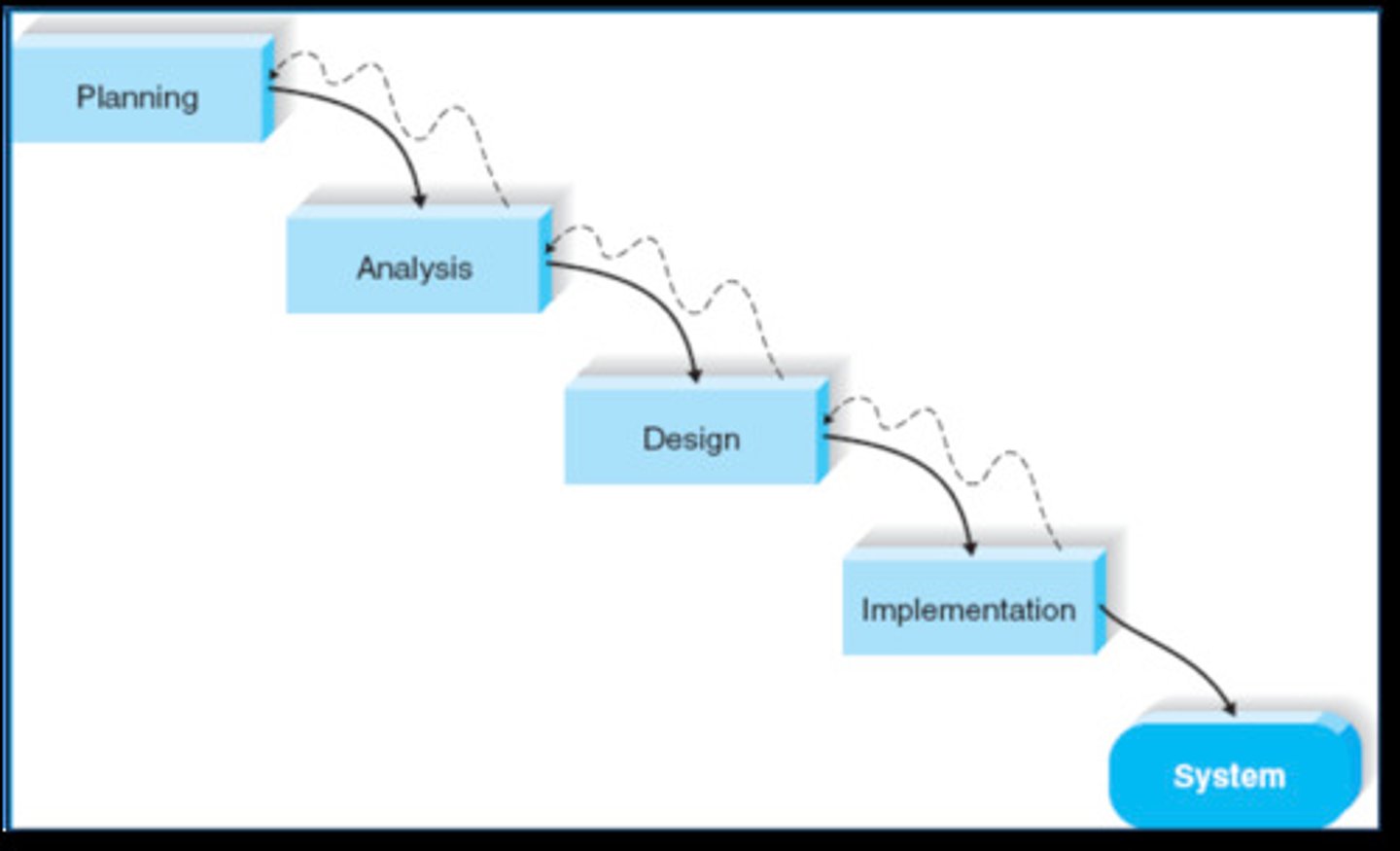
Waterfall Development
This is a sequential design process, used in software development processes, in which progress is seen as flowing steadily downwards (like a waterfall) through the phases of conception, initiation, analysis, design, construction, testing, production/implementation and maintenance.
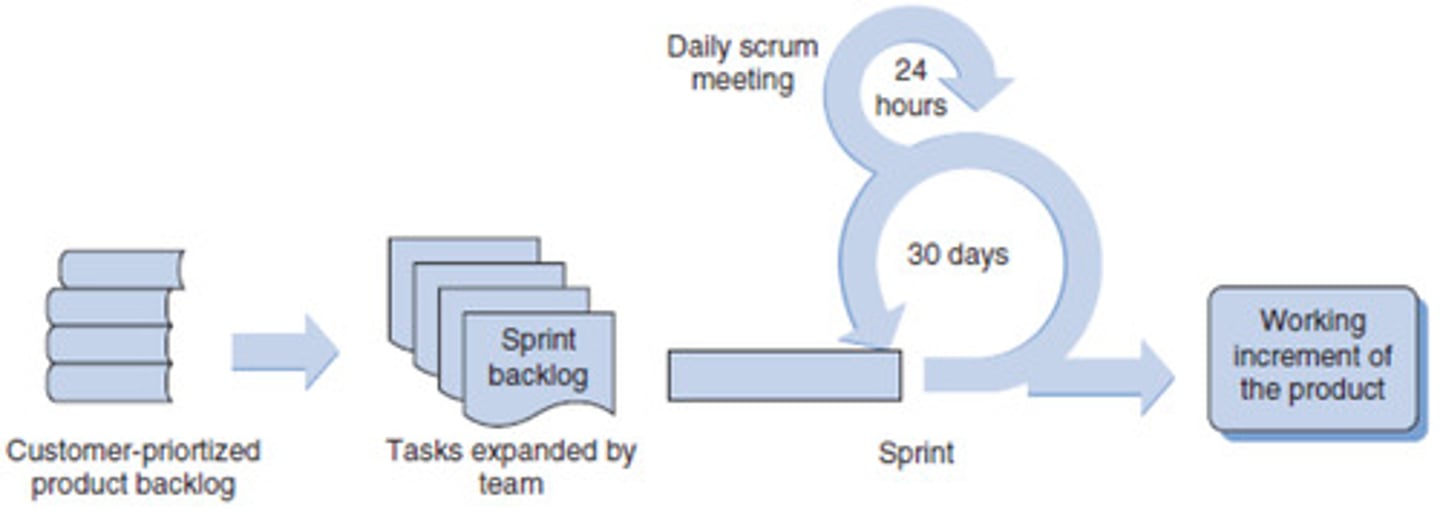
Agile Development
This is an alternative to traditional project management where emphasis is placed on empowering people to collaborate and make team decisions in addition to continuous planning, continuous testing and continuous integration.
Usability
This is a quality attribute that assesses how easy user interfaces are to use.

Accessibility
This refers to the design of products, devices, services, or environments for people with disabilities.
Privacy
This is the ability of individuals and groups to determine for themselves when, how and to what extent information about themselves is shared with others. At its extreme, this becomes anonymity

Anonymity
The situation in which someone's name is not given or known

Security
This refers to the protection of hardware, software, machines and networks from unauthorized access.

Reliability
This refers to the operation of hardware, the design of software, the accuracy of data or the correspondence of data with the real world.

Integrity
This refers to safeguarding the accuracy and completeness of stored data.

Intellectual Property
This includes ideas, discoveries, writings, works of art, software, collections and
presentations of data. Copyright, trademarks and patents exist to protect intellectual property.

Authenticity
This means establishing a user's identity beyond reasonable doubt. Authenticating the user is crucial in many scenarios, particularly in business and legal matters.

Digital Divide
The growth of the use of IT systems has led to disparities in the use of, and access to, information technologies.

Surveillance
This is the use of IT to monitor the actions of people. For example, monitoring may be used to track, record and assess employees' performance.

Policies
These are enforceable measures intended to promote appropriate and discourage inappropriate use relating to information technologies. They can be developed by governments, businesses, private groups or individuals. They normally consist of rules governing access to, or use of, information, hardware, software and networks.
