AP Biology - Biochemistry
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Atoms
Building blocks of matter
25 elements are essential for life
4 of those elements make up 96% of living matter
Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Nitrogen (N)
Valence shells
The electrons in the outermost portion
This guides reactions
Guiding reactions
Tendency for atoms to fill or empty their valence shells
Covalent bond
Two atoms that share a pair of electrons
Strong, stable
Both atoms holding onto electrons
forms molecules
Nonpolar
Pair of electrons shared equally by two atoms
Atoms involved have similar electronegativity
Polar
Pair of electrons shared unequally by two atoms
Ex: H20
Oxygen is way more electronegative than water
Hydrogen bond
Intermolecular force (Happens between molecules)
Weak bond
Polar water creates molecular attractions
Attraction between positive H in one H2O to a negative O in another H2O
Cohesion/Adhesion
H2O to H2O (Cohesion)
H bonding between H2O molecules
Surface tension
H bonding with other (Adhesion)
Capillary action
Water is a good solvent
Polarity makes water a really good solvent
Easy for things to be dissolved in water
Things that aren't polar or don’t have charge can’t dissolve in water (oils)
H2O surrounds + and - ions
Density
Why is ice floating important?
Ice insulates water below allowing life to survive winters
If ice sank
Bodies of water would freeze
High specific heat
Amount of energy required to 1g to 1 degree (C)
H2O moderates temperatures on earth
Lots of water in the air stabilizes temperatures in the air
If water got hot really fast it would be hard to live on Earth
High Heat of Vaporization
Takes a lot of energy to get water to move from liquid to gas taking heat with it
When we sweat, water molecules absorb lots of heat from our body to evaporate which cools us nicely
Large bodies of water (oceans, lakes) absorb and release heat slowly, moderating Earth’s climate.
pH scale
Water ionizes
H(+) splits off from H2O, leaving OH(-)
if [H+] = [-OH], water is neutral
if [H+] > [-OH], water is acidic
if [H+] < [-OH], water is basic
Buffer
A solution that resists significant changes to its pH when small amounts of strong acid or base are added
Maintains a stable environment
Why is carbon so special?
All life is built on carbon
Organic = carbon based
Tetravalent (4 bonds) = good builder
What is an isomer?
Molecules with the same molecular formula but different structures
Different chemical properties
Different biological functions
FORM FITS FUNCTION
Functional groups
Parts of an organic molecule that give it distinctive properties
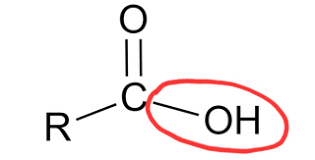
Hydroxyl
C-C-O-H
Alcohols, names end in -ol
Donates H+. acidic
Increase polarity
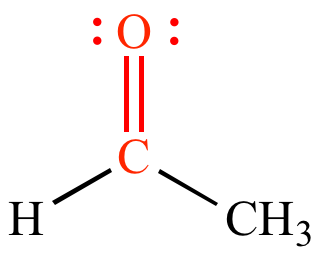
Carbonyl
C double bonded to O increases polarity
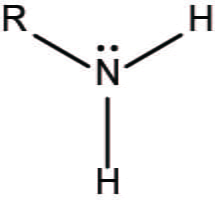
Amino
-NH2
Amines are basic, they pull H+ out of a solution
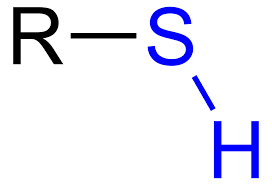
Sulfhydryl
Compounds with SH = thoils
SH groups stabilize the structure of proteins = tertiary structure
Polar
Phosphate
P bonded to 4 O
Lots of negative charge
Highly reactive
Transfers energy between organic molecules
Acidic, releases H
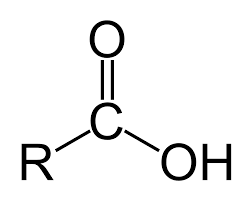
Carboxyl
Acids, they donate H+
COOH
Polymers
Long molecules built by linking repeating building blocks in a chain.
Monomer
The building blocks themselves
How to build a macromolecule/polymer
Condensation ←→Dehydration
Joins monomers by “taking” H2O out
One monomer donates -OH
Other monomer donates H+
Together this forms H2O
How to break a macromolecule/polymer
Hydrolysis (Opposite of dehydration synthesis)
Use H2O to breakdown polymers
Cleave off one monomer at a time
H2O is split into H+ and -OH
H+ and -OH attach to ends
What are the main purposes of carbs?
Energy
Energy storage
Raw materials
Structural materials (building)
Main formula for carbs
(CH2O)x
Composed of C, H, and O
Similar carbons and oxygens
Where is the energy stored?
Energy is stored in C—C bonds
This is a direct relationship to potential ATP (Energy currency)
More bonds = more potential
Simple to complex carbs
Monosaccharides (1)
Simple on monomer sugars
glucose
Disaccharides
2 monomers
sucrose
Polysaccharides
Large polymers
starch
What is the bond type for carbohydrates?
Glycosidic linkage
Disaccharides seem to hold hands
Monosaccharides seem to be more independent
Diversity of polysaccharides
Costs little energy to build
Easily reversible = easy to break/build
Function of polysaccharides
Energy storage
Starch (plants)
glycogen (animals)
Alpha formation glycosidic linkage (Enzyme)
Structure
cellulose (plants)
chitin (athropods, fungi)
NO Human enzyme (Beta formation glycosidic)
Cellulose
Most abundant organic compound on Earth
Herbivores have developed a mechanism to digest cellulose (mutualistic)
Most carnivores have not
What are the primary purposes of lipids (fats)?
Fat
Long term energy storage
Insulation
Shock absorption
Lipids are nonpolar due to the hydrocarbon chains (H-C)
Lack oxygen so electronegativity is similar
Monomer base
Fatty acids
DO NOT FORM POLYMERS
What is the bond name for a lipid?
Ester linkage
Types of fats
Saturated
All C bonded to H
NO double C-C bonds
long, straight chains
Unsaturated
C-C double bonds
Kinks in the chain
Phospholipids structure
Glycerol + 2 fatty acids + PO4
Polar “head”
Nonpolar “tails”
This makes phospholipids amphipathic (polar and nonpolar)
They are found in cell membranes
Cholesterol/steroids structure
4 fused carbon rings
Different steroids are created by attaching different functional groups to rings
Different structures creates different functions
Purposes and functions of proteins
Most structurally and functionally diverse group
Enzymes
Structure
Carriers and transport
Cell communication
Defense
Movement
Storage
Monomer for proteins
Amino Acid
20 different amino acids
Polymer for proteins
Polypeptide
Bond name for proteins
Peptide bond
Amino group (NH2) to Carboxyl (COOH) of another
Primary (1st degree)
Order of amino acids in a chain
Sequence is determined by gene (DNA)
Slight change affects function
Secondary (2nd degree)
“local folding”
folding short sections of polypeptide
Hydrogen bonds between folded section
Forms sections of 3D structure
Alpha Helix
Beta pleated sheets
Tertiary (3rd degree)
“Whole molecule folding”
Interactions between distant amino acids
These interactions are nonpolar
Covalent bonds in sulfhydryls stabilize the protein’s shape
Every protein folds to this level
Quaternary (4th degree)
More than one polypeptide chain folded together
Only then does polypeptide become functional protein
Most proteins fold to this level
Denature/renature
Unfolding of a protein
Conditions that disrupt H bonds, ionic bonds, disulfide bridges
pH, temp, salinity
destroys functionality
Function/purpose of nucleic acids
Genetic material
stores information
Transfers information
Monomer of nucleic acid
Nucleotide
Nitrogen base, pentose sugar, phosphate group
Polymer of nucleotide
DNA - double helix
RNA - single helix
Types of nitrogen bases
Purines
Double ring as N base
Adenine (A)
Guanine (G)
Pyrimidines
Single ring as N base
Cytosine (C)
Thymine (T)
Uracil (U)
Bond name for Nucleic Acids
Phosphodiester bond (Covalent)
Sugar to PO4 bond
Base pairings
Nucleotides between DNA strand
Purine::Pyrimidine
A::T/U (2 H bonds)
G::C (3 H bonds)
When does DNA need to be replicated?
2 strands are complimentary to each other
Have one, can build other
Have one, can build the whole/
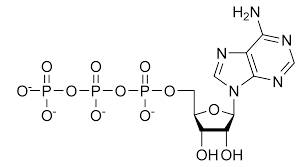
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate
Energy carrying molecule in cells
Nitrogen base, sugar, and phosphate