echocardiography
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Equipment required in echocardiography
US machine, table, restraint, ECG pads, sector transducers (to get between ribs)
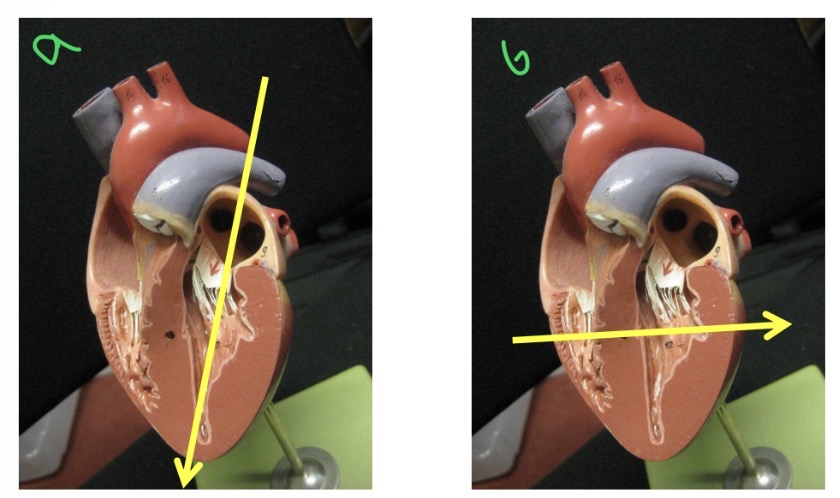
Types of views - a
Long axis view
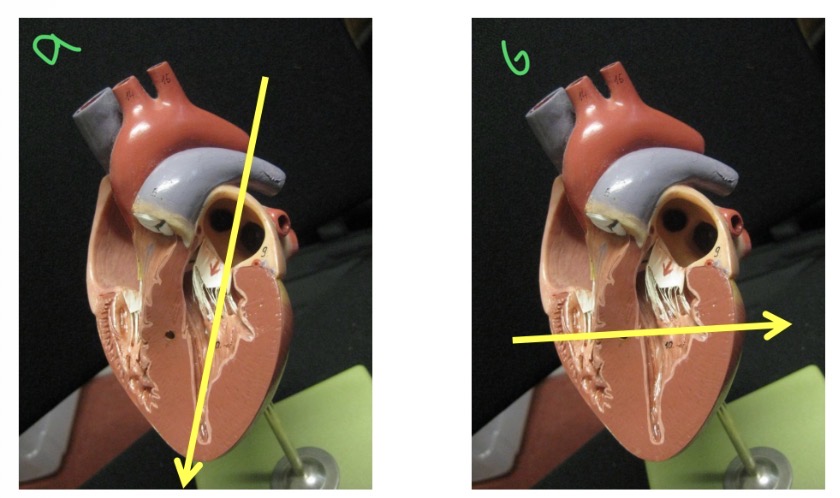
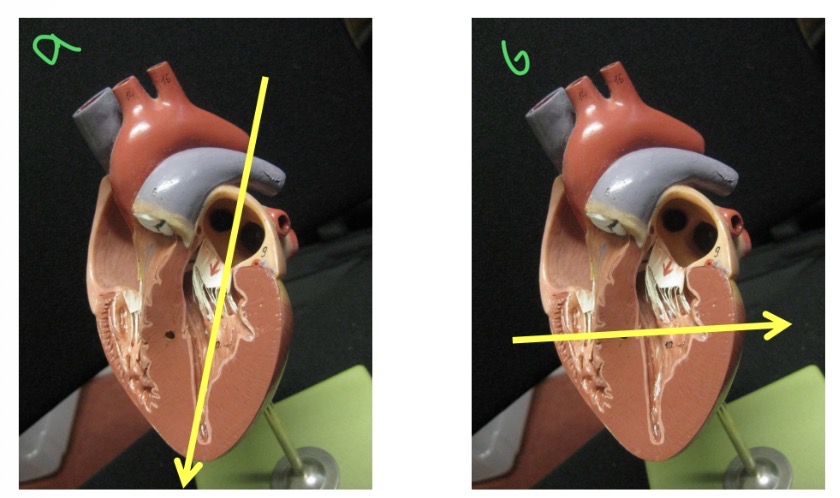
Types of views - B
Short axis view
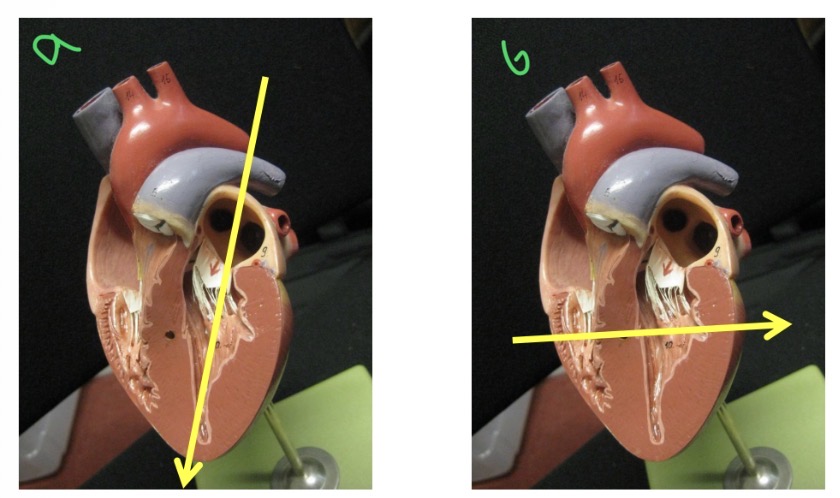
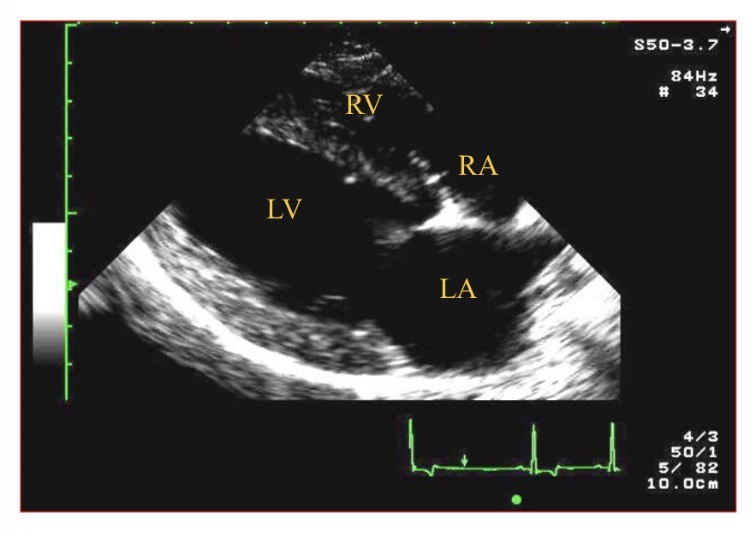
Types of views - Which is best to see most cardiac issues
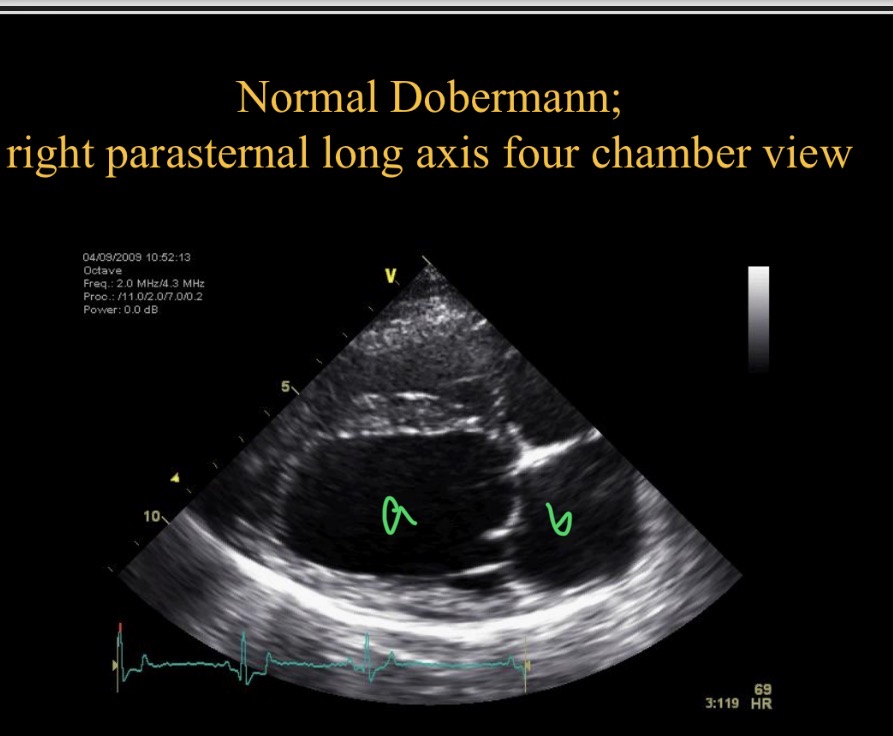
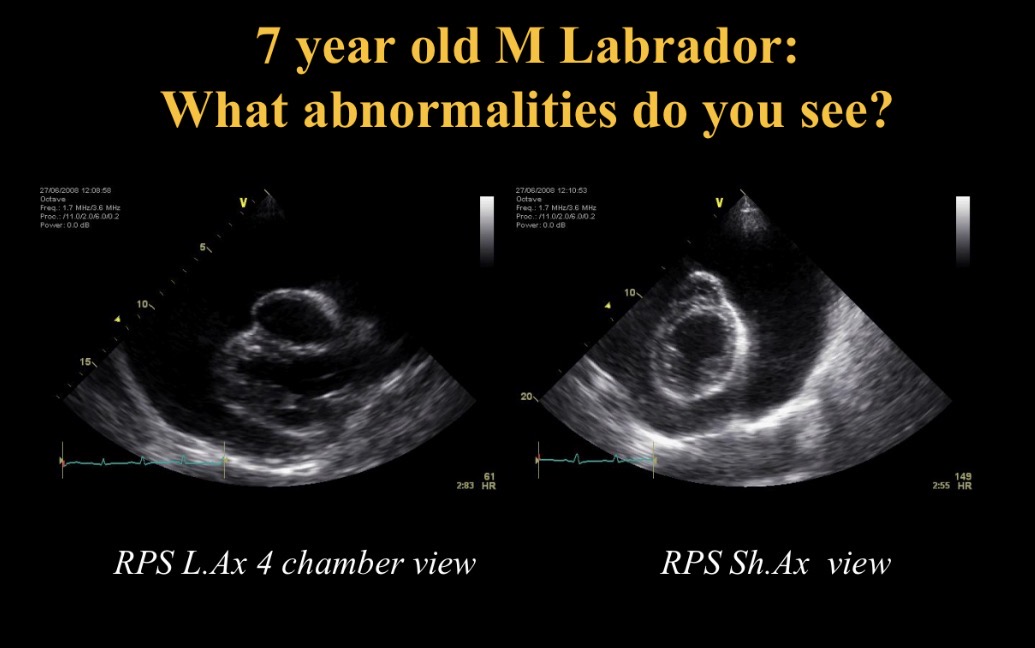
R para sternal long axis 4 chamber view
Types of views - RPS view which chamber is clostest to probe
RV
Timings- end diastole
Start of QRS complex
Timings- End systole
Smallest LV dimension/ end of T wave
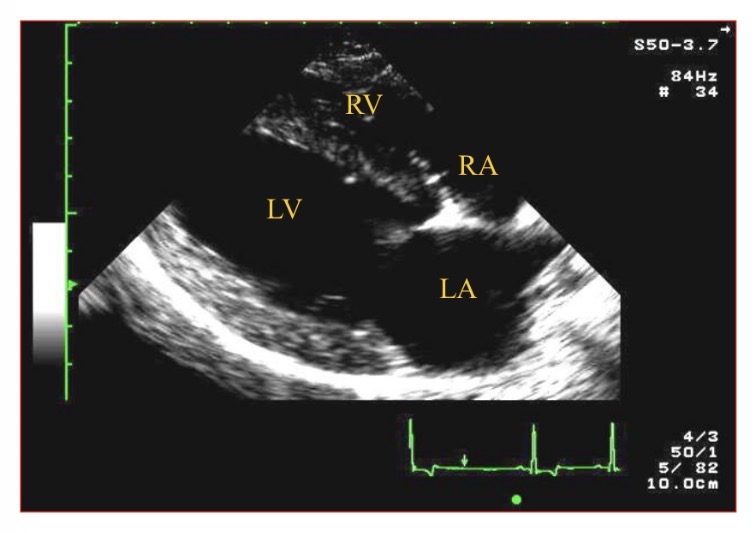
Views - which structures on R of screen (except L apical 4 chamber view)
Basilar structures/ R sided
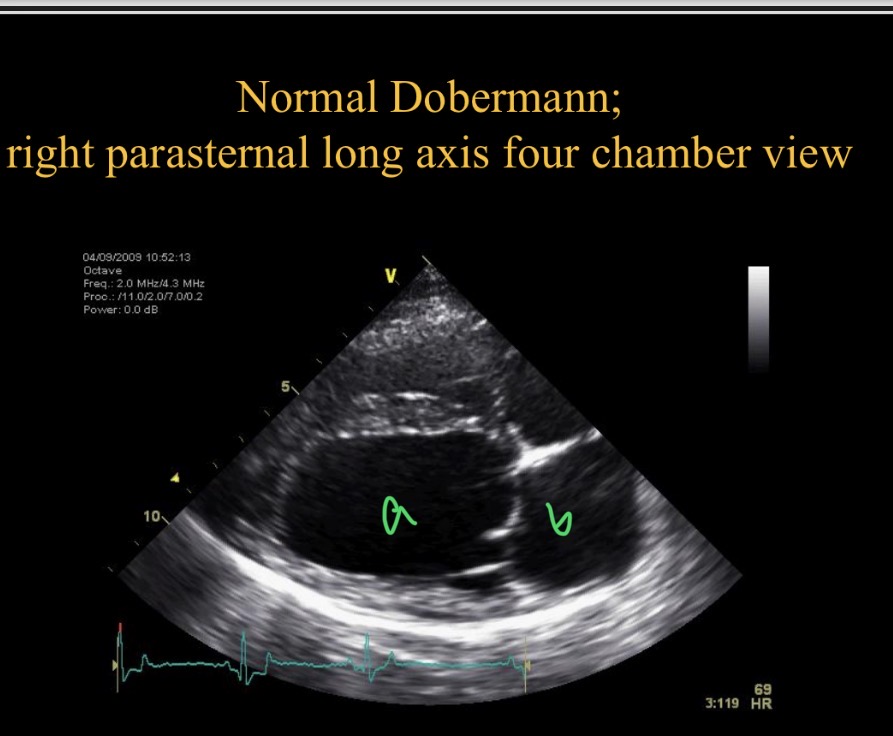
Which chamber is A
LV
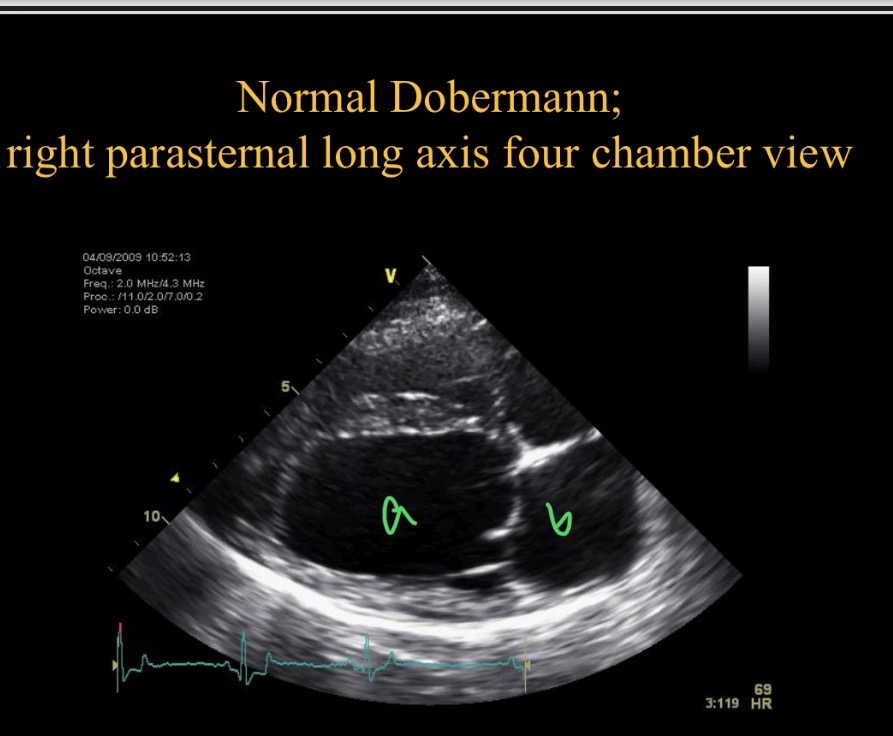
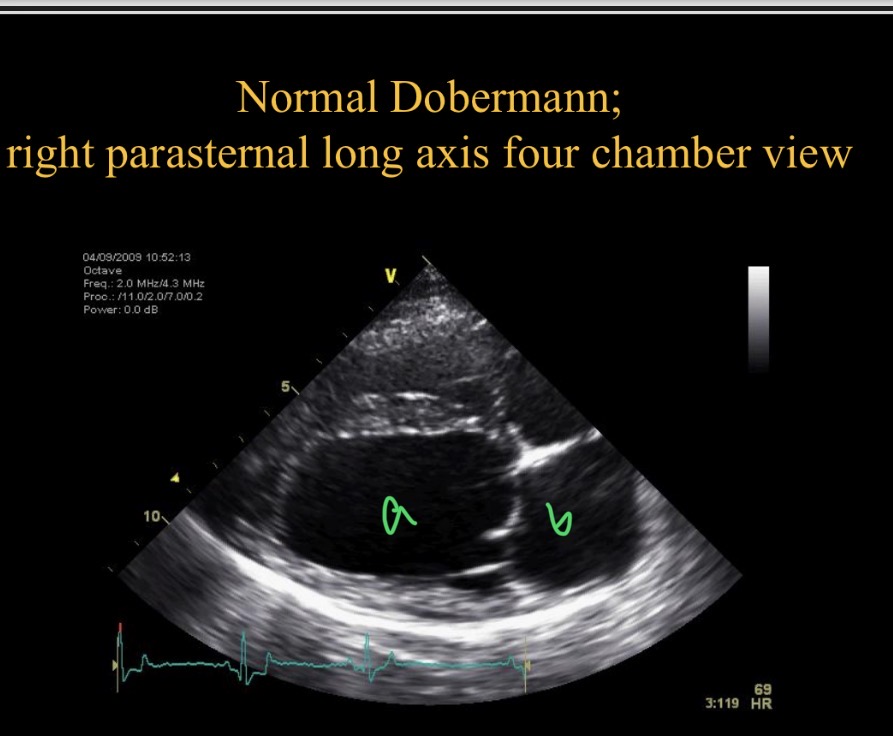
Which chamber is B
LA
LV wall thickness
¼ - 1/3 chamber diameter
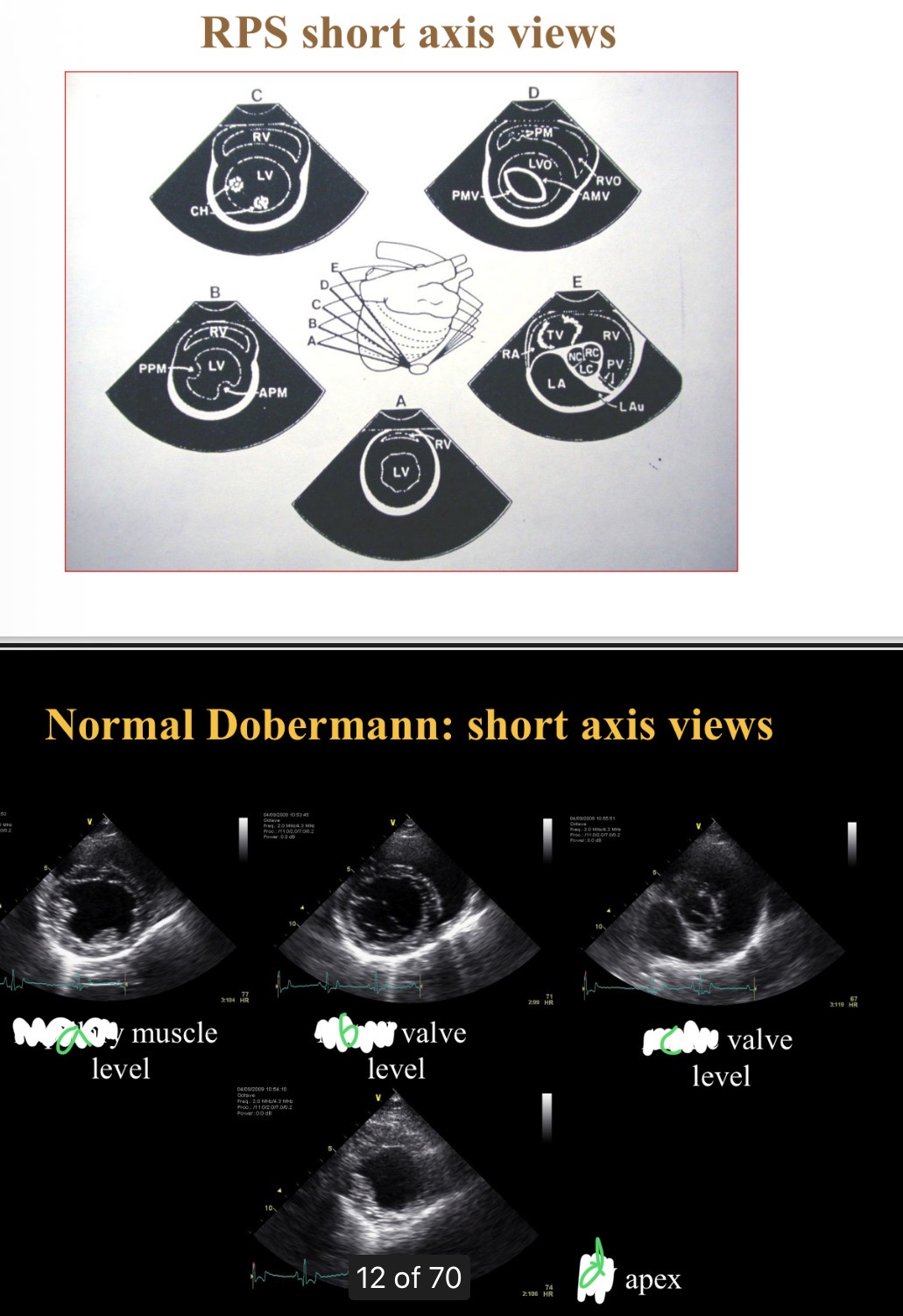
Levels of short axis views - a
Papillary
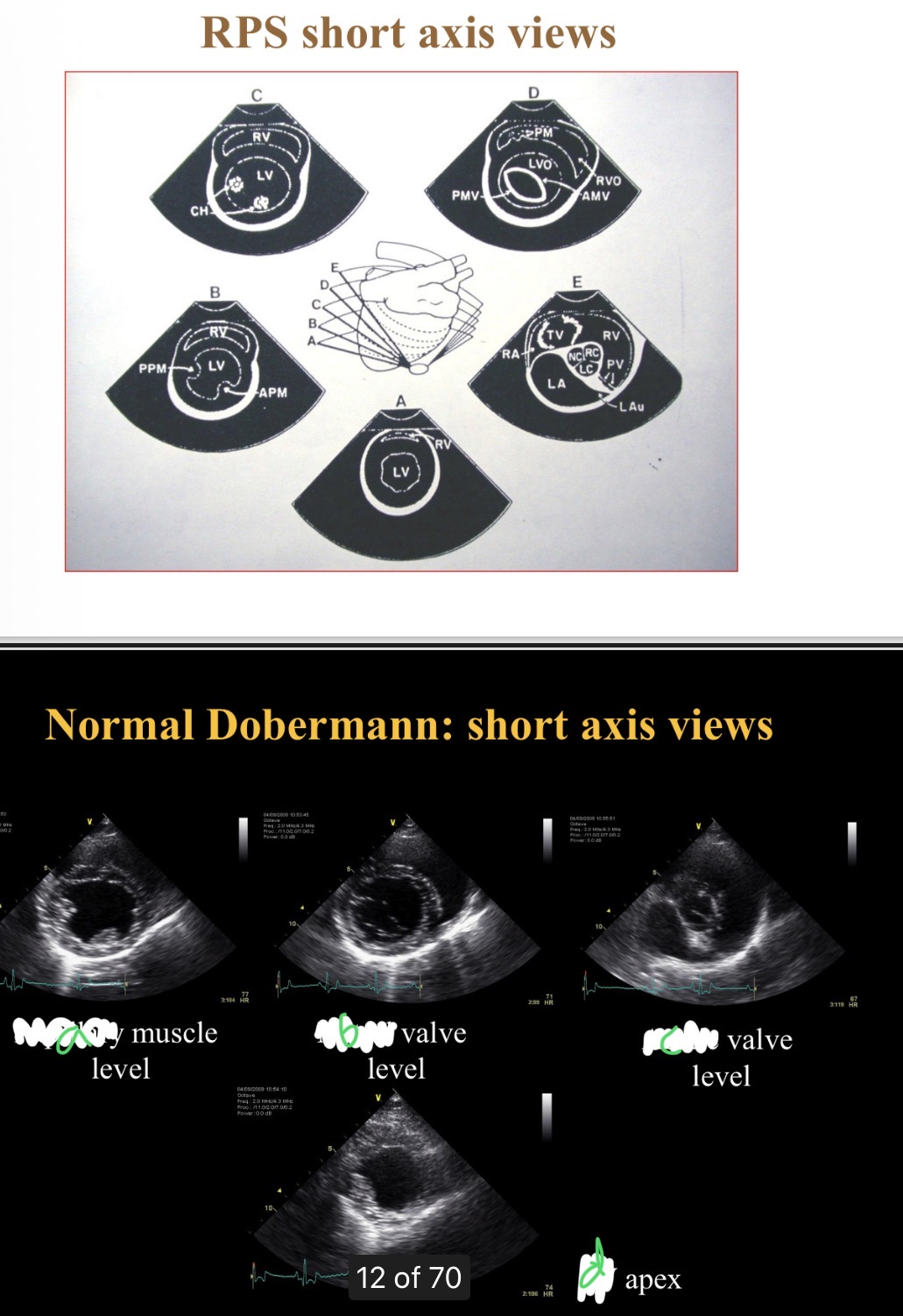
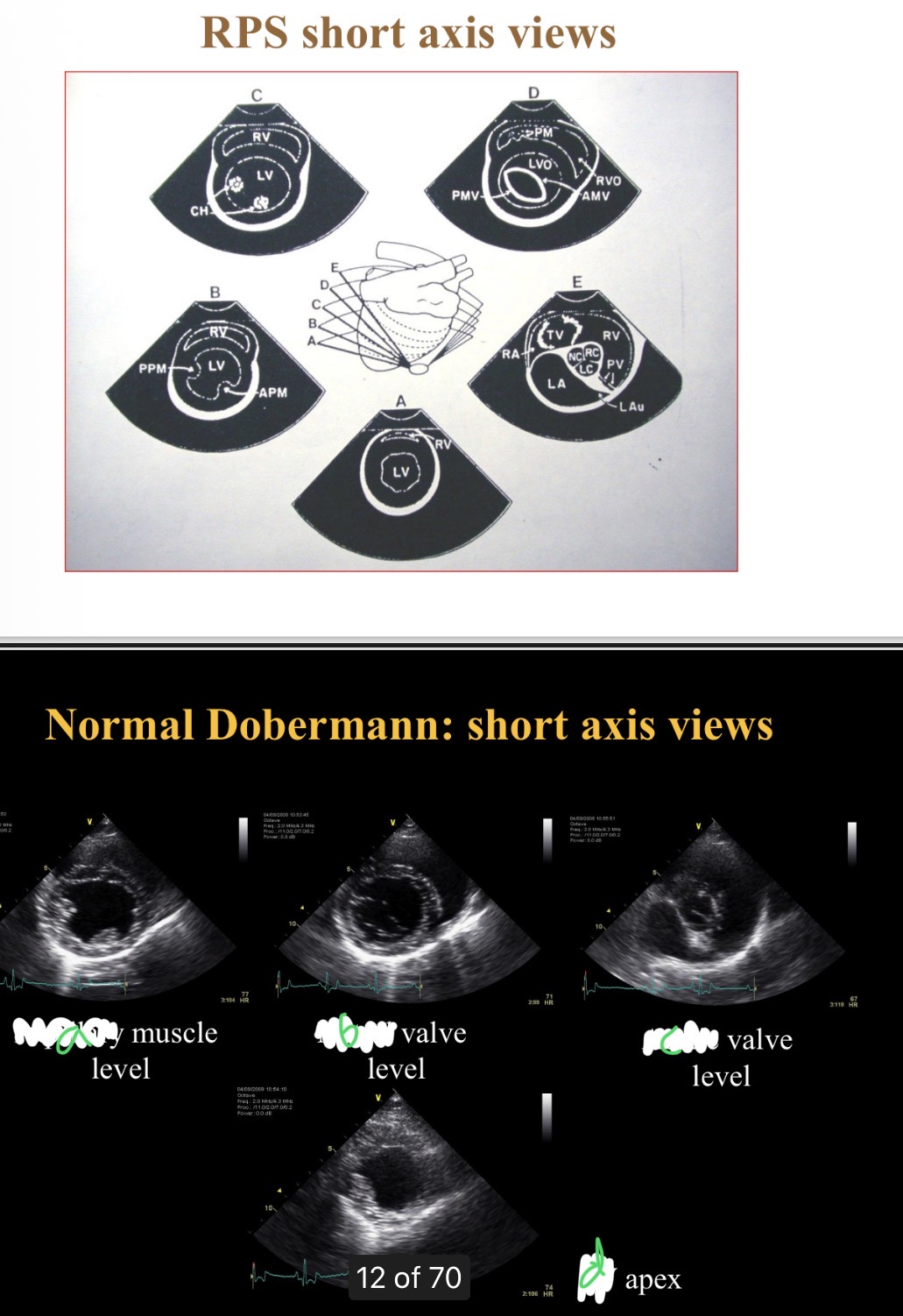
Levels of short axis views - B
Mitral
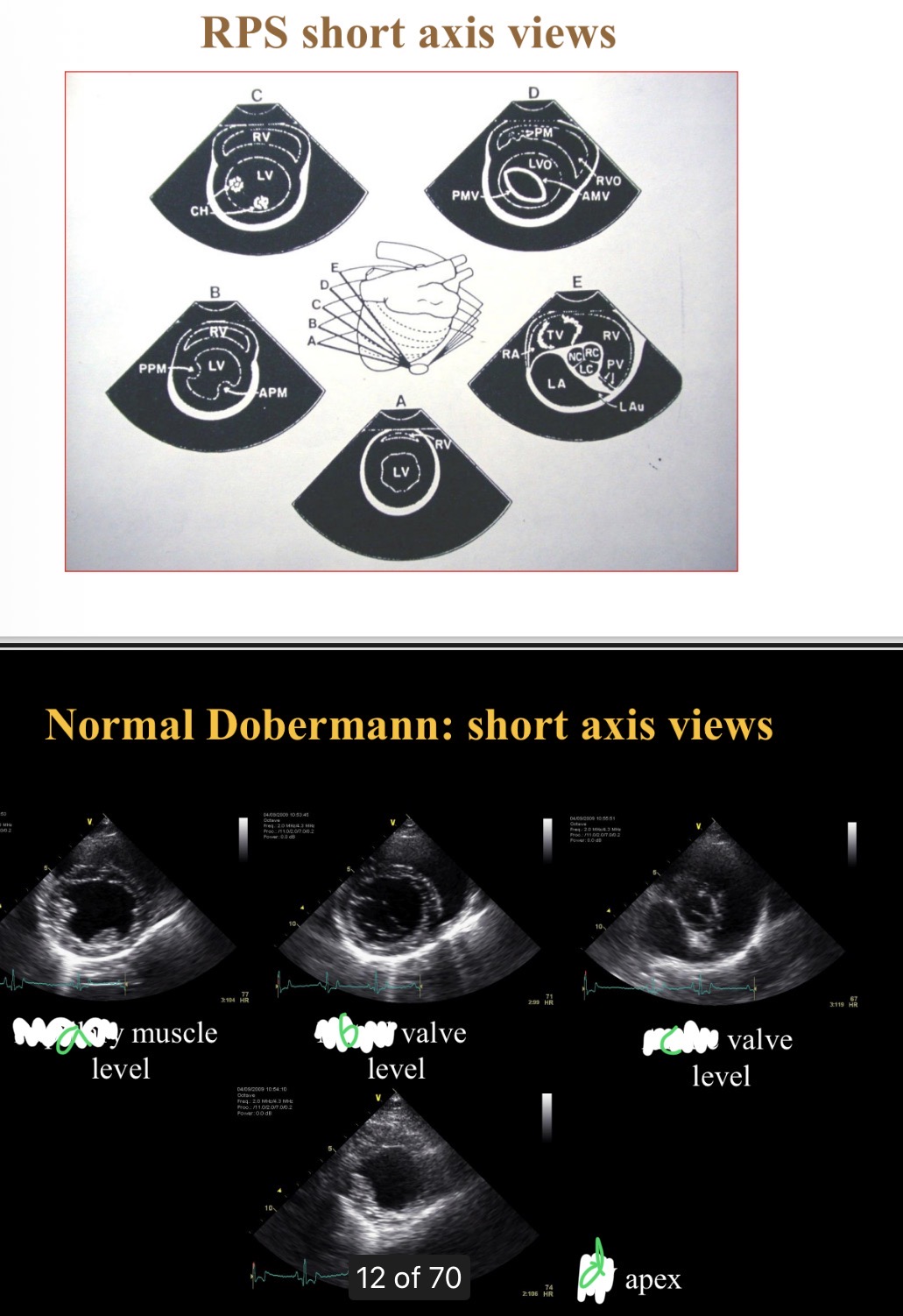
Levels of short axis views - C
Aortic
Levels of short axis views - D
LV
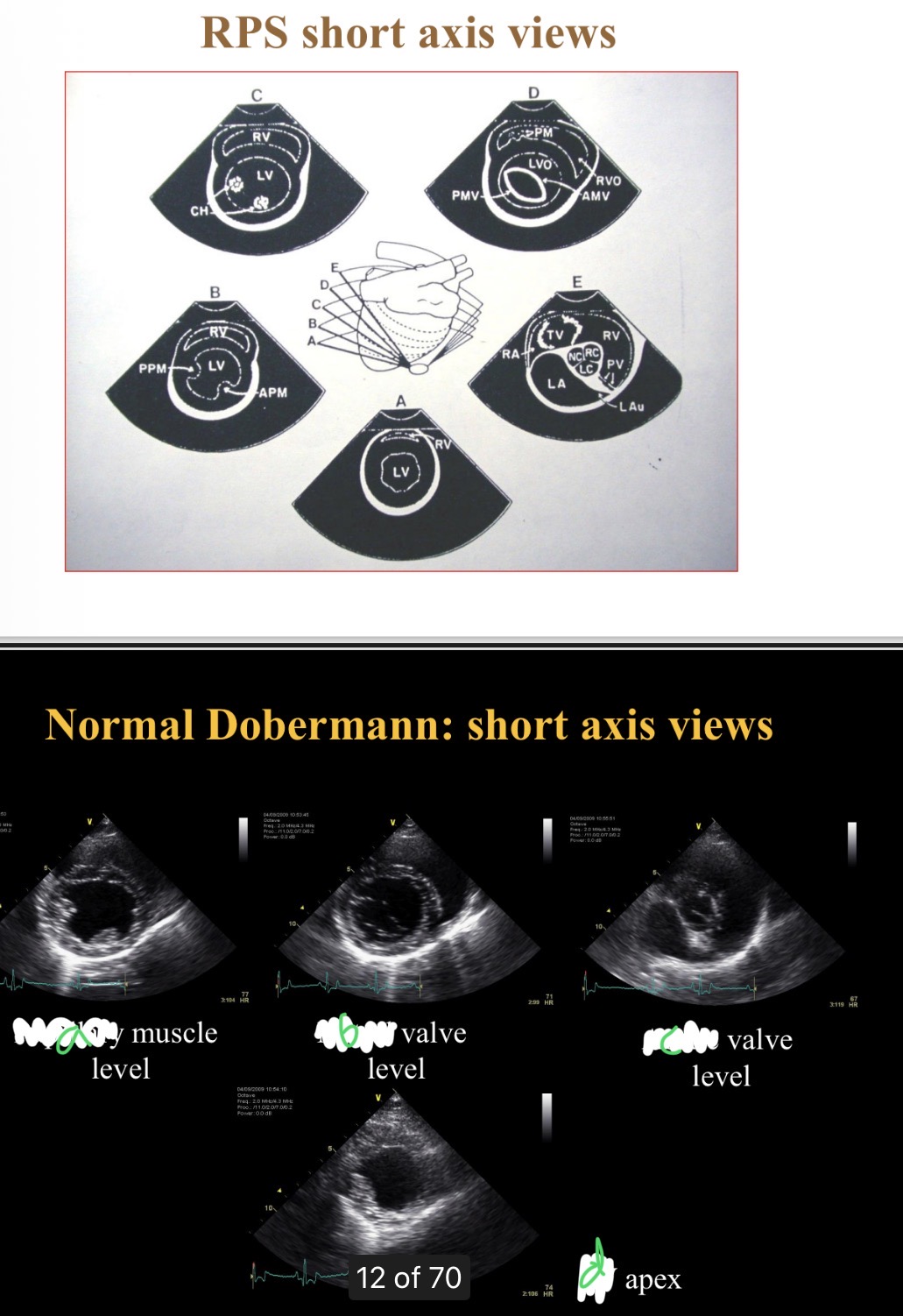
What level is at widest part of heart
Chordae tendinae
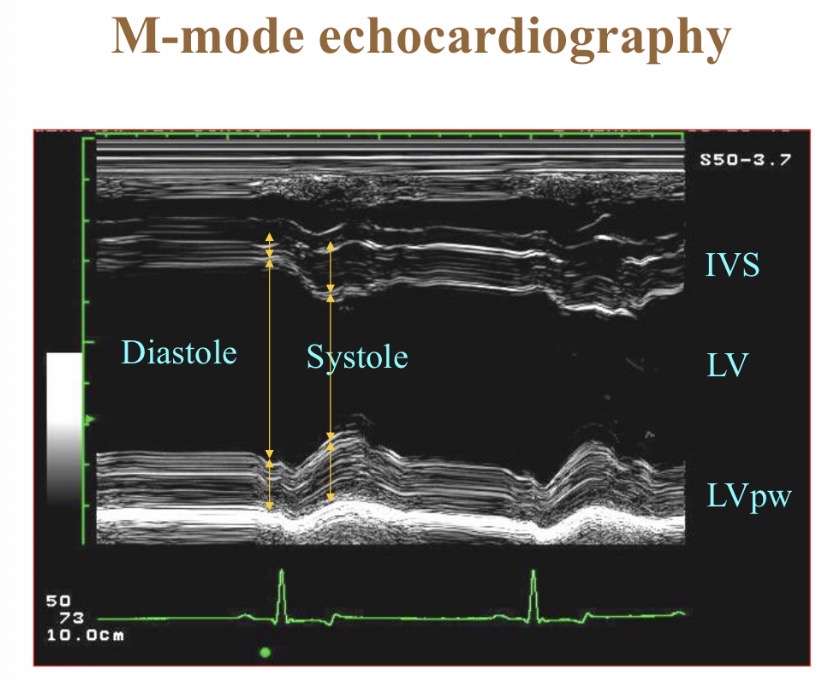
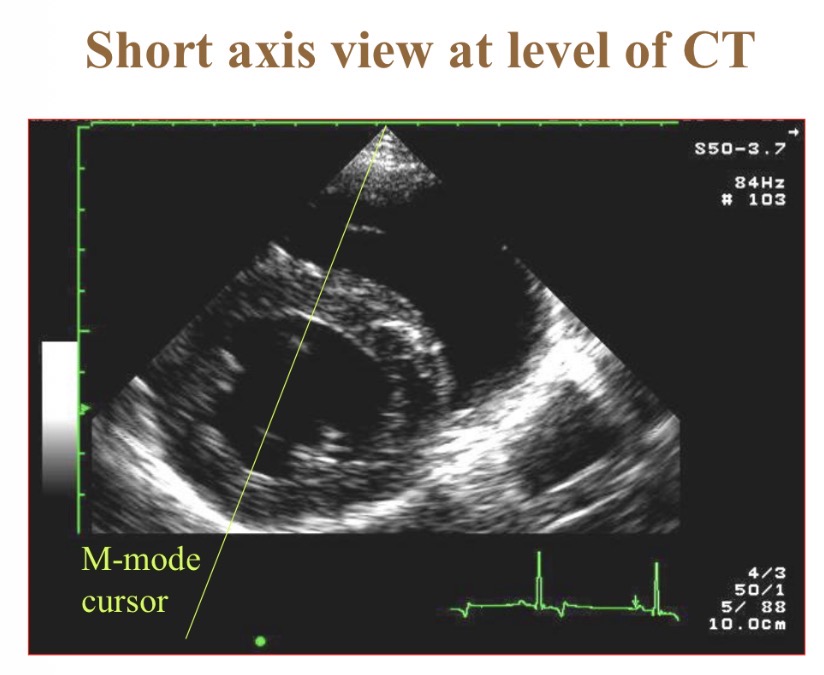
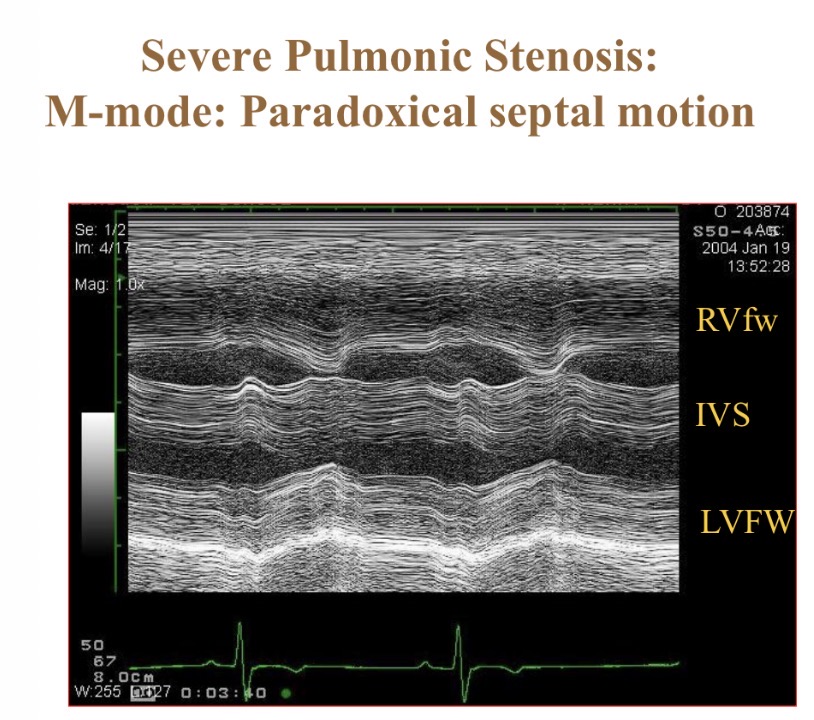
What does M-mode echocardiography show
Wall thickness/position over time/ ECG
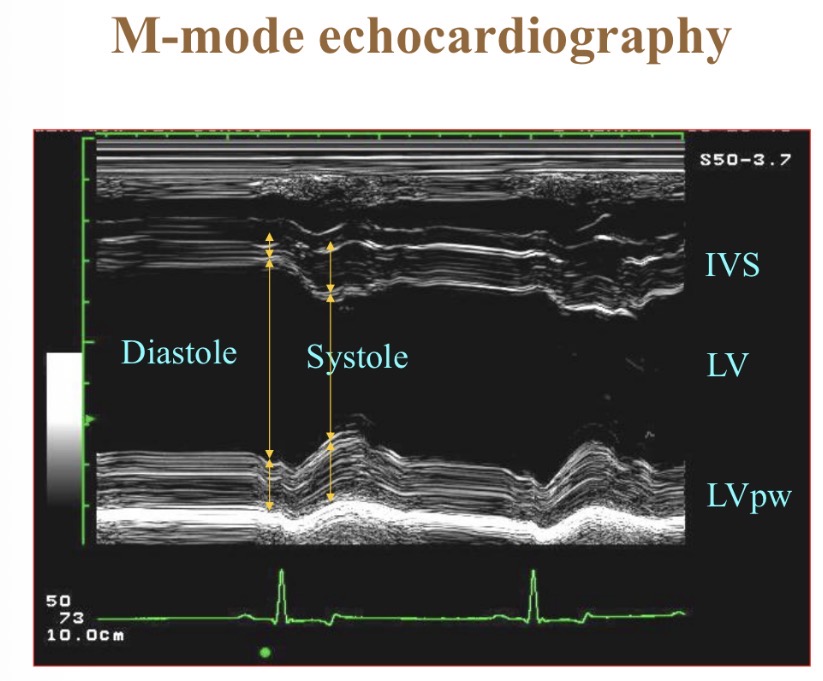
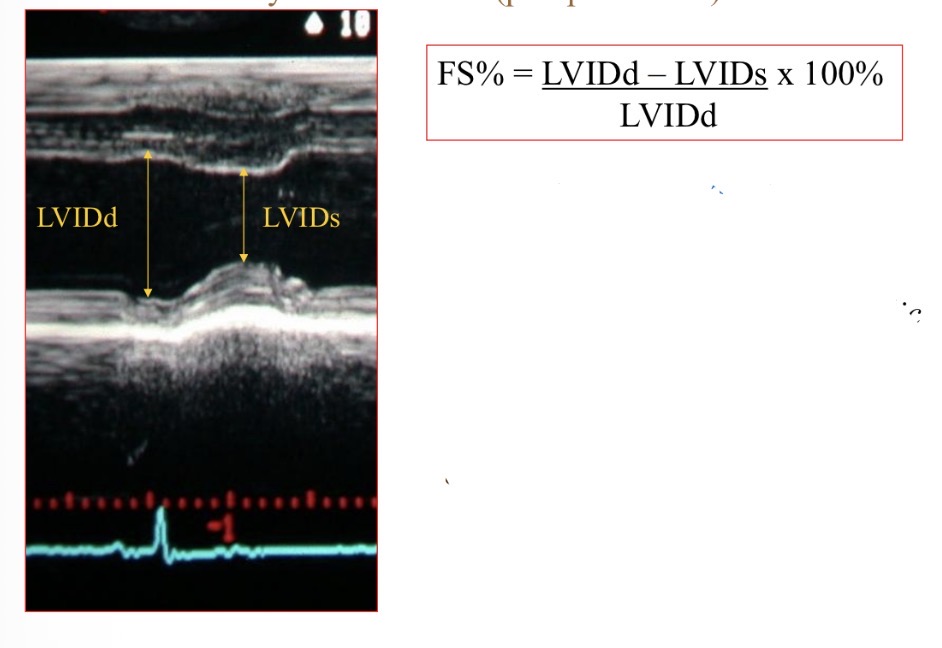
Fractional shortening shows what
Contractility, systolic function
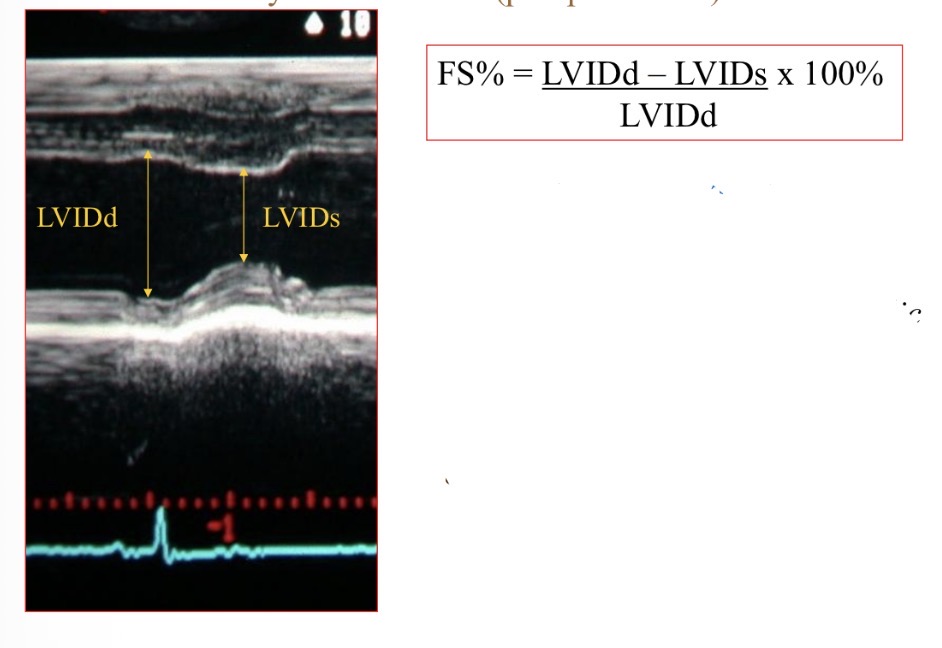
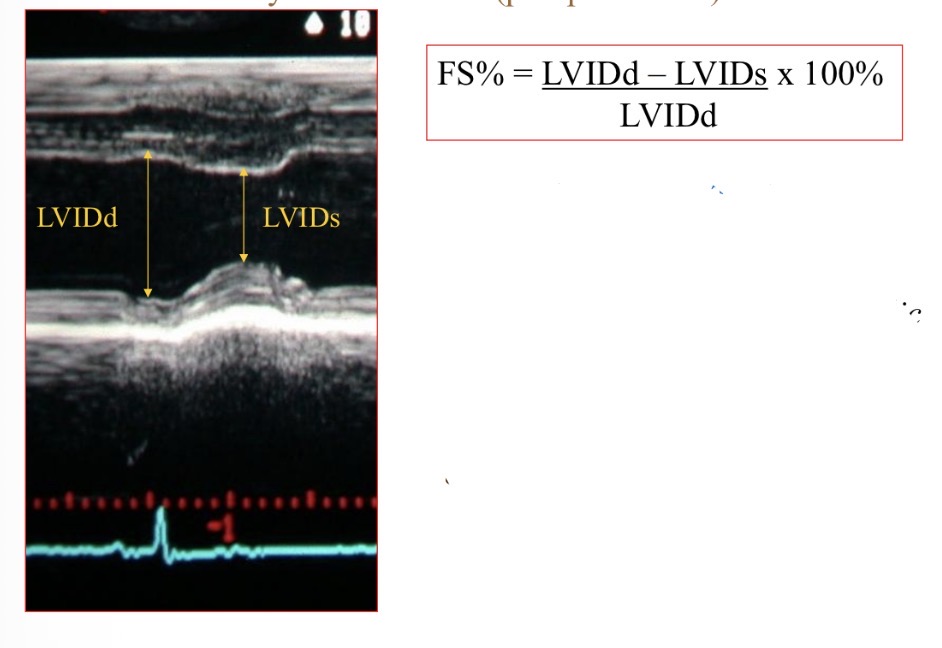
Fractional shortening normal value
>25%
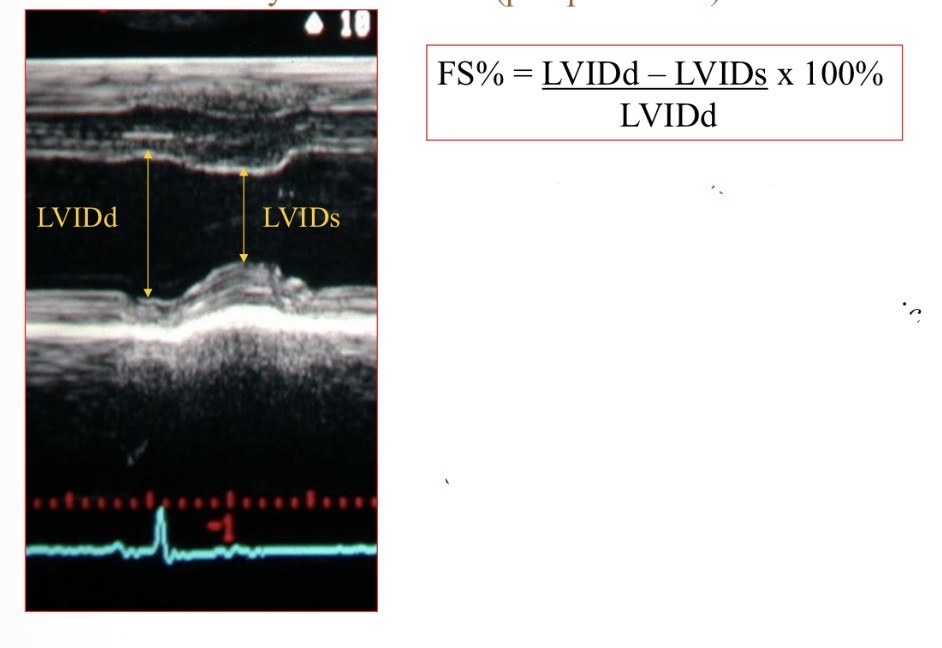
Fractional shortening not reliable when
Significant mitral regurgitation
Wall motion abnormalities
R heart disease with pressure overload
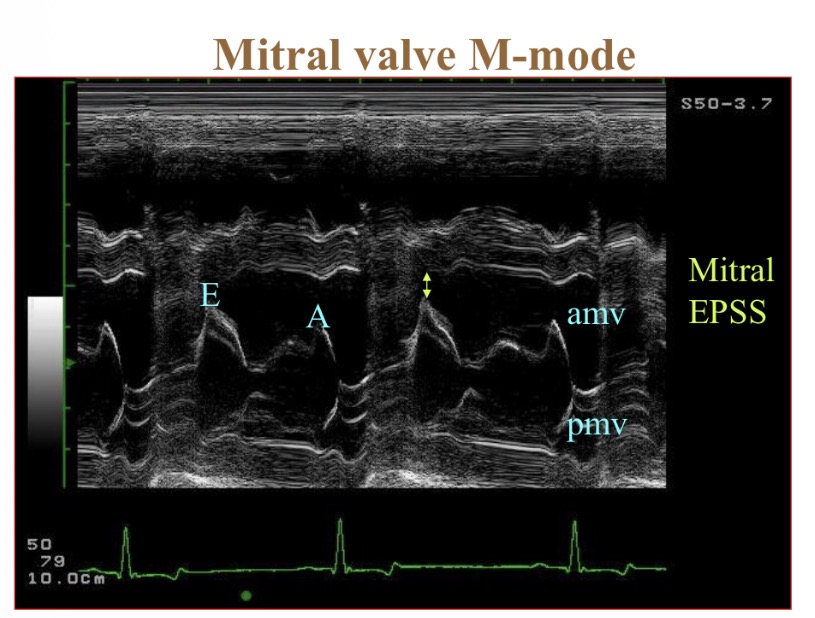
How many times does M valve open in systole
2
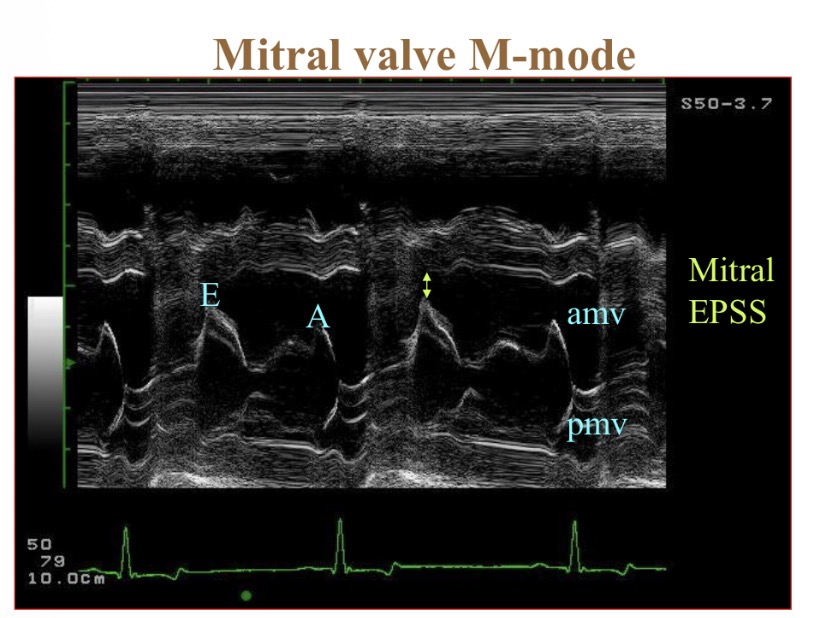
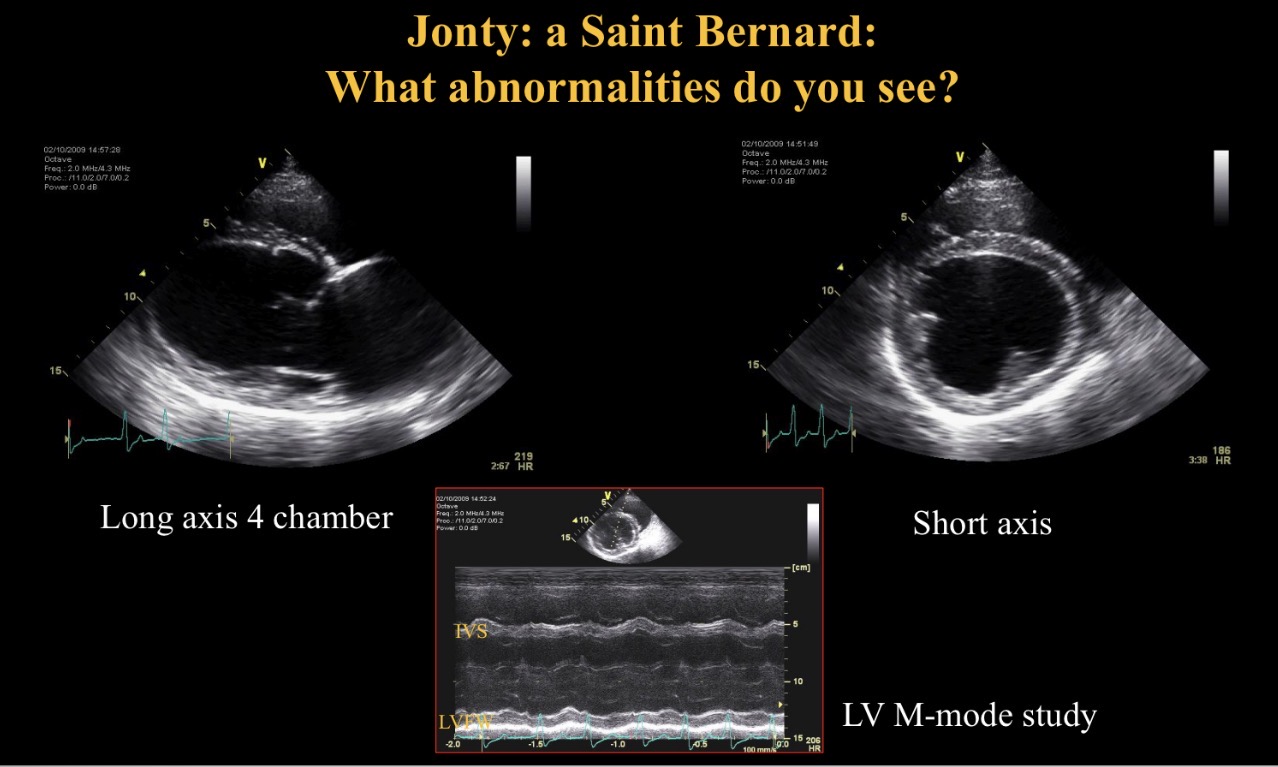
What to assess in initial home view
Chamber size
Wall thickness
Systolic function
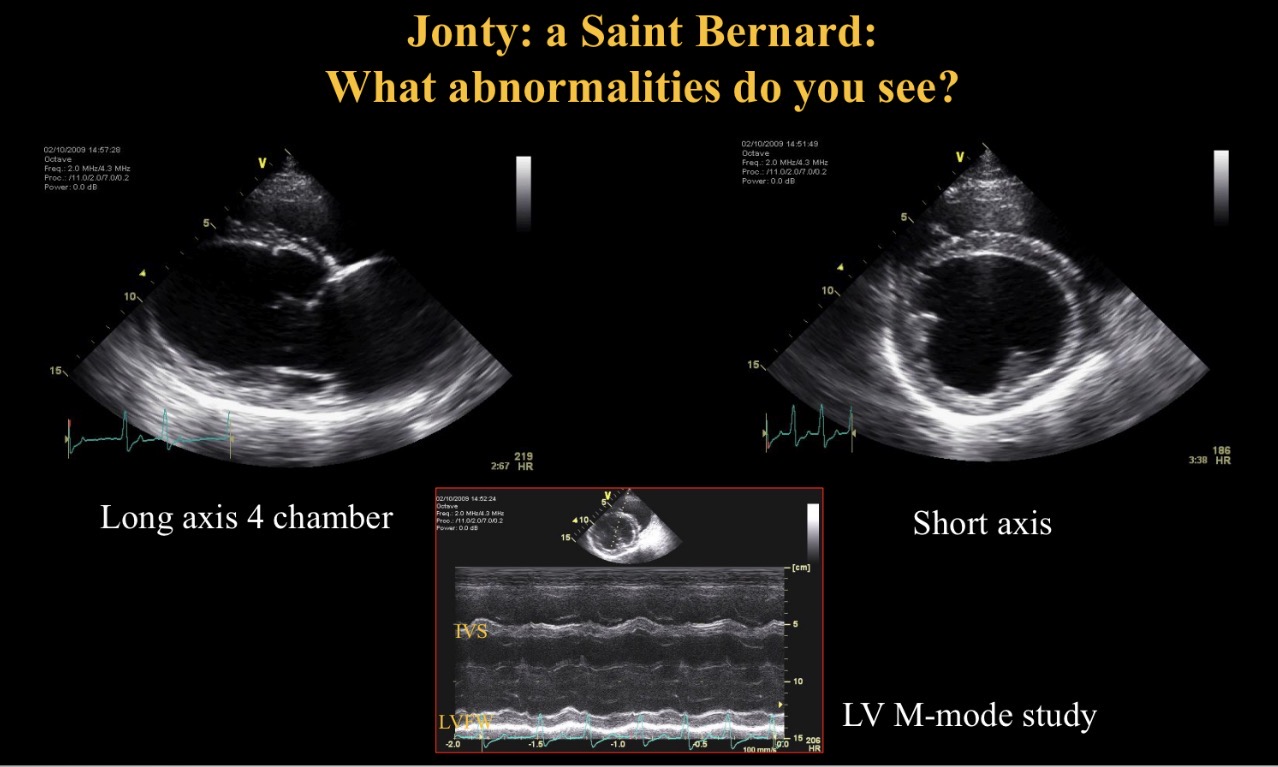
Abnormality seen
Arrhythmia
LV dilated + hypokinetic
Inc EPSS
→ dilated CMP
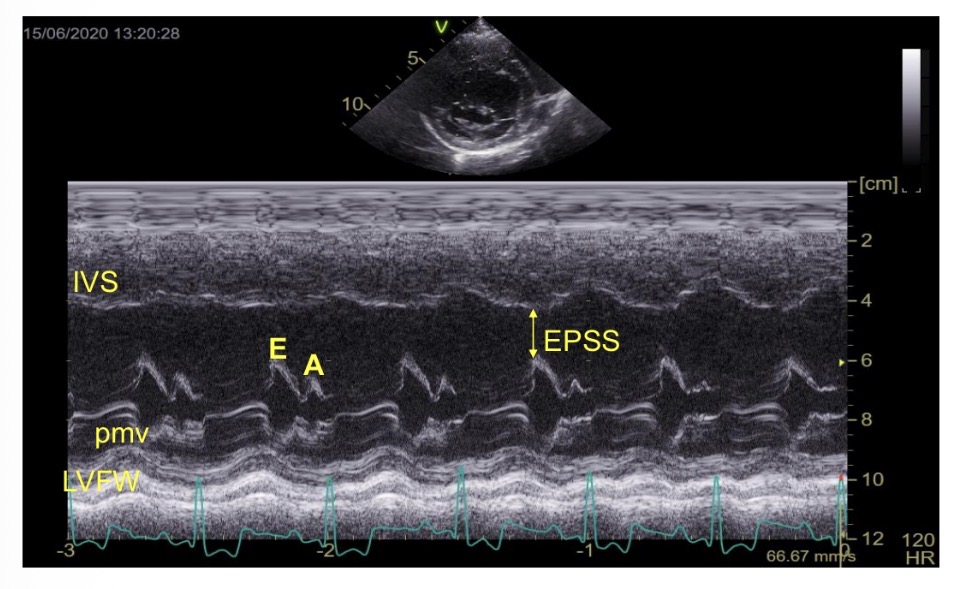
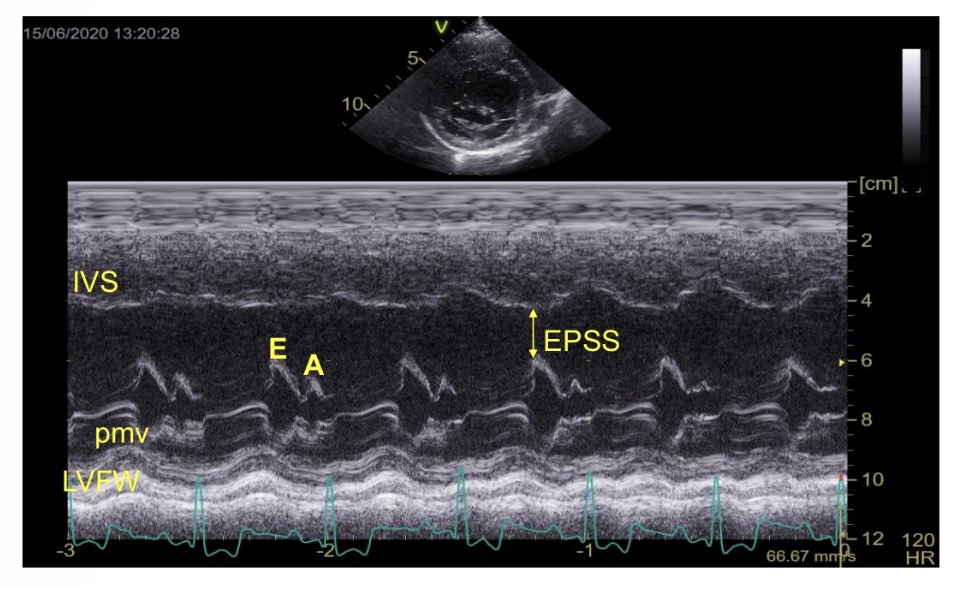
What is EPSS
E point to septal separation
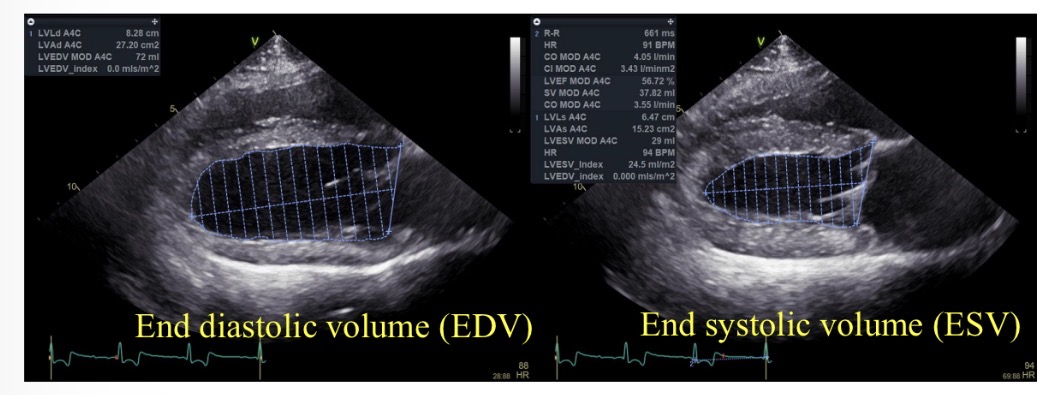
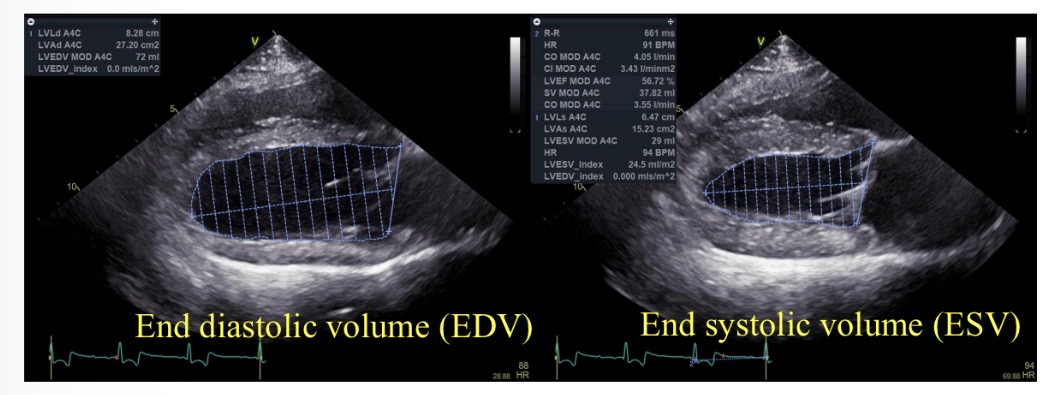
Ejection fraction (%) equation
((EDV-ESV) / EDV) x 100
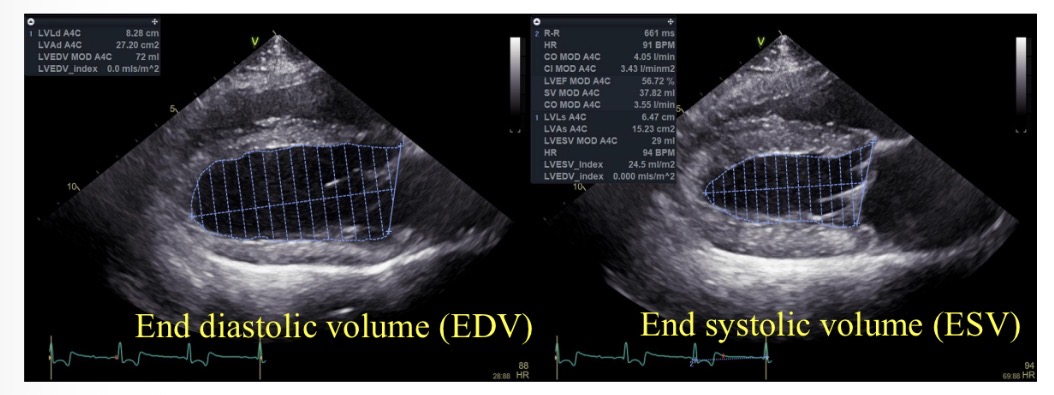
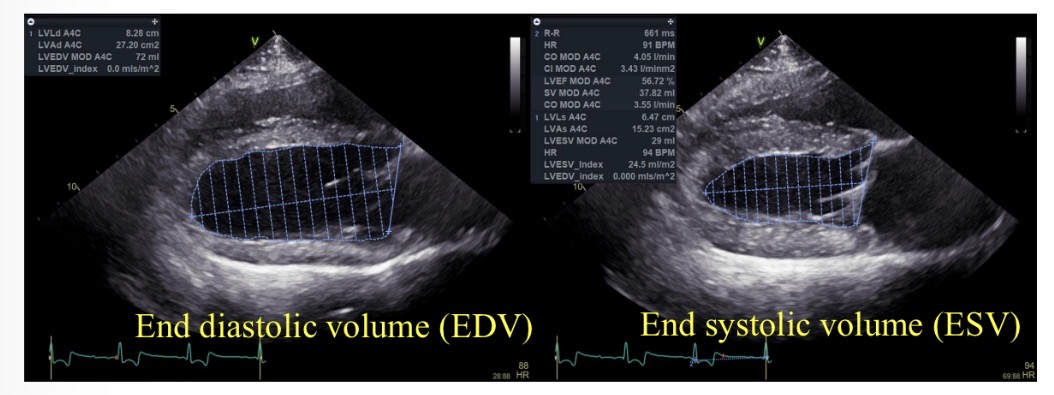
Normal ejection fraction
>50%
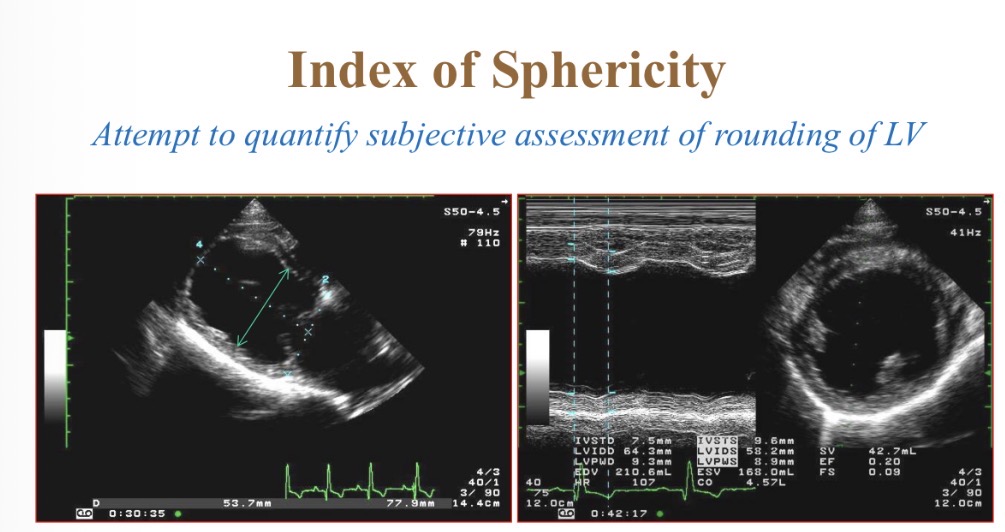
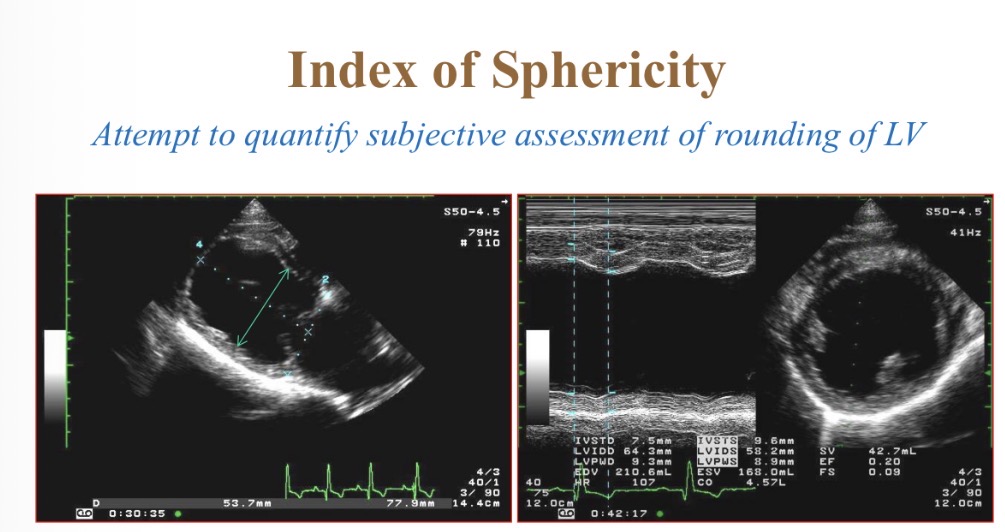
Index of sphericity for LV equation
LV length in diastole / LV width
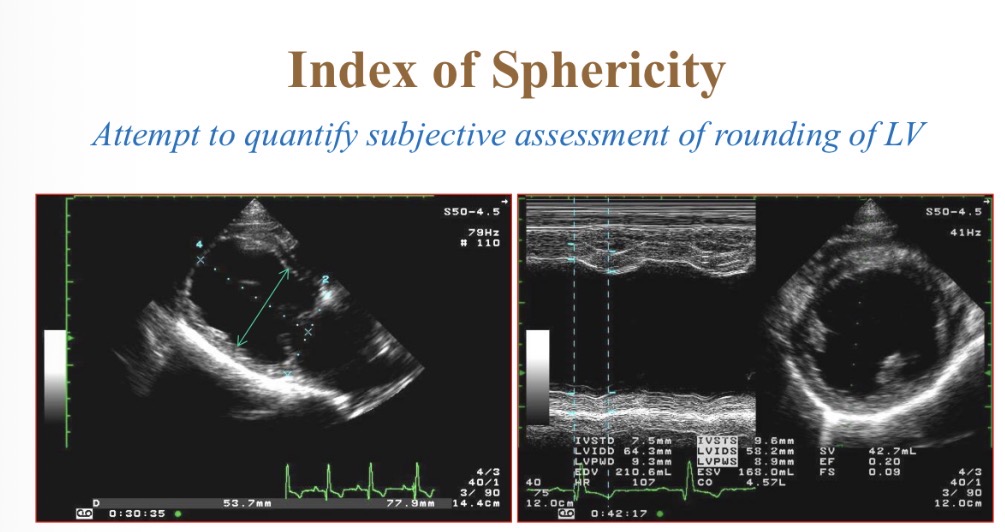
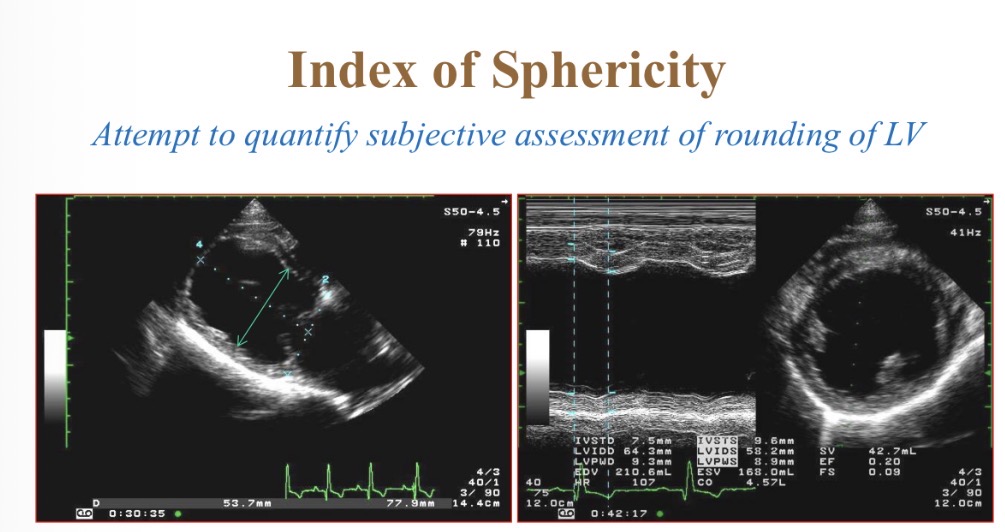
Index of sphericity for LV normal value
>1.7
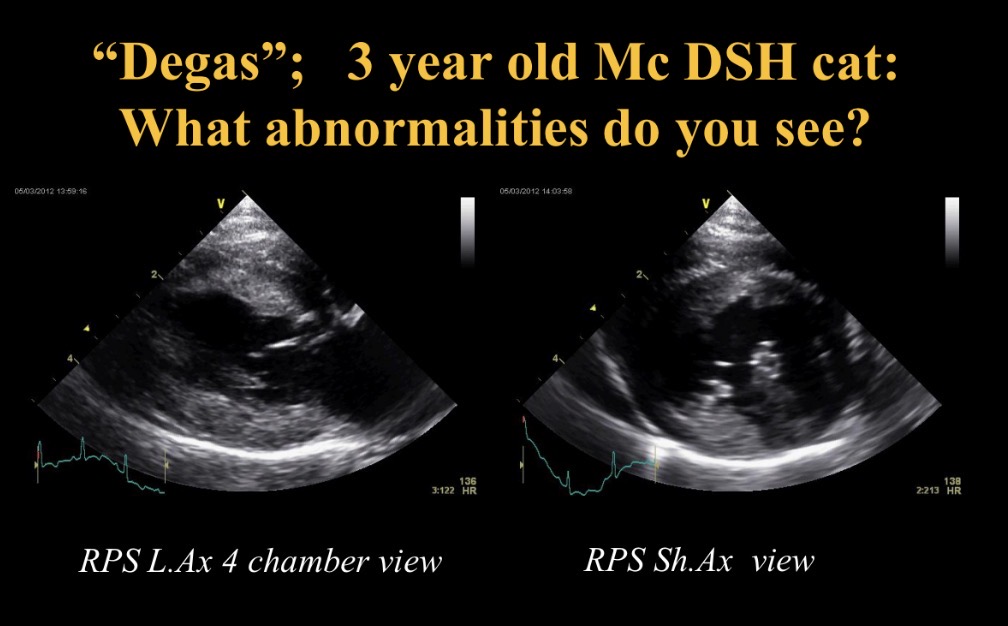
Abnormalities seen + potential causes
Concentric hypertrophy of LV
→ sub aortic stenosis, systemic hypertension, hypertrophic CMP
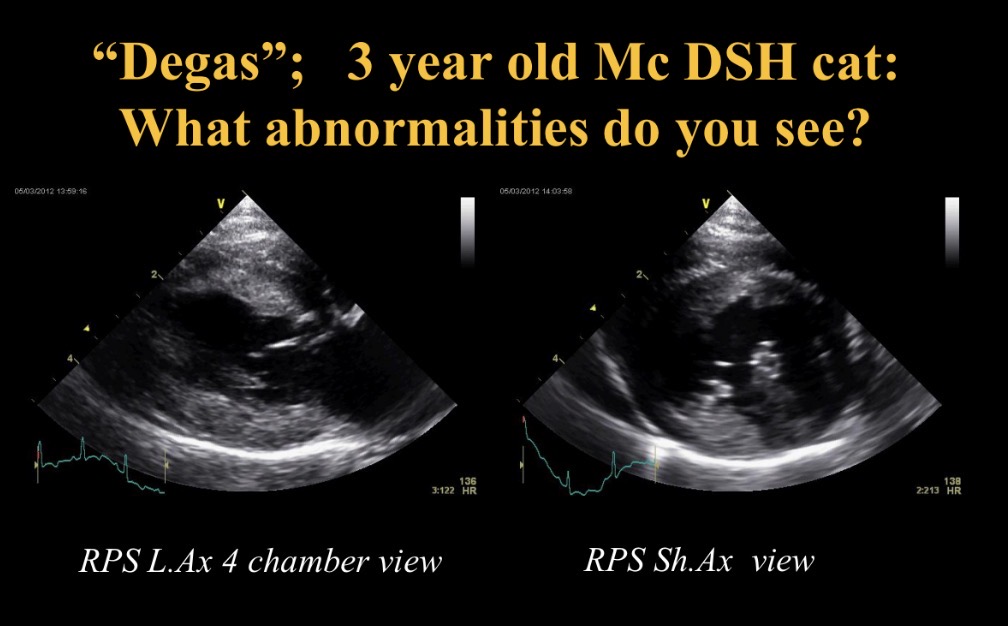
Abnormalities seen +CS/ what happens
Pericardial effusion (attached to heart base, collapsed RA in diastole)
→ collapse, R heart failure
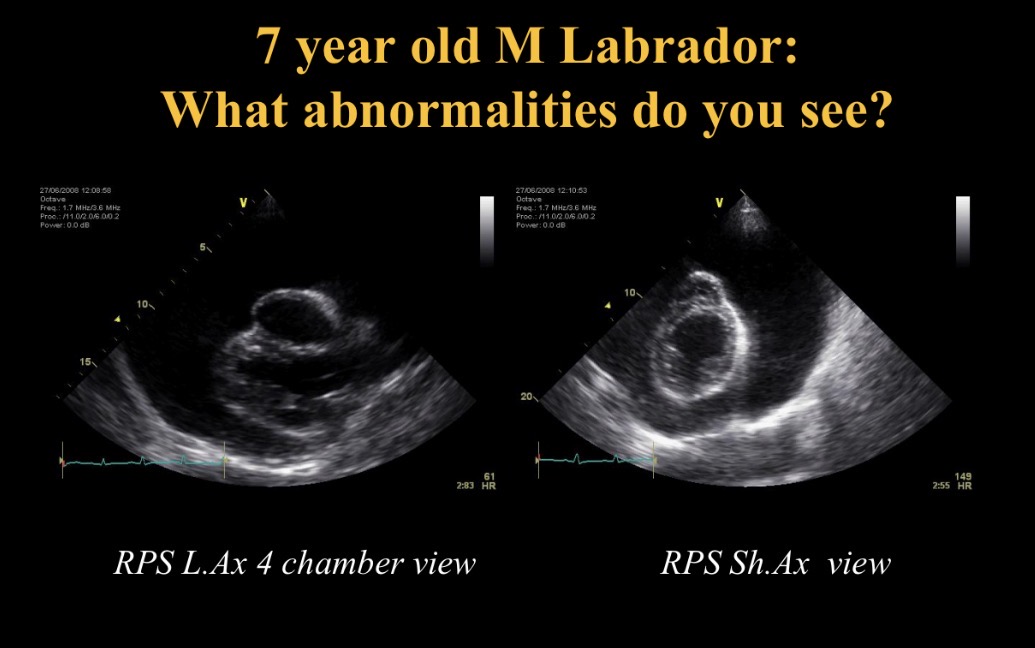
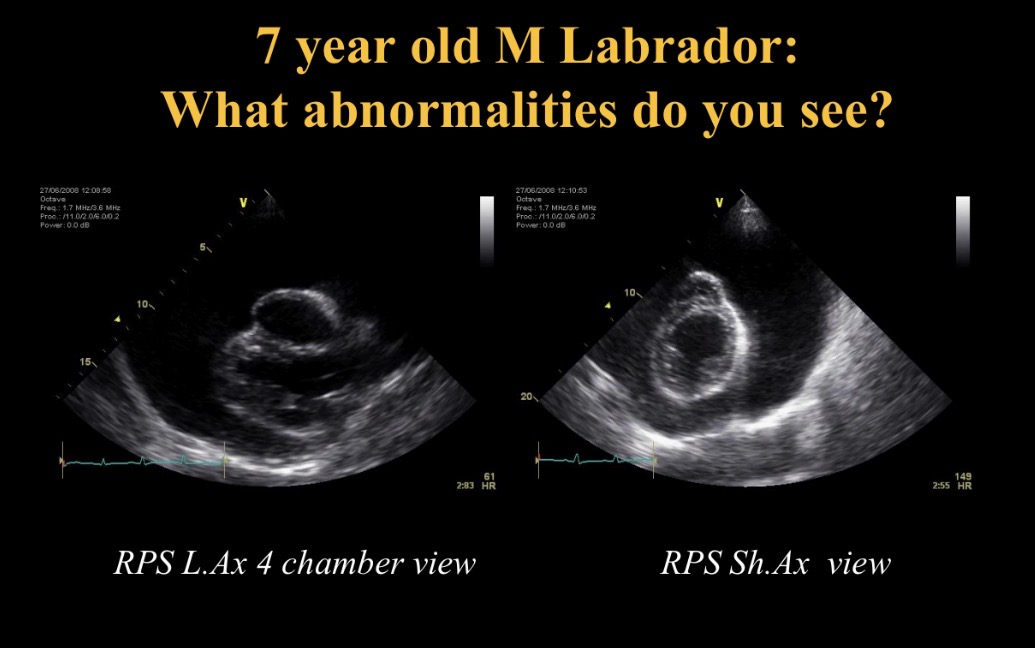
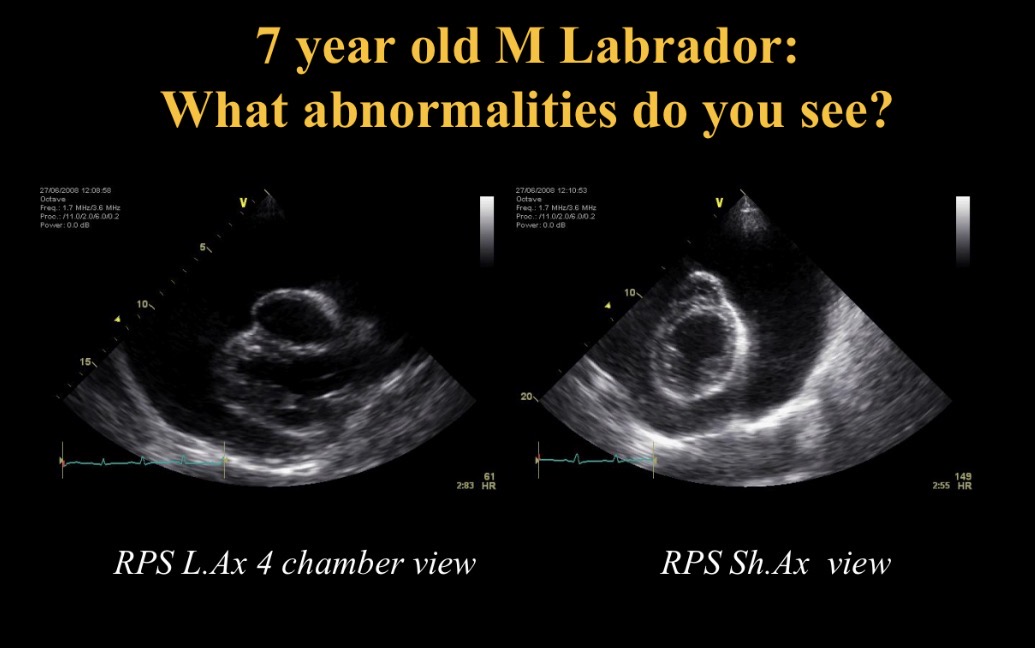
Cardiac tamponade
Collapsed RA due to pericardial effusion
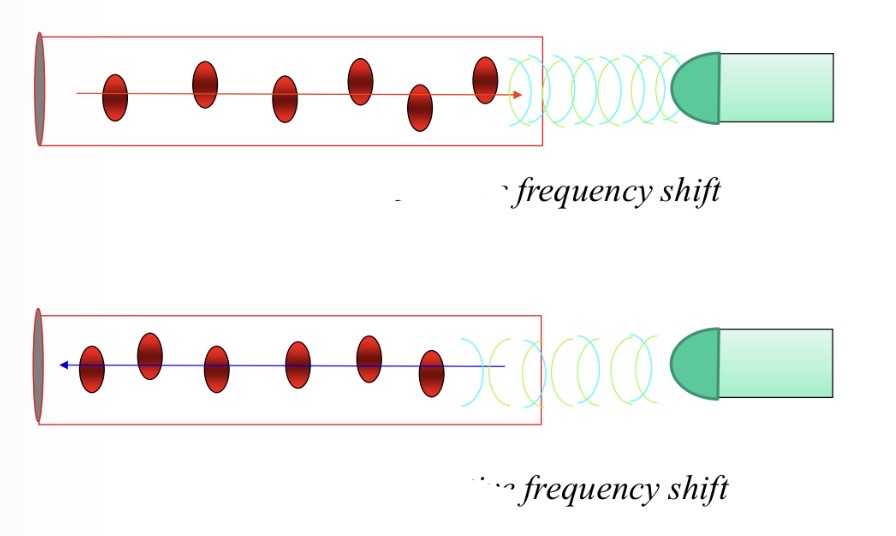
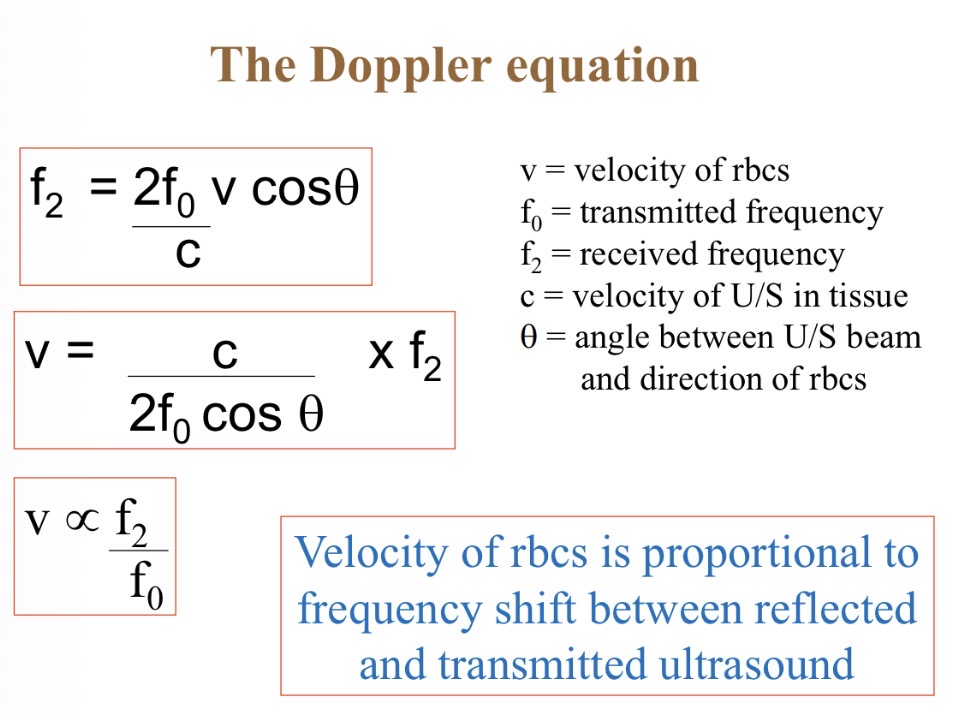
How does a Doppler work
Blood towards transducer → high frequency reflection → positive frequency shift
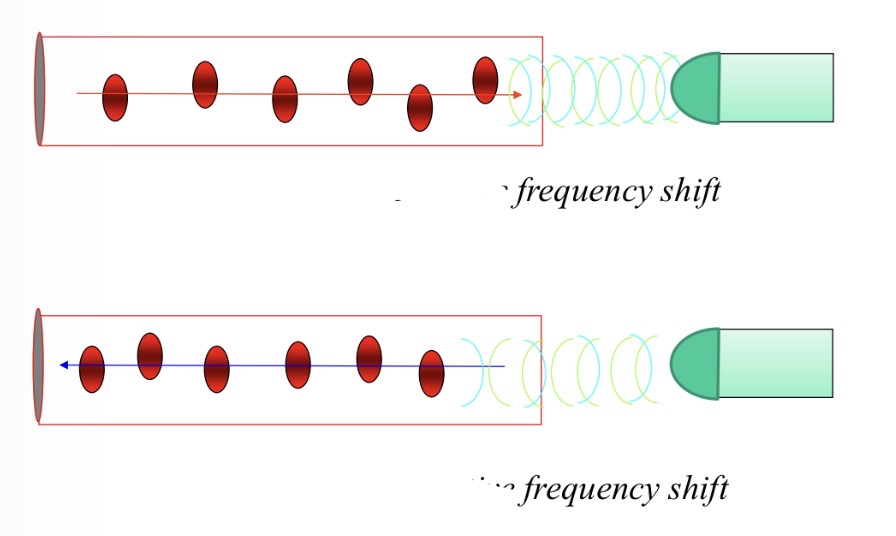
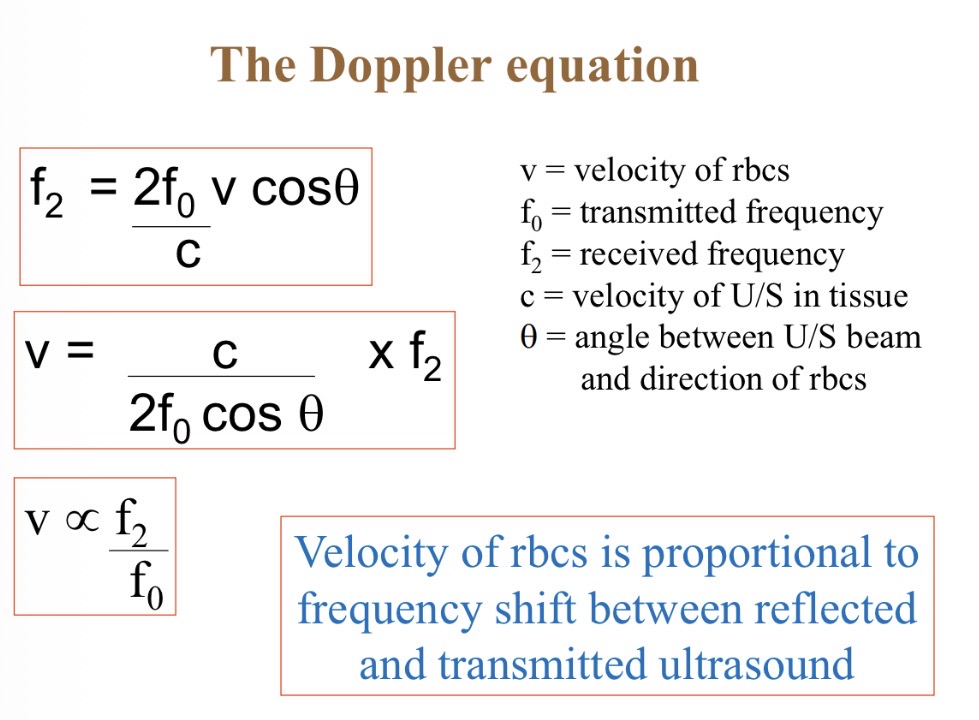
Why is it important for Doppler to be parallel to blood flow
Cos = 1 so accurate reading of blood velocity
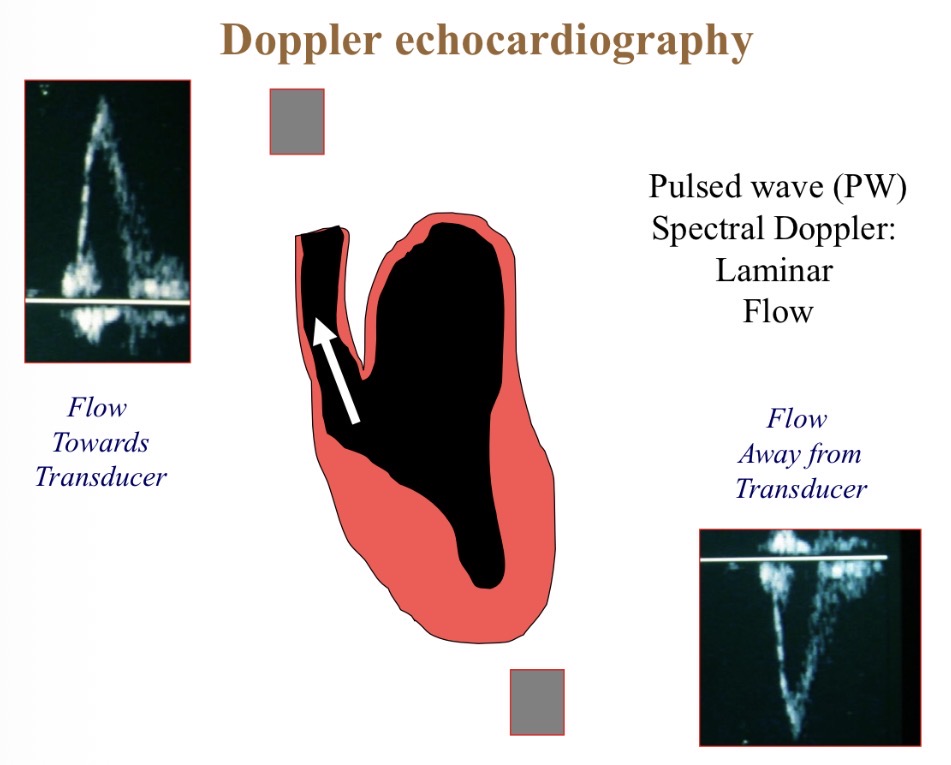
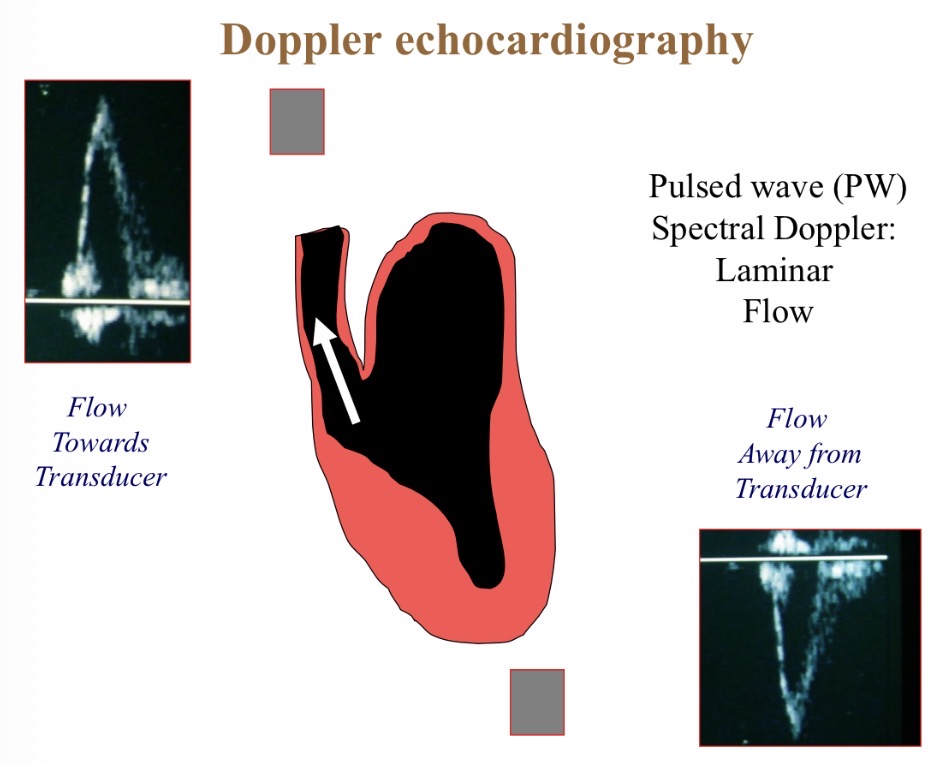
What does the blue line show
RBC velocity (acceleration + deceleration)
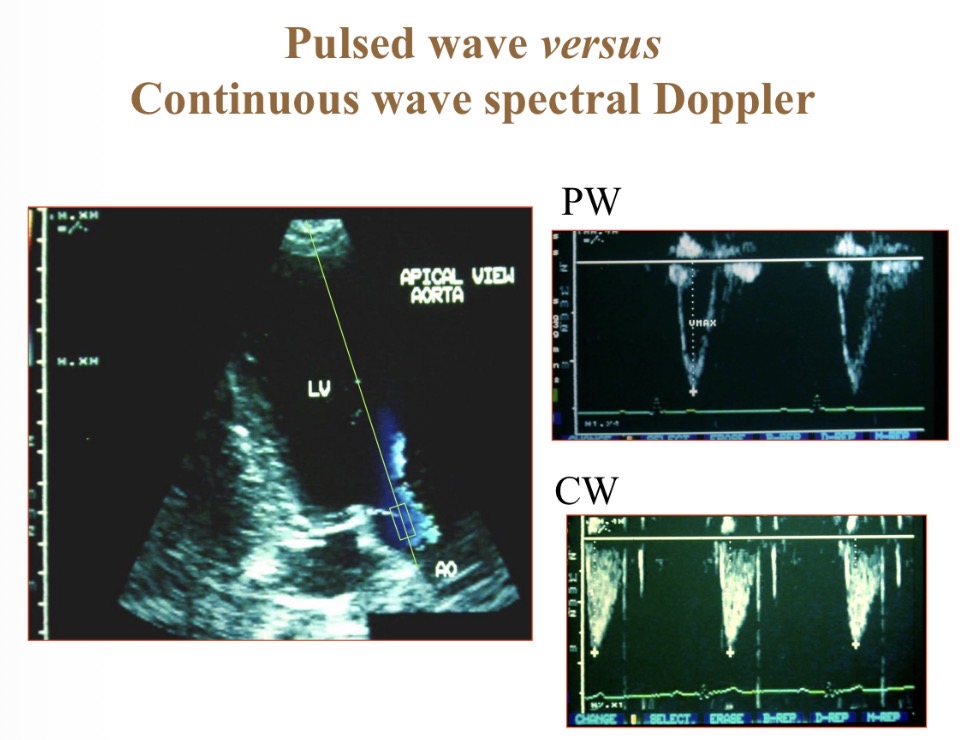
Pulsed wave Doppler
Focuses on 1 area (box) so more accurate than continuous
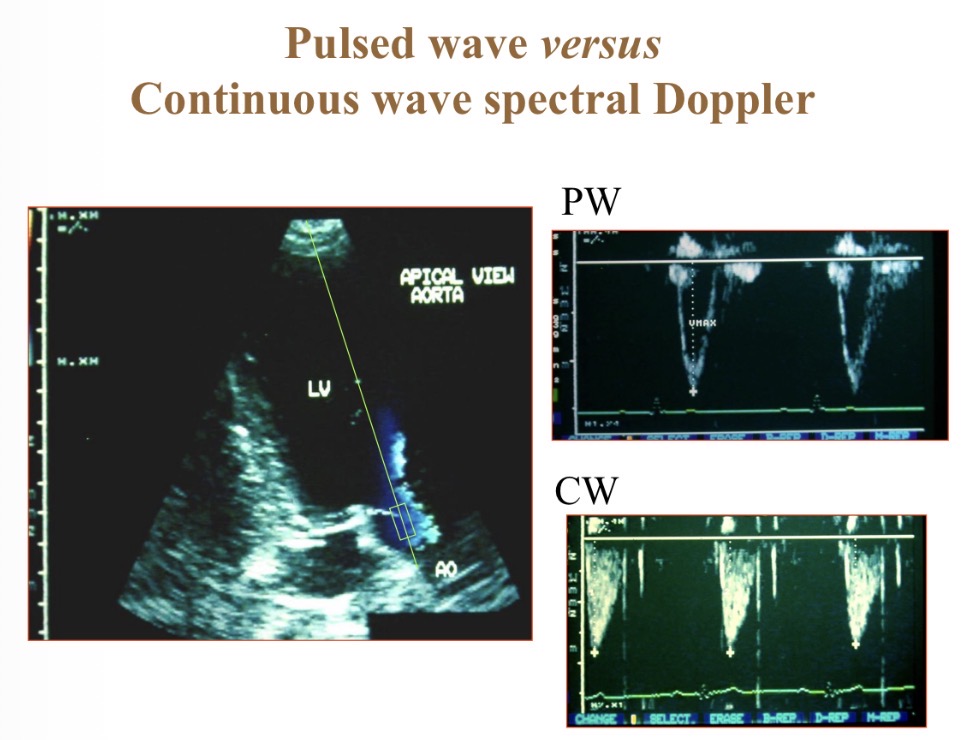
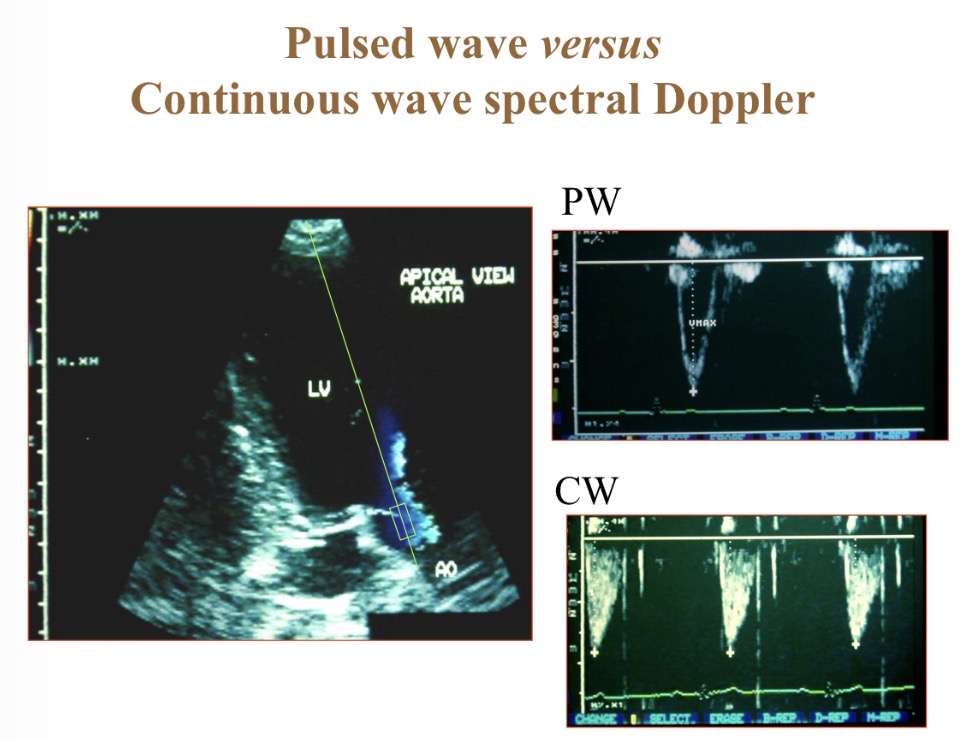
Continuous wave Doppler
Shows velocity at multiple depths
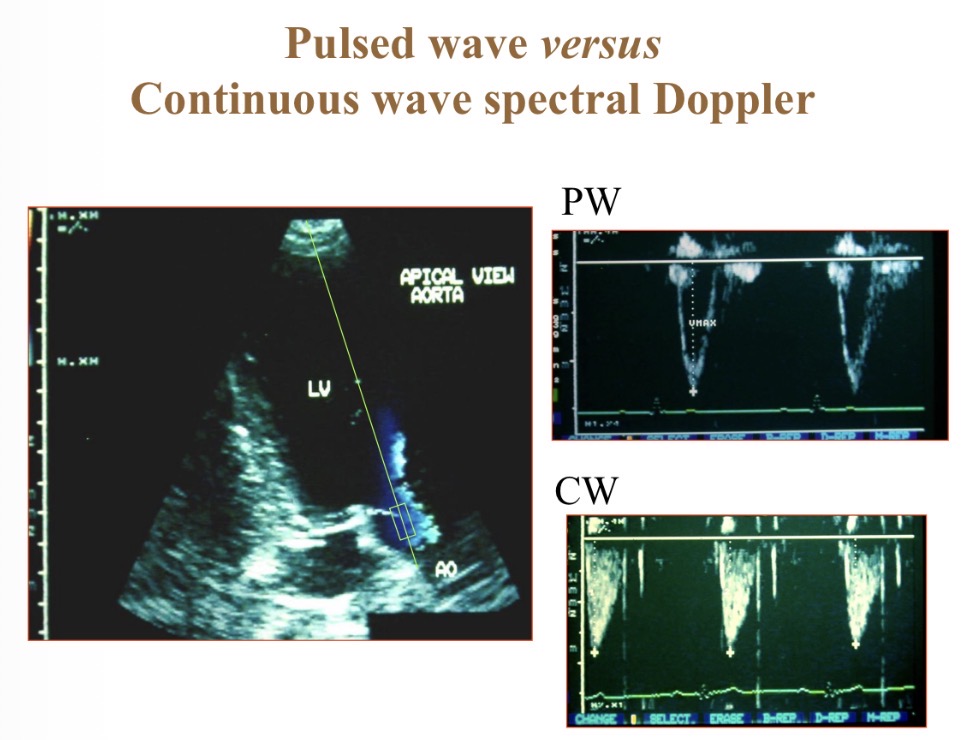
Pulsed vs continuous wave spectral Doppler
P- spatially specific
C- depth recording, high velocity

Which shows laminar flow
A


When is turbulent flow seen
Valve regurgiation

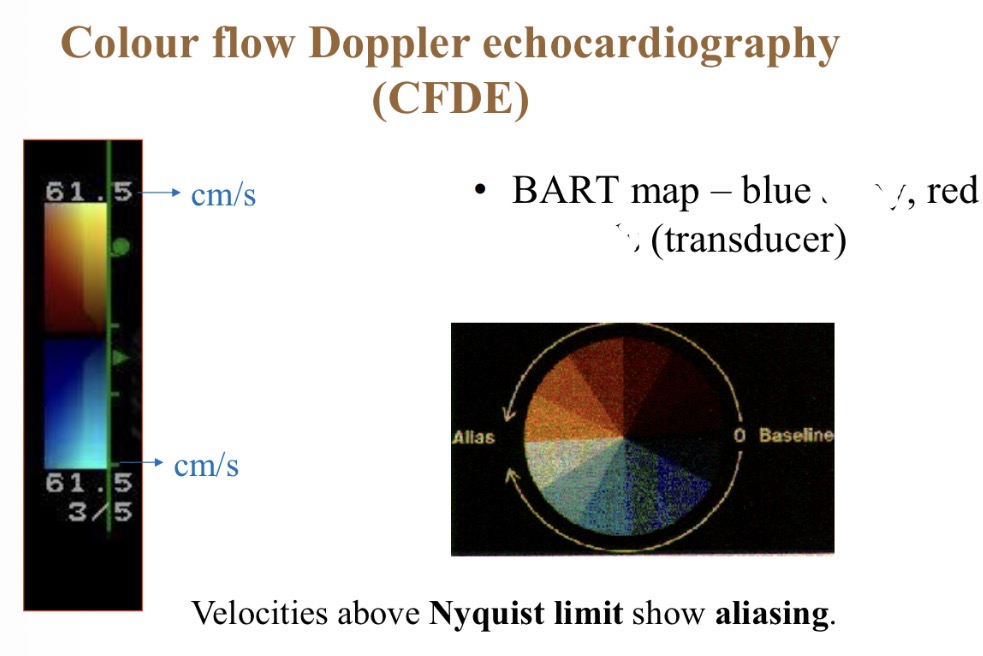
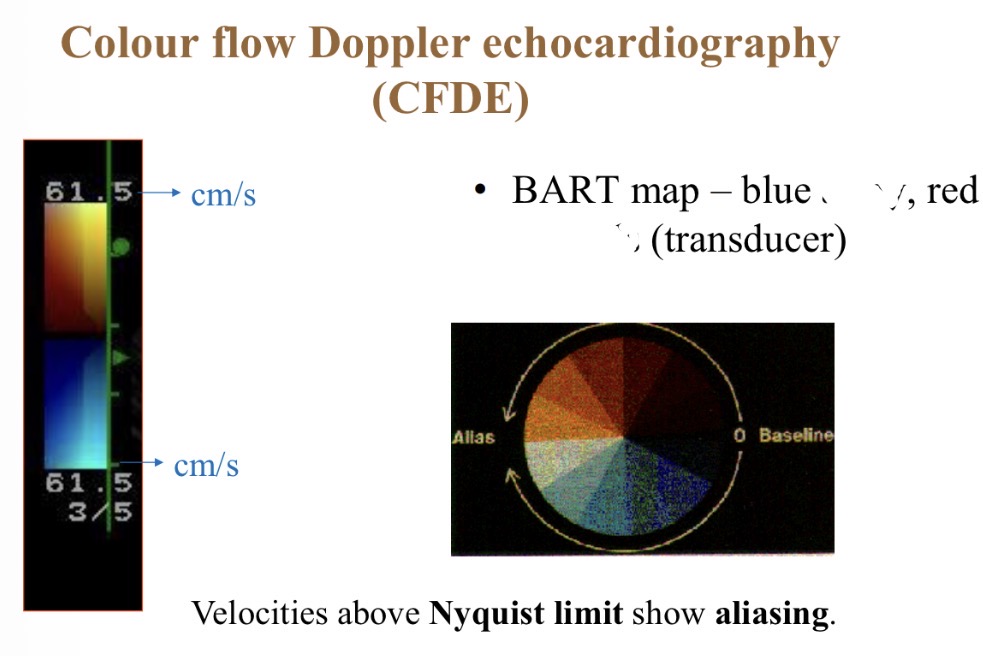
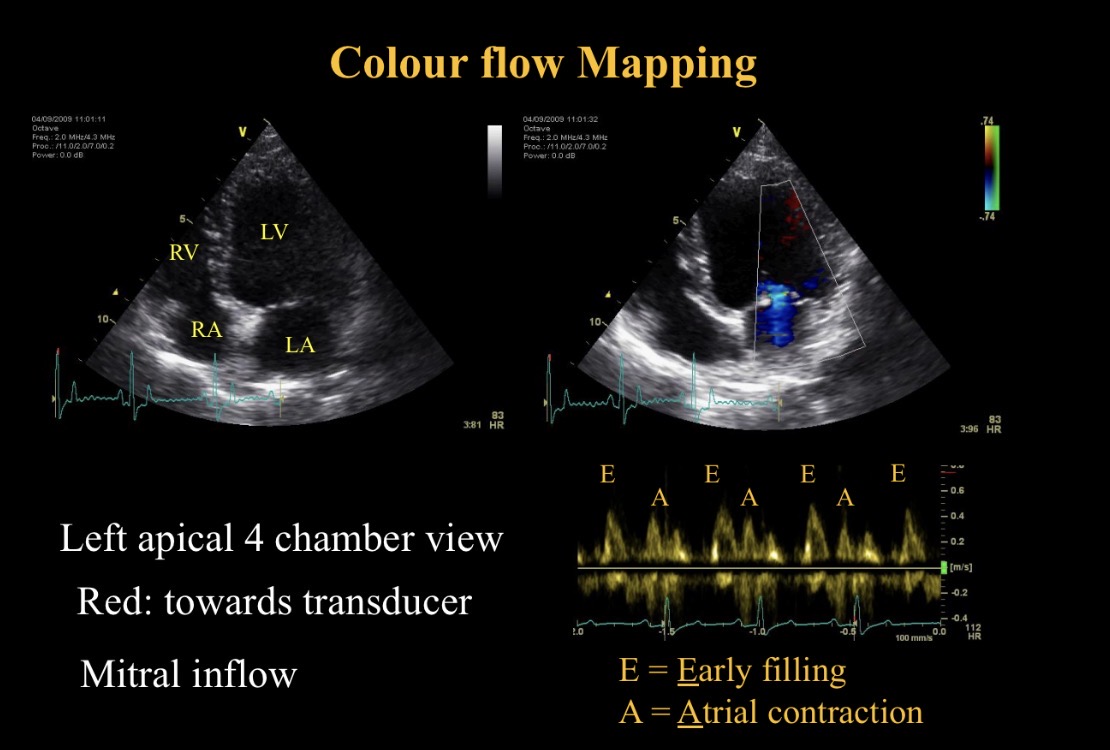
Colour flow Doppler - red colour meaning
Towards probe
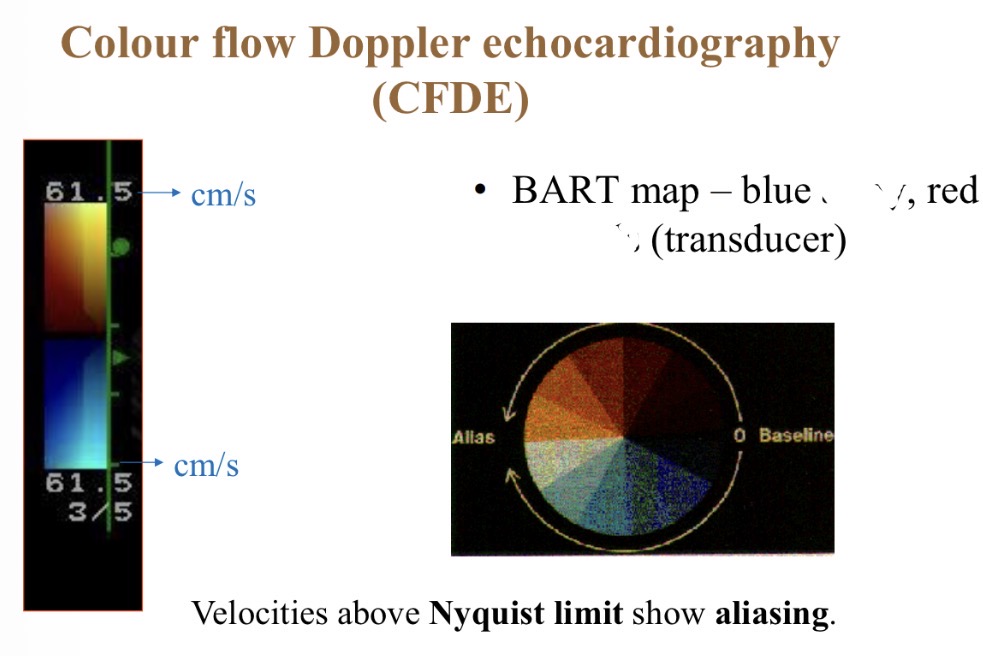
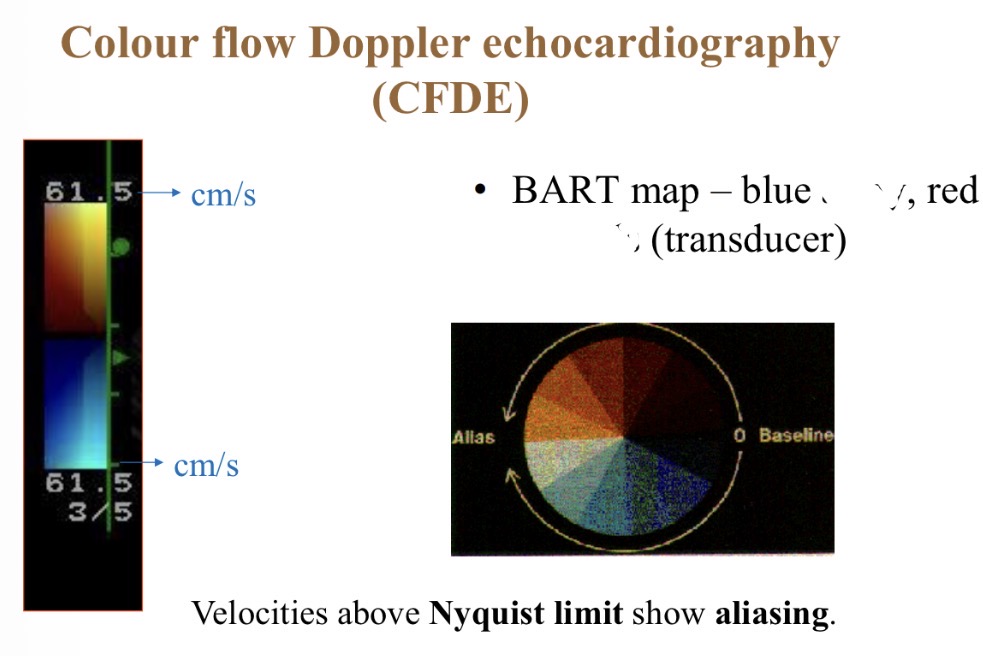
Colour flow Doppler - Blue colour meaning
Away from probe
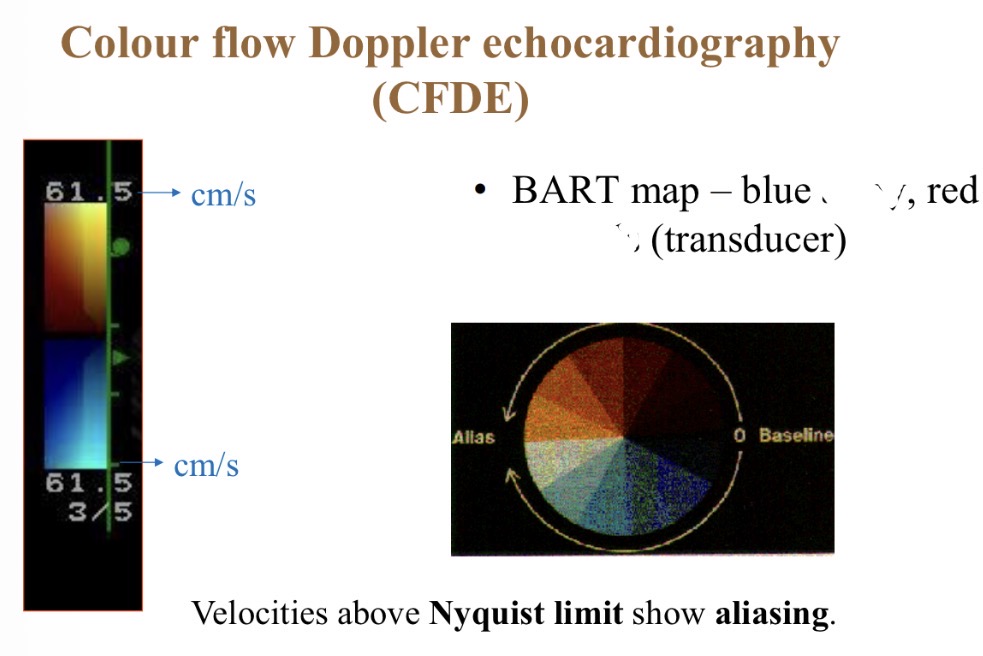
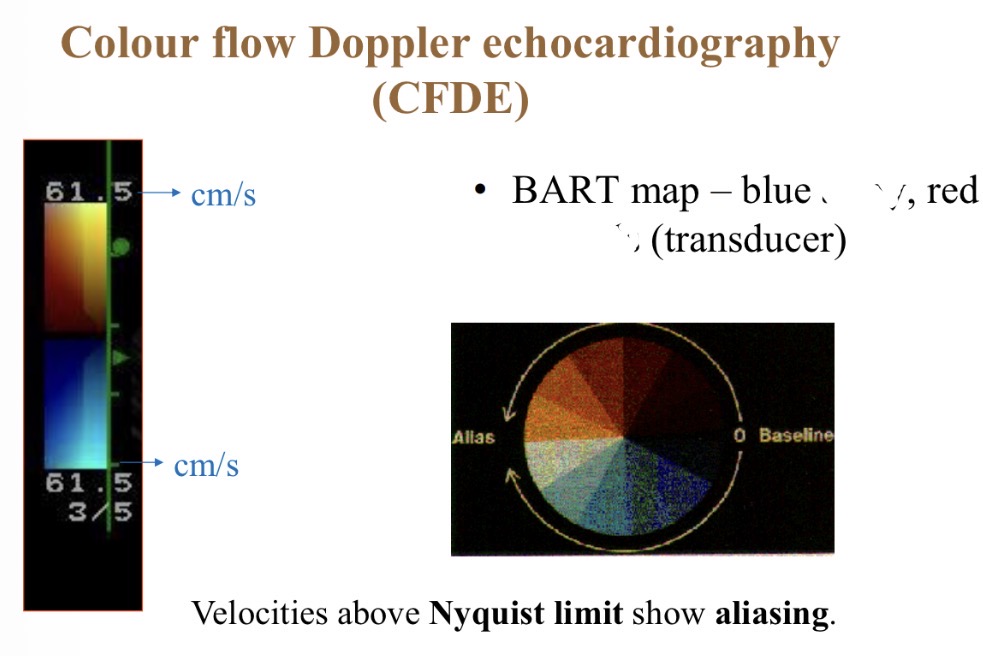
Colour flow Doppler - Best range for accurate colours
1- 80cm/s
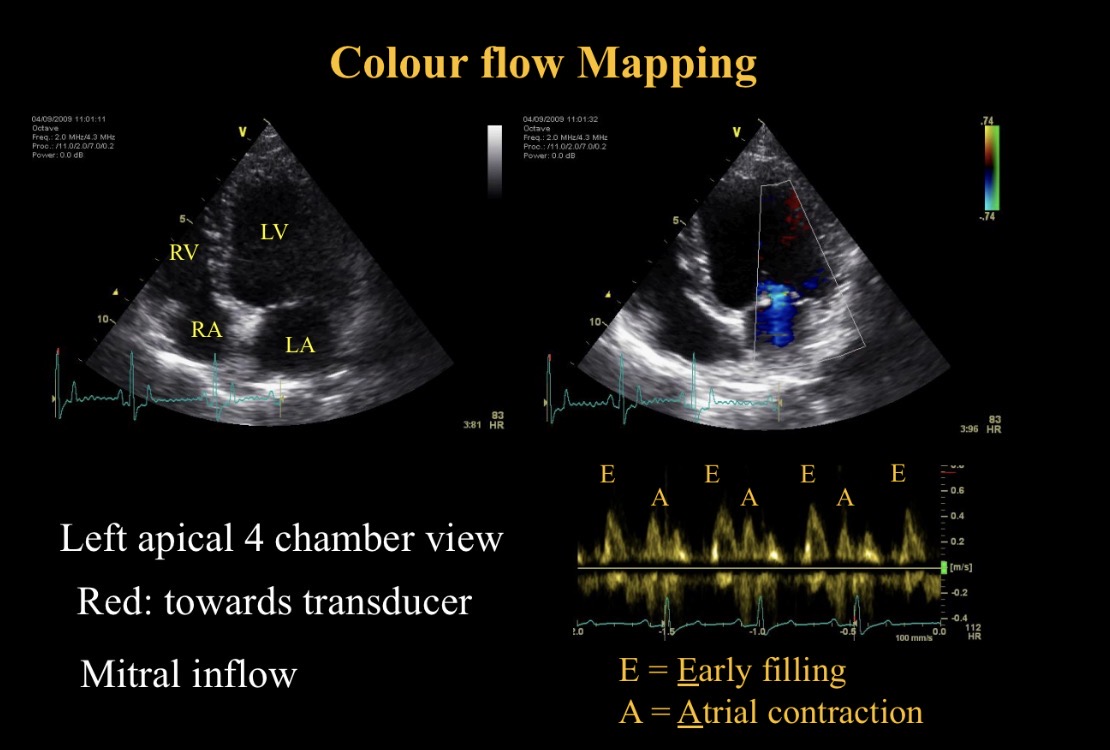
E peak meaning
Early filling - mitral valve opening
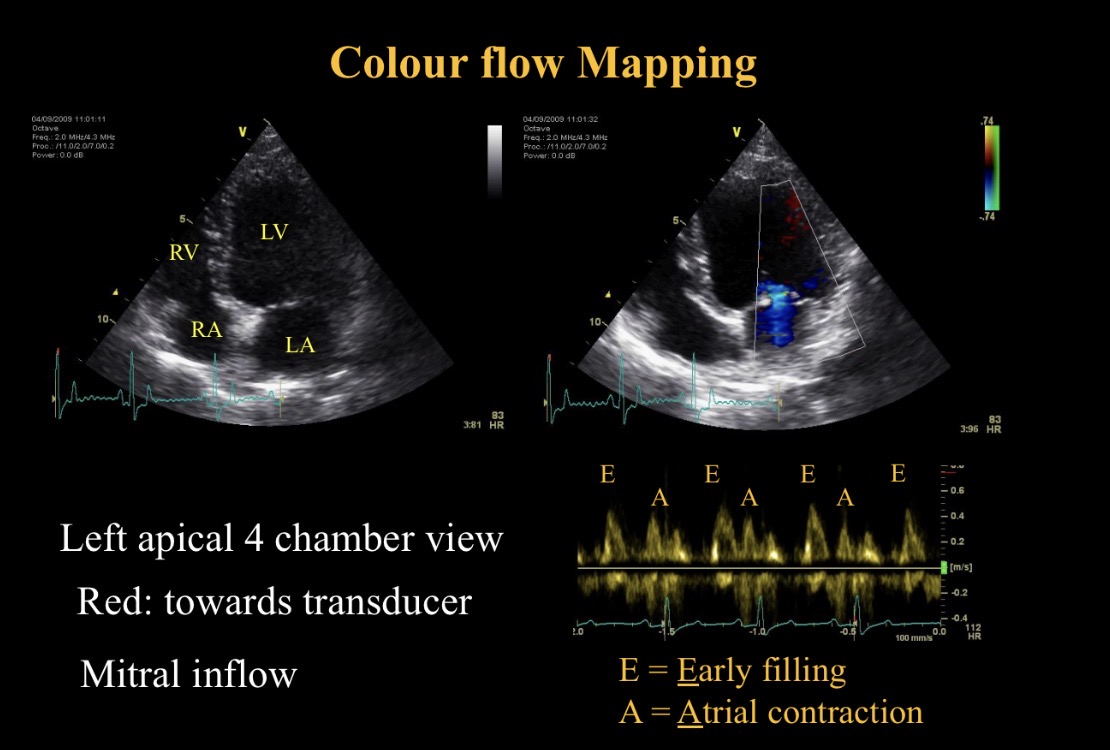
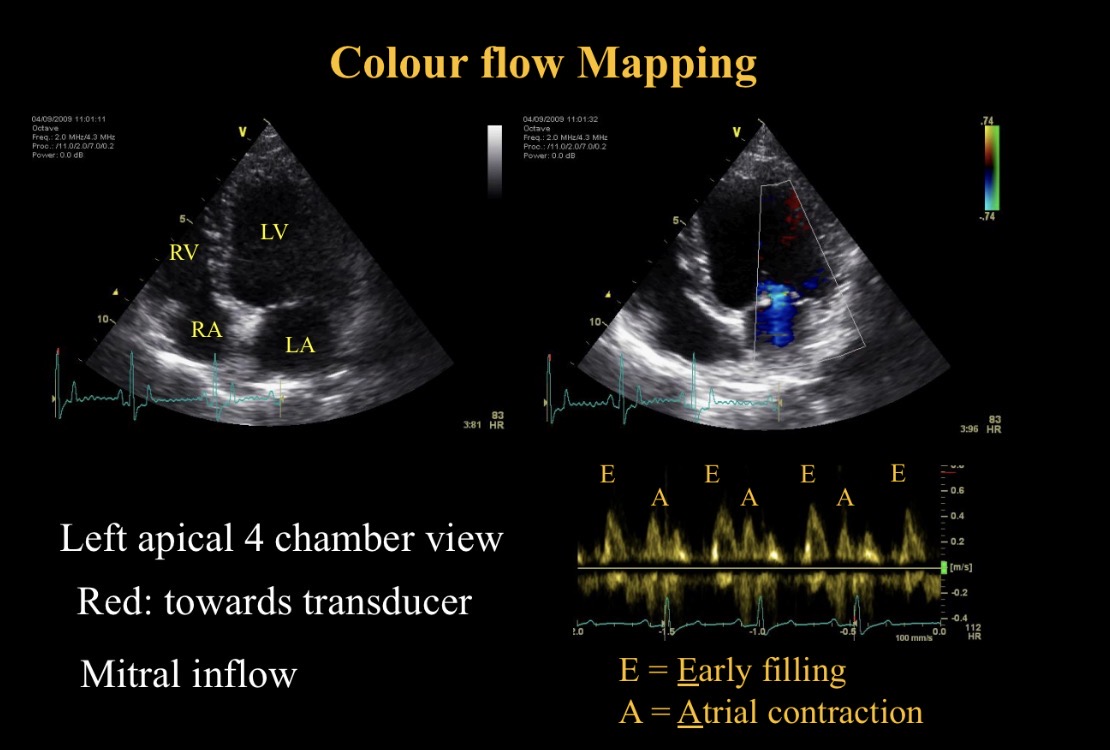
A peak meaning
A contraction
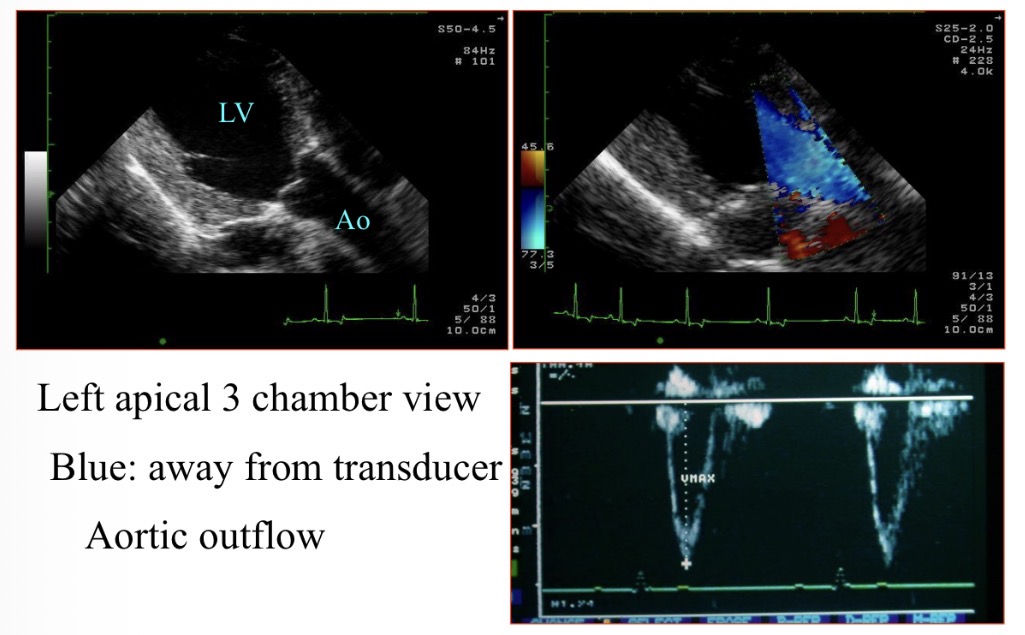
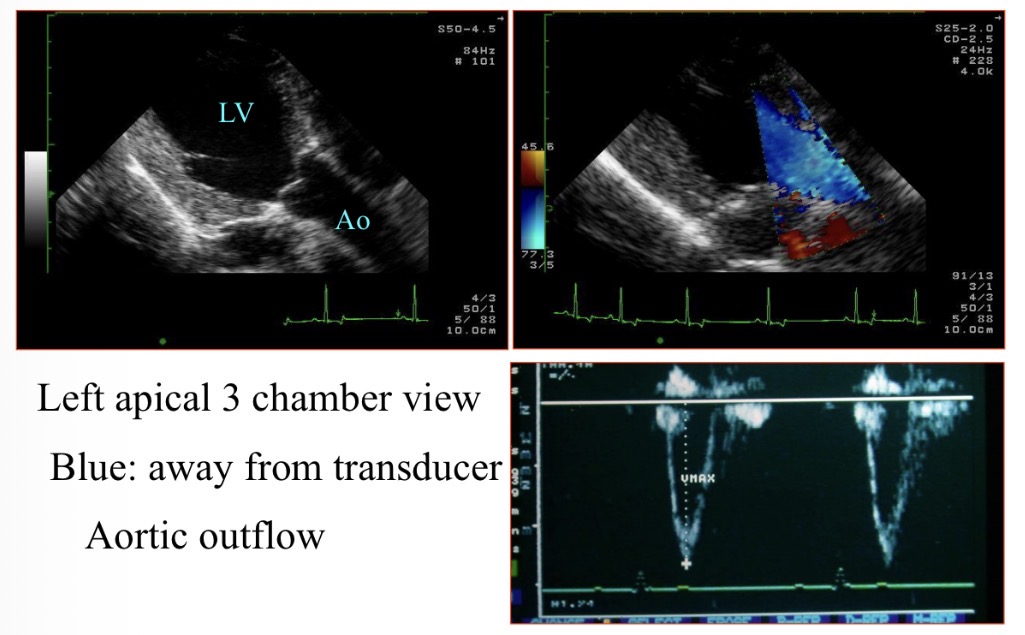
Why is the blood blue when moving LV → aorta
Away from probe
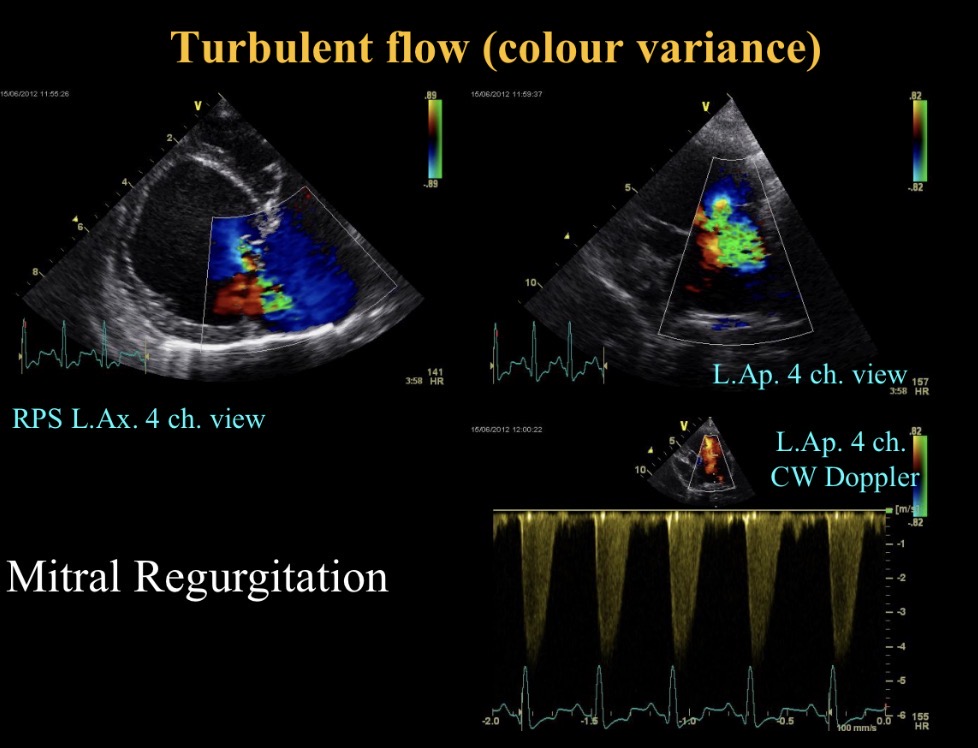
Green colour meaning + common cause
Turbulent flow (M regurgitation)
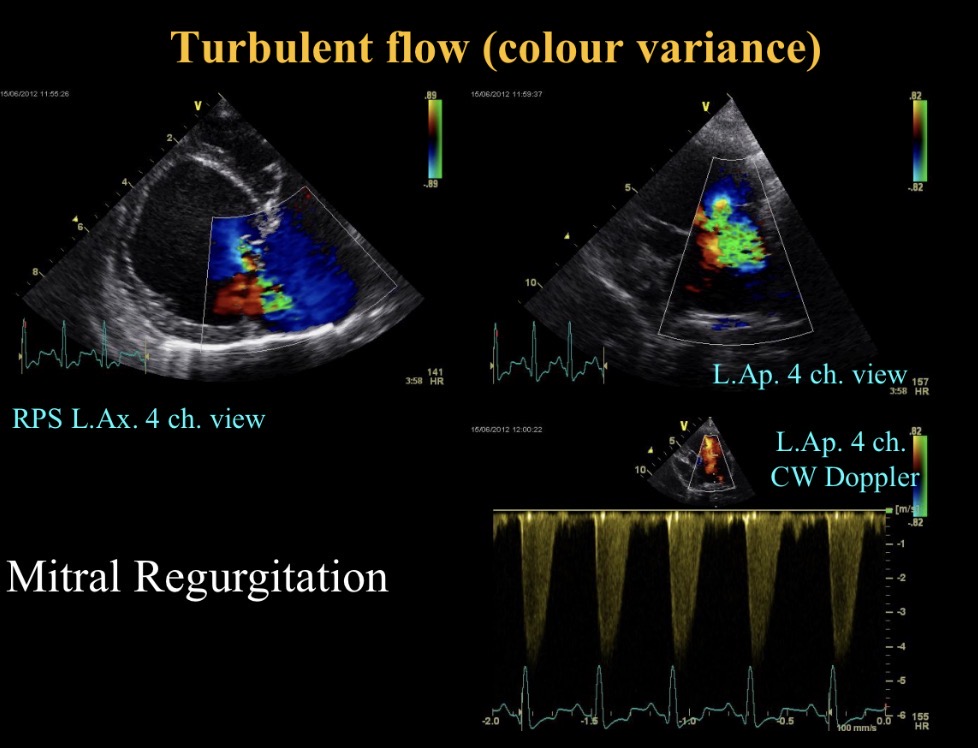
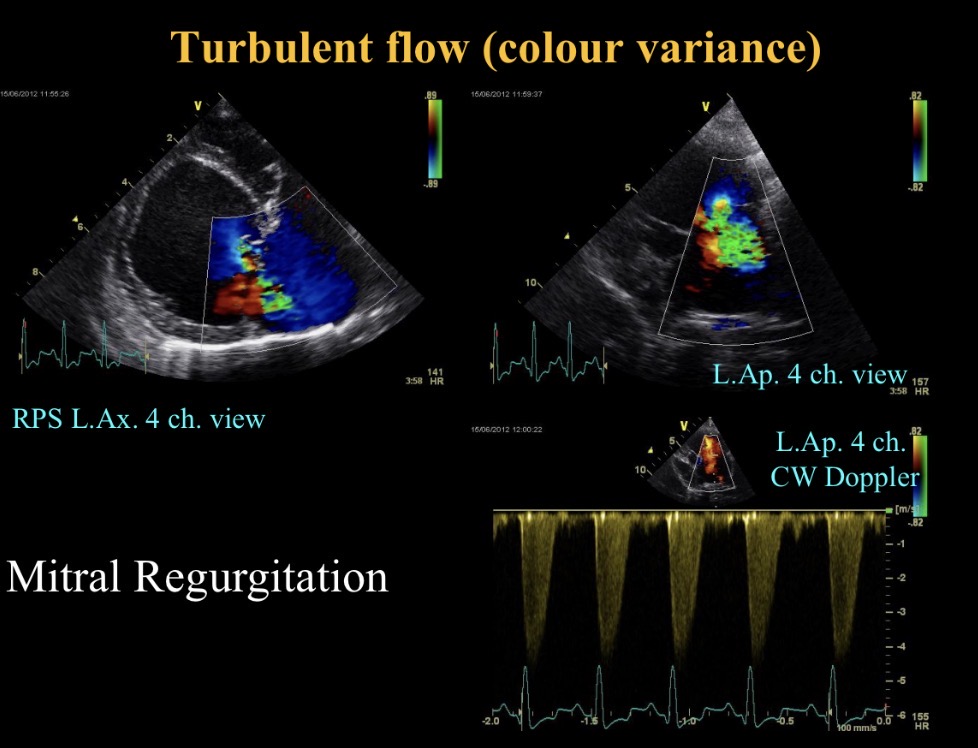
When is continuous wave used (view)
Parallel to flow
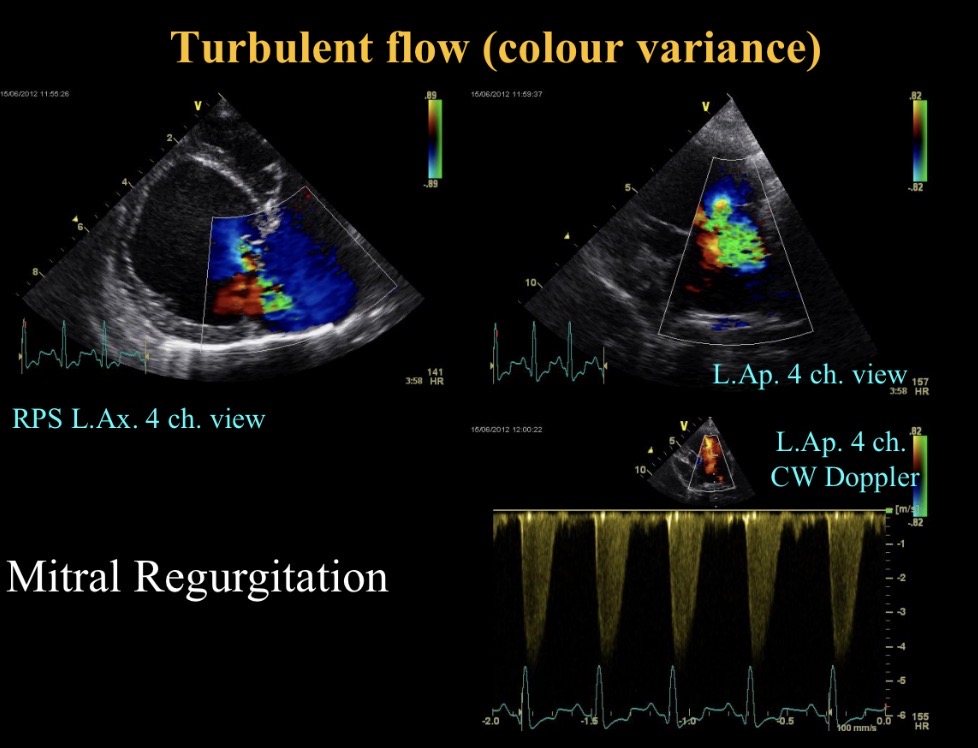
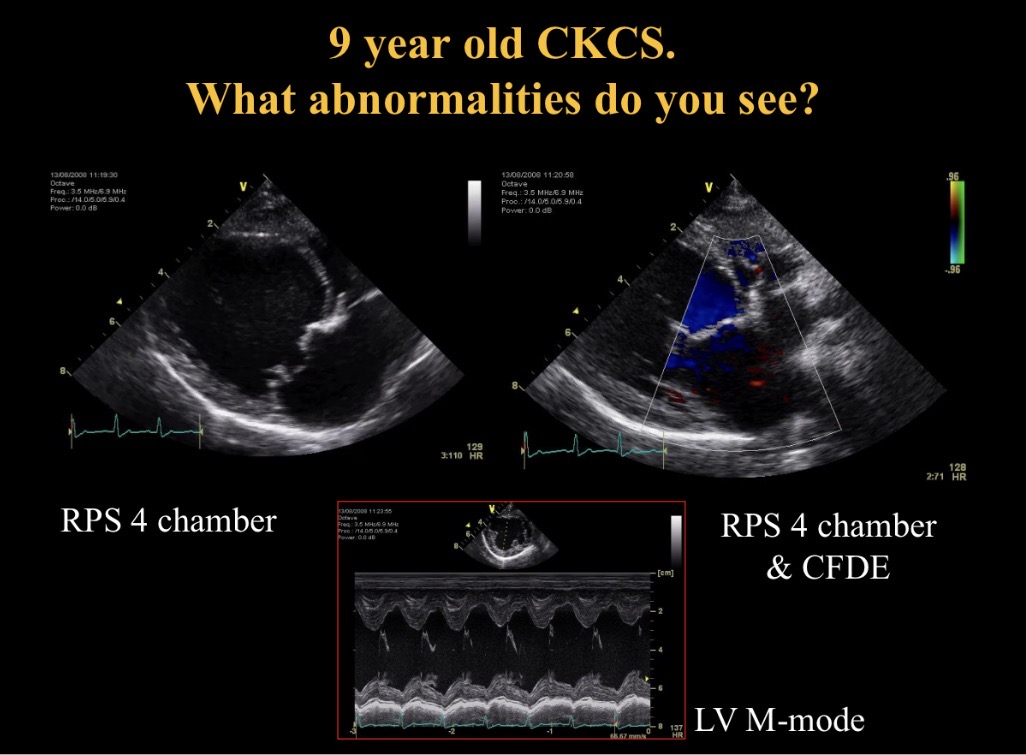
Abnormalities seen
M valve nodular thickening, prolapse + sev M regurgitation
LA dilation
Nodules moving with valve so not endocarditis
Myxomatous mitral valve disease
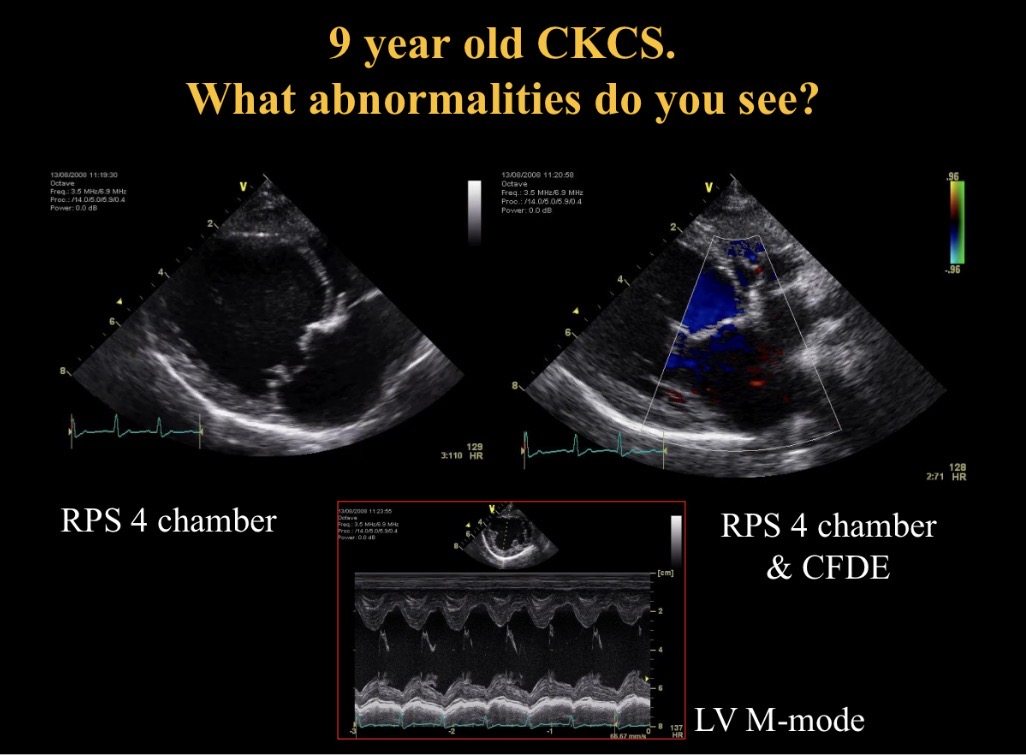
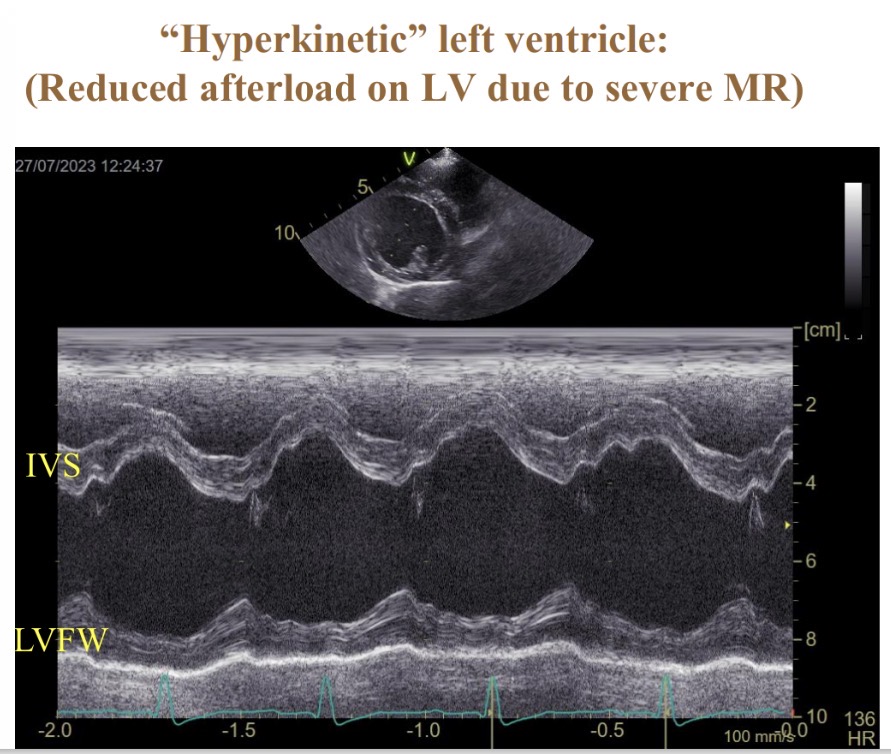
What is IVS (hyperkinetic in mitral valve disease)
Inter V septum
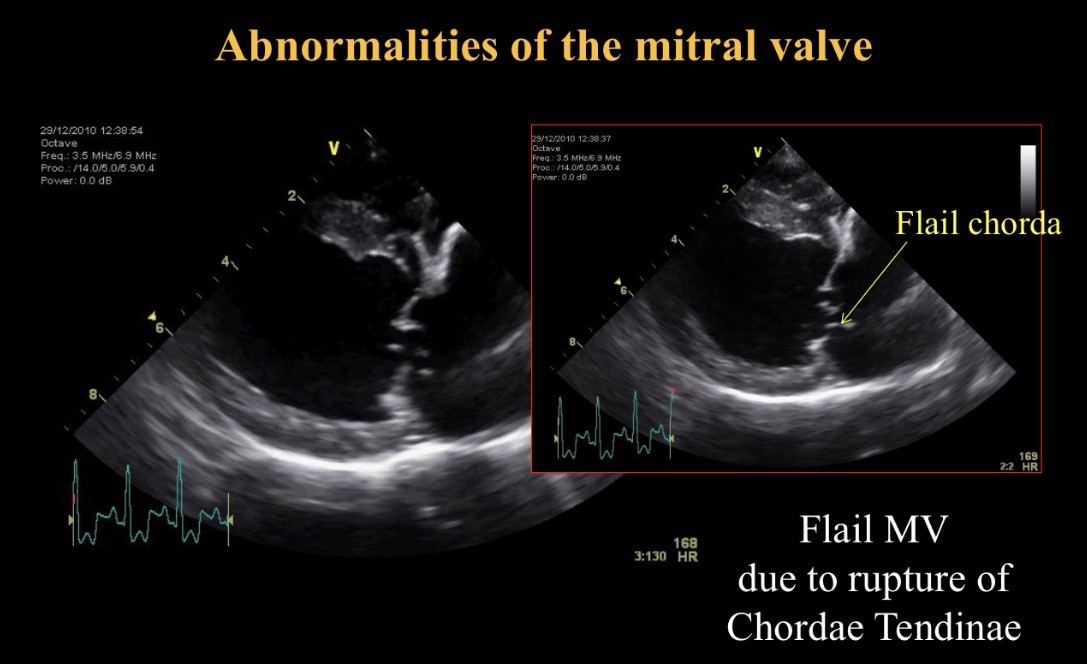
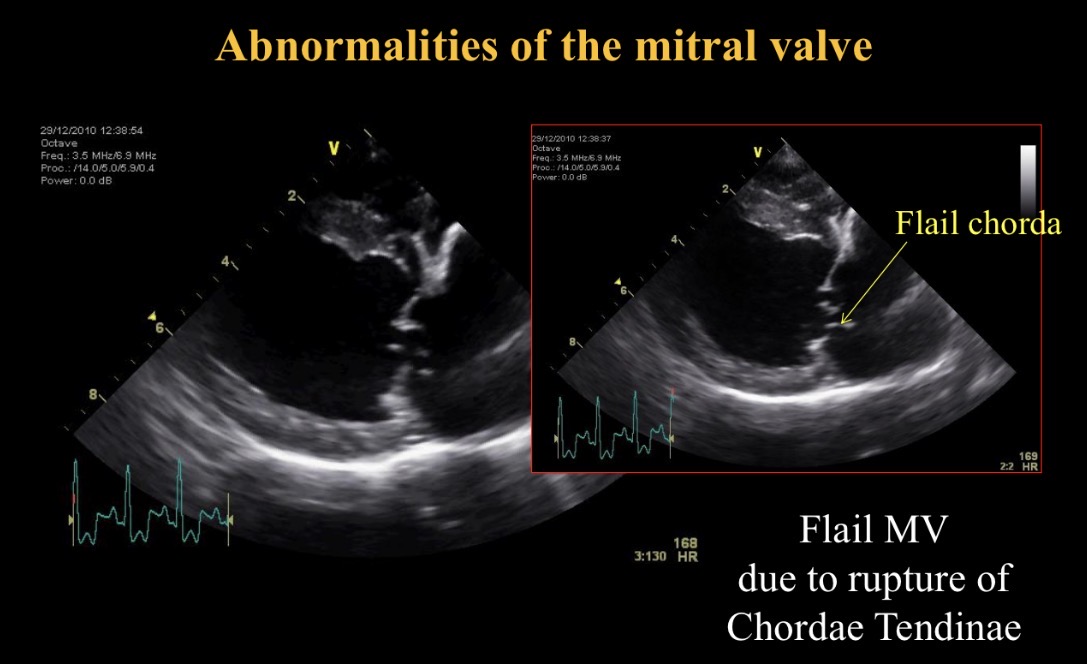
Flail chorda def
Ruptured chordae tendinae in mitral valve disease
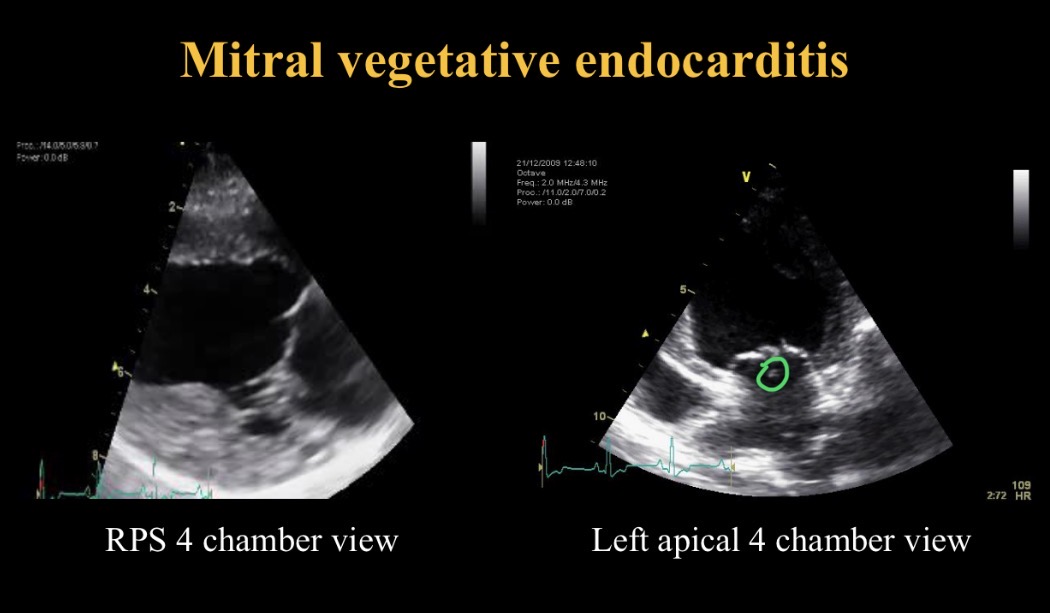
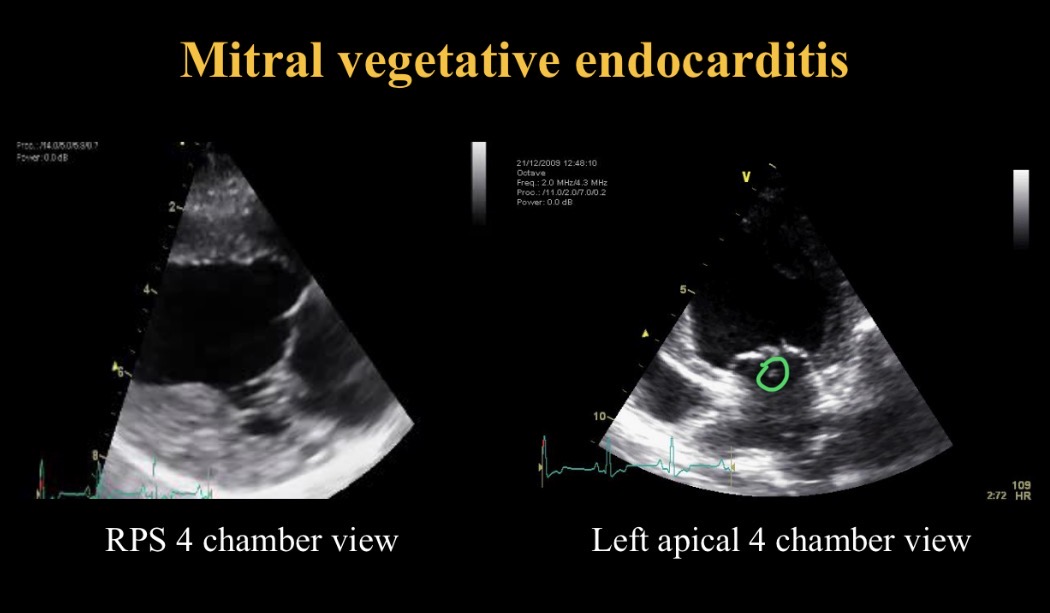
Endocarditis appearance
Nodules move independently of valve (thromboemboli)
Inf CS
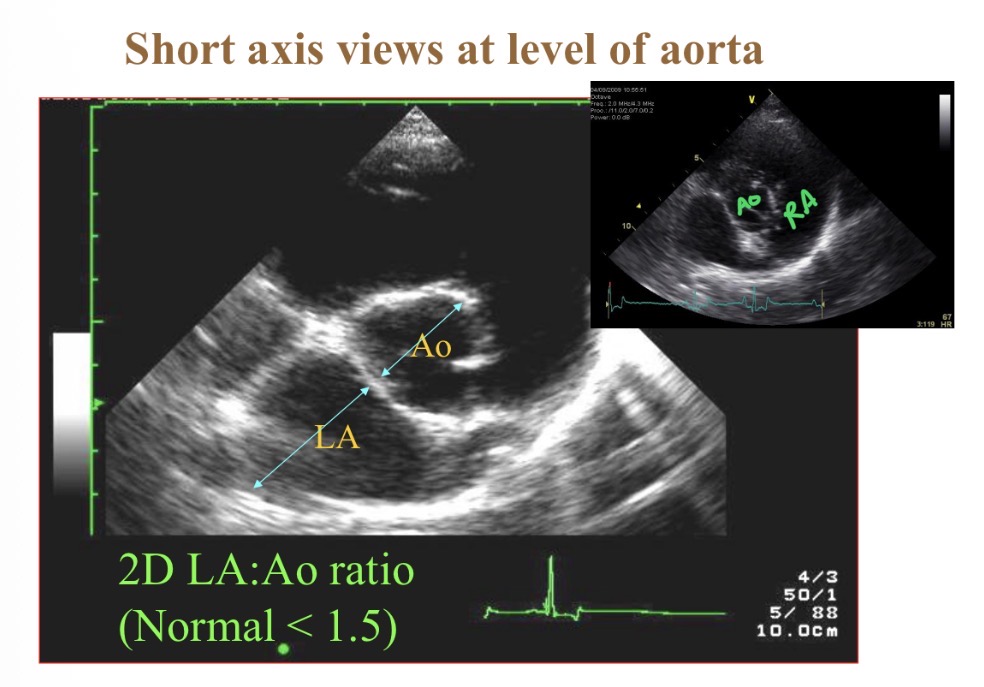
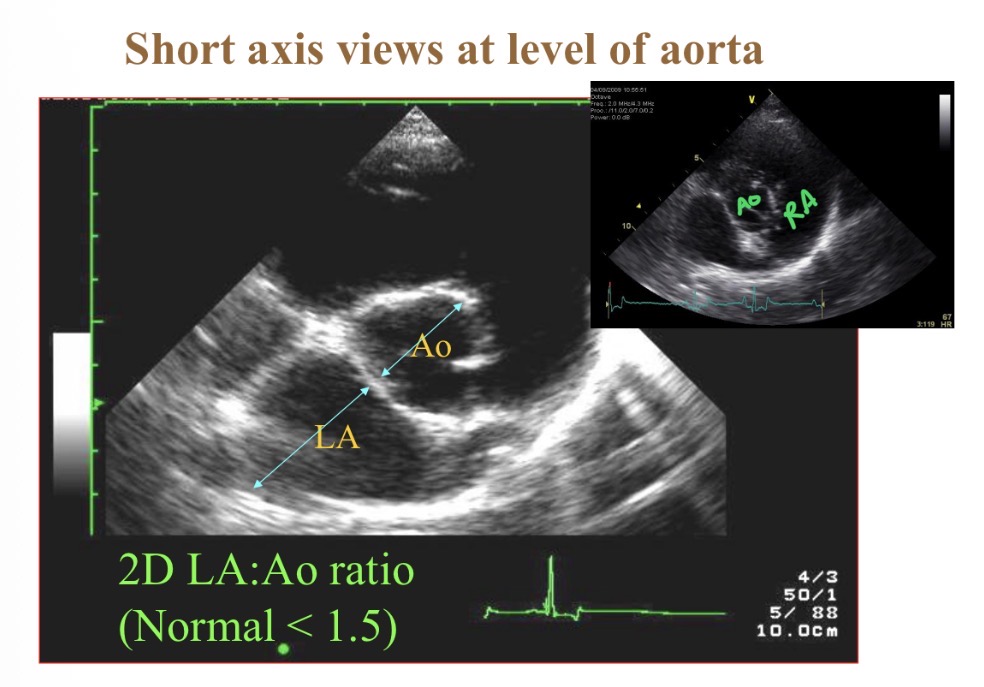
What is most central structure in short axis view at base
Aorta
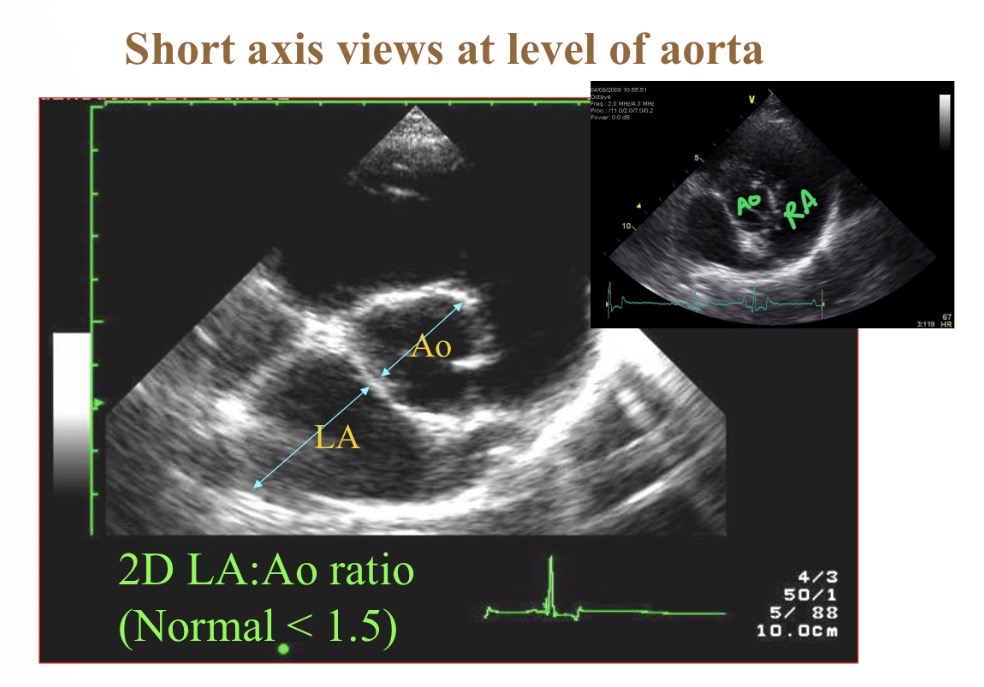
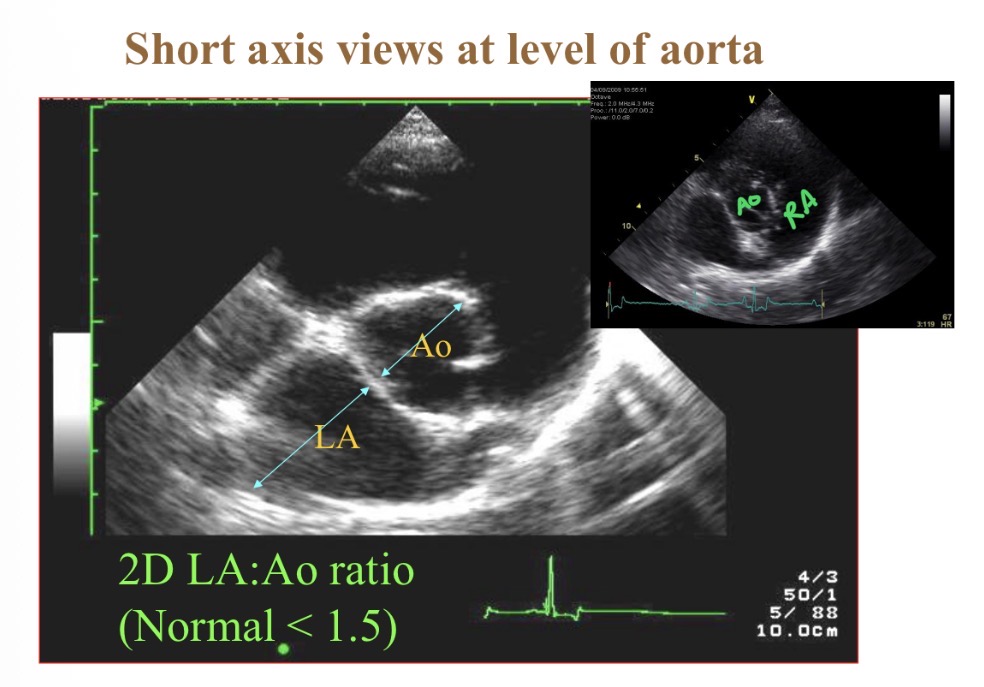
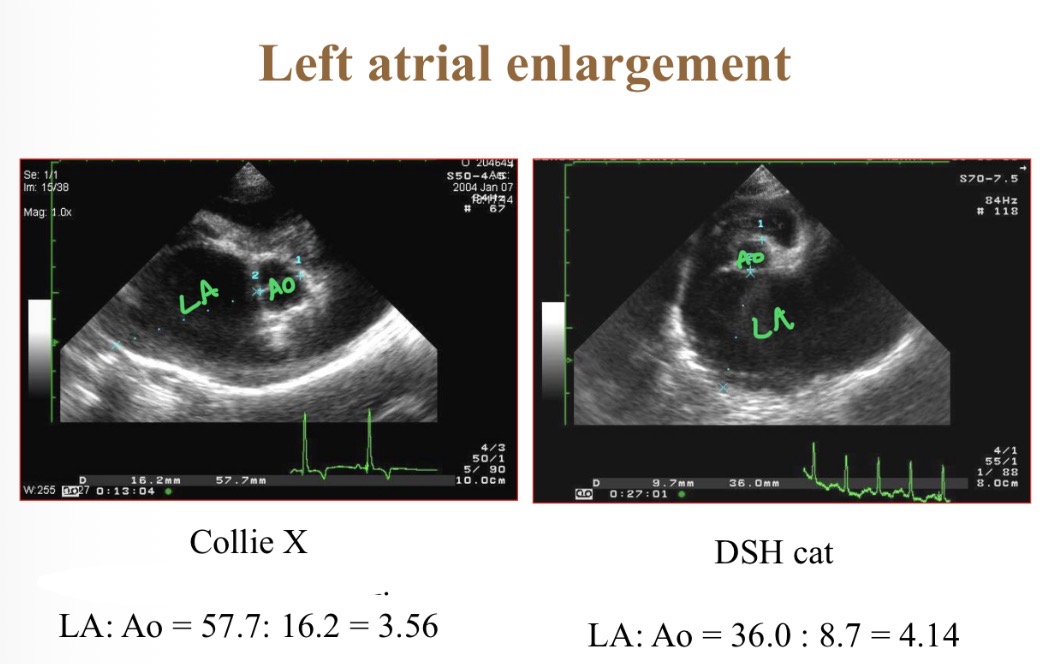
Normal LA: Ao diameter
<1.5:1
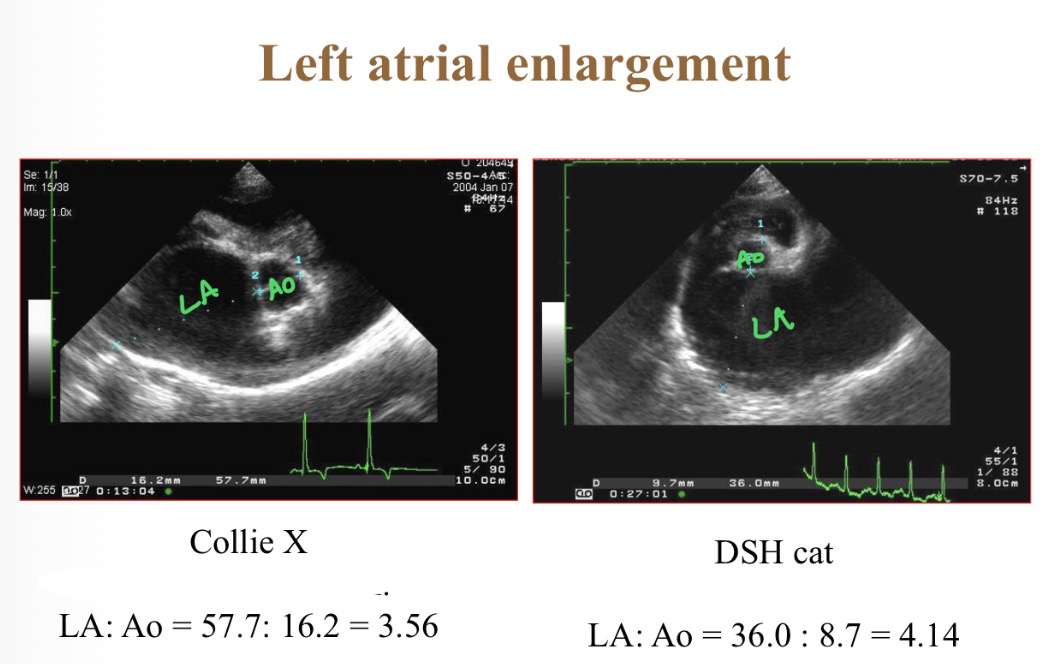
Causes of LA enlramgent
Mitral regurgitation
HCM
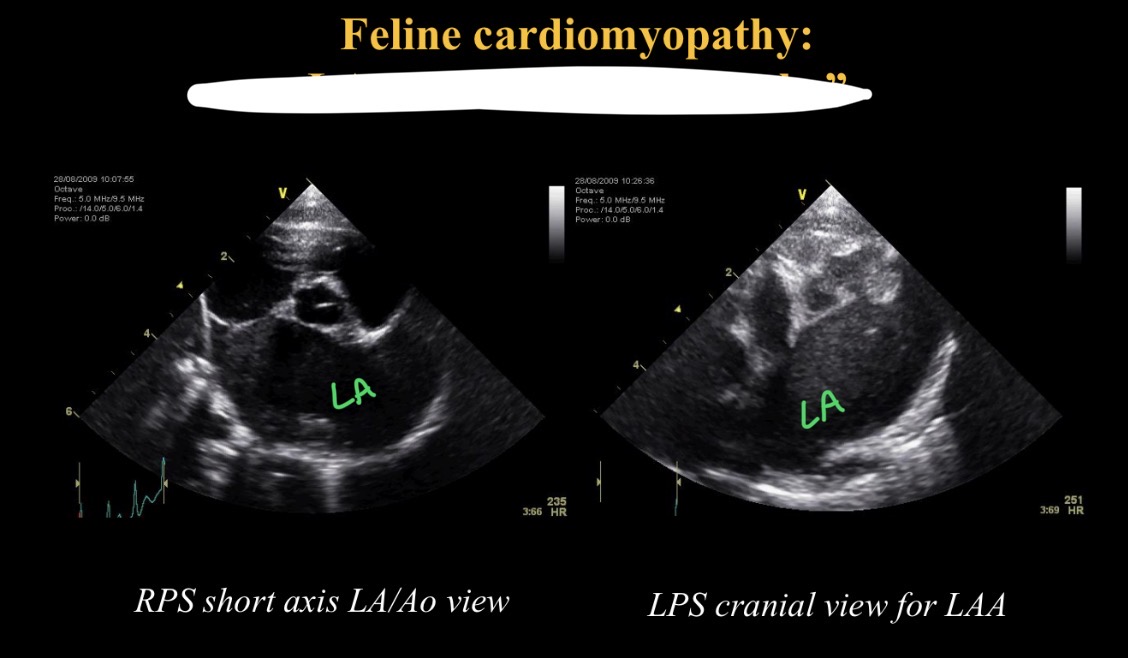
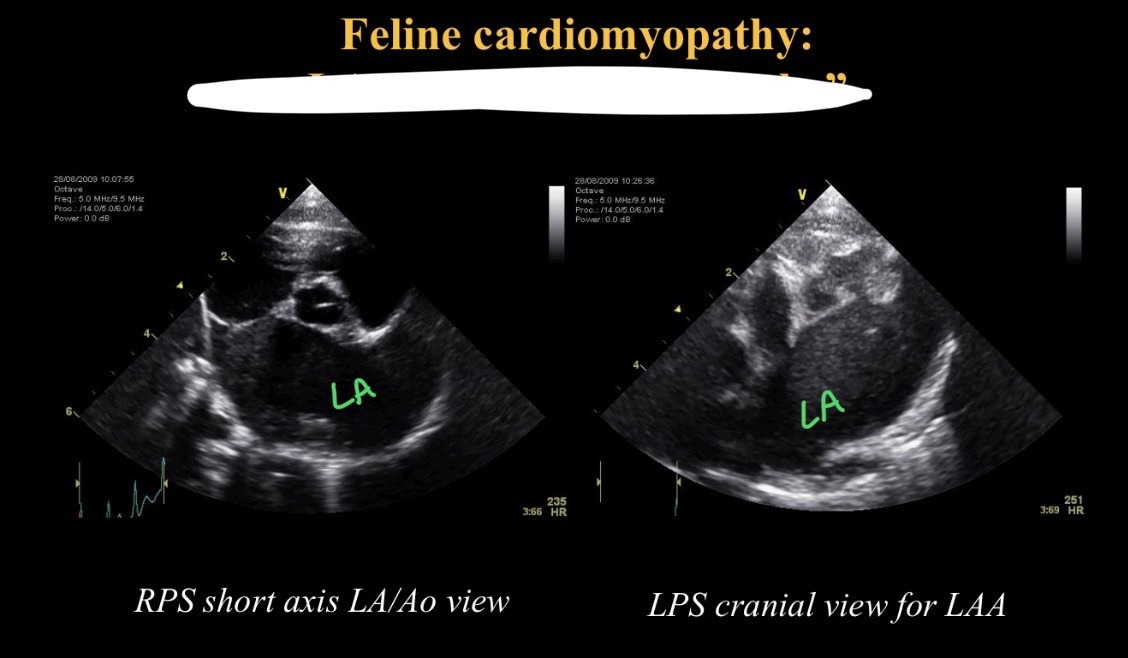
Swirling appearance in LA cause / def
Saddle thrombi → LA thrombus (smoke)
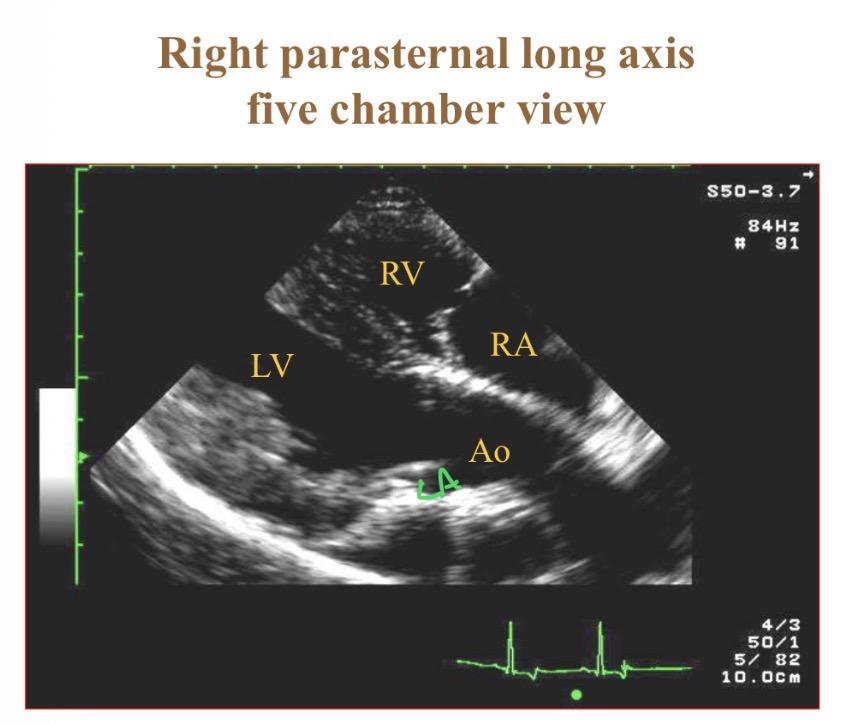
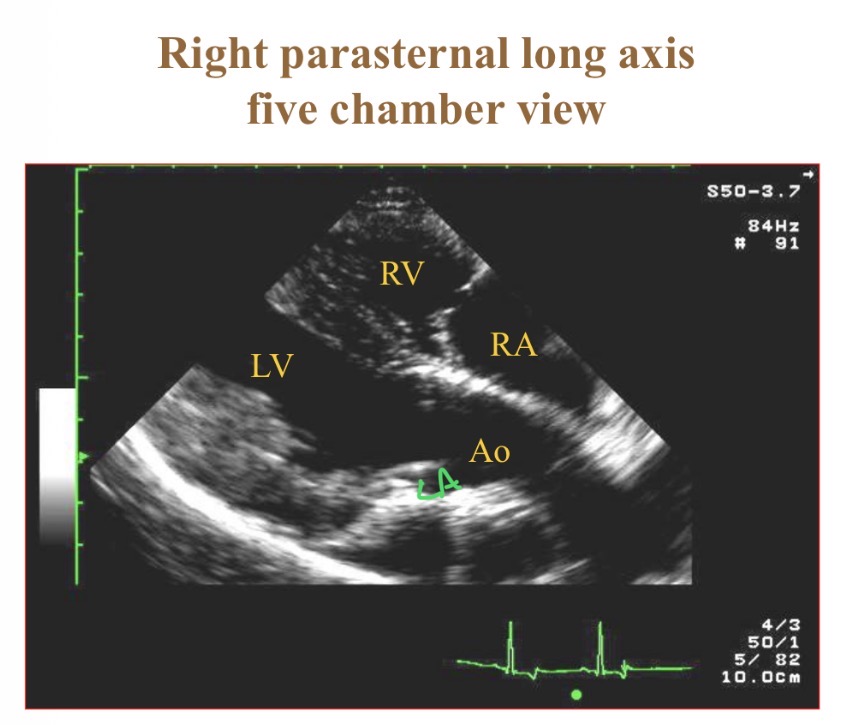
Structures in 5 chamber view
RV, LV, LA, RA, aorta
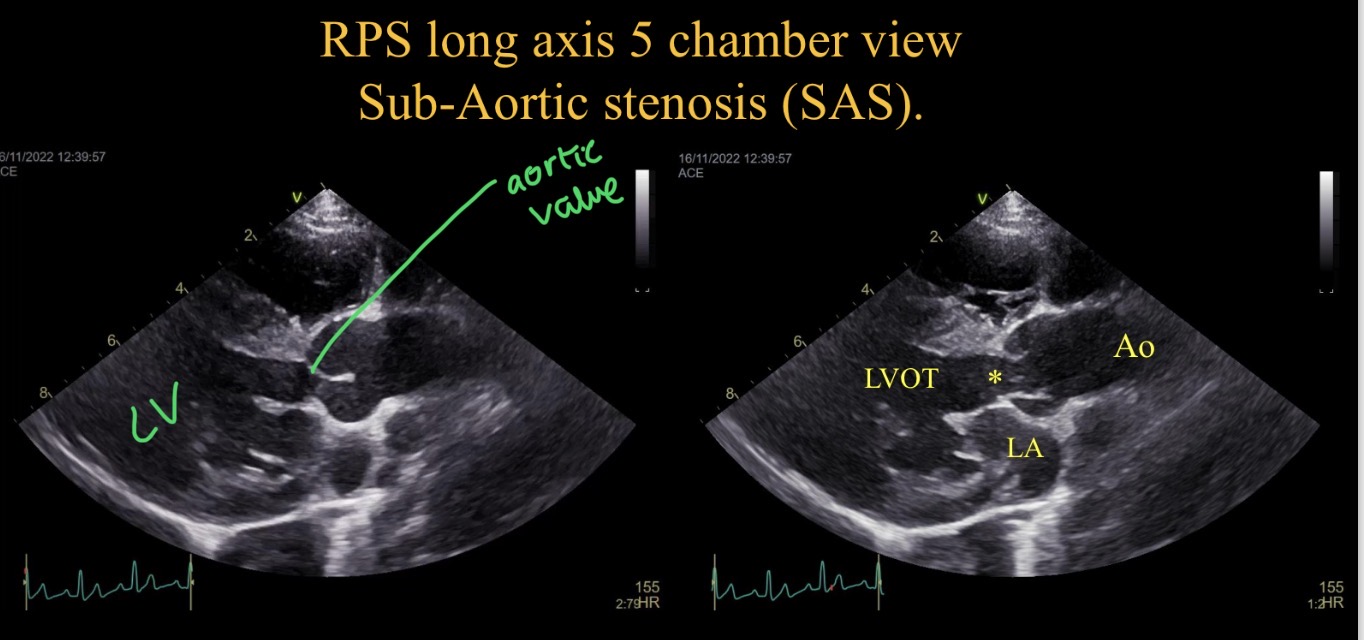
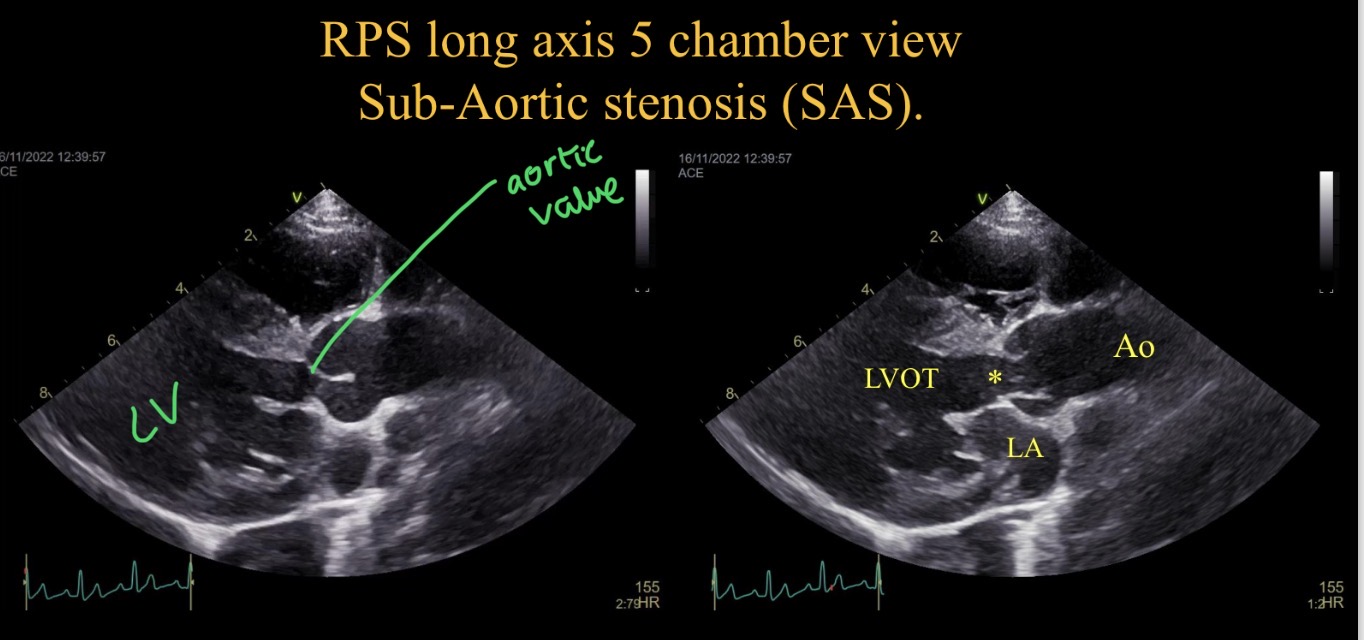
Sub aortic stenosis appearance
LV concentric hypertrophy
Turbulence at narrowing
Aortic regurgiation
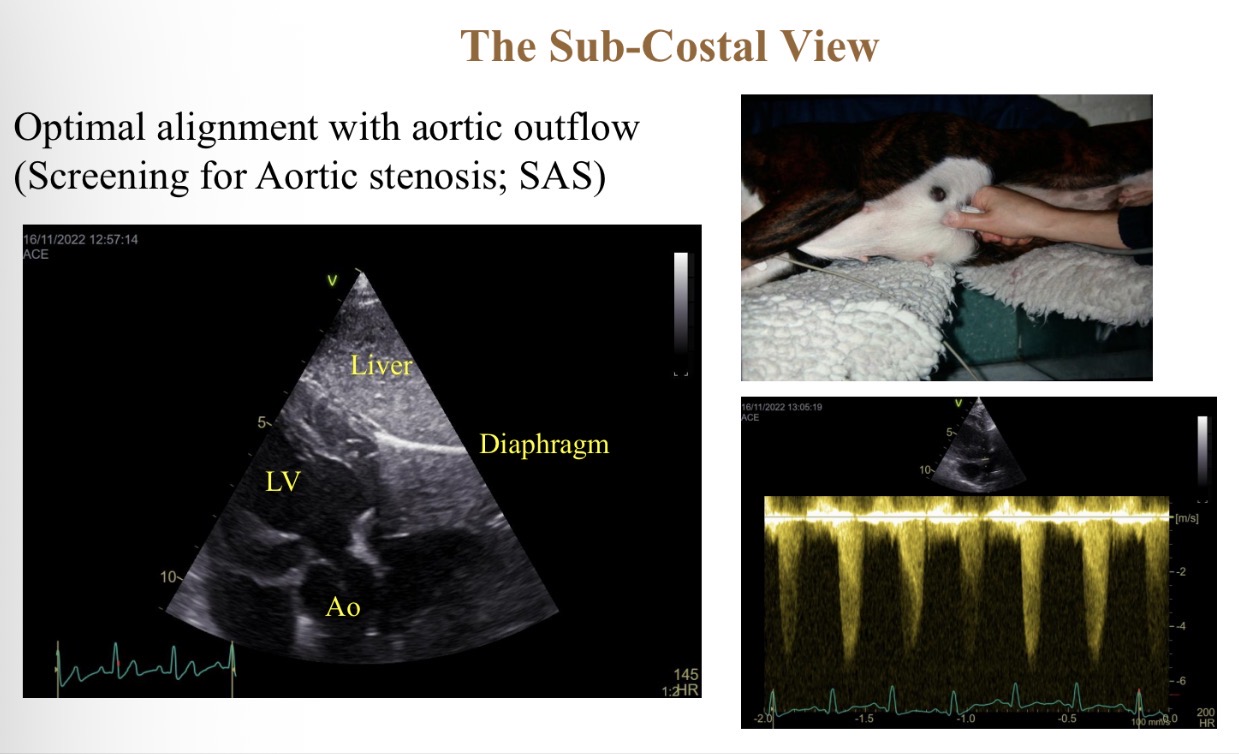
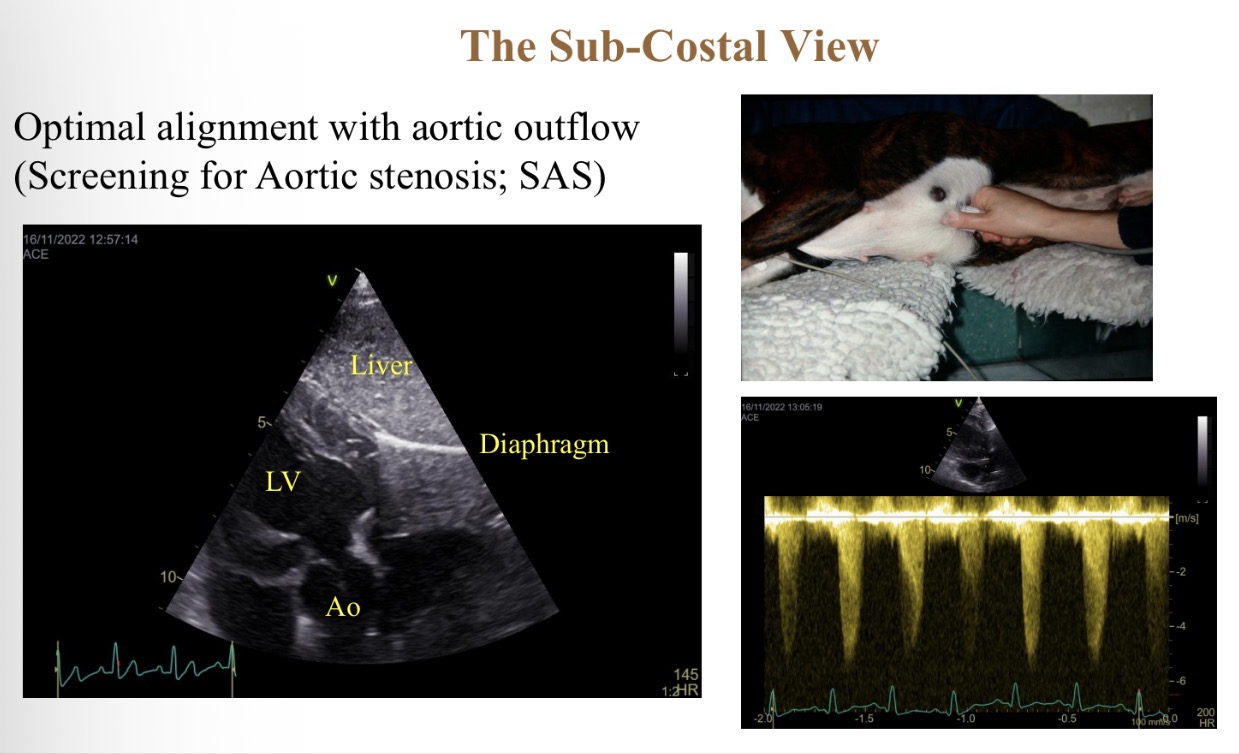
Sub costal view features
Probe parallel with aorta flow (press hard into chest)
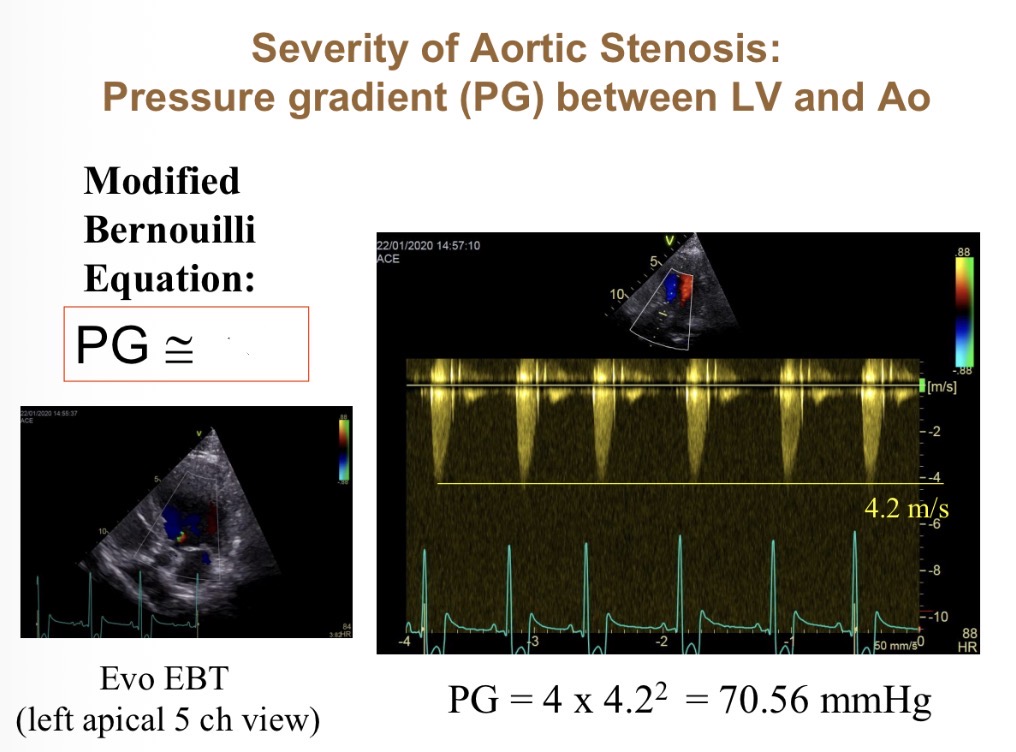
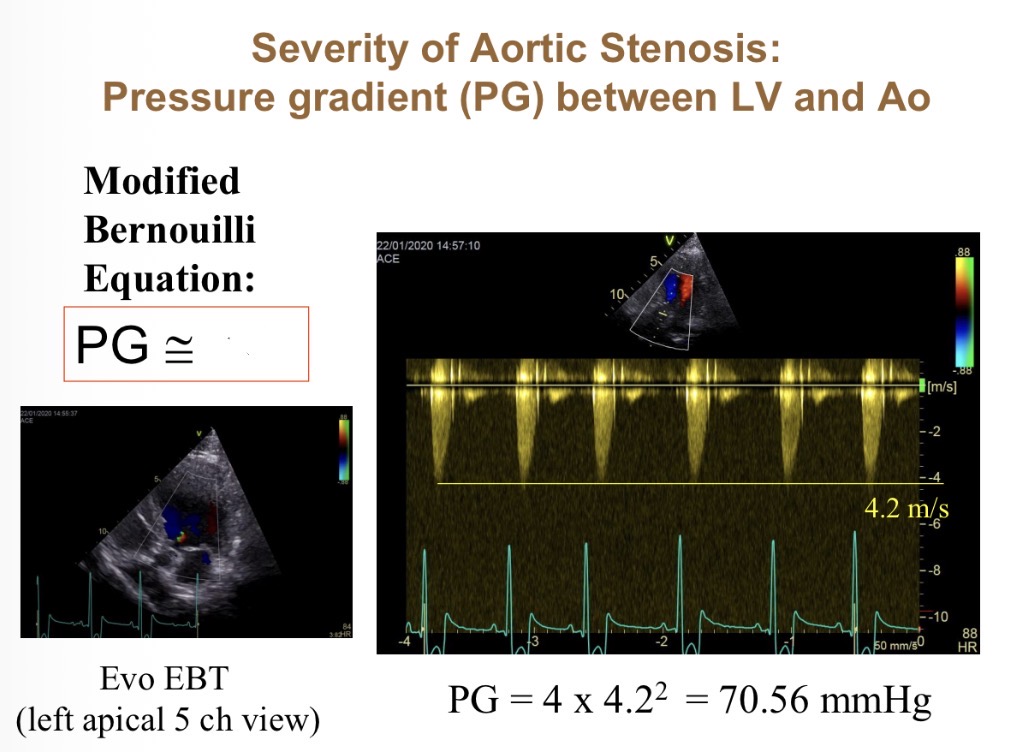
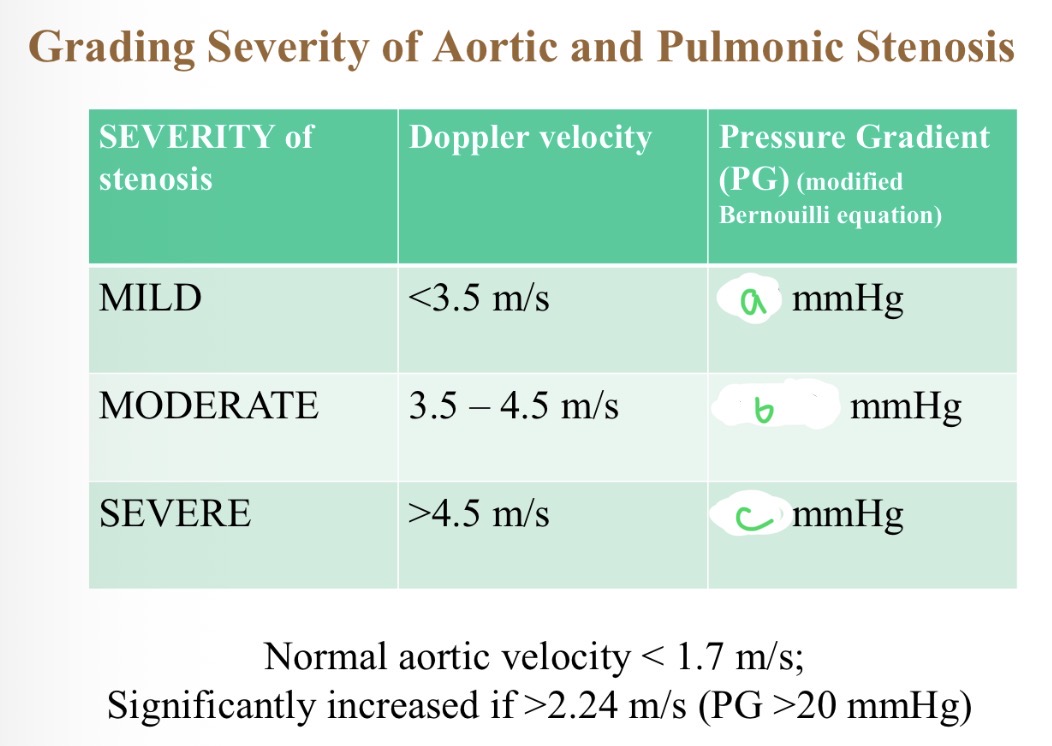
How does pressure gradient vary with velocity (equation)
PG = 4 x velocity²
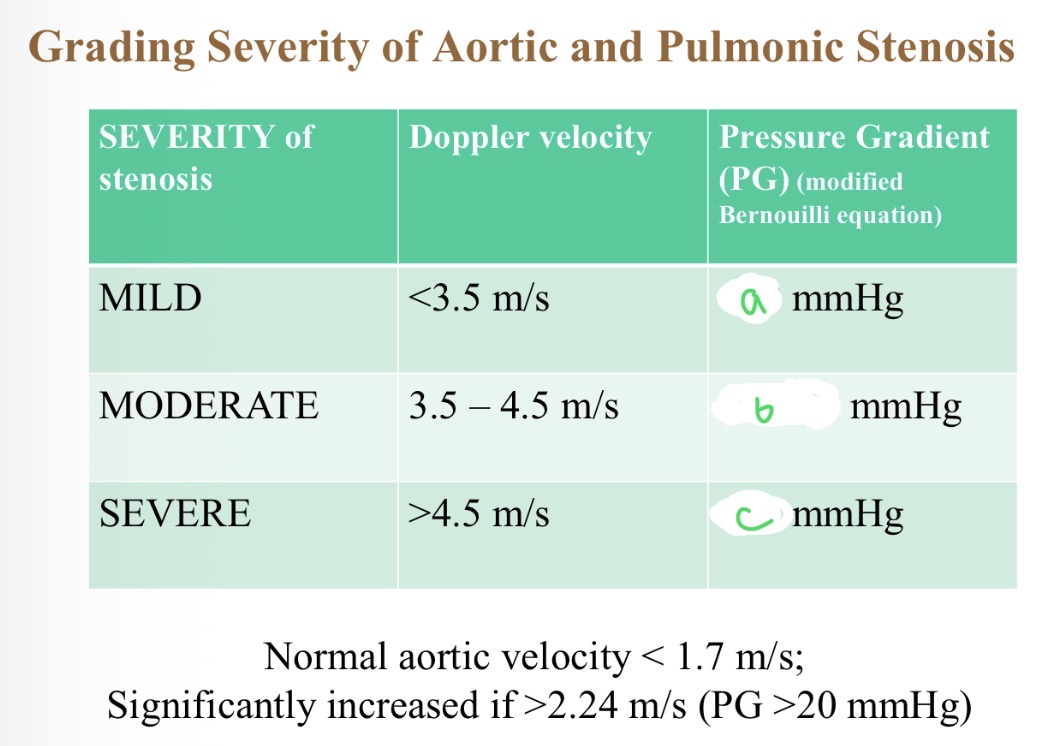
Severity of stenosis with pressure - a
<50
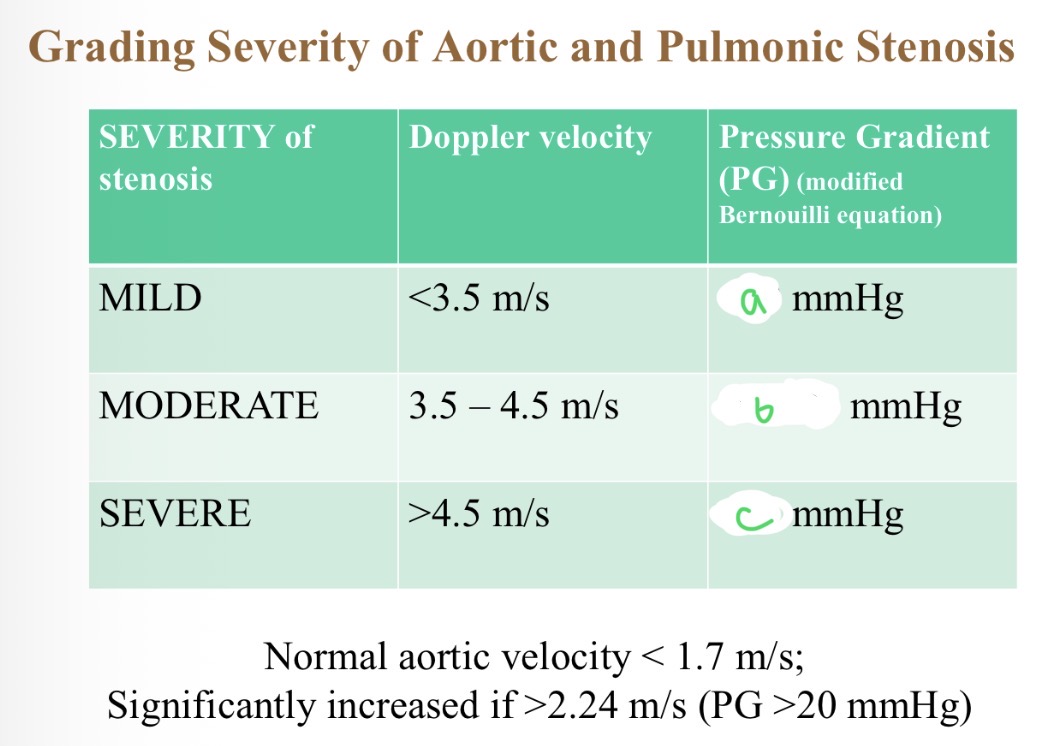
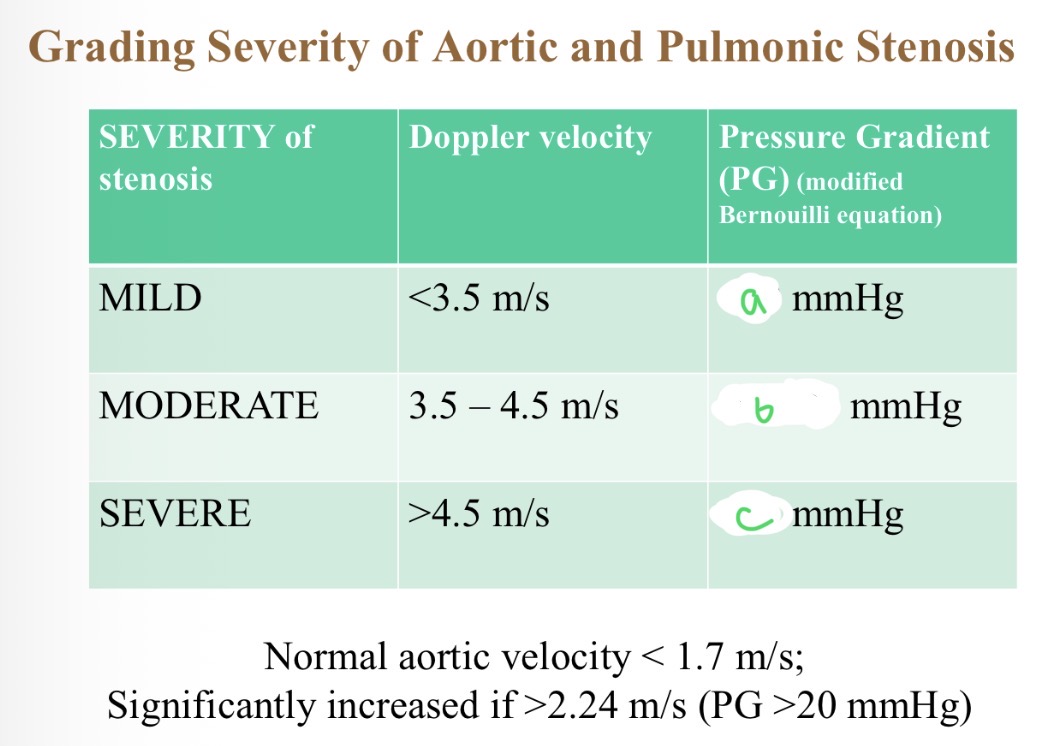
Severity of stenosis with pressure - B
50-80
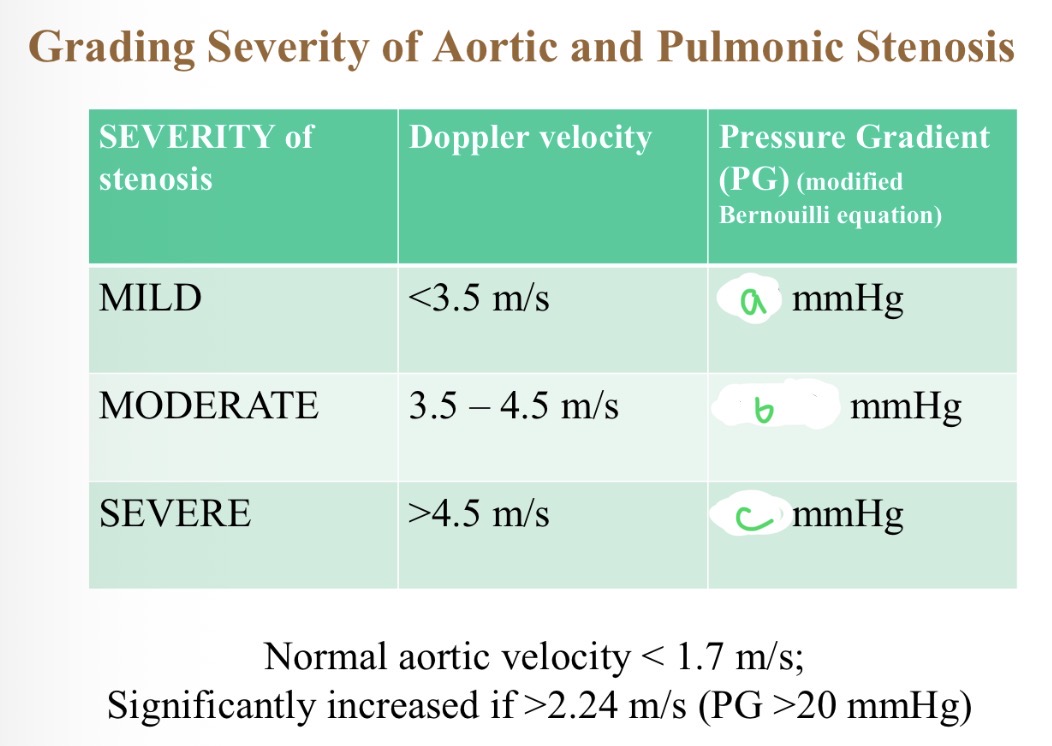
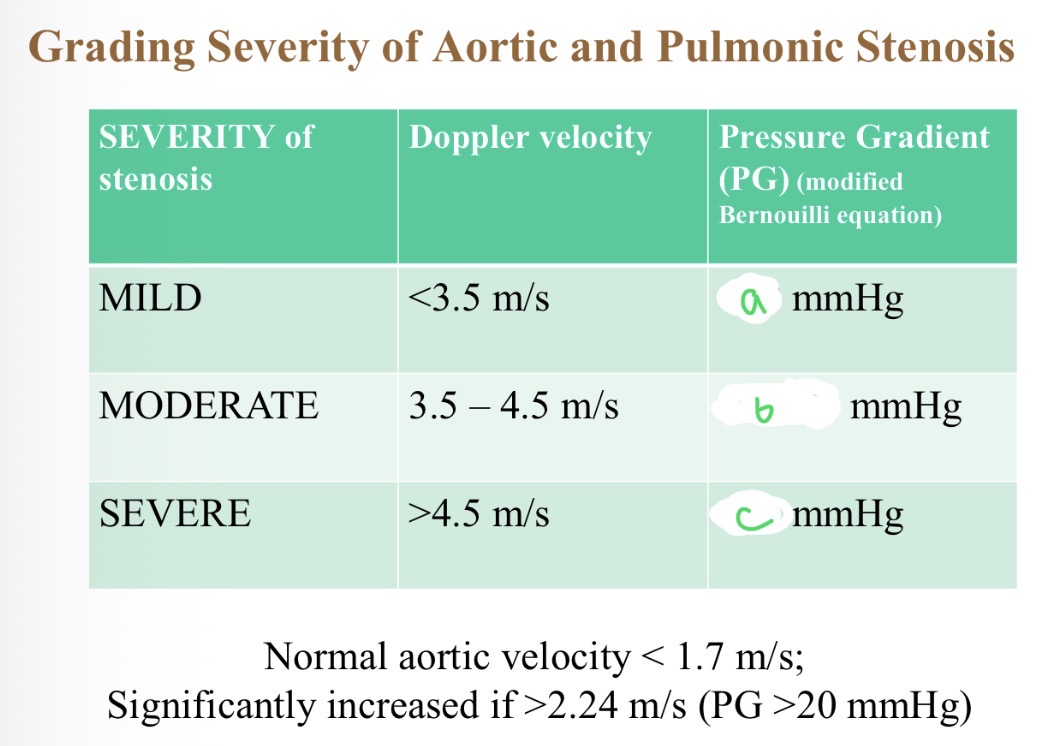
Severity of stenosis with pressure - C
>80
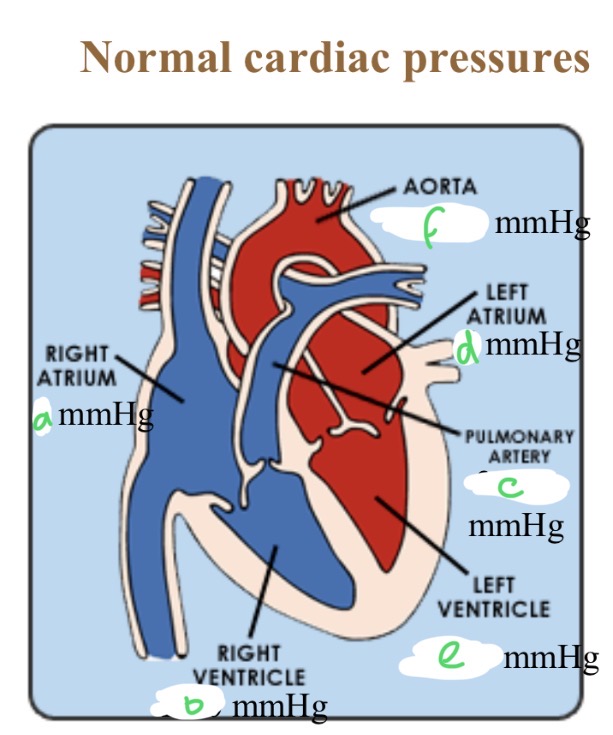
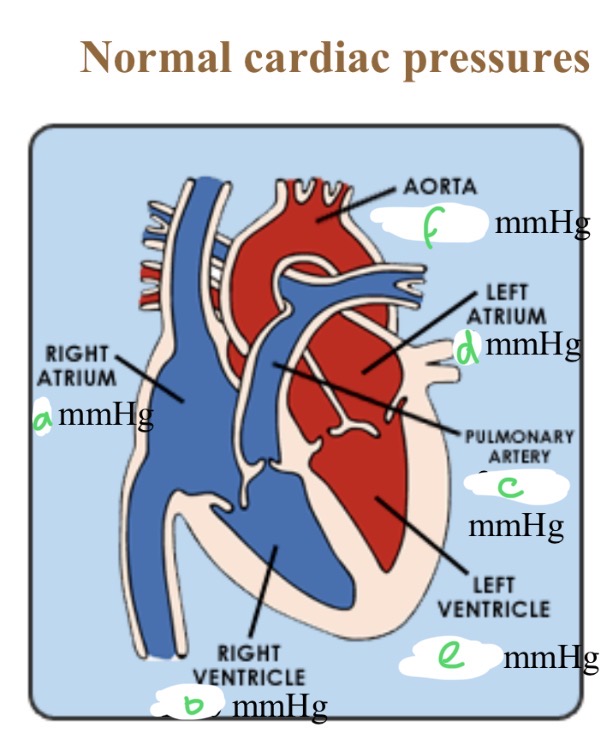
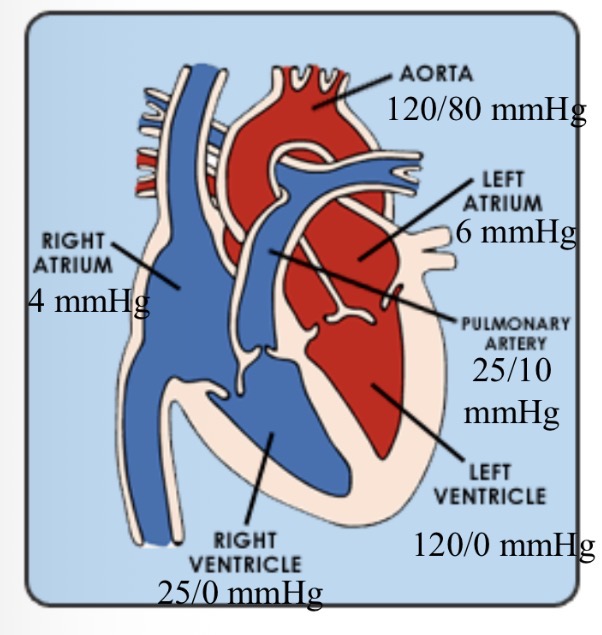
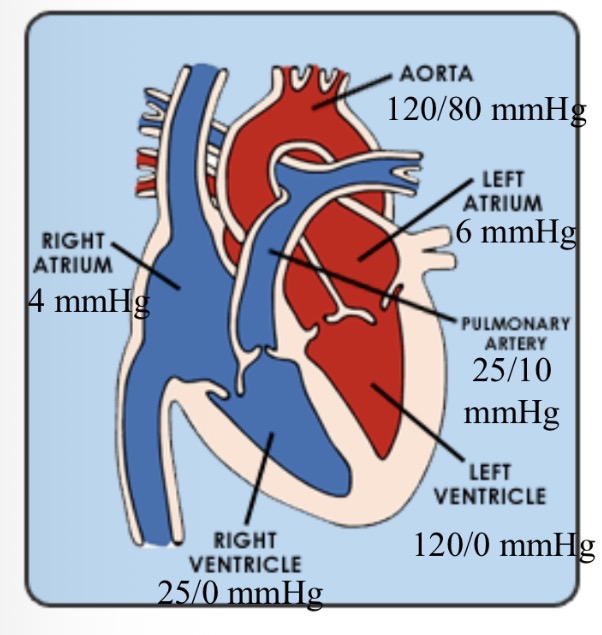
Normal cardiac pressures - RA
4
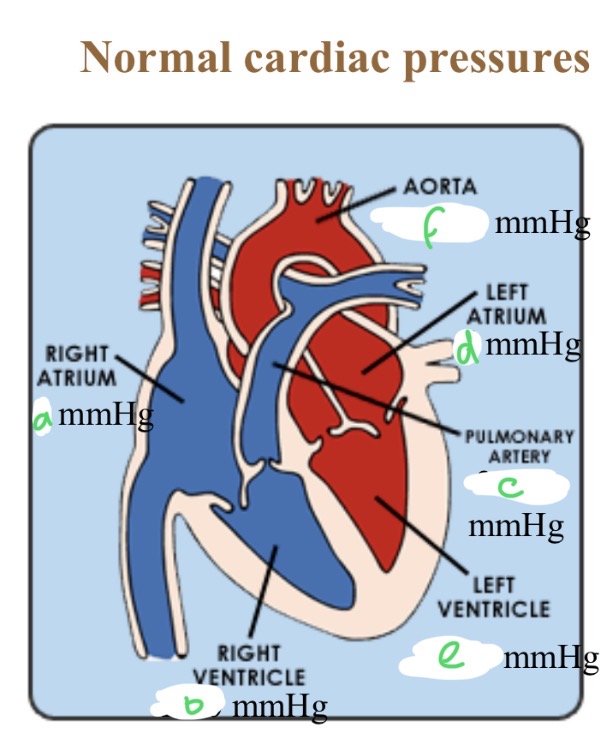
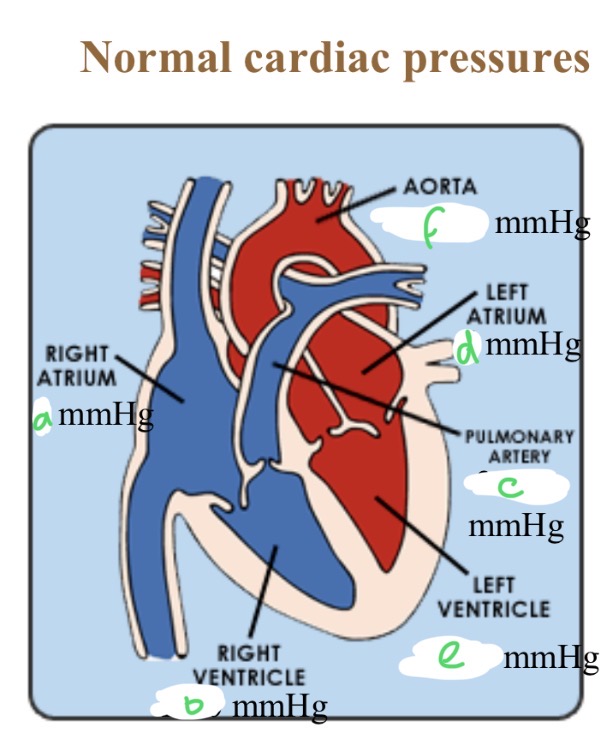
Normal cardiac pressures - RV
25/0
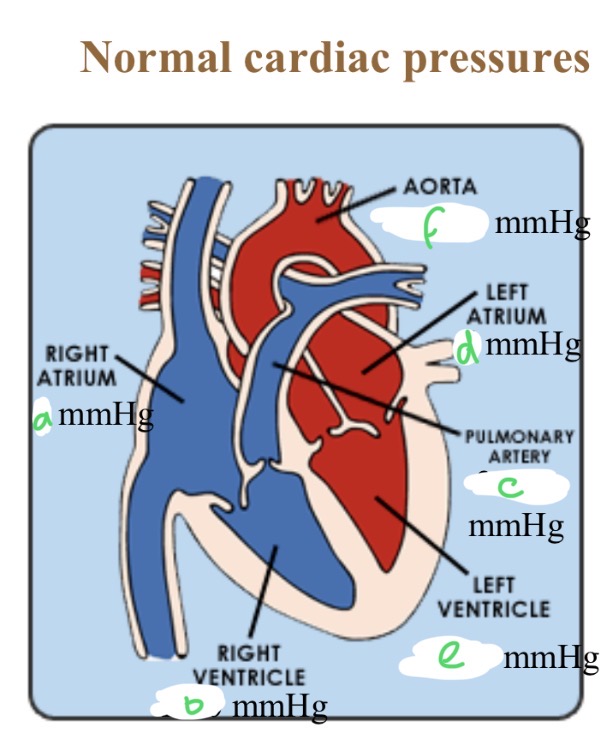
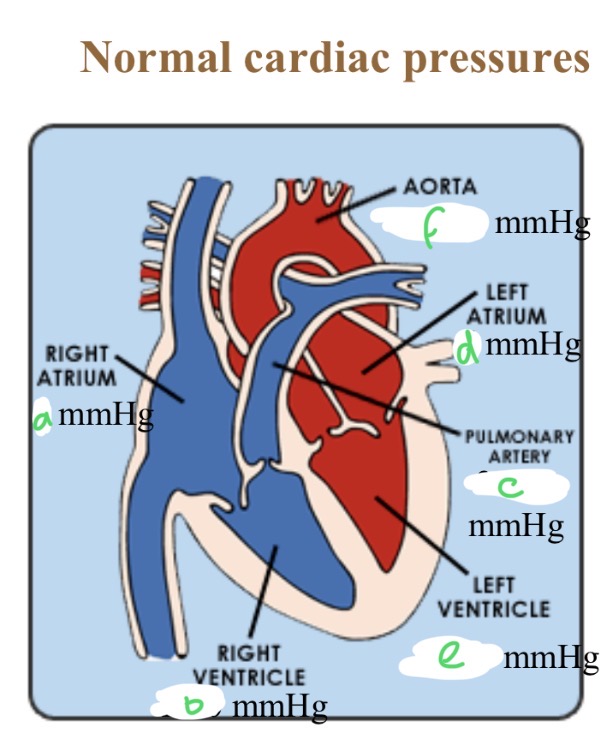
Normal cardiac pressures - pul a
25/10
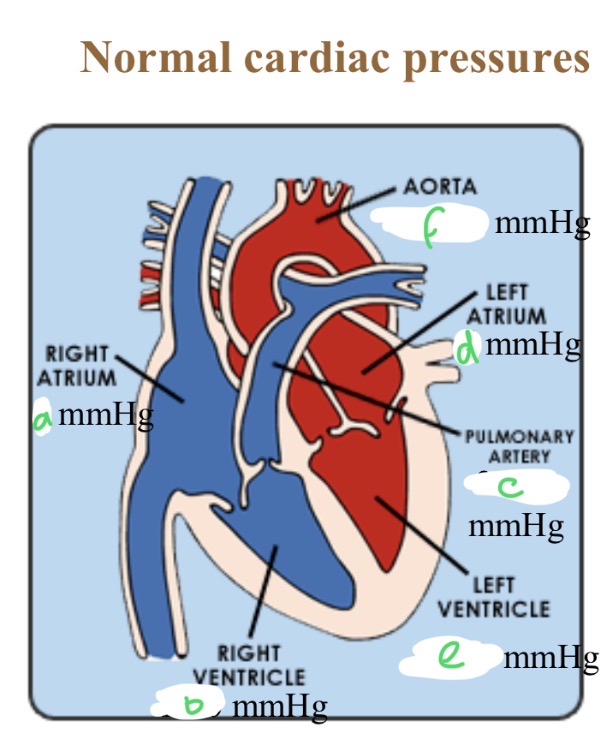
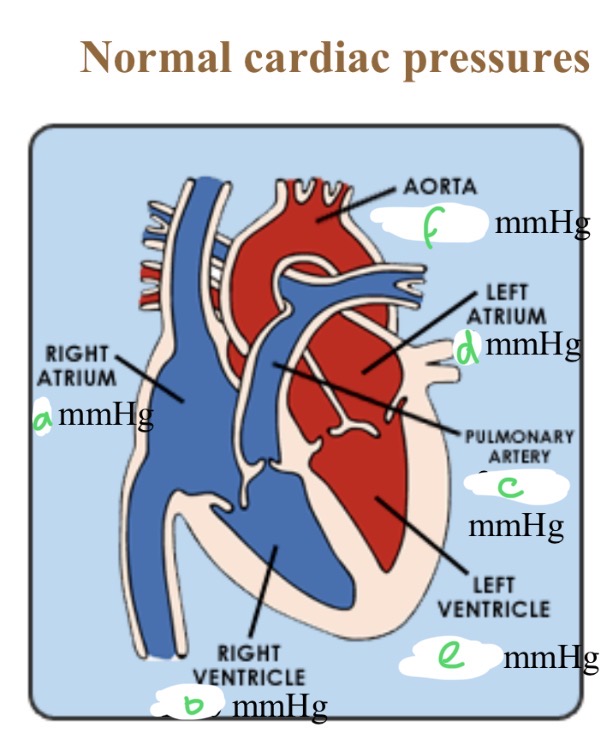
Normal cardiac pressures - LA
6
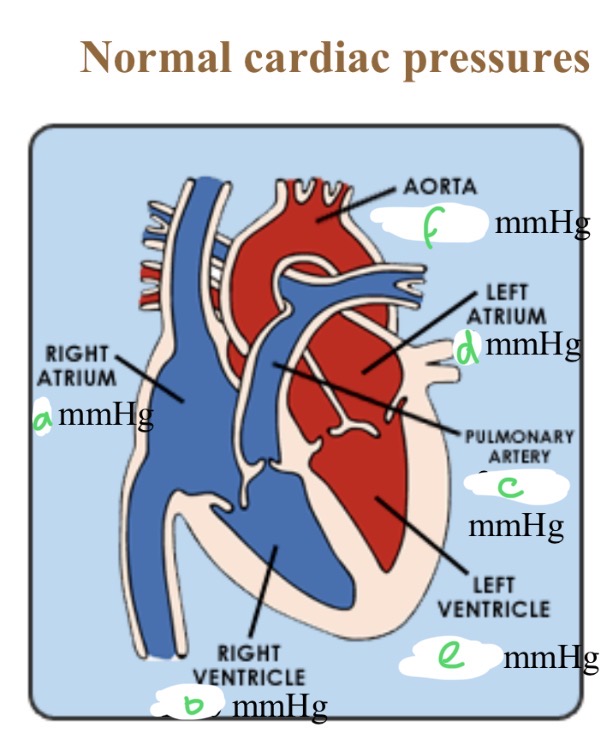
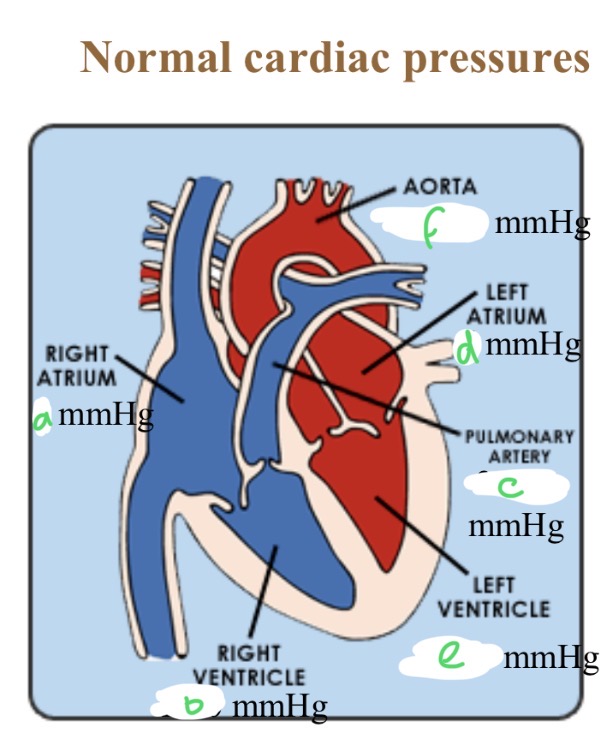
Normal cardiac pressures - LV
120/0
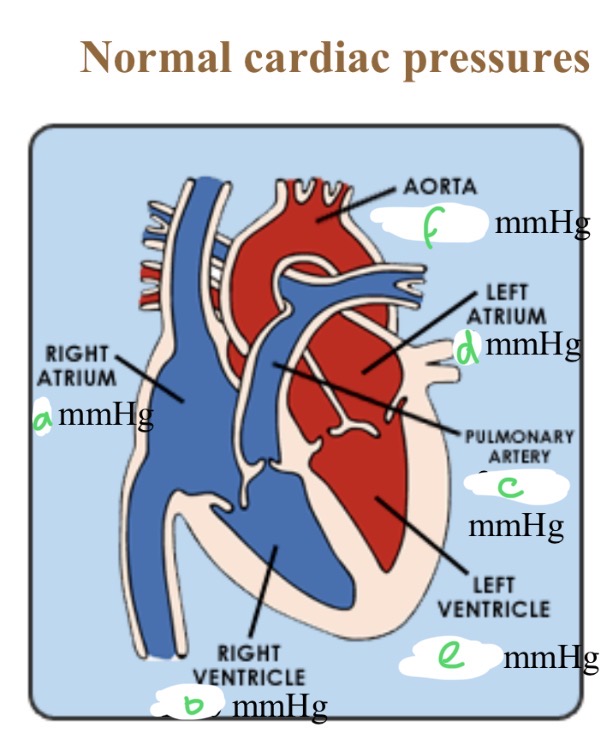
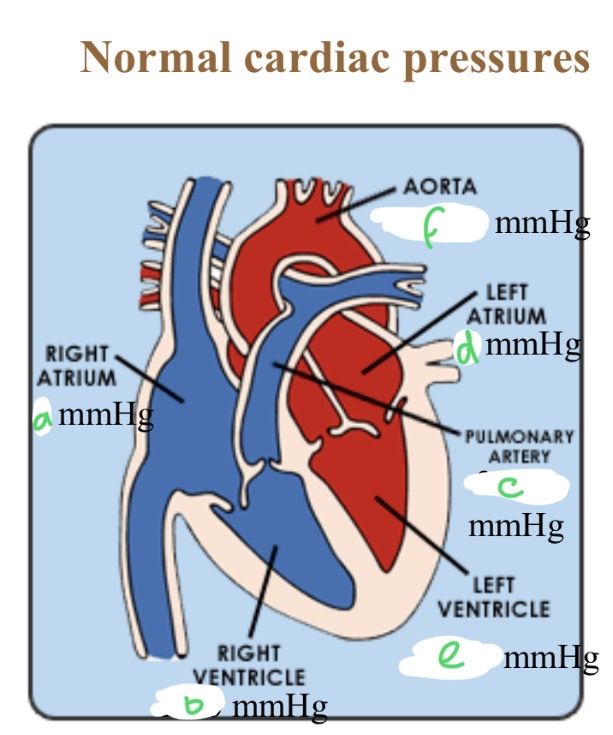
Normal cardiac pressures - aorta
120/80
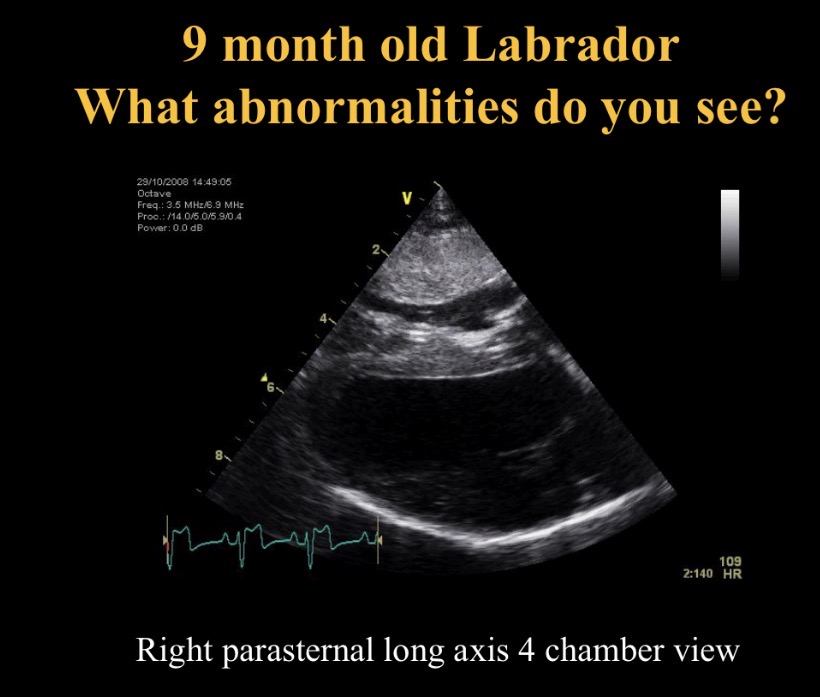
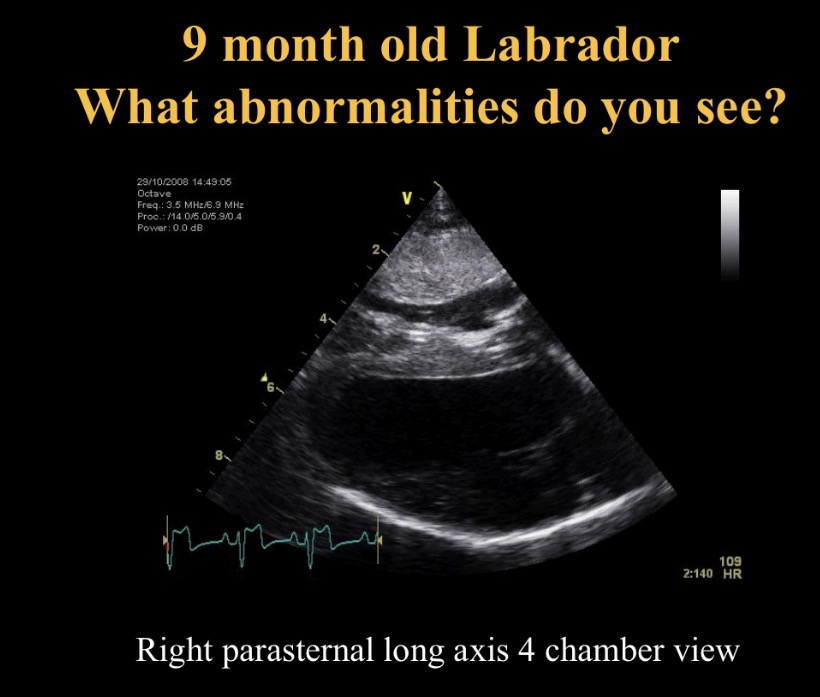
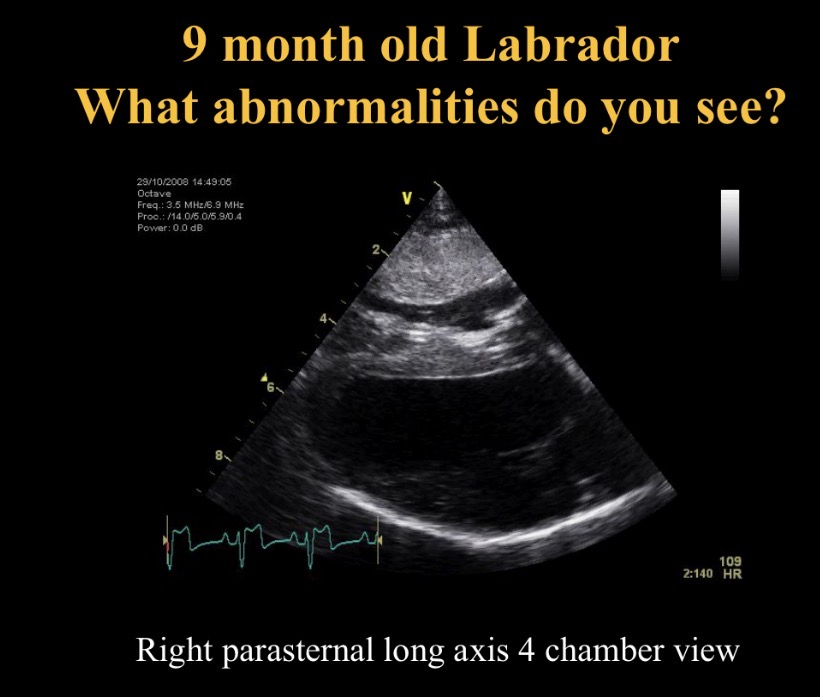
Abnormality seen + causes
RV concentric hypertrophy (squashed LV)
Pul stenosis, pul hypertension
Super thick wall meaning
Myocyte hyperplasia so congenital
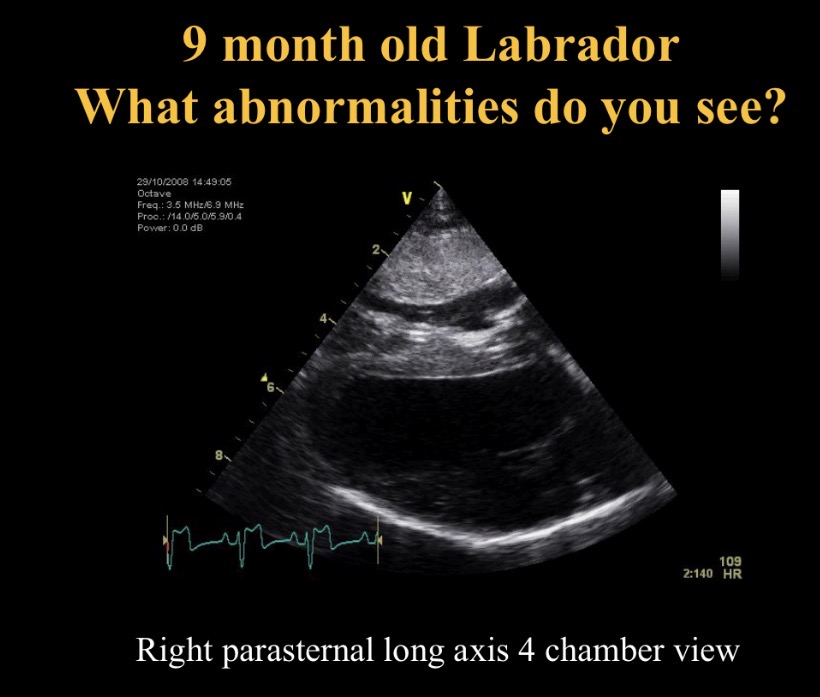
How to calculate RV pressure in pul stenosis
PG of RV-PA + normal PA pressure
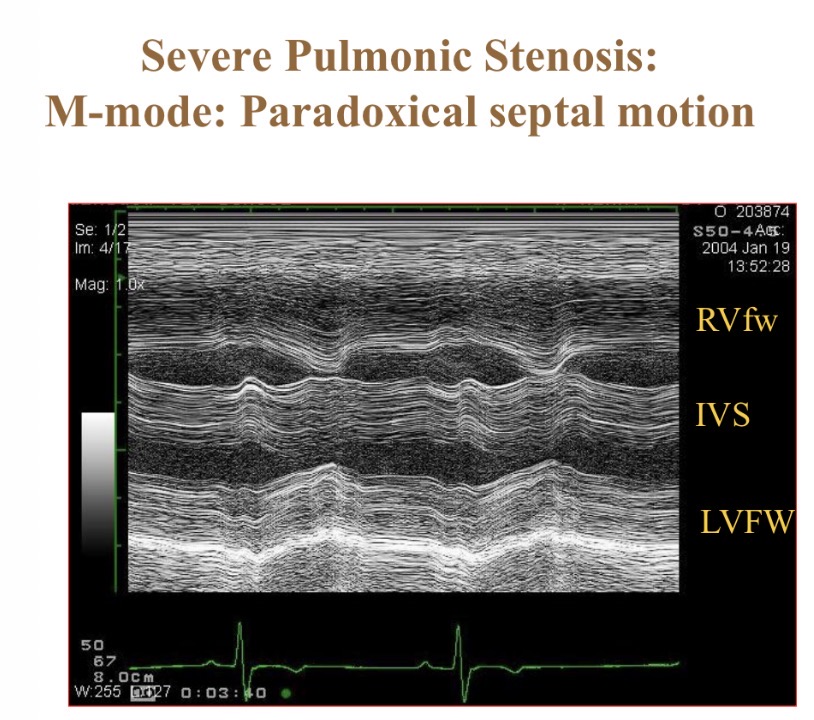
When are the walls moving together (parallel movment(
Systole
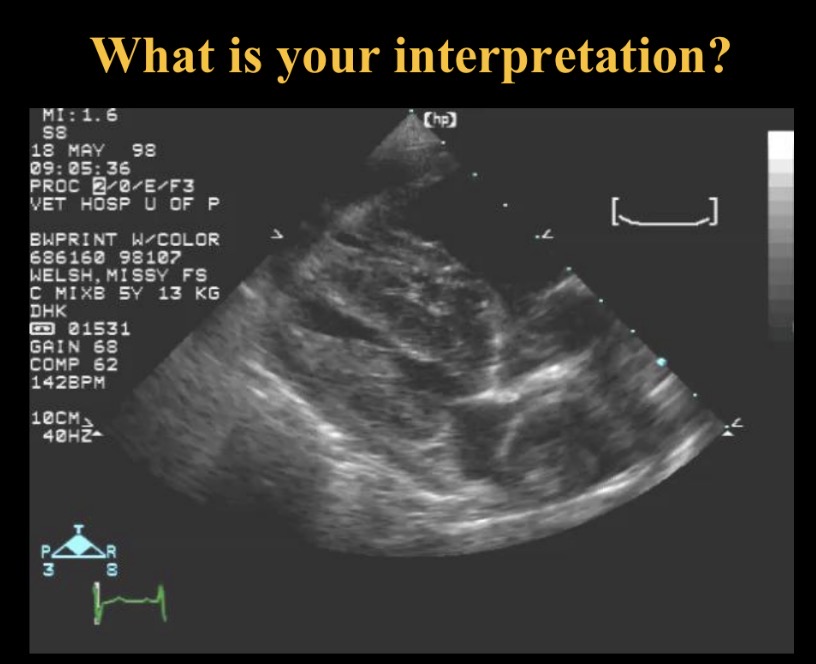
Abnormality seen (R long axis view)
RV pressure overload from pul hypertension → LV underfilled
Pericardial effusion
Abnormal structures in RA (dirofilaria)
R pul a thrombus
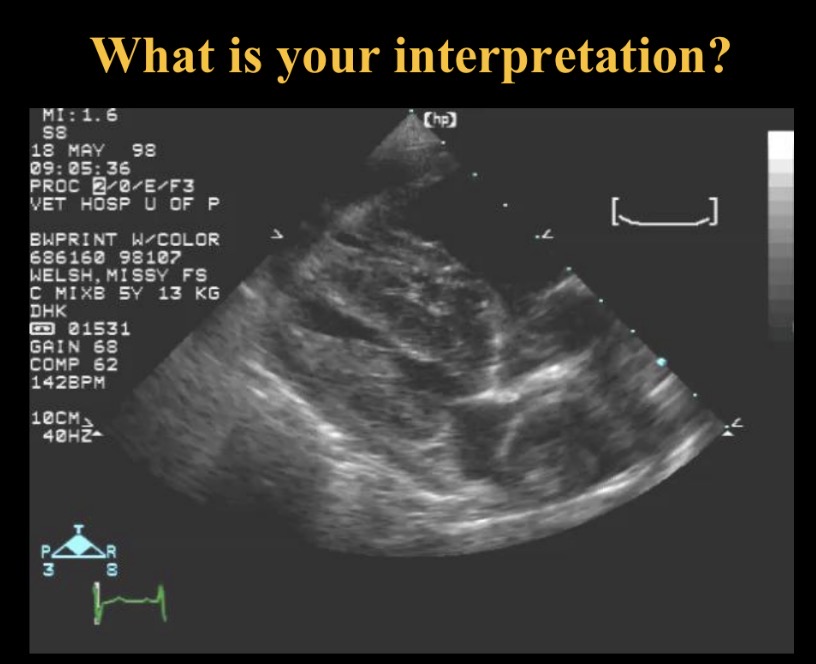
Dirofilariasis (caval syndrome) normally found
Pul a, RA, RV
How to extract dirofilaria worms
Jug vein
Worm species found in heart from lungs
Dirofilaria
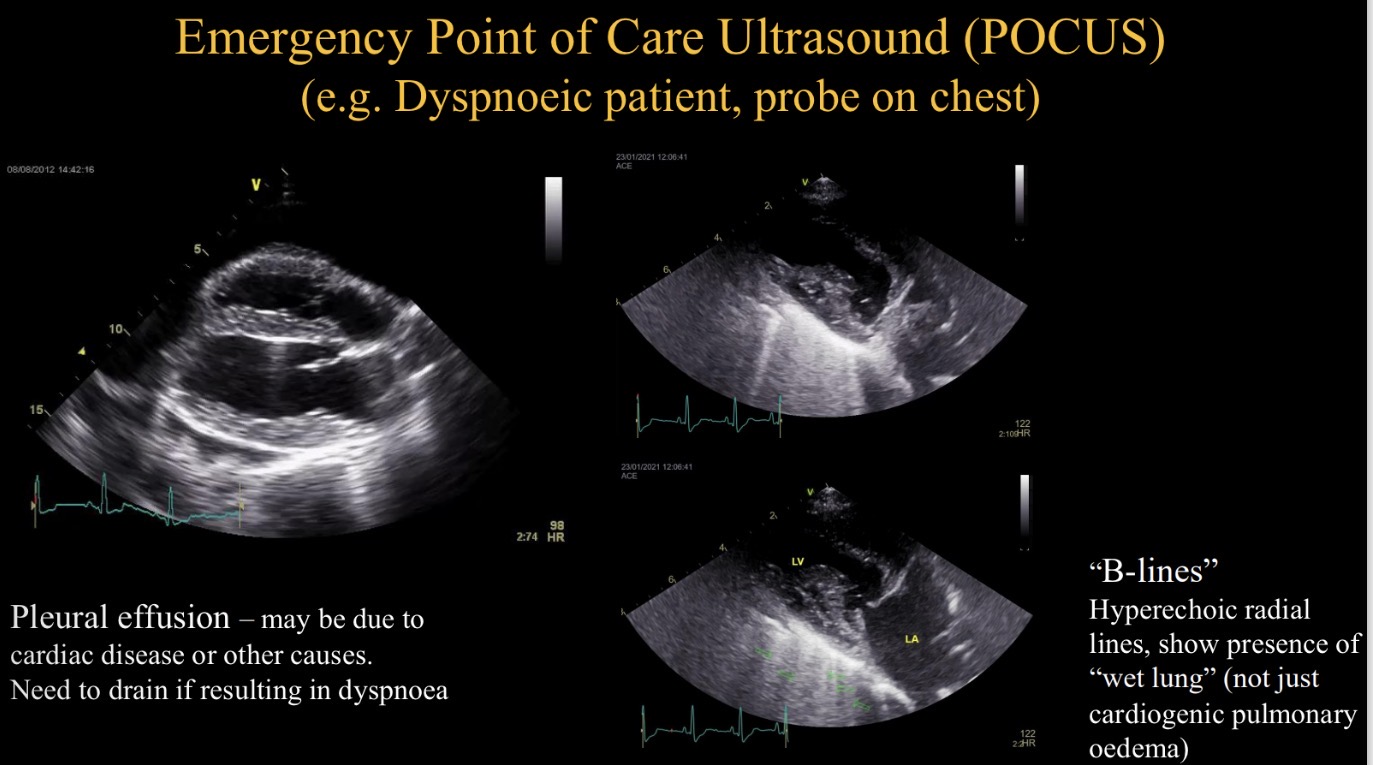
POCUS stands for
Emergency point of care US
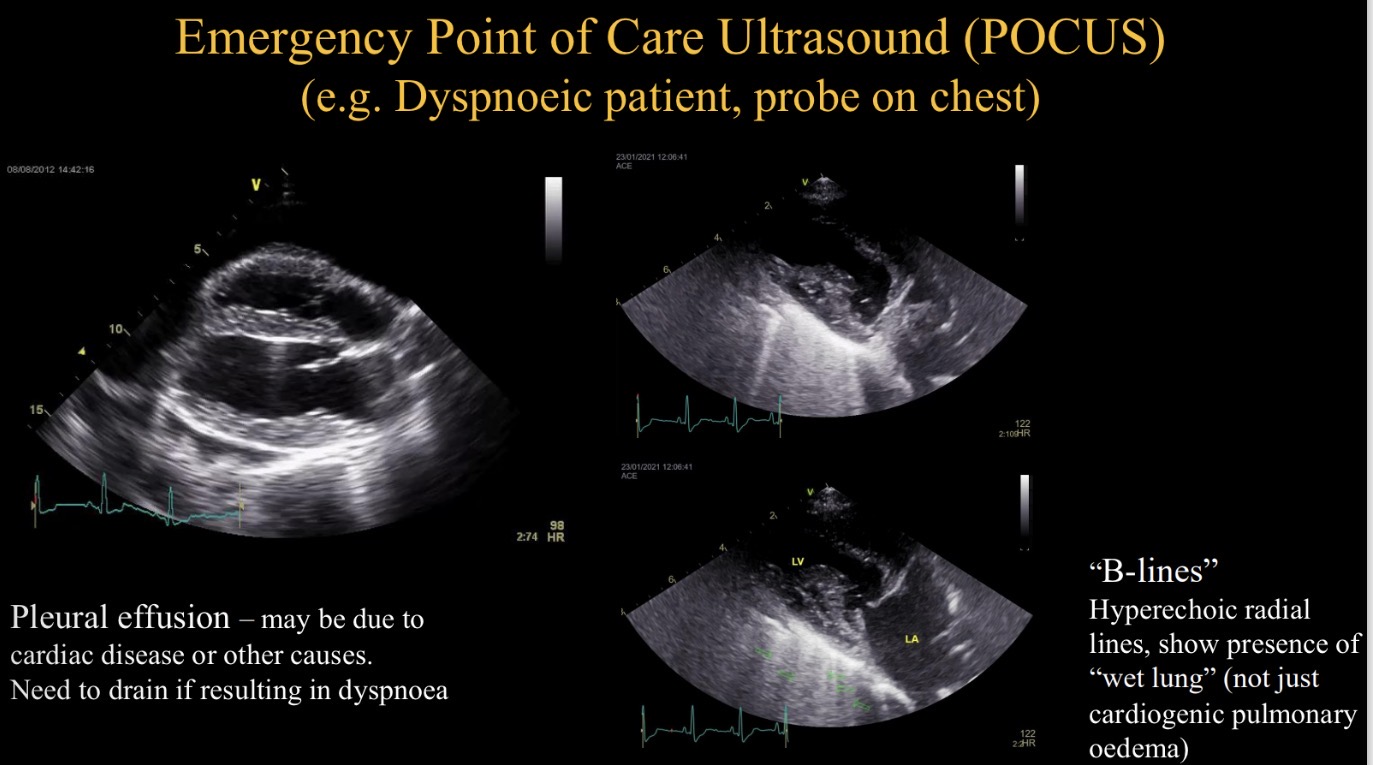
Purpose of POCUS in dyspnoeic animal
Identify pleural effusion + drain
Identify hyperechoic lines (B lines)