Unit 3: Biomolecules
4.9(34)
Card Sorting
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:10 AM on 10/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
1
New cards
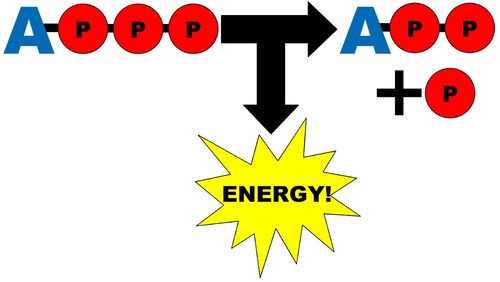
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
main energy source that cells use for most of their work
2
New cards
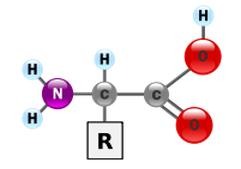
Amino acid
monomer that makes up proteins
3
New cards
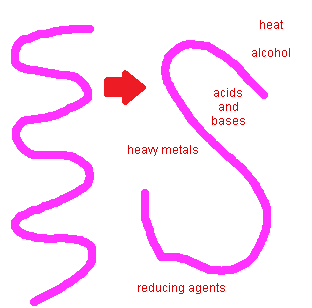
Denaturation
loss of normal shape of a protein due to heat or other factors
4
New cards
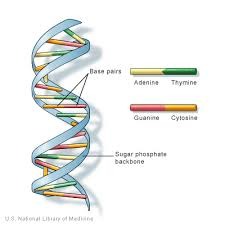
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
molecule responsible for inheritance. Nucleic acid that contains the sugar deoxyribose
5
New cards
Nucleic acid
a complex organic substance present in living cells, especially DNA or RNA, whose molecules consist of many nucleotides linked in a long chain.
6
New cards
Nucleotide
building block (monomer) of nucleic acid polymers
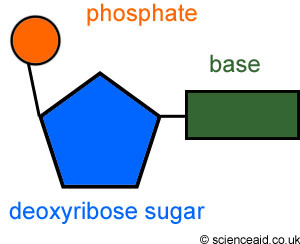
7
New cards
Polypeptide
chain of linked amino acids
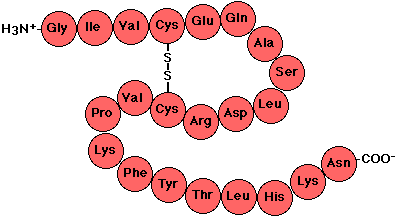
8
New cards
Protein
polymer constructed from a set of 20 amino acid monomers
9
New cards
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
nucleic acid containing sugar ribose
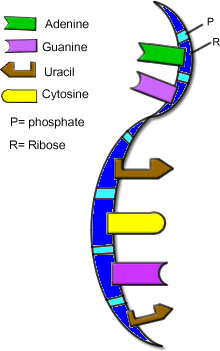
10
New cards
Carbohydrate
organic compound made of sugar molecules

11
New cards
Cellulose
polysaccharide consisting of glucose monomers that reinforces plant-cell walls
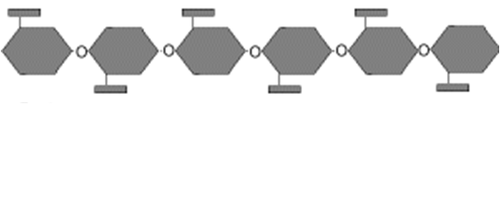
12
New cards
Disaccharide
sugar with two monosaccharides
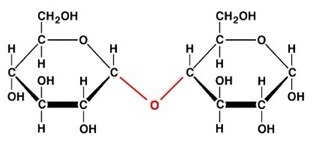
13
New cards
Fat
organic compound consisting of a three-carbon backbone (glycerol) attached to three fatty acids
14
New cards
Glycogen
polysaccharide in animal cells that consists of many glucose monomers
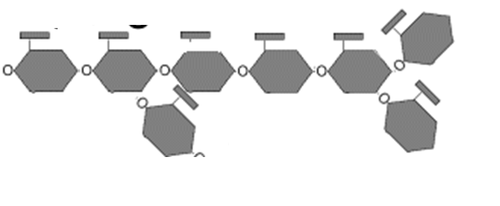
15
New cards
Hydrophilic
attracts water molecules
16
New cards
Hydrophobic
avoids water molecules
17
New cards
Inorganic molecule
non-carbon based molecule

18
New cards
Lipid
one of a class of water avoiding compounds

19
New cards
Monomer
small molecular unit that is the building block of a larger molecule
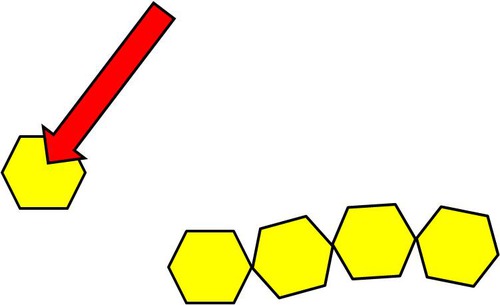
20
New cards
Monosaccharide
sugar containing one sugar unit
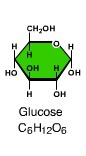
21
New cards
Organic molecule
carbon based molecule
22
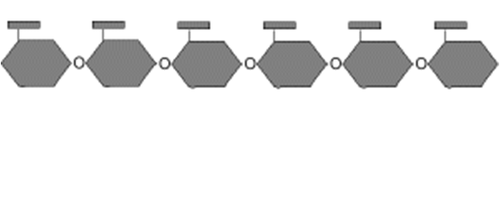
New cards
Polymer
long chain of small molecular units
23
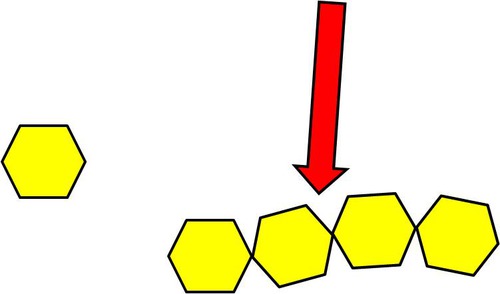
New cards
Polysaccharide
long polymer chain made up of simple sugar monomers
24
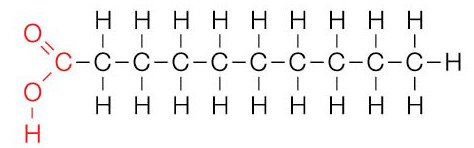
New cards
Saturated fat
fat in which all three fatty acid chains contain the maximum possible number of hydrogen atoms
25
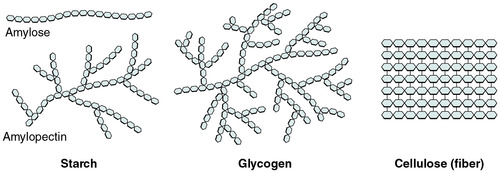
New cards
Starch
polysaccharide in plant cells that consists entirely of glucose monomers
26
New cards
Steroid
lipid molecule with four fused rings
27
New cards
Unsaturated fat
fat with less than the maximum number of hydrogens in one of more of its fatty acid chains