Behavioral Neuroscience Test #1
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
A scientist who holds a monistic philosophy would endorse which of the following statements?
a. The universe is a mental construction.
b. Everything is made of matter and energy.
c. The left hemisphere of the brain is the location of the mind.
d. The mind is not composed of matter.
e.The body is physical whereas the mind is spiritual.
b. Everything is made of matter and energy.
Eduardo wants to understand the development of the human brain by comparing it to the brains of other species and theorizing about the environmental pressures that helped to shape those brains over the long process of historical time. Which perspective on behavioral neuroscience is Eduardo adopting?
a.evolutionary perspective
b.clinical perspective
c.historiography
d.computational perspective
e.conscious awareness perspective
a. evolutionary perspective
Generalization is to __________, whereas reduction is to __________.
a. identifying simple causes of complex behaviors; identifying general rules that govern behavior across multiple organisms
b. ignoring data that don’t fit with previous explanations; identifying general rules that govern behavior across specific organisms
c. identifying general rules that govern behavior across multiple organisms; identifying simple causes of complex behaviors
d. organizing data in terms of general rules; identifying the smallest components of a neuron
c. identifying general rules that govern behavior across multiple organisms; identifying simple causes of complex behaviors
The term “neuraxis” refers to
a.the frontal portions of the brain
b. a plane that divides the two hemispheres into right and left halves.
c. a plane that divides the brain into top and bottom halves.
d. an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain.
d. an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain.
In a human, the spine is __________ to the stomach.
a.Anterior
b.Posterior
c.Ventral
d.Lateral
e. Dorsal
e. Dorsal
Ingo got a summer job working in a neuroanatomy laboratory. His supervisor told him, “I want you to divide this brain into front and back halves, and then to create thin sections of the back half.”
“Right on,” Ingo replied, as he began to correctly make __________ slices of the brain by cutting straight down from the dorsal to the ventral surface along the plane that is parallel to the face.
a. Midsagittal
b.Sagittal
c.Rostral
d.Coronal
e.Ventral
d. Coronal
Sheryl slices through the brain and removes a small portion of the top of the brain. Looking at what remains, she notices that lateral ventricles are visible on the left and right sides. Along which plane did she slice the brain?
a. coronal
b.ipsilateral
c.sagittal
d. horizontal
e. contralateral
d. horizontal
CSF flows in which of the following directions?
a.From the arachnoid granules to the third ventricle
b.From the lateral ventricle to the choroid plexus
c. From the third ventricle to the lateral ventricles
d.From the cerebral aqueduct to the fourth ventricle
d. From the cerebral aqueduct to the fourth ventricle
Compared to the others, the ___________ layer of the meninges is the thickest and toughest.
a.dura mater
b.midsagittal sinus
c.arachnoid membrane
d.Pia mater
a. dura mater
Which term captures the direction that is toward the chin for the brain and toward the belly for the spinal cord?
a.Dorsal
b.Lateral
c. Posterior
d.Ventral
e.Anterior
d. Ventral
In the central nervous system, the _____________ cells are responsible for creating the white matter.
a.Astrocytes
b.Microglia
c.Schwann cells
d. Oligodendrocytes
d.Oligodendrocytes
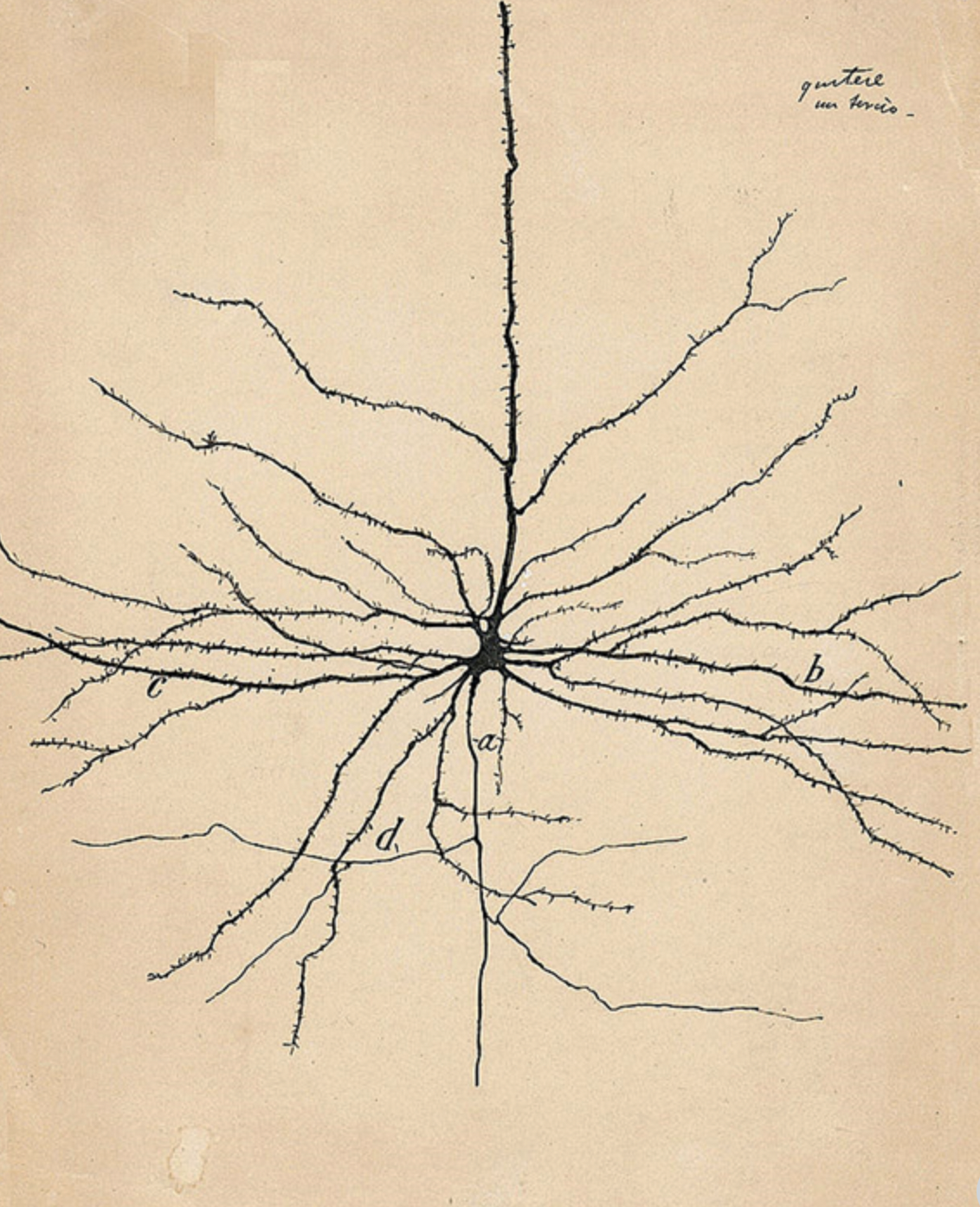
Which of the following is NOT an appropriate description of the cell pictured?
a.Multipolar
b.Spiny
c.Non-spiny
d. Neuron
c.Non-spiny
In a multipolar neuron, the portion that carries information toward the cell body is called the _____________.
a. dendrite
b. axon terminal
c. presynaptic membrane
d.soma
a. dendrite
Why is the blood-brain barrier weaker in one brain area?
a.To allow waste to exit the brain
b.To permit entry of immune cells into the brain
c.To allow passage of lactate into the brain
d.To allow the brain to detect toxins and trigger vomiting
d.To allow the brain to detect toxins and trigger vomiting
During the course of prenatal development, the neural tube will eventually form the _________________________.
a.brain
b.spinal cord
c.heart and lungs
d.brain and spinal cord
d.brain and spinal cord
True or False? Axons always synapse onto dendritic spines.
True
False
False
Early researchers knew nothing about how mammalian brains are organized, so they used neuroanatomical tracing techniques to establish how brain areas are connected. More specifically, to determine where the neurons in a given area send their axonal projections, they injected ______________ tracers into that brain area.
a.retrograde
b.anterograde
c.axoplasmic
d.antibody
b.anterograde
Vernon took a sharp turn and fell head first off his electric scooter. Unfortunately, he wasn’t wearing a helmet and suffered brain damage. Which cell of the nervous system were the first to rush to the site of injury?
a.Oligodendrocytes
b.Astrocytes
c.Microglia
d.Schwann cells
c.Microglia
Which of the following development phases continue past adolescence?
a.Neural migration
b.Apoptosis
c.Neural tube development
d.Myelination
e.Neural proliferation
d.Myelination
Imagine that a new species of rodent-like creatures has been discovered, and you are a scientist tasked with helping determine whether and how their nervous systems are similar to lab mice (Mus musculus). Your group decided to focus on the cortex and to first measure cell density and then visualize the location of cells that express the protein vGlut (a marker for cells containing glutamate). Which combination of neuroanatomical techniques will you use?
a.Nissl staining and retrograde tracing
b.Retrograde tracing and immunohistochemistry
c.Golgli staining and immunohistochemistry
d.Nissl staining and immunohistochemistry
d.Nissl staining and immunohistochemistry
At rest, the force(s) that drive K+ out of the cell include:
a.the concentration gradient and the sodium-potassium pump
b.only the sodium-potassium pump
c.the concentration gradient and the electrostatic gradient
d.only the concentration gradient
e.only the electrostatic gradient
d.only the concentration gradient
True or False? Neurons are the only cells with negative resting membrane potentials?
True
False
False
The NA+/K+ pump serves to do which of the following?
a.Produce action potentials
b.Maintain the concentration gradients for Na+ and K+
c.Produce saltatory conduction
d.Reduce the refractory period
e.Inactivate voltage-gated channels
b.Maintain the concentration gradients for Na+ and K+
Calcium plays a role in neurotransmitter release and can be involved in the generation of postsynaptic potentials.
True
False
True
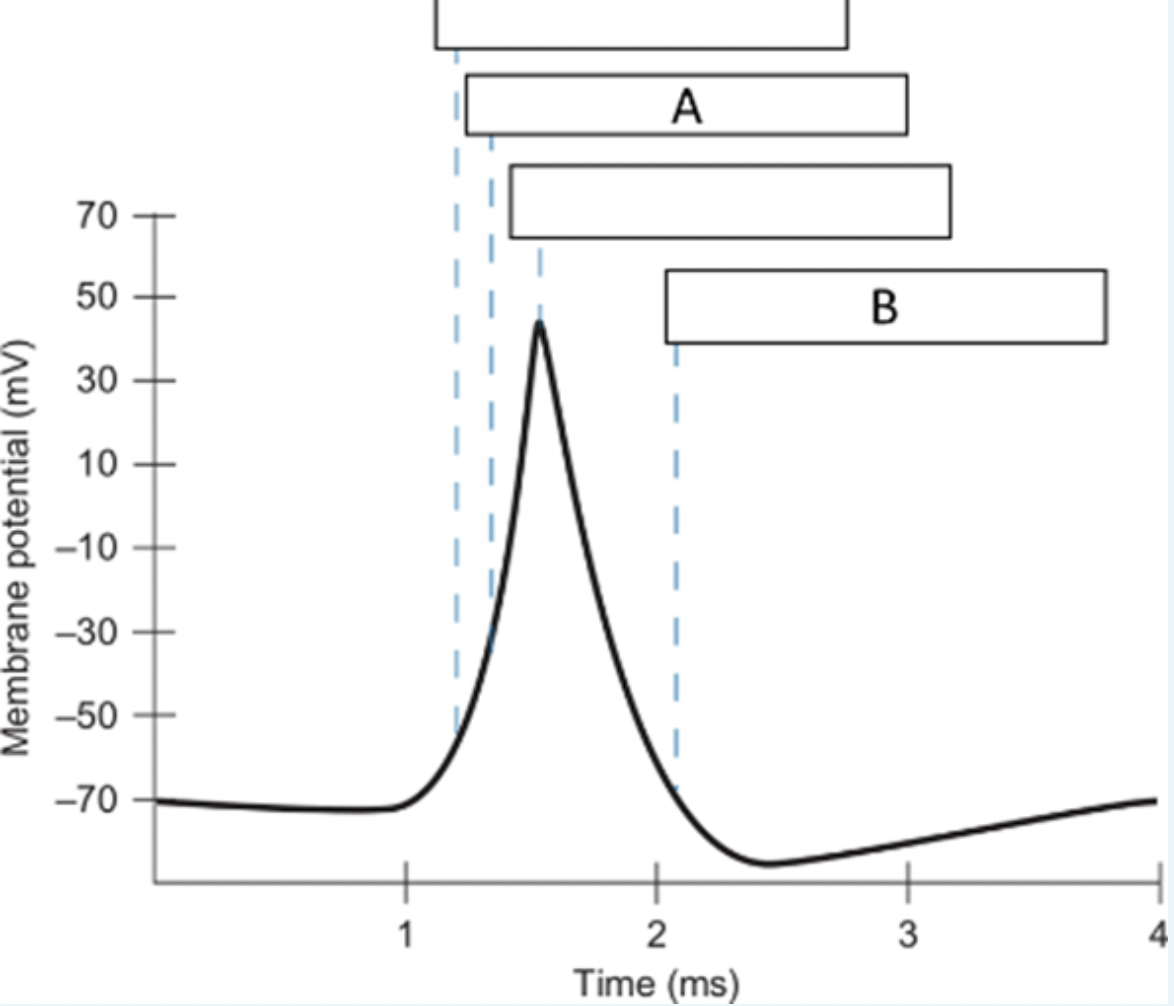
What is happening at location B on the voltage trace?
a.Sodium channels open
b.Sodium channels inactivate
c.Potassium channels open
d.Potassium channels start to close
d.Potassium channels start to close
Which glial cell provides the structural support necessary for saltatory conduction in the CNS?
a.Oligodendrocytes
b.Schwann cells
c.Astrocytes
d.Microglia
a.Oligodendrocytes
For a signal to cross the synapse between two neurons, a ___________ is released from the presynaptic cell and it activates or inhibits the postsynaptic cell.
a.protein
b.kinesin
c.dynein
d.neurotransmitter
e.mitochondria
d.neurotransmitter
Action potentials are _______________ while postsynaptic potentials are _______________.
a.Graded; all-or-none
b.Energy-independent; energy-dependent
c.Non-decremental; decremental
d.Hyperpolarizing events; depolarizing events
c.Non-decremental; decremental
Channels that produce postsynaptic potentials are ________-gated while channels that produce action potentials are _________-gated.
a.voltage; ligand
b.ligand; voltage
c.voltage; chemical
d.ligand; chemical
b.ligand; voltage
Neurons communicate different information by varying the ______ of their action potentials, which in turn varies the amount of neurotransmitter that is released.
a.magnitude
b.frequency
c.pattern
d.shape
e.a & d
f. b & c
f. b & c
Reductionism
seeking to interpret complex phenomena in terms of simpler phenomena
Generalization
Seeking universal or general explanations