Ap Human Geo - 6.1-6.4 vocab quiz
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Ecumene
a variety of community types with a range of population densities.
ex: rural, urban, and suburban areas.
Rural
with low concentrations of people.
ex: farms and villages.
Urban
with high concentrations of people.
ex: cities.
Suburbs
primary residential areas near cities.
ex: i live in one.
Settlement
a place with a permanent human population.
ex: European settlements.
Urbanization
the process of developing towns and cities.
ex: describing a region as urbanied indicates that cities are present there.
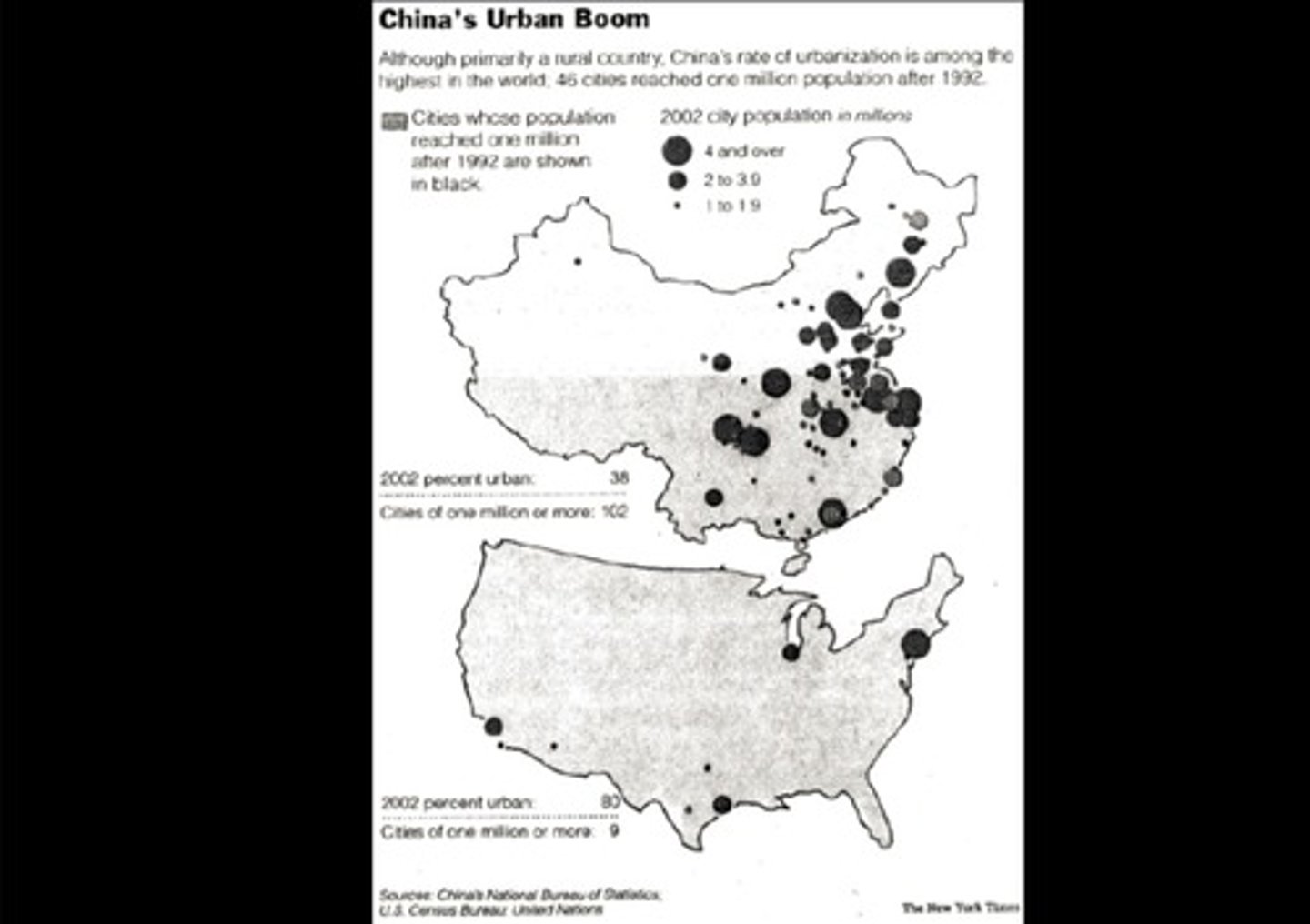
Percent Urban
an indicator of the proportion of the population that lives in cities and towns as compared to those that live in rural areas.
ex: see picture.
Site
describes the characteristics at the immediate location.
ex: physical features, climate, labor force, and human structures.
Situation
refers to the location of a place relative to its connectivity to other places.
ex: near a gold mine.
City-State
a city that with its surrounding territory forms an independent state.
ex: has its own political system and functioned independently from other city-states.
Urban Hearth
area generally associated with defensible sites and river valleys in which seasonal floods and fertile soils allowed for an agricultural surplus.
ex: the Nile River Valley and Nile Delta in modern Egypt.
Urban Area
usually defined as a central city plus land developed for commercial, industrial, or residential purposes, and includes the surrounding suburbs.
ex: New York.
City
a higher-density area with territory inside officially recognized political boundaries.
ex: nyc.
Metropolitan Area (metro area)
a collection of adjacent cities economically connected, across which population density is high and continuous.
ex: Denver, Colorado.
Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA)
In the United States, a central city of at least 50,000 population, the county within which the city is located, and adjacent counties meeting one of several tests indicating a functional connection to the central city.
ex: New York City, New York and New Jersey.
Micropolitan Statistical Area
cities of more than 10,000 inhabitants (but less than 50,000), the county in which they are located and surrounding counties with a high degree of integration.
ex: Boone, North Carolina.
Nodal Region
focal point in a matrix of connections
ex: the circulation area of the New York Times in New York.
Social Heterogeneity
the population of cities, as compared to other areas, contains a greater variety of people.
ex: diversity in cultural interests and languages spoken.
Time-Space Compression
through processes such as globalization time is accelerated and the significance of space is reduced.
ex: messages and communication travels faster now than it did in the 1700s.
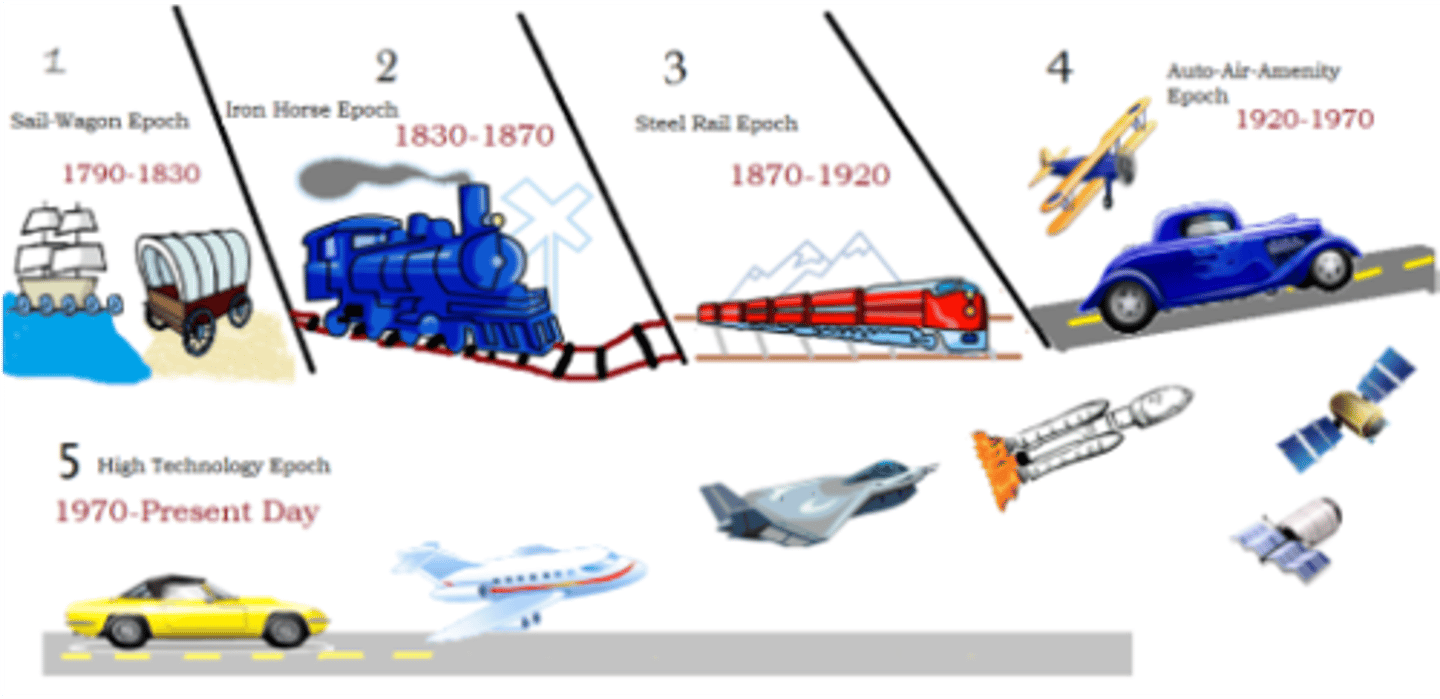
Borchert's Transportation Model
describes urban growth based on transportation technology.
ex: see picture.
Pedestrian Cities
cities shaped by the distances people could walk.
ex: the earliest urban centers; Copenhagen, Denmark.
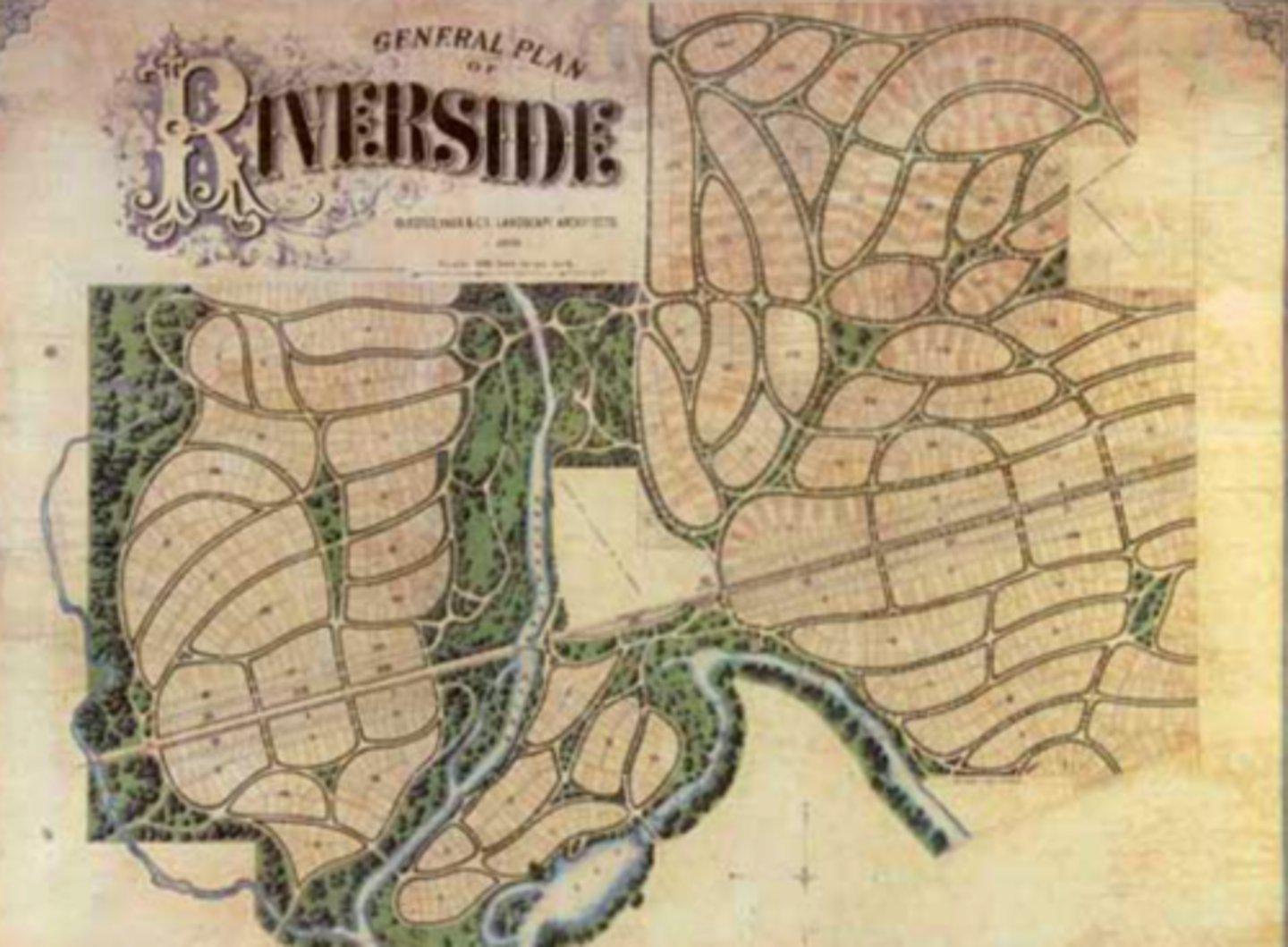
Streetcar Suburbs
communities that grew up along rail lines.
ex: often creates a pinwheel city.
Suburbanization
the process of people moving, usually from cities, to residential areas on the outskirts of cities.
ex: sKings County, New York served New York City as farmland in the 18th century, with boats carrying produce across the East River.
Sprawl
the rapid expansion of the spatial extent of a city and occurs for numerous reasons.
ex: see picture. (centripetal + centrifugal forces).
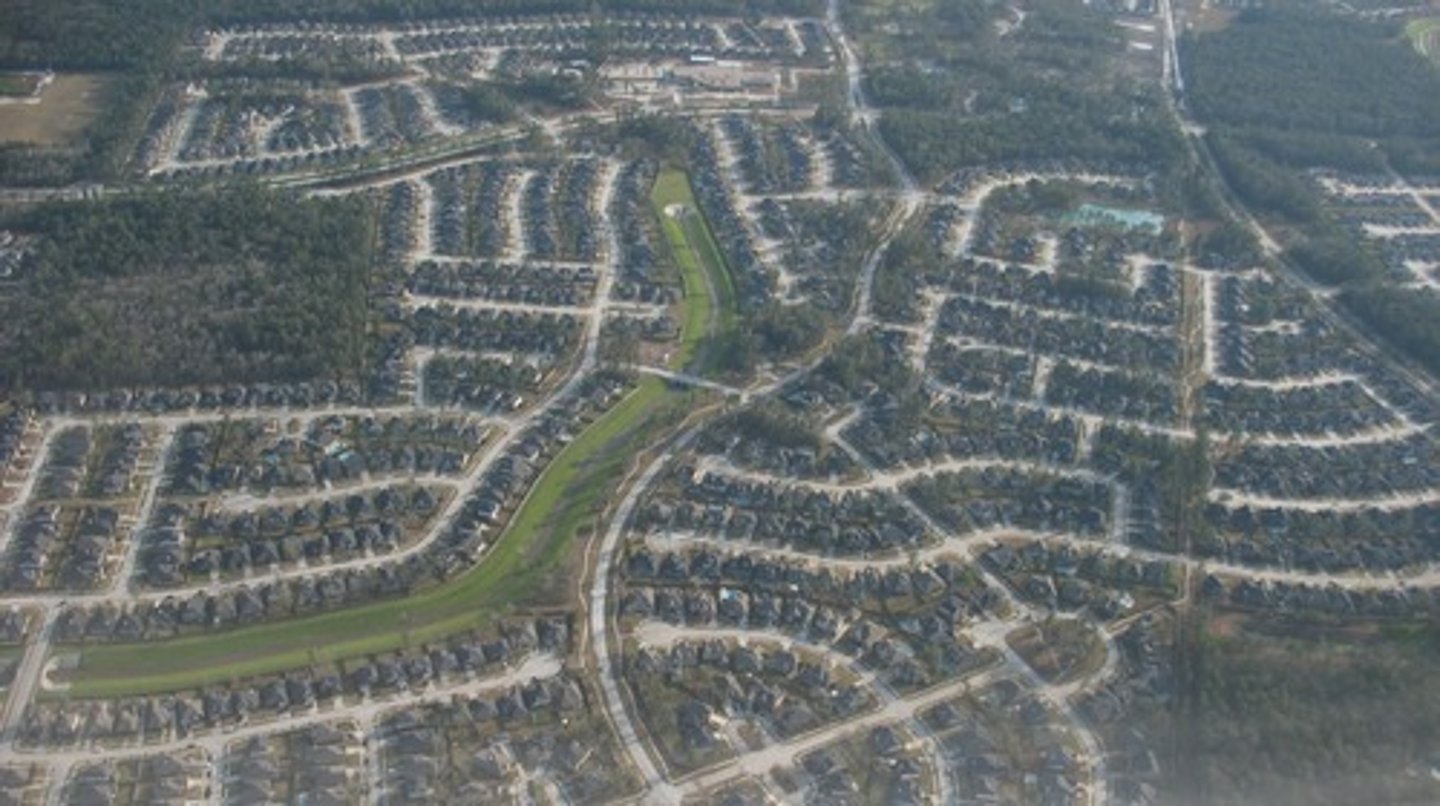

Leap-Frog Development
a specific process that encourages spraws; where developers purchase land and build communities beyond the periphery of the city's built area.
ex: Atlanta, grew and now covers over 8,300 square miles and contains 6 million people.
BoomBurbs
rapidly growing communities (over 10 percent per 10 years); have a total population of over 100,000 people, and are not the largest city in the metro area.
ex: do not usually have a dense urban center; Mesa-Arizona, Plano-Texas, Riverside-California.
Edge Cities
nodes of economic activity that have developed in the periphery of large cities.
ex: usually have tall office buildings, a concentration of retail shops, junction of major transportation routes.
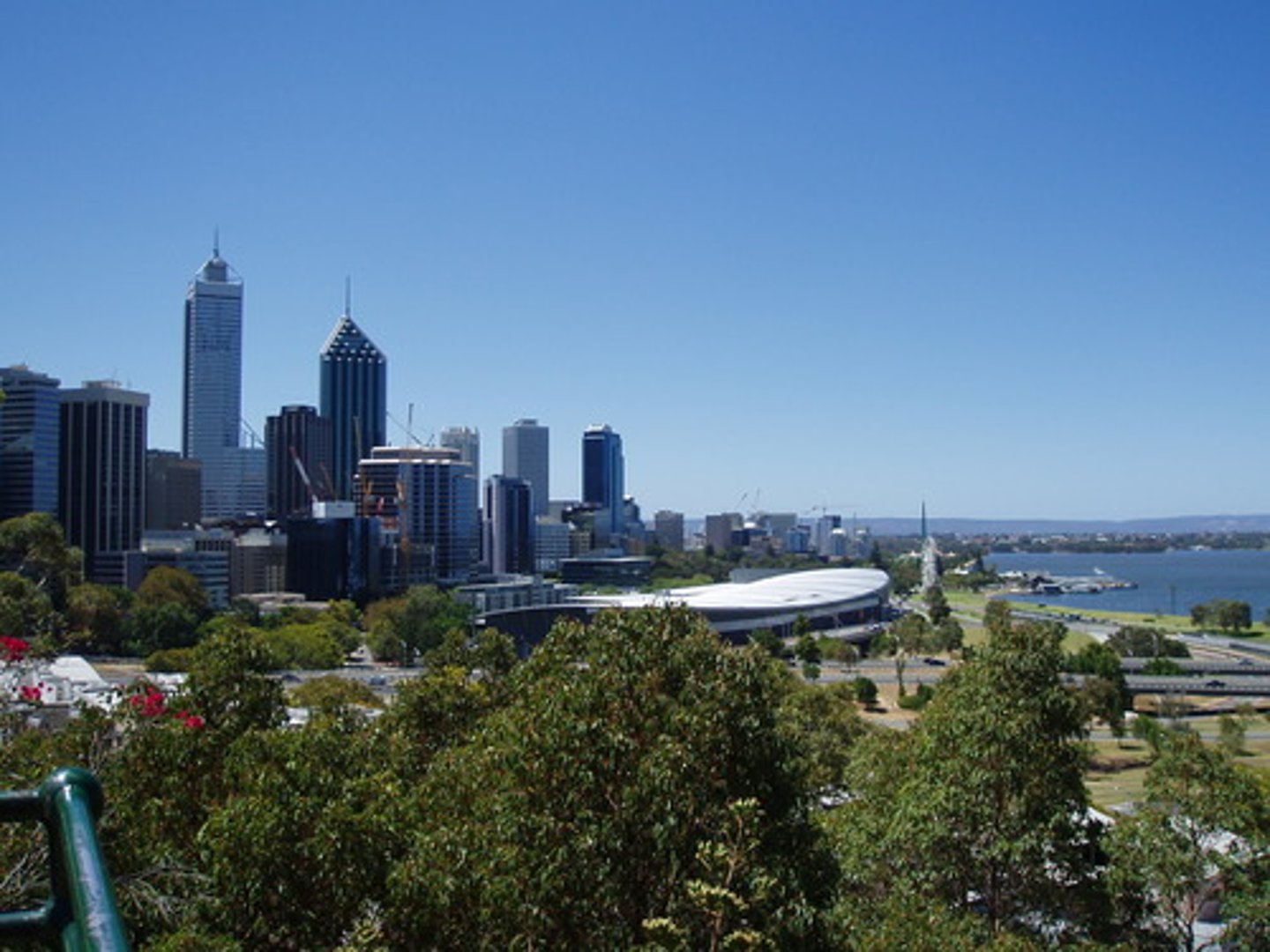

Counter Urbanization (urbanization)
the counter-flow of urban residents leaving cities.
ex: cities are destinations for many of the world's migrants.
Exurbs
the prosperous residential districts beyond the suburbs.
ex: see picture.

Reurbanization
some suburbanites have returned to live in cities.
ex: see picture.
Megacities
have a population of more than 10 million people.
ex: London, UK.
Metacities
continuous urban area with a population greater than 20 million people; attributes if a network of urban areas that have grown together to form a larger interconnected urban system.
ex: Shenzhen, China.
Megalopolis
describes a chain of connected cities.
ex: string of cities from Boston, thorough NYC, to Philadelphia and Baltimore.
Conurbanization
an uninterrupted urban are made of towns, suburbs, and cities.
ex: in colorado Highland ranch is a conurbation area because there are more cities around it.
World Cities (global cities)
exert influence far beyond their national boundaries.
ex: Paris + Tokyo.
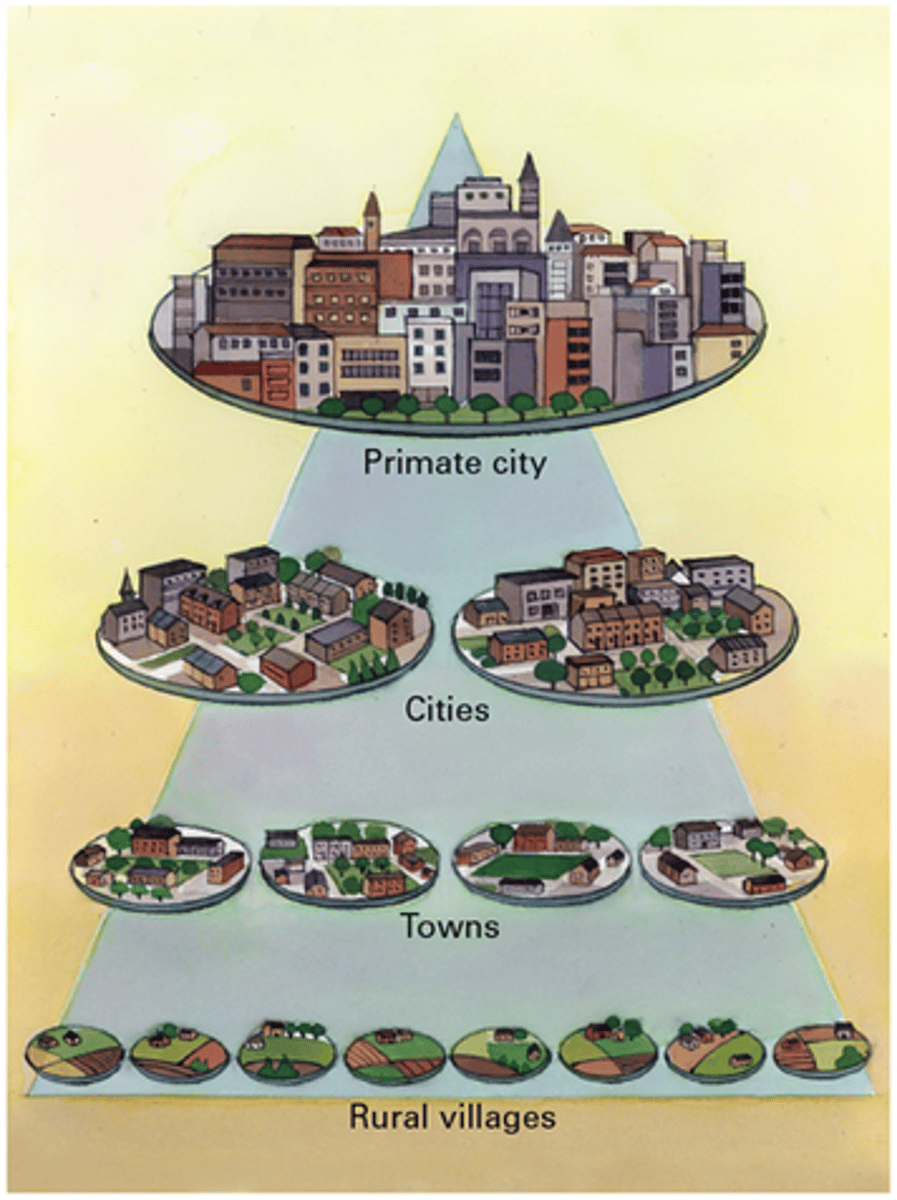
Urban Hierarchy
a ranking of settlements according to their size and economic functions.
ex: according to size and economic functions.
Nodal Cities
command centers on a regional and occasionally national level.
ex: Denver, Phoenix, and Minneapolis.
Urban System
an interdependent set of cities that interact on the regional, national, and global scale.
ex: Karachi, Pakistan.
Rank-Size Rule
a pattern of settlements in a country, such that the nth largest settlement is 1/n the population of the largest settlement.
ex: describes one way in which the sizes of cities within a region may develop.
Higher-Order Services
usually expensive, need a large number of people to support, and are only occasionally utilized.
ex: major sports teams, large malls, luxury car dealerships, and large specialized hospital research.
Lower-Order Services
usually less expensive than a higher-order service, require a small population to support, and are used on a daily or weekly basis.
ex: gas stations, local grocery stores, or small restaurants.
Primate City
a city that ranks first in a nation in terms of population and economy.
ex: The United Kingdom exhibits urban primacy.
Gravity Model
states that larger and closer places will have more interactions than places that are smaller and farther from each other.
ex: gravity model of migration.
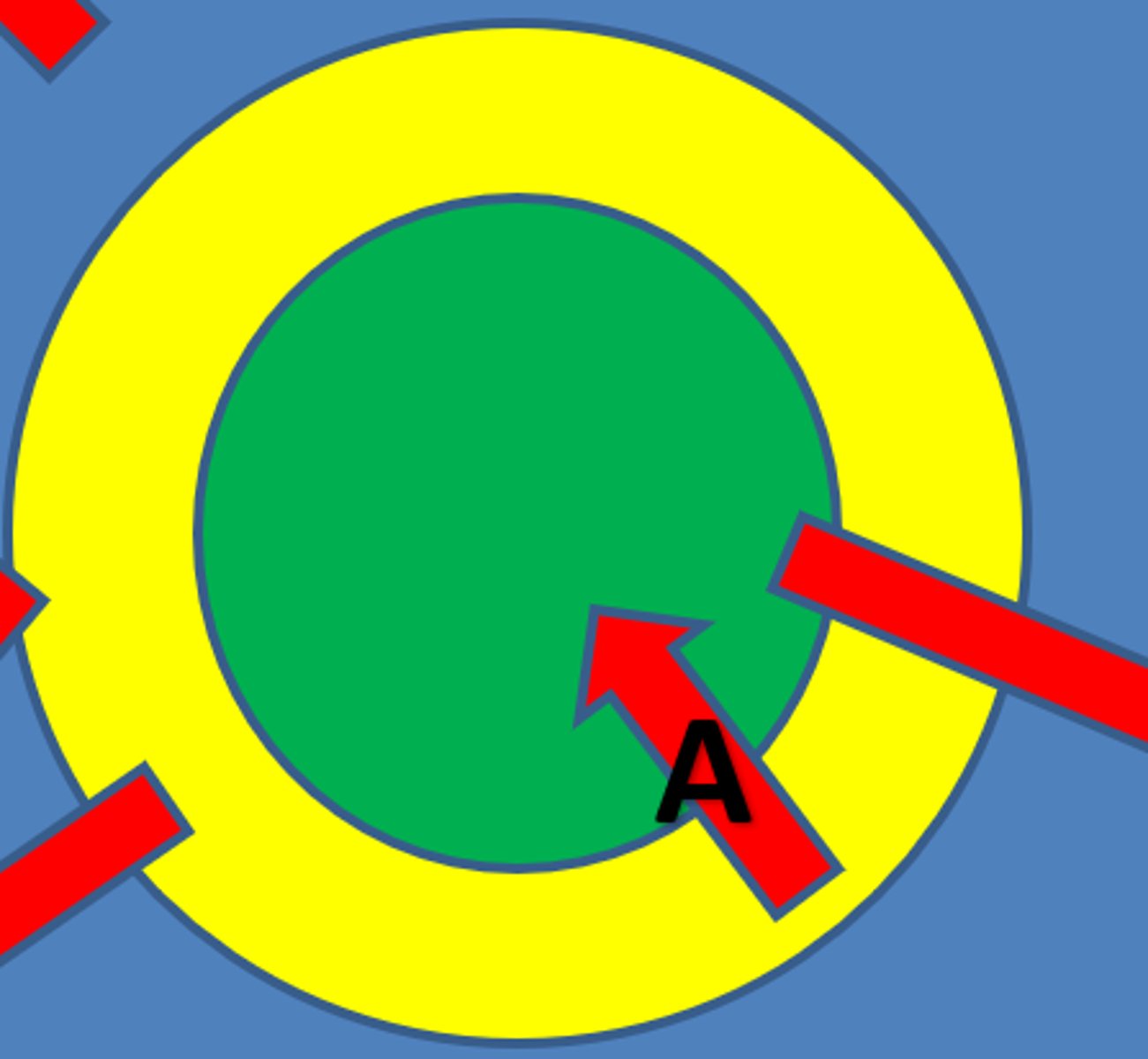
Central Place Theory
a theory that explains the distribution of services, based on the fact that settlements serve as centers of market areas for services; larger settlements are fewer and farther apart than smaller settlements and provide services for a larger number of people who are willing to travel farther.
ex: see picture.
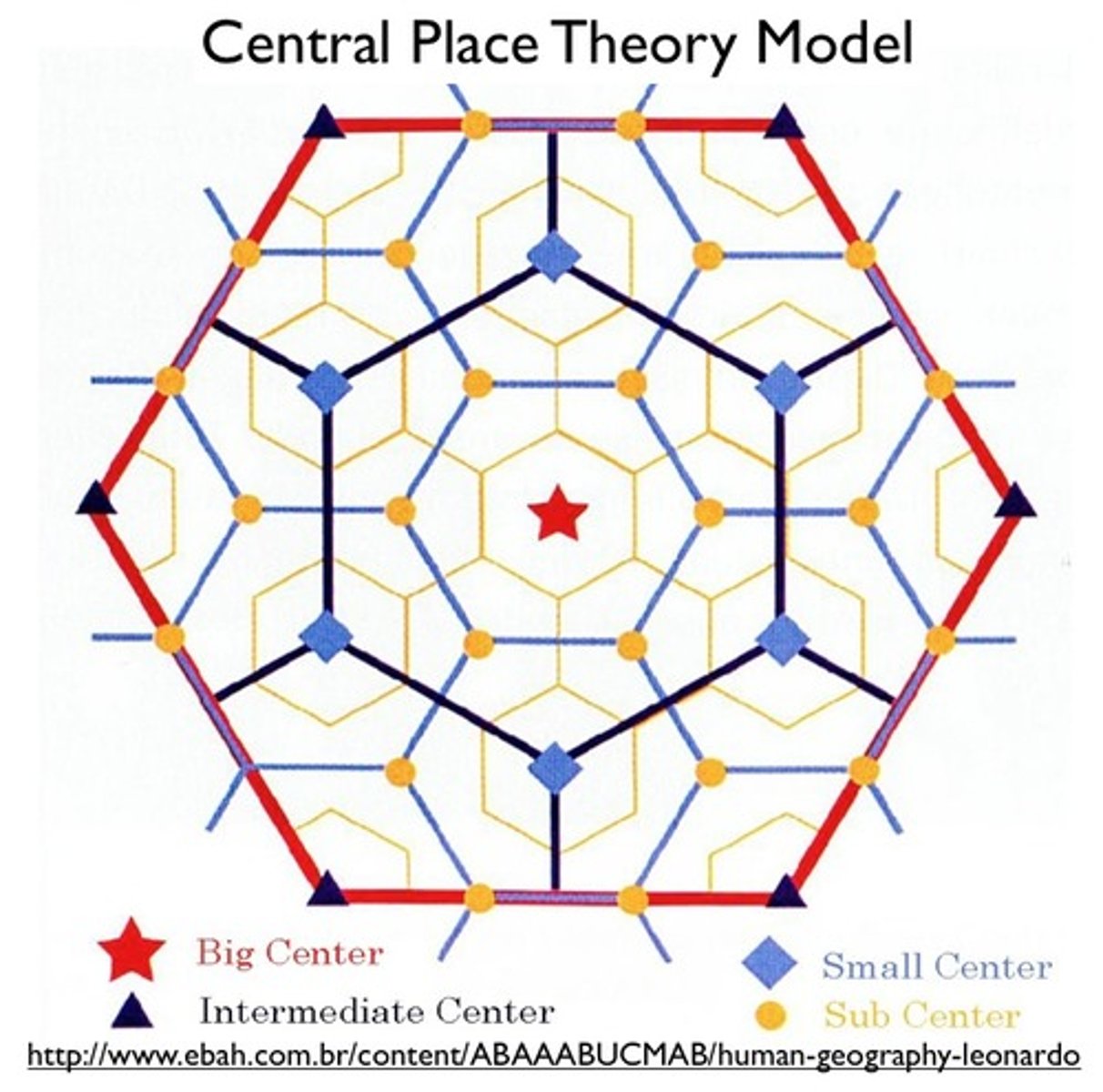
Central Place
a location where people go to receive goods and services.
ex: major city.
Market Area
zone that contains people who will purchase goods or services.
ex: my neighborhood.

Hexagonal Hinterlands
the shape of the market areas in the central place theory.
ex: see picture.
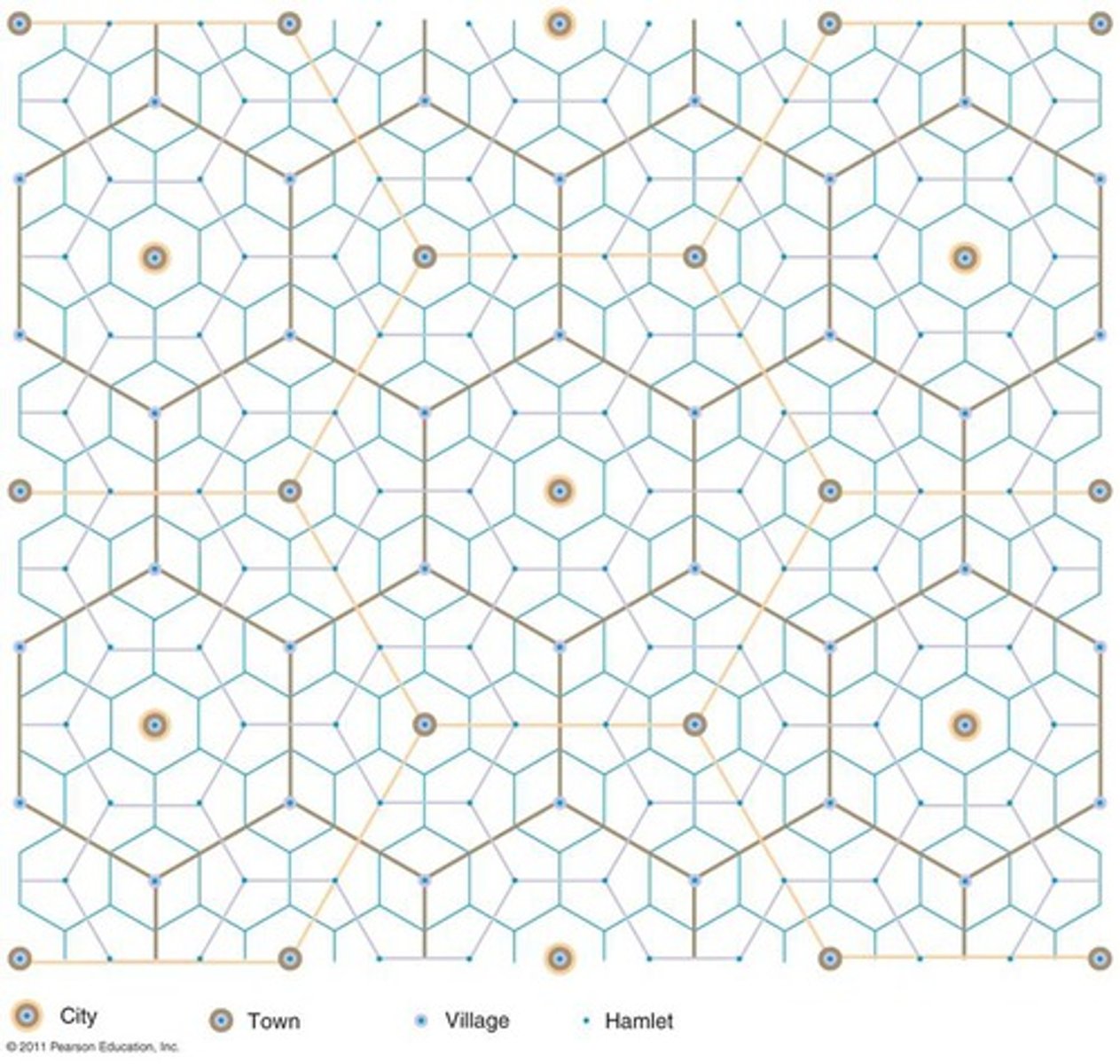
Threshold
the size of population necessary for any particular service to exist and remain profitable.
ex: crossing the threshold.
Range
the distance people will travel to obtain specific goods or services.
ex: my mom would go far for a prep o irl.