ocr biology
1/525
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
526 Terms
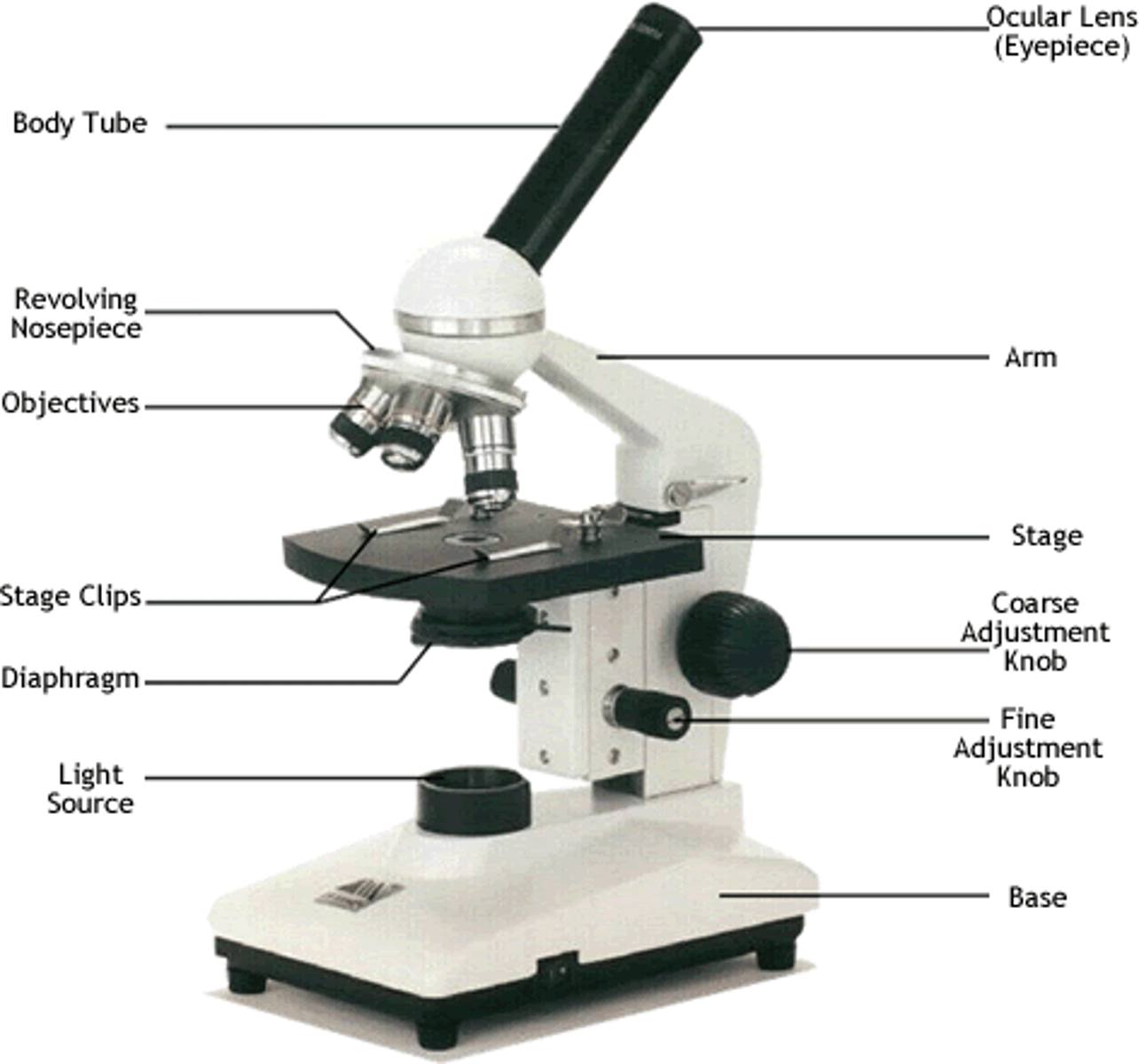
what are the different parts of a light microscope
(see diagram)
how do light microscopes work
-visible light is passed through a specimen
-refracted through two lenses (objective and eyepiece lenses)
why do microscopy specimens need to be stained
-allows the specimen to be seen under the microscope
-different cells/organelles to be distinguished
how are specimens prepared to be viewed under a light microscope
-cut into very thin sections,
-laid flat on a glass slide
-stains added
-glass cover slip is added from an angle so air is not trapped underneath
-slide is placed on stage under lowest power lens and focused before higher power lenses can be used
how do you convert from m->mm->um->nm
x1000->x1000->x1000
how do you convert nm->um->mm->m
/1000->/1000->/1000
define magnification
the degree to which the size of an image is larger than the object itself
define resolution
the ability of a microscope to distinguish between two points (the amount of detail)
what is the formula for magnification
I = A x M (image size = actual size x magnification)
how do you prepare a dry mount
take a thin slice of the specimen and place it in the middle of a clean slide using tweezers then add a cover slide
how do you prepare a wet mount
place specimen on microscope slide and add a drop of distilled water, then add the cover slip from an air to prevent air bubbles getting trapped
how should scientific diagrams be drawn
-title,
-magnification
-smooth
-continuous lines
-no shading
what are the two types of graticule (microscope ruler)
eyepiece and stage/slide graticules
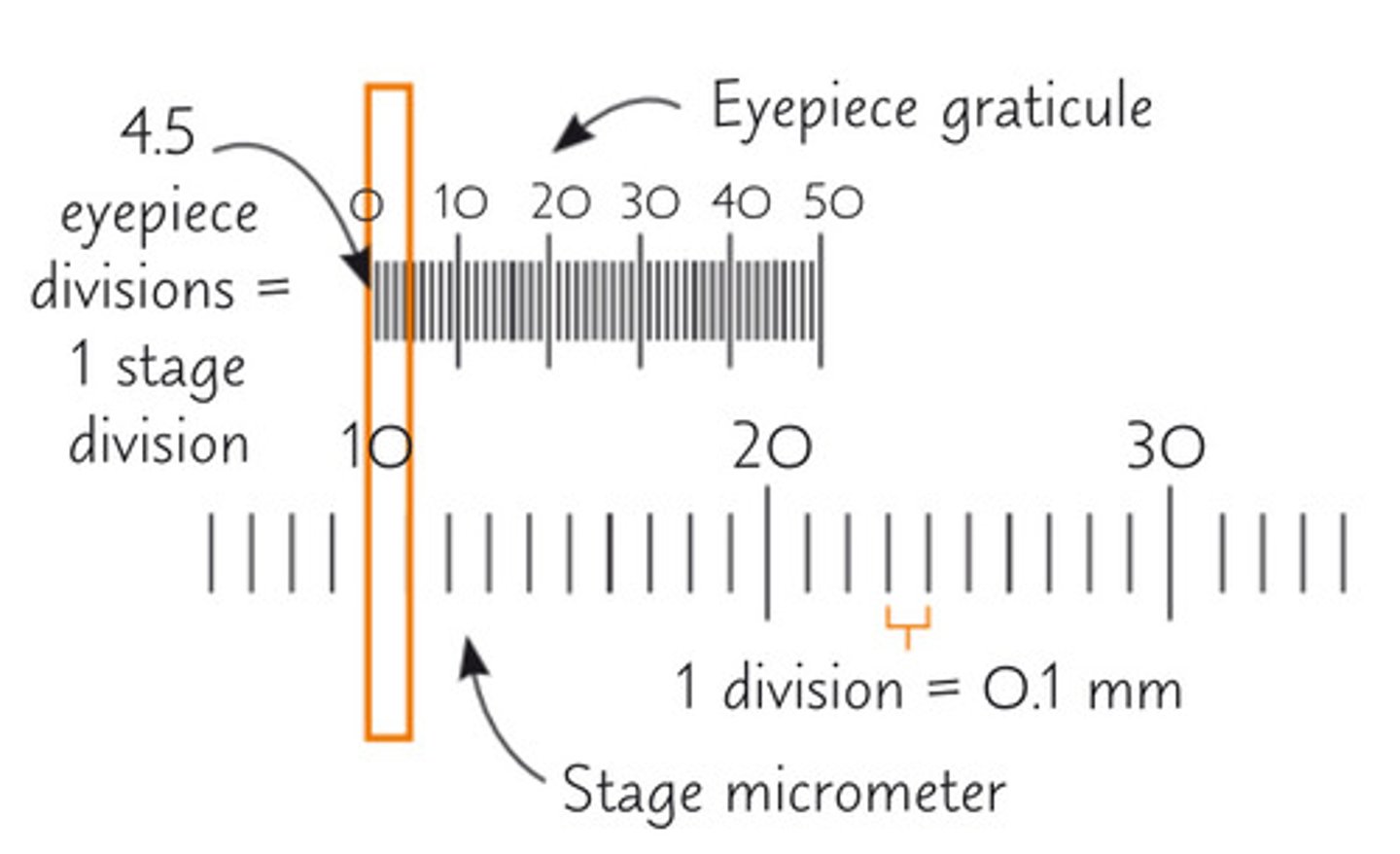
how do you calibrate an eyepiece graticule
-Line up the stage micrometer and eyepiece graticule whilst looking through the eyepiece
-Count how many divisions on the eyepiece graticule fit into one division on the micrometer scale
-Each division on the micrometer is 10μm, so this can be used to calculate what one division on the eyepiece graticule is at the current magnification
describe a light microscope
-uses light focussed by glass lenses,
-image can be viewed directly
-staining of specimen is required
describe a scanning electron microscope
electrons are reflected by specimen
uses electrons focussed by electromagnetic lenses,
cannot use live specimens
describe a transmission electron microscope
-higher density parts absorb more electrons and appear darker,
-uses electrons focussed by electromagnetic lenses in vacuum
-image is seen on a fluorescent screen
what are the advantages of a light microscope
-inexpensive,
-portable,
-can use living specimens,
-easy to use
what are the disadvantages of a light microscope
-low magnification and resolution,
-specimens need staining
what are the advantages of a scanning electron microscope
-can take 3D images, -high magnification and resolution
what are the disadvantages of a scanning electron microscope
-large,
-expensive,
-needs training to use
-dead
-complex staining method
what are the advantages of a transmission electron microscope
-highest magnification and resolution
what are the disadvantages of a transmission electron microscope
-large
-expensive
-needs training to use,
-specimen must be dead
-specimen must be stained
-must be v thin
which is the only type of microscope that can produce 3D images
scanning electron microscope
what are organelles
-small structures within cells,
-each of which has a specific function
what are eukaryotes
-cells which have a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles
what is the ultrastructure of a cell
-the fine detail of the structure within cells (viewed with an electron microscope)
which organelles are found in animal cells but not in plant cells
-centrioles
-lysosomes
which organelles are found in plant cells but not animal cells
-cell wall,
-permanent vacuole
-chloroplasts
what is the function of the plasma (cell surface) membrane
-regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cells
-has receptor molecules so can respond to chemicals like hormones
what is the function of the cell wall
support and protect the cell
what is the function of the nucleus
-controls the cells activities by controlling the transcription of DNA
-pores allow substances to move between the nucleus and cytoplasm,
-the nucleolus makes ribosomes
what is the function of the permanent vacuole
-stores nutrients
-water
-waste
what is the function of lysosomes
contain digestive enzymes that break down waste material (e.g. pathogens)
what is the function of ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
what is the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum
makes and processes proteins
what is the function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum
synthesises and processes lipids
what is the function of vesicles
-to transport molecules into, out of, and around a cell between organelles
-formed by the golgi apparatus/ER/cell surface
what is the function of the golgi apparatus
makes and packages proteins and lipids (also makes lysosomes)
what is the function of mitochondria
site of aerobic respiration
produce ATP
what is the function of chloroplasts
where photosynthesis occurs
what is the function of centrioles
-involved with the separation of chromosomes during cell division
what is the the cytoskeleton
a large network of proteins fibres with several roles
which two types of protein make up the cytoskeleton
actin filaments and microtubules
what are actin filaments
-small strands 7nm in diameter support the cell and give it mechanical strength,
-large strands 10nm in diameter anchor the nucleus and can extend between cells for communication
what are microtubules
-stacks of protein 18-30nm in diameter made from tubulin proteins
-assist microfilaments in giving the cell shape and support
-form the cilia, undulipodia and centrioles
-contain motor proteins that use ATP to move the cell's contents along the fibres
what is the function of the cytoskeleton
-helps a cell keep its shape
-moves chromosomes during cell division
-moves organelles around the cell
-extends into cilia and flagella to help cell movement (structure, transport and movement)
what is the function of flagella
-allow cells to move around
what is the function of cilia
move substances along the cell's surface
are eukaryotic or prokaryotic cells larger
eukaryotic:10-100um > prokaryotic:<2um
how is the DNA in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells different
eukaryotic: linear , prokaryotic: circular
where is DNA found in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
eukaryotic: nucleus , prokaryotic: cytoplasm
what are cell walls made from in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
-eukaryotic: cellulose in plants/chitin in fungi , -prokaryotic: polysaccharides
which type of cell has membrane bound organelles
eukaryotic cells only
what are flagella (when present) made from in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
-eukaryotic: microtubules in 9+2 formation
-prokaryotic: protein flagellin arranged in a helix
how does the size of ribosomes vary between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
-eukaryotic: >20nm (80S) -prokaryotic: <20nm (70S)
which organelles are found in prokaryotic cells but not eukaryotic cells
Plasmids: loops of DNA
Capsule surrounding the cell wall: gives protection from the immune system
Flagella: locomotion
how do eukaryotic cells divide
mitosis and meiosis
how do prokaryotic cells divide
binary fission
how do eukaryotic cells reproduce
sexually and asexually
how do prokaryotic cells reproduce
asexually
how do organelles work together to produce and secrete a protein
-mRNA copies gene and leaves nucleus through pores
-mRNA attaches to ribosome which synthesises a protein
-protein is packaged into vesicles and transported to golgi,
-vesicle fuses with golgi and is packaged and modified,
-then collected in a vesicle and transported to the cell surface membrane
-fuses with it and the substance leaves the cell
what are the functions of water
-reactant
-solvent
-habitat
-used to transport substances
-used to control temperature
what is the structure of water
-polar molecule with covalent bonds between the hydrogen and oxygen atoms
-hydrogen bonds between molecules
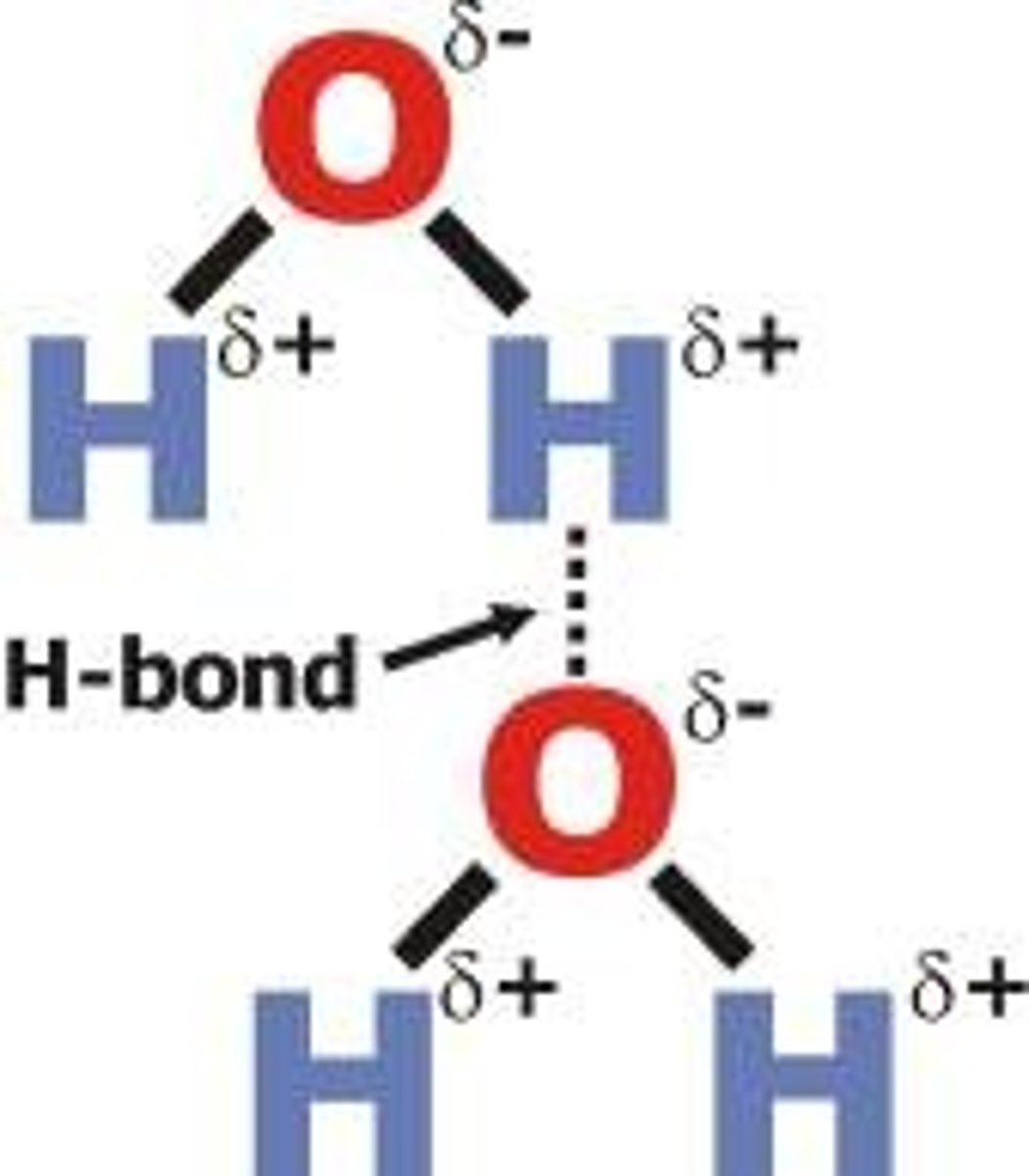
why is water a polar molecule
-because it is covalently bonded
-delta (partial charges) accumulate: a δ- charge on the oxygen and δ+ charges on the hydrogens
why do hydrogen bonds form between water molecules
-the partial delta charges attract
-oxygen of one water molecule is attracted to a hydrogen from another molecule to form a hydrogen bond
-ndividually weak but collectively strong
what are the properties of water
-cohesion
-adhesion
-high specific heat
-high heat of vaporization
-less dense as a solid,
-good solvent
what are the advantages of water having a high specific heat capacity
-water doesn't experience rapid temperature changes which makes it a more stable habitat than on land
what are the advantages of water having a high latent heat of vaporisation
-water must absorb a lot of energy before it can evaporate
-helps organisms to cool down by processes such as sweating and transpiration
what are the advantages of water being less dense as a solid
-ice floats to the top of the body of water
-acting as a insulator
-habitat for some species
what are the advantages of water being cohesive
-water molecules are attracted to each other by hydrogen bonds
-so water can flow and be transported e.g. up plant stems
what are the advantages of water being a good solvent
-water is a good solvent because the δ+ hydrogens are attracted to negative ions
-δ- oxygens are attracted to positive ions
-ions can dissolve in water and be transported
define adhesion
attraction between molecules of different substances
define cohesion
attraction between molecules of the same substance
define latent heat of vaporisation
the amount of (heat) energy required to change the state of a substance from liquid to gas
define specific heat capacity
it is the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1°C
what are macromolecules
large complex molecules e.g. proteins
what are polymers
large, complex molecules composed of long chains of monomers joined together
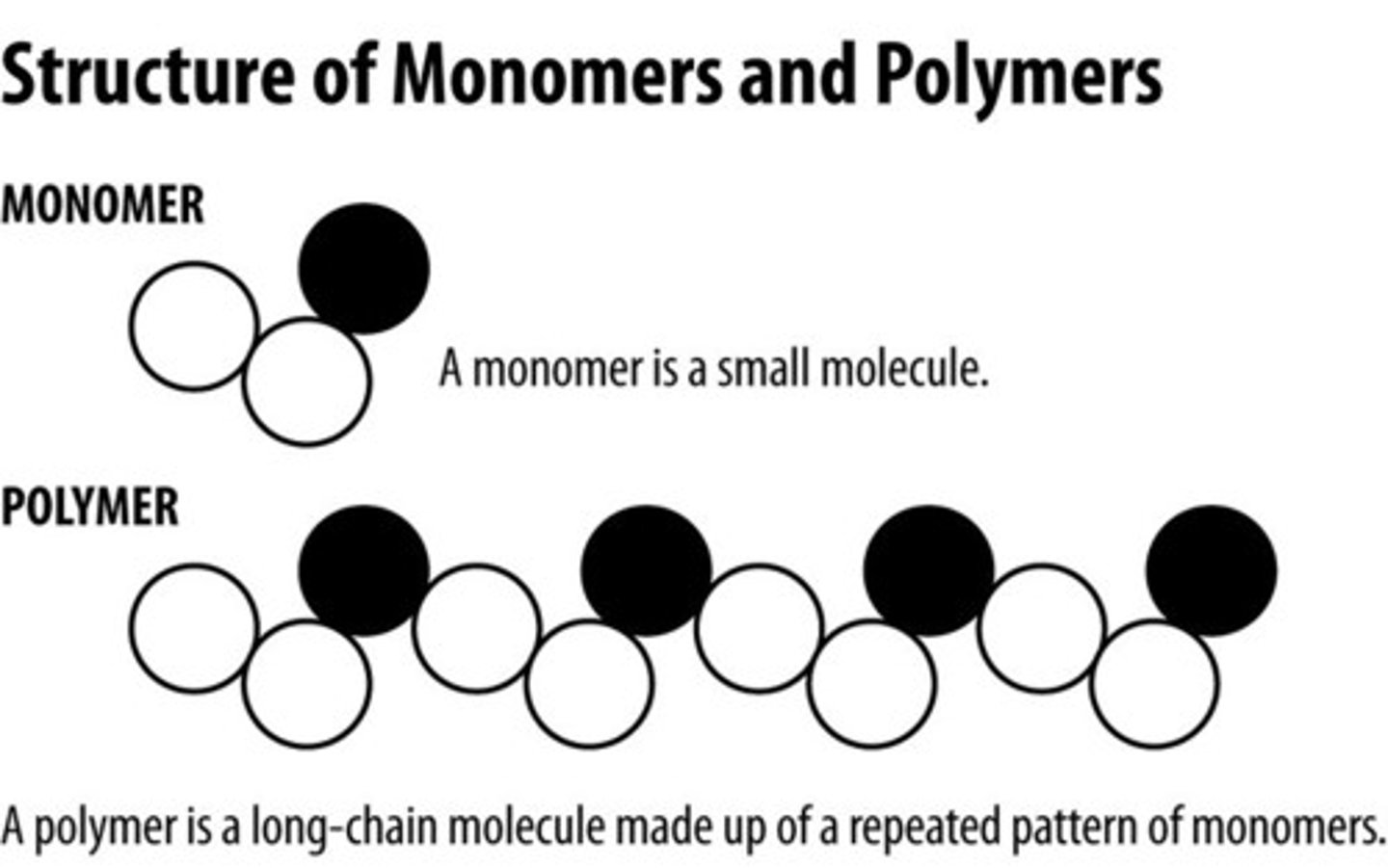
what are monomers
small, basic molecular units
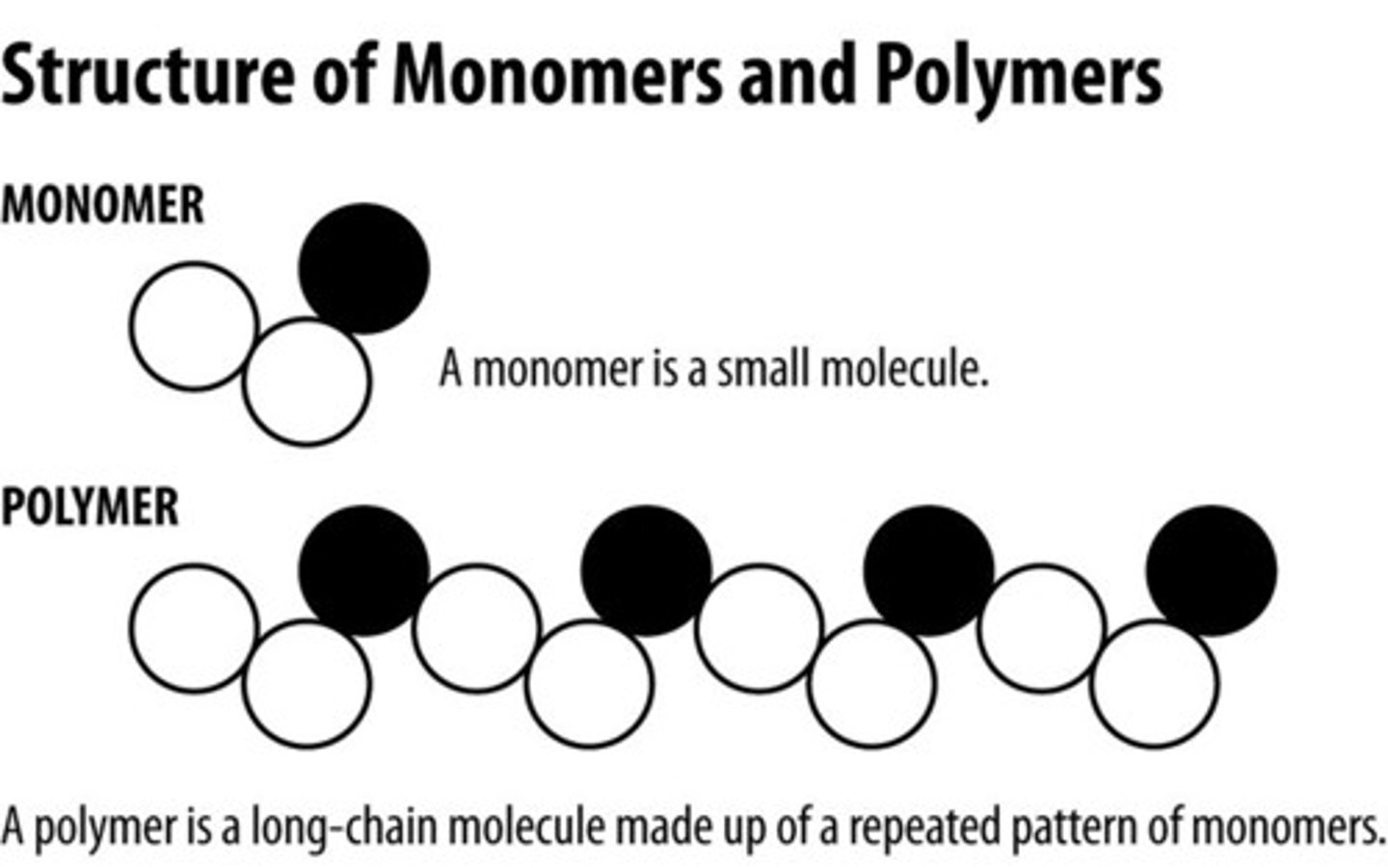
how are polymers made
-form chemical bonds between monomers and also produces water
how are polymers broken down
-break chemical bonds between monomers using water
which are the only elements found in carbohydrates
carbon (C), hydrogen (H) oxygen (O)
What is the ration of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen in carbohydrates
1:2:1 (CH2O)n
what are the bonds in carbohydrates called
glycosidic bonds
what are the monomers in carbohydrates called
monosaccharides
give three examples of monosaccharides
fructose, galactose, glucose
are monosaccharides soluble in water
yes
give three examples of disaccharides
lactose, maltose, sucrose
are disaccharides soluble in water
yes
give three examples of polysaccharides
cellulose, glycogen, starch
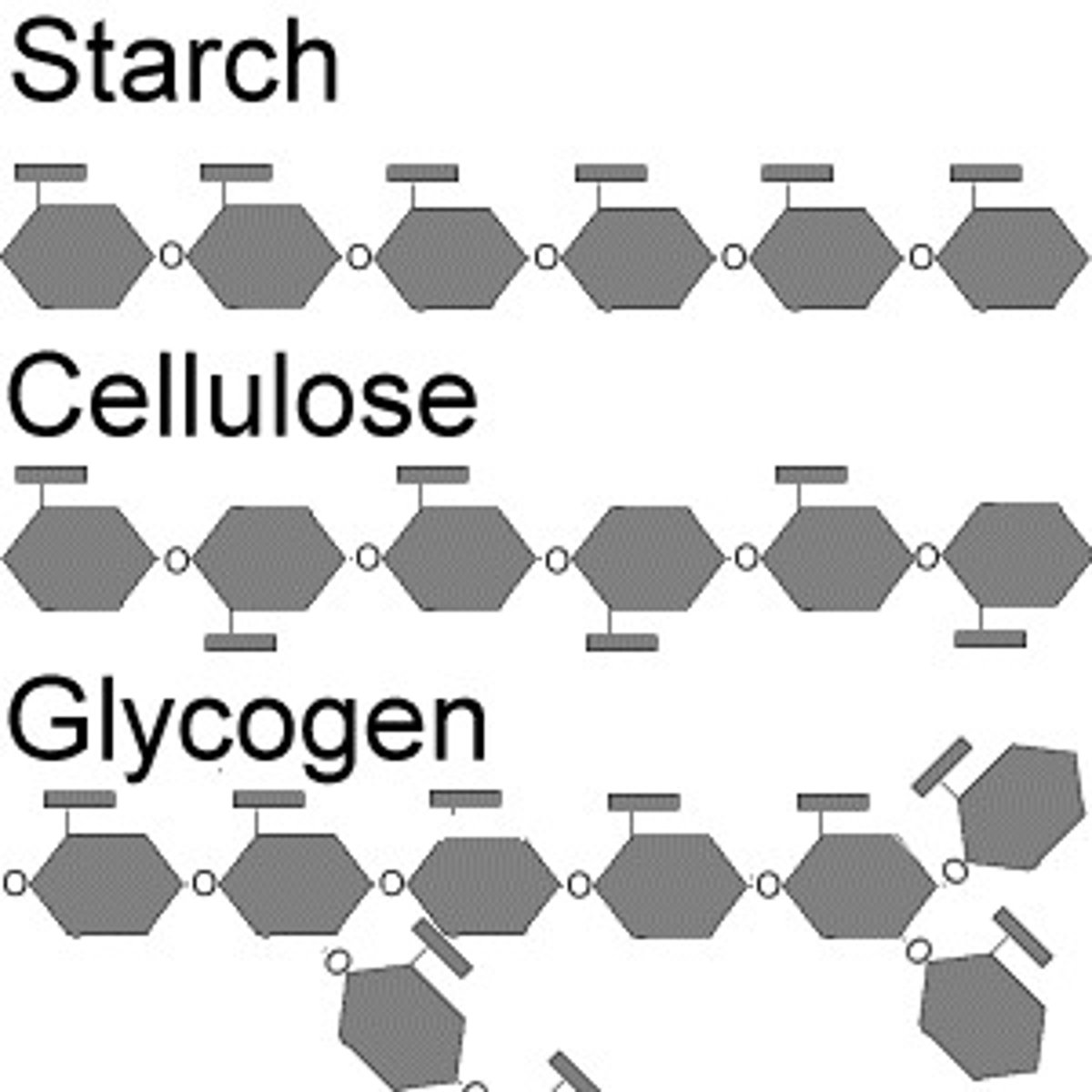
are polysaccharides soluble in water
no
what are the functions of carbohydrates
source of energy, used as storage, make up 10% of organic matter in the body
how are monosaccharides classified by their number of carbon atoms
triose (3 carbons), pentose (5 carbons), hexose (6 carbons)
what type of monosaccharide is glucose
hexose (6 carbons)
what are the two structural isomers of glucose
alpha (α) and beta (β) have the same chemical formula but a different structural formula
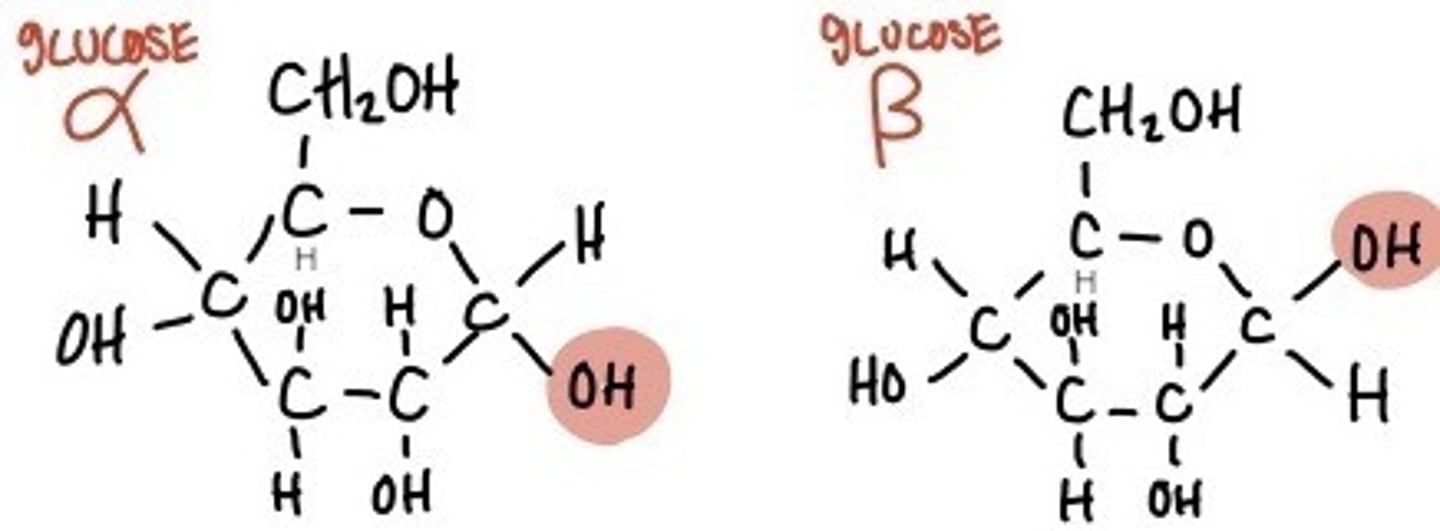
what is the difference between alpha and beta glucose
-alpha glucose the right hydroxyl group (OH) is below the plane
-beta glucose the right hydroxyl group (OH) is above the plane
what is the function of glucose
main energy source in animals and plants
what type of monosaccharide is ribose
pentose (5 carbons)
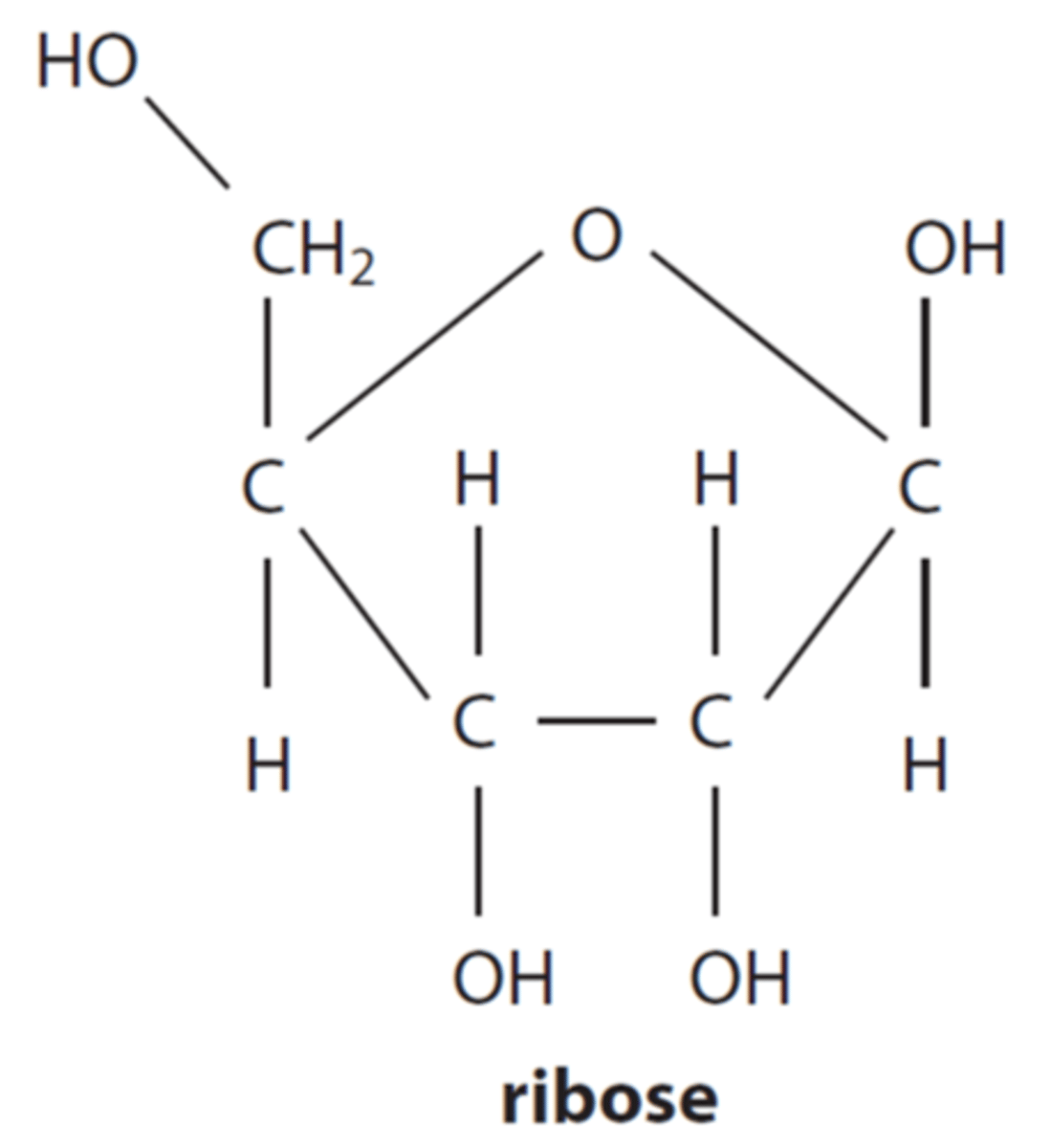
how is the structure of ribose different to glucose
5 carbons instead of 6, so one less C+H+OH
what is the function of ribose
the sugar component of RNA nucleotides