Sexually Transmitted Infections Chapters 5
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
FACTORS PLACING TEENAGERS AT RISK FOR STIS
-Female anatomy
-Teenagers' feelings of invincibility
-Unprotected intercourse
-Partnerships of limited duration
-Obstacles to using the health care system
Chlamydia: manifestation
-may be asymptomatic
-dysuria
-urinary frequency
-dyspareunia
-cervical discharge
-endocervicitis
-inflammations of the rectum and lining of the eye, can infect throat
gonorrhea manifestations
-may be asymptomatic
-dysuria
-urinaryfrequency
-vaginal discharge
-dyspareunia
-endocervicitis
-arthritis
-PID
-rectal infection
genital herpes manifestation
-blister-like genital lesions
-dysuria
-fever
-headache
-muscle aches
-malaise
when you treat chlamydia you also must treat
ghonorhea
syphilis disease is divided into
4 stages
primary stage of syphilis
-chancre on place of bacteria entrance
-concave sore
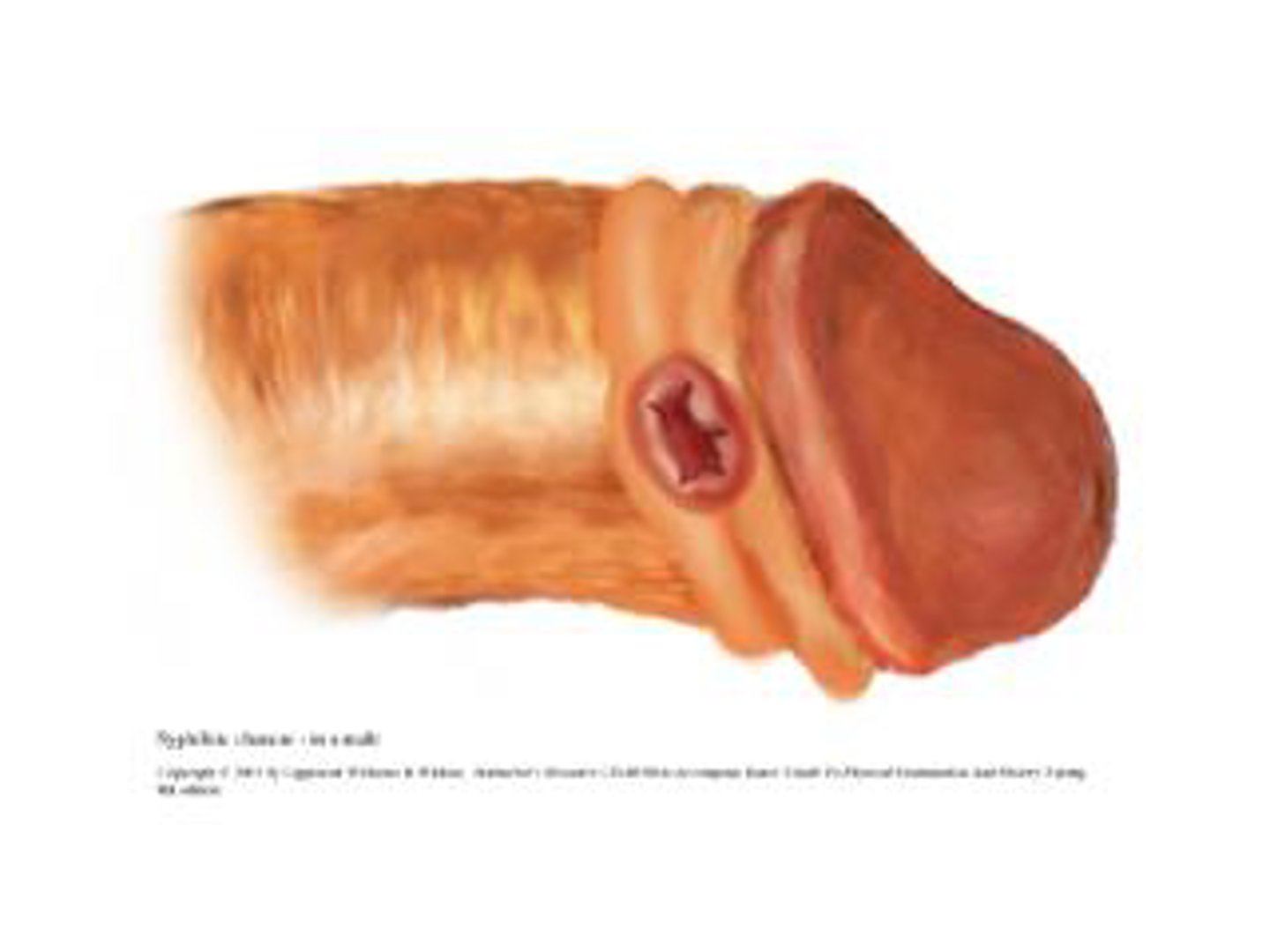
secondary stage of syphilis
maculopapular rash, sore throat, lymphadenopathy,flu-like symptoms
Latent stage of syphilis
no symptoms; can be infective first 1-2 years of latency, some will go on to develop tertiary infections
Tertiary stage of syphilis
tumors of the skin, bones, and liver, CNS symptoms,CV symptoms; usually not reversible
CNS syphilis sx include
dementia and memory loss
Trichomoniasis is caused by a
-Trichomonas vaginalis is an ovoid, single-cell protozoan parasite
-sexually transmitted
-can also live on damp/wet surfaces and poorly cleaned/maintained hot tubs, drains, towels, and bathing suits.
Trichomoniasis manifestations
-may be asymptomatic
-dysuria
-urinary frequency
-vaginal discharge
-dyspareunia
-lower abdominal pain
thrichomoniasis has what color discharge
A heavy yellow/green or grayish frothy or bubbly discharge
Trichomoniasis cervix characteristics
-bleeding on contact
-petichiae on cervix
Trichomoniasis vaginal characteristics
-Vaginal pruritus and vulvar soreness
-Vaginal odor described as foul
-Vaginal or vulvar erythema
trichomoniasis tx
-A single 2-g dose of oral metronidazole (Flagyl), tinidazole (Tindamax), or secnidazole for both partners is a common treatment for this infection.
-Multidose therapy, consisting of 500 mg twice a day for 5 to 7 days, is also available and is the preferred treatment in females when using metronidazole
trichomaniasis diagnostic test
nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs),
genital warts manifestations
-wart-like lesions that are soft, moist, or flesh colored
-appear on the vulva and cervix and inside; also surrounding the vagina and anus
-sometimes appear in cauliflower-like clusters, and are either raised or flat, and small or large
open discussion includes
-Client's sexual habits
-Appropriate anticipatory guidance
-Methods to prevent recurrent STIs
most common causes of vaginitis
-Candida: fungus
-Trichomonas: protozoan
-Gardnerella: bacterium
candida is
fungus
trichamonas is
protazoan
candida is
fungus
VULVOVAGINAL CANDIDIASIS NURSING MANAGEMENT
EDUCATION
Prevention of VULVOVAGINAL CANDIDIASIS
-Cotton underwear
-Avoidance of irritants
-Good body hygiene
-Avoidance of douching or super-absorbent tampons
why do you want to avoid douching
-take out good and bad bacteria
bacterial vagniosis is the most prevalent cause of
vaginal discharge
BV vaginal discharge is
Thin, white/grayish vaginal discharge that adheres to the vaginal mucosa
PH for BV
higher than 4.5
bacterial vaginosis smell
fishy
-(secretion is mixed with a drop of 10% potassium hydroxide on a slide, producing a characteristic stale fishy odor)positive whiff test
_______ women of asymotomatic with bacterial vaginosis
50%-75%
risk factors for bacterial vaginosis
-Multiple sex partners
-Douching
-Lack of vaginal lactobacilli
where can you get good bacteria
-probiotics (yogurt/supps)
BV tx
-treatment for BV typically includes oral or vaginal metronidazole (Flagyl)
- clindamycin (Cleocin) cream.
infections that cause cervicitis are
chlamydia
ghonnorrhea
untreated chlamydia leads to
-cervicitis
-urethritis
-PID
-which leads to infertility
-chronic pelvic pain
-ectopic pregnancies
chlamydia untreated in preganncy
-premature rupture of membranes
-preterm labor
-low-birth-weight newborns
--phthalmia neonatorum, which is an acute mucopurulent conjunctivitis occurring in the first month of birth.
chlamydia is the ______
most common bacterial STI in the US
chlamydia is majorly ____
asymptomatic
chlamydia is caused by
Chlamydia trachomatis (intracellular parasite)
therapeutic management of chlamydia
o Antibiotics (doxycycline, azithromycin)o Combination regimen if gonorrhea also presento Screening
ABX used to treat chlamydia or ghonnorrhea are
doxycycline and azithromycin
-shot in butt
nursing assessment for chlamydia includes
-risk factors
-CM
-lab tests
chlamydia risk factors
-adolescence
-multiple sex partners
-new sex partner
-sex without condom
-oral contraceptive use
-pregnancy
-history of another STI
chlamydia manifestations
-mucopurulent vaginal discharge
-urethritis
-bartholinitis
-endometritis
-salpingitis
-dysfunctional uterine bleeding
chlamydia testing
-Urine testing or swab specimen culture
-immunofluorescence
-EIA
-nucleic acid amplification
second most common STI in the US is
ghonorrhea
careful because ghonnorrhea is _____ and you must _____
-highly contagious
-report to health care organizations
gonorrhea cause is
aerobic gram-negative intracellular diplococcus
site of infection for gonorrhea
-columnar epithelium of endocervix
-almost exclusively gotten through sex
management for gonorrhea is
-ceftriaxone (Rocephin) 500 mg for pregnant and nonpregnant females weighing less than 150 kg (CDC, 2022a).
-If chlamydia has not been ruled out, proper treatment for chlamydia should be started
risk factors for gonorrhea
-low socioeconomic status
-urban living
-single status
-inconsistent use of barrier contraceptives
-age <20 years, multiple sex partners
manifestations of gonorrhea
-most asymptomatic;
-abnormal vaginal discharge
-dysuria
-cervicitis
-abnormal vaginal bleeding
-Bartholin abscess
-PID
if a women gives birth with gonorrhea beware of
neonatal conjunctivitis
-give azithromycin/erythromycin eye drops
ghonnorrhea if untreated can lead to
-organism ascends upward through the endocervical canal to the endometrium of the uterus further on to the fallopian tubes, and out into the peritoneal cavity.
-When the peritoneum and the ovaries become involved, the condition is known as PID
- If gonorrhea remains untreated, it can enter the bloodstream and produce a disseminated gonococcal infection.
-This severe form of infection can invade the joints (arthritis), the heart (endocarditis), the brain (meningitis), and the liver (toxic hepatitis).
NURSING MANAGEMENT:CHLAMYDIA AND GONORRHEA
-Treatment strategies
-Referrals
-Preventive measures
-Education and counseling
-Sexual history
-Public education
-Safe sex practices
genital herpes simplex is a
-Recurrent lifelong viral infection
how do you get genital herpes simplex
-Transmission via contact with mucous membranes or breaks in skin with visible or non visible lesions
-Kissing, sexual contact, and vaginal delivery
with herpes even after tx
you shed the virus, still drink from other ppls cups. Can still spread it
true or false a baby can get genital herpes
true, via vaginal delivery
therapeutic management for herpes
-No cure
- Antiretroviral therapy to reduce or suppress symptoms, shedding,and recurrent episodes16
primary episode herpes
-(most severe and prolonged)
-multiple painful vesicular lesions
- mucopurulent discharge
-superinfection with candida
-fever, chills, malaise, dysuria, headache, genital irritation
-inguinal tenderness
-lymphadenopathy
-vulva, vagina, and perineal areas.
recurrent herpes infection
-more localized and quicker resolution
-tingling
-itching
-pain
-unilateral genital lesions (more localized)
diagnosis of herpes simplex is confirmed by
viral culture of fluid from vesicle
Primary syphilis
chancre, painless bilateral adenopathy
secondary symphilis
-flu-like symptoms
-rash on trunk/palms/soles
-alopecia
-adenopathy
latency syphylis
-absence of manifestations
-positive serology
tertiary syphylis
-life-threatening heart disease
-neurologic disease
tests for syphylis
-DRL and RPR
-FTA-ABS, TPPA
-TPHA
syphylis tx
- An injection of penicillin G can cure primary, secondary, or early latent syphilis.
-Preparation, dosage, and treatment length depend on the disease stage
- For late latent syphilis, three doses of penicillin at weekly intervals are needed.
-Pregnant people should be treated with the same regimen for whichever stage they present with.
-Other medications, such as doxycycline, are available if the patient is allergic to penicillin.
-Patients should be reevaluated at 6 and 12 months after treatment for primary or secondary syphilis with additional serologic testing.
-Patients with latent syphilis should be followed up with clinically and serologically at 6, 12, and 24 months
NURSING MANAGEMENT OF HERPES AND SYPHILIS
- Education
- Referral to support group
- Coping skills
- Options for treatment and rehabilitation
PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE results from
-Result of ascending poly microbial infection of upper female reproductive tract
-Frequently from untreated chlamydia or gonorrhea
therapeutic management for PID
-Empiric broad-spectrum antibiotics
-Oral fluid
-Bed rest
- Pain management
Nursing management of PID
-RISKS
-CM
-DX
PID manifestations
-lower abdominal tenderness
-adnenal tenderness
-cervical motion tenderness
-fever
-dysmenorrhea
-dysuria
-dyspareunia
PID dx
-endometrial biopsy
-transvaginal ultrasound
-laparoscopic examination
nursing management of PID
-hydration
-analgesics
-education to prevent recurrence
-risk assessment
-sexual counseling
HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS IS THE
most common viral infection in the US
how does HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS manifest
-Genital warts or condylomata
-warts can cause cervical cancer
HPV nursing assessment
-Risk factors.
-Manifestations
- HPV test
HPV manifestations
most asymptomatic; visible genital warts.
HPV diagnostic test
Pap smears
therapeautic management for HPV
-primary prevention via vaccine and education
-at age 11 up until 45
-treatment of lesions and warts
-secondary prevention via education
NURSING MANAGEMENT FOR HPV
-Teaching about prevention to Promotion of vaccines and screening tests
-Education about link between HPV and cervical cancer
HPV tx
none for virus
-only treat warts
hepatitis A spreads via
GI tract
hepatitis B spreads via
body fluids
theraputic management for hep a and b
-prevention through immunization
nursing management hepatitis
-screening/vaccination
how many types of HPV can cause cervical cancer
16 and 18
mursing assessment hepatitis
-blood titers along with clinical manifestations
scabies
-intensely pruritic dermatitis with lesions
pubic lice
pruritus with lice or nits
tx for ectoparasitic infections
-permethrin cream
-lindane shampoo
-decontamination of bedding and clothing
-treatment of familymembers and sexual partners
-3 teared approach
3 teared approach
1. eradicate infestation
2. remove nits
3. prevent spread or recurrence
HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS
-causes AIDS
-mostly through sex
-increasing in adolescents
-FETAL/NEONATAL EFFECTS
HIV manifestations
-acute phase; asymptomatic with viral replication
-immunosuppression with opportunistic infection
-AIDS
diagnoses for AIDS
western blot test
therapeutic managaement of HIV
ART (Antiretroviral therapy)